Figure 5.
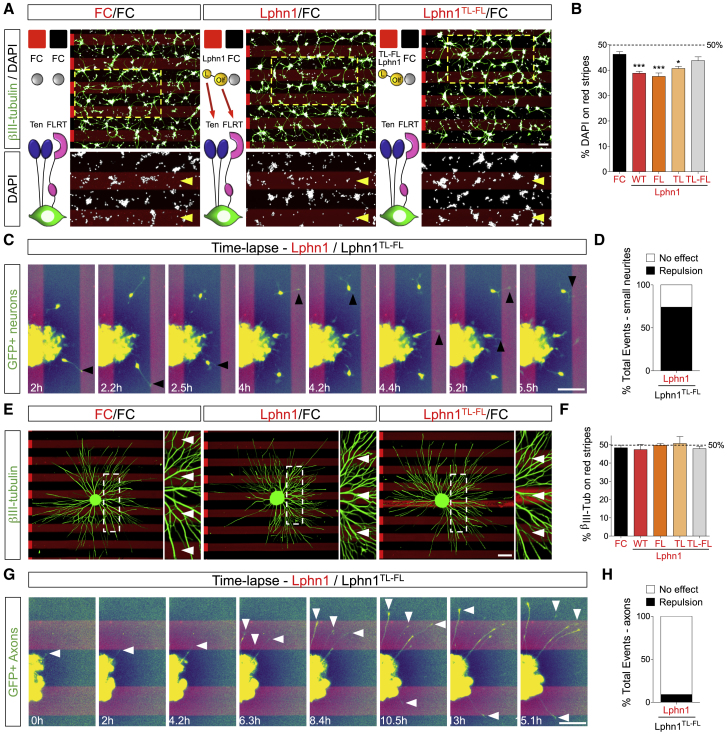
Latrophilin1 Interaction with Teneurins and FLRTs in Trans Induces Repulsion
(A) E15.5 dissociated cortical neurons were grown on alternate stripes containing FC (black) and Lphn1 Lec-Olf proteins (red). Neurons were stained with anti- β-III-tubulin to visualize neurites (green) and nuclei (DAPI, white). In the magnified inset images, the red Lphn-containing stripes are indicated by yellow arrowheads.
(B) The percentage of DAPI+ pixels on red stripes was quantified. n = 3 different experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA test with Tukey’s post hoc analysis.
(C) GFP+ neurons exiting cortical explants grown on alternating Lphn1 (red) and Lphn1TL-FL (black) stripes. Snapshots from a time-lapse experiment are shown. Neurons prefer to migrate on Lphn1TL-FL in these experiments. A repulsive event was defined as a contact between a small neurite and Lphn1 stripes lasting less than 3 frames. Black arrowheads indicate repulsive events.
(D) Quantification of the data shown in (C); n > 30 contacts.
(E) E15.5 cortical explants were grown on stripes as in (A) and stained with anti- β-III-tubulin to visualize axons.
(F) Quantification of data shown in (E). n = 3 different experiments.
(G) GFP+ axons exiting cortical explants grown on alternating Lphn1 (red) and Lphn1TL-FL (black) stripes. Snapshots from a time-lapse experiment are shown. No preference for black or red stripes was observed. A repulsive event was defined as a contact between an axon and Lphn1 stripes lasting less than 3 frames. White arrowheads indicate growth cones that are not repelled from Lphn1 stripes.
(H) Quantification of the data shown in (G); n > 20 contacts.
Scale bars represent 300 μm (A), 200 μm (C and G), and 200 μm (E).