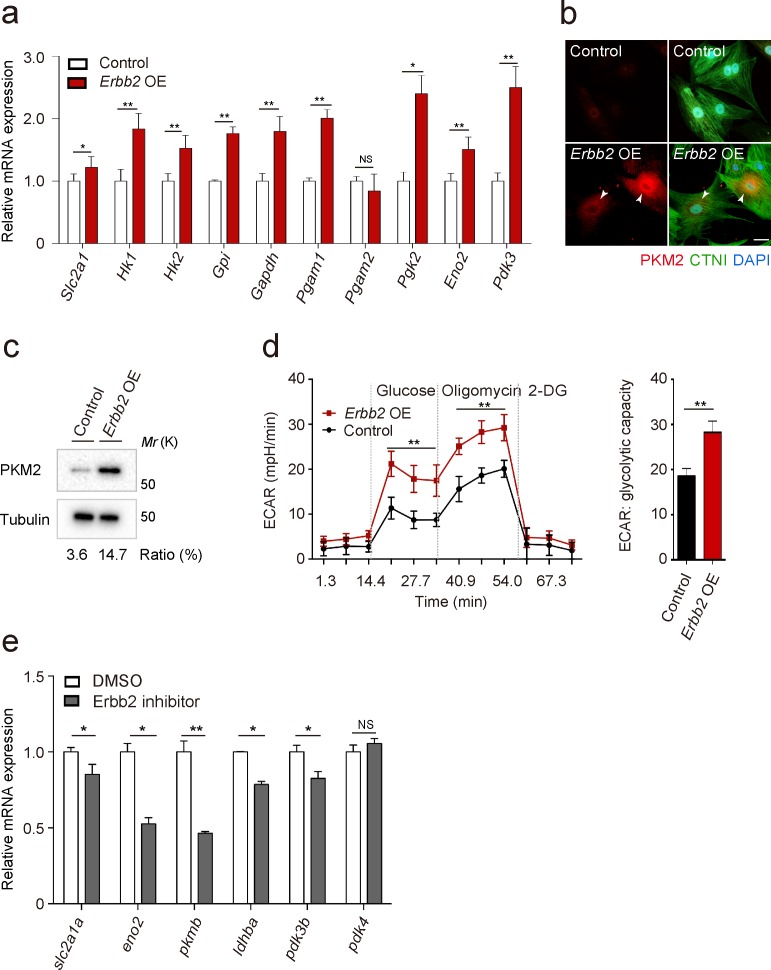
Figure 2. ERBB2 signaling activates glycolysis in cardiomyocytes.
(a) qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of glycolytic enzyme genes in control and Erbb2 overexpressing (OE) rat neonatal CMs (n = 3). Error bars, s.e.m. (b) Staining for PKM2, CTNI and DNA (DAPI) in control and Erbb2 OE rat neonatal CMs; arrowheads point to PKM2+ CMs. (c) Western blot analysis of PKM2 levels in control and Erbb2 OE rat neonatal CMs. (d) Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) analysis in control and Erbb2 OE rat neonatal CMs; glycolytic capacity shown on the right (n = 7). Error bars, s.d. (e) qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of glycolytic enzyme genes in DMSO and Erbb2 inhibitor treated zebrafish hearts (n = 3). Error bars, s.e.m.; *p<0.05 and **p<0.001 by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS, not significant. Scale bar, 20 μm.
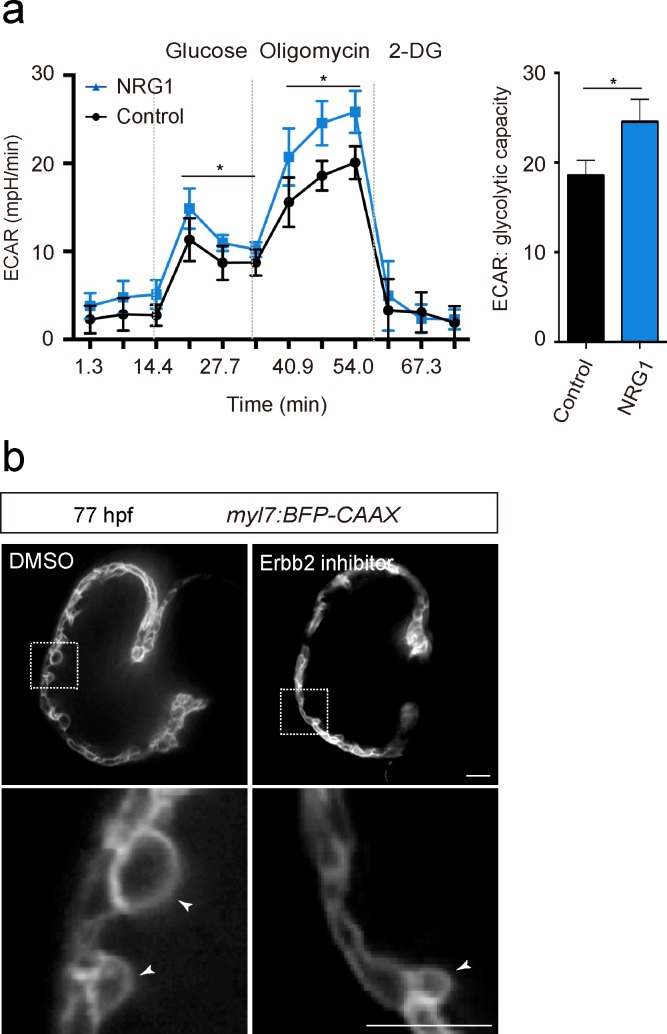
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. NRG1/ERBB2 signaling activates glycolysis in CMs.
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Uncropped images related to western blotting data.