Figure 4.
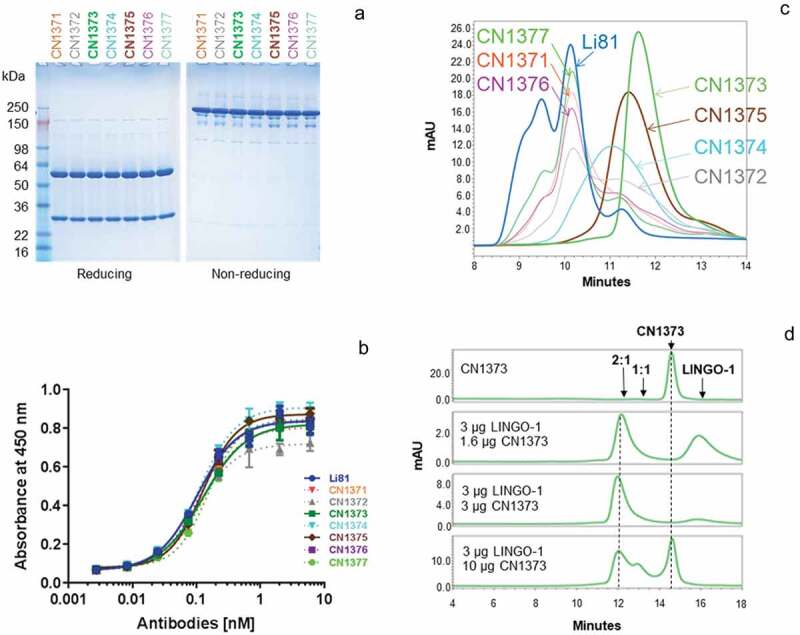
Biochemical attributes of Li81 variants targeting secondary binding site contacts. (a) Samples (4 µg/lane) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. Samples on the left were analyzed under reducing conditions, and samples on the right were analyzed under non-reducing conditions. Molecular weight markers and their apparent molecular masses are shown at the left of the panel. (b) The apparent affinities of the seven secondary binding site mutants for LINGO-1 were measured by a direct-binding ELISA. Data are plotted as absorbance at 450 nm versus concentration. (c) Samples, each containing 10 µg LINGO-1 ectodomain and 10 µg of of one of the mutant mAbs, were subjected to SEC on an analytical SEC column using PBS as the mobile phase. The column effluent was analyzed for absorbance at 280 nm. (d) Samples containing CN1373 mAb alone, or 3 µg LINGO-1 ectodomain and 1.6, 3, or 10 µg of CN1373 mAb, were subjected to SEC with in-line light scattering.
