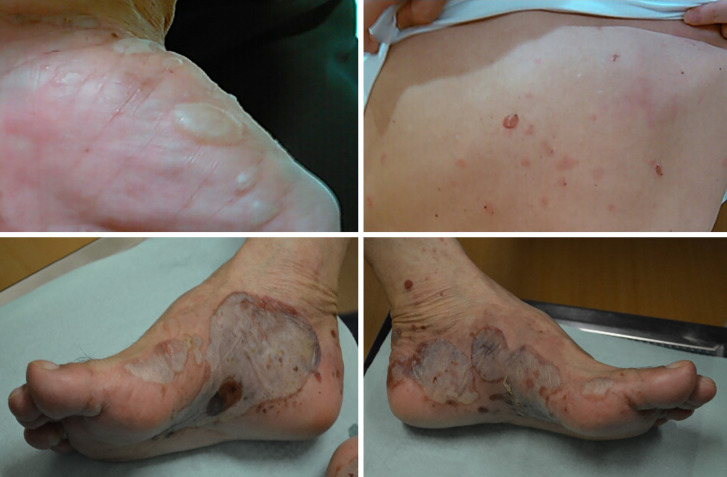
A 60-year-old man with lung cancer (adenocarcinoma, PD-L1>75%) started to receive pembrolizumab (200 mg/body) every 3 weeks. After 6 cycles, fluid-filled blisters with eroded areas appeared on the skin of his hand, back and leg (Picture 1). A skin biopsy revealed the linear deposition of immunoglobulin G with C3 deposition on the epidermal basement membrane (Picture 2). Bullous pemphigoid as an immune-related adverse event was thus diagnosed, and pembrolizumab was discontinued. Corticosteroid pulse therapy and subsequent oral corticosteroids were started, and the skin eruption transiently improved. However, repetitive exacerbation related to steroid reduction was observed, and oral prednisolone (20 mg) was used to control it. While the incidence of bullous pemphigoid as a side effect of pembrolizumab is very low (under 0.1%), only a dozen cases of bullous pemphigoid associated with anti-PD-1 antibody treatment have been reported (1,2), and physicians should keep such side effects in mind.
Picture 1.
Picture 2.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1. Zumelzu C, Alexandre M, Le Roux C, et al. Mucous membrane pemphigoid, bullous pemphigoid, and anti-programmed death-1/ programmed death-ligand 1: a case report of an elderly woman with mucous membrane pemphigoid developing after pembrolizumab therapy for metastatic melanoma and review of the literature. Frontiers Med 5: 268, 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Adachi E, Honda T, Nonoyama S, et al. Severe bullous pemphigoid in a metastatic lung cancer patient treated with pembrolizumab. J Dermatol 46: e232-e233, 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]