The authors wish to make the following corrections to this paper [1]:
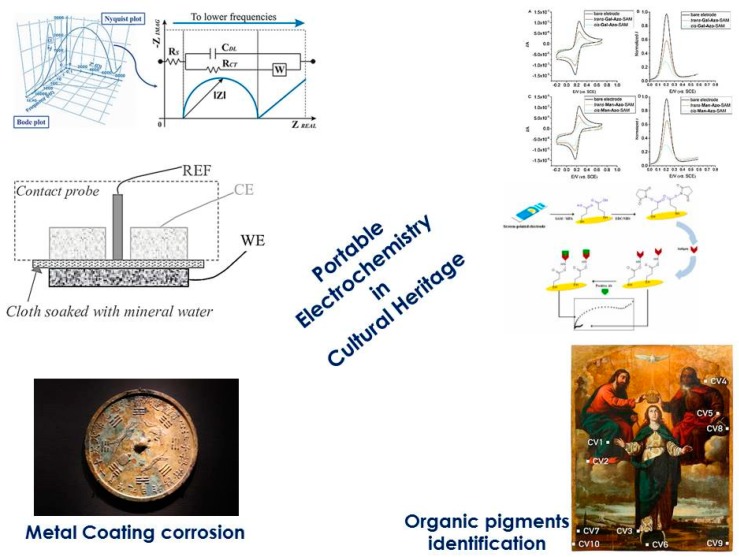
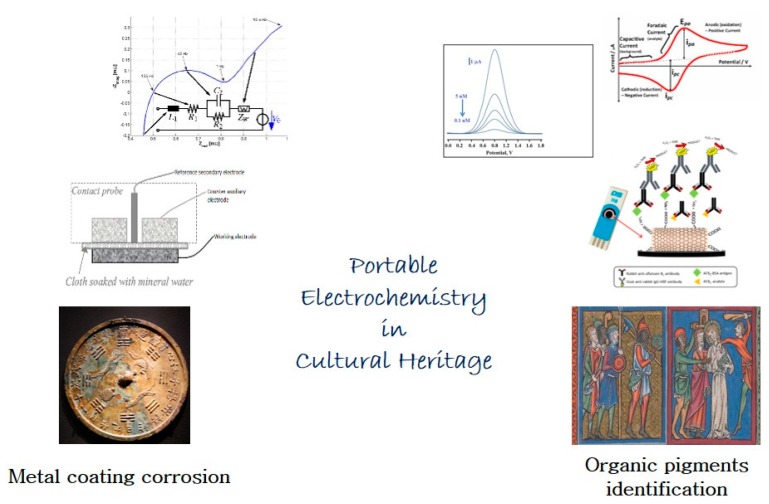
1. The graphical abstract should be replaced with
instead of
2. The citation in Figure 2 is incorrect and should be revised from Reference [30] to [28]. The correct caption should be “Figure 2. A contact probe (CP), reproduced and reprinted with permission from [28].” Furthermore, Reference [28] should be revised to “Letardi, P.; Albini, M.; Joseph, E. EIS measurements for treatment testing: the case of a bio-based method applied on outdoor bronze statues in Switzerland. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.14293/S2199-1006.1.SOR-.PPANDZU.v1 (accessed on 27 September 2019).”
3. The third paragraph in Section 2 should be revised to read “Setup 2 is a gel cell, with a silver/silver chloride secondary electrode and agar or agarose as the gelling agent [30–32], which is useful for immobilizing alkaline chloride solutions, thus simulating what happens inside the pores of concrete and plaster surfaces [33]” from “Setup 2 is a gel cell, with silver/silver chloride secondary electrode and agar or agarose as gelling agent [31,32] useful for immobilizing alkaline chloride solutions, simulating what happens inside the pores of concrete and plaster surfaces [33].”
4. The citation in Figure 3 is incorrect and should be revised from Reference [30] to [50]. The correct caption should be “Figure 3. (A) Solid agarose gel electrolyte: scheme (up) and photograph (down); (B) zoom of a solid agarose gel. Reproduced and reprinted here with permission from [31] and [50], respectively.”
5. The citation in Figure 4 is incorrect and should be revised from Reference [41] to [30]. The correct caption should be “Figure 4. (a) EC showing an ideal metal-coating system; (b) a damaged coating; and (c) different EC schemes proposed to represent archaeological copper alloys. Reproduced and reprinted with permission from [30].”
6. Citations should be added in Scheme 2. The correct caption should be “Scheme 2. Equivalent Circuits (ECs) reported in Table 1, in particular: (A) represents the AC: Alternative Current Impedance Spectroscopy for copper in the simulated tap water. (B) Represents the electrical equivalent circuit used for fitting the EIS data in the presence of a copper/alloy-coated patina. (C) Shows the EIS measuring principle and the corresponding EC carried out on the iron/steel-coated patina. (D1) Cell design scheme (left); bronze coupons used for the electrochemical tests (middle D2) and the equivalent electrical circuits (D3) were used to analyze the EIS data. (a) is the equivalent circuit with two nested CPE-R pairs, and (b) is the second CPE replaced by a generalized finite-length Warburg impedance. Reproduced and reprinted with permission from [32,60,67,72], respectively.”
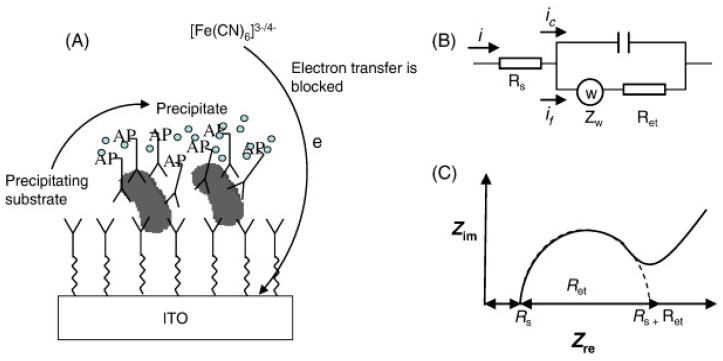
7. Figure 10 should be replaced with
Figure 10.
(A) The operating principle concerning the electrochemical impedance biosensor for bacteria quantification. (B) The Randles model equivalent circuit, and (C) the typical Nyquist plot (Zim vs. Zre) of the Faradaic impedance spectrum of the electrochemical device when in the presence of the redox probe. Reproduced and reprinted with permission from [94].
instead of
Figure 10.
(A) Cross-section of the biosensor prototype. (B) The analytical signals of fluorescent-labeled Listeria cells. (C) Typical impedance growth curves of Listeria cells. Reproduced and reprinted with permission from [21].
The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers by these changes.
Reference
- 1.Valentini F. Smart Electrochemical Portable Tools for Cultural Heritage Analysis: A Review. Sensors. 2019;19:4303. doi: 10.3390/s19194303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]