Abstract
Building on previous studies that report thinning of the macula in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients, the use of optical coherence tomography (OCT) has been proposed as a potential biomarker for AD. However, other studies contradict these results. A total of 930 participants (414 cognitively healthy people, 192 with probable amnestic MCI, and 324 probable AD patients) from a memory clinic were consecutively included in this study and underwent a spectral domain OCT scan (Maestro, Topcon) to assess total macular volume and thickness. Macular width measurements were also taken in several subregions (central, inner, and outer rings) and in layers such as the retinal nerve fiber (RNFL) and ganglion cell (CGL). The study employed a design of high ecological validity, with adjustment by age, education, sex, and OCT image quality. AD, MCI, and control groups did not significantly vary with regard to volume and retinal thickness in different layers. When these groups were compared, multivariate-adjusted analysis disclosed no significant differences in total (p = 0.564), CGL (p = 0.267), RNFL (p = 0.574), and macular thickness and volume (p = 0.380). The only macular regions showing significant differences were the superior (p = 0.040) and nasal (p = 0.040) sectors of the inner macular ring. However, adjustment for multiple comparisons nullified this significance. These results are not supporting existing claims for the usefulness of macular thickness as a biomarker of cognitive impairment in a memory unit. OCT biomarkers for AD should be subject to further longitudinal testing.
Subject terms: Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's disease
Introduction
The diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most frequent neurodegenerative disease, requires clinical diagnostic criteria which do not get to differentiate this disease accurately from other causes of dementia1.
Before dementia phase is established, cognition problems develop in a slow but progressive way, and can interfere limitedly in daily activities. This prodromal stage, called mild cognitive impairment (MCI), is a clinically heterogeneous syndrome and a consequence of different etiologies. Its definition has expanded in recent years2–4. MCI symptoms can also be stable for many years or even disappear; however, it is clear that the amnestic and multidomain MCI raises the progression risk to AD5,6. It is complicated to make a correct diagnosis of AD, especially in its MCI stage; therefore, the search for low-cost and innocuous biomarkers is important7. Even when a set of biomarkers have been approved and incorporated into the new clinical diagnostic criteria8,9, most demonstrate suboptimal test precision and involve either prohibitive costs or substantially invasive processes10,11.
The retina is a part of the central nervous system (CNS). with shared embryological origins. Unmyelinated axons of neurons in the ganglion cell layer (CGL) build the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). These fibers continue as the optic nerve into the brain.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a cheap, efficient and noninvasive transpupillary technique that facilitates objective in vivo retinal quantification12. OCT is utilized regularly in clinical ophthalmology to assess retinal integrity and is a promising tool for neurological investigation because of its high correlation with a number of visual electrophysiological tests13,14 and considerable reliability in a wide range of neurological pathologies15,16.
Visual symptoms such as impairment of both contrast and color sensitivity and perception of motion and depth are regularly observed in AD and other neurodegenerative conditions17,18. They are typically considered a consequence of damage to associative visual cortical areas19,20; however, there is growing evidence that neuroretinal involvement may also be a contributing factor21, and this has generated interest in the quest for retinal AD biomarkers22,23. A significant number of postmortem pathological studies have outlined RNFL and GCL reduction in AD patients24,25, although others have provided divergent results26.
Retinal thinning is found in AD and many other CNS conditions, including neuromyelitis optica, Parkinson’s disease27,28. One hypothesis highlights that it is a consequence of retrograde degeneration of the axons of the CGL or the typical pathological deposits of Alzheimer’s Disease in the retina. Indeed, initial histological studies24,25 have not identified neurofibrillary tangles or beta-amyloid plaques in AD patients’ retina. However more recent studies state to have found them29,30. The macula contains most of the retinal neurons’ bodies, and therefore, macular volume evaluation may determine neuronal loss, showing if and how the neurodegeneration is taking place. Controls appear to have a higher macular volume than AD but lower relative to amnestic MCI31. Gliosis or inflammation in the prodromal phase of AD might be a possible explanation for this finding.
Studies on macular thinning are not fully conclusive because of their small sample size, significant heterogeneity in their methods32–34, and divergent results. Compared with cognitively healthy persons, most studies provide evidence of macular volume and thickness reduction in people with cognitive impairment (either MCI or AD), affecting primarily either the inner and outer rings25,35 or the fovea15. With one exception31, people with AD show a larger reduction in macular thickness than those with MCI in articles cited earlier. Macular layer segmentation reveals CGL and RNFL atrophy in people with AD and is associated with disease severity36 and axonal damage. However, recent studies do not provide evidence of retinal thinning in the macula37,38 and the optic disc39,40.
The goal of this paper is to assess the clinical usefulness and viability of the analysis of all main macular parameters obtained through OCT automatic segmentation in the differentiation of controls, MCI, and AD in the work routine of a memory unit (MU).
Results
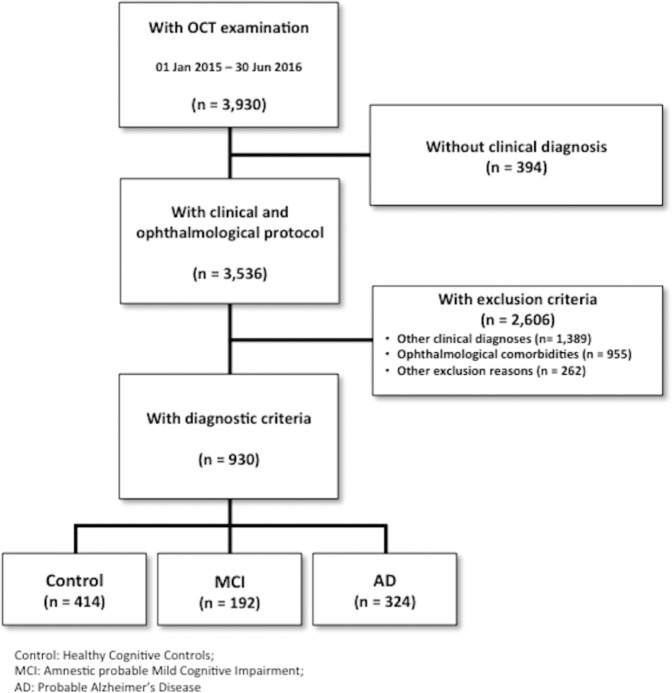
A total of 3,930 people attending a MU participated in this study. Ninety percent of them were given a clinical diagnosis. The selection algorithm’ s details is depicted in Fig. 1. An amount of 955 participants were excluded because of several eye diseases. Among them, the most prevalent41 were glaucoma (30,6%) and degenerative maculopathy (30,3%).
Figure 1.
Patient selection and study cohort flowchart. Eligible population and selection of the study sample for this study through inclusion and exclusion criteria. Figure 1 was published previously in https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-34577-3.pdf.
A total of 930 subjects were deemed to meet all the inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria: 414 people were allocated to the control group, 192 to the MCI one, and 324 to the Alzheimer’s Disease group. Their demographical features are shown in Table 1. Cognitively healthy persons were the youngest and demonstrated the greatest educational attainment. They showed the best Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores as well. The MCI patients were younger and had better MMSE scores than the AD group.
Table 1.
Baseline demographics.
| Mean | SD | Intergroup Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education (years) | Control | 10.96 | 4.13 | <0.001+ |
| MCI | 7.00 | 4.32 | ||
| AD | 6.14 | 4.08 | ||
| Total | 8.46 | 4.72 | ||
| Age (years) | Control | 65.93 | 9.01 | <0.001+ |
| MCI | 76.46 | 7.14 | ||
| AD | 78.99 | 7.87 | ||
| Total | 73.05 | 10.23 | ||
| MMSE (points) | Control | 29.29 | 1.00 | <0.001+ |
| MCI | 25.14 | 2.97 | ||
| AD | 20.28 | 3.98 | ||
| OCT Image Quality (%) | Control | 47.81 | 7.57 | <0.001+ |
| MCI | 44.59 | 8.23 | ||
| AD | 43.23 | 10.33 | ||
| Total | 45.41 | 9.09 | ||
| Gender (% women) | Control | 67.7% | <0.001* | |
| MCI | 56.2% | |||
| AD | 74.0% | |||
| Total | 67.8% | |||
Demographic features including age, gender, education, MMSE scores, and OCT quality image among groups are summarized. All the analyzed characteristics were significantly different among diagnostic groups.
*Pearson’s chi2 test;
+1-factor ANOVA;
Table 1 was published previously in https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-34577-3.pdf.
Each covariate’s contribution to mean retinal thickness variance is summarized in Table 2. The key factor explaining the variability of macular thickness was age, which demonstrated a greater effect size and correlation than the diagnosis itself. OCT image quality did not significantly affect macular thickness variability among diagnostic groups.
Table 2.
Contribution of every covariate to variance of the macular thickness.
| Covariate | Significance | D.f. | Partial Eta2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education | 0.859 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Gender | 0.053 | 1 | 0.004 |
| Age | 0.0001 | 1 | 0.070 |
| OCT image quality | 0.639 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Diagnosis | 0.564 | 2 | 0.001 |
Correlation between demographical and ophthalmic covariates with the dependent variable is shown.
D.f.: degrees of freedom.
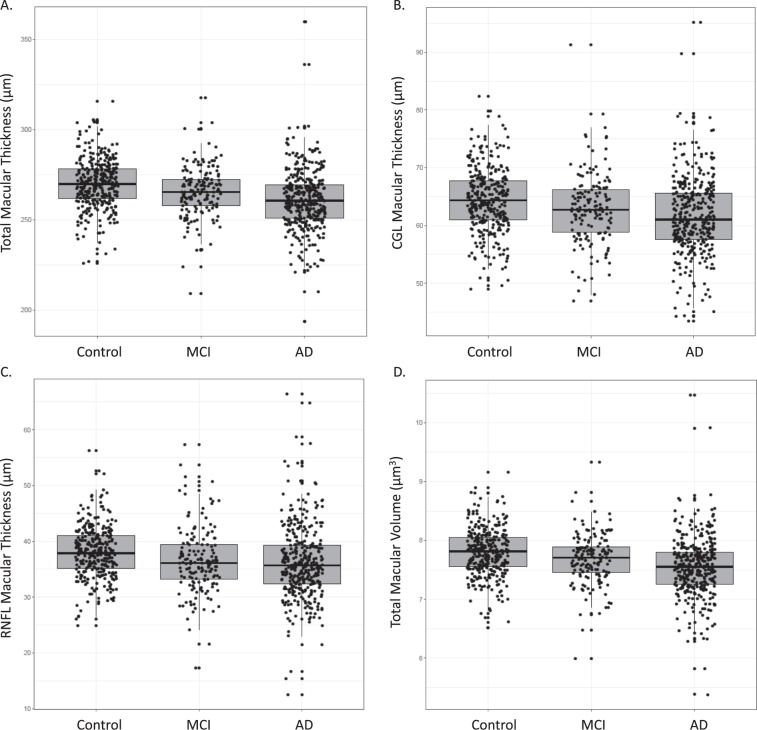
We analyzed several macular parameters: mean thickness and volume (Table 3), thickness of macular layers (Table 4), and ETDRS sectors (Table 5). A box plot for macular variables was shown: total thickness (Fig. 2A), CGL thickness (Fig. 2B) RNFL thickness (Fig. 2C) and volume (Fig. 2D). Given the demographic differences among groups, we adjusted all macular variables in a multivariate model, including the next covariates: age, education, gender and OCT image quality. No significant differences in total (p = 0.564), CGL (p = 0.267), RNFL (p = 0.574), and macular thickness and volume (p = 0.380) were identified among diagnostic groups. Macular thickness was also compared regionally using Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS)–defined areas42. The superior (p = 0.040) and nasal (p = 0.040) sectors of the inner macular ring were the only macular regions showing significant differences among groups. The effect size was modest: the width of controls was only about 4 μm higher than the AD patients in both variables. However, significance disappeared after adjustment for multiple comparisons.
Table 3.
Mean macular thickness and volume differences among diagnostic groups.
| Group (N) | Mean | SD | Meanaa | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean macular thickness p = 0.482 | ||||
| Control (414) | 275.28 | 13.95 | 271.52aa | 0.87 |
| MCI (192) | 270.66 | 15.24 | 272.51aa | 1.18 |
| AD (324) | 267.09 | 17.76 | 270.83aa | 0.94 |
| Macular volume p = 0.380 | ||||
| Control (414) | 7.78 | 0.39 | 7.68aa | 0.02 |
| MCI (192) | 7.65 | 0.43 | 7.70aa | 0.03 |
| AD (324) | 7.54 | 0.51 | 7.65aa | 0.03 |
Raw and adjusted mean overall total macular thickness (μm) and volume (μm3), standard deviation (SD), and standard error of the mean (SEM). After a multivariate adjustment (aa), no significant differences among diagnostic groups were detected. Dispersion data are shown as SEM.
SD: standard deviation; aaafter adjustment; SEM: standard error of the mean; p: significance; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; MCI: mild cognitive impairment.
Table 4.
Mean macular layer differences among diagnostic groups.
| Variable | Mean | SD | Meanaa | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganglion cell layer width p = 0.267 | ||||
| Control (414) | 64.11 | 5.38 | 62.59aa | 0.33 |
| MCI (192) | 62.68 | 6.27 | 63.51aa | 0.42 |
| AD (324) | 61.58 | 6.55 | 63.05aa | 0.36 |
| Mean macular RNFL width p = 0.574 | ||||
| Control (414) | 37.91 | 4.56 | 37.22aa | 0.32 |
| MCI (192) | 36.30 | 6.01 | 36.67aa | 0.41 |
| AD (324) | 36.11 | 6.62 | 36.79aa | 0.35 |
Raw and adjusted mean overall total macular thickness (μm), standard deviation (SD), and standard error of the mean (SEM). After a multivariate adjustment (aa), no significant differences among diagnostic groups were detected. Dispersion data are shown as SEM.
SD: standard deviation; aaafter adjustment; SEM: standard error of the mean; p: significance; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; MCI: mild cognitive impairment.
Table 5.
Macular sectors’ (ETDRS regions) thickness differences among diagnostic groups.
| Group (N) | Mean | SD | Meanaa | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETDRS Center p = 0.735 | ||||
| Control (414) | 247.82 | 22.52 | 246.29aa | 1.48 |
| MCI (192) | 246.76 | 25.59 | 246.89aa | 1.91 |
| AD (324) | 243.19 | 30.03 | 245.08aa | 1.61 |
| ETDRS Inner-Temporal p = 0.125 | ||||
| Control (414) | 299.92 | 16.03 | 296.04aa | 1.10 |
| MCI (192) | 293.86 | 19.97 | 295.30aa | 1.42 |
| AD (324) | 288.50 | 23.59 | 292.70aa | 1.20 |
| ETDRS Inner-Superior p = 0.040 | ||||
| Control (414) | 312.45 | 16.22 | 307.81aa | 1.12 |
| MCI (192) | 306.04 | 20.08 | 308.21aa | 1.44 |
| AD (324) | 299.45 | 24.29 | 304.12aa | 1.22 |
| ETDRS Inner-Nasal p = 0.040 | ||||
| Control (414) | 313.25 | 17.30 | 309.43aa | 1.14 |
| MCI (192) | 306.00 | 21.21 | 307.53aa | 1.47 |
| AD (324) | 300.75 | 23.35 | 304.74aa | 1.24 |
| ETDRS Inner-Inferior p = 0.095 | ||||
| Control (414) | 309.88 | 16.22 | 305.44aa | 1.12 |
| MCI (192) | 303.72 | 20.36 | 305,70aa | 1.44 |
| AD (324) | 297.71 | 24.06 | 302.24aa | 1.22 |
| ETDRS Outer-Temporal p = 0.683 | ||||
| Control (414) | 252.95 | 16.95 | 249.78aa | 1.05 |
| MCI (192) | 248.50 | 18.13 | 249.81aa | 1.35 |
| AD (324) | 245.24 | 20.85 | 248.54aa | 1.14 |
| ETDRS Outer-Superior p = 0.306 | ||||
| Control (414) | 268.68 | 14.84 | 264.59aa | 0.94 |
| MCI (192) | 264.31 | 17.20 | 266.51aa | 1.24 |
| AD (324) | 260.31 | 20.01 | 264.25aa | 1.05 |
| ETDRS Outer-Nasal p = 0.397 | ||||
| Control (414) | 285.41 | 17.711 | 281.18aa | 1.04 |
| MCI (192) | 281.28 | 18.226 | 283.61aa | 1.34 |
| AD (324) | 278.55 | 20.230 | 282.60aa | 1.13 |
| ETDRS Outer-Inferior p = 0.819 | ||||
| Control (414) | 258.07 | 14.391 | 254.62aa | 0.95 |
| MCI (192) | 253.72 | 16.979 | 255.57aa | 1.23 |
| AD (324) | 251.43 | 19.813 | 254.78aa | 1.04 |
Different raw and adjusted macular thickness (μm), standard deviation (SD), and standard error of the mean (SEM). After a multivariate adjustment, significant differences between diagnostic groups have appeared in the superior and nasal areas of the inner ring. After a correction for multiple comparisons, no significant differences among diagnostic groups were detected. Dispersion is shown as SEM.
Figure 2.
Macular parameters for each diagnostic group. This box plot represents the macular parameter for each diagnostic group (control, MCI, AD). No differences have been found among the three clinical categories. The bottom and top of the box are the first and third quartiles, and the band inside the box represents the median. AD: Alzheimer’s disease; MCI: mild cognitive impairment. (A) Macular Thickness (Total). (B) Macular Thickness (CGL). (C) Macular Thickness (RNFL). (D) Total Macular Volume.
Discussion
We have conducted a cross-sectional study about differences in macular measurements in healthy controls and MCI and AD dementia groups, employing a large sample of varied ages, cognitive stages, and metabolic diseases to improve its ecological validity. The only requisite to allow participant with a particular disease into the study was that it did not alter retinal structure or cause OCT artifacts. For example, diabetic patients were permitted as long as they did not have diabetic retinopathy.
Our data show that the differences on macular quantifications between controls and AD patients are so small that such changes are less than both the intraindividual reliability of the technique and the age effect. (For example, mean macular thickness has less than 1 μm difference after adjustment.) Therefore, the use of macular thickness as a biomarker in a memory unit might not be sufficiently reliable so far.
Most patients were able to collaborate during OCT performance. The study’s sample size was one of the largest collected so far. Our study results contrasted with some previous works that found significant differences in macular thickness and volume between cognitive groups. Older literature on this matter had not provided solid conclusions so far. While some research suggested that macular thinning might correlate with cognitive diagnoses25,35, recent studies did not evidence any significant macular thickness reduction37,38,43,44, even using amyloid-proven status to confirm diagnoses37. One study even noted an increase in foveal thickness and volume in AD38. Our study showed a more prominent reduction in the macula’s inner ring than in the outer ring and not vice versa as was noted in a recent meta-analysis32. Pertinent to our findings may be the fact that the inner ETDRS zones contained more neurons; thus, neurodegeneration was expected to be most prominent there. The reduction did not demonstrate statistical significance adjusted by multiple comparisons. Contrary to other investigations45, our study did not identify any significant reduction in other macular layers such as RNFL or CGL.
The discrepancies observed in our data compared with previous literature could be related to several confounders. In the first instance, meta-analysis had evidenced heterogeneity in study design and in the clinical diagnosis of MCI and AD. Most previous studies were underpowered sample sizes and case-control designs where participants were prominently selected32–34. Only one eye per patient was included in some studies, while others included both. In addition, several OCT techniques and brands were used. Participant inclusion in most of former literature was not consecutive, and researchers were not blinded to the clinical diagnosis before OCT was performed, risking bias and overestimation of test accuracy46,47. Clinical criteria provided the basis for some studies, while others were supported by biomarkers. Furthermore, publication bias is identified, with an overrepresentation of smaller positive studies32, possibly leading to the true effect’s overestimation.
To avoid bias, first, we consecutively included every patient between 50 and 95 years of age who attended the MU no matter their cognitive picture and formal education. We used a standardized protocol for diagnosis that included extended neuropsychological test battery and neuroimaging procedures. The neurologist and optometrist were blinded to all actions executed on the same participant by their counterpart.
Second, probably given the difficulties inherent in recruiting cases and controls with extreme ages (old cognitive controls and young people with dementia), the assessed age range in existing studies was significantly limited (between 70 and 80 years in average). Cognitive impairment taking place at extreme ages was therefore not considered, although it was well-established that rates of cognitive decline varied according to the age48.
Third, AD and glaucoma were comorbid pathologies and shared mechanisms of pathophysiology with the same final result: retinal neurodegeneration49. It was therefore not easy to differentiate retinal changes due to AD from those caused by glaucoma. A similar dynamic was observed between AD and macular degeneration, another disease associated with age. Almost a quarter of eligible subjects in our cohort were not included because of ophthalmological comorbidities, primarily glaucoma and macular degeneration. Since these retinal pathologies also affected retinal thickness, the establishment of OCT as biomarker in a standard cognitive healthcare could be difficult or even unfeasible for a relatively large proportion of elderly subjects.
Factors that can significantly affect cognitive results, such as educational achievements or OCT image quality, were rarely considered in previous papers. Our study tested education, age, sex, and OCT image quality as covariates and demonstrated that age appeared to have the greatest influence in macular thickness variability. OCT signal strength was not an influential covariate in the macula, unlike in the optic disc40.
A few limitations of our study should be acknowledged. On one hand, our model’s covariates could not be enough to control intergroup variability due to potential eye confounders, such as axial length and optic disc area that have not been considered50. On the other hand, the study elicits only cross-sectional results, so we are not able to draw any substantive conclusions about how macular thinning can evolve. We are considering a longitudinal study to clarify the dynamics of macular thickness.
Many other OCT findings, including alterations in vascular layer and network, have been highlighted and could be relevant biomarkers for AD classification and progression51–53. In fact, successful retinal AD biomarkers might only be discovered after the integration of both neuroretinal and retinovascular in a composite biomarker. Advances in both OCT technology and inclusion of positron emission tomography (PET) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers to ameliorate diagnostic certainty54,55 and to confirm the sensitivity and specificity of OCT could provide a greater insight into the relationship between brain pathology and retinal features.
Methods
Participant selection and characterization: the NORFACE cohort
The Neuro-Ophthalmology Research at Fundació ACE (NORFACE) cohort was established in 2014 to facilitate research in retinal biomarkers of AD and interrogate the thought-provoking relationships between retinal pathophysiology and AD. Recruitment of participants is prospective and consecutive from Fundació ACE-Institut Català de Neurociències Aplicades’s Memory Clinic in Barcelona, Spain. Standardized neuropsychological and medical examinations56,57 are used in a multidisciplinary approach to diagnose and care for patients with neurodegenerative diseases58.
As part of routine medical care and diagnostic workup, blood screening for syphilis, serum vitamin B12 and folate levels, and liver, renal, and thyroid functions are performed. Additionally, neuroimaging with structural brain MRI or head CT are employed to improve diagnostic certainty. These tests are followed by a clinical and neuropsychological examination and then reviewed by a multidisciplinary team to arrive at a consensus-based diagnosis58.
As part of the NORFACE cohort, each patient undergoes a complete neuro-ophthalmological interview and examination done by an optometrist. The assessment includes review of the ophthalmological history, visual acuity assessment, intraocular pressure measurement, and spectral domain OCT examination. The optometrist and neurologist have been blinded to each other’s evaluation data.
Optical coherence tomography
Macular measurements were assessed by imaging patients with a 3D-OCT Maestro®, Fast Map software version 8.40 (Topcon Co., Tokyo, Japan). Importantly, the availability of high-resolution B-scan mode made pupil dilatation unnecessary. The OCT capture was merged with a real-color fundus picture captured by an internal camera.
The Topcon Advanced Boundary Segmentation (TABS) algorithm was employed to carry out automatic retina layer segmentation59. TABS has proven efficacious in treating ophthalmological diseases by providing accurate and consistent measurements of retina images across blood vessel shadows. Automatic segmentation seems to be less precise but more repeatable than manual one and this is an important issue in massive screening studies60. Macular thickness data were also shown in three concentric rings (ETDRS map) centered on the foveola. These were situated like this: a central macular ring, 1 mm from the fovea; an inner macular ring, 3 mm from the fovea; and an outer macular ring, 6 mm from the fovea. The inner and outer rings were each composed of four quadrants (superior, inferior, nasal, and temporal). Macular data were segmented in RNFL and CGL.
OCT data from only one eye (right) were analyzed for this study. The same optometrist screened all images for possible abnormalities after each OCT imaging session. Cases with abnormal findings were then reviewed by a consultant ophthalmologist who specialized in retinal pathology for a diagnostic report.
Eligibility criteria
All individuals between 50 and 95 years of age consecutively evaluated at Fundació ACE´s Memory Clinic who fulfilled the control, MCI, or AD diagnostic criteria described below were considered eligible for inclusion in the study. The control group was selected for (a) the absence of significant symptoms (CDR = 0) and (b) having a normal age, gender, and education-adjusted performance on the Neuropsychological Battery of Fundació ACE (NBACE)56,57. The MCI group participants were required to (a) meet the Petersen criteria for amnestic MCI61 and (b) demonstrate an absence of significant signs of cerebrovascular or psychiatric disease. The last criterion was imposed to heighten the probability of AD as the underlying etiology for MCI62. The AD group was exclusively composed of subjects who met the National Institute of Neurologic and Communicative Disorders and Stroke-Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association (NINCDS-ADRDA) criteria for probable AD63. Importantly, these inclusion criteria ensured the absence of other diseases capable of producing similar symptoms, thereby yielding a study cohort with high probability of “pure” AD etiology.
Patients were excluded from the study if they were unable to understand or collaborate in the neuro-ophthalmological evaluation, if there was only data derived from the left eye, or if there was the presence of OCT artifacts or diseases that might affect OCT measurement such as retinal or ocular diseases.
Ethical considerations
The ethics committees of both the Hospital Clínic I Provincial and the Hospital Vall D’Hebron (Barcelona, Spain) approved this study and its observation of informed consent protocols in accordance with Spanish biomedical laws (Law 14/2007, July 3, about biomedical research; Royal Decree 1716/2011, November 18) and the guidelines set out in the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants signed the informed consent forms.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using IBM SPSS 20 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and in conformity with APOSTEL guidelines64. All data were tested for normality, skew, and restriction of range. All quantitative variables followed a normal distribution. The results of quantitative variables were presented as mean ± SD, while categorical variables were displayed by range, number and percentage.
The demographic attributes, clinical diagnoses, and OCT measurements were compared using the chi-squared test and parametric Student t-test. The differences in macular parameters between subgroups adjusted by age, education, gender, and image quality were tested using ANCOVA, with the different variables of macular thickness and volume as dependent factors and clinical groups as independent factors (three categories). Age, gender, years of education, and OCT image quality were factored into the model as adjustment variables. All the predictors’ explained variance was derived by calculating eta2 for each factor of the model. The threshold for a significant effect was set at p < 0.05.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the study participants and their families for their collaboration, and Topcon for its reliability as technological partnership. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement N° 796706 awarded to MM; from Fundació ACE Institut Català de Neurociències Aplicades in Barcelona, Spain and from a donation of “La nit de l’Alzheimer”, a charity dinner initiative that took place on August 8th 2016 as part of the “Festival Castell de Peralada”. The neuro-ophthalmology exam devices were acquired with a grant EFSD/Lilly Mental Health and Diabetes 2013 Programme of the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes (EFSD) awarded to the project “Retinal neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes as biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease” under the leadership of CH.
The present work was performed as part of Domingo Sánchez Ruiz’ doctoral program with title “Clinical Utility of OCT in diagnosing and monitoring of cognitive impairment” in the Department of Surgery and Morphological Sciences at Universitat Autonoma Barcelona (Barcelona, Spain).
Author contributions
D.S.R is the main author of this work. This study was conceived by D.S.R. and A.R. Data were acquired, prepared, processed, or managed by J.M. and D.S.R. Ophthalmological screening was performed by M.C.M. Statistics were conceived and data were analyzed by S.V. The manuscript was written by D.S.R. Data was interpreted by D.S.R., A.R., M.M., S.V., M.C.M. and O.R.G. The manuscript was critically revised by M.M., A.P., G.M., S.M.G., I.D.R., I.H., C.A., M.R.R., L.V., A.M., S.G., M.A.S.S., M.A., G.O., A.E., A.P.C., A.S., N.R., A.C., R.S., C.H., L.T., M.B. and A.R.
Data availability
The data sets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Beach TG, Monsell SE, Phillips LE, Kukull W. Accuracy of the Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease at National Institute on Aging Alzheimer Disease Centers, 2005–2010. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012;71:266–273. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31824b211b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Morris JC, et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment Represents Early-Stage Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001;58:124–129. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bondi MW, et al. Neuropsychological Criteria for Mild Cognitive Impairment Improves Diagnostic Precision, Biomarker Associations, and Progression Rates. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2014;42:275–289. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Petersen RC, et al. Mild cognitive impairment: A concept in evolution. J. Intern. Med. 2014;275:214–228. doi: 10.1111/joim.12190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Espinosa A, et al. A longitudinal follow-up of 550 mild cognitive impairment patients: evidence for large conversion to dementia rates and detection of major risk factors involved. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2013;34:769–780. doi: 10.3233/JAD-122002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gainotti G, Quaranta D, Vita MG, Marra C. Neuropsychological predictors of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2014;38:481–495. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jack CR, Holtzman DM. Biomarker modeling of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2013;80:1347–1358. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McKhann G, et al. The diagnosis of Dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers. Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dubois B, et al. Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: A new lexicon. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:1118–1127. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Engler H, et al. Two-year follow-up of amyloid deposition in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2006;129:2856–2866. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Diniz BSO, Pinto JA, Forlenza OV. Do CSF total tau, phosphorylated tau, and β-amyloid 42 help to predict progression ofmild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 2008;9:172–182. doi: 10.1080/15622970701535502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Puliafito CA, et al. Imaging of macular diseases with optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmol. 1995;102:217–229. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(95)31032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kromer R, Serbecic N, Hausner L, Froelich L, Beutelspacher SC. Comparison of visual evoked potentials and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2013;4:203. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2013.00203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Parisi V, et al. Correlation between optical coherence tomography, pattern electroretinogram, and visual evoked potentials in openangle glaucoma patients. Ophthalmol. 2001;108:905–912. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00644-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Polo V, et al. Reliability and validity of Cirrus and Spectralis optical coherence tomography for detecting retinal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Eye. 2014;28:680–690. doi: 10.1038/eye.2014.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garcia-Martin E, et al. Ability and reproducibility of Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography to detect retinal nerve fiber layer atrophy in Parkinson’s disease. Ophthalmol. 2012;119:2161–2167. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Iseri PK, Altinas Z, Tokay T, Yüksel N. Relationship between Cognitive Impairment and Retinal Morphological and Visual Functional Abnormalities in Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2006;26:18–24. doi: 10.1097/01.wno.0000204645.56873.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Katz B, Rimmer S. Ophthalmologic manifestations of Alzheimer’s disease. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1989;34:31–43. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(89)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cogan DG. Visual disturbances with focal progressive dementing disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1985;100:68–72. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9394(14)74985-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Clark AW, Coyle JT, DeLong MR. Alzheimer disease: evidence for selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis. Ann. Neurol. 1981;10:122–126. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Berisha F, Feke GT, Trempe CL, McMeel JW, Schepens CL. Retinal abnormalities in early Alzheimer’s disease. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007;48:2285–2289. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.MacGillivray TJ, et al. Retinal imaging as a source of biomarkers for diagnosis, characterization and prognosis of chronic illness or long-term conditions. Br. J. Radiol. 2014;87(1040):20130832. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ikram MK, Cheung CY, Wong TY, Chen CPLH. Retinal pathology as biomarker for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2012;83:917–922. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2011-301628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hinton DR, Sadun AA, Blanks JC, Miller CA. Optic- nerve degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986;315:485–487. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608213150804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sadun AA, Bassi CJ. Optic nerve damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Ophthalmol. 1990;97:9–17. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(90)32621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Davies DC, McCoubrie P, McDonald B, Jobst KA. Myelinated axon number in the optic nerve is unaffected by Alzheimer’s disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1995;79:596–600. doi: 10.1136/bjo.79.6.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ratchford JN, et al. Optical coherence tomography helps differentiate neuromyelitis optica and MS optic neuropathies. Neurol. 2009;73:302–308. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181af78b8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Martinez-Lapiscina EH, et al. Retinal thickness measured with optical coherence tomography and risk of disability worsening in multiple sclerosis: A cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:574–584. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jentsch S, et al. Retinal fluorescence lifetime imaging ophthalmoscopy measures depend on the severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93:241–247. doi: 10.1111/aos.12609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dentchev T, Milam AH, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Dunaief JL. Amyloid-beta is found in drusen from some age-related macular degeneration retinas, but not in drusen from normal retinas. Mol. Vis. 2003;9:184–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ascaso FJ, et al. Retinal alterations in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: an optical coherence tomography study. J. Neurol. 2014;8:1522–1530. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7374-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Den Haan J, Verbraak FD, Visser PJ, Bouwman FH. Retinal thickness in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagnosis. 2017;6:162–170. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.12.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Coppola G, et al. Optical Coherence Tomography in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thomson KL, Yeo JM, Waddell B, Cameron JR, Pal S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer change in dementia, using optical coherence tomography. Alzheimers. Dement. Diagnosis, Assess. Dis. Monit. 2015;1:136–143. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2015.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Larrosa JM, et al. Potential new diagnostic tool for Alzheimer’s disease using a linear discriminant function for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014;5:3043–3051. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Garcia-Martin E, et al. Ganglion cell layer measurements correlate with disease severity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016;6:454–459. doi: 10.1111/aos.12977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Den Haan J, et al. Retinal Imaging Retinal thickness as a potential biomarker in patients with amyloid-proven early-and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagnosis. 2019;11:463–471. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Poroy C, Yücel AÂ. Optical Coherence Tomography: Is Really a New Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease? Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2018;2:119–125. doi: 10.4103/aian.AIAN_368_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kromer R, et al. Detection of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects in Alzheimer’s Disease Using SD-OCT. Front. psychiatry. 2014;5:22. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sánchez D, et al. Usefulness of peripapillary nerve fiber layer thickness assessed by optical coherence tomography as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:16345. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34577-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Marquié M, et al. Visual impairment in aging and cognitive decline: experience in a Memory Clinic. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:8698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45055-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs–an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10 Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Ophthalmol. 1991;98:786–806. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(13)38012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lad EM, et al. Evaluation of inner retinal layers as biomarkers in mild cognitive impairment to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0192646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Knoll B, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: Case-control study and meta-analysis. Alzheimers. Dement. 2016;4:85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Salobrar-Garcia E, et al. Analysis of Retinal Peripapillary Segmentation in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015;2015:636548. doi: 10.1155/2015/636548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lijmer JG, et al. Empirical evidence of design-related bias in studies of diagnostic tests. J.A.M.A. 1999;282:1061–1066. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.11.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Whiting P, et al. Sources of variation and bias in studies of diagnostic accuracy: a systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004;140:189–202. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-3-200402030-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bernick C, Cummings J, Raman R, Sun X, Aisen P. Age and rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease: implications forclinical trials. Arch. Neurol. 2012;69:901–905. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.3758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ghiso J, Doudevski I, Ritch R, Rostagno A. Alzheimer’s disease and glaucoma: mechanistic similarities and differences. J. Glaucoma. 2013;22:S36–S38. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e3182934af6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Budenz DL, et al. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmol. 2007;114:1046–1052. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.08.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Marziani E, et al. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell layer thickness in Alzheimer’s disease using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013;54:5953–5958. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cheung CYL, et al. Microvascular network alterations in the retina of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers. Dement. 2014;10:135–142. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.de Jong FJ, et al. Retinal vascular caliber and risk of dementia: the Rotterdam study. Neurol. 2011;76:816–821. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31820e7baa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ossenkoppele R, et al. Prevalence of amyloid PET positivity in dementia syndromes: a meta-analysis. J.A.M.A. 2015;313:1939–1349. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bouwman FH, et al. CSF biomarker levels in early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2009;30:1895–1901. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Alegret M, et al. Normative data of a brief neuropsychological battery for Spanish individuals older than 49. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2012;34:209–202. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2011.630652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Alegret M, et al. Cut-off scores of a Brief Neuropsychological Battery (NBACE) for Spanish Individual adults older than 44 years old. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–8. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Boada M, et al. Design of a comprehensive Alzheimer’s disease clinic and research center in Spain to meet critical patient and family needs. Alzheimers. Dement. 2014;10:409–415. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yang Q, et al. Automated layer segmentation of macular OCT images using dual-scale gradient information. Opt. Express. 2010;18:21293–21307. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.021293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nagarkatti-Gude N, et al. Optical Coherence Tomography Segmentation Errors of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Persist Over Time. J. Glaucoma. 2019;28:368–374. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Petersen RC, et al. Practice parameter: early detection of dementia: mild cognitive impairment (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurol. 2001;56:1133–1142. doi: 10.1212/WNL.56.9.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lopez OL, et al. Prevalence and Classification of Mild Cognitive Impairment in the Cardiovascular Health Study Cognition Study. Arch. Neurol. 2003;60:1385. doi: 10.1001/archneur.60.10.1385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.McKhann G, et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. 1984;34:939–944. doi: 10.1212/WNL.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cruz-Herranz A, et al. The APOSTEL recommendations for reporting quantitative optical coherence tomography studies. Neurol. 2016;86:2303–2309. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.