Abstract
The G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor (GPER) is a novel membrane-bound receptor that mediates non-genomic actions of the primary female sex hormone 17β-estradiol. Studies over the past two decades have elucidated the beneficial actions of this receptor in a number of cardiometabolic diseases. This review will focus specifically on the cardiac actions of GPER, since this receptor is expressed in cardiomyocytes as well as other cells within the heart and most likely contributes to estrogen-induced cardioprotection. Studies outlining the impact of GPER on diastolic function, mitochondrial function, left ventricular stiffness, calcium dynamics, cardiac inflammation, and aortic distensibility are discussed. In addition, recent data using genetic mouse models with global or cardiomyocyte-specific GPER gene deletion are highlighted. Since estrogen loss due to menopause in combination with chronological aging contributes to unique aspects of cardiac dysfunction in women, this receptor may provide novel therapeutic effects. While clinical studies are still required to fully understand the potential for pharmacological targeting of this receptor in postmenopausal women, this review will summarize the evidence gathered thus far on its likely beneficial effects.
Keywords: diastolic dysfunction, estrogen, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, calcium homeostasis, chymase, inflammation, oxidative stress, LV remodeling
Introduction
Among measures of cardiac function, diastolic performance is one of the most comprehensive—integrating myocardial relaxation, mitochondrial bioenergetics, cardiomyocyte/myocardial structure, and left ventricular (LV) ejection with respect to proximal aortic distensibility—and is a potential barometer of cardiac health (1). LV diastolic function is impaired by all of the common pathological processes that affect LV function or produce LV hypertrophy or fibrosis, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, sleep apnea, ischemia, aortic stenosis, and can occur before development of symptoms or changes in electrocardiogram and wall motion (2). The heart is designed to be a supple, elastic muscle that fills with blood easily at low pressure. Diastolic dysfunction with elevated filling pressures is a central feature of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (3) and disproportionally affects women with a sex ratio of about 2:1 (4–6). HFpEF is the most common form of heart failure (3, 7) and is outpacing other forms of heart failure as a result of the expanding elderly population (7–9).
Despite a marked female sex-specific predilection in HFpEF, relatively little is known regarding the mechanisms by which sex hormones, particularly the estrogens, and estrogen receptors (ERs) impact diastolic function. Over the last decade, we and others have explored the roles of the newest estrogen receptor, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER; previously known as GPR30), in the maintenance of cardiac function and structure after estrogen loss. In this review, the effects of pharmacologic activation of GPER by its specific agonist G1 on mitigating the adverse consequences of estrogen loss on relaxation, mitochondrial function, LV stiffness, and aortic distensibility will be presented. The influence of global and cardiomyocyte-specific GPER gene deletion on function and structure at the cardiomyocyte, whole heart, and conduit vessel levels will also be discussed.
What is Diastolic Dysfunction?
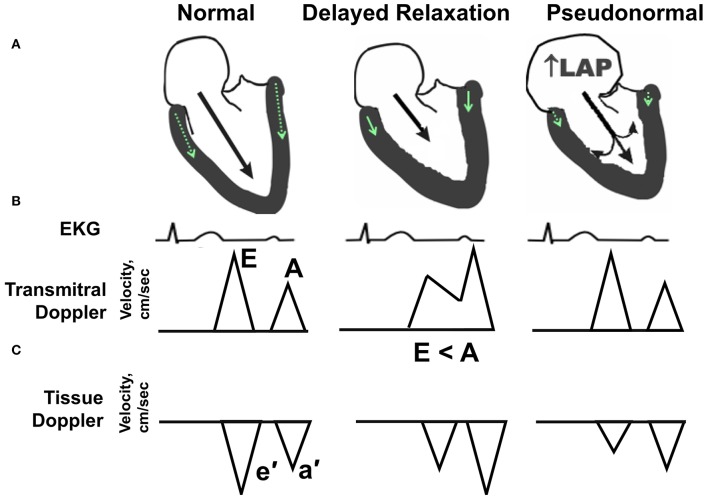
Diastolic dysfunction denotes a condition whereby the LV cannot fill adequately despite normal filling pressure. Slowing, delayed, and incomplete myocardial relaxation results from alterations in intracellular calcium handling, impairments in energy metabolism, and increases in LV stiffness due to hypertrophic and/or interstitial remodeling. Elevations in LV filling pressure initially compensate, but eventually pulmonary congestion develops as a result of increased left atrial (LA) pressure (10). While a wide range of diastolic function parameters can be obtained by Doppler-echocardiography (11), a simple composite of blood flow and tissue Doppler measures, as reviewed by ourselves and others (12–14) can sensitively detect and predict diastolic dysfunction in humans (15–17), non-human primates (18, 19), and preclinical rodent research models (20–25). The spectrum of diastolic dysfunction is portrayed schematically in Figure 1. Essentially, as described in detail by Nagueh and colleagues in the American Society of Echocardiography and European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging Guideline (11), the healthy adult LV fills primarily during the early filling phase of diastole, defined by transmitral Doppler E wave velocity, followed by a small contribution from atrial systole, defined by the late or transmitral A wave. Normally, E is equal to or greater than A. In addition, the longitudinal and radial myocardial fibers adjacent to the mitral annulus elongate and “twist” during early filling, creating a “suction-like” effect that helps propel blood into the LV. This motion of the mitral annulus during diastole is measured using tissue Doppler, and is termed e′. With increasing age (>50 years), in the initial stages of hypertension, and even in asymptomatic ischemia, early filling is slowed, delayed, or impaired and atrial contraction increases to partly compensate and augment ventricular volume. In this scenario, E wave velocity is less than the A wave velocity (e.g., E < A). In addition to the changes in filling dynamics, myocardial relaxation, assessed as e′, is reduced. With progressive worsening of diastolic dysfunction, LA size and pressure increase. Because the LA functions as a reservoir to help maintain an appropriate atrioventricular pressure gradient during diastole, this increase in LA pressure that occurs with progressive deterioration of diastolic function helps “load” blood into the non-compliant LV. In so doing, the transmitral flow velocity profile may appear normal (e.g., E > A); however, given that the mitral annular motion, or e′, remains reduced, the mitral inflow velocity profile represents a “pseudonormal” pattern, indicative of increased severity of diastolic dysfunction. Normally, the LV produces suction in order to fill while in the presence of advanced diastolic dysfunction, the left atrium produces loading in order to compensate and achieve adequate filling.
Figure 1.
Echocardiographic hallmarks in the spectrum of diastolic dysfunction. (A) Schematic long-axis, sagittal view of the left atrium and left ventricle showing transmitral Doppler filling (black arrow) and septal and lateral mitral annular motion (small green arrow within LV wall) during early diastole. (B) Graphic representation of early and late transmitral Doppler-derived wave patterns in relation to the electrocardiogram (EKG). (C) Graphic representation of early and late tissue Doppler-derived mitral annular wave patterns. (Left) Normal diastolic function. The majority (80%) of left ventricular (LV) filling occurs during the early phase of diastole, as depicted by a relatively long black arrow extending from the mitral leaflets into the LV apex. The longer the arrow, the higher the relative velocity of early filling, or E wave, compared with late filling (A wave). Normally, E velocity is equal to or greater than A velocity. (Middle) Impaired relaxation or stage I diastolic dysfunction. With aging, mild hypertension or pressure overload, and/or ischemia, early filling (E wave) is impaired or reduced as depicted by a shorter extension of the black arrow into the LV apex. Also, late filling (A wave) is increased, due to a more vigorous atrial contraction to partly compensate and augment ventricular volume. The ratio of early-to-late-filling velocity is <1, or E < A, in this stage of diastolic dysfunction. Also, septal and lateral mitral annular velocities (e′) are reduced when compared with “normal” (green arrow). (Right) Pseudonormal pattern or Stage II diastolic dysfunction. With progressive worsening of diastolic dysfunction, LA size, and pressure increase. Because the LA functions as a reservoir to help maintain an appropriate atrioventricular pressure gradient during diastole, this increase in LA pressure (LAP) helps load blood into the non-compliant LV. With progressive worsening of diastolic dysfunction, LA size, and pressure increase. While the transmitral flow velocity profile appears normal, the mitral annular motion, or e′, remains reduced. In this situation, the mitral inflow profile is termed “pseudonormal”.
What Evidence Supports a Role for Estrogen in the Maintenance of Diastolic Function?
The increased prevalence of HFpEF in older women compared with men of the same age appears related to the loss ovarian hormones, and primarily estrogens, that occur during menopause (7, 26). Epidemiologic evidence further suggests that premature or early natural menopause (27–29) and a shorter total reproductive duration positively associate with incident heart failure (30). Hall et al. (30) showed that the incidence of HFpEF was higher in postmenopausal women who were nulliparous, further suggesting a role of endogenous estrogens in the pathogenesis of the disease process. Importantly, diastolic dysfunction, the harbinger of HFpEF, was recently described as part of the “postmenopausal syndrome” (31). When compared with premenopausal women, postmenopausal women exhibit a higher prevalence of LV filling abnormalities. Moreover, when older women are compared with their age-matched male counterparts, the likelihood of manifesting more prominent diastolic dysfunction is increased (32–34). Findings from small clinical (35–39) and animal studies, as reviewed by us (40) and others (31, 41), document estrogen therapy efficacy in improving diastolic function and/or limiting increases in LV mass and interstitial remodeling after surgically induced or natural menopause. These data affirm estrogen's role in the preservation of diastolic function in the female heart.
Estrogen Receptors in the Heart
Estrogen mediates its actions on the heart through three identified ERs. Estrogen receptor subtypes α (ERα) and β (ERβ) are classical nuclear hormone receptors, which bind estrogen and translocate to the nucleus to regulate target gene expression. However, molecular signaling is also induced by estrogen outside of the nucleus. While some intracellular signaling may be initiated by truncated forms of the steroid ERs (42), a membrane-bound ER distinct from ERα and ERβ was identified as the orphan receptor GPR30 before being renamed GPER (43, 44). GPER binds estradiol (E2) at a similar nanomolar affinity as ERα and ERβ and exerts comparable actions on calcium mobilization and phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation (45). ERα and GPER are expressed at similar levels in cardiac tissue from male and female rodents (46) as well as from humans (47). In contrast, reports of ERβ expression in the heart are conflicting, with ERβ mRNA detected in human cardiac tissue (48) but remaining below detectable levels in rodent cardiac tissue (46, 49). Based on observed improvement in cardiac function in response to E2 treatment in postmenopausal women (50) and in ovariectomized (OVX) rats (21), researchers have attempted to identify the primary receptor mediating estrogen's cardioprotective effects. Despite the inability to detect ERβ mRNA in some rodent models, administration of a novel ERβ agonist (βLGND2) attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis (51) and genetic deletion of ERβ removes female sex-based cardioprotection in a model of pressure overload (52). These studies indicate that ERβ may be upregulated in the heart during disease or impact cardiac function through infiltrating cells rather than in cardiomyocytes. While studies using selective ERα and ERβ agonists indicate that both receptors induce cardioprotection (53), direct comparisons of genetic ERα and ERβ knockout (KO) mice indicate a dominant role for ERβ (54). However, assessing the double ER KO mouse in addition to each receptor KO individually showed no differences in infarct size, suggesting physiological redundancy or compensation (55).
GPER is expressed on the plasma and intracellular membranes of cardiac cells, including cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibroblasts, mast cells, and endothelial cells (56–59). To clarify the roles of GPER in the heart, pharmacologic approaches using the selective agonist G1 and antagonists G15 or G36 are commonly used. In Table 1, we summarize the ability of relevant hormones, natural estrogens, and drug molecules to bind to and activate signaling through GPER and ERα/β. G1 is the most commonly used tool for studying GPER. This non-steroidal, high-affinity (Kd = 11 nM) and highly selective GPER agonist was developed from a library of 10,000 molecules and does not activate the classical estrogen receptors at concentrations up to 10 μM (63). G15 and G36 are antagonists of GPER with low affinity binding to the classical estrogen receptors (64). While the exact signaling actions and transduction pathways of cardiac GPER are not completely understood, they are likely dependent on the cell type, site of action and the relative levels in comparison with the other estrogen receptors (46). The selective GPER agonist G1 modulates fast transduction pathways in the heart that are involved in (1) controlling intracellular calcium via actions on cardiac channels and pumps, (2) regulating phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3Ks) and extracellular signal-related kinases (ERKs), and (3) modulating cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (see sections Effects of Estrogen and GPER Activation on ICa,L and Estrogen, GPER, and SERCA2a and Its Regulatory Proteins below). The rapid signaling events following GPER activation also lead to inhibition of the expression of cell cycle genes, such as cyclin B1 and CDK1, which are involved in cardiac fibroblast and mast cell proliferation and contribute to interstitial remodeling (see sections GPER Inhibits Interstitial Remodeling and GPER and Cardiac Chymase/Ang II below). Moreover, GPER activation by G1 reduces remodeling promoted by hypertrophic regulators, including angiotensin II and endothelin-1, via inhibition of 1/2 ERK signaling and upregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways (see section GPER and Anti-hypertrophic Remodeling below).
Table 1.
Ligands of GPER and ERs (60).
| DPN | PPT | 17β-Estradiol | Genistein BPA Nonylphenol DDT | Tamoxifen Raloxifene | ICI182,780 | G-1 | G15 G36 | Quercetin (61, 62) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERα/β | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | – | n.d | n.d. | + |
| GPER | n.d. | +? | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | −− | ++ |
DPN, diaryl propionitrile; PPT, propylpyrazoletriol; BPA, bisphenol A; DDT, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Plus (+) symbol denotes weak agonist; Double plus (++) symbol denotes strong agonist; Minus (–) symbol denotes weak antagonist; Double minus (– –) symbol denotes strong antagonist; n.d., no reported data. Question mark (?) denotes interpret with care until confirmed by additional approaches.
Since only a limited number of studies have explored the actions of GPER in diastolic function, future studies are needed to deepen our understanding of its effects in the various cardiac cell populations. Elucidation of these cell-type specific signaling mechanisms will help to clarify the therapeutic potential of cardiac GPER activation in preventing and/or halting the progression of cardiac diseases that involve diastolic dysfunction. Herein, where data exists, we include the signaling pathways of an activated GPER that are linked to the physiologic underpinnings of diastolic function preservation in the context of estrogen deprivation (Figure 2). Initial work showed that administration of the GPER agonist G1 prevents diastolic dysfunction and LV remodeling in OVX (25) and salt-loaded (65) mRen2.Lewis rats. To tease out more precise information about the functional role of GPER in the heart, we generated a novel conditional mouse model where GPER was specifically deleted in cardiomyocytes (23). Therefore, the remainder of the review will examine the evidence that links GPER to the preservation of myocardial relaxation and LV structure in the female heart after estrogen loss during hypertension, heart failure, and normal aging.
Figure 2.

GPER in the functional circle of diastology of the female heart. Diastolic function is an appropriate barometer of overall heart health as it reflects cellular and subcellular events responsible for maintaining myocardial relaxation, cardiomyocyte calcium homeostasis, mitochondrial bioenergetics, antioxidant defense, left ventricular (LV) and myocyte structure, and proximal aortic distensibility. Loss of ovarian estrogens due to aging/menopause or surgery lead to impairments in myocardial/cardiomyocyte relaxation, increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and impaired oxidant defenses and bioenergetics, hypertrophic and/or interstitial remodeling, and aortic stiffening. Preclinical studies show that activation of the non-canonical estrogen receptor, GPER, by its agonist G1 or estradiol (E2) favorably regulates and likely integrates components of relaxation, mitochondrial function, LV structure, LV ejection, and aortic compliance, to preserve diastolic function in the female heart.
GPER and Myocardial/Cardiomyocyte Relaxation
Overview of Cardiac Ca2+ Machinery Involved in Contraction and Relaxation
Maintaining cardiomyocyte calcium concentration [Ca2+]i within a tightly controlled range is critical for normal systolic and diastolic function. In adult cardiomyocytes, the L-type Ca2+ channel is the main pathway for Ca2+ influx. The Na/Ca2+ exchanger is quantitatively the most important pathway for Ca2+ efflux out of the cardiomyocyte. The sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) pumps and the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release channels (ryanodine receptors) are pivotal in determining [Ca2+]i and subsequent contraction and relaxation.
At the initiation of myocardial contraction, depolarization of the cardiomyocyte leads to activation of the inward Ca2+ current conducted via L-type Ca2+ channels Cav1.2 (ICa,L). This is the main trigger for Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, termed Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR). CICR involves ryanodine receptors (RyR), of which RyR2 is the predominant myocardial isoform. ICa,L and CICR together increase the concentration of intracellular Ca2+ that binds to troponin C on myofilaments to initiate myocardial contraction.
Myocardial relaxation begins when ATP hydrolyzes and actin-myosin cross-bridges unlink. Removal of cytoplasmic Ca2+ and subsequent dissociation of Ca2+ from troponin is required for myocardial relaxation. This involves multiple components, including Ca2+ reuptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum via SERCA2a (responsible for 70% cytoplasmic Ca2+ removal in humans) and activation of the sarcolemmal Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX, 28%) and, to a lesser extent, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA, 2%) (66). ICa,L also contributes to the filling status of the SR and myocardial relaxation. Other important processes allowing myocardial relaxation and diastolic ventricular filling include deactivation of the thin myofilaments, modulated by troponin and tropomyosin, and cross-bridge cycling, as recently reviewed (67).
We will briefly discuss the effects of estrogen on components of myocardial Ca2+ signaling, with a focus on mechanisms that regulate myocardial relaxation and the known role of GPER. A summary of the proteins/messengers examined in this context is provided in Table 2.
Table 2.
Effect of E2 and GPER on proteins/messengers involved in Ca2+-dependent cardiac function.
| Ca2+ signaling protein involved | Assay | Model/Intervention/Treatment | Tissue/cells examined | Effects of intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-type Ca2+ channels (Cav1.2) | Agonist-induced Ca2+ signal | G1 (68) G1 (69) G36 (69) |
ISO-induced HFpEF myocytes (68) Male LV myocytes (69) Male LV myocytes (69) |
Restored ISO-induced Ca2+ transient amplitude (68) ↓ ISO-induced Ca2+ signals (69) ↑ ISO-induced Ca2+ signals (69) |
| Electrically stimulated Ca2+ transient | E2 (70–72) RVT (73) E2, raloxifene (71) E2/OVX (72) OVX (74) |
Ventricular myocytes (70, 71, 73) ERα−/−, ERβ−/− myocytes (71) LV apical myocytes (72) Ventricular myocytes (74) |
↓ amplitude (70, 71, 73), delay recovery from inactivation (70) ↓ cell shortening (71) ↓ amplitude (71) ↑ amplitude (72) ↓ amplitude (74) |
|
| ISO-induced cAMP Basal cAMP |
E2 (75) OVX (72) OVX/E2 or G1 (72) |
Perfused heart (75) LV apex (72) LV apex (72) |
↓ cAMP (75) ↓ cAMP (72) Restored to sham level (72) |
|
| Cav1.2 mRNA immunoblotting |
OVX (72) E2/OVX (72) |
LV apical myocytes (72) LV apical myocytes (72) |
↓ mRNA (72) Restored to sham level (72) | |
| RyR2 | Immunoblotting | G1/ OVX-HTN (25) | LV tissue (25) | No change (25) |
| Caffeine-induced SR Ca2+ release | OVX (74) | Ventricular myocytes (74) | ↑ SR Ca2+ release (74) | |
| 45Ca2+ flux | OVX (76) E2/OVX (76) PKA (-)/ OVX (76) |
LV myocytes (76) LV myocytes (76) LV myocytes (76) |
↑45Ca2+ flux (76) Restored to sham level (76) Restored to sham level (76) |
|
| SR Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) | Agonist-induced SR Ca2+ accumulation | G1 (24) | Saponin-skinned myocytes (24) | ↑ Ca2+ accumulation (24) |
| SR Ca2+ uptake | OVX (77) E2/OVX (77) Progesterone/OVX (77) |
LV tissue (77) LV tissue (77) LV tissue (77) |
↓ uptake (77) Restored uptake (77) Restored uptake (77) |
|
| Immunoblotting | OVX (76) E2/OVX (76) G1/OVX old-aged (24) |
LV myocytes (76) LV myocytes (76) LV tissue (24) |
No change (76) No change (76) ↑ expression (24) |
|
| Phospholamban (PLB) | PLB mRNA PLB immunoblot |
G1/OVX-HTN (25) OVX/MCT-PAH (20) OVX/G1/MCT-PAH (20) |
LV tissue (25) RV tissue (20) RV tissue (20) |
No change (25) ↓pPLB/PLB expression (20) Restored normal expression (20) |
| Ser16 PLB phosphorylation | OVX (77) | LV tissue (77) | No change | |
| Thr17 PLB phosphorylation | OVX (77) E2/OVX (77) Progesterone/OVX (77) |
LV tissue (77) LV tissue (77) LV tissue (77) |
↓ Thr17 phosphorylation (77) Restored Thr17 phosphorylation (77) Restored Thr17 phosphorylation (77) |
|
| Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) | Na+-dependent Ca2+ uptake | OVX (76) E2/OVX (76) PKA(–)/OVX (76) |
LV myocytes (76) LV myocytes (76) LV myocytes (76) |
↑ Na+-dependent Ca2+ uptake (76) Restored to sham level (76) Restored to sham level (76) |
E2, estrogen; ER, estrogen receptor; HTN, hypertension; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; ISO, isoproterenol; LV, left ventricular; MCT-PAH, monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension; OVX, ovariectomized; pPLB, phosphorylated phospholamban; PKA, protein kinase A; RV, right ventricular; RVT, right ventricular free wall thickness; RyR, ryanodine receptor; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Effects of Estrogen and GPER Activation on ICa, L
While being a key contributor to systolic Ca2+ increase, ICa,L is also a main source for refilling SR Ca2+ in smooth muscle (78), and directly regulates diastolic Ca2+ level in ventricular myocytes (79). Thus, it significantly affects myocardial relaxation. Overall, there is abundant evidence that estrogen inhibits ICa,L via Cav1.2 in cardiomyocytes.
The involvement of GPER in controlling myocardial contraction by mediating the inhibitory effects of E2 on ICa,L can now be deduced from observations made even before GPER was recognized as an ER. The negative inotropic effect of E2 was reported in the early 1990s. Indeed, E2 causes a decrease in cell shortening associated with reduced action potential duration; in patch-clamp and fluorescent measurements, E2 decreases the peak inward Ca2+ current and delays recovery of ICa,L from inactivation (70). The phytoestrogen resveratrol was later shown to inhibit the amplitude of electrically stimulated Ca2+ transients and cell shortening in ventricular cardiomyocytes (73). In line with earlier observations (70, 73), E2 (0.1–1 nM) reduces heart rate and pressure and cAMP production in the isolated perfused heart treated with isoproterenol; these effects are not inhibited by tamoxifen, an ERα/ERβ antagonist, and at the time were attributed to activation of an unknown membrane receptor (75). We now know that 4-OHT, a metabolite of tamoxifen, is a GPER agonist (45, 80). Later studies confirmed the inhibitory effect of E2 on ICa,L and further showed that genetic deletion of ERα or ERβ does not affect this inhibition (71). In the same studies, raloxifene, an antagonist of ERα/ERβ and agonist of GPER with a functional effective dose of 100 nM (44, 80), decreased ICa,L in cardiomyocytes from wild-type, ERα KO, and ERβ KO animals. Howlett's group also observed that electrically stimulated Ca2+ transients are larger in ventricular myocytes from OVX mice compared with sham female mice (74). We now know that a likely explanation for these observations was that they were mediated by GPER. Initial evidence supporting a role of GPER came from Tran's group, and indicated that GPER activation using G1 (0.001–1 μM) suppresses the isoproterenol-stimulated increases in LV contraction, Ca2+ signals, and ICa,L in intact hearts and in ventricular cardiomyocytes freshly isolated from male mice; these effects are associated with inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent phosphorylation of Cav1.2 (69). Taken together, the reported effects of E2 and GPER activation on cardiomyocyte ICa,L and Ca2+ transients have been consistently inhibitory and suggest that E2 and GPER prevent excessive cardiac contraction in response to acute stimuli.
In stressed cardiomyocytes, the picture appears to be different. The cardiac [Ca2+]i regulatory systems are influenced by the activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) via beta-adrenergic receptor (β-AR)-mediated, cAMP-dependent mechanisms. Estrogen alters gene expression of β-ARs and calcium-handling proteins (81). Preliminary data from Cheng's lab demonstrated that chronic in vivo G1 treatment restores normal myocyte basal and β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR)-mediated contraction, relaxation, and Ca2+ signals, leading to regression of LV dysfunction in a male mouse model of isoproterenol-induced HFpEF (68). These observations are consistent with reduced receptor sensitivity that is typically seen in heart failure. The ability of G1 to restore these parameters suggest that chronic GPER activation re-sensitizes cardiac β-AR regulation in this HFpEF model (68). These data also mirror those reported in a study of the apical myocardium, in which expression of the Cav1.2α subunit and ICa,L were lower in apical myocytes from male or OVX mice compared with sham female mice, and E2 treatment of myocytes from OVX animals corrected these differences (72). The reduction in the amplitude of electrically stimulated Ca2+ transients in myocytes isolated from OVX female mice were restored by G1, to an extent similar to that achieved with E2 treatment. Moreover, blockade of GPER with G15 reversed the benefit of E2 while other ER antagonists had no effect. This data suggests that the protective effects of E2 on ICa,L are mediated in part through GPER in this model. Adrenergic stress-induced declines in contraction amplitude and calcium transients in OVX myocytes were also eliminated via E2/GPER as were decreases in cAMP concentration. Overall, existing data suggest that E2 and GPER activation reduce electrically stimulated or agonist-induced Ca2+ signals and contraction in the normal myocardium yet prevent the inhibition of these functions in stressed myocardium.
Estrogen, GPER, and SERCA2a and Its Regulatory Proteins
SERCA2a is the main mechanism by which SR Ca2+ is refilled during diastole; it also is responsible for removing 70% of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in human cardiomyocytes (66). Several factors control SERCA2a activity. Phospholamban (PLB) is a trans-SR membrane protein that directly interacts with SERCA2a and reduces its activity by lowering its Ca2+ affinity (82). PLB phosphorylation at Ser16 and Thr17 in its cytoplasmic domain disinhibits SERCA2a. Phosphorylation of PLB at Ser16 is mediated by protein kinase A, while Thr17 is phosphorylated by Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) (83, 84). By stimulating PLB phosphorylation, β-AR activation promotes SERCA activity, which increases the rate of Ca2+ sequestration in diastole and facilitates myocardial relaxation (83, 85). Sarcolipin (SLN) is another trans-SR membrane protein that regulates SERCA activity; genetic knockout of SLN enhances SR Ca2+ uptake and cardiac contractility (86). Similar to PLB, SLN reduces the Ca2+ affinity of SERCA2a, though the underlying mechanisms are still a source of debate.
GPER improves LV lusitropy in models of hypertension and aging (24, 25, 65). GPER may increase intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and improve diastolic function by increasing either the expression and/or activity of SR Ca2+ regulatory proteins. Past reports showed that estrogen increases the expression of SERCA2a, while its expression is decreased in OVX animal models. We found no evidence for changes in SERCA2, PLB, calmodulin, or RYR2 gene or protein expression in cardiac tissues with chronic G1 treatment (50 μg/kg/day) of OVX mRen2.Lewis rats with systemic hypertension, despite improvements in myocardial relaxation (25). However, chronic activation of GPER with G1 (400 μg/kg/day) attenuates the adverse effects of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) on SERCA2a and the ratio of phosphorylated PLB to total PLB in an OVX model (20). G1-mediated improvements in Ca2+ regulatory proteins are accompanied by a reversal in PAH-induced LV diastolic dysfunction, pulmonary artery flow, and right ventricular (RV) dysfunction when compared with vehicle-treated counterparts (20). In a normotensive aging model (26-month-old OVX-Brown Norway Fischer 344 rats), 8 weeks of G1 treatment reverses the adverse effects of age and E2 loss on myocardial relaxation, in part via increases in SERCA2 protein expression (24). In addition to changes in SERCA and PLB expression/phosphorylation profiles, the improvement in cardiac function with G1 treatment in these models could also be due in part to improvements in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity and vascular tone. The effects of G1 on the vascular endothelium likely involve stimulation of Ca2+/calmodulin signaling network activities (87), including GPER activation per se (87, 88), upregulation of the Ca2+-dependent interaction between eNOS and calmodulin (87), improvement in the eNOS phosphorylation profile (87, 89), and optimization of vascular Ca2+ signaling via combined effects on influx (90) and efflux pathways (91).
To determine whether specific changes in SR Ca2+ uptake by GPER activation are associated with improvements in myocardial relaxation, we performed ex vivo studies in saponin-skinned muscle fascicles from 8-month-old female Wistar rats (24). SR Ca2+ content was evaluated by caffeine-induced tension under various loading conditions. Compared with vehicle, treatment with G1 increases SR Ca2+ accumulation in a concentration- and loading time-dependent manner suggesting that chronic GPER activation may increase cardiac Ca2+ mobilization not only by increasing the number of SERCA2 pumps, but by also augmenting SERCA activity (24). These data are consistent with a report on an OVX rat model; in that study, 10 weeks after OVX, SR Ca2+ uptake is reduced, with decreased SERCA activity and expression level, and Thr17 phosphorylation of PLB is reduced but Ser16 phosphorylation was unchanged. Interestingly, supplementation with either E2 or progesterone prevents the OVX-related reductions in cardiac SERCA expression and activity and Thr17 PLB phosphorylation (77). However, Yang et al. (92) reported that cardiomyocytes from OVX guinea pigs have 22% larger SR Ca2+ stores and higher frequency of Ca2+ sparks and waves than sham animals; addition of E2 prevents these changes. Similarly, Howlett's group showed that the caffeine-induced SR Ca2+ release signal, an indirect indicator of SR Ca2+ content, is larger in cardiomyocytes from OVX than from sham C57BL/6 mice (74). While these results appear to be contradictory, it is important to note that, in addition to differences in model species, treatment conditions, and dosing, the loss of progesterone with OVX may also play a significant role in the observed effects in each study, as suggested by data from Bupha-Intr and Wattanapermpool (77). Overall, studies using the specific GPER agonist G1 support a role for GPER in influencing SR Ca2+ uptake in the heart to improve diastolic function. Further studies using GPER KO models, especially cardiac-specific GPER−/− cardiomyocytes, will provide further insights.
Estrogen and the Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger
The NCX is responsible for removal of ~28% of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in human cardiomyocytes and as such is an important determinant of diastolic function. However, the effects of estrogen on cardiac NCX are unclear. Estrogen has been reported to increase, have no effect, or decrease NCX expression. In one study, NCX expression was increased by E2 and was decreased in untreated OVX rats (93). In other studies, no change was observed in the expression of NCX expression by estrogen treatment or OVX (25, 94). Kravtsov et al. (76) determined NCX activity in the heart from OVX rats. In their study, NCX activity, measured as Na+-dependent 45Ca2+ uptake, was increased by OVX, and E2 replenishment abolished this increase (76). Mechanistically, the effect of E2 loss and restoration was associated with changes in PKA-mediated activation of NCX and not on changes in the expression level of NCX. However, no study to date has specifically examined if GPER activation mediates the effects of E2 on NCX activity in cardiac tissue.
GPER, Bioenergetics, and Mitochondrial ROS
Diastolic function is an energy-requiring process in that ATP is necessary for the sequestration of cytoplasmic Ca2+ back into the SR during diastole. As the heart possesses the highest content of mitochondria of any tissue (95), even slight alterations in mitochondrial cellular energy production contribute to impairment of myocardial relaxation. Indeed, an increasing body of literature suggests that abnormalities in cardiomyocyte mitochondrial function and structure are important factors in the pathogenesis of HFpEF (96, 97). Specifically, elevated and pathologic reactive oxygen species (ROS) production has been implicated in mitochondrial damage, resulting in a mismatch between ATP production and energy demand, while also activating signaling pathways that further contribute to LV remodeling, all of which lead to diastolic dysfunction.
The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in ROS accumulation and/or alterations in mitochondrial bioenergetics in the estrogen-deficient heart is still emerging, as are the mitochondria-related effects of E2 that are mediated through GPER (98). In a recent general population study (Flemish Study on Environment, Genes, and Health Outcomes), individuals with normal and abnormal diastolic function were found to have different levels of circulating metabolites indicative of energy substrate utilization and protection again oxidative stress (99). In another cohort from that study (100), mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), a circulating marker of mitochondrial dysfunction, was positively associated with female sex, while mtDNA levels were reduced in women receiving estrogen/progesterone treatment. With regard to cardiac pathology, one preclinical study using OVX CTnT-Q92 transgenic mice as a model of human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy showed that E2 replacement reduces oxidative damage and improved decrements in mitochondrial bioenergetics and diastolic function (101). Potential mechanisms underlying the estrogen-mediated protection from mitochondrial-derived oxidative injury include decreasing ROS accumulation by increasing respiratory chain efficiency; reducing apoptotic leakage of cytochrome C; upregulating mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes such as manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase; and decreasing NADPH oxidases (NOX4) (102–105). Pharmacologic interventions in isolated cardiomyocytes and in ischemia-reperfusion-challenged hearts indicate that GPER activation by G1 reduces oxidative stress by limiting cytochrome C release and inhibiting mitochondrial pore opening, respectively (106–108). Our data from the novel cardiomyocyte-specific GPER KO female mouse developed in the Groban laboratory extend these findings with more direct evidence of the potential importance of cardiac GPER in the maintenance of mitochondrial processes that counteract ROS accumulation in the female heart (23). In brief, treatment of female GPER KO mice with the mitochondrial antioxidant MitoQ attenuates the adverse effects of cardiomyocyte GPER deletion on myocardial relaxation, filling pressures, interstitial remodeling, and oxidative damage (109). MitoQ also limits the genomic responses to increased oxidative stress and decreases oxidant defense related to cardiomyocyte-specific GPER deficiency (109). Taken together, GPER appears to have a regulatory role in aspects of mitochondrial function that balance ROS formation and antioxidant defense, which in turn has the potential to impact intracellular calcium homeostasis (110), thereby contributing to the maintenance of diastolic function after estrogen loss.
As diastolic dysfunction accounts for half of what drives HFpEF symptoms and adverse clinical events, it is also important to consider the impact of systemic inflammation, coronary microcirculatory disturbances, skeletal muscle weakness, pulmonary disease, and renal dysfunction (111). Indeed, the most current paradigm of HFpEF goes well beyond diastolic dysfunction. For instance, systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and/or endothelial dysfunction contribute to capillary rarefraction and mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle and myocardium of HFpEF patients (112–114), impairing oxygen delivery and utilization, and adversely affecting exercise tolerance (115, 116). While it is not entirely clear what role estrogen deficiency and/or GPER deactivation might have on these extracardiac parameters linked to HFpEF (117), future preclinical studies focusing on this paradigm may reveal therapeutic strategies that can be personalized to prevent the development of this disorder in postmenopausal women.
GPER and LV Structure
In addition to the cellular mechanics of myocardial relaxation and subcellular mitochondrial energy-producing processes required, the structure of the myocardium at both cardiac muscle cell and LV chamber levels determines LV ventricular distensibility and stiffness. At the cellular level, isolated cardiomyocytes from preclinical models of diastolic heart failure exhibit increases in diameter without changes in length, which correspond to increases in LV wall thickness with normal or near-normal end diastolic volumes (118), a pattern indicative of concentric LV remodeling. In vitro cardiomyocyte functional data from patients with HFpEF further indicate increased stiffness and decreased distensibility, with resting tensions two times that of normal cardiomyocytes (119, 120). Translating this to the tissue level, a relatively stiff, non-distensible ventricle requires higher pressures to achieve filling of a given volume. Conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiographic techniques estimate filling pressure (see section What is Diastolic Dysfunction? above and Figure 1). The effects of GPER activation on components of LV remodeling, and potential mechanisms in the context of the renin angiotensin system and local inflammatory/immune processes, are presented in Table 3.
Table 3.
Anti-remodeling effects of GPER activation in cardiac tissue and cells.
| Species or cells | Models/Strains | G1 treatment | Effects of intervention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat | mRen2.Lewis rats/OVX (25) | s.c., 50 μg/kg/day, for 2 weeks |
Limited OVX-induced ↑ LV filling pressure, LV mass, wall thickness, interstitial collagen deposition, and cardiac ANF and BNP mRNA levels |
| mRen2.Lewis rats/high salt diet (65) | s.c., 40 nmol/kg/hr, for 2 weeks | Improved myocardial relaxation and reduced cardiac myocyte hypertrophy and wall thickness | |
| F344BN old-aged rats/OVX (24) | s.c. 100 μg/kg/day, for 8 weeks | Reversed adverse effects of age and estrogen loss on myocardial relaxation and interstitial collagen deposition | |
| Wistar rats/OVX + monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension (20) | s.c., 400 μg/kg/day, for 14 days after the onset of disease | Limited adverse effects of pulmonary hypertension on RV interstitial fibrosis, RV free wall thickening, and LV diastolic function | |
| Wistar rats/myocardial infarction (121) | 50 μg/kg per day, gastric gavage, for 4 weeks | Attenuated LV hypertrophy, assessed by cardiomyocyte size, to an extent similar to E2 | |
| Wistar rats/OVX and diabetes mellitus (122) | i.p. injection, 50 μg/kg, every 4 days for 4 weeks |
Improved cardiac weight, atherogenic and cardiovascular risk indices; meanwhile GPER antagonism with G15 exacerbated cardiac weight and atherogenic indices | |
| SD rats/OVX + ISO-induced heart failure (123) | s.c.,120 μg/kg·d, for 14 days | Decreased cardiac BNP, reduced cardiac fibrosis, and enhanced contraction | |
| Mouse | C57BL/6 mice/OVX & myocardial infarction (124) | i.p. injection, 35 μg/kg/d, for 4 weeks |
Reduced myocardial fibrosis and infarct area |
| Ramp3+/+ and Ramp3−/− (125) | s.c., 0.1 mg/kg/day, for 40 days | Reduced perivascular fibrosis and cardiomyocyte area in RenTgMK/Ramp3+/+ male mice | |
| Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes | ET-1 (100 nmol/l) for 48 h (126) | 10 nmol/l for 48 h | Abolished hypertrophic actions of ET-1, which was reversed by G15; siRNA silencing of GPER inhibited antihypertrophic effect of E2 |
| 100 nM of Ang II for 24 h (127) | 1,000 nM for 24 h | Attenuated Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and downregulated mRNA levels of ANF and BNP |
|
| H9c2 cardiomyocytes | Ang II (10−7M) for 24 h (25) | 10−7 M for 24 h | Inhibited Ang II-induced hypertrophy, evidenced by reductions in cell size, protein content per cell, and ANF mRNA levels; G15 inhibited protective effects of G1 or E2 |
| Adult rat cardiac fibroblasts | Growth medium with 10% FBS (57) | 0.01–10 μM for 24 h | Inhibited proliferation of rat cardiac fibroblasts |
ANF, atrial natriuretic factor; Ang II, angiotensin II; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; E2, estradiol; ET-1, endothelin-1; FBS, fetal bovine serum; i.p., intraperitoneal; ISO, isoproterenol; LV, left ventricular; OVX, ovariectomized; RV, right ventricular; s.c., subcutaneous; μg, micrograms; SD, Sprague Dawley.
GPER and Anti-hypertrophic Remodeling
Preclinical studies reveal that GPER activation by E2 or G1 prevents hypertrophic remodeling, independent of its effects on blood pressure. We have shown that high salt or estrogen deprivation in hypertensive mRen2.Lewis rats increases LV mass, wall thickness, and myocyte size and is attenuated by chronic G1 treatment (25, 65). Moreover, ventricular hypertrophy assessed by cardiomyocyte size after infarction by coronary ligation in OVX Wistar rats is attenuated to a similar extent by G1 and E2 (121). Lee et al. (121) further showed that GPER and ERα activation converge to elicit post-ischemic antihypertrophic remodeling via a PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent pathway. In cultured primary neonatal cardiomyocytes (127) and H9c2 cells (25), GPER activation by G1 attenuates angiotensin II (Ang II)- and endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced hypertrophy, respectively, as demonstrated by reductions in atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) mRNA expression levels, cell size, and protein content. The protective effects of GPER involved inhibition of ERK1/2 signaling and an upregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway (127). The latter is known to effect autophagy, which is important in the preservation of cell homeostasis. In another study using neonatal cardiomyocytes, ET-1–induced hypertrophy was prevented by E2/GPER via inhibition of ERK1/2 signaling (126).
GPER Inhibits Interstitial Remodeling
Alterations in the extracellular matrix, specifically increases in collagen, with corresponding increments in the width and continuity of fibrillar components (128), further contribute to diastolic dysfunction through increases in chamber stiffness. Interstitial and perivascular collagen deposition are enhanced in physiopathologic situations that commonly manifest diastolic dysfunction such as aging, hypertension, pressure overload hypertrophy, and estrogen loss. E2 or GPER activation with G1 prevents increases in OVX-related effects on profibrotic gene expression, fibroblast proliferation, and collagen deposition in rodent and non-human primate models of normative cardiac aging, hypertension, and pulmonary hypertension (19–21, 24). However, it is worth mentioning that increased cardiac collagen after estrogen loss may not be universal, nor is its effect on increasing passive chamber stiffness (129). Whether length of time of estrogen deprivation, animal species and strain, and the type physiologic stress account for these discrepancies is not entirely clear. Nonetheless, in vitro studies demonstrate the capacity of E2 to regulate the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts and their collagen production (130), effects that are deemed to be partly mediated by GPER. We recently confirmed GPER expression in cardiac fibroblasts of male Sprague Dawley rats and further demonstrated the efficacy of G1 on inhibiting cardiac fibroblast proliferation in a dose-dependent manner (57). These findings were confirmed in vivo in OVX-mRen2.Lewis females, in which 2 weeks of G1 treatment limits estrogen deficiency-induced increases in LV cardiac fibroblast number, proliferation, and gene expression levels of the cell cycle proteins, CDK1, and Cyclin B1 (57).
GPER and Cardiac Chymase/Ang II
Activation of the renin angiotensin system (RAS) is one mechanism for LV hypertrophic and interstitial remodeling that contributes to LV stiffness and diastolic dysfunction. Indeed, Ang II is involved in tissue remodeling and the induction of fibrosis (131). While RAS blockade is a widely used approach to treat heart failure, including HFpEF (132–134), the clinical benefits gained from RAS blockers in halting or reversing disease progression has fallen short of expectations (135–138). These drugs may have limited ability to suppress Ang II synthesis at the intracellular spaces where Ang II is formed and exerts its trophic and profibrotic actions (139, 140). Findings from the Ferrario lab (140–144) and others (145–148) suggest that chymase, not angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), is the major Ang II-forming enzyme in both human and rat hearts, and produces Ang II from the substrate angiotensin I (Ang I) or angiotensin-(1–12) [Ang-(1–12)].
With respect to estrogen status (intact vs. OVX) and LV diastolic dysfunction, we demonstrated a positive relationship between cardiac chymase-forming Ang II and echo-derived filling pressures in normotensive Wistar Kyoto female rats (149) and hypertensive mRen.Lewis rats (150). OVX-related increases in chymase and Ang II expression were further associated with increases in cardiac fibrosis. Because mast cells are a major source of chymase (151, 152) and generate Ang II from Ang I or Ang-(1–12) (153), we also determined the impact of mast cell inhibition by the mast stabilizer cromolyn sulfate on OVX-induced diastolic dysfunction (154). In brief, 8 weeks of cromolyn sulfate administered subcutaneously to OVX-BNF344 rats attenuates the adverse effects of estrogen loss on diastolic function, interstitial collagen deposition, and collagen type 1A mRNA levels. Even though cardiac chymase activity in OVX rats is not overtly reduced by cromolyn (P < 0.06), cardiac Ang II content is reduced when compared with OVX vehicle, suggesting a role for mast cell derived-factors and chymase/Ang II in the progression of cardiac aging and diastolic dysfunction after estrogen loss (154). Indeed, E2 treatments favorably regulate cardiac mast cell number and prevent the adverse effects of OVX on cardiac remodeling and LV function in an Ang II-dependent rodent model of hypertension and LV diastolic dysfunction (150) and in models of surgically induced pressure overload (155) and volume overload (156, 157).
Although the mechanisms by which estrogen regulates cardiac mast cell number are not entirely clear, it appears to be mediated in part through GPER. Findings from us suggest that GPER is expressed in RBL-2H3 mast cells (58) and that GPER activation by its agonist G1 inhibits serum-induced proliferation of these cells through interaction with the cell cycle protein CDK1. GPER blockade by G15, but not by ERα or ERβ antagonists, completely prevents E2-induced inhibition of mast cell proliferation (58). This effect was confirmed in vivo in OVX-mRen2.Lewis rats; 2 weeks of G1 treatment decreases cardiac mast cell number and chymase expression/Ang II levels, and limits gene and protein expression of cell cycle proteins (58). Taken together, these data suggest that the inhibitory effects of GPER on extracellular matrix remodeling may in part involve cardiac mast cell chymase/Ang II modulation.
GPER and Cardiac Inflammation
Another indirect way by which GPER activation could prevent OVX-induced remodeling and diastolic dysfunction is through modulation of local inflammatory defense mechanisms (111, 158).
Using cardiomyocyte-specific GPER KO mice (23), we found an intriguing relationship between loss of cardiac GPER and the NLRP3 inflammasome, which includes NLRP3, caspase-1, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-18. The NRLP3 inflammasome is formed and activated by various stimuli, including oxidative stress, and participates in the pathogenesis of hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and other cardiovascular diseases (159). Characterization of innate immunity gene transcripts in hearts from 6-month-old cardiomyocyte-specific GPER KO mice and their GPER-intact wild-type littermates revealed that expression of NLRP3 and IL-18 are increased nearly three-fold (22). The importance of NLRP3 upregulation in GPER KO-induced heart failure was further confirmed in an in vivo study showing that, compared with vehicle-treated KO mice, 8 weeks of treatment with a NLRP3 inhibitor, MCC950 (10 mg/kg, i.p., 3 times per week), significantly limits hypertrophic remodeling and improves LV systolic and diastolic function (22). Consistent with a potential role of GPER in inflammasome deactivation, gene expression levels of key inflammatory genes, and cytokines related to inflammasome biology, including IL-18, IL-33, NLRP3, and caspase-1, were reduced in hearts of OVX-mRen2.Lewis rats treated with G1 compared with vehicle (unpublished data).
Whether G1/GPER-mediated anti-inflammatory responses are related to its effects on mast cells, as discussed previously, is not known. Mast cells are potent innate immune cells that accumulate in chronically inflamed tissues. The IL-1 family of cytokines, and particularly IL-33, activate mast cells and prime them to respond to inflammatory signals (160). If estrogen loss leads to a low-grade, chronic inflammatory state (161) in the female heart, the role of mast cells may evolve and continue to “feed the fire” via ongoing mediator release, such as chymase, thereby contributing to LV stiffness through hypertrophic cardiomyocyte and interstitial remodeling.
GPER, LV Ejection, and Proximal Aortic Distensibility
LV ejection with respect to proximal aortic distensibility is another factor that contributes to diastolic function in the female heart. During systole, the long axis of the left ventricle normally shortens by pulling the aortic annulus toward the relatively fixed LV apex (162, 163). Displacement of the aortic annulus and sinotubular junction without concomitant movement of the aortic arch during systole promotes longitudinal stretch of the proximal aorta (162, 164, 165). While the aortic stretch that occurs during systole imposes a systolic load on the heart, it actually enhances early diastolic filling by serving as a reservoir for elastic energy (165). With loss of aortic distensibility due to advancing age, and presumably estrogen deficiency (163), or HFpEF (166) the displacement of the aortic annulus is reduced, as is the longitudinal long axis force or shortening of the left ventricle, leading to less stored elastic energy and impaired LV filling (167). Interestingly, postmenopausal women are more susceptible to the adverse effects of greater proximal aortic stiffness and pulsatile load on diastolic function and ventricular-arterial interaction than men of the same age (168–170). Moreover, the relationship between aortic impedance and diastolic dysfunction and ventricular-arterial coupling in women might be independent of LV remodeling (168), suggesting an additional contribution of aortic impedance to diastolic dysfunction in women.
Although the exact role of estrogen/GPER in aortic–ventricular interactions with respect to diastolic function is not known, recent preclinical studies suggest that GPER activation limits aortic stiffening and remodeling. GPER is expressed in both endothelial and smooth muscle cells of the aorta (59, 171) and GPER activation induces vasodilation similar to that seen with E2 (89, 172). In contrast to resistance arteries, GPER-induced vasorelaxation in the aorta is less robust (173) and the contribution of endothelial vs. smooth muscle signaling is more variable (59, 171). Interestingly, aortic GPER expression is downregulated in diabetes (174) but is functionally enhanced during pregnancy (171). In contrast to the extensive work assessing aortic reactivity, less is known about the impact of GPER on passive structural properties of conduit arteries. In the mRen2 rat model of hypertension, pharmacological activation of GPER in salt-loaded females significantly decreases aortic wall thickness without impacting blood pressure (175). GPER is also protective during carotid injury, where adenovirus-induced restoration of GPER protein expression is associated with a reduction in wall thickness in both male and female rats (176). While Ang II-induced hypertension is not impacted by GPER deletion, pulse pressure, and aortic wall thickness are significantly greater in female cardiomyocyte-specific GPER KO vs. wild-type mice (177). Therefore, while the role of GPER in proximal aortic distensibility has not yet been directly measured, published studies suggest that it most likely is another important factor impacting diastolic function.
Translational Perspective
The sex-differential in the prevalence and incidence of human HFpEF is stark. Among women age >/ = 65 years, nearly 90% of new cases of heart failure are HFpEF. In the small number of men who develop HFpEF, the underlying characteristics differ markedly from that seen in women with predominantly ischemic heart disease, mildly dilated LV, and borderline/mild levels of systolic dysfunction. Thus, classic HFpEF is nearly exclusively a disorder of older, post-menopausal women. Despite this overwhelming magnitude of this profound biologic signal, its fundamental basis has not been systematically examined. Doing so could produce major insights into the initiation and progression of human HFpEF. Thus, the emerging data reviewed above has the potential to promote key advances in the understanding of human HFpEF and novel approaches to interrupting the pathways that lead to one of its precursors, diastolic dysfunction. This is greatly needed given the disappointing results of the recent PARAGON trial (178), and the other 7 large randomized trials of HFpEF that failed to achieve their pre-determined primary endpoint (179).
Conclusion
Improvements in preventive medicine and health habits by positively lengthening the human life-span have brought to the forefront the impact of the menopause decline in women's cardioprotection. Estrogen-mediated cardiac health in women, using diastolic function as its monitor, is influenced by non-genomic mechanisms through GPER in the heart, in part by counteracting age and/or estrogen loss-dependent abnormalities in myocardial relaxation, cardiomyocyte Ca2+ homeostasis, mitochondrial function, and anti-hypertrophic/interstitial processes (Figure 2).
Author Contributions
LG conceived and designed the manuscript. LG, Q-KT, and SL drafted the manuscript. Q-KT, HW, XS, LG, and SL created the tables and figures. DK provided the translational perspective. DK, CF, and CC were involved in critically reviewing and revising the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the manuscript to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ACE
angiotensin-converting enzyme
- ANF
atrial natriuretic factor
- Ang I
angiotensin I
- Ang II
angiotensin II
- Ang-(1-12)
angiotensin-(1-12)
- β-AR
beta-adrenergic receptor
- BNP
brain natriuretic peptide
- Ca2+
calcium
- CaMKII
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- CICR
calcium-induced calcium release
- E2
estradiol
- EKG
electrocardiogram
- eNOS
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ER
Estrogen receptor
- ERα
Estrogen receptor subtype α
- ERβ
Estrogen receptor subtype β
- ET-1
endothelin-1
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- GPER
G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor
- GPR30
G-protein-coupled receptor
- HFpEF
heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- HTN
hypertension
- ICa,L.
L-type calcium channels Cav1.2
- i.p.
intraperitoneal
- IL
interleukin
- ISO
isoproterenol
- KO
knockout
- LA
left atrium
- LAP
left atrial pressure
- LV
left ventricular
- MCT
monocrotaline
- MnSOD
manganese superoxide dismutase
- mtDNA
mitochondrial DNA
- NCX
sodium/calcium exchanger
- NOX4
NADPH oxidases
- OVX
ovariectomy
- PAH
pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PKA
protein kinase A
- PLB
phospholamban
- PMCA
plasma membrane calcium ATPase
- pPLB
phosphorylated phospholamban
- RAS
renin angiotensin system
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- RV
right ventricular
- RVT
right ventricular free wall thickness
- RyR
ryanodine receptor
- s.c.
subcutaneous
- SD
Sprague Dawley
- SLN
sarcolipin
- SR
sarcoplasmic reticulum
- SERCA2a
sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase 2a.
Footnotes
Funding. This work was supported by grants from the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute PO1HL051952 (CF and LG), R15HL112184 (Q-KT), R01HL133619 (SL), and the National Institute on Aging R01AG033727 (LG), R21AG061588 (LG), R01AG049770 (CC), R01AG18915 (DK), and P30AG021332 (DK) of the National Institute of Health and Iowa Osteopathic & Educational Research IOER-091707 and IOER-O91807 (Q-KT).
References
- 1.Groban L, Kitzman DW. Diastolic function: a barometer for cardiovascular risk? Anesthesiology. (2010) 112:1303–6. 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181da89e4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kitzman DW, Little WC. Left ventricle diastolic dysfunction and prognosis. Circulation. (2012) 125:743–5. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.086843 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pfeffer MA, Shah AM, Borlaug BA. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in perspective. Circ Res. (2019) 124:1598–617. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.313572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gori M, Lam CSP, Gupta DK, Santos ABS, Cheng S, Shah AM, et al. Sex-specific cardiovascular structure and function in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. (2014) 16:535–42. 10.1002/ejhf.67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scantlebury DC, Borlaug BA. Why are women more likely than men to develop heart failure with preserved ejection fraction? Curr Opin Cardiol. (2011) 26:562–8. 10.1097/HCO.0b013e32834b7faf [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Masoudi FA, Havranek EP, Smith G, Fish RH, Steiner JF, Ordin DL, et al. Gender, age, and heart failure with preserved left ventricular systolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2003) 41:217–23. 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02696-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dunlay SM, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:591–602. 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pirmohamed A, Kitzman DW, Maurer MS. Heart failure in older adults: embracing complexity. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2016) 13:8–14. 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2016.01.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Upadhya B, Taffet GE, Cheng CP, Kitzman DW. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the elderly: scope of the problem. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2015) 83:73–87. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.02.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nagueh SF. Left ventricular diastolic function: understanding pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prognosis with echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2019). 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.10.038. [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF, III, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the american society of echocardiography and the European association of cardiovascular imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2016) 17:1321–60. 10.1093/ehjci/jew082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mitter SS, Shah SJ, Thomas JD. A test in context: E/A and E/e' to assess diastolic dysfunction and LV filling pressure. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:1451–64. 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.12.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ho CY, Solomon SD. A clinician's guide to tissue Doppler imaging. Circulation. (2006) 113:e396–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.579268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Groban L, Dolinski SY. Transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of diastolic function. Chest. (2005) 128: 3652–63. 10.1378/chest.128.5.3652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groban L, Sanders DM, Houle TT, Antonio BL, Ntuen EC, Zvara DA, et al. Prognostic value of tissue Doppler-Derived E/e' on early morbid events after cardiac surgery. Echocardiography. (2010) 27:131–8. 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2009.01076.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Swaminathan M, Nicoara A, Phillips-Bute BG, Aeschlimann N, Milano CA, Mackensen GB, et al. Utility of a simple algorithm to grade diastolic dysfunction and predict outcome after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. (2011) 91:1844–50. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, Miller FA, Oh JK, Redfield MM, et al. Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study. Circulation. (2000) 102:1788–94. 10.1161/01.CIR.102.15.1788 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Groban L, Kitzman DW, Register TC, Shively CA. Effect of depression and sertraline treatment on cardiac function in female nonhuman primates. Psychosom Med. (2014) 76:137–46. 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Michalson KT, Groban L, Howard TD, Shively CA, Sophonsritsuk A, Appt SE, et al. Estradiol treatment initiated early after ovariectomy regulates myocardial gene expression and inhibits diastolic dysfunction in female cynomolgus monkeys: potential roles for calcium homeostasis and extracellular matrix remodeling. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7:e009769. 10.1161/JAHA.118.009769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alencar AKN, Montes GC, Costa DG, Mendes LVP, Silva AMS, Martinez ST, et al. Cardioprotection induced by activation of GPER in ovariectomized rats with pulmonary hypertension. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2018) 73:1158–66. 10.1093/gerona/gly068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jessup JA, Wang H, MacNamara LM, Presley TD, Kim-Shapiro DB, Zhang L, et al. Estrogen therapy, independent of timing, improves cardiac structure and function in oophorectomized mRen2.Lewis rats. Menopause. (2013) 20:860–8. 10.1097/GME.0b013e318280589a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang H, Sun X, Hodge HS, Ferrario CM, Groban L. NLRP3 inhibition improves heart function in GPER knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 514:998–1003. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang H, Sun X, Chou J, Lin M, Ferrario CM, Zapata-Sudo G, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) leads to left ventricular dysfunction and adverse remodeling: a sex-specific gene profiling analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2017) 1863:1870–82. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.10.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alencar AK, da Silva JS, Lin M, Silva AM, Sun X, Ferrario CM, et al. Effect of age, estrogen status, and late-life GPER activation on cardiac structure and function in the Fischer344xBrown Norway female rat. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2017) 72:152–62. 10.1093/gerona/glw045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang H, Jessup JA, Lin MS, Chagas C, Lindsey SH, Groban L. Activation of GPR30 attenuates diastolic dysfunction and left ventricle remodelling in oophorectomized mRen2.Lewis rats. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 94:96–104. 10.1093/cvr/cvs090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tadic M, Cuspidi C, Plein S, Belyavskiy E, Heinzel F, Galderisi M. Sex and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: from pathophysiology to clinical studies. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:E792. 10.3390/jcm8060792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Appiah D, Schreiner PJ, Demerath EW, Loehr LR, Chang PP, Folsom AR. Association of age at menopause with incident heart failure: a prospective cohort study and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e003769. 10.1161/JAHA.116.003769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ebong IA, Watson KE, Goff DC, Bluemke DA, Srikanthan P, Horwich T, et al. Age at menopause and incident heart failure. Menopause. (2014) 21:585–91. 10.1097/GME.0000000000000138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rahman I, Akesson A, Wolk A. Relationship between age at natural menopause and risk of heart failure. Menopause. (2015) 22:12–6. 10.1097/GME.0000000000000261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hall PS, Nah G, Howard BV, Lewis CE, Allison MA, Sarto GE, et al. Reproductive factors and incidence of heart failure hospitalization in the women's health initiative. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2017) 69:2517–26. 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.03.557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Maslov PZ, Kim JK, Argulian E, Ahmadi A, Narula N, Singh M, et al. Is cardiac diastolic dysfunction a part of post-menopausal syndrome? JACC Heart Fail. (2019) 7:192–203. 10.1016/j.jchf.2018.12.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Okura H, Takada Y, Yamabe A, Kubo T, Asawa K, Ozaki T, et al. Age- and gender-specific changes in the left ventricular relaxation: a Doppler echocardiographic study in healthy individuals. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2009) 2:41–6. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.108.809087 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dalen H, Thorstensen A, Vatten LJ, Aase SA, Stoylen A. Reference values and distribution of conventional echocardiographic Doppler measures and longitudinal tissue Doppler velocities in a population free from cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2010) 3:614–22. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.926022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Borlaug BA, Redfield MM, Melenovsky V, Kane GC, Karon BL, Jacobsen SJ, et al. Longitudinal changes in left ventricular stiffness: a community-based study. Circ Heart Fail. (2013) 6:944–52. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Duzenli MA, Ozdemir K, Sokmen A, Gezginc K, Soylu A, Celik C, et al. The effects of hormone replacement therapy on myocardial performance in early postmenopausal women. Climacteric. (2010) 13:157–70. 10.3109/13697130902929567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gokce M, Karahan B, Erdol C, Kasap H, Ozdemirci S. Left ventricular diastolic function assessment by tissue Doppler echocardiography in relation to hormonal replacement therapy in postmenopausal women with diastolic dysfunction. Am J Ther. (2003) 10:104–11. 10.1097/00045391-200303000-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Voutilainen S, Hippelainen M, Hulkko S, Karppinen K, Ventila M, Kupari M. Left ventricular diastolic function by Doppler echocardiography in relation to hormonal replacement therapy in healthy postmenopausal women. Am J Cardiol. (1993) 71:614–7. 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90525-H [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aldrighi JM, Alecrin IN, Caldas MA, Gebara OCE, Ramires JAF, Rosano GMC. Effects of estradiol on myocardial global performance index in hypertensive postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2004) 19:282–92. 10.1080/09513590400017464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fak AS, Erenus M, Tezcan H, Caymaz O, Oktay S, Oktay A. Effects of a single dose of oral estrogen on left ventricular diastolic function in hypertensive postmenopausal women with diastolic dysfunction. Fertil Steril. (2000) 73:66–71. 10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00451-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhao Z, Wang H, Jessup JA, Lindsey SH, Chappell MC, Groban L. Role of estrogen in diastolic dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2014) 306:H628–40. 10.1152/ajpheart.00859.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li S, Gupte AA. The role of estrogen in cardiac metabolism and diastolic function. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J. (2017) 13:4–8. 10.14797/mdcj-13-1-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang Z, Zhang X, Shen P, Loggie BW, Chang Y, Deuel TF. A variant of estrogen receptor-α, hER-α36: transduction of estrogen- and antiestrogen-dependent membrane-initiated mitogenic signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2006) 103:9063–8. 10.1073/pnas.0603339103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ, Dong J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. (2005) 146:624–32. 10.1210/en.2004-1064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. XCVII. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor and its pharmacologic modulators. Pharmacol Rev. (2015) 67:505–40. 10.1124/pr.114.009712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science. (2005) 307:1625–30. 10.1126/science.1106943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hutson DD, Gurrala R, Ogola BO, Zimmerman MA, Mostany R, Satou R, et al. Estrogen receptor profiles across tissues from male and female Rattus norvegicus. Biol Sex Differ. (2019) 10:4. 10.1186/s13293-019-0219-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Patel VH, Chen J, Ramanjaneya M, Karteris E, Zachariades E, Thomas P, et al. G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1 expression in rat and human heart: protective role during ischaemic stress. Int J Mol Med. (2010) 26:193–9. 10.3892/ijmm_00000452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Leibetseder V, Humpeler S, Zuckermann A, Svoboda M, Thalhammer T, Marktl W, et al. Time dependence of estrogen receptor expression in human hearts. Biomed Pharmacother. (2010) 64:154–9. 10.1016/j.biopha.2009.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pugach EK, Blenck CL, Dragavon JM, Langer SJ, Leinwand LA. Estrogen receptor profiling and activity in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2016) 431:62–70. 10.1016/j.mce.2016.05.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pines A, Fisman EZ, Drory Y, Shapira I, Averbuch M, Eckstein N, et al. The effects of sublingual estradiol on left ventricular function at rest and exercise in postmenopausal women: an echocardiographic assessment. Menopause. (1998) 5:79–85. 10.1097/00042192-199805020-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pedram A, Razandi M, Korach KS, Narayanan R, Dalton JT, Levin ER. ERbeta selective agonist inhibits angiotensin-induced cardiovascular pathology in female mice. Endocrinology. (2013) 154:4352–64. 10.1210/en.2013-1358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Skavdahl M, Steenbergen C, Clark J, Myers P, Demianenko T, Mao L, et al. Estrogen receptor-beta mediates male-female differences in the development of pressure overload hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2005) 288:H469–76. 10.1152/ajpheart.00723.2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Arias-Loza PA, Hu K, Dienesch C, Mehlich AM, Konig S, Jazbutyte V, et al. Both estrogen receptor subtypes, alpha and beta, attenuate cardiovascular remodeling in aldosterone salt-treated rats. Hypertension. (2007) 50:432–8. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.106.084798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Babiker FA, Lips D, Meyer R, Delvaux E, Zandberg P, Janssen B, et al. Estrogen receptor beta protects the murine heart against left ventricular hypertrophy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26:1524–30. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000223344.11128.23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Luo T, Liu H, Kim JK. Estrogen protects the female heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury through manganese superoxide dismutase phosphorylation by mitochondrial p38beta at threonine 79 and serine 106. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0167761. 10.1371/journal.pone.0167761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Deschamps AM, Murphy E. Activation of a novel estrogen receptor, GPER, is cardioprotective in male and female rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2009) 297:H1806–13. 10.1152/ajpheart.00283.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang H, Zhao Z, Lin M, Groban L. Activation of GPR30 inhibits cardiac fibroblast proliferation. Mol Cell. Biochem. (2015) 405:135–48. 10.1007/s11010-015-2405-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhao Z, Wang H, Lin M, Groban L. GPR30 decreases cardiac chymase/angiotensin II by inhibiting local mast cell number. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 459:131–6. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lindsey SH, Cohen JA, Brosnihan KB, Gallagher PE, Chappell MC. Chronic treatment with the G protein-coupled receptor 30 agonist G-1 decreases blood pressure in ovariectomized mRen2.Lewis rats. Endocrinology. (2009) 150:3753–8. 10.1210/en.2008-1664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Prossnitz ER, Barton M. Estrogen biology: new insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2014) 389:71–83. 10.1016/j.mce.2014.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Masuhara M, Tsukahara T, Tomita K, Furukawa M, Miyawaki S, Sato T. A relation between osteoclastogenesis inhibition and membrane-type estrogen receptor GPR30. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2016) 8:389–94. 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.10.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Maggiolini M, Vivacqua A, Fasanella G, Recchia AG, Sisci D, Pezzi V, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates c-fos up-regulation by 17beta-estradiol and phytoestrogens in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:27008–16. 10.1074/jbc.M403588200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bologa CG, Revankar CM, Young SM, Edwards BS, Arterburn JB, Kiselyov AS, et al. Virtual and biomolecular screening converge on a selective agonist for GPR30. Nat Chem Biol. (2006) 2:207–12. 10.1038/nchembio775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dennis MK, Field AS, Burai R, Ramesh C, Petrie WK, Bologa CG, et al. Identification of a GPER/GPR30 antagonist with improved estrogen receptor counterselectivity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2011) 127:358–66. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Jessup JA, Lindsey SH, Wang H, Chappell MC, Groban L. Attenuation of salt-induced cardiac remodeling and diastolic dysfunction by the GPER agonist G-1 in female mRen2.Lewis rats. PLoS ONE. (2010) 5:e15433. 10.1371/journal.pone.0015433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bers DM. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. (2002) 415:198–205. 10.1038/415198a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chung JH, Biesiadecki BJ, Ziolo MT, Davis JP, Janssen PM. Myofilament calcium sensitivity: role in regulation of in vivo cardiac contraction and relaxation. Front Physiol. (2016) 7:562. 10.3389/fphys.2016.00562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhang XW, Li TK, Wang H, Cheng HJ, Li WM, Ferrario CM, et al. Chronic GPER activation attenuates cardiac dysfunction in a male mouse model of progressive heart failure: insights into cellular mechanisms (Abstract, American Heart Association Scientific Sessions). Circulation. (2016) 134(Suppl. 1):A12559. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Whitcomb V, Wauson EM, Clayton S, Giles J, Tran QK. Regulation of Beta adrenoreceptor-mediated myocardial contraction and calcium dynamics by the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1. Biochem Pharmacol. (2019) 21:113727 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Jiang C, Poole-Wilson PA, Sarrel PM, Mochizuki S, Collins P, MacLeod KT. Effect of 17 beta-oestradiol on contraction, Ca2+ current and intracellular free Ca2+ in guinea-pig isolated cardiac myocytes. Br J Pharmacol. (1992) 106:739–45. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14403.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ullrich ND, Krust A, Collins P, MacLeod KT. Genomic deletion of estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ does not alter estrogen-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ influx and contraction in murine cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2008) 294:H2421–7. 10.1152/ajpheart.01225.2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Machuki JO, Zhang HY, Geng J, Fu L, Adzika GK, Wu L, et al. Estrogen regulation of cardiac cAMP-L-type Ca(2+) channel pathway modulates sex differences in basal contraction and responses to beta2AR-mediated stress in left ventricular apical myocytes. Cell Commun Signal. (2019) 17:34 10.1186/s12964-019-0346-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Liew R, Stagg MA, MacLeod KT, Collins P. The red wine polyphenol, resveratrol, exerts acute direct actions on guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. (2005) 519:1–8. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.06.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Parks RJ, Bogachev O, Mackasey M, Ray G, Rose RA, Howlett SE. The impact of ovariectomy on cardiac excitation-contraction coupling is mediated through cAMP/PKA-dependent mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2017) 111:51–60. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.07.118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Li HY, Bian JS, Kwan YW, Wong TM. Enhanced responses to 17beta-estradiol in rat hearts treated with isoproterenol: involvement of a cyclic AMP-dependent pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2000) 293:592–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kravtsov GM, Kam KW, Liu J, Wu S, Wong TM. Altered Ca(2+) handling by ryanodine receptor and Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchange in the heart from ovariectomized rats: role of protein kinase A. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2007) 292:C1625–35. 10.1152/ajpcell.00368.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bupha-Intr T, Wattanapermpool J. Regulatory role of ovarian sex hormones in calcium uptake activity of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2006) 291:H1101–8. 10.1152/ajpheart.00660.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Hirota S, Janssen LJ. Store-refilling involves both L-type calcium channels and reverse-mode sodium-calcium exchange in airway smooth muscle. Eur Respir J. (2007) 30:269–78. 10.1183/09031936.00008507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sankaranarayanan R, Kistamas K, Greensmith DJ, Venetucci LA, Eisner DA. Systolic [Ca(2+)]i regulates diastolic levels in rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. (2017) 595:5545–55. 10.1113/JP274366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Petrie WK, Dennis MK, Hu C, Dai D, Arterburn JB, Smith HO, et al. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-selective ligands modulate endometrial tumor growth. Obstetrics Gynecol Int. (2013) 2013:472720. 10.1155/2013/472720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Machuki JO, Zhang HY, Harding SE, Sun H. Molecular pathways of oestrogen receptors and beta-adrenergic receptors in cardiac cells: recognition of their similarities, interactions and therapeutic value. Acta Physiol. (2018) 222:e12978. 10.1111/apha.12978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kadambi VJ, Ponniah S, Harrer JM, Hoit BD, Dorn GW, II, Walsh RA, et al. Cardiac-specific overexpression of phospholamban alters calcium kinetics and resultant cardiomyocyte mechanics in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. (1996) 97:533–9. 10.1172/JCI118446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wegener AD, Simmerman HK, Lindemann JP, Jones LR. Phospholamban phosphorylation in intact ventricles. Phosphorylation of serine 16 and threonine 17 in response to beta-adrenergic stimulation. J Biol Chem. (1989) 264:11468–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hagemann D, Kuschel M, Kuramochi T, Zhu W, Cheng H, Xiao RP. Frequency-encoding Thr17 phospholamban phosphorylation is independent of Ser16 phosphorylation in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:22532–6. 10.1074/jbc.C000253200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gustavsson M, Verardi R, Mullen DG, Mote KR, Traaseth NJ, Gopinath T, et al. Allosteric regulation of SERCA by phosphorylation-mediated conformational shift of phospholamban. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2013) 110:17338–43. 10.1073/pnas.1303006110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bhupathy P, Babu GJ, Periasamy M. Sarcolipin and phospholamban as regulators of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2007) 42:903–11. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.03.738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Tran QK, Firkins R, Giles J, Francis S, Matnishian V, Tran P, et al. Estrogen enhances linkage in the vascular endothelial calmodulin network via a feedforward mechanism at the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:10805–23. 10.1074/jbc.M115.697334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Tran QK, Vermeer M. Biosensor-based approach identifies four distinct calmodulin-binding domains in the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e89669. 10.1371/journal.pone.0089669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Fredette NC, Meyer MR, Prossnitz ER. Role of GPER in estrogen-dependent nitric oxide formation and vasodilation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2018) 176:65–72. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.05.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Terry LE, VerMeer M, Giles J, Tran QK. Suppression of store-operated Ca(2+) entry by activation of GPER: contribution to a clamping effect on endothelial Ca(2+) signaling. Biochem J. (2017) 474:3627–42. 10.1042/BCJ20170630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Tran QK, VerMeer M, Burgard MA, Hassan AB, Giles J. Hetero-oligomeric complex between the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 and the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 4b. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:13293–307. 10.1074/jbc.M114.628743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yang HY, Firth JM, Francis AJ, Alvarez-Laviada A, MacLeod KT. Effect of ovariectomy on intracellular Ca(2+) regulation in guinea pig cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2017) 313:H1031–43. 10.1152/ajpheart.00249.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chu SH, Goldspink P, Kowalski J, Beck J, Schwertz DW. Effect of estrogen on calcium-handling proteins, beta-adrenergic receptors, and function in rat heart. Life Sci. (2006) 79:1257–67. 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.03.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Fares E, Pyle WG, Ray G, Rose RA, Denovan-Wright EM, Chen RP, et al. The impact of ovariectomy on calcium homeostasis and myofilament calcium sensitivity in the aging mouse heart. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e74719. 10.1371/journal.pone.0074719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Park SY, Gifford JR, Andtbacka RH, Trinity JD, Hyngstrom JR, Garten RS, et al. Cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle mitochondrial respiration: are all mitochondria created equal? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2014) 307:H346–52. 10.1152/ajpheart.00227.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Brown DA, Perry JB, Allen ME, Sabbah HN, Stauffer BL, Shaikh SR, et al. Expert consensus document: mitochondrial function as a therapeutic target in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2017) 14:238–50. 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kumar AA, Kelly DP, Chirinos JA. Mitochondrial dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. (2019) 139:1435–50. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Mahmoodzadeh S, Dworatzek E. The role of 17beta-estradiol and estrogen receptors in regulation of Ca(2+) channels and mitochondrial function in cardiomyocytes. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:310 10.3389/fendo.2019.00310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Zhang Z-Y, Marrachelli VG, Thijs L, Yang W-Y, Wei F-F, Monleon D, et al. Diastolic left ventricular function in relation to circulating metabolic biomarkers in a general population. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e002681. 10.1161/JAHA.115.002681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Andersson DC, Fauconnier J, Yamada T, Lacampagne A, Zhang S-J, Katz A, et al. Mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species contributes to the β-adrenergic stimulation of mouse cardiomycytes. J Physiol. (2011) 589:1791–801. 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.202838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Chen Y, Zhang Z, Hu F, Yang W, Yuan J, Cui J, et al. 17β-estradiol prevents cardiac diastolic dysfunction by stimulating mitochondrial function: a preclinical study in a mouse model of a human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2015) 147:92–102. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.12.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Borrás C, Gambini J, López-Grueso R, Pallardó FV, Viña J. Direct antioxidant and protective effect of estradiol on isolated mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2010) 1802:205–11. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Viña J, Gambini J, García-García FJ, Rodriguez-Mañas L, Borrás C. Role of oestrogens on oxidative stress and inflammation in ageing. Hormone Mol Biol Clin Investig. (2013) 16:65–72. 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chen JQ, Cammarata PR, Baines CP, Yager JD. Regulation of mitochondrial respiratory chain biogenesis by estrogens/estrogen receptors and physiological, pathological and pharmacological implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2009) 1793:1540–70. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.06.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Rattanasopa C, Phungphong S, Wattanapermpool J, Bupha-Intr T. Significant role of estrogen in maintaining cardiac mitochondrial functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2015) 147:1–9. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sbert-Roig M, Bauzá-Thorbrügge M, Galmés-Pascual BM, Capllonch-Amer G, García-Palmer FJ, Lladó I, et al. GPER mediates the effects of 17β-estradiol in cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2016) 420:116–24. 10.1016/j.mce.2015.11.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Bopassa JC, Eghbali M, Toro L, Stefani E. A novel estrogen receptor GPER inhibits mitochondria permeability transition pore opening and protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2010) 298:H16–23. 10.1152/ajpheart.00588.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Feng Y, Madungwe NB, da Cruz Junho CV, Bopassa JC. Activation of G protein-coupled oestrogen receptor 1 at the onset of reperfusion protects the myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy. Br J Pharmacol. (2017) 174:4329–44. 10.1111/bph.14033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Wang H, Sun X, Lin MS, Ferrario CM, Van Remmen H, Groban L. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) deficiency induces cardiac remodeling through oxidative stress. Transl Res. (2018) 199:39–51. 10.1016/j.trsl.2018.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Dworatzek E, Mahmoodzadeh S. Targeted basic research to highlight the role of estrogen and estrogen receptors in the cardiovascular system. Pharmacol Res. (2017) 119:27–35. 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.01.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Shah SJ, Kitzman DW, Borlaug BA, van Heerebeek L, Zile MR, Kass DA, et al. Phenotype-specific treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a multiorgan roadmap. Circulation. (2016) 134:73–90. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Mohammed SF, Hussain S, Mirzoyev SA, Edwards WD, Maleszewski JJ, Redfield MM. Coronary microvascular rarefaction and myocardial fibrosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. (2015) 131:550–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.009625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Molina AJ, Bharadwaj MS, Van Horn C, Nicklas BJ, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J, et al. Skeletal muscle mitochondrial content, oxidative capacity, and Mfn2 expression are reduced in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction and are related to exercise intolerance. JACC Heart Fail. (2016) 4:636–45. 10.1016/j.jchf.2016.03.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kitzman DW, Nicklas B, Kraus WE, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J, Morgan TM, et al. Skeletal muscle abnormalities and exercise intolerance in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2014) 306:H1364–70. 10.1152/ajpheart.00004.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Haykowsky MJ, Tomczak CR, Scott JM, Paterson DI, Kitzman DW. Determinants of exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure and reduced or preserved ejection fraction. J Appl Physiol. (2015) 119:739–44. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00049.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Weiss K, Schar M, Panjrath GS, Zhang Y, Sharma K, Bottomley PA, et al. Fatigability, exercise intolerance, and abnormal skeletal muscle energetics in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. (2017) 10:e004129. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Sickinghe AA, Korporaal SJA, den Ruijter HM, Kessler EL. Estrogen contributions to microvascular dysfunction evolving to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:442. 10.3389/fendo.2019.00442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Aurigemma GP, Gaasch WH. Clinical practice. Diastolic heart failure. N Engl J Med. (2004) 351:1097–105. 10.1056/NEJMcp022709 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Borbely A, van der Velden J, Papp Z, Bronzwaer JG, Edes I, Stienen GJ, et al. Cardiomyocyte stiffness in diastolic heart failure. Circulation. (2005) 111:774–81. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000155257.33485.6D [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.van Heerebeek L, Borbely A, Niessen HW, Bronzwaer JG, van der Velden J, Stienen GJ, et al. Myocardial structure and function differ in systolic and diastolic heart failure. Circulation. (2006) 113:1966–73. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.587519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lee TM, Lin SZ, Chang NC. Both GPER and membrane oestrogen receptor-alpha activation protect ventricular remodelling in 17β oestradiol-treated ovariectomized infarcted rats. J Cell Mol Med. (2014) 18:2454–65. 10.1111/jcmm.12430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Azizian H, Khaksari M, Asadi Karam G, Esmailidehaj M, Farhadi Z. Cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of G-protein coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) on postmenopausal type 2 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 108:153–64. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Kang S, Liu Y, Sun D, Zhou C, Liu A, Xu C, et al. Chronic activation of the G protein-coupled receptor 30 with agonist G-1 attenuates heart failure. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e48185. 10.1371/journal.pone.0048185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wang X, Lu L, Tan Y, Jiang L, Zhao M, Gao E, et al. GPR 30 reduces myocardial infarct area and fibrosis in female ovariectomized mice by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Life Sci. (2019) 226:22–32. 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lenhart PM, Broselid S, Barrick CJ, Leeb-Lundberg LM, Caron KM. G-protein-coupled receptor 30 interacts with receptor activity-modifying protein 3 and confers sex-dependent cardioprotection. J Mol Endocrinol. (2013) 51:191–202. 10.1530/JME-13-0021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Goncalves GK, Scalzo S, Alves AP, Agero U, Guatimosim S, Reis AM. Neonatal cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by endothelin-1 is blocked by estradiol acting on GPER. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2018) 314:C310–22. 10.1152/ajpcell.00060.2017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Pei H, Wang W, Zhao D, Su H, Su G, Zhao Z. G Protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via the regulation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR signalling and autophagy. Int J Biol Sci. (2019) 15:81–92. 10.7150/ijbs.28304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Weber KT, Brilla CG. Structural basis for pathologic left ventricular hypertrophy. Clin Cardiol. (1993) 16(5 Suppl. 2):Ii10–4. 10.1002/clc.4960161404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Farre N, Jorba I, Torres M, Falcones B, Marti-Almor J, Farre R, et al. Passive stiffness of left ventricular myocardial tissue is reduced by ovariectomy in a post-menopause mouse model. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:1545. 10.3389/fphys.2018.01545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Dubey RK, Gillespie DG, Jackson EK, Keller PJ. 17Beta-estradiol, its metabolites, and progesterone inhibit cardiac fibroblast growth. Hypertension. (1998) 31(1 Pt 2):522–8. 10.1161/01.HYP.31.1.522 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Lijnen PJ, Petrov VV, Fagard RH. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by angiotensin II. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. (2000) 22:709–23. 10.1358/mf.2000.22.10.802287 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Cleland JGF, Tendera M, Adamus J, Freemantle N, Polonski L, Taylor J. The perindopril in elderly people with chronic heart failure (PEP-CHF) study. Eur Heart J. (2006) 27:2338–45. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Flather MD, Yusuf S, Køber L, Pfeffer M, Hall A, Murray G, et al. Long-term ACE-inhibitor therapy in patients with heart failure or left-ventricular dysfunction: a systematic overview of data from individual patients. ACE-Inhibitor Myocardial Infarction Collaborative Group. Lancet. (2000) 355:1575–81. 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02212-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Massie BM, Carson PE, McMurray JJ, Komajda M, McKelvie R, Zile MR, et al. Irbesartan in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:2456–67. 10.1056/NEJMoa0805450 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ferrario CM, Mullick AE. Renin angiotensin aldosterone inhibition in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Res. (2017) 125(Pt A):57–71. 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.05.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Reyes S, Varagic J, Ahmad S, VonCannon J, Kon ND, Wang H, et al. Novel cardiac intracrine mechanisms based on Ang-(1-12)/Chymase axis require a revision of therapeutic approaches in human heart disease. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2017) 19:16. 10.1007/s11906-017-0708-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Dusing R. Mega clinical trials which have shaped the RAS intervention clinical practice. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. (2016) 10:133–50. 10.1177/1753944716644131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Brugts JJ, van Vark L, Akkerhuis M, Bertrand M, Fox K, Mourad JJ, et al. Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on mortality and major cardiovascular endpoints in hypertension: a number-needed-to-treat analysis. Int J Cardiol. (2015) 181:425–9. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.11.179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Ferrario CM, Ahmad S, Varagic J, Cheng CP, Groban L, Wang H, et al. Intracrine angiotensin II functions originate from noncanonical pathways in the human heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2016) 311:H404–14. 10.1152/ajpheart.00219.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Dell'Italia LJ, Collawn JF, Ferrario CM. Multifunctional role of chymase in acute and chronic tissue injury and remodeling. Circ Res. (2018) 122:319–36. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Ahmad S, Varagic J, Groban L, Dell'Italia LJ, Nagata S, Kon ND, et al. Angiotensin-(1-12): a chymase-mediated cellular angiotensin II substrate. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2014) 16:429. 10.1007/s11906-014-0429-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Ahmad S, Varagic J, Voncannon JL, Groban L, Collawn JF, Dell 'italia LJ, et al. Primacy of cardiac chymase over angiotensin converting enzyme as an angiotensin- (1–12) metabolizing enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2016) 478:559–64. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Ahmad S, Wei C-C, Tallaj J, Dell'Italia LJ, Moniwa N, Varagic J, et al. Chymase mediates angiotensin-(1-12) metabolism in normal human hearts. J Am Soc Hypertens. (2013) 7:128–36. 10.1016/j.jash.2012.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Ahmad S, Simmons T, Varagic J, Moniwa N, Chappell MC, Ferrario CM. Chymase-dependent generation of angiotensin II from angiotensin-(1-12) in human atrial tissue. PLoS ONE. (2011) 6:e28501. 10.1371/journal.pone.0028501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Tojo H, Urata H. Chymase inhibition and cardiovascular protection. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. (2013) 27:139–43. 10.1007/s10557-013-6450-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Urata H, Kinoshita A, Misono KS, Bumpus FM, Husain A. Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem. (1990) 265:22348–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Balcells E, Meng QC, Hageman GR, Palmer RW, Durand JN, Dell'Italia LJ. Angiotensin II formation in dog heart is mediated by different pathways in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. (1996) 271(2 Pt 2):H417–21. 10.1152/ajpheart.1996.271.2.H417 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kovarik JJ, Kopecky C, Antlanger M, Domenig O, Kaltenecker CC, Werzowa J, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor therapy on the regulation of the plasma and cardiac tissue renin-angiotensin system in heart transplant patients. J Heart Lung Transplant. (2017) 36:355–65. 10.1016/j.healun.2016.08.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.da Silva JS, Gabriel-Costa D, Wang H, Ahmad S, Sun X, Varagic J, et al. Blunting of cardioprotective actions of estrogen in female rodent heart linked to altered expression of cardiac tissue chymase and ACE2. J Renin Angiotens Aldosterone Syst. (2017) 18:147032031772227. 10.1177/1470320317722270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Wang H, Jessup JA, Zhao Z, Da Silva J, Lin M, Macnamara LM, et al. Characterization of the cardiac renin angiotensin system in oophorectomized and estrogen-replete mRen2.Lewis rats. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e76992. 10.1371/journal.pone.0076992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Levick SP, Meléndez GC, Plante E, McLarty JL, Brower GL, Janicki JS. Cardiac mast cells: the centrepiece in adverse myocardial remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. (2011) 89:12–9. 10.1093/cvr/cvq272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Levick SP, Widiapradja A. Mast cells: key contributors to cardiac fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:E231. 10.3390/ijms19010231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ferrario Carlos M, Ahmad S, Nagata S, Simington Stephen W, Varagic J, Kon N, et al. An evolving story of angiotensin-II-forming pathways in rodents and humans. Clin Sci. (2014) 126:461–9. 10.1042/CS20130400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Wang H, da Silva J, Alencar A, Zapata-Sudo G, Lin MR, Sun X, et al. Mast cell inhibition attenuates cardiac remodeling and diastolic dysfunction in middle-aged, ovariectomized Fischer 344 x Brown Norway rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2016) 68:49–57. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Li J, Jubair S, Janicki JS. Estrogen inhibits mast cell chymase release to prevent pressure overload-induced adverse cardiac remodeling. Hypertension. (2015) 65:328–34. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04238 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Brower GL, Gardner JD, Janicki JS. Gender mediated cardiac protection from adverse ventricular remodeling is abolished by ovariectomy. Mol Cell Biochem. (2003) 251:89–95. 10.1023/A:1025438000942 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Lu H, Meléndez GC, Levick SP, Janicki JS. Prevention of adverse cardiac remodeling to volume overload in female rats is the result of an estrogen-altered mast cell phenotype. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 302:H811–7. 10.1152/ajpheart.00980.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Mocan M, Mocan Hognogi LD, Anton FP, Chiorescu RM, Goidescu CM, Stoia MA, et al. Biomarkers of inflammation in left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. Dis Markers. (2019) 2019:7583690. 10.1155/2019/7583690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Garg NJ. Inflammasomes in cardiovascular diseases. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. (2011) 1:244–54. 10.1007/978-3-319-89390-7_2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Lunderius-Andersson C, Enoksson M, Nilsson G. Mast cells respond to cell injury through the recognition of IL-33. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:82. 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Abu-Taha M, Rius C, Hermenegildo C, Noguera I, Cerda-Nicolas JM, Issekutz AC, et al. Menopause and ovariectomy cause a low grade of systemic inflammation that may be prevented by chronic treatment with low doses of estrogen or losartan. J Immunol. (2009) 183:1393–402. 10.4049/jimmunol.0803157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Bell V, Mitchell WA, Sigurethsson S, Westenberg JJ, Gotal JD, Torjesen AA, et al. Longitudinal and circumferential strain of the proximal aorta. J Am Heart Assoc. (2014) 3:e001536. 10.1161/JAHA.114.001536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bell V, McCabe EL, Larson MG, Rong J, Merz AA, Osypiuk E, et al. Relations between aortic stiffness and left ventricular mechanical function in the community. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e004903. 10.1161/JAHA.116.004903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Kazui T, Izumoto H, Yoshioka K, Kawazoe K. Dynamic morphologic changes in the normal aortic annulus during systole and diastole. J Heart Valve Dis. (2006) 15:617–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Bell V, Mitchell GF. Influence of vascular function and pulsatile hemodynamics on cardiac function. Curr Hypertens Rep. (2015) 17:580. 10.1007/s11906-015-0580-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hundley WG, Kitzman DW, Morgan TM, Hamilton CA, Darty SN, Stewart KP, et al. Cardiac cycle-dependent changes in aortic area and distensibility are reduced in older patients with isolated diastolic heart failure and correlate with exercise intolerance. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2001) 38:796–802. 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01447-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Bell V, Sigurdsson S, Westenberg JJ, Gotal JD, Torjesen AA, Aspelund T, et al. Relations between aortic stiffness and left ventricular structure and function in older participants in the age, gene/environment susceptibility–Reykjavik Study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2015) 8:e003039. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.114.003039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Coutinho T, Borlaug BA, Pellikka PA, Turner ST, Kullo IJ. Sex differences in arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial interactions. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 61:96–103. 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Waddell TK, Dart AM, Gatzka CD, Cameron JD, Kingwell BA. Women exhibit a greater age-related increase in proximal aortic stiffness than men. J Hypertens. (2001) 19:2205–12. 10.1097/00004872-200112000-00014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Shim CY, Park S, Choi D, Yang WI, Cho IJ, Choi EY, et al. Sex differences in central hemodynamics and their relationship to left ventricular diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2011) 57:1226–33. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.09.067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Mata KM, Li W, Reslan OM, Siddiqui WT, Opsasnick LA, Khalil RA. Adaptive increases in expression and vasodilator activity of estrogen receptor subtypes in a blood vessel-specific pattern during pregnancy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2015) 309:H1679–96. 10.1152/ajpheart.00532.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Lindsey SH, Carver KA, Prossnitz ER, Chappell MC. Vasodilation in response to the GPR30 agonist G-1 is not different from estradiol in the mRen2.Lewis female rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2011) 57:598–603. 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182135f1c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Reslan OM, Yin Z, do Nascimento GR, Khalil RA. Subtype-specific estrogen receptor-mediated vasodilator activity in the cephalic, thoracic, and abdominal vasculature of female rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2013) 62:26–40. 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31828bc88a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Li ZL, Liu JC, Liu SB, Li XQ, Yi DH, Zhao MG. Improvement of vascular function by acute and chronic treatment with the GPR30 agonist G1 in experimental diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e38787. 10.1371/journal.pone.0038787 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Liu L, Kashyap S, Murphy B, Hutson DD, Budish RA, Trimmer EH, et al. GPER activation ameliorates aortic remodeling induced by salt-sensitive hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2016) 310:H953–61. 10.1152/ajpheart.00631.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Gros R, Hussain Y, Chorazyczewski J, Pickering JG, Ding Q, Feldman RD. Extent of vascular remodeling is dependent on the balance between estrogen receptor alpha and G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor. Hypertension. (2016) 68:1225–35. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07859 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Ogola BO, Zimmerman MA, Sure VN, Gentry KM, Duong JL, Clark GL, et al. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor protects from angiotensin II-induced increases in pulse pressure and oxidative stress. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:586. 10.3389/fendo.2019.00586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Solomon SD, McMurray JJV, Anand IS, Ge J, Lam CSP, Maggioni AP, et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:1609–20. 10.1056/NEJMoa1908655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Harper AR, Patel HC, Lyon AR. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Clin Med. (2018) 18(Suppl. 2):s24–9. 10.7861/clinmedicine.18-2-s24 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]