Abstract.
We introduce a method for quantitative hyperspectral optical imaging in the spatial frequency domain (hs-SFDI) to image tissue absorption () and reduced scattering () parameters over a broad spectral range. The hs-SFDI utilizes principles of spatial scanning of the spectrally dispersed output of a supercontinuum laser that is sinusoidally projected onto the tissue using a digital micromirror device. A scientific complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor camera is used for capturing images that are demodulated and analyzed using SFDI computational models. The hs-SFDI performance is validated using tissue-simulating phantoms over a range of and values. Quantitative hs-SFDI images are obtained from an ex-vivo beef sample to spatially resolve concentrations of oxy-, deoxy-, and met-hemoglobin, as well as water and fat fractions. Our results demonstrate that the hs-SFDI can quantitatively image tissue optical properties with 1000 spectral bins in the 580- to 950-nm range over a wide, scalable field of view. With an average accuracy of 6.7% and 12.3% in and , respectively, compared to conventional methods, hs-SFDI offers a promising approach for quantitative hyperspectral tissue optical imaging.
Keywords: tissue optical properties, hyperspectral, spatial frequency domain imaging, supercontinuum laser
1. Introduction
Biomedical hyperspectral imaging (HSI) combines high-resolution spectral and spatial content, in order to characterize tissue structure and composition. Because HSI typically employs hundreds or thousands of optical wavelengths, multiple endogenous and exogenous tissue components with unique spectral signatures can be resolved. Various HSI technical approaches have been developed for biomedical applications—most based on designs that generate reflectance and/or fluorescence maps over a continuous spectral bandwidth.1–3 Hyperspectral content can be used in conjunction with computational models of light transport and various statistical methods, such as principal component analysis, to calculate optical and physiological properties for each pixel.4–6 However, these methods generally require assumptions or approximations about certain tissue features, such as scattering properties and water concentration.7,8 Unlike temporally or spatially resolved approaches, they do not independently separate and map subsurface tissue absorption and reduced scattering parameters, and , respectively, for each wavelength and pixel.9 Changes in each of these parameters occur with spatial and temporal variations in tissue molecular composition and structure. As a result, quantitatively characterizing these light–tissue interactions over a broad spectral range with high temporal resolution can be important in accurately recovering dynamics of multiple endogenous and exogenous tissue chromophores.10,11
Spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) is a wide-field, noncontact, model-based technique that quantitatively separates light absorption from scattering on a pixel-by-pixel basis by calculating the modulation transfer function of structured light projected onto the tissue.12 SFDI has been used extensively to characterize the optical and physiological properties of tissue and visualize quantitative maps of tissue oxy/deoxyhemoglobin concentrations, both in-vivo and ex-vivo.13–15 Hyperspectral SFDI methods were first introduced using a liquid crystal tunable filter (LCTF) in conjunction with an imaging camera and a conventional broadband source in order to serially acquire hyperspectral maps of tissue and .16 This system can generate hyperspectral content that is limited by the speed and spectral performance features of the LCTF. Hyperspectral SFDI has also been developed using a single snapshot imager to characterize mouse brain,17 and has been combined with a hyperspectral line-scan camera to track brain tumor drug delivery in a rat model.18
More common SFDI approaches employ multiple discrete light sources combined time-sharing schemes for acquiring spectral content.19 These methods gain speed by sacrificing spectral content and typically employ a limited number of wavelengths, e.g., 2 to 10. However, with the development of real-time SFDI methods using square waves and fixed pattern projection combined with innovative image demodulation strategies,20–22 spatial frequency modulation no longer imposes an imaging speed/informatics bottleneck. As a result, new SFDI strategies for increasing spectral content have been introduced using temporally encoded light sources23 and single-pixel compressive sensing.24 To maximize information content from tissues, these methods should provide sufficient bandwidth and resolution to probe multiple endogenous and exogenous chromophores simultaneously, typically in the 100 to 200 nm bandwidth range, with resolution that is on the order of 5 to 10 nm. In addition, for characterizing endogenous tissue components, spectral regions with high-value information content can span broadly from the visible to the near-infrared (NIR), which puts significant demands on strategies for achieving quantitative hyperspectral content.
In this work we seek to significantly expand spectral content using a single supercontinuum laser to obtain broadband images distributed into 1000 spectral bins from 580 to 950 nm over a field of view (FOV). Wavelength-tunability is achieved using dispersive optics and a scannable slit. A digital micromirror device (DMD) is employed in pulse width modulation (PWM) mode for three-phase sinusoidal projection. Images are formed using a high-speed scientific complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (sCMOS) camera that sequentially captures one spatial slice () of a spectral data cube while continuously sweeping through all wavelengths (). Similar approaches for supercontinuum spectral selection have been introduced previously using both temporal encoding of spectral bins25 and spatial filtering.26,27 The exposure time for the camera in the internal running mode and the translation speed of the slit results in 1000 image captures across the spectrum. To decouple the contributions of the chromophores of interest, however, 5- to 10-nm spectral intervals are sufficient. Therefore, we used only 208 spectral bins for optical property calculations in this paper. Acquiring 1000 spectral bins in a broad bandwidth, however, gives the ability to capture absorption signatures and dynamics of chromophores without presumption on their existence in the sample. An example can be the breakdown of hemoglobin in burn wounds by observing temporal evolution of absorption spectra.28 Another example is temperature-dependent changes in NIR water absorption spectra.29
We assessed the hs-SFDI performance by measuring tissue phantoms over a range of optical absorption and reduced scattering values and then compared the results with a commercial SFDI instrument and spectrophotometer data. Our results show that hs-SFDI can be used to quantitatively image tissue absorption and scattering properties and provide spectral fingerprints of multiple chromophores including oxy- deoxy- and met-hemoglobin, as well as tissue water and fat. These parameters are clinically useful and can be incorporated in applications such as burn wound and diabetic foot ulcer assessments,30,31 as well as imaging hemodynamics and microvascular function in diseases where tissue composition, blood flow, and metabolism are compromised.32
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hyperspectral SFDI Instrument
The hyperspectral SFDI system is based on a 5-ps diode pumped Yb fiber laser supercontinuum source (SC 400-2, Fianium, United Kingdom). Once spectrally broadened, the source generates picosecond pulses with a broadband spectrum of 400 to 2100 nm at a maximum total power of 2 W. Bandpass filtering of the broadband laser source is achieved by utilizing a folded prism Martinez compressor design. A prism (PS858, Thorlabs, Newton, New Jersey) spatially disperses the illumination beam on a Plössl lens.33 The Plössl lens brings the illumination beam to a line focus onto a slit (VA100, Thorlabs, Newton, New Jersey), which is mounted on a linear stage (TLS13E, Zaber Technologies Inc., Vancouver, British Columbia), in front of a mirror to fold the design to be more compact. This configuration allows for tuning the spectral bandwidth and central wavelength of the broadband laser output. The Plössl lens is moved down from the optical axis to steer the beam so that it can be easily picked off with a D-mirror after the second pass through the prism. The Plössl lens consists of two achromatic doublet lenses in a symmetrical placement. This configuration ensures a flat-field curvature for the entire line focus where the slit selects the spectral output. The flat-field curvature then helps proper collimation of beam once spectrally selected. Another advantage of the Plössl lens is to help mitigate chromatic aberration.
The wavelength-tuned beam is then expanded. To reduce spatial heterogeneity, the beam is transmitted through a high grit diffuser (DG100-600-B, Thorlabs, Newton, New Jersey) prior to the DMD (CEL5500, Digital Light Innovation, Austin, Texas). The DMD produces 8-bit grayscale sinusoidal patterns through the time-sharing PWM method. The spatially modulated light is imaged onto the sample and the diffusely reflected light is captured via a high-speed sCMOS camera (ORCA-Flash 4.0 V2, Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., Japan). To increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), pixels are binned by a factor of 4, which gives an image resolution of over a FOV. The camera captures images using the internal running mode to achieve highest acquisition rate at a constant exposure time, 50 ms, which is adjusted to the pattern refresh rate of the DMD. The proposed setup has the flexibility to optimize light throughput by adjusting slit speed and camera integration time.
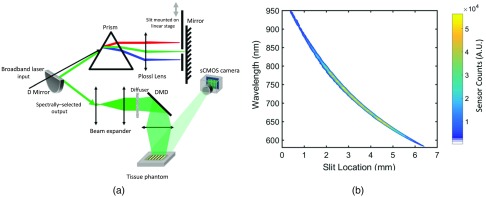
The start and end locations of the motorized stage are chosen with margins to allow for cruising at constant speed within the desired spectral range, 580 to 950 nm. The camera and DMD are controlled by trigger signals from the stage via Arduino Due microcontroller (Sparkfun Electronics, Niwot, Colorado) once the slit reaches both ends of the spectrum. Each scan of the moving slit provides 1000 images. A schematic of the instrument is shown in Fig. 1(a).
Fig. 1.
(a) Schematic representation of the hs-SFDI instrument and tissue phantom: supercontinuum input is first dispersed via a prism and imaged onto a mirror placed at the focal point of a cylindrical lens. A slit mounted on a linear stage selects the spectral output, which is spatially modulated via a DMD and projected onto the tissue phantom. The tissue phantom is made of solid silicone background with four wells that are filled with solutions of absorptive dyes and IL. (b) Slit location-central wavelength plot. Each slit location of the hs-SFDI instrument corresponds to a tuned spectral bin from the broadband source. Spectral bins are measured using a spectrometer and are shown with color-coded sensor counts.
2.2. Spectral Characterization
Figure 1(b) shows a plot of slit location as a function of wavelength. Intensity profile across the spectrum is also shown with a peak intensity at 740 nm. We chose 1000 slit locations corresponding to 1000 spectral bins in the 580- to 950-nm region and measured the output spectra using a spectrometer (Blue Wave, Stellar Net Inc., Tampa, Florida). Slit width was set to . Mean and standard deviation (SD) of full width at half maximum (FWHM) was calculated to be 17.25 and 5.69 nm, respectively. As expected, lower (, refractive index of prism material; , Wavelength) at longer wavelengths on the dispersive prism led to increasing spectral bandwidth, reaching 26.42 nm for the 950-nm spectral bin.
Most of the spectral features of the tissue main chromophores (oxy/deoxy/methemoglobin, fat, and water) in the first optical window (600 to 1000 nm) are broader than the instrument bandwidth using the hs-SFDI instrument.
2.3. SFDI Processing
In this paper, we have used a single spatial frequency () sinusoidal pattern at three rad-shifted phases, which were then inserted into the following SFDI demodulation Eq. (1):
| (1) |
where is demodulated reflectance at pixel () and is the intensity of phase at pixel (). The DC demodulated reflectance is acquired by averaging over phase-shifted single frequency images [Eq. (2)]
| (2) |
The following procedure is then performed to calculate the optical properties of a sample.
-
1.
Demodulated AC and DC images are calculated for a calibration phantom using the hs-SFDI instrument.
-
2.
The calibration phantom construction is fully described in Refs. 12, 34, and 35. Briefly, a solid silicone-based tissue phantom is made with titanium(IV) oxide () as scattering and India ink as absorptive agents. Thin samples of the calibration phantom are measured via inverse adding doubling (IAD) technique36 to characterize the wavelength-dependent optical properties.
-
3.
A forward Monte Carlo (MC) simulation of radiative transport in turbid media is performed using previously acquired optical properties and true diffuse reflectance values are calculated for both AC and DC components.
-
4.
The sample’s AC and DC components are divided by their calibration images and are multiplied by the MC-derived diffuse reflectance values to correct for instrument response and to calculate absolute diffuse reflectance values of the sample.
-
5.
AC- and DC-calibrated reflectance values are finally inserted to an inverse MC solver to extract a unique pair of optical properties (absorption and reduced scattering). We used a lookup table derived from white MC simulations.12,37 The acceptance angle of the camera was considered in the SFDI model and a Henyey Greenstein phase function was used. The refractive index is set to 1.4 for the beef and 1.33 for phantom measurements. The SFDI model used for this paper is based on volume scattering and does not account for surface scattering of the sample. However, it has been shown that decoupling of volume and surface scattering from reflectance data can be accomplished via a modified solution of the radiative transfer equation. 38
3. Results
3.1. Multiconcentration Liquid Phantom
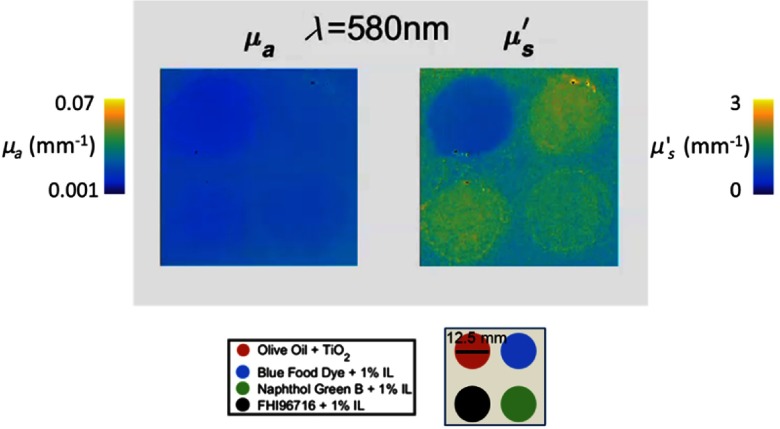
To experimentally validate the performance of the broadband hyperspectral imager, we performed a series of controlled tissue phantom measurements to demonstrate that the instrument can quantify absorption and reduced scattering over a wide spectral range. Solid tissue phantoms were fabricated from silicone, as described in Sec. 2.3. We then inserted 12.5-mm diameter cylindrical molds in the base phantom. Once the base phantom was cured, we removed the cylindrical molds and poured the liquid solutions in the resulting “wells.” A schematic of the tissue phantom is shown in Fig. 1(a).
Distilled water-based solutions of Naphthol Green B at multiple concentrations [0.25, 0.03125, 0.0375, 0.04275, and 0.05 gram per liter (g/L)] were prepared and measured with a custom-built spectrophotometer to calculate the absorption coefficients from 580 to 950 nm. Turbid versions of the same solutions were prepared by adding intralipid (IL) (Fresenius Kabi, Uppsala, Sweden): one milliliter (mL) of 20% IL was added to 19 mL of each solution, poured into the wells of the phantom, and measured with the hyperspectral SFDI instrument. The measurement was performed over 1000 spectral bins in the 580- to 950-nm region; however, we selected 208 linearly spaced bins for our final analysis.
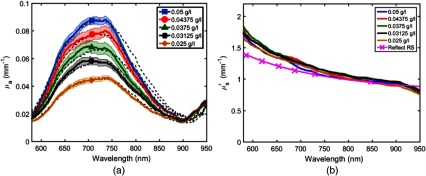
Figure 2(a) shows absorption coefficient values of 5 Naphthol Green B solutions determined using the hyperspectral SFDI instrument and the spectrophotometer. The values of these solutions range from 0.015 to , whereas range from 0.75 to . Figure 2(b) shows reduced scattering plots for the five solutions. The optical properties in Fig. 2 are determined by averaging over a region of interest (ROI) in the center of each well. Average standard deviations in absorption and reduced scattering maps of these ROIs are 0.0019 and , which give coefficients of variation of 3.949% and 3.614%, respectively.
Fig. 2.
(a) Plot of bulk spectra for five concentrations of Naphthol Green B in 1% IL. Each data point corresponds to the mean value of over a ROI. About 208 data points in the 580- to 950-nm region are plotted for each concentration. Colored lines are from the hs-SFDI instrument and black dashed lines are spectrophotometer measurements. Mean spatial standard deviation of hs-SFDI-derived values over specified ROIs is . (b) Plot of bulk spectra for five concentrations of Naphthol Green B solutions in 1% IL. The hs-SFDI reduced scattering values are compared to those obtained using a conventional SFDI instrument, Reflect RS™. Mean standard deviation of hs-SFDI-derived values over specified ROIs is .
The average difference between recovered values determined using the hs-SFDI instrument and spectrophotometer values was 6.7% (SD 6.8%). We expected similar values for these solutions since the dominant scattering contribution originated from their comparable IL concentrations. We showed that the hs-SFDI-fitted values were within 12.3% (SD 6.9%) of 1% IL values measured by a conventional SFDI instrument. A commercially available SFDI measurement system, Reflect RS™ (Modulated Imaging, Inc., Irvine, California), was used to image reduced scattering coefficients of 1% IL solutions at six wavelengths between 580 and 850 nm. We then fitted a power series to 6 data points and compared Reflect RS™ reduced scattering values with hs-SFDI data at 208 spectral bins in the 580- to 950-nm region.
Although there is larger error in scattering at short wavelengths, the fact that precision of scattering spectra for different dye concentrations is acceptable (1% to 2.5% coefficient of variation in the 680- to 950-nm range) implies that there may be systematic errors that cause this discrepancy. One of our suspicions is the chromatic aberration on the h-SFDI setup, which can add more “blurring” to the fringes, thus jeopardizing the SFDI algorithm to report higher scattering values.
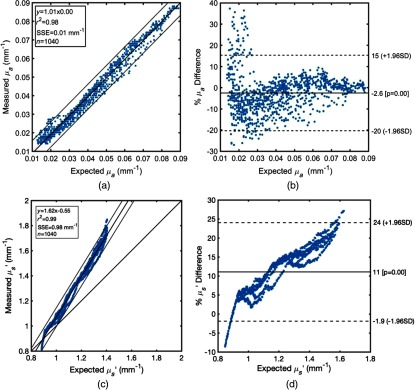
Figure 3(a) shows fit intervals for the expected values, spectrophotometer results, and those obtained using the hs-SFDI instrument for all five solutions at 208 wavelengths. Figure 3(b) shows Bland–Altman plots39 of recovered optical absorption for the same data set. About 94% of hs-SFDI measurements are within of the mean difference indicating a close agreement between the two approaches. The data points with errors larger than are more significant for absorption coefficients , specifically for wavelengths longer than 750 nm, where the bandwidth of spectral bins becomes larger due to lower imposed by the dispersive prism in our optical design. However, other factors, such as the partial volume effect from the surrounding medium at lower absorption values and low SNR at longer wavelengths, could also contribute to this result. Figure 3(c) shows fit intervals for the expected values from Reflect RS™ and hs-SFDI results for the five solutions at 208 wavelengths. Figure 3(d) shows Bland–Altman plots of recovered reduced scattering.
Fig. 3.
(a) Comparison between absorption coefficients extracted from spectrophotometer (expected ) and hs-SFDI (measured ). Scatter plot with regression fit and confidence intervals for slope and fit. (b) Bland–Altman plots of mean and percentage difference between spectrophotometer (expected ) and hs-SFDI data (measured ). Dashed lines show intervals for times standard deviation of percentage difference. The absorption percentage differences are calculated by using the spectrophotometer values in the denominator. (c) Comparison between fitted reduced scattering coefficients extracted from Reflect RS™ (expected ) and hs-SFDI (measured ). Scatter plot with regression fit and confidence intervals for slope and fit. (d) Bland–Altman plots of mean and percentage difference between Reflect RS™ (expected ) and hs-SFDI data (measured ). Dashed lines show intervals for times standard deviation of percentage difference. The reduced scattering percentage differences are calculated by using the fitted Reflect RS™ values in the denominator.
3.2. Multidye Phantom
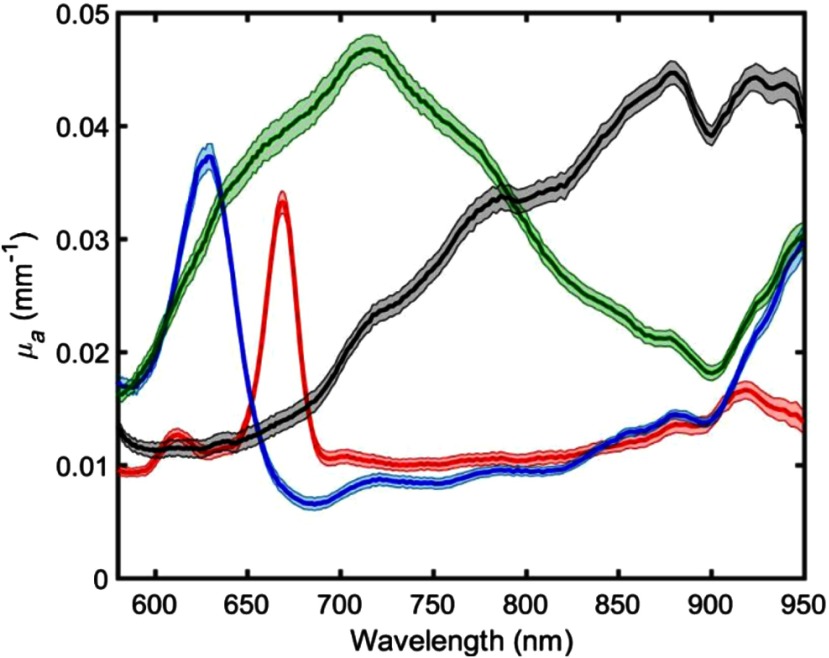
To test spectral resolution, solutions of four compounds with absorption peaks at 636, 675/930, 730, and 910 nm were fabricated: blue food dye (Ateco, Glen Cove, New York), extra virgin olive oil, Naphthol Green B (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri), and FHI96716 dye (Fabricolor Holding Int’l, Paterson, New Jersey), respectively. We then made turbid versions of these solutions by adding 20% IL so that the resulting concentrations of IL were 1%, except for the olive oil, which was mixed with . The four solutions were then poured in wells of a silicone phantom built using the same method described in Sec. 3.1. The concentrations of Naphthol Green B solutions were chosen to be within the range of brain and skin tissues commonly measured with SFDI.28,40 Also, at lower absorption values, there are limitations with accuracy of IAD. Therefore, in this study we measured phantoms in the absorption range where our calibration technique provided reliable values.
We measured these solutions using the hs-SFDI instrument and extract and for 1000 spectral bins in the 580- to 950-nm range. Figure 4 shows absorption spectra for the four solutions. The optical properties are determined by averaging over a ROI in the center of each well. The spectral shapes of these solutions agree with the expected absorption spectra trends for each. There is, however, some cross talk between the FHI96716 sample and the calibration phantom in the 890- to 910-nm region. The calibration phantom has an absorption peak in the 910-nm region that is consistent with the absorption of silicone. The contribution of the 910-nm peak is visible in the absorption spectra of the sample. Therefore, the calibration procedure, discussed in Sec. 2.3, has not completely corrected for instrument response and absorption features of the calibration phantom.
Fig. 4.
Plot of bulk spectra for four solutions: three water-soluble dyes with 1% IL concentration. Olive oil is mixed with known concentration of (0.65 g/L). Each data point corresponds to the mean value of an optical property over a ROI. About 208 data points in the 580- to 950-nm region are plotted for each concentration.
On the scattering values, however, there were increased deviations in reduced scattering values between the three solutions with 1% IL concentrations, compared to Sec. 3.1. This could be related to photons propagating through multiple media in the phantom with different refractive indices and optical properties or minor spatial variations in the calibrated reflectance. Therefore, scattering plot is not presented in this section.
Figure 5 shows a movie of the spectral cube (, and ) for absorption and reduced scattering coefficients of the multiwell phantom. While averaging over the center of each well gives a bulk optical property value, there are partial volume effects next to the edges as large path lengths allow photons from the solid medium to enter each well and contribute to the localization of optical properties.
Fig. 5.
Spectral cube (, and ) for absorption and reduced scattering coefficients of the multiwell phantom. Schematic representation of the wells with the silicone-based solid background is shown (Windows Media Player, 782 KB).
3.3. Beef Sample
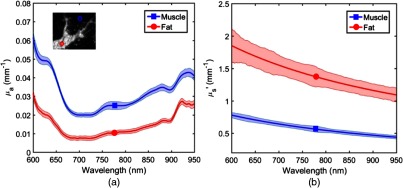
To characterize a more realistic biological specimen, we measure a sirloin beef sample with distinct regions of the primary tissue chromophores: hemoglobin, water, and lipid. Figure 6 shows absorption and reduced scattering spectra for two () ROIs located on the fatty and muscle part of the sample. ROIs are chosen on smooth areas of the sample to avoid artifacts from very steep angles.
Fig. 6.
Plot of (a) bulk spectra and (b) spectra at two ROIs (): fat (red) and muscle (blue).
The absorption spectra have local maxima, as shown in Fig. 6(a), at 600 and 630 nm mostly due to deoxy/oxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin absorption, respectively. These peaks are noticeable for both ROIs since the diffuse light field samples a larger volume than the specified ROI and there is spatial heterogeneity in three dimensions (i.e., partial volume effect). An increase in absorption values at 850 nm and longer wavelengths is seen in both fatty and muscle components. There is also a distinct lipid absorption peak at about 920 nm in the spectrum acquired from the fat ROI. The overall trend and magnitude of absorption and reduced scattering spectra on the muscle ROI agree with previous studies.41,42 The fat ROI values are consistently greater than muscle and, when fitted to a standard Mie theory model:43 , scattering prefactor (A), and scattering power (b) are, respectively, and 1.043 for fatty tissue and and 1.248, for muscle tissue. These values are comparable with previous reports in Ref. 44 as average (standard deviation) of A and b parameters for fatty tissue from six studies are 1.288 and 0.672(0.242), respectively. The average (standard deviation) of A and b parameters of muscle/heart tissue from four studies are 0.531 and 1.609 (0.722), respectively.
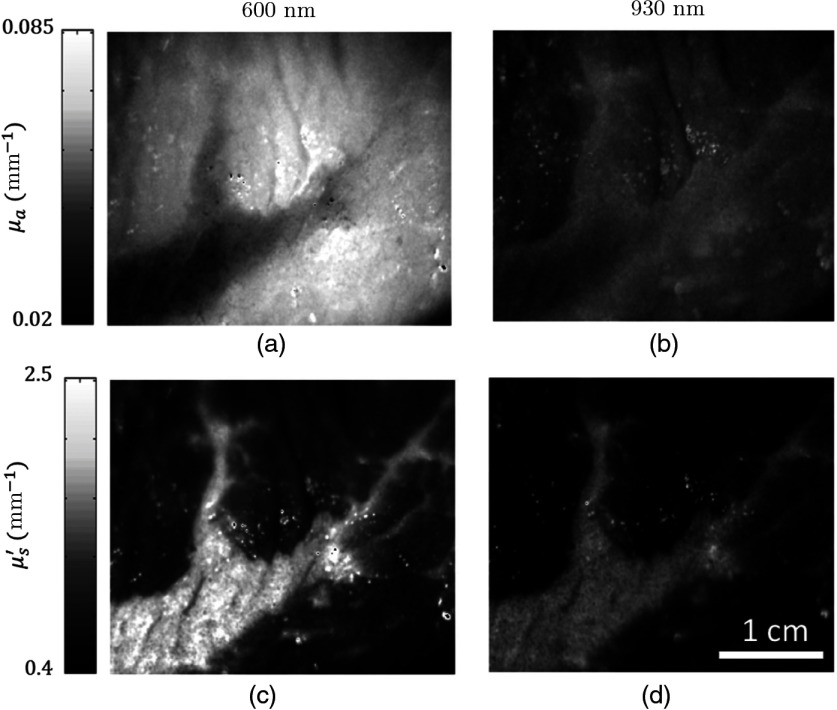
Figure 7 shows absorption and reduced scattering maps at two wavelengths (600 and 930 nm).
Fig. 7.
(a), (b) The and (c), (d) maps of the beef sample at 600 and 930 nm. The dominant spatial contrast between fat and muscle arises from oxy/deoxyhemoglobin absorption at 600 nm while increases in both lipid and water absorption at 930 nm reduces absorption contrast between these components. Higher A and lower b parameters in the fat region cause decrease in contrast between the fat and muscle regions in the reduced scattering map. Also, at longer NIR wavelengths, higher scattering-to-absorption ratios and therefore partial volume effect cause lower spatial resolution.
Finally, we fitted the absorption spectra at two () ROIs (fat and muscle regions) to five chromophores: oxyhemoglobin (), deoxyhemoglobin (Hb), methemoglobin (MetHb), fat, and water using the Beer–Lambert law, published extinction coefficient values,45 and MATLAB (Mathworks Inc., Natick, Massachusetts) linear least-squares solver. Table 1 shows calculated values and standard deviations for each chromophore.
Table 1.
Chromophore concentration in micromolar () and fraction values for two ROIs (fatty and muscle) in the beef sample. Standard deviations across pixel values within each ROI are included in parentheses.
| Hb () | () | MHb () | Fat (fraction) | Water (fraction) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat ROI | 0.10(0.08) | 41.7(4.54) | 4.0(0.05) | 0.7503(0.04) | 0.5211(0.06) |
| Muscle ROI | 1.3(0.73) | 92.3(8.19) | 9.1(0.57) | 0.4186(0.05) | 0.5948(0.05) |
The calculated values match with expected higher hemoglobin concentrations and water fraction in the muscle. Overlap of MetHb with fat and water absorption peaks and the large bandwidth of spectral bins in the 850- to 950-nm region decrease our ability to fully decouple these chromophores, thus causing a possible underestimation of MetHb and an overestimation of fat in the muscle ROI. We exclude spectral bins in the 580- to 600-nm region in the chromophore fitting procedure due to low SNR imposed by hemoglobin absorption in the sample. In general, there are many issues including type of skeletal muscle, date of harvesting, packaging, and the aging procedure that can cause variations in the sample’s constituents. Depth of interrogation also differs across the spectral bandwidth, which can prevent sampling the same volume of tissue. Full control over these parameters is out of the scope of this study but may allow for more accurate estimation of tissue constituents.
4. Discussion
In this paper, we introduce a design for quantitative, hyperspectral SFDI of tissue optical properties over a broad range of optical wavelengths. One of the challenges with our current wavelength-tuning configuration is acquisition speed. It takes about 150 s to acquire a hyperspectral cube using conventional three-phase sinusoidal projection since the slit scans a 6.3-mm line at 0.1 mm/s; equivalent to a total bandwidth of 370 nm. In principle, the scanning slit can move at a maximum speed of 6.5 mm/s, which enables it to cover the entire bandwidth in less than a second and 3 s for a total of three phases. However, at our current large FOV (), this requires a much higher sinusoidal pattern refresh rate on the DMD and lower exposure times on the camera, which are not possible with the current components.
One solution we have introduced that overcomes this refresh rate limitation of the DMD is to employ square waves rather than sinusoidal patterns. The 8-bit sinusoidal refresh rate on the current DMD is 60 Hz. This increases to 5 kHz for binary square wave patterns. This approach has been utilized in a video-rate multispectral SFDI instrument to track hemodynamics in a preclinical rat model of cardiac arrest and resuscitation.46 In addition, square pattern illumination can synthesize multiple spatial frequency components (fundamental and harmonic) to probe multiple depths.21 In the case of homogeneous samples, using diffuse reflectance values at multiple spatial frequencies can also help minimize and fitting errors.47 The alternative solution would be single snapshot techniques, which do not require three phase projections.48 However, these techniques require a large number of cycles in the modulation pattern to mitigate ringing artifacts and may not be applicable to small FOVs.22
Choosing an optimized exposure time of the camera is mainly dependent on total light throughput, power distribution on both tails of the spectral bandwidth, and sensitivity of the camera sensor. When exposure time is set to a constant value for all spectral bins, diffuse reflectance of a 1% absorbing material (Spectralon, Lab Sphere, North Sutton, New Hampshire) shows a peak at 740 nm. Total number of counts on the sensor then decreases up to 4.5-fold for both tails of the spectra at 580 and 950 nm. Therefore, exposure time at spectral bins with lower throughput needs to be increased to enhance SNR. It is worth mentioning that refresh rate of the DMD needs to be adjusted accordingly in the case of sinusoidal illumination. Another optimization step can involve replacing the diffuser, which was installed to homogenize the beam profile with a higher throughput light pipe homogenizing rod (48-582, Edmund Optics, Barrington, New Jersey). The quantum efficiency of the camera at wavelengths longer than 900 nm is below 25% as compared to 82% at around 580 nm. All the lenses in the proposed optical configuration have antireflection coating in the 650- to 1000-nm range. Achieving high SNR at wavelengths longer than 900 nm can be important for decoupling the absorption contribution of fat and water in biological tissue, which have peaks at 930 and 970 nm, respectively.
Despite the limitations, our slit-scanning approach provides flexibility in selecting the bandwidth and central wavelength of supercontinuum source even outside our current operating spectral range, 580 to 950 nm, e.g., short-wave infrared (900 to 1700 nm). However, the slit-scanning decreases a large portion of light throughput by passing the input beam through multiple lenses. Alternate wavelength-tuning approach is to integrate an acousto-optic tunable filter to the light path for rapid wavelength selection.
5. Conclusion
We have demonstrated the integration of a versatile wavelength-tuning configuration for a supercontinuum laser-based projection unit for a hyperspectral SFDI instrument that records tissue optical properties over 1000 wavelength bands (from 580 to 950 nm). We validated the performance of the hs-SFDI instrument to quantity and decouple optical properties, absorption, and reduced scattering, in a range of tissue-simulating phantoms, by comparing absorption values to spectrophotometer measurements. Average absorption values were within 6.7% of the spectrophotometer data. Reduced scattering coefficients were within 12.3% of those obtained using a conventional SFDI instrument. The effects of spectral range and resolution were shown by measuring a tissue phantom consisting of four wells with distinct spectral signatures. We also performed an ex-vivo measurement of a beef sample to quantify and spatially resolve spectral fingerprints of a variety of tissue-containing molecules such as oxy-, deoxy-, and met-hemoglobin, as well as water and fat.
While there are challenges in accelerating image acquisition on the hs-SFDI system, techniques such as integration with single-pixel SFDI techniques,24 encoding hyperspectral information in the illumination beam via light labeling,25,49 and acousto-optic tunable filters have potential to resolve the spectral-temporal performance trade-off.
Despite these challenges, our study provides a platform to characterize and localize tissue structure and constituents with millimeter spatial resolution over a scalable FOV using quantitative continuous hyperspectral optical-property content.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding provided by the National Institute of Health (NIH) NIBIB Biomedical Technology Research Center LAMMP: P41EB015890, the NIH Grant No. R21EB020953, the Military Medical Photonics Program: AFOSR Grant No. FA9550-17-1-0193, and Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily reflect the views of the NIH and United States Air Force.
Biography
Biographies of the authors are not available.
Disclosures
B. J. T. and A. J. D. are cofounders of Modulated Imaging (MI), Inc. and disclose patents in SFDI that are to the regents of the University of California. These patents have been licensed to MI, Inc. This work was completed using federally funded sources without support or participation from MI, Inc. The other authors have no competing financial interests to disclose.
References
- 1.Leavesley S. J., et al. , “Hyperspectral imaging fluorescence excitation scanning for colon cancer detection,” J. Biomed. Opt. 21(10), 104003 (2016). 10.1117/1.JBO.21.10.104003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kiyotoki S., et al. , “New method for detection of gastric cancer by hyperspectral imaging: a pilot study,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(2), 026010 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.2.026010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Akbari H., et al. , “Hyperspectral imaging and quantitative analysis for prostate cancer detection,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(7), 0760051 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.076005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bjorgan A., Randeberg L. L., “Estimation of skin optical parameters for real-time hyperspectral imaging applications,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(6), 066003 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.6.066003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dicker D. T., et al. , “Differentiation of normal skin and melanoma using high resolution hyperspectral imaging,” Cancer Biol. Ther. 5(8), 1033–1038 (2006). 10.4161/cbt [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Randeberg L. L., Larsen E. L. P., Svaasand L. O., “Characterization of vascular structures and skin bruises using hyperspectral imaging, image analysis and diffusion theory,” J. Biophotonics 3(1–2), 53–65 (2010). 10.1002/jbio.200910059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vogel A., et al. , “Using noninvasive multispectral imaging to quantitatively assess tissue vasculature,” J. Biomed. Opt. 12(5), 051604 (2014). 10.1117/1.2801718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vasefi F., et al. , “Transillumination hyperspectral imaging for histopathological examination of excised tissue,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(8), 086014 (2011). 10.1117/1.3623410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O’sullivan T. D., et al. , “Diffuse optical imaging using spatially and temporally modulated light,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(7), 071311 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.071311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Duann J.-R., et al. , “Separating spectral mixtures in hyperspectral image data using independent component analysis: validation with oral cancer tissue sections,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(12), 126005 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.12.126005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Poh C. F., et al. , “Fluorescence visualization detection of field alterations in tumor margins of oral cancer patients,” Clin. Cancer Res. 12(22), 6716–6722 (2006). 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cuccia D. J., et al. , “Quantitation and mapping of tissue optical properties using modulated imaging,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(2), 024012 (2009). 10.1117/1.3088140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nandy S., et al. , “Characterizing optical properties and spatial heterogeneity of human ovarian tissue using spatial frequency domain imaging,” J. Biomed. Opt. 21(10), 101402 (2016). 10.1117/1.JBO.21.10.101402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gioux S., et al. , “First-in-human pilot study of a spatial frequency domain oxygenation imaging system,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(8), 086015 (2011). 10.1117/1.3614566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nadeau K. P., et al. , “Quantitative assessment of renal arterial occlusion in a porcine model using spatial frequency domain imaging,” Opt. Lett. 38(18), 3566–3569 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.003566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mazhar A., et al. , “Wavelength optimization for rapid chromophore mapping using spatial frequency domain imaging,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(6), 061716 (2010). 10.1117/1.3523373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weber J. R., et al. , “Multispectral imaging of tissue absorption and scattering using spatial frequency domain imaging and a computed-tomography imaging spectrometer,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(1), 011015 (2011). 10.1117/1.3528628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Singh-Moon R. P., et al. , “Spatial mapping of drug delivery to brain tissue using hyperspectral spatial frequency-domain imaging,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(9), 096003 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.9.096003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tabassum S., et al. , “Feasibility of spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) for optically characterizing a preclinical oncology model,” Biomed. Opt. Express 7(10), 4154–4170 (2016). 10.1364/BOE.7.004154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nadeau K. P., Durkin A. J., Tromberg B. J., “Advanced demodulation technique for the extraction of tissue optical properties and structural orientation contrast in the spatial frequency domain,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(5), 056013 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.5.056013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nadeau K. P., et al. , “Multifrequency synthesis and extraction using square wave projection patterns for quantitative tissue imaging,” J. Biomed. Opt. 20(11), 116005 (2015). 10.1117/1.JBO.20.11.116005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vervandier J., Gioux S., “Single snapshot imaging of optical properties,” Biomed. Opt. Express 4(12), 2938–2944 (2013). 10.1364/BOE.4.002938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Applegate M. B., Roblyer D., “High-speed spatial frequency domain imaging with temporally modulated light,” J. Biomed. Opt. 22(7), 076019 (2017). 10.1117/1.JBO.22.7.076019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Torabzadeh M., et al. , “Compressed single pixel imaging in the spatial frequency domain,” J. Biomed. Opt. 22(3), 030501 (2017). 10.1117/1.JBO.22.3.030501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Domingue S. R., Winters D. G., Bartels R. A., “Hyperspectral imaging via labeled excitation light and background-free absorption spectroscopy,” Optica 2(11), 929–932 (2015). 10.1364/OPTICA.2.000929 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.van der Mark M., Desjardins A., “Diffuse Spectroscopy with Very High Collection Efficiency,” in Laser Sci. to Photonic Applications (2013). 10.1364/CLEO_AT.2011.ATuB4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dunsby C., et al. , “An electronically tunable ultrafast laser source applied to fluorescence imaging and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy,” J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 37, 3296–3303 (2004). 10.1088/0022-3727/37/23/011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bernal N. P., et al. , “Impact of hemoglobin breakdown products in the spectral analysis of burn wounds using spatial frequency domain spectroscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 24(2), 020501 (2019). 10.1117/1.JBO.24.2.020501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chung S. H., et al. , “Non-invasive tissue temperature measurements based on quantitative diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) of water,” Phys. Med. Biol. 55(13), 3753–3765 (2010). 10.1088/0031-9155/55/13/012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nguyen J. Q., et al. , “Spatial frequency domain imaging of burn wounds in a preclinical model of graded burn severity,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(6), 066010 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.6.066010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yafi A., et al. , “Quantitative skin assessment using spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) in patients with or at high risk for pressure ulcers,” Lasers Surg. Med. 49(9), 827–834 (2017). 10.1002/lsm.v49.9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yazdi H. S., et al. , “Mapping breast cancer blood flow index, composition, and metabolism in a human subject using combined diffuse optical spectroscopic imaging and diffuse correlation spectroscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 22(4), 045003 (2017). 10.1117/1.JBO.22.4.045003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Domingue S. R., Bartels R. A., “Nearly transform-limited sub-20-fs pulses at 1065 nm and enabled by a flat field ultrafast pulse shaper,” Opt. Lett. 40(2), 253–256 (2015). 10.1364/OL.40.000253 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Saager R. B., et al. , “Low-cost tissue simulating phantoms with adjustable wavelength-dependent scattering properties in the visible and infrared ranges,” J. Biomed. Opt. 21(6), 067001 (2016). 10.1117/1.JBO.21.6.067001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Durkin A. J., et al. , “Fabrication and characterization of silicone-based tissue phantoms with tunable optical properties in the visible and near infrared domain,” Proc. SPIE 6870, 687007 (2008). 10.1117/12.764969 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Prahl S. A., van Gemert M. J. C., Welch A. J., “Determining the optical properties of turbid media by using the adding-doubling method,” Appl. Opt. 32(4), 559–568 (2009). 10.1364/AO.32.000559 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Laser Microbeam and Medical Program, “Virtual photonics technology initiative,” https://virtualphotonics.org (2014).
- 38.Nothelfer S., et al. , “Spatial frequency domain imaging using an analytical model for separation of surface and volume scattering,” J. Biomed. Opt. 24(7), 071604 (2018). 10.1117/1.JBO.24.7.071604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bland J. M., Altman D. G., “Measuring agreement in method comparison studies,” Stat. Methods Med. Res. 8(2), 135–160 (1999). 10.1177/096228029900800204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin A. J., et al. , “Spatial frequency domain imaging of intrinsic optical property contrast in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease,” Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39(4), 1349–1357 (2011). 10.1007/s10439-011-0269-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Filatova S. A., Shcherbakov I. A., Tsvetkov V. B., “Optical properties of animal tissues in the wavelength range from 350 to 2600 nm,” J. Biomed. Opt. 22(3), 035009 (2017). 10.1117/1.JBO.22.3.035009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xia J. J., et al. , “Characterizing beef muscles with optical scattering and absorption coefficients in VIS-NIR region,” Meat Sci. 75(1), 78–83 (2007). 10.1016/j.meatsci.2006.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Michels R., Foschum F., Kienle A., “Optical properties of fat emulsions,” Opt. Express 16(8), 5907–5925 (2008). 10.1364/OE.16.005907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jacques S. L., “Optical properties of biological tissues: a review,” Phys. Med. Biol. 58, R37 (2013). 10.1088/0031-9155/58/11/R37 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zijlstra W. G., Buursma A., Meeuwsen-van der Roest W. P., “Absorption spectra of human fetal and adult oxyhemoglobin, de-oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, and methemoglobin,” Clin. Chem. 37(9), 1633–1638 (1991). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wilson R. H., et al. , “High-speed spatial frequency domain imaging of rat cortex detects dynamic optical and physiological properties following cardiac arrest and resuscitation,” Neurophotonics 4(4), 045008 (2017). 10.1117/1.NPh.4.4.045008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lin A. J., et al. , “Visible spatial frequency domain imaging with a digital light microprojector,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(9), 096007 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.9.096007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Valdes P. A., et al. , “qF-SSOP: real-time optical property corrected fluorescence imaging,” Biomed. Opt. Express 8(8), 3597–3605 (2017). 10.1364/BOE.8.003597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Torabzadeh M., et al. , “Hyperspectral characterization of tissue simulating phantoms using a supercontinuum laser in a spatial frequency domain imaging instrument,” Proc. SPIE 10486, 104860G (2018). 10.1117/12.2291369 [DOI] [Google Scholar]