Abstract
Recent lineage tracing studies revealed that mammary gland homeostasis relies on unipotent stem cells. However, whether and when lineage restriction occurs during embryonic mammary development and which signals orchestrate cell fate specification remain unknown. Using a combination of in vivo clonal analysis with whole mount immunofluorescence and mathematical modelling of clonal dynamics, we found that embryonic multipotent mammary cells become lineage restricted surprisingly early in development, with evidence for unipotency as early as E12.5 and no statistically discernable bipotency after E15.5. To gain insights into the mechanisms governing the switch from multipotency to unipotency, we used gain-of-function Notch1 mice and demonstrated that Notch activation cell autonomously dictates luminal cell fate specification to both embryonic and basally committed mammary cells. These functional studies have important implications for understanding the signals underlying cell plasticity and serve to clarify how reactivation of embryonic programs in adult cells can lead to cancer.
Introduction
Due to its unique capacity for rapid growth and regeneration, the mammary gland represents an ideal system to study stem cell plasticity and lineage specification, and their contribution to tissue morphogenesis and remodelling. The mammary epithelium is initially specified at embryonic day E11.5 as a skin placode, after which signals from surrounding ERα-expressing stromal cells direct the formation of spherical mammary buds1. The mammary buds invaginate into the underlying mesenchyme and after E15.5, they start invading the fad pad precursor and organise into primitive tubular structures that develop into small rudimentary trees shortly before birth, at E18.52. During puberty, serial rounds of ductal branching and elongation lead to the specification of a complex branched epithelial network3,4. The mammary ductal tree is composed of two epithelial compartments: cells facing the ductal lumen are polarized cuboidal epithelial cells that constitute the luminal epithelium (called luminal cells or LC), while cells found in the outer layer, in contact with the basal membrane, are myoepithelial cells, which express Smooth Muscle Actin (SMA) conferring contractile capacity, termed basal cells (BC). Luminal cells can be further subdivided in two populations, depending on their expression of the hormone receptors Estrogen-α (ERα) and Progesterone (PR).
Pioneering studies explored the capacity of single mammary cells to reconstitute a functional gland when orthotopically transplanted in the cleared fat pad of host mice, and defined a small subset of basal cells as multipotent mammary stem cells (MaSC)5,6, assumed to be responsible for the homeostatic maintenance of the tissue throughout adult life. However, more recent lineage tracing studies based on targeted promoters generated conflicting data on whether mammary multipotent cells truly exist during development and adult reproductive life in vivo, or whether lineage-restricted progenitors are induced to behave in a multipotent manner following transplantation7–11. Lineage tracing provides the means to identify stem cells and track their progeny in vivo and in situ, by genetically labelling stem cells in their physiological niche, so that their derived daughter cells retain marker expression. Indeed, clonal analyses using specific promoters for genes expressed either in the luminal or in the basal compartment of the mammary epithelium, have shown that all mammary stem cells show unipotency in vivo during puberty and adulthood8,10,12–18. However, none of these prior studies has carefully examined how embryonic MaSCs contribute to postnatal development. Although some findings support the existence of multipotent stem cells during embryogenesis8,11,18, as population-based studies, the question of whether individual embryonic stem cells exhibit multipotent potential at the clonal level or comprise distinct cell subsets already committed toward a specific cell lineage remains unsolved. The Notch signalling pathway has been linked to stem cell maintenance and cell fate specification in many tissues and it has been shown to promote luminal differentiation in the mammary gland19. Through clonal analysis of Notch1-labelled cells in the pubertal gland, we have previously demonstrated that the Notch1 receptor labels exclusively ERα-negative (ERαneg) luminal progenitors. Notch1-expressing mammary cells are strictly unipotent in adult mice, but surprisingly can give rise to a progeny composed of all types of mammary cells in transplantation experiments or when tracing is initiated in embryos, demonstrating cell plasticity11. These results are in agreement with other studies showing that different glandular epithelia (mammary gland, prostate, sweat glands) initially develop from multipotent SCs, which are progressively replaced by unipotent progenitors during post-natal development8,11,20–22. Here, we used our Notch1-CreERT2 mouse line (N1CreERT2)23 to genetically mark embryonic mammary cells and tracked their progeny throughout development, to define the developmental timing for the acquisition of mammary cell identity and lineage commitment. As the use of a single-colour reporter can lead to misinterpretation of lineage tracing results, because clones derived from distinct lineage-committed progenitors could be merged when analysed in the post-natal gland, we have used the multicolour Confetti reporter mouse and whole mount imaging of the ductal tree, to genetically map the fate of mammary cells during the first wave of mammary development and branching, starting at embryonic day E12.5. Mathematical modelling of our experimental data clearly indicated the presence of unipotent cells committed to a unique lineage already in the E12.5 embryonic mammary bud, thus remarkably early in mammary gland morphogenesis.
Surprisingly, embryonic mammary cells from E15.5 onwards do not seem to retain multilineage potential in vivo, although they are still undifferentiated cells, which will acquire a basal or luminal identity only at birth. In addition, to define the mechanisms regulating the observed restriction in lineage potential during mammary development, we have used Notch1 gain-of-function mice, and found that intrinsic cell autonomous signals can impose a specific cell fate to both embryonic and post-natal lineage-restricted mammary cells. These functional studies have important implications for understanding stem cell plasticity and lineage potential in vivo and to explore the possibility that reactivation of embryonic developmental programs in adult cells could lead to cancer24–26.
Results
Mammary basal and luminal identities are defined at birth
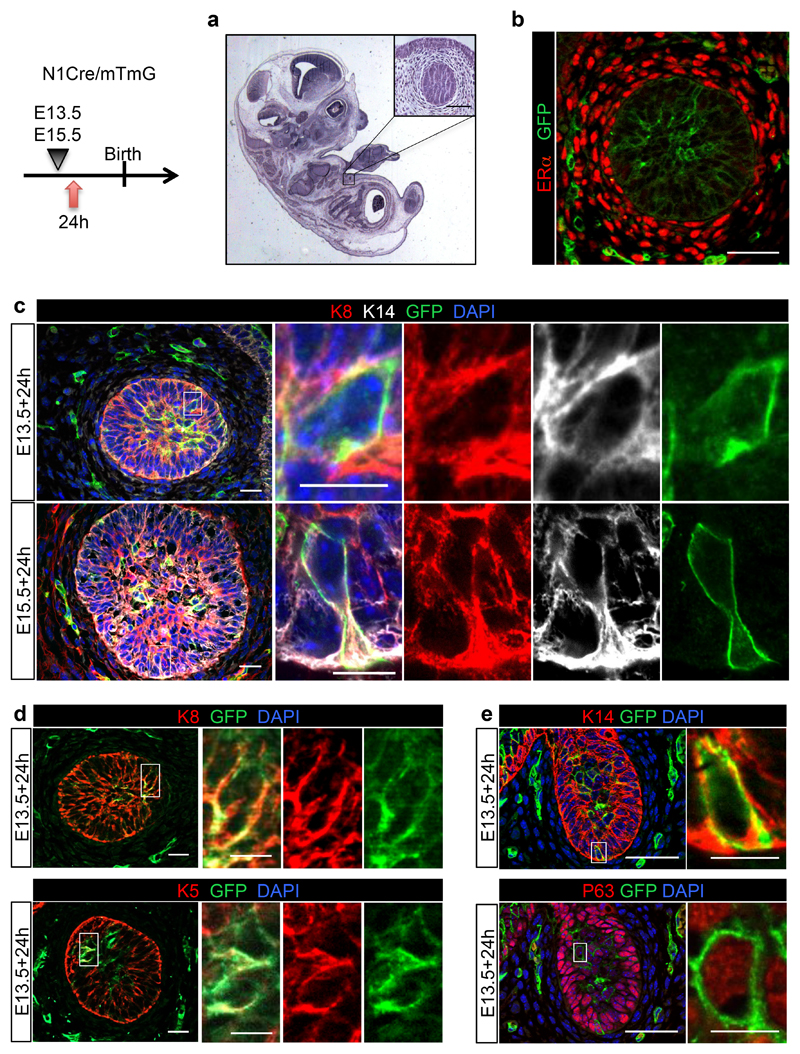
To induce clonal labelling at early developmental times, pregnant N1CreERT2 mice crossed to a double fluorescent reporter line (R26mTmG)27 (henceforth called N1Cre/mTmG) were induced using a low dose of tamoxifen (0.1mg/g of mouse body weight). Analysis of marked cells 24h following Cre induction at E13.5 and E15.5, revealed that the Notch1 receptor is expressed in most of the cells comprising the mammary bud, as also demonstrated by Notch1 in situ hybridisation (Supplementary Fig. 1a), all of which express both basal and luminal markers (K5, K14 and p63 for basal cells, BCs and K8 for luminal cells, LCs) (Fig. 1; Fig. 4a-b), consistently with previous reports1,28–32. When we examined the progeny derived from these cells after a 6-week chase, we found that embryonic Notch1pos mammary cells, at the population level, give rise to both BCs (CD24+/CD29high) and LCs (CD24+/CD29low) (Fig. 2a) in a comparative proportion to that observed in unlabelled mammary epithelial cells (MEC) (Fig. 2c), indicating that cells targeted by the Notch1 promoter in embryogenesis show no lineage bias. Representative dot plots to illustrate the gating strategy are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1b.
Figure 1. Embryonic mammary buds co-express luminal and basal markers.
Representative sections of mammary embryonic buds of N1Cre/mTmG embryos induced with tamoxifen at E13.5 (a, b, c, upper panel, d, e), or at E15.5 (c lower panel) and analysed 24h later by: hematoxylin coloration (a); immunostaining using an anti-ERα antibody (in red in b); immunofluorescence for the luminal marker K8 (in red, in c and d, upper panel) and the basal markers K14 (in white in c and in red in e, upper panel); K5 (in red, bottom panel in d); and p63 (in red, lower panel in e). GFPpos cells in green represent N1Cre-labelled embryonic cells in b-e. DAPI stains the nuclei in blue in c, e. Split channels for each colour are shown in the inset magnifications in c-d. 3 individual embryos for induction at E13.5 and 3 individual embryos for induction at E15.5. Scale bars correspond to 20 μm in b-e, and 10 μm in the magnifications in c-e.
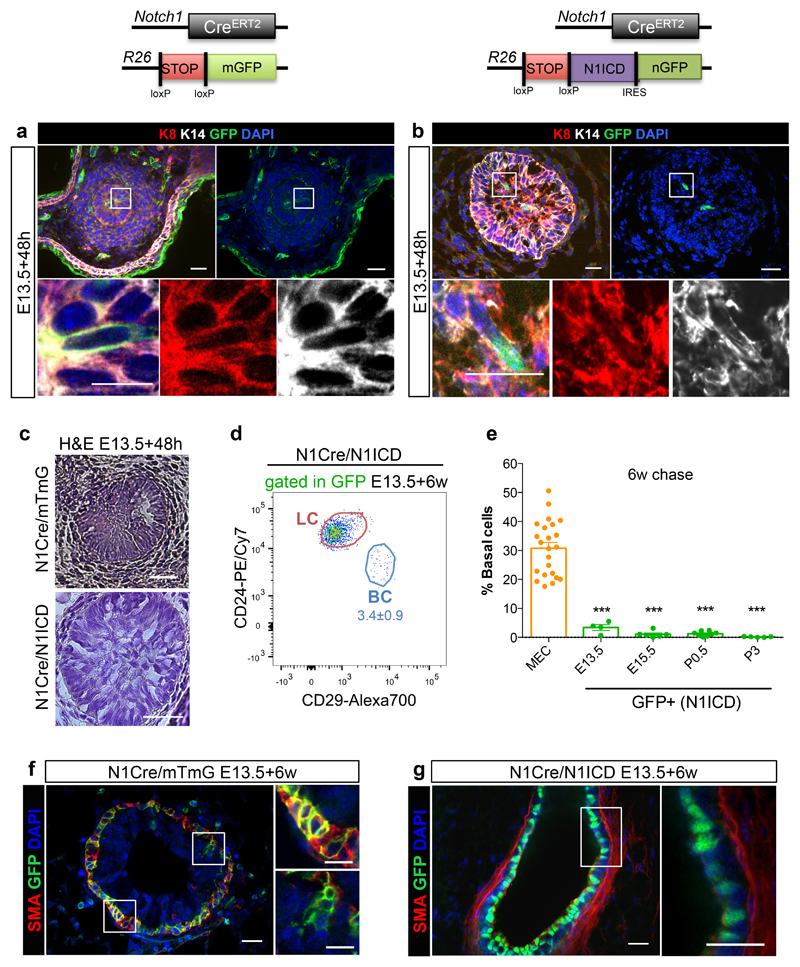
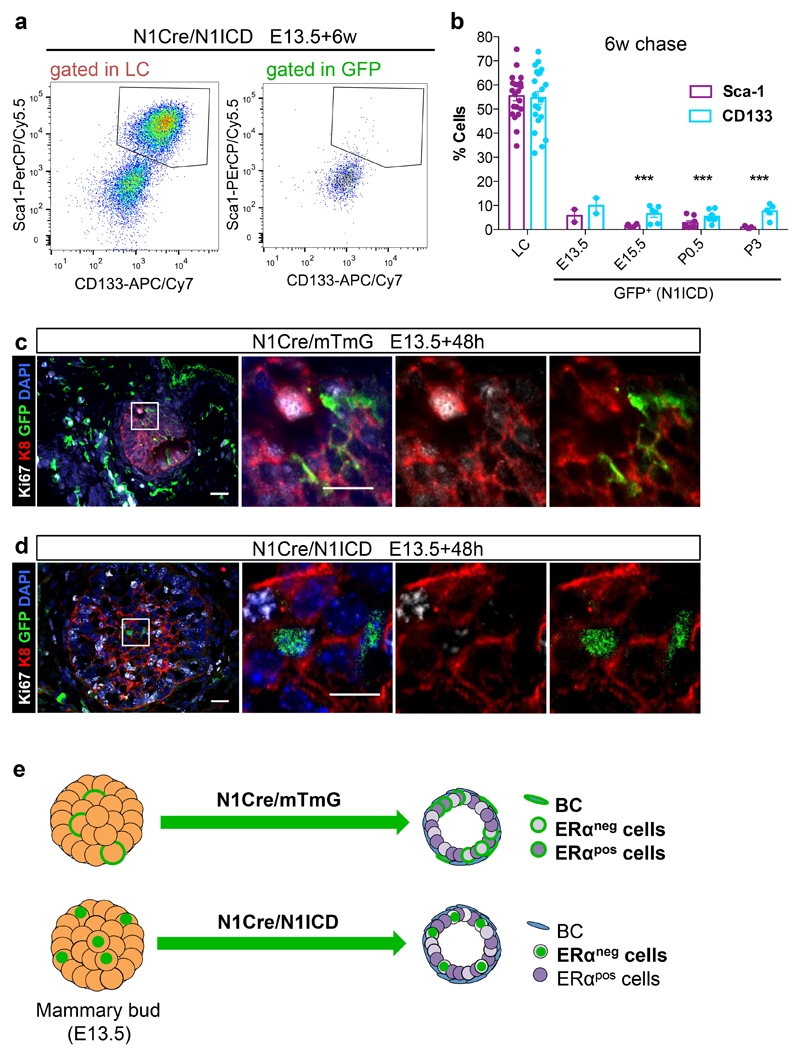
Figure 4. Notch1 activation in embryos locks multipotent stem cells into a luminal unipotent cell fate.
a-c. Representative sections of N1Cre/mTmG (a, c) and N1Cre/N1ICD (b, c) induced at E13.5 and analysed 48h later, by immunofluorescent staining for the basal marker K14 (in white), the luminal marker K8 (in red) and anti-GFP (green) (a, b), or stained with hematoxylin (c). Notch1-derived lineages are labelled in green by membrane-bound GFP in the N1Cre/mTmG model (a) and by nuclear GFP in N1Cre/N1ICD mice (b). DAPI stains nuclei in blue in a, b; 2 embryos per genotype. Schematic diagrams of the N1Cre/mTmG and the N1Cre/N1ICD mice are shown above panel a and b respectively. d. Representative FACS dot plot of luminal (LC) and basal cells (BC) within the GFPpos population in N1Cre/N1ICD mice 6 weeks after tamoxifen induction at E13.5; n=4 mice. e. FACS quantification of the percentage of BC within MEC (in orange) or within GFPpos cells (in green) in N1Cre/N1ICD mice induced with tamoxifen at the indicated developmental times and analysed after a 6-week chase; n=4, 6, 8, and 5 biologically independent animals induced at E13.5, E15.5, P0.5 and P3, respectively. The orange dots represent the MEC population from all mice analysed (n=23). p-values were calculated using Mann-Whitney test: p=0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001 and p<0.0001, respectively. f-g. Representative sections of N1Cre/mTmG (f) and N1Cre/N1ICD (g) induced at E13.5 and analysed 6 weeks later, by immunofluorescent staining for the basal marker SMA (in red) and anti-GFP (green). Notch1-derived lineages are labelled in green by membrane-bound GFP in the N1Cre/mTmG model (f) and by nuclear GFP in N1Cre/N1ICD (g) mice. DAPI stains nuclei in blue; 5 and 4 mice, respectively. Scale bars correspond to 20 μm or 10 μm (in magnifications). Graphs indicate average values ± SEM. ***p< 0.001. Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
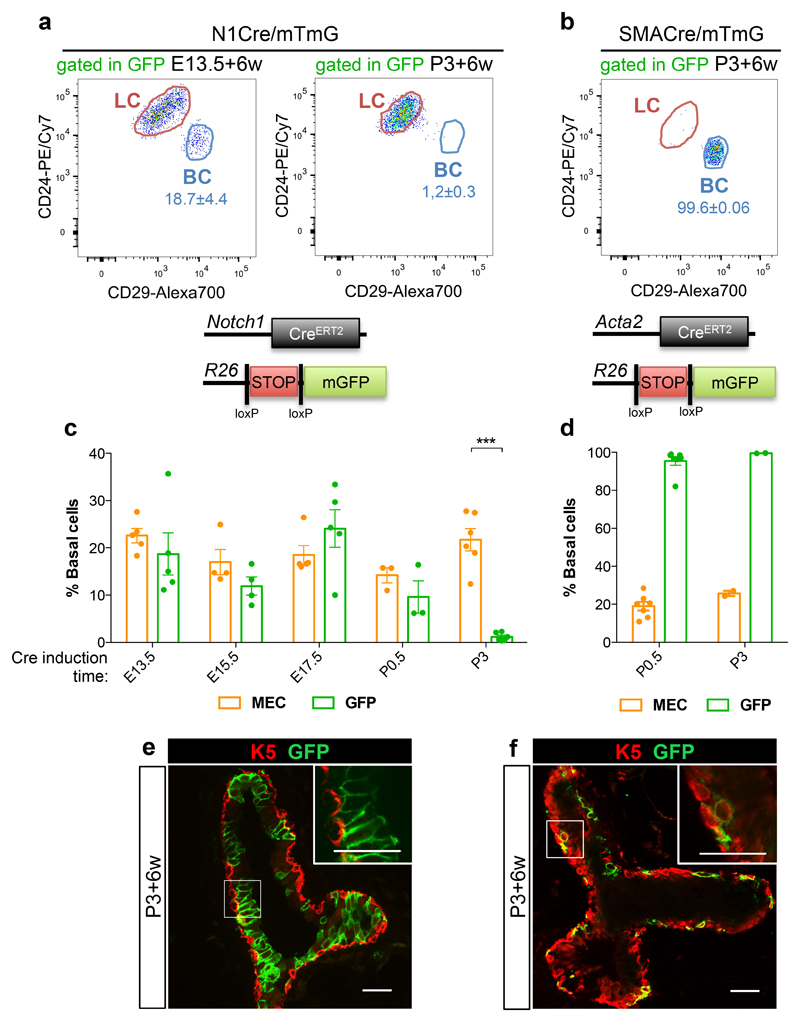
Figure 2. Luminal and basal identities are specified at birth.
a-b. Representative FACS dot plots of luminal (LC) and basal cells (BC) gated within the GFPpos population in N1Cre/mTmG (a) or SMACre/mTmG (b) mice 6 weeks after tamoxifen induction at E13.5 (a) or at P3 (a-b) quantified in c and d. c-d. FACS quantification of GFPpos BC (in green) as compared to the proportion of BC within Mammary Epithelial Cells (MEC, in orange) in N1Cre/mTmG (c) or SMACre/mTmG (d) mice, 6 weeks after tamoxifen induction at the indicated developmental times; n=5, 4, 5, 3 and 6 independent mice for N1Cre/mTmG induced at E13.5, E15.5, E17.5, P0.5 (MEC: 19.01±2.27, GFP: 95.45±2.26) and P3 (MEC: 25.67±1.37 and GFP: 99.56±0.06), respectively; n=7 and 2 biologically independent animals for SMACre/mTmG induced at P0.5 and P3, respectively. Schematic diagrams of the Notch1-CreERT2 and SMA-CreERT2 (Acta2-CreERT2) crossed to Rosa26mTmG mice are shown above each graph. e-f. Representative sections of mammary ducts analysed by immunofluorescent staining for K5 (in red) in N1Cre/mTmG (e) and SMACre/mTmG (f) mice, 6 weeks after tamoxifen induction at P3. Lineages derived from Notch1pos or SMApos cells are marked by membrane-bound GFP in green; 2 mice for each line. Scale bars correspond to 20 μm in e-f and 10 μm in the insets. Graphs show mean ± SEM. p=0.000006 in (c) and p=0.00000000002 and 0.0003 for P0.5 and P3 respectively (d), using two-tailed unpaired Welsh’s t-test. *** p<0.001. Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
To define the developmental timing of mammary cell identity acquisition, we induced N1CreERT2/R26mTmG mice at different developmental times and analysed their progeny in the pubertal gland. While embryonic induction of GFP expression resulted in GFP-labelled lineages that included both BCs and LCs, from post-natal day P3 onwards, Notch1-derived cells were exclusively luminal, as assessed both by FACS quantification and by immunostaining (Fig. 2a,c,e). Consistently, tracing clonal lineages derived from a basally expressed Cre line, Acta2-CreERT2 (called SMA-Cre)33, revealed that SMA-expressing basal cells labelled at birth exclusively gave rise to basal progeny (Fig. 2b,d,f). These results indicate that, for the vast majority of MaSCs (if not all), mammary luminal and basal identities are resolved at birth, and that BCs and LCs represent distinct and self-sustained lineages throughout adult life.
Interestingly, within the luminal lineage, Notch1pos embryonic cells can give rise to both ERαpos (Scapos/CD133pos) and ERαneg (Sca-/CD133-) daughter cells, at an unbiased ratio when compared to total LCs (Supplementary Fig. 2a). As Notch1 expression is restricted to ERαneg unipotent luminal progenitors in 4 week-old pubertal mice11, we traced post-natal cells by inducing mice at different developmental times and found that Notch1 expression becomes progressively restricted to ERαneg cells (Sca-/CD133-) shortly before puberty, between 2 and 3 weeks of age (Supplementary Fig. 2b). Importantly, when we assessed if single Notch1-expressing LCs labelled at birth could give rise to both ERαpos and ERαneg cells using the multicolour Confetti reporter mouse34, we found that clones of luminal cells labelled by the same colour were exclusively composed of either ERαpos or of ERαneg cells (Supplementary Fig. 2c). These results indicate that luminal cells are composed of two distinct lineages maintained by unipotent luminal progenitors, in agreement with two recent studies demonstrating that ERαpos and ERαneg luminal cells represent two independent lineages maintained by distinct stem cells in adult mice35,36.
Therefore, the N1CreERT2 line labels different types of mammary cells: undifferentiated cells in the embryo, luminal cells after birth (from P3 to P21) and exclusively ERαneg luminal progenitors at the onset of puberty (after P21) and allowed us to infer the critical developmental times for mammary lineage specification, an unexplored and important question to define how cell identity is specified and how the adult mammary cell types are determined during development.
Notch1pos embryonic mammary cells reveal unipotent cell fate potential in early mammogenesis
To determine whether embryonic MaSC exhibit bipotency at the cellular level and, if so, when this potential is lost during development, we crossed N1CreERT2 mice to the multicolour Confetti reporter line to trace the fate of individual mammary cells, imaging whole mount mammary glands of two-week-old mice, after induction during embryogenesis (from E12.5 to E17.5). Due to extensive cell rearrangements occurring during branching morphogenesis10,13,14, clones derived from embryonic labelling were composed of scattered cells throughout the gland. Our multicolour strategy was chosen with the aim of distinguishing clones derived from different stem cells, as they would be marked stochastically by one of the four colours resulting from the initial recombination event.
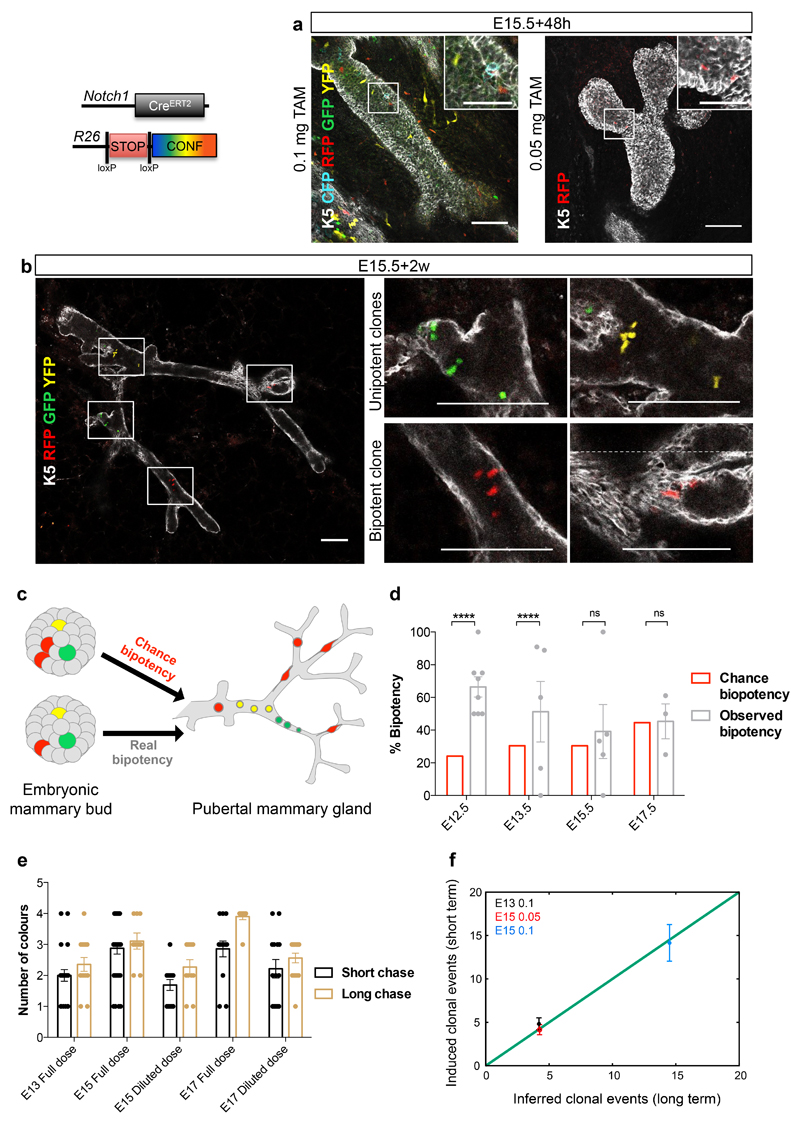
To resolve individual clonal events, we scored all cells labelled by the same Confetti colour throughout the whole gland. Strikingly, even with these very strict criteria, we found a high proportion of unicolour cell clusters (“unipotent clones”), belonging exclusively to the basal or luminal lineage (Fig. 3b, GFP and YFP labelled cells), which increased at late embryogenesis, suggesting that some cells acquire unipotency as early as E12.5 (Supplementary Fig. 5a). Since cells of the same colour could appear in the basal and luminal compartments through the chance induction of distinct unipotent progenitors (“chance bipotency” in Fig. 3c), we used a statistical method10 designed to assess the existence and relative abundance of true bipotent clones. For each induction time point, we tested the null hypothesis that all seemingly bipotent events arose by chance induction of independently labelled unipotent cells. This was achieved by simulating the stochastic labelling of unipotent LC and BC progenitors, taking into account three measured parameters: 1) the recombination efficiency, fit based on the average abundance of floxed colours per gland, both initially (Fig 3a,e and Supplementary Fig. 3) and after a longer chase (Fig. 3b,d and Supplementary Fig. 4-5); 2) the fraction of each recombined colour and 3) the relative frequency of luminal and basal induction. All three parameters were validated for robustness (see Theory Methods and Supplementary Fig. 5d-m for details).
Figure 3. Notch1pos embryonic mammary cells show unipotent cell fate potential.
a-b. Single Z-stacks of wholemount immunostaining of mammary trees from N1Cre/Confetti mice, induced with 0.05mg or 0.1mg of tamoxifen at E15.5, analysed 48h (a) and 2 weeks later (b). Immunostaining for K5 (white) marks basal cells. GFP (green), Cyan (blue), YFP (yellow), RFP (red) mark Notch1-derived lineages considered as unique clones derived from one ESC; 98 glands in 30 embryos and 139 clones from 65 glands in 21 mice. Images were acquired as different tiles without overlap and stitched juxtaposed. Dotted line in (b) demarcates the stitching. c. Schematic diagram illustrating how 2 independent labelling events of unipotent cells (red cells, “chance bipotency”) can be confused with the unique labelling of a multipotent stem cell (red cell, “real bipotency”). d. Percentage of theoretical chance bipotency (red) compared to experimentally scored bipotency (grey) in 1-2 week-old N1Cre/Confetti mice induced with tamoxifen at indicated embryonic stages. n= 8, 5, 5, 3 independent animals induced at E12.5, E13.5, E15.5, E17.5. p values = P<0.0001, P<0.0001, P=0.5 and P=0.43. Tamoxifen dose was adjusted at each time point to reach comparable recombination efficiency, indicated by the average number of floxed colours/gland (see Methods). e. Average number of colours/gland from mice induced at indicated time points, with indicated doses, analysed after 48h (short chase, in black) or at P7 (long chase, in brown). Recombination efficiency (short chase) reflects the number of colours found at P7 (long chase) at each tamoxifen dose (differences not significant). n=22, 32, 13, 14, 14 independent mammary glands for short times, and n=14, 9, 11, 10, 16 for long chase. f. Number of induced clonal events scored after a short chase vs number of inferred clonal events estimated from a long chase. n=12, 9, 8 biologically independent animals induced at E13.5 full dose (black dots), E15.5 diluted dose (red dots) and E15.5 full dose (blue dots). Two-tailed binomial test was applied to assess statistical differences between groups. Graphs show mean ± SEM. Source data in Supplementary Table 1. Scale bars are 100 μm or 50 μm in the magnifications in (a), 100 μm in (b).
The observed percentages of bipotent clones were then compared with the theoretical probability of “chance bipotency” (Fig. 3c-d)10. As shown in Fig. 3d, the null hypothesis could not be rejected (at 95% confidence level) at E15.5 and E17.5, meaning that “chance bipotency” could account for all observed bipotent events. This suggests that, after E15.5, Notch1pos embryonic mammary cells do not show significant multilineage potential in vivo (see Theory Methods and Supplementary Fig. 5b-k). By contrast, the probability of “chance bipotency” accounted for only one half of the experimentally observed bipotency at E12.5 and E13.5, indicating that multipotent cells are present at these embryonic stages. Importantly, as the recombination efficiency (parameter 1) is a key input of the model, we validated it by performing short-term tracing, measuring the number of labelled singlets and doublets, which well correlated with the inferred recombination efficiency from the long-term tracing (Fig. 3f). These results suggest that progressive restriction in lineage potential occurs as early as E12.5, whereas mammary embryonic cells from E15.5 onwards present no evidence for a significant multipotent behaviour, despite co-expressing basal and luminal markers, and continuing to contribute to both lineages until birth (Fig. 1 and Fig.2a,c).
Notch1 dictates luminal ERαneg cell fate in embryogenesis
To investigate whether embryonic cell fate is controlled by internal signals or by environmental/positional cues, we targeted Notch1-expressing cells from the early embryo (E13.5) to puberty with a transgenic line allowing constitutive Notch1 activation (Rosa-N1ICD-IRES-nGFP)37. We induced the mosaic expression of the ligand-independent active form of the Notch1 receptor (Notch1 Intracellular Domain or N1ICD) and found that cells expressing active Notch1 exclusively give rise to LC (Fig. 4d,e,g), and specifically of the ERαneg (Sca1neg/CD133neg) lineage (Fig. 5a,b), at any developmental stage (from E13.5 to P3), including when induction is performed in embryonic cells. Of note, embryonic cells expressing N1ICD still co-express luminal and basal markers and do not seem to undergo substantial changes in epithelial cell morphology 48h after Notch activation (Fig 4a-c). Moreover, no statistically significant differences could be observed in their proliferative activity within 48h, compared to control N1CreERT2/R26mTmG cells (Fig 5c, d). Surprisingly, when we targeted mammary embryonic cells with the N1CreERT2/N1ICD line, we could not observe any difference in epithelial layer integrity and in the ratio between LCs and BCs compared to N1CreERT2/R26mTmG mice after a 6-week chase (Supplementary Fig. 6a), suggesting a possible compensation from untargeted wild type cells. Although Notch1 is also expressed in some stromal cells during embryogenesis (Fig. 1, Supplementary Fig. 6b-e), Notch1 constitutive activation did not affect these cells even after a 6-week chase (Supplementary Fig. 6c-e). These results demonstrate that intrinsic signals can dictate a switch from multipotency to unipotency and that Notch1 signalling instructs embryonic mammary cells to differentiate exclusively as luminal ERαneg cells (Fig. 5e).
Figure 5. Notch1 dictates luminal ERαneg cell fate.
a. Representative FACS dot plots of CD133 and Sca1 expression in total luminal cells (gated in LC) or GFPpos LC (gated in GFP) in N1Cre/N1ICD mice 6 weeks after tamoxifen induction at E13.5, 2 independent mice. b. FACS data quantification showing the percentage of luminal cells (LC) or of N1ICD-expressing cells (GFP) that presents Sca1 (in purple) or CD133 (in blue) expression, after a 6-week chase of N1Cre/N1ICD mice induced with tamoxifen at the indicated times. N=2, 6, 8, and 5 biologically independent animals induced at E13.5, E15.5, P0.5 and P3, respectively; n=21 in the LC graph. Graphs show mean ± SEM: 5.7±2.6 for Sca-1 and 9.9±3.2 for CD133 (E13.5), 1.7±0.3 for Sca-1 and 6.5±1.4 for CD133 (E15.5), 2.8±0.8 for Sca-1 and 5.4±0.9 for CD133 (P0.5), 0.9±0.2 for Sca-1 and 7.6±1.3 for CD133 (P3). p=***p<0.001 using two-tailed unpaired Welsh’s t-test. c-d. Representative sections of N1Cre/mTmG (c) and N1Cre/N1ICD (d) mice induced at E13.5 and analysed 48h later, by immunofluorescent staining for the luminal marker K8 (in red) and the proliferation marker Ki67 (in white). Notch1-derived lineages are labelled in green by membrane-bound GFP in the N1Cre/mTmG model (c) and by nuclear GFP in N1Cre/N1ICD (d) mice. DAPI stains nuclei in blue; 2 biologically independent animals. e. Schematic diagram illustrating how Notch1 activation (N1Cre/N1ICD) imposes a luminal ERαneg cell fate to embryonic cells (E13.5), which would otherwise be able to give rise to all mammary cell types (N1Cre/mTmG). Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
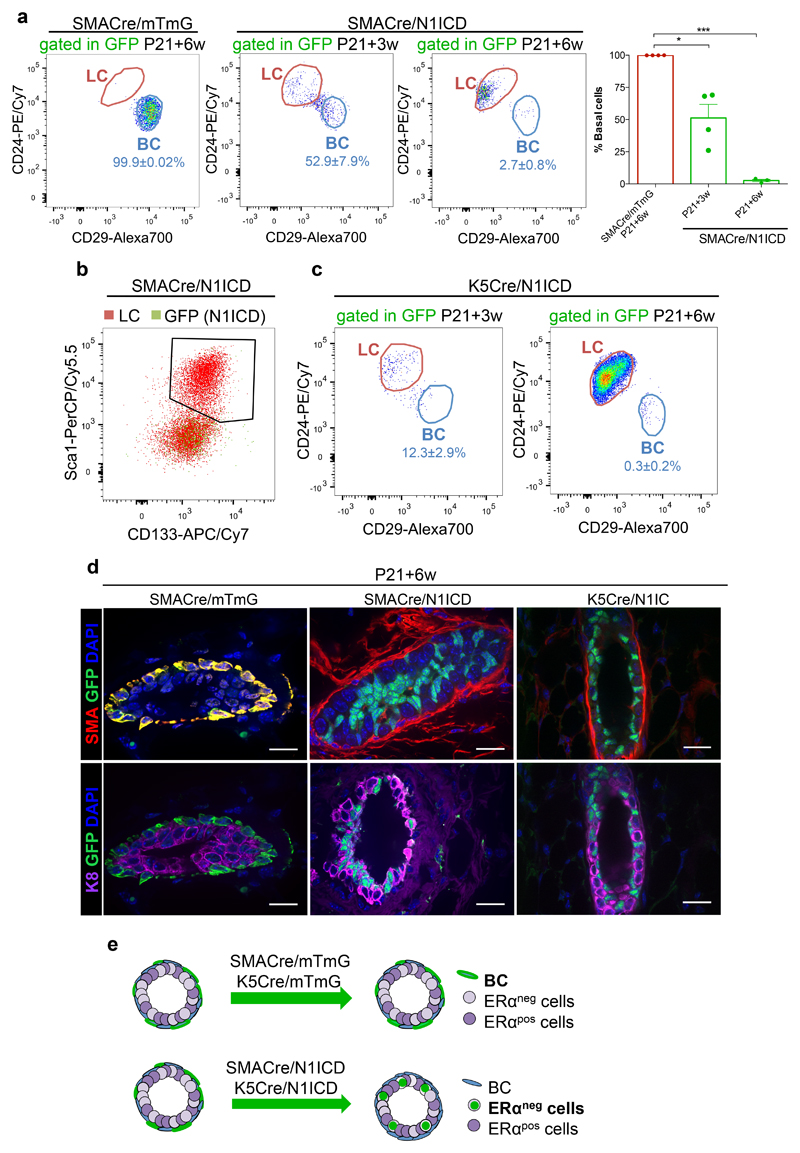
Ectopic Notch1 activation can switch the fate of committed mammary epithelial cells
Although our lineage tracing results, consistent with other studies performed using different promoters8,10,13–18, have established that the postnatal mammary gland harbours exclusively unipotent stem cells, recent works revealed the considerable plasticity of mammary stem cells upon oncogenic induction or following transplantation8,11,15,38. We thus assessed the plasticity of fully committed pubertal cells, by ectopic activation of the Notch pathway, an essential critical determinant of luminal cell fate specification (Fig. 4-5 and Ref.19). To this end, we ectopically expressed the constitutively active form of Notch1 in committed basal cells using two basal Cre lines, SMA-CreERT2 and K5-CreERT2 39, crossed to Rosa-N1IC-IRES-nGFP mice. Strikingly, ectopic Notch1 activation in BCs (SMACre/N1ICD and K5Cre/N1ICD) at the onset of puberty is sufficient to entirely switch their identity to ERαneg LCs (Fig. 6). Interestingly, the switch from basal to luminal ERαneg cells occurs progressively, since a 3-week chase after induction at P21 (P21+3w) still presents some labelled basal cells, but a 6-week chase demonstrated a complete shift from basal to luminal ERαneg cells (P21+6w) (Fig. 6a,b,d,e and Supplementary Fig. 7). The same cell fate switch was obtained when different types of BCs16 were targeted, using either SMA-CreERT2 or K5-CreERT2 (Fig. 6c,d,e), demonstrating that Notch signalling impacts lineage specification at different levels of the basal cell hierarchy. To characterise how the observed cell fate switch occurs in time, we have analysed the cellular responses to Notch activation in mice where N1ICD expression was induced for different chase periods, compared to control mice. We observed that some cells acquire a luminal position already during the first week after Notch1 activation (P21+72h and P21+1w in Supplementary Fig. 7b) and co-expression of luminal and basal keratins (K8 and K14) is notable in some cells that migrated towards the duct lumen (indicated by an arrow in panel P21+3w of Supplementary Fig. 7b), while it takes 6 weeks before the cell fate switch is complete (P21+6w, Fig. 6 and Supplementary Fig. 7).
Figure 6. Ectopic Notch1 activation switches the fate of committed mammary cells.
a. Representative FACS plots and quantification of the percentage of BC within the GFPpos population of SMACre/mTmG (left panel, n=4 biologically independent animals) or SMACre/N1ICD (right panel) induced at P21 and analysed after 3 weeks (n=5 mice) or 6 weeks (n=3 mice). Graphs show mean ± SEM: 51.3±10.5 (3w chase) and 2.6±1.0 (6w chase). P-vales were calculated using two-tailed unpaired Welsh’s t-test: p= 0.0189 and p<0.0001. b. Dot plot of Sca1pos/CD133pos cells among total LC (in red) and GFPpos cells (in green) in SMACre/N1ICD mice (P21+6-week chase); n=4 biologically independent animals. c. Representative FACS plots of K5Cre/N1ICD induced at P21 and analysed after 3 weeks or 6 weeks; n=3 independent animals. d. Representative paraffin sections of mammary ducts from SMACre/mTmG (left panel) or cryosections of glands from SMACre/N1ICD (middle panel) or K5Cre/N1ICD (right panel) females induced with tamoxifen at P21 and analysed 6 weeks later by immunofluorescent staining using anti-SMA (in red) or anti-K8 (in purple) antibodies. SMA-derived lineages are labelled in green by membrane-bound GFP in the SMACre/mTmG model and by nuclear GFP in SMACre/N1ICD mice; 4 biologically independent animals. Scale bars correspond to 20 μm. e. Schematic diagram illustrating how ectopic Notch1 activation in basal cells (SMACre/N1ICD or K5Cre/N1ICD) imposes a luminal ERαneg cell fate even to already committed basal cells. ***p<0.001 and *p<0.05. Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
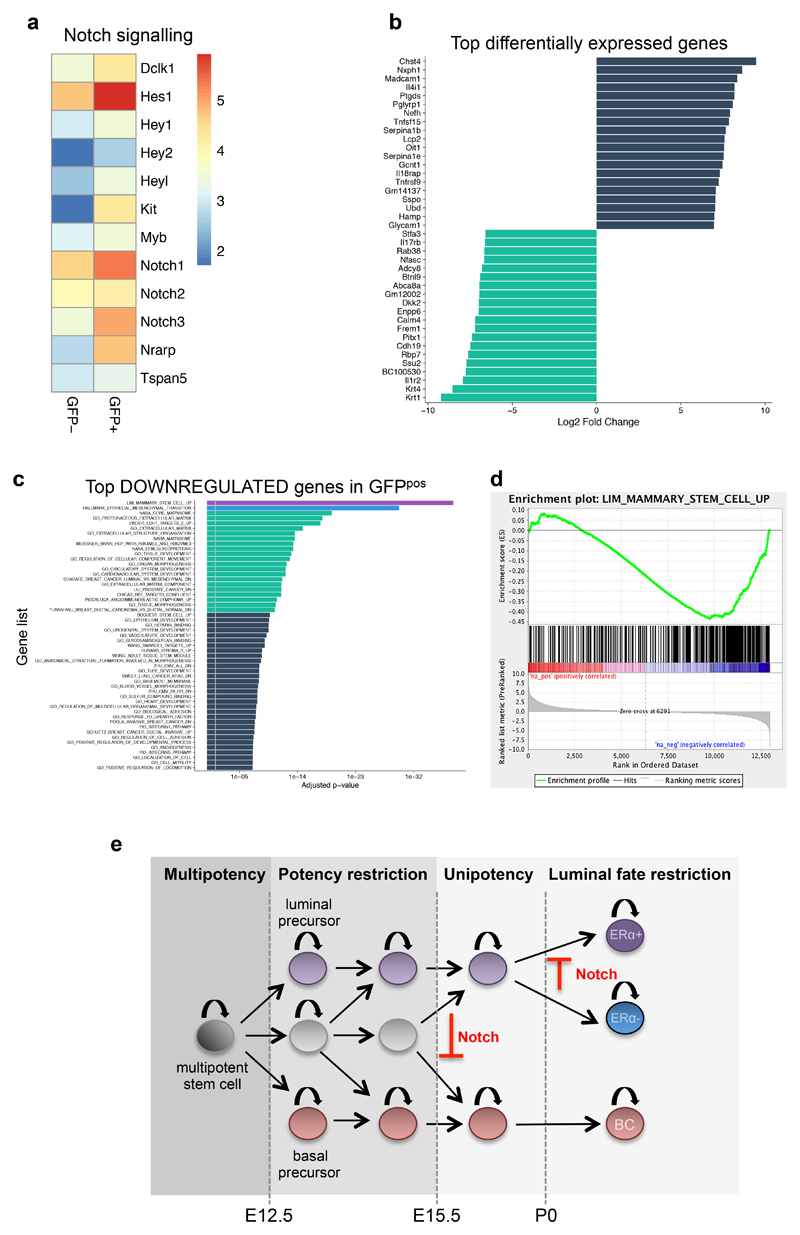
Since no major differences in terms of proliferation or apoptosis were observed in GFPpos cells after N1ICD induction (Supplementary Fig. 7b), we sought for mechanistic insights underlying the observed cell fate switch, by performing a whole-genome transcriptomic analysis of cells expressing N1ICD 72h after induction (in the SMACre model), to detect the early transcriptional responses to Notch activation. As expected, we found an upregulation of Notch target genes (Fig. 7a). Remarkably, we clearly identified by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) a highly significant reduction in expression of genes belonging to the “Mammary Stem Cell UP” gene signature within genes downregulated in the targeted cells (GFPpos) (Fig.7c-d). This signature represents genes highly expressed in BCs, defined as “Mammary stem cells” based on their high mammary repopulation capacity in transplantation assays40. In addition, Extracellular Matrix and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) gene signatures, features that have been associated with BCs41, were also significantly downregulated upon Notch activation. Overall, by both GO analysis (Fig. 7c) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) (Fig. 7d), we reveal that GFPpos cells negatively correlate with a basal signature, indicating that they lose their basal identity before they acquire a definitive luminal signature, as the increased expression of luminal cell markers (namely luminal cytokeratins K8, K18 and K19) is evident, but not yet statistically significant after only 72h of Notch activation.
Figure 7. Transcriptomic analysis of the basal to luminal switch induced by Notch1 activation.
a. Heatmap of Notch1 related genes, using the log(fpkm) of the average expression values (fpkm) of 3 replicates each for GFPneg and GFPpos cells. b. Transcripts with more than five Log2 Fold Change (FC) differences obtained by RNA-seq of GFPneg and GFPpos sorted cells from SMA/N1ICD mice 72h after TAM induction; the blue bars correspond to the transcripts that are overexpressed, and the green bars indicate the transcripts that are downregulated. c. Over-represented GO categories among the top genes significantly downregulated upon Notch activation. d. Gene Set Enrichment analysis (GSEA) showing the inverse correlation between genes expressed upon Notch activation (in GFPpos cells) compared to the GO signature of “Mammary_Stem_Cell_Up”. A set of 12984 genes from three replicates was pre-ranked based on log2 fold changes. e. Model of the differentiation hierarchy during embryonic mammary gland development. Multipotent mammary stem cells are present in the early mammary placode, but at E12.5 some lineage restriction starts to occur, as unipotent luminal or basal precursor can be found at a frequency of about 30-40%, while the remaining MaSCs are still multipotent. Starting at embryonic day E15.5, no statistically discernable multipotency can be observed, suggesting that prenatal growth and branching of the mammary gland is supported by unipotent luminal or basal progenitors. At P0, an additional degree of fate restriction establishes two independently sustained luminal lineages, ERpos and ERneg luminal cells. Notch signalling prevents the generation of basal precursors during mammary embryogenesis and blocks ERpos cell fate specification.
These results show that the unipotency of mammary stem cells belies a remarkable degree of plasticity that allows cell autonomous factors to redirect cell identity and differentiation potential, irrespective of the cellular environment (i.e. contact with the basement membrane) and the degree of commitment of the targeted cells.
Discussion
We showed that early embryonic development of the mouse mammary gland relies on the proliferative activity of multipotent stem cells that progressively differentiate into lineage-restricted unipotent precursors that fuel post-natal growth. Of relevance, Blanpain and colleagues have observed a similar switch from multipotency to unipotency during the course of embryonic development, using K14 and K5 lineage tracing experiments46. Statistical analysis of lineage labelled cells suggests that Notch1pos mammary cells have become restricted to generate basal or luminal progeny by E15.5 (Fig. 7e). Although we cannot exclude the existence of embryonic quiescent bipotent cells29 that are not targeted by N1CreERT2, the representative composition of bipotent clones labelled by the N1CreERT2 line prior to E15.5 reflects the general tissue growth both in cell proportion and composition, providing support to the concept that we are assessing the generic behaviour of the majority of embryonic cells. Therefore, our studies suggest that, if such cells exist, they must be rare and act in parallel to the cells expressing the Notch1 receptor, while the bulk of mammary embryonic growth proceeds from a population of unipotent basally and luminally-committed progenitors. Lineage potential restriction coincides with the initiation of branching morphogenesis around E15.5, suggesting that the two processes might be linked, possibly through mechano-sensitive pathways, though the mechanisms underlying lineage restriction in this context still remain unknown.
It has been previously reported that surface ectodermal cells can integrate into the mammary bud at the early times of bud invagination42. Notably, we could observe a high number of GFPpos cells in the prospective surface epidermis (see Fig. 4a and Supplementary Fig. 6b). This is not surprising, as the Notch1 receptor has been reported to be expressed in the early embryonic epidermis, where it is required for regulating epidermal keratinocyte specification43. Whether embryonic skin and mammary stem cells, due to their common origin from an ectodermal progenitor and the fact that they both specify ectodermal appendages, may share some characteristics and may be regulated by the same molecular pathways, such as Notch signalling repressing p63 in both epithelia, is a possibility that is worth considering.
Our findings also reveal the extensive and durable plasticity of basal mammary stem cells. The mechanisms used by stem cells to acquire a specific identity and lineage potential are the same as those that can be hijacked by oncogenes to induce cellular transformation in several tissues44, so their elucidation is also relevant to understand the origin of cancer. Here, we show that Notch activation can impose a cell fate switch on both undifferentiated (with N1CreERT2/N1ICD mice induced during embryogenesis, Fig. 5e) and committed (with SMACreERT2/N1ICD mice induced at P21, Fig. 6e) mammary cells, driving a progressive transition into unipotent ERneg luminal progenitors (Fig. 7e). In the accompanying paper, Blanpain and colleagues observed a complementary cell fate switch induced by expression of ΔNp63 in either embryonic or committed luminal cells46. As ΔNp63 has been shown to be negatively regulated by Notch signaling in the mammary gland45, our two studies describe mechanisms dictating cell fate specification in the mouse mammary gland. Indeed, such events may constitute a key early-stage of pre-neoplastic transformation, leading to mammary tumors development. Undoubtedly, the expression of intrinsic determinants should result from the exposure of individual cells to distinct environmental cues; it follows that the position that each embryonic cell acquires during tissue morphogenesis (i.e. their contact with the basement membrane or their facing the ductal lumen) might also contribute to establishing its identity as a BC or LC and to limit its lineage potential. Future investigations would be required to further understand the dynamic behaviour and plasticity of embryonic MaSCs.
Online Methods
Mice
N1CreERT2 23, SMA-CreERT2 43 and K5-CreERT2 mice 44 were crossed to the double fluorescent reporter Rosa26mT/mG 27, to the multicolour R26R-Confetti mouse reporter33, or to a conditional gain-of-function Notch1 mutant mouse (Rosa-N1IC-IRES-nGFP)36. Reporter expression was induced in N1CreERT2 or SMA-CreERT2 females by intraperitoneal tamoxifen injection of pregnant females at E11.5, E12.5, E13.5, E15.5 or E17.5, followed by C-section at E19.5 due to delivery failure caused by tamoxifen. Newborn pups were adopted by foster mothers. Postnatal induction was done at P0 and P3 by injecting lactating mothers, and at P10, P15 and P21 by injecting the pups. Females were injected with 0.1mg/g of mouse body weight of tamoxifen free base (Euromedex). For experiments using the Confetti reporter, the dose of tamoxifen was adjusted to 0.05 mg/g and to 2µg/g of mouse body weight for injections at E15.5 and E17.5 respectively, to achieve the same frequency of recombination (2-2.5 average floxed colours per gland). For each experiment, four mammary glands of at least three mice were analyzed. No fluorescence was observed in non-induced mice. For EdU (5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine) labelling experiments, mice were injected intra-peritoneally with 20mg/kg bodyweight of EdU 2 hours prior to isolation of mammary glands. We have exclusively analyzed female mice and no randomization methods were performed.
Ethics Statement
All studies and procedures involving animals were in strict accordance with the recommendations of the European Community (2010/63/UE) for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and other Scientific Purposes. The project was specifically approved by the ethics committee of the Institut Curie CEEA-IC #118 and approved by the French Ministry of Research with the reference #04240.03. We comply with internationally established principles of replacement, reduction, and refinement in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NRC 2011). Husbandry, supply of animals, as well as maintenance and care of the animals in the Animal Facility of Institut Curie (facility license #C75–05–18) before and during experiments fully satisfied the animal’s needs and welfare. Suffering of the animals has been kept to a minimum; no procedures inflicting pain have been performed.
Wholemount and two-dimensional immunostaining
For whole mount staining of N1Cre/confetti animals, glands from mice at 7 or 15 days of age were dissected ad incubated with 2.5mg/ml collagenase (C0130, Sigma) and 300μg/ml hyaluronidase (Sigma H3506) for 30 min to 1 hour at 37ºC under gentle shaking. Intact glands were washed in PBS and fixed with 4% PFA for 2 hours at room temperature. For Supplementary Fig. 2, glands from 6-week old mice were incubated in 600 U/ml collagenase and 200 U/ml hyaluronidase for 1 hour at 37ºC under gentle shaking. Tissue fragments were washed in PBS by serial pulse centrifugations at 1200 rpm and fixed with 4% PFA for 20 min at room temperature. Two-dimensional staining was performed with 5 or 30 μm sections. Freshly dissected mammary glands were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 2 hours and embedded in paraffin for animals crossed to the Rosa26mT/mG reporter, or in optimal cutting temperature (OCT) medium (VWR International) for animals crossed to Rosa-N1IC-ires-nGFP. Sections were stained according to Rodilla et al. 11. Antibodies used were chicken anti-GFP (1:1000 dilution, Ab13970, Abcam), rabbit anti-GFP (1:800 dilution, a generous gift from Monique Arpin), human anti-GFP (1:400 dilution, hVHH anti-GFP hFC, Recombinant Antibody Platform, Institut Curie), rabbit anti-K5 (1:800 dilution PRB-160P, Covance), mouse anti-SMA (1:800 dilution, #A2547, SIGMA), rabbit anti-K8 (1:800 dilution ab53280, Abcam), mouse-anti-K8 (1:400 dilution MMS-162P, Covance), rat anti-K8/K18 (1:300 dilution TROMA-1, DSHB), mouse anti-ERα (1:200 dilution M7047; Dako); mouse anti-p63 (1:600 dilution Ab3239, Abcam), rabbit anti-K14 (1:1000 dilution, ab181595, Abcam) and rabbit anti-cleaved Caspase-3 (1:200 dilution, 9661, Cell Signaling). Fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibodies included AlexaFluor 488-conjugated anti-chicken IgG, Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and Cy3- conjugated anti-mouse IgG for paraffin sections, and AlexaFluor 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG, Cy5-conjugated anti-rabbit and anti-mouse IgG, Cy2 and Cy3-conjugated anti-human IgG, and Cy3 and Cy5 anti-rat IgG for frozen sections. It is noteworthy that after paraffin embedding, the red Tomato signal is completely lost, as well as the GFP signal; for this reason, when we analyzed paraffin-embedded sections we always used anti-GFP antibodies and we could safely use Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies, as no signal in the red channel was evident. All secondary antibodies were used at 1:1000 dilutions and were purchased from Molecular Probes and Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc. EdU detection was performed using the Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 647 Imaging Kit (Molecular Probes), according to manufacturer’s instructions. At least three independent investigators have counted the coloured clones generated in the wholemount experiments, and two investigators were blinded. The number of counted clones was: 50 clones in 24 glands from 8 animals induced at E12; 33 clones in 14 glands from 5 animals induced at E13; 45 clones in 17 glands from 7 animals induced at E15, and 45 clones in 17 glands from 3 animals induced at E17.
RNAscope in situ hybridisation
RNA in situ hybridisation for mouse Notch1 (404641-C1) was performed manually according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Advanced Cell Diagnostics, Inc.). In brief, 7-μm paraformaldehyde-fixed, OCT-embedded frozen tissue sections were pre-treated with heat and protease before hybridisation with the target oligonucleotide probes. Preamplifier, amplifier and alkaline-phosphatase-labelled oligonucleotides were then hybridised sequentially, coupled with a fluorescent conjugate. Each sample was quality controlled for RNA integrity with an RNAscope probe specific to PolR2A RNA (320881) and for background with a probe specific to bacterial dapB RNA (320881). Specific RNA staining signal for Notch1 was identified as red punctate dots. Samples were counterstained with antibodies to K8 and GFP and with DAPI. The experiment was performed on 4 embryos from three different mothers for each probe.
Microscopy and image acquisition
For image acquisition of stained sections, we used a PLAN APO 63x/1.4NA objective on an upright spinning disk (CSU-X1 scan-head from Yokogawa) microscope (Carl Zeiss, Roper Scientific France), equipped with a CoolSnap HQ2 CCD camera (Photometrics). Images were captured using Metamorph. Confetti images were acquired using a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSM780 or LSM880, Carl Zeiss) with a LD LCI PLAN-APO 25× / 0.8NA OIL objective. Acquisition settings were the following: zoom 0.6, xy pixel size 554nm, spectral emission filters (bandwidth): 414-485nm, 490-508nm, 535-553nm, 588-615nm, 641-735nm and laser wavelengths: 405, 488, 514, 561 and 633nm. Wholemount images were acquired in different tiles and stitched without overlap by juxtaposition using the Zeiss software Zen Black 14.0.8.201. Image processing was performed using Fiji Software, version 2.0.0.
Mammary gland dissociation and Flow cytometry
Single cell dissociation was performed through enzymatic digestion with 600 U/mL collagenase (Sigma) and 200 U/mL hyaluronidase (Sigma) for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were further dissociated in TrypLE (Gibco) for 3 min, in 5 mg/mL dispase (Roche) and 0.1 mg/mL DNase I (Sigma) for 5 min, and then in 0.63% NH4Cl and filtered through a 40 μm cell strainer to obtain a single cell preparation for FACS. Cell labelling, and flow cytometry were performed as previously described in Rodilla et al., 2015. Dead cells (DAPI+), and CD45+/CD31+/Ter119+ (Lin+) non-epithelial cells were excluded before analysis using LSRII or FACS ARIA flow cytometers (BD). The following antibodies were used in 1:100 final concentration: biotin anti-CD133 (BioLegend), PE/Cy7 anti-mouse CD24 (BioLegend), PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-mouse Sca-1 (BioLegend), AlexaFluor700 anti-mouse/rat CD29 (BioLegend), PE anti-mouse CD49b (BioLegend); lineage markers: APC anti-mouse CD31 (BioLegend), APC anti-mouse Ter119 (BioLegend), APC anti-mouse CD45 (BioLegend); APC/Cy7 Streptavidin; isotype controls: PE rat IgM (BioLegend), PerCP/Cy5.5 rat IgGa (BioLegend). The purity of sorted populations was about 95%. The results were analyzed using FlowJo software and the data processing with Prism-graphpad.
RNA Sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from basal GFP+ and GFP- populations from mammary glands of SMACre/N1ICD mice, using Qiagen RNeasy kit according to manufacturer’s instructions. Library preparation was performed at Integragen (http://www.integragen.com/). All DNA libraries were quantified by qPCR. Only DNA with adapters ligated to both ends could be measured, as only these fragments can be amplified to generate material for sequencing. This quantification was able to qualify the DNA library, which was then ready to generate clusters to the expected density. The library was sequenced on paired end 2x75b run on the Illumina HiSeq4000. Image analysis and base calling was performed using Illumina Real Time Analysis (2.7.7) with default parameters.
RNA Sequencing analysis
Quality control and raw sequences cleaning
Quality of reads was assessed for each sample using FastQC (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Raw reads were trimmed to remove the first three bases of the first read using Cutadapt tool (Martin et al., 2011).
Sequence alignment and quantification of gene expression
A subset of 500,000 reads from each Fastq file was aligned to the reference mouse genome mm10 with TopHat2 45 to determine insert sizes with Picard (https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/). Full Fastq files were aligned to the reference mouse genome mm10 with TopHat2 (-p 24 -r 150 -g 2 --library-type fr-secondstrand)45. We removed reads mapping to multiple locations. We quantified gene expression using transcriptome annotations from Gencode (vM14). We used HTSeq 46 to obtain the number of reads associated to each gene in the Gencode database (restricted to protein-coding genes, antisense and lincRNAs). We used the Bioconductor DESeq package47 to import raw HTSeq counts for each sample into R statistical software and extract the count matrix. After normalizing for library size, we normalized the count matrix by the coding length of genes to compute FPKM scores (number of fragments per kilobase of exon model and millions of mapped reads).
Differential expression analysis
Only genes expressed in at least one sample (FPKM≥0.1) were considered for downstream analysis. The Bioconductor Limma package48 was used to test for differential expression and a q-value threshold of ≤0.15 was applied to define differentially expressed genes.
Gene set enrichment analysis
Hypergeometric tests were used to identify overrepresented gene sets from the MSigDB v5 database49 adjusted for mouse organism based on The Jackson Laboratory Human and Mouse Homology and provided by The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research (http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/software/MSigDB/). P-values were corrected for multiple testing with the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. GSEA v3.0 was used to generate Fig. 7d and calculate the enrichment score.
Statistical analysis of chance bipotency
In order to distinguish “real” bipotency of individual mammary progenitors and “chance bipotency” associated with the random and simultaneous labelling of unipotent basal and luminal progenitors of the same colour with a given mammary gland, we resorted to a statistical analysis and numerical simulations of random clonal induction.
Description of the method
We tested the null hypothesis that all bipotent events could be explained by “chance bipotency” in a purely unipotent framework, by calculating for each time point the probability of chance bipotency, which depends on three experimentally measured parameters10: 1/ the induction rate μ (fitted via the average number of confetti colours in a given gland, see Fig. S5g-h), 2/ the relative chimerism (i.e. the relative frequency of RFP, GFP, CFP and YFP cells), 3/ the relative induction of basal vs. luminal cell (assessed by assuming that progenitors are unipotent and counting the relative probability of finding luminal vs. basal clones of a given colour in a gland). These three parameters are integrated in the simulation in the following way:
-
1/
We ran stochastic simulation of a given mammary gland, numerically simulating the random induction of n cell on average per gland (giving rise to a Poisson distribution of number of cells induced), with the average number of event per gland fitted as described above from the average number of colours in a given gland. For each time point, we ran n=1.000.000 simulations, corresponding each to a single mammary gland), in order to be able to get global statistics, but also detailed statistics on the “chance potency” of each individual confetti colour.
-
2/
We then choose the confetti colour of each of the nlab labelled cells in a given gland, as a stochastic process where the probability of each colour corresponds to the experimentally observed global colour ratio.
-
3/
We finally choose the fate (basal or luminal) of each of the nlab labelled cells in a given gland, again as stochastic process (binomial distribution), where the probability of each outcome is parameter 3 mentioned above. One should note that, as we explore the “unipotent” null hypothesis here, mixed basal/luminal clones are counted here as two separate unipotent clones to calculate the basal/luminal induction ratio. However, as discussed below and on Extended Data Fig. 5l-m, we subsequently validated parameter 3 further to show that the results were also consistent when considering the unipotent clones only.
As mentioned, we thus measured all three parameters for each time point, and ran numerical simulations using the respective parameters for each time point. In particular, as the induction frequency (parameter 1) varied significantly between different time points, and as this parameter is particularly crucial to set the probability of “chance bipotency” (for very rare inductions, the probability is close to zero; for mosaic labelling, the probability is close to 100%), we adjusted the induction frequency at each time point in the simulations to match the respective average number of colours. For instance, at E15.5 (0.05 mg/g tamoxifen), we found 2.2 colours on average, which translated into an average induction frequency of 4.2 independent precursors per mammary gland. It should be noted that we excluded from the analysis the rare clones containing a single cell, as this leaves the issue of potency undetermined.
Controls to assess method robustness
In Supplementary Fig. 5g-h, we display a sensitivity analysis for E15.5 parameters, where we varied the induction frequency (parameter 1), to show its dependency on 1/ the average number of colours per gland, and 2/ the fraction of “chance” bipotency. As discussed in the legend of Supplementary Fig. 5, this sensitivity analysis was performed using the relative chimerism extracted from either the E12 or E17 dataset, to show that 1/ the balance of the four confetti colours was not significantly modified between the first and last induction time points used in this study, 2/ the predicted “chance” potency depended only very weakly on the time point chosen for the values of the relative colour frequencies (discrepancies increase at very high inductions doses, given the fact that the number of colours becomes very sensitive on the probability of CFP induction, which is rare and thus associated with high variance and uncertainty).
Moreover, as this analysis reveals parameter 1 to be the most crucial for the prediction of change bipotency, we sought to experimentally validate the values that we inferred from long-term tracings. We thus repeated the tracings using the same doses, but collecting samples 48h after induction, in order to allow enough time for the recombination to occur, but not enough for large-scale clonal dispersion. We also tested both Tamoxifen doses at E15.5, to validate the higher induction we inferred for 0.1mg at E15.5. Importantly, both doses as E15.5 and the E13.5 time point displayed excellent agreement (Fig. 3f) between the measured clonal induction on short-term tracings (number of labelled singlets or doublets per mammary gland) and the inferred clonal induction on long-term tracings. This validates both the inference method and the predictions on change potency. Of note, we tried to apply the same method for E17.5+48h short-term tracings, but found that clones were already dispersed on long distances in the gland, due to the several steps of branching at this point, which made it impossible to assess clones reliably.
Next, we sought to validate further our estimation of parameter 3, which is also important for the prediction of chance bipotency (in the limit of pure induction of luminal cells, there would be zero chance bipotency). We therefore re-plotted the observed vs predicted potencies for E15 and E17 inductions, but segregating unipotent basal and unipotent luminal in separate categories. This provides a safety check to verify that the parameter 3 also predicts well the ratio of basal to luminal unipotent clones (where the cell of origin is un-ambiguous). Indeed, if for instance, basal cells where much more bipotent than luminal cells, our theory could over-estimate basal unipotency, and our estimate of Parameter 3 could be biased by basal, but not luminal, bipotency. Importantly, we did not find statistical differences between experimental and predicted distributions (Supplementary Figure 5l-m, P=0.25 at E15, P=0.79 at E17, Chi-squared tests), demonstrating robustness of our results. At E15, one should note that the theory slightly over-estimates basal potency, although one would need much higher statistics to test if there really is a small basal population retaining residual E15 bipotency. At E17, the theory predicts nearly perfectly both basal and luminal unipotency.
Finally, as an additional test of the method, we sought to test whether the stochastic induction modelled reproduced well the experimental distribution of number of colours per gland (as we only used the average number of colours per gland). We thus computed the predicted value from the same simulations as above, and found a good quantitative agreement with the data, validating our hypothesis of stochastic (Poisson) induction of labelled cells in different glands (Supplementary Fig. 5i-k) at all time points.
Results on “chance bipotency”
To statistically test the validity of the null, unipotent hypothesis, at each time point, we then compared the theoretical probability of finding “chance bipotency” to its experimental counterpart. Given that there are only two categories (“unipotent” or “bipotent”), we used two-tailed binomial tests to calculate P-values associated with the hypothesis at each time point (except for Supplementary Fig. 5l-m which have three categories and where we used a chi-squared test). Accordingly, on the graphs of Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 5b-m, all error bars are calculated as the standard deviation of the binomial distributions underlying the experimentally measured probabilities – although this gives very similar standard deviations to the ones computed based on biological replicates, see Supplementary Fig. 5a. As discussed in the main text, we find very significant bipotency at E12.5 and E13.5 (P<0.0001), with more than half of the observed bipotency being “real”, rather than occurring by chance. On the other hand, we do not find statistically significant “real” bipotency at E15.5 and E17.5 (P=0.5 and P=0.43). Of note, in the findings reported in the main text, we used lower and lower doses of Tam as a function of time, in order to maintain the relative induction at a constant level (as monitored by the average number of colours in Fig. 3d). This behaviour is logical, as the number of cells in a given mammary gland increases steadily as a function of time, so that the number of floxed cells per gland is expected to increase throughout embryogenesis, requiring lower and lower doses for a clonal analysis. Nevertheless, for the sake of completeness, we also analysed E15.5 glands induced at a higher dose of 0.1mg/g of tamoxifen (i.e. the E12.5/E13.5 dose). Although the fraction of observed bipotency is much higher than for the 0.05 mg/g tamoxifen experiment, the difference is fully in line with the theoretical prediction for this induction dose (3.3 colours for 0.1mg tamoxifen vs. 2.2 colours for 0.05mg), as shown in Supplementary Fig. 5b. Remarkably, we still could not find statistically significant differences between observed and “chance” bipotency (P=0.12, two-tailed binomial test). Finally, we challenged our statistical analysis by testing whether our results were consistent when examining separately each confetti colour. CFP was so rare that only 1 or 2 clones could be observed at each time point, preventing any robust statistical test on this colour. However, YFP, RFP and GFP are still recombined with consistently different efficiencies, with YFP being the rarest of the three. This provided a platform to test our hypothesis of “chance bipotency”, as one would predict a higher probability of “chance bipotency” for GFP/RFP than for YFP. Supplementary Fig. 5b-f shows observed vs “chance” bipotency percentages for each three colours, at all four time points. Importantly, we find consistent results with the global results: at E15.5 and E17.5, we do not find any colour in which the differences between observed and “chance” bipotency are statistically different (P>0.3 in all cases). Importantly, the observed and “chance” potencies were consistently higher for more represented colours, and lower for less frequent colours. Similarly, at E12.5 and E13.5, we found consistent statistically significant (and large) excesses in observed bipotency compared to “chance” (P<0.05 in all cases, except for E13 RFP, P=0.11, which could be due to the relatively small number of RFP events – 11 in total at E13).
Code availability statement
Computer codes used in this study are available upon request.
Statistics and Reproducibility
Experiments were performed in biological and technical replicates as stated. Each experiment was repeated independently at least two times, with similar results. For each experiment, we have used at least n=2 animals, and experiments with at least n=4 were used to calculate the statistical value of each analysis. All graphs show mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis to compare differences between groups implied two-tailed unpaired Welsh’s t-tests, unless otherwise stated.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Prof. Spyros Artavanis-Tsakonas for generously sharing the N1CreERT2 mice and to Prof. Pierre Chambon and Daniel Metzger for kindly providing the SMA-CreERT2 (Acta2-CreERT2) and K5-CreERT2 mice. Likewise, we wish to acknowledge Prof. Shahragim Tajbakhsh for the mTmG reporter line and Prof. Hans Clevers for sharing the Confetti reporter mouse. We are also grateful to the members of the Glukhova laboratory, especially Marisa Faraldo and Marie-Ange Deugnier, for technical advice and constructive discussions. We would like to acknowledge the Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Platform at Institute Curie for their expertise, in particular Zosia Maciorowski; the In Vivo Experimental Facility, mainly Sonia Jannet, for help in the maintenance and care of our mouse colony and the Experimental Pathology facility at Curie Hospital for paraffin sample preparation.
Funding: This work was supported by Paris Sciences et Lettres (PSL* Research University), the French National Research Agency (ANR) grant number ANR-15-CE13-0013-01, the Canceropole Ile-de-France (grant # 2015-2-APD-01-ICR-1) and by Labex DEEP ANR-Number 11-LBX-0044 to SF; by the Wellcome Trust grant number 098357/Z/12/Z to BDS and 110326/Z/15/Z to EH. AML was funded by a post-doctoral fellowship from the Fondation de France. EH was funded by a Junior Research Fellowship from Trinity College (Cambridge University), a Sir Henry Wellcome Fellowship from the Wellcome Trust, and acknowledges the Bettencourt-Schueller Young Researcher Prize for support. The PICT-IBiSA imaging platform was funded by ANR-10-INBS-04 (France-BioImaging), ANR-11 BSV2 012 01, ERC ZEBRATECTUM N°311159, ARC SFI20121205686 and from the Schlumberger Foundation. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Data availability
RNA sequencing data that support the findings of this study have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under accession code GSE105432. Source data have been provided as Supplementary Table 1. All other data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author Contributions. A.M.L, V.R., M.H., E.H. and S.F. conceived and designed the experiments and analysed the data; A.M.L, V.R., C.L. and M.H. performed all experiments; O.R. and O.L. performed the 3D image analysis; S.R. analysed the RNA sequencing data, A.M.L, V.R., E.H., B.D.S and S.F. wrote the manuscript.
Competing Financial Interest. All authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Wansbury O, et al. Transcriptome analysis of embryonic mammary cells reveals insights into mammary lineage establishment. Breast cancer research: BCR. 2011;13:R79. doi: 10.1186/bcr2928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Robinson GW. Cooperation of signalling pathways in embryonic mammary gland development. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:963–972. doi: 10.1038/nrg2227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Veltmaat JM, Mailleux AA, Thiery JP, Bellusci S. Mouse embryonic mammogenesis as a model for the molecular regulation of pattern formation. Differentiation. 2003;71:1–17. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.2003.700601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Watson CJ, Khaled WT. Mammary development in the embryo and adult: a journey of morphogenesis and commitment. Development. 2008;135:995–1003. doi: 10.1242/dev.005439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stingl J, Raouf A, Eirew P, Eaves CJ. Deciphering the mammary epithelial cell hierarchy. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1519–1522. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.14.2983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shackleton M, et al. Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell. Nature. 2006;439:84–88. doi: 10.1038/nature04372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rios AC, Fu NY, Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE. In situ identification of bipotent stem cells in the mammary gland. Nature. 2014;506:322–327. doi: 10.1038/nature12948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Van Keymeulen A, et al. Distinct stem cells contribute to mammary gland development and maintenance. Nature. 2011;479:189–193. doi: 10.1038/nature10573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang D, et al. Identification of multipotent mammary stem cells by protein C receptor expression. Nature. 2015;517:81–84. doi: 10.1038/nature13851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wuidart A, et al. Quantitative lineage tracing strategies to resolve multipotency in tissue-specific stem cells. Genes Dev. 2016;30:1261–1277. doi: 10.1101/gad.280057.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rodilla V, et al. Luminal Progenitors Restrict Their Lineage Potential during Mammary Gland Development. PLoS Biol. 2015;13:e1002069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Blanpain C, Simons BD. Unravelling stem cell dynamics by lineage tracing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:489–502. doi: 10.1038/nrm3625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scheele CL, et al. Identity and dynamics of mammary stem cells during branching morphogenesis. Nature. 2017;542:313–317. doi: 10.1038/nature21046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Davis FM, et al. Single-cell lineage tracing in the mammary gland reveals stochastic clonal dispersion of stem/progenitor cell progeny. Nat Commun. 2016;7 doi: 10.1038/ncomms13053. 13053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Koren S, et al. PIK3CA(H1047R) induces multipotency and multi-lineage mammary tumours. Nature. 2015;525:114–118. doi: 10.1038/nature14669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Prater MD, et al. Mammary stem cells have myoepithelial cell properties. Nature cell biology. 2014 doi: 10.1038/ncb3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Blaas L, et al. Lgr6 labels a rare population of mammary gland progenitor cells that are able to originate luminal mammary tumours. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18:1346–1356. doi: 10.1038/ncb3434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.van Amerongen R, Bowman AN, Nusse R. Developmental stage and time dictate the fate of Wnt/beta-catenin-responsive stem cells in the mammary gland. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11:387–400. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bouras T, et al. Notch signaling regulates mammary stem cell function and luminal cell-fate commitment. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:429–441. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Choi N, Zhang B, Zhang L, Ittmann M, Xin L. Adult murine prostate basal and luminal cells are self-sustained lineages that can both serve as targets for prostate cancer initiation. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:253–265. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lu CP, et al. Identification of stem cell populations in sweat glands and ducts reveals roles in homeostasis and wound repair. Cell. 2012;150:136–150. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ousset M, et al. Multipotent and unipotent progenitors contribute to prostate postnatal development. Nature cell biology. 2012;14:1131–1138. doi: 10.1038/ncb2600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fre S, et al. Notch lineages and activity in intestinal stem cells determined by a new set of knock-in mice. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Howard BA, Veltmaat JM. Embryonic mammary gland development; a domain of fundamental research with high relevance for breast cancer research. Preface. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2013;18:89–91. doi: 10.1007/s10911-013-9296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zvelebil M, et al. Embryonic mammary signature subsets are activated in Brca1-/- and basal-like breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15:R25. doi: 10.1186/bcr3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Spike BT, et al. A mammary stem cell population identified and characterized in late embryogenesis reveals similarities to human breast cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:183–197. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muzumdar MD, Tasic B, Miyamichi K, Li L, Luo L. A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Genesis. 2007;45:593–605. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Asselin-Labat ML, et al. Gata-3 is an essential regulator of mammary-gland morphogenesis and luminal-cell differentiation. Nature cell biology. 2007;9:201–209. doi: 10.1038/ncb1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boras-Granic K, Dann P, Wysolmerski JJ. Embryonic cells contribute directly to the quiescent stem cell population in the adult mouse mammary gland. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16:487. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0487-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mills AA, et al. p63 is a p53 homologue required for limb and epidermal morphogenesis. Nature. 1999;398:708–713. doi: 10.1038/19531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moumen M, et al. The mammary myoepithelial cell. Int J Dev Biol. 2011;55:763–771. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.113385mm. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun P, Yuan Y, Li A, Li B, Dai X. Cytokeratin expression during mouse embryonic and early postnatal mammary gland development. Histochemistry and cell biology. 2010;133:213–221. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0662-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wendling O, Bornert JM, Chambon P, Metzger D. Efficient temporally-controlled targeted mutagenesis in smooth muscle cells of the adult mouse. Genesis. 2009;47:14–18. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Snippert HJ, et al. Intestinal crypt homeostasis results from neutral competition between symmetrically dividing Lgr5 stem cells. Cell. 2010;143:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang C, Christin JR, Oktay MH, Guo W. Lineage-Biased Stem Cells Maintain Estrogen-Receptor-Positive and -Negative Mouse Mammary Luminal Lineages. Cell Rep. 2017;18:2825–2835. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Van Keymeulen A, et al. Lineage-Restricted Mammary Stem Cells Sustain the Development, Homeostasis, and Regeneration of the Estrogen Receptor Positive Lineage. Cell Rep. 2017;20:1525–1532. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.07.066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Murtaugh LC, Stanger BZ, Kwan KM, Melton DA. Notch signaling controls multiple steps of pancreatic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:14920–14925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2436557100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Van Keymeulen A, et al. Reactivation of multipotency by oncogenic PIK3CA induces breast tumour heterogeneity. Nature. 2015;525:119–123. doi: 10.1038/nature14665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Indra AK, et al. Temporally-controlled site-specific mutagenesis in the basal layer of the epidermis: comparison of the recombinase activity of the tamoxifen-inducible Cre-ER(T) and Cre-ER(T2) recombinases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:4324–4327. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.22.4324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lim E, et al. Transcriptome analyses of mouse and human mammary cell subpopulations reveal multiple conserved genes and pathways. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12:R21. doi: 10.1186/bcr2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ye X, et al. Distinct EMT programs control normal mammary stem cells and tumour-initiating cells. Nature. 2015;525:256–260. doi: 10.1038/nature14897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee MY, et al. Ectodermal influx and cell hypertrophy provide early growth for all murine mammary rudiments, and are differentially regulated among them by Gli3. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tadeu AM, Horsley V. Notch signaling represses p63 expression in the developing surface ectoderm. Development. 2013;140:3777–3786. doi: 10.1242/dev.093948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Blanpain C, Fuchs E. Stem cell plasticity. Plasticity of epithelial stem cells in tissue regeneration. Science. 2014;344 doi: 10.1126/science.1242281. 1242281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yalcin-Ozuysal O, et al. Antagonistic roles of Notch and p63 in controlling mammary epithelial cell fates. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1600–1612. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wuidart A, et al. Early lineage segregation of multipotent embryonic mammary gland progenitors. 2018 doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.