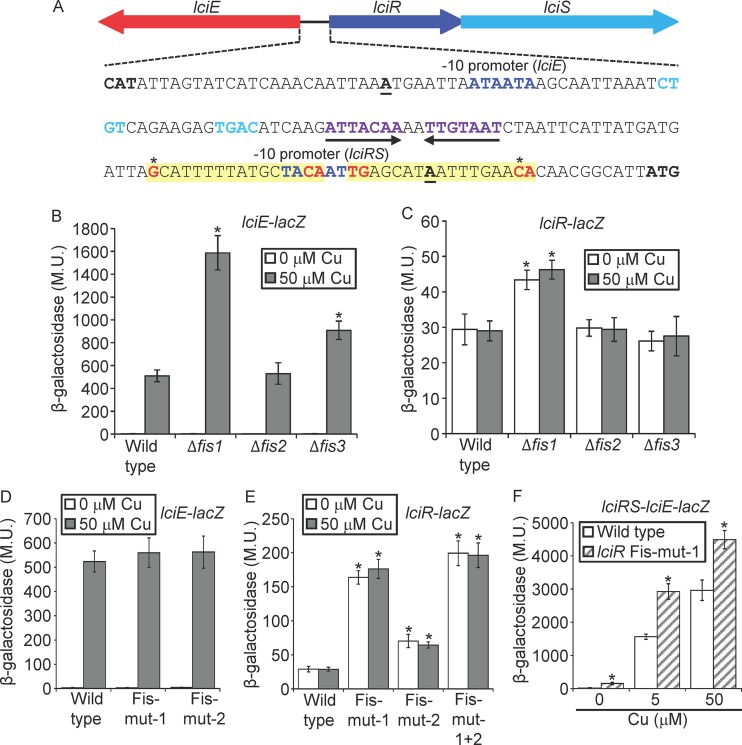
FIG 6.
lciRS-lciE island is repressed by Fis. (A) The intergenic DNA sequence located between lciE and lciR. The lciR and lciE −10 promoter elements are in dark blue, and the nucleotides representing the LciR consensus are in purple (the inverted-repeat sequence) or light blue (the two sequences located between the inverted repeat and the −10 promoter of lciE); the inverted repeat is also marked with arrows. The transcription start sites are boldface and underlined. The putative lciR Fis regulatory elements are shaded in yellow, conserved nucleotides of the Fis consensus are marked in red, and the nucleotides mutated are marked by asterisks. (B and C) The expression levels of the lciE-lacZ fusion (B) and the lciR-lacZ fusion (C) were examined in the wild-type strain and in the three fis deletion mutants at the stationary phase. Expression was examined with (gray bars) and without (white bars) 50 μM copper. The levels of expression of the lacZ fusions were found to be significantly different (*, P < 10−5, paired Student's t test) between expression of the wild-type strain and each fis deletion mutant under the same conditions. (D and E) The levels of expression of wild-type lciE-lacZ fusion and the two lciE-lacZ fusions containing mutations (mut-1 and mut-2) in the putative Fis regulatory elements (D) and wild-type lciR-lacZ fusion and the three lciR-lacZ fusions containing mutations (mut-1, mut-2, and mut-1 + 2) in the putative Fis regulatory elements (E) were examined with (gray bars) and without (white bars) 50 μM copper. The levels of expression of the lacZ fusions were found to be significantly different (*, P < 10−5, paired Student's t test) between fusions containing the wild-type regulatory region and the mutated regulatory region under the same copper concentrations. (F) The levels of expression of wild-type lciRS-lciE-lacZ fusion (white bars) and the same fusion containing a mutation in the downstream Fis regulatory element of lciR (hatched gray bars) were examined in the lciRS-lciE deletion mutant without copper and with 5 μM and 50 μM copper. The levels of expression of the lacZ fusions were found to be significantly different (*, P < 10−5, paired Student's t test) between the wild-type fusion and the mutated fusion under the same copper concentrations. β-Galactosidase activity was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Data (expressed in Miller units [M.U.]) are the averages ± standard deviations (error bars) of the results from at least three different experiments.