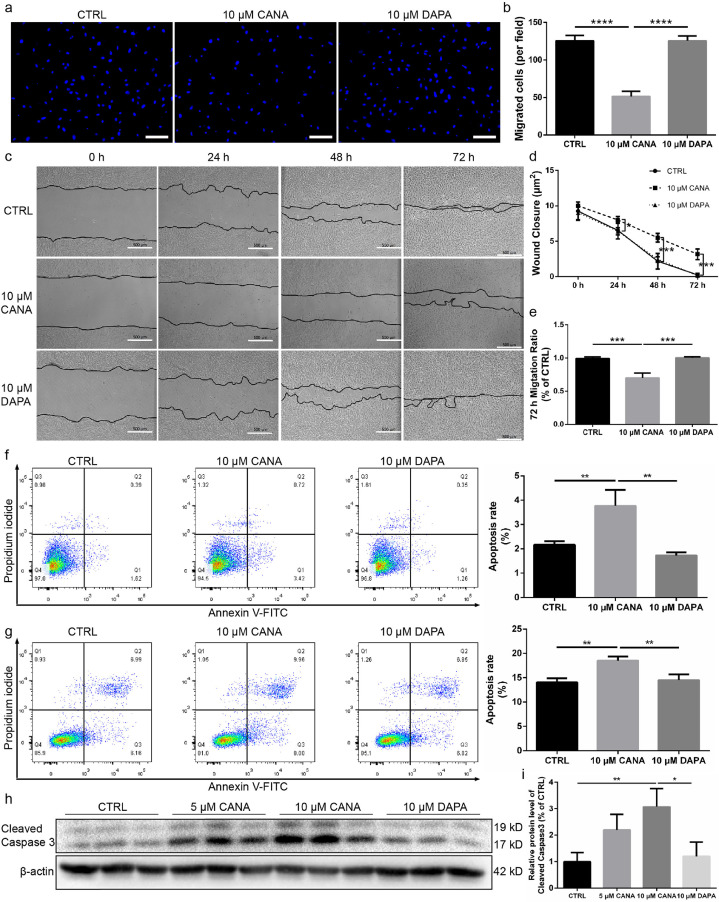
Fig. 3.
CANA treatment attenuated MSC migration and increased the apoptosis of MSCs under both normal and stress conditions. (a) MSCs were treated with either CANA (10 μM) or DAPA (10 μM) for 48 h. Each group of MSCs was subjected to Transwell migration assays, and representative images of cells migrating to the lower surface are shown. Scale bars: 100 μm. (b) Cells that migrated to the lower surface were counted for each group, and the data are shown in a bar graph (n = 3). (c) MSCs were treated with either CANA or DAPA as described in (a). A wound healing assay was performed to detect the migration ability of MSCs at the indicated timepoints. Scale bars: 500 μm. (d) Wound closure of each group shown in (c) was indicated by the remaining area that was not covered by cells in the scratched zone (n = 3). (e) The migration ratio of each group (72 h following scratching) shown in (c) was quantified (n = 3). (f) CANA- (10 μM, 48 h) or DAPA-treated (10 μM, 48 h) MSCs were stained with Annexin V and PI followed by flow cytometry analysis. The apoptosis rate in each group was calculated, and the data are shown in a bar graph (n = 3). (g) CANA- (10 μM, 48 h) or DAPA-treated (10 μM, 48 h) MSCs were stimulated with or without H2O2 (100 nmol) for 2 h. The apoptosis rate in each group was measured and calculated as described in (f), and all the data are shown in a bar graph (n = 3). (h) MSCs were treated as mentioned in (g), and the protein expression level of cleaved caspase 3 was evaluated using SDS-PAGE. β-actin served as an internal reference. (i) Quantification of protein expression is presented as the ratio of cleaved caspase 3/β-actin, and the data are shown in a bar graph (n = 3). Data are means ± SDs, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.