Abstract
Background
Accidental ingestion or consumption of supra-therapeutic doses of methadone can result in neurological sequelae in humans. We aimed to determine the neurological deficits of methadone-poisoned patients admitted to a referral poisoning hospital using brain magnetic resonance (MR) and diffusion weighted (DW) imaging.
Methods
In this retrospective study, brain MRIs of the patients admitted to our referral center due to methadone intoxication were reviewed. Methadone intoxication was confirmed based on history, congruent clinical presentation, and confirmatory urine analysis. Each patient had an MRI with Echo planar T1, T2, FLAIR, and DWI and apparent deficient coefficient (ADC) sequences without contrast media. Abnormalities were recorded and categorized based on their anatomic location and sequence.
Results
Ten patients with abnormal MRI findings were identified. Eight had acute- and two had delayed-onset encephalopathy. Imaging findings included bilateral confluent or patchy T2 and FLAIR high signal intensity in cerebral white matter, cerebellar involvement, and bilateral occipito-parietal cortex diffusion restriction in DWI. Internal capsule involvement was identified in two patients while abnormality in globus pallidus and head of caudate nuclei were reported in another. Bilateral cerebral symmetrical confluent white matter signal abnormality with sparing of subcortical U-fibers on T2 and FLAIR sequences were observed in both patients with delayed-onset encephalopathy.
Conclusions
Acute- and delayed-onset encephalopathies are two rare adverse events detected in methadone-intoxicated patients. Brain MRI findings can be helpful in detection of methadone-induced encephalopathy.
Keywords: Methadone, Acute encephalopathy, Delayed leukoencephalopathy, Magnetic resonance imaging
Background
Methadone is a synthetic opioid that is increasingly used as an analgesic and in maintenance therapy of opioid-addicted patients [1, 2]. Accidental ingestion of methadone or consumption of its supra-therapeutic doses have been shown to cause multi-organ damage in both humans and animals [1, 3–5].
There have been several previous case reports describing acute-onset encephalopathy (AOE) and delayed-onset leukoencephalopathy (DOL) as adverse complications of methadone intoxication [4–6]. AOE presents with MRI abnormalities within the first admission of the patient. DOL, however, manifests with abnormalities detected on MRI in patients who have initially responded to treatment (complete resolution of symptoms), but are then re-admitted after a period of lucidity (usually days to weeks post the primary event) with neurological or psychiatric deterioration [7–10].
AOE is one of the severe neurologic complications of methadone intoxication, that has previously been associated with carbon monoxide and heroin toxicities [7, 8]. To date, eight case reports have been published reporting AOE associated with methadone toxicity, ages ranging from 22-month-old to 65 years old [1, 4, 5, 11–16]. These cases have reported a range of neurologic complications, including restrictive diffusion throughout the cerebral gray matter, bilateral diffuse cerebellar edema or infarction, hippocampal and basal ganglia (globus pallidus), fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) intensities, absence of central intracranial blood flow, supra and infratentorial gray matter thickening, and non-enhancing T2 hyperintensities and restriction diffusion in the white matter of both hemispheres with sparing of subcortical U fibers [4, 5, 11–16].
DOL was first described in a 24-year-old patient who developed apathy and disorientation after the initial improvement from a mixed methadone-benzodiazepine poisoning [16]. Other case studies have reported a range of DOL symptoms, including disorientation, paranoid and bizarre behavior, and severe progressive cognitive decline with bilateral cerebral white matter hyperintensities. MRI changes in these case reports have included diffuse abnormal T2 and FLAIR signals in the corona radiate, centrum semiovale and subcortical white matter throughout all lobes, and signal abnormalities in temporomesial, substantia nigra, and basal ganglia [6, 8, 9, 12, 13, 17–21]. The aim of our study was to identify and describe the pattern of neurological deficits and associated brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) changes in methadone-poisoned patients.
Methods
In this retrospective file audit, the clinical records of all patients admitted to our referral poisoning hospital with the diagnosis of methadone intoxication between May 2016 and March 2018 were reviewed. A total of 2930 cases were identified, of whom only 10 fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
Definitions
Methadone intoxication was defined based on history, clinical presentations of respiratory depression (opioid toxidrome) or loss of consciousness (LOC) responsive to administration of naloxone, as well as detection of methadone in urine analysis. The patients were classified into two subtypes: acute- and delayed-onset encephalopathy (AOE and DOL, respectively) based on clinical history. Patients with persistent neurological deficits in their first admission were categorized to have AOE based on their MRI changes. Those who had been discharged after either complete or partial recovery from acute intoxication, but then deteriorated with neurological signs or symptoms within several days or weeks necessitating readmission were considered to have DOL [7–9]. The most prevalent delayed symptoms included psychotic delirium, fluctuating state of consciousness, depression, apathy, and bizarre behaviors [9–13]. Complete knowledge of time courses and clinical presentation was a prerequisite in categorization of the patients. Imaging was performed due to persistent neurological deficits several days after admission or if there was re-occurrence of neurotoxicity after a lucid interval of at least 1 week.
Inclusion criteria
AOE: Patients who had been admitted due to methadone intoxication and had undergone imaging due to persistent neurological deficits were enrolled in AOE group.
DOL: Neurological deficits were defined as a deterioration of neurologic function leading to readmission within one to 3 weeks after discharge without any new toxic exposure. Patients fulfilling this criteria were enrolled into the DOL group.
Exclusion criteria
If methadone diagnosis was not confirmed after the review of the history, presentation, and urine analysis. Patients who had co-ingestions confirmed by urine analysis were also excluded (e.g. Alcohol). Any cases with possible intoxication, with a coingestants known to cause MRI complications (carbon monoxide [CO], methanol, cyanide, etc.) were excluded.
Imaging
Scans were performed by a 1.5-T multi-planar MRI device. Echo planar T1 (TR: 591 ms, TE:15 ms, Spatial Resolution: 6.2 mm slice thickness, FoV: 230 mm*230 mm), T2 (TR: 4048 ms, TE:90 ms, Spatial Resolution: FLAIR, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent deficient coefficient (ADC) sequences without contrast media were performed. The scan time was 15 min. All images were reviewed by a single radiologist experienced in MRI. Detected abnormalities were recorded and categorized based on their anatomic location and sequence. The areas with both restriction in DWI and low signal in abnormal diffusion restriction (ADC) were considered abnormal.
Results
Eight patients had a brain MRI performed during their first admission due to persistent neurological deficit despite active treatment (AOE group; Tables 1 and 2). This group included four children (aged 23 months to 16 years) who had accidentally ingested methadone. The other two had developed new neurological deficits days after the initial recovery from intoxication (DOL group; Table 3). All ten patients had abnormal findings on MRI.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients with AOE
| Patient number | Age/ Sex | Initial presentation | Urine toxicology | Time to imaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 yr, F | Cyanosis | Methadone | Day 5 |
| 2 | 16 yr, F | Apnea | Methadone | Day 7 |
| 3 | 23mo, M | Cyanosis | Methadone, benzodiazepine | Day 5 |
| 4 | 30 yr, M | Intoxication then witnessed apnea | Methadone | Day 2 |
| 5 | 31 yr, M | Confusion then witnessed apnea | Methadone, opiate | Day 12 |
| 6 | 32 yr, F | LOC | Methadone | Day 3 |
| 7 | 33 yr, M | LOC | Methadone, opiate | Day 2 |
| 8 | 5 yr, M | LOC | Methadone | Day 2 |
Table 2.
Brain MRI findings in patients with AOE
| Number | Age/ Sex | Bilateral cerebral white matter T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity | Bilateral cerebellar white and gray matter T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity | Bilateral parieto-occipital T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity (PRES features) | Internal capsule involvement | Other structures | Infarction | Hemorrhage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 yr, F | Yes | Yes | Yes | – | – | No | No |
| 2 | 16 yr, F | Yes | – | – | – | – | No | No |
| 3 | 23mo, M | Yes | – | – | – | – | No | No |
| 4 | 30 yr, M | – | Yes |
Yes With restriction in DWI and low signal in ADC sequences |
– | – | No | No |
| 5 | 31 yr, M | Yes | – | – | Yes | Splenium of corpus callosum | No | No |
| 6 | 32 yr, F | – | – |
Yes With restriction in DWI and low signal in ADC sequences |
– | – | No | No |
| 7 | 33 yr, M | Yes | – | – | Yes with restriction in DWI and ADC sequences | – | No | No |
| 8 | 5 yr, M | – | Yes |
Yes With restriction in DWI and low signal in ADC sequences |
– | Globus pallidus and caudate nuclei | No | No |
Table 3.
Clinical characteristics and brain MRI findings of patients with DOL
| Number | Age/ Sex | Toxic agent | Clinical presentation in relapse phase | Time to relapse after initial intoxication | Initial imaging | Delayed phase brain MRI findings | DWI and ADC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 47 yr, M | Methadone | Disorientation, seizure like activity | 9 days | No | Confluent bilateral symmetrical cerebral white matter T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity with sparing of sub cortical U-fibers | No restriction |
| 10 | 49 yr, M | Methadone | Confusion | 18 days | No | Confluent bilateral symmetrical cerebral white matter T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity with sparing of sub cortical U-fibers | No restriction |
AOE group
Seven patients in this group were male and median age was 23 years [range; 23 months to 33 years). Based on urine analysis, three cases had positive urine for other drugs. One had received benzodiazepine as a part of medical management. Other two were multi-opioid abusers, but had only overdosed on methadone. Imaging findings in this group included bilateral confluent or patchy T2 and FLAIR high signal intensity areas in cerebral white matter in six (Fig. 1), cerebellar involvement in four (Fig. 2), and bilateral occipitoparietal cortex signal abnormality (low on T1 and high on T2) associated with diffusion restriction (confirmed with low signal intensity in ADC) in three cases (Fig. 3) and without restriction in one case. Internal capsule involvement was detected in two patients with hyper-signal corpus callosum in one. Abnormalities in the globus pallidus and the head of caudate nuclei were reported in only one patient. The MRIs were performed at 2- and 12-day intervals after initial presentation with methadone intoxication (defined as the primary toxic event).
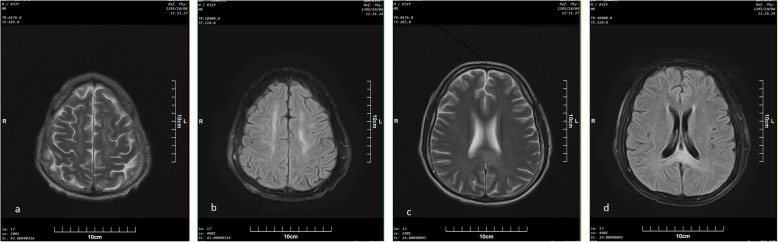
Fig. 1.
Axial (a) T2 and (b) FLAIR sequences of a 31-year-old man (patient number 5) , 12 days after presenting to emergency department with AOE symptoms, symmetric areas of hyperintensity in both centrum semiovale are seen. Axial (c) and (d) FLAIR sequences of the same patient at the mid ventricular level show hyperintensity in the splenium of corpus callosum
Fig. 2.
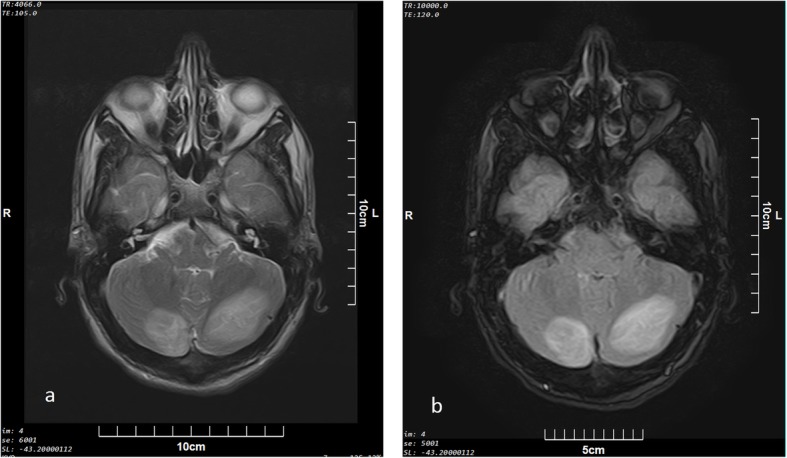
Axial (a) T2 and (b) FLAIR sequences from posterior fossa at the level of fourth ventricle in a 30 year old male ( patient number 4) two days after primary symptoms of AOE, high signal areas are seen in posterior part of cerebellum with gray and white mater involvement
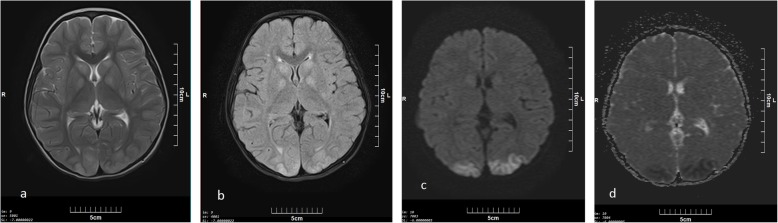
Fig. 3.
Axial (a) T2 and (b) FLAIR sequences of a 5- year-old boy (patient number 8) , two days after initial presentation of AOE , bilateral symmetric hyperintense areas are seen in basal ganglia (globus pallidus and head of caudate) in keeping with cortical and subcortical hyperintense areas in occipital lobes which has restricted in DWI (c) with low ADC signal (d)
DOL group
The two patients in this group were 47 and 49 years old and had a 9- and 18-day lucid interval, respectively, between the initial presentation and clinical relapse (Table 3). Confluent bilateral symmetrical cerebral white matter signal abnormality with sparing of subcortical U-fibers on T2 and FLAIR sequences were observed in both of these patients (Fig. 4).
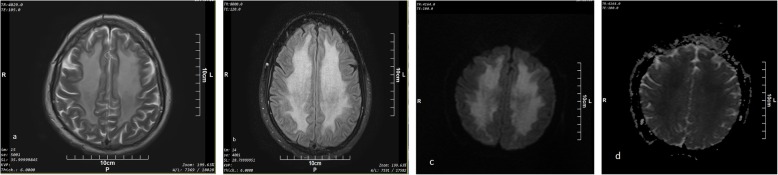
Fig. 4.
Axial (a) T2 and (b) FLAIR sequences in a 47-year-old male with DOE (patient number 9) above the ventricular level show confluent bilateral symmetrical cerebral white mater hyperintensity with sparing of subcortical U-fibers. Axial (c) DWI and (d) ADC sequences also show T2 shine through phenomenon without any evidence of diffusion restriction
Discussion
Methadone-induced encephalopathy is a rare event. To date, this phenomenon remains poorly characterized [4, 5, 21]. The brain MRI changes reported in the literature are summarized in Table 4 and include: cerebellum abnormalities [1, 4, 10–14], bilateral cerebral white matter abnormalities [4, 5, 11, 12, 14], signal changes in hippocampus [10], globus pallidus [13], and in a single case report in the head of caudate nuclei [4]. In addition, there is a single case report of a 2-year-old infant found to have cerebral white matter, cerebellar, and globus pallidus hypodensities based on computed tomography (CT) scan [22].
Table 4.
Summary of published case reports of AOE
| Author(s) | Age/sex | Clinical presentation | Clinical findings in discharge | Lab Data | Time to imaging | MRI findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anselmo M. Et al (2005) [10] | 3yo, M | LOC, irregular breathing, low BP | Mild Ataxia | Urine toxicology: positive for methadone after 36 h | Day 6 | High T2 in cerebellar hemispheres and hippocampus |
| Mills F. Et al (2008) [11] | 3yo, F | LOC, hard breathing, hypothermia | Spastic dysplasia and dystonia | Urine toxicology: positive for methadone | Day 2 | FLAIR: damage to gray matter and white matter of cerebellum with marked swelling |
| Riascos R (2008) [12] | 22mo,- | LOC | Brain death | Urine toxicology: positive for methadone, acetaminophen and salicylate | In admission day | Diffuse bilateral cerebellar infarction, absence of central intra cranial blood flow, supra and infra tentorial gray matter thickening |
| Corré J. Et al (2013) [13] | 29yo, M | LOC, hypothermia, bradypnea | Good recovery, except persistent renal failure and kinetic cerebellar syndrome | Blood analysis was positive for alcohol, cannabis, methadone (146 ng/ml), and benzodiazepines | At first day of admission. | FLAIR and DWI: high in both cerebellar and basal ganglia (globus pallidus) |
| Metkees M. Et al (2015) [14] | 15yo, F | LOC, hypothermia, hypercapnia, HTN | Death | Detailed history revealed methadone ingestion of unknown quantity | Not mentioned | T2 and DWI: high in white matter of both hemisphere (sparing sub cortical U-fibers and deep gray matter, cortical or cerebellar) |
| Cerase A. Et al (2011) [4] | 49yo, M | LOC | Complete recovery after 3 mo. | Serum toxicology: positive for methadone | Not mentioned | T2 and FLAIR: high in white matter of right cerebellum and deep gray and white matter of both cerebral hemispheres. |
| R.A. Salgado et al. (2009) [5] | 65yo, F | Apathy, a catatonic state with extreme rigidity, reflexes in the upper limbs, and a bilaterally positive Babinski sign | In the following month, the patient slowly recovered. | Serum and urine toxicology shows large amount of methadone | Day 27 | FLAIR and T2: symmetric signal intensity abnormality in the deep white matter of both cerebral hemisphere with sparing of sub cortical U-fibers without corresponding diffusion restriction |
| Rando J. (2016) [1] | 14yo, M | Hypothermia, HTN, respiratory depression | Aphasia, truncal ataxia | Serum toxicology: positive for methadone | In admission day | FLAIR: cereberallitis |
In our AOE patients, the most frequent MRI finding was bilateral confluent or patchy cerebral white matter hyperintensity (n = 5). Cerebellar abnormalities were detected in only three cases despite this was the most common observed abnormality in previous studies [1, 10, 13]. A consistent (n = 4) and new finding in these patients was bilateral parieto-occipital cortex T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity. This radiological finding has also been reported in patients with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES [23];). PRES has been reported as a consequence of or in conjunction with a variety of critical illness states including severe hypertension, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, thrombocytopenic thrombotic purpura, and in association with drug toxicities such as cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, interferon [23–25], and opiates such as morphine [26, 27]. In keeping with the findings in PRES, three of our patients had bilateral parieto-occipital cortex restriction in DWI which was confirmed by ADC sequence. Additionally, restriction was observed in one patient with internal capsule involvement (case 7). Restriction in bilateral cerebral white matter has previously been reported secondary to methadone toxicity [4, 11]. One study suggested that “deep watershed infarct” resulted in the restriction imaging observed [11]. Given our observations and previous published reports, it can be postulated that the changes in AOE due to methadone could result in PRES.
We also had two patients who had internal capsule involvement. This finding is in accordance with previously published reports as a characteristic of heroin toxicity [28]. In our both patients, morphine and methadone were detected in urine analysis. Therefore, heroin use cannot be ruled out. Additional confirmatory testing for supplementary heroin metabolites would have been useful in these two individuals. However this was not available in our center. One of them (Case 5) demonstrated lesions in splenium of corpus callosum, a finding never reported before in either heroin or methadone intoxication. This finding may be a transient lesion of splenium and has been associated with various clinical conditions such as seizures, metabolic disturbances, infections, CNS malignancy, and drugs and toxins (antidepressants, antiepileptics, antipsychotics, chemotherapy agents, and pesticides) [15, 28–38]. We also had a single patient (case 8) who showed involvement of the globus pallidus and head of caudate nuclei. This finding has been observed in association with methadone toxicity [4, 13]. Previously, brain imaging changes associated with methadone intoxication were suggested to be as a consequence of hypoxic events secondary to overdose [12]. However, hypoxia-associated cerebral adverse effects on imaging seem to be only a result of prolonged hypoxia [39, 40]. Majority of our patients did not have a persistent documented hypoxic insult. Brain neuroimaging was performed on admission, and before the worsening of patient’s condition. Secondly, brain and cerebellar damage demonstrated at both diagnosis and follow-up showed a clear-cut prominent involvement of the subcortical white matter. In adulthood, hypoxic-ischemic insults usually result in watershed zone infarcts when mild to moderate, and affect the gray matter in the basal ganglia, thalami, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampi when severe. Furthermore, severe insult generally includes a stage of diffuse cerebral edema with loss of differentiation between gray and white matter, a finding that was not noted in the patients reported. Furthermore, acute and early subacute phases of hypoxia-induced encephalopathy primarily affect the basal ganglia, thalamus, and cortex [41]. We reported bilateral cerebral white matter and cerebellum abnormalities as the most common brain MRI finding.
To date, only 8 case reports evaluating 11 patients have been published reporting delayed-onset methadone-induced leukoencephalopathy [6, 10, 16–20], summarized in Table 5. The most frequent imaging findings in case reports of patients with DOL is bilateral cerebral white matter T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity [6, 8, 9, 16, 18, 20] followed by corpus callosum [9, 16] and globus pallidus [8] involvement. This is in keeping with our observation of bilateral cerebral white matter hyperintensity. However, the findings in DOL group are not generalizable, as there were only two cases in this group, who also lacked imaging in their acute phase for comparison with the DOL phase imaging. Furthermore, during examination of DWI and ADC, no restriction was found in either case. Four patients have been described with restriction in DWI scans, although a correlation with ADC was not reported in them [9, 17, 18, 20]. It is possible that the restrictions observed in these patients is related to T2 shine through, as this phenomenon has also been observed in our patients.
Table 5.
Summary of published works on DOL
| Author(s) year | Age/ Sex | Toxic agent | Time to relapse after initial intoxication | Clinical presentation in relapse phase | First imaging findings | Delayed phase MRI findings | DWI and ADC sequences findings | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ljungar B. et al. 2014 [17] | 34 yr, M | Methadone | 33 days | Physical, psychological and cognitive deterioration | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | Cystic changes in bilateral cerebral white matter | Hyperintensity in DWI without ADC confirmation | Recovery |
| Mittal M. et al. 2010 [6] | 38 yr, M | Methadone, benzodiazepine | 3 weeks | Physical, psychological and behavioral manifestations | No imaging | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | No restriction | Partial recovery |
| Arciniegas 2004 [16] | 24 yr, M | Methadone, diazepam | Not mentioned | Apathy, disorientation | No imaging | Cerebral white matter and corpus callosum T2 hyperintensity | Not mentioned | Partial recovery |
| Torralba A- Moron 2016 [8] | 42 yr, M | Methadone, alcohol, benzodiazepine | 13 days | Myoclonus, fluctuated consciousness, | Normal CT scan | Cerebral white matter and globous pallidus T2 hyperintensity | Not mentioned | Lack of attention and dysexecutive and amnestic abnormalities persisted |
| 43 yr, M | Methadone | Not mentioned | low level of consciousness and a bradypnoea | Not mentioned | Cerebral white matter and globous pallidus T2 hyperintensity | Not mentioned | death | |
| Zanin A. 2010 [19] | 30mo, F | Methadone | 19 days | Agitation, slurred speech, abnormal movement | Normal | Tempromesial, Substantia Nigra and basal ganglia | No restriction | Recovery after 2 month |
| Andrew Meyer M. 2013 [20] | 43 yr, F | Methadone, diazepam | 3 weeks | Forgetful& confused, social withdrawal, lack of hygiene | No imaging | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | Hyperintensity in DWI without ADC confirmation | Recovery |
| Carroll I. 2012 [9] | 43 yr, F | Alprazolam, methadone | 33 days | Apathy, inappropriate behavior | No imaging | Cerebral white matter and corpus callosum T2 hyperintensity | Corpus Collosum hyperintensity in DWI without ADC confirmation | Full recovery after 6 month |
| Shprecher D. 2008 [18] | 39 yr, F | Methadone, cocaine | 4 weeks | disorientation | No imaging | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | Hyperintensity in DWI without ADC confirmation | Partial recovery |
| 58 yr, F | methadone | 21 days | Paranoid and inappropriate behavioral | No imaging | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | Not mentioned | Partial recovery | |
| 56 yr, F | Methadone, fentanyl, benzodiazepine | 15 days | Cognitive deterioration | Not mentioned | Cerebral white matter T2 hyperintensity | Hyperintensity in DWI without ADC confirmation | Partial recovery |
Almost all published case reports to date are in adult patients, except for a single case of 30-month-old infant. There are no previous publications on DOL due to other reasons (strangulation, CO poisoning, benzodiazepine overdose, etc.) in adults younger than 30 years [7]. Since both of our patients were also adults, it is possible that DOL is a phenomenon more common among adult patients. DOL has been previously suggested to be due to hypoxia [6, 16]. However, given that neither of our patients had history of prolonged unconsciousness or respiratory depression, hypoxia as an etiology can be excluded. The lucid intervals of one to 5 weeks have been reported in earlier case reports [7], which was reinforced with our cases.
Conclusion
Methadone intoxication can result in a spectrum of encephalopathies ranging from AOE to DOL which can be diagnosed using MRI findings. Future studies on larger sample sizes are required to elucidate this association with its possible imaging findings. Our study is the first to demonstrate that MRI changes due to methadone intoxication can parallel those observed in PRES in both adults and children. Given that both heroin and morphine have been previously reported to present with changes suggestive of PRES, it is reasonable to extrapolate this to be an opioid class effect. In DOL, bilateral T2 and FLAIR white matter hyperintensity was the common finding. Therefore, in patients with a recent history of methadone intoxication who represent with relapsing neurological symptoms, DOL needs to be considered.
Acknowledgements
This manuscript is based on the thesis of Dr. Naseri.
Abbreviations
- ADC
Apparent deficient coefficient
- AOE
Acute-onset encephalopathy
- CNS
Central nervous system
- CO
Carbon monoxide
- CT
Computed tomography
- DOL
Delayed-onset leukoencephalopathy
- DWI
Diffusion weighted imaging
- FLAIR
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- LOC
Loss of consciousness
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PRES
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
Authors’ contributions
HHM is the guarantor of integrity of the entire study. NZ, MHM and HHM gave the study concepts and designed the study. NJ, MHM, and ZN did the literature research. HHM performed the data analysis. HHM performed the statistical analysis. ZN prepared the manuscript draft and NJ did edit the final manuscript. All co-authors approved final submitted manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences fund this study with no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the local ethics committee at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (no 14911, IR.SBMU.REC.1397.011). Informed written consent was taken from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Rando J, Szari S, Kumar G, Lingadevaru H. Methadone overdose causing acute cerebellitis and multi-organ damage. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(2):343.e1–343.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.06.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Corkery JM, Schifano F, Ghodse AH, Oyefeso A. The effects of methadone and its role in fatalities. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2004;19(8):565–576. doi: 10.1002/hup.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aghabiklooei A, Edalatparvar M, Zamani N, Mostafazadeh B. Prognostic Factors in Acute Methadone Toxicity: A 5-Year Study. J Toxicol. 2014;2014:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2014/341826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cerase A, Leonini S, Bellini M, Chianese G, Venturi C. Methadone-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy: Diagnosis and follow-up by magnetic resonance imaging including diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps. J Neuroimaging. 2011;21(3):283–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Salgado RA, Jorens PG, Baar I, Cras P, Hans G, Parizel PM. Methadone-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy: MR imaging and MR proton spectroscopy findings. Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(3):565–566. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mittal M, Wang Y, Reeves A, Newell K. Methadone-induced delayed posthypoxic encephalopathy: Clinical, radiological, and pathological findings. Case Rep Med. 2010;2010:22–26. doi: 10.1155/2010/716494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zamora CA, Nauen D, Hynecek R, Ilica AT, Izbudak I, Sair HI, et al. Delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy: A case series and review of the literature. Brain Behav. 2015;5(8):1–12. doi: 10.1002/brb3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Torralba-Morón Á, Ortiz-Imedio J, Morales-Conejo M, Ruiz-Morales J, Guerra-Vales JM. Delayed leukoencephalopathy: Three case reports and a literature review. 2016. pp. 1–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Carroll I, Heritier Barras A-C, Dirren E, Burkhard PR, Horvath J. Delayed leukoencephalopathy after alprazolam and methadone overdose: A case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012;114(6):816–819. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.12.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Anselmo M, Rainho AC, do Carmo Vale M, Estrada J, Valente R, Correia M, et al. Methadone intoxication in a child: Toxic encephalopathy? J Child Neurol. 2006;21(7):618–620. doi: 10.1177/08830738060210071101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mills F, MacLennan SC, Devile CJ, Saunders DE. Severe cerebellitis following methadone poisoning. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38(2):227–229. doi: 10.1007/s00247-007-0635-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Riascos R, Kumfa P, Rojas R, Cuellar H, Descartes F. Fatal methadone intoxication in a child. Emerg Radiol. 2008;15(1):67–70. doi: 10.1007/s10140-007-0627-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Corré J, Pillot J, Hilbert G. Methadone-Induced Toxic Brain Damage. Case Rep Radiol. 2013;2013:1–2. doi: 10.1155/2013/602981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Metkees M, Meesa IR, Srinivasan A. Methadone-induced acute toxic leukoencephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol. 2015;52(2):256–257. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cho J-S, Ha S-W, Han Y-S, Park S-E, Hong K-M, Han J-H, et al. Mild Encephalopathy with Reversible Lesion in the Splenium of the Corpus Callosum and Bilateral Frontal White Matter. J Clin Neurol. 2007;3(1):53. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Arciniegas DB, Frey KL, Anderson CA, Brousseau KM, Harris SN. Amantadine for neurobehavioural deficits following delayed post-hypoxic encephalopathy. Brain Inj. 2004;18(12):1309–1318. doi: 10.1080/02699050410001720130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bileviciute-Ljungar I, Häglund V, Carlsson J, Von Heijne A. Clinical and radiological findings in methadone-induced delayed leukoencephalopathy. J Rehabil Med. 2014;46(8):828–830. doi: 10.2340/16501977-1820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shprecher DR, Flanigan KM, Smith AG, Smith SM, Schenkenberg T, Ph D, et al. Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Delayed Hypoxic. Low Extrem. 2008;20(4):473–7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 19.Zanin A, Masiero S, Severino MS, Calderone M, Da Dalt L, Laverda AM. A delayed methadone encephalopathy: Clinical and neuroradiological findings. J Child Neurol. 2010;25(6):748–751. doi: 10.1177/0883073809343318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Meyer MA. Delayed post-hypoxic leukoencephalopathy: case report with a review of disease pathophysiology. Neurol Int. 2013;5(3):13. doi: 10.4081/ni.2013.e13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li W, Li Q, Wang Y, Zhu J, Ye J, Yan X, et al. Methadone-induced Damage to White Matter Integrity in Methadone Maintenance Patients: A Longitudinal Self-control DTI Study. Sci Rep. 2016;6(January):1–8. doi: 10.1038/srep19662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hassanian-moghaddam H, Zamani N. An Overview on Methadone-Intoxicated Patients. 2016. pp. 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hobson EV, Craven I, Catrin BS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: A truly treatable neurologic illness. Perit Dial Int. 2012;32(6):590–594. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2012.00152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Al-Sherif AH. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES): Restricted Diffusion does not Necessarily Mean Irreversibility. Polish J Radiol. 2015;80:210–216. doi: 10.12659/PJR.893460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rijkers K. An unusual case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient being weaned from intrathecal morphine. Int Med Case Rep J. 2016;9:117–120. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S98569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Eran A, Barak M. Combined General and Spinal Anesthesia with Intrathecal Morphine. 2009. pp. 609–612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lapat KD, Yousaf M, Joshi TR. Heroin-induced toxic leukoencephalopathy. Appl Radiol. 2016;45(3):36–37. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Keogh CF, Andrews GT, Forkheim KE, Graeb DA. Neuroimaging Features of Heroin Inhalation Toxicity: “Chasing the Dragon”. Image (Rochester, NY) 2003;180(3):847–850. doi: 10.2214/ajr.180.3.1800847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Edwards TJ, Sherr EH, Barkovich AJ, Richards LJ. Clinical, Genetic and Imaging Findings Identify New Causes for Corpus Callosum Development Syndromes. Brain. 2014;137(6):1579–1613. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Naik K, Mali R, Kunam S, Saroja A. ‘Wine Glass’ sign in recurrent postpartum hypernatremic osmotic cerebral demyelination. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2013;16(1):106. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.107719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tada H, Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Oba H, Maeda M, Tsukahara H, et al. Clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Neurology. 2004;63(10):1854–1858. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000144274.12174.CB. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garg R, Malhotra H, Sharma P, Vidhate M. Boomerang sign: Clinical significance of transient lesion in splenium of corpus callosum. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15(2):151. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.95005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vyas S, Khandelwal N, Singh P, Gogoi D. Transient splenial lesion: Further experience with two cases. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2010;20(4):254. doi: 10.4103/0971-3026.73531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Maeda M, Shiroyama T, Tsukahara H, Shimono T, Aoki S, Takeda K. Transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum associated with antiepileptic drugs: evaluation by diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(8):1902–1906. doi: 10.1007/s00330-002-1679-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Starkey J, Kobayashi N, Numaguchi Y, Moritani T. Cytotoxic Lesions of the Corpus Callosum That Show Restricted Diffusion: Mechanisms, Causes, and Manifestations. RadioGraphics. 2017;37(2):562–576. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hornik A, Rodriguez Porcel FJ, Agha C, Flaster M, Morales Vidal S, Schneck MJ, et al. Central and Extrapontine Myelinolysis Affecting the Brain and Spinal Cord. An Unusual Presentation of Pancreatic Encephalopathy. Front Neurol. 2012;3. Available from:. 10.3389/fneur.2012.00135/abstract. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Loh Y. Restricted Diffusion of the Splenium in Acute Wernicke’s Encephalopathy. J Neuroimaging. 2005;15(4):373–375. doi: 10.1177/1051228405279037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kimura K, Fuchigami T, Ishii W, Imai Y, Tanabe S, et al. Mumps-virus-associated clinically mild encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Int J Clin Pediatr. 2012;1(4-5):124–8.
- 39.Weiss N, Galanaud D, Carpentier A, Naccache L, Puybasset L. Clinical review: Prognostic value of magnetic resonance imaging in acute brain injury and coma. Crit Care. 2007;11(5):1–12. doi: 10.1186/cc6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Heinz UE, Rollnik JD. Outcome and prognosis of hypoxic brain damage patients undergoing neurological early rehabilitation Neurology. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1175-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Haaga JR, Boll DT. CT and MRI of the whole body. 6. 1994. pp. 577–578. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.