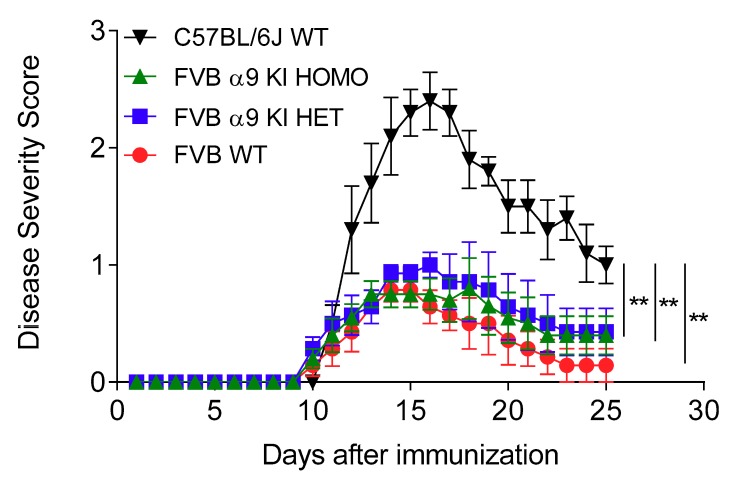
Figure 5.
Effects of a nAChR α9 subunit gain-of-function (GOF) mutation on EAE severity. EAE disease symptom evaluation was done for groups of wild-type (WT) mice on the C57BL/6J background (C57BL/6J WT, ▼n = 5), or for nAChR α9 subunit knock-in heterozygotes (FVB α9 KI HET, ■, n = 7), homozygotes (FVB α9 KI HOMO, ▲, n = 10) or their WT littermate controls (FVB WT, ⬤, n = 7) on the FVB.129P2-Pde6b+ Tyrc-ch/AntJ (FVB) background. Reduced EAE severity was seen on FVB WT, FVB α9 KI HET, and FVB α9 KI HOMO mice as compared to C57BL/6J WT mice. Mean ± S.E.M.; Mann–Whitney test; ** p < 0.01 for the FVB cohorts relative to C57BL/6J WT mice.