Abstract
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), alternatively known as liver pericytes, can differentiate into myofibroblasts and secrete extra-cellular matrix components, thereby promoting wound healing and fibrosis. Studying HSCs can provide insights into the pathological mechanisms governing these processes. HSC isolation methods typically comprise of enzymatic digestion followed by density gradient centrifugation and/or Fluorescent Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) mediated sorting. In this protocol, we describe a step-wise method for HSC isolation that utilizes Pronase and Collagenase for enzymatic tissue dissociation, followed by an Optiprep based density gradient centrifugation. The isolation can be performed using common media and buffers, and without the use of any special equipment for liver perfusion and HSC isolation. The technique yields ex vivo HSCs, suitable for use in assays.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cells, extracellular matrix, Enzymatic digestion, Pronase, Optiprep
Background
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) harbor in the perisinusoidal space amidst the endothelial cells and hepatocytes. Under homeostatic conditions, HSCs assume a quiescent state comprising about 15% of the liver resident cells (Friedman, 2008). Upon activation, HSCs can differentiate into myofibroblasts producing copious amount of extra-cellular matrix components, such as collagen.
Originally, rat livers were utilized for HSC isolation during the 1980s ( Knook et al., 1982 ; Friedman et al., 1985 ). Owing to the ability of quiescent HSCs to store vitamin A in lipid droplets, isolation was based on density gradient separation. On similar lines, vitamin A rich mouse HSCs localize in the upper layers in density gradients ( Chang et al., 2014 , Maschmeyer et al., 2011 ). Subsequently developed FACS based methods explore the inherent vitamin A fluorescence to sort HSCs ( Mederacke et al., 2015 ).
Our method was implemented in our recent studies on pericyte induced wound healing ( Minutti et al., 2019 ) and is advantageous as a rapid, inexpensive method to yield around 2 x 105 HSCs and takes about 3.5 h. HSCs isolated using our method can be used in gene expression studies, in vitro differentiation assays and can be applied to wild type as well as genetically modified mice.
Materials and Reagents
Culture hood for sterile work
Dissection scissors (Any available dissection scissors can be used)
Forceps- 2 pairs (preferably blunt forceps from any manufacturer are preferred)
Ice box
Tissue culture treated T75 flask (Corning, catalog number: S430641)
0.22 μm sterile syringe filters (Millex/Millipore Sigma, catalog number: SLGP033RS)
10 ml syringes (BD Plastipak, catalog number: 302188)
30 ml Universal Containers (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12511299)
27 G needles, disposable, ‘’ (BD, catalog number: 305109)
Nybolt mesh or 70 µm Cell Strainer (Falcon, catalog number: 352350)
15 ml tubes (Sarstedt 62.554.502)
50 ml tubes (Sarstedt 62.548.004)
Disposable 5 ml and 10 ml pipettes
100 mm x 20 mm (D x H) Tissue-culture treated culture dishes (Corning, catalog number: 430167)
Taqman probes, used for Acta2 (Mm00725412_s1) and Rn18s (Mm03928990_g1) from Applied Biosystems for validation in Figure 4
4 x Mice
DNase 1, Grade II, from bovine pancreas (Roche, catalog number: 10104159001)
Collagenase B (Roche, catalog number: 11088807001)
Protease from Streptomyces griseus (Pronase) (Sigma, catalog number: P5147)
Hanks Balanced Salt Solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9394)
Axis-Shield Density Gradient Media OptiPrepTM (Abbott Diagnostics Technologies AS, catalog number: 1114542)
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high glucose, pyruvate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 41966)
Fetal Bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, catalog number: 10500064)
Penicillin-Streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15140122)
L-Glutamine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25030081)
Trypsin 0.25% EDTA (Gibco, catalog number:25200056)
Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8537)
Red Blood Cell Lysing Buffer Hybri-Max (Sigma, catalog number: R7757)
Ethanol absolute > 99.8% (VWR, 20821.330P)
Enzymes (see Recipes)
Complete DMEM (see Recipes)
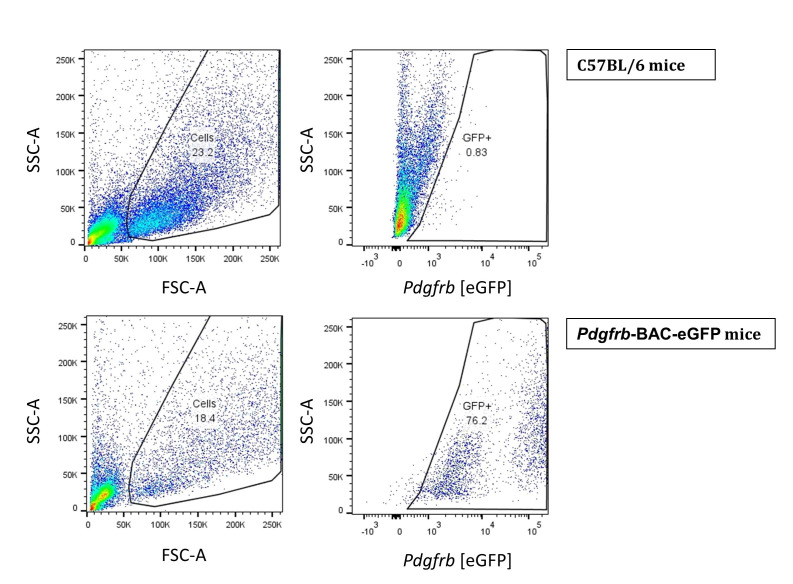
Figure 4. Flow cytometry of isolated pericytes.
HSCs from WT C57BL/6 mice Pdgfrb-BAC-eGFP mice were acquired on the BD LSRII flow cytometer and analyzed using FlowJo Software Version 10.
Equipment
Milligram Balance
CO2 chamber for mouse asphyxiation (Any available apparatus approved by the animal ethics committee and the animal facility may be used.)
Incubator-shaker or water bath (Grant W28)
Refrigerated centrifuge for 15- and 50-ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5810R)
Inverted microscope (Zeiss Primovert)
Incubator for culturing cells (Wolflabs, Binder CB160)
Procedure
-
Liver perfusion and isolation (Figure 1 and Video 1)
Pool the livers from 4 mice for setting up HSC isolation and culture.
Euthanize 1-2 mice at a time according to a method approved in your Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) Protocol.
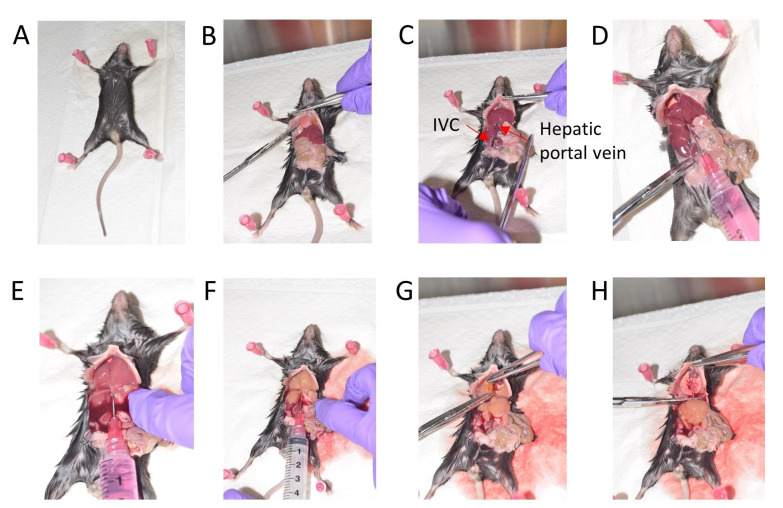
After confirming death, cut the mouse skin along the midline from the abdomen to the thoracic cavity. Cut the diaphragm, effectively exposing the visceral organs (Figures 1A and 1B).
Gently move the liver lobes where the diaphragm was cut and then move the intestine to your right side to expose the inferior vena cava (Figure 1C).
Fill a 10 ml syringe with ice cold HBSS and use a 27G needle to inject this HBSS into the hepatic portal vein to perfuse the liver (Figure 1D).
Immediately cut off the inferior vena cava (IVC) to release the pressure, once you begin washing with HBSS via the portal vein (Figures 1E and 1F).
-
Use at least 10 ml HBSS to wash each liver.
Note: Euthanizing 1-2 mice at a time helps preserve tissue integrity and leads to efficient flushing of the livers resulting in a cleaner HSC preparation.
Gently cut off the gall bladder amidst the liver lobes taking care to avoid puncturing it (Figure 1G).
Collect the lobes of the liver in a 30 ml universal container with 10 ml ice cold HBSS (Figure 1H).
Proceed to enzymatic digestion.
-
Enzymatic digestion
Under a sterile culture hood, drain the HBSS from the universal containing the livers.
-
Mince the livers in the same 30 ml universal container using sterile scissors and forceps (sprayed with 70% ethanol) and add 10 ml of Collagenase B and 10 ml of Pronase to the minced livers.
Note: Pre-warm the Collagenase B and Pronase for 15 min in a 37 °C water bath.
Add 2 ml DNase 1 solution to prevent clumping of cells.
Mix the contents well by inverting the tube 3-4 times and place the universal in an incubator-shaker at 37 °C for 20 min.
Pour the digest through a 70 μm cell strainer for collection into a 50 ml tube. Use the flat side of a 10 ml syringe plunger to gently press and force the liver digest from the cell strainer into the 50 ml tube and top up with cold HBSS to stop the enzymatic reaction.
Centrifuge at 600 × g (around 1,800 rpm for a benchtop centrifuge), at room temperature for 7 min.
Pre-cool the centrifuge to 4 °C for the density gradient step.
-
Assembling the density gradient (Figure 2)
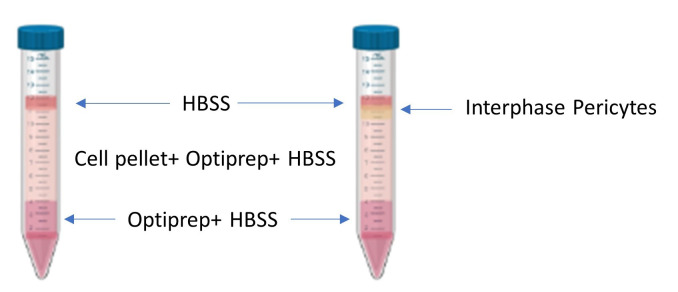
For the bottom-most layer of the gradient, add 3.2 ml Optiprep to 4.8 ml HBSS. Split the 8 ml into two 15 ml tubes.
For the intermediate phase, homogenize the cell pellet from Step B6 by gently tapping the 50 ml tube at the base and add HBSS to make the total volume 8.9 ml.
Add 5.9 ml of Optiprep to the 8.9 ml cell pellet resuspended in HBSS. Mix using a 10 ml pipette.
Using a 5 ml pipette, gently add an equal volume dropwise on top of the 4 ml bottom phase to each 15 ml tube using the slowest setting on the pipette-aid. The volume in each 15 ml tube should be around 10.5-11 ml combining both phases.
Finally, for the top phase, gently add 0.5 ml HBSS over the intermediate phase.
Centrifuge the two 15 ml tubes at 1,400 × g (around 2,500 rpm) for 20 min at 4 °C without break and at a slow acceleration.
-
Washing and plating
The HSCs are in the second layer from the top, beneath the HBSS and appearing as a thick white band.
Gently remove this layer comprising about 0.5 to 1 ml, using a 1 ml micropipette, from each 15 ml tube and put in a new 50 ml tube. Tap and mix cells and add 2 ml DNase. Top up with HBSS up to 50 ml and spin down at 600 × g for 7 min at room temperature.
Aspirate the supernatant and mix the pellet. Add 3 ml of RBC lysis buffer and incubate at 37 °C for 4-5 min.
Add 2 ml DNase solution to prevent clumping of cells. Wash with HBSS and spin down at 600 × g for 7 min.
Aspirate the HBSS, mix the pellet and resuspend in about 10 ml prewarmed complete DMEM (see Recipes).
Plate 10 ml of the cell suspension in a 100 mm plate or in a T75 flask as preferred. The preparation looks messy immediately after isolation.
Incubate at 37 °C in 5% CO2 environment.
-
After 24 h, gently rotate the plate in the palm of your hand to displace the thick sticky layer. To obtain a clear preparation, aspirate the media and wash 3-4 times with 3 ml warm PBS. Resuspend in complete DMEM or proceed to trypsinization to set up a new experiment.
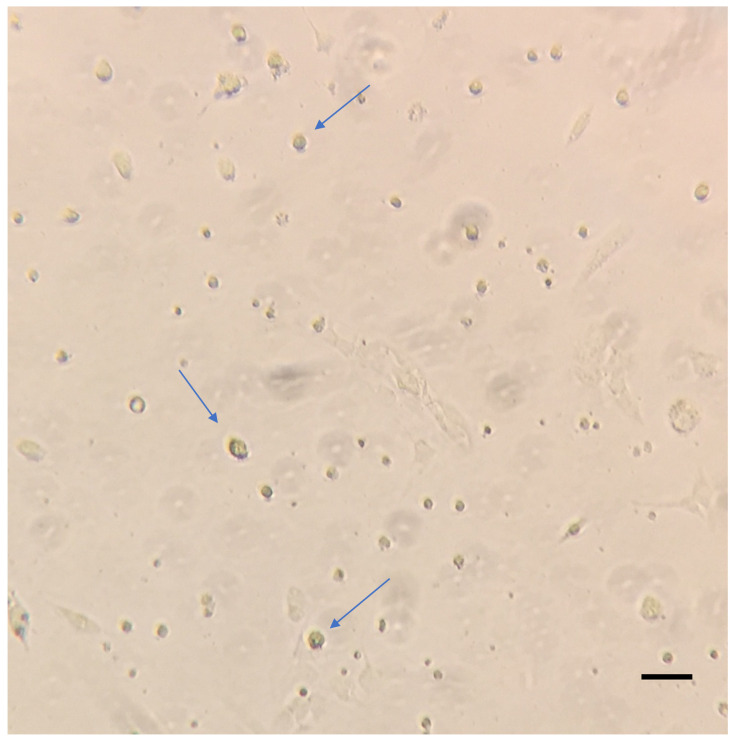
Figure 3. Representative image of HSCs 24 h post isolation.
Isolated HSCs cultured in 100 mm plates were washed with warm PBS and imaged on the Zeiss primovert at 10x magnification. The blue arrows indicate the adhered HSCs. Scale bar = 200 µm. About 2-2.5 x 105 HSCs can be obtained by this method.
-
Trysinization
Trypsinization of HSCs during the early stages after first wash is a delicate process. After 3 washes with pre-warmed PBS, add 3 ml trypsin and incubate at 37 °C for 4 min with pipetting up and down about 5 times during the incubation.
Stop the reaction with ice cold HBSS and spin down at 600 × g for 7 min to count cells and re-plate them.
For trypsinization at later stages, incubate for 5-6 min and proceed in a similar way.
-
Validation
Let the HSCs isolated using the optiprep method to adhere overnight. After 24 h, wash, trypsinize and analyze the cells using flow cytometry (Figure 4). Since Pdgfrb is a prominent marker of HSCs ( Henderson et al., 2013 ), we used Pdgfrb-BAC-eGFP reporter mice to validate Pdgfrb-eGFP expressing cells alongside cells isolated from WT C57BL/6 mice used as a negative control.
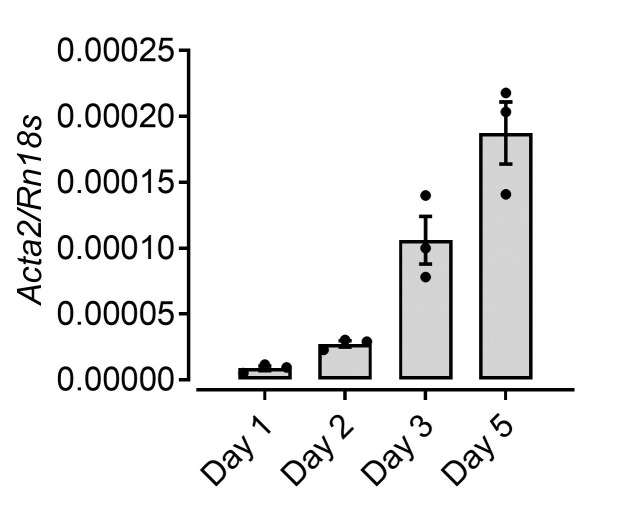
As an additional validation of HSC differentiation, we cultured the isolated cells in complete DMEM for 5 days and harvested the samples intermittently for the analysis of Acta2 gene expression (Figure 5). Alpha smooth muscle actin (Acta2) is a reliable marker of HSC differentiation.
Figure 1. Stepwise depiction of mouse liver perfusion.
A. Position the mouse for dissection. B. Expose the visceral organs and cut the diaphragm. C. Gently move the intestine to the right side. D. Inject 1x HBSS via the Hepatic portal vein. E. Cut the Inferior vena cava (IVC). F. Wash with 1x HBSS. G. Remove the gall bladder. H. Dissect out the liver.
Video 1. Mouse liver perfusion.
This video was made at Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU), Portland according OHSU Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) Protocol guidelines and approved by the Department of Comparative Medicine.
Figure 2. Density gradient pre and post centrifugation.
A depiction of the layers before centrifugation (left) and after centrifugation (right). The isolated pericytes localize at the phase between the top layered HBSS and the middle layer containing the cell pellet homogenized with HBSS and Optiprep.
Figure 5. Increased Acta2 expression upon differentiation of HSCs culture.
mRNA levels of a-smooth muscle actin (Acta2) from HSCs isolated and cultured in complete DMEM over 5 days analyzed by RT-qPCR.
Notes
For a high yield of HSCs, use old mice for isolation or mice subjected to overnight fasting.
Recipes
-
Enzymes
DNase 1: 0.025% in 10 ml HBSS
Collagenase B solution: 0.2% in 10 ml HBSS
Pronase (Protease from Streptomyces griseus): 1% in 10 ml HBSS
Note: Filter all the enzyme solutions using a 10 ml syringe and a 0.22 μM filter into a new sterile universal tube.
-
Complete DMEM (for culture)
20% FBS
1% Penicillin-Streptomycin
1% L-Glutamine
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Neil Henderson for provision of Pdgfrb-BAC-eGFP mice. The work was supported by the European Union grant CIG-631413 (‘‘EGF-R for Immunity’’) and the Medical Research Council (MR/M011755/1). This protocol has been modified from Graham, 2002.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Ethics
Animal experiments were approved by University of Edinburgh Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body and were performed under the project license PPL70/8470 granted by the UK government Home Office.
Imaging and videography of the mouse dissection was conducted with the approval of Oregon Health and Science University–Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) with the kind support of Dr. Kim Saunders and Dr. Anupriya Agarwal.
Citation
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used.
References
- 1. Chang W., Yang M., Song L., Shen K., Wang H., Gao X., Li M., Niu W. and Qin X.(2014). Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells from mouse liver. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin(Shanghai) 46(4): 291-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Friedman S. L.(2008). Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 88(1): 125-172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Friedman S. L., Roll F. J., Boyles J. and Bissell D. M.(1985). Hepatic lipocytes: the principal collagen-producing cells of normal rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82(24): 8681-8685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Graham J. M.(2002). Fractionation of hepatic nonparenchymal cells. Scientific World Journal 2: 1347-1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Henderson N. C., Arnold T. D., Katamura Y., Giacomini M. M., Rodriguez J. D., McCarty J. H., Pellicoro A., Raschperger E., Betsholtz C., Ruminski P. G., Griggs D. W., Prinsen M. J., Maher J. J., Iredale J. P., Lacy-Hulbert A., Adams R. H. and Sheppard D.(2013). Targeting of α integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med 19(12): 1617-1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Knook D. L., Seffelaar A. M. and de Leeuw A. M.(1982). Fat-storing cells of the rat liver. Their isolation and purification. Exp Cell Res 139(2): 468-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Maschmeyer P., Flach M. and Winau F.(2011). Seven steps to stellate cells. J Vis Exp (51). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Mederacke I., Dapito D. H., Affo S., Uchinami H. and Schwabe R. F.(2015). High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc 10(2): 305-315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Minutti C. M., Modak R. V., Macdonald F., Li F., Smyth D. J., Dorward D. A., Blair N., Husovsky C., Muir A., Giampazolias E., Dobie R., Maizels R. M., Kendall T. J., Griggs D. W., Kopf M., Henderson N. C. and Zaiss D. M.(2019). A macrophage-pericyte axis directs tissue restoration via amphiregulin-induced transforming growth factor beta activation. Immunity 50(3): 645-654 e646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]