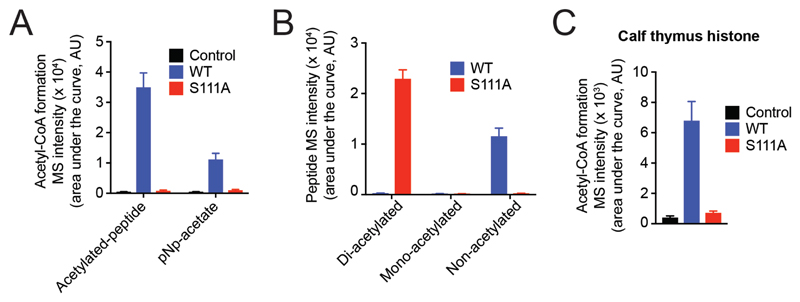
Figure 7. ABHD14B performs a lysine deacetylase reaction on peptide and protein substrates.
(A) Formation of acetyl-CoA by WT human ABHD14B, but not S111A human ABHD14B, when incubated with enzyme equimolar concentration of the di-acetylated (Lys9/14) histone H3 peptide (1 – 20) and excess CoA (25 μM). The control samples for this assay is the entire mixture without enzyme. (B) Formation of non-acetylated peptide from the starting di-acetylated (Lys9/14) histone H3 peptide (1 – 20) (2.5 μM) by WT human ABHD14B (2.5 μM) in the presence of excess CoA (25 μM). The S111A human ABHD14B (2.5 μM) has no activity against the di-acetylated peptide substrate. (C) Formation of acetyl-CoA by WT human ABHD14B (2.5 μM), but not S111A human ABHD14B (2.5 μM), when incubated with histone preparations from calf thymus (100 ng) and excess CoA (25 μM). The control samples for this assay is the entire mixture without enzyme. All LC-MS data represented in (A), (B), and (C) is the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments.