Abstract
Background
Obesity is a global epidemic, and it is widely known that increased Body mass index (BMI) is associated with alterations in respiratory mechanics. Bariatric surgery is established as an effective treatment for this condition.
Objective
To assess the safety and effectiveness of different ventilation strategies in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery.
Methods
A systematic review of randomized clinical trials aimed at evaluating ventilation strategies for obese patients was carried out. Primary outcomes: in-hospital mortality, adequacy of gas exchange, and respiration mechanics alterations.
Results
Fourteen clinical trials with 574 participants were included. When recruitment maneuvers (RM) vs Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) were compared, RM resulted in better oxygenation p = 0.03 (MD 79.93), higher plateau pressure p < 0.00001 (MD 7.30), higher mean airway pressure p < 0.00001 (MD 6.61), and higher compliance p < 0.00001 (MD 21.00); when comparing RM + Zero end-expiratory pressure (ZEEP) vs RM + PEEP 5 or 10 cmH2O, RM associated with PEEP led to better oxygenation p = 0.001 (MD 167.00); when comparing Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) 40 cmH2O + PEEP 10 cmH2O vs CPAP 40 cmH2O + PEEP 15 cmH2O, CPAP 40 + PEEP 15 achieved better gas exchange p = 0.003 (MD 36.00) and compliance p = 0.0003 (MD 3.00).
Conclusion
There is some evidence that the alveolar recruitment maneuvers associated with PEEP lead to better oxygenation and higher compliance. There is no evidence of differences between pressure control ventilation (PCV) and Volume control ventilation (VCV).
Keywords: Systematic review, Mechanical ventilation, Obesity, Meta-analysis
Background
Obesity is a global epidemic that causes major economic, social and psychological impacts [1]. Body mass index (BMI) values above 30 Kg/m [2] can result in a reduction in life expectancy similar to that caused by smoking [2, 3]. Bariatric surgery is an effective intervention against weight gain and the majority of people who undergo such surgery show an improvement in, or the resolution of, conditions such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension and obstructive sleep apnaea [4].
The growing number of bariatric surgeries highlights the importance of invasive ventilator support. Anesthetic induction in obese patients can result in a significant reduction in respiratory compliance and increase resistance and pressure in the airway [5]. A correlation has also been found between a high BMI and an increase in breathing effort and a reduction in oxygenation levels, which may lead to atelectasis and slower weaning from mechanical ventilation [6, 7].
To date, no standard ventilation strategy has been established for obese patients, although there is some evidence that recruitment maneuvers (RM) combined with Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) improves oxygenation and compliance in comparison with other strategies [8]. A systematic review can therefore make a significant contribution to the decision-making process of healthcare professionals, particularly surgeons and anesthesiologists, when choosing the best ventilation strategy during the surgery and anesthesia of obese patients, with the aim of reducing complications, costs and mortality.
Objectives
To assess the effectiveness and safety of different ventilation strategies for obese participants undergoing bariatric surgery under general anesthesia.
Methods
The methodology described by the Cochrane Collaboration was employed in this systematic review [9].
This research was approved by the ethics committee of the federal university of São Paulo - Unifesp - CAAE: 57099216.0.0000.5505.
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated different ventilation strategies for obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery, under general anesthesia, regardless of age and gender, were included.
Obesity was defined as BMI greater than 30 Kg/m2 [10].
Primary outcomes: in hospital mortality, adequacy of intra-operative gas exchange, pulmonary mechanics (plateau pressure, mean airway pressures, lung compliance and lung resistance) alteration.
Secondary outcomes: Intraoperative and postoperative respiratory complications such barotrauma, hemodynamic instability, pneumonia, atelectasis, reintubation, self-extubation and the need for noninvasive mechanical ventilation measured in hours or days; cardiovascular responses; need for hospitalization in the intensive care unit (ICU) and length of stay (LOS) in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).
Search methods for identification of studies
Searches (see attachment) were performed in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials; MEDLINE via Ovid (1966 to present); old MEDLINE (1951 to present); and EMBASE via Ovid (January 1990 to present), without language or location restrictions. The highly sensitive Cochrane filter for randomized controlled trials was applied to the MEDLINE and EMBASE searches. Trial registers such as www.clinicaltrials.gov and the Current Controlled Clinical Trials Website (http://www.controlled-trials.com/) were also searched for ongoing trials.
Data collection and analysis
Two authors (GMCS and SAZ) independently screened all the potential studies identified and coded them as ‘retrieve’ (eligible or potentially eligible/unclear) or ‘do not retrieve’. The full-text reports/publications were then retrieved and two authors independently screened the full text and identified the studies for inclusion. Disagreements were resolved through discussion or if required consultation with a third author. Duplicates were excluded and multiple reports of the same study were collated so that each study, rather than report, is the unit of interest in the review. The selection process was recorded in appropriate detail, as set out in the complete PRISMA flow diagram [11].
The authors were contacted and additional details were requested. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or by involving a third author.
Assessment of risk of bias in the included studies
Risk of bias was assessed at study level using Cochrane’s ‘Risk of Bias’ tool [12]. Two review authors (GMCS and SAZ) independently assessed the methodologic quality of each study included and resolved their disagreements by discussion.
Data synthesis
To consider the measures of treatment effect for dichotomous outcomes, the total number of events within each randomized group were entered and the risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. For data presented in other forms, such as odds or hazard ratios, the generic variance option was used, although different effect measures (odds, risk or hazard ratios) were not combined in the same model. Mean differences were calculated for continuous outcomes measured on the same scale in different studies.
Assessment of heterogeneity
Statistical heterogeneity was evaluated by assessing forest plots and examining the I2 value, which describes the proportion of total variation across studies caused by heterogeneity rather than chance [9]. An I2 value greater than 50% was considered as the cut-off point to identify the presence of considerable heterogeneity [9].
Results
The initial search identified 1018 citations through database searches and manual searches (Fig. 1). After screening by title and abstract, full-text articles of 40 studies that were potentially eligible for inclusion in the review were obtained. A total of 25 of these were excluded due to not being randomized, presenting data in graphs, did not present data for extraction or did not respond to the PICO of this review. Following this process, fourteen studies were included in the review (Table 1).
Fig. 1.
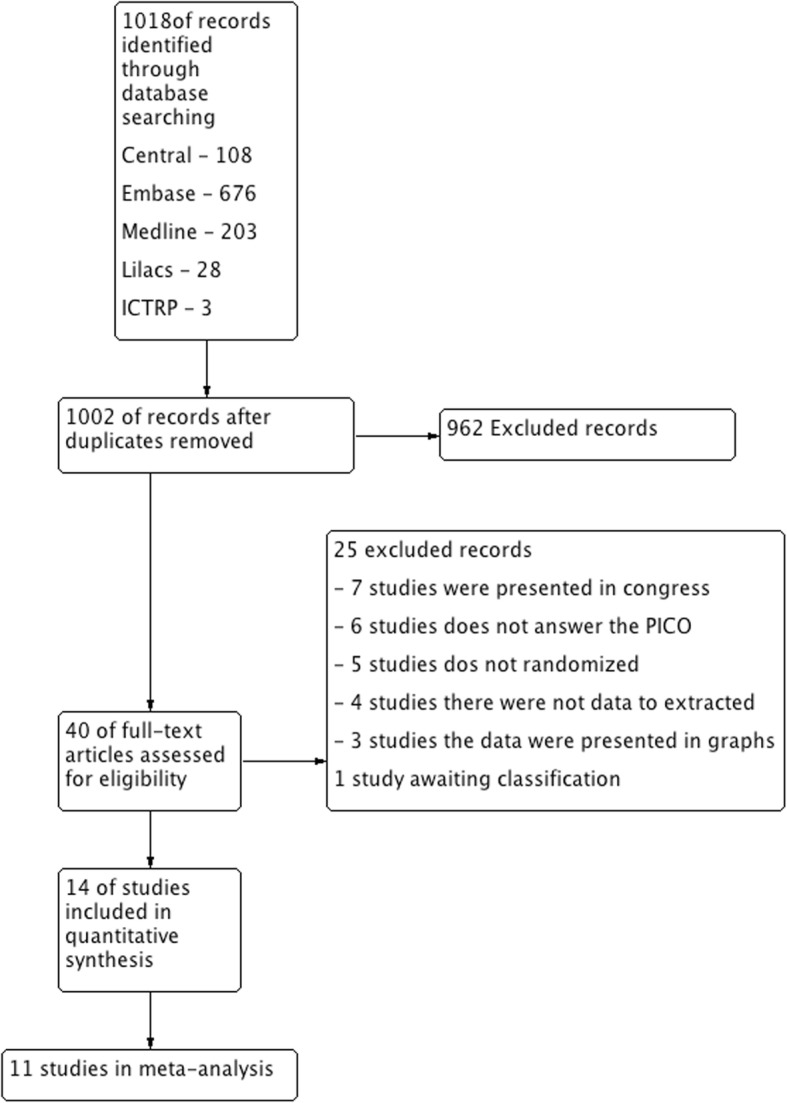
Study flow diagram
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| Study | Sample | Ventilation strategies | Intervention | Outcomes of interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltieri 2015 [13] | n = 40, BMI between 40 and 55 kg m-2 | Mode VCV, FiO2 between 40 and 60%, Vt = 6–8 ml/kg, PEEP = 5 cmH2O (except the G-intra) | Pré-group (n = 10): NPPV before surgery for 1 h | Length of stay in PACU |
| Intra group (n = 10): PEEP = 10 cmH2O throughout the surgery. | ||||
| Cadi 2008 [14] | n = 36, BMI > 35 kg m-2 | VCV: VC = 8 ml/kg; RR = 14 irpm; I:E = 1:2; FiO2 = 60%; PEEP = 5 cmH2O and ispiratory pressure to keep VC = 8 ml/kg | PCV (n = 18): I:E = 1:2; FiO2 = 60%; PEEP = 5 cmH2O and inspiratory pressure to keep VC = 8 ml/kg | Gas exchange PaO2/FiO2; |
| Pulmonary mechanics; | ||||
| Ccardiovascular responses | ||||
| Chalhoub 2007 [15] | n = 52, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | VCV: VC = 10 ml/kg; I:E = 1:4; FiO2 = 40%; RR to keep EtCO2 between 30 and 35 mmHg | Group 2 (n = 26): ARM (VCM) plus PEEP = 8 cmH2O. | Cardiovascular responses |
| VCM with pressure of 40 cmH2O for 15 s | ||||
| De Baerdemaeker 2008 [16] | n = 24, BMI > 35 kg m-2 | VCV: VC = 10 ml/kg, RR =12 irpm, I:E = 1:2, PEEP = 5 cmH2O e FiO2 = 50% | PCV (n = 12): inspiratory pressure to keep VC = 10 ml/kg and limited at 35 cmH2O, EtCO2 between 35 and 40 mmHg, PEEP = 5 cmH2O | Pulmonary mechanics; |
| Cardiovascular responses | ||||
| Defresne 2014 [17] | n = 50, BMI > 35 kg m-2 | VCV: VC = 6 ml/kg; PEEP = 10 cmH2O e RR to keep Etco2 between 4,7 e 6 Kpa. | MR (n = 25): inspiratory pressure = 40 mmHg for 40s twice, 5 min after the pneumoperitoneum and 5 min after the pneumoperitoneum plus PEEP = 10 cmH2O | Pulmonary mechanics |
| El-Sayed 2012 [18] | n = 56, BMI > 50 kg m-2 | Group 1: VCV, FiO2 = 50%; vc = 8–10 ml/kg; I:E = 1:2; PEEP = 0 cmH2O; RR to keep EtCO2 between 30 and 35 mmHg; | Group 2(n = 19): VCM of 40 cmH2O for 15 s plus PEEP = 15 cmH2O. | Gas exchange PaO2/FiO2 |
| Group 3 (n = 18): VCM of 40 cmH2O for 15 s plus PEEP = 15 cmH2O plus NPPV 12/8. | Pulmonary mechanics | |||
| Cardiovascular responses | ||||
| Intraoperative and postoperative Respiratory complications | ||||
| Futier E 2011 [19] | n = 66, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | Group 1: VCV, VC = 8 ml/kg; RR to keep PaO2 between 35 and 42 mmHg, I:E = 1:2; PEEP = 10 cmH2O e FiO2 = 50% | Group 2(n = 22): NPPV | Cardiovascular responses |
| Group 3 (n = 22): NPPV plus ARM (after intubation) | ||||
| ARM with VCM of 40 cm H2O during 40s. | ||||
| Mousa 2013 [20] | n = 30, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | PCV: FiO2 = 50%; PEEP = 5 cmH2O; inspiratory pressure to keep VC with 8 ml/kg; RR to keep EtCO2 between 35 and 40 mmHg | I:E (n = 15) = 1:1 | Pulmonary mechanics |
| Cardiovascular responses | ||||
| Reinius 2009 [21] | n = 30, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | VCV: FiO2 = 50%; PEEP = 0 cmH2O; VC = 10 ml/kg; RR = 12 irpm ou EtCO2 between 34 and 41 mmHg; I:E = 1:2 | - Group ARM plus ZEEP (n = 10) | Gas exchange PaO2/FiO2 |
| - Group MR plus PEEP = 10 cmH2O (n = 10) | Pulmonary mechanics | |||
| ARM was performed with inspiratory pressure = 55 cmH2O plus inspiratory hold of 10s, | Cardiovascular responses | |||
| Remístico P 2011 [22] | n = 30, BMI 35,6 kg m-2 | VCV: Details not described in the article | Experimental group: (n = 15): ARM with PEEP of 30 cmH2O plus inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O above PEEP, for 2 min, after pneumoperitoneum. | Cardiovascular responses |
| Souza 2009 [23] | n = 47, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | VCV: VC = 8–10 ml/kg; FiO2 = 50%; PEEP = 5 cmH2O e FR between 12 and 14 irpm. | Group ARM 10, 15 and 20 (n = 17): progressive increase of PEEP to 10, 15 and 20 cmH2O plus 40s inspiratory hold in each step for 2 min. | Gas exchange PaO2/FiO2 |
| Pulmonary mechanics | ||||
| Group ARM 30 (n = 16): PEEP of 30 cmH2O for 2 min plus inspiratory hold of 40s. | ||||
| After the ARM the PEEP was keep in 5 cmH2O. | ||||
| Sprung 2009 [24] | n = 20, BMI = > 40 kg m-2 | VCV: RR = 8 irmp (or to keep EtCO2 between 40 and 45 mmHg); VC = 8 ml/kg; PEEP = 4 cmH2O; I:E = 1:2; FiO2 = 50% | ARM (n = 8): progressive increase of PEEP to 4, 10, 15 for three cycles and after more 20 cmH2O of PEEP for 10 cycles, after the ARM the PEEP was keep in 12 cmH2O | Gas exchange PaO2/FiO2 |
| Pulmonary mechanics | ||||
| Talab 2009 [7] | n = 58, BMI between 30 and 50 kg m-2 | VCV: FiO2 = 50%; VC between 8 and 10 ml/kg; RR to keep EtCO2 between 32 and 36 mmHg; | Group VCM plus ZEEP (n = 19) | Cardiovascular responses |
| Group VCM plus PEEP = 10 cmH2O (n = 20) | Intraoperative and postoperative Respiratory complications | |||
| VCM was apply for 7–8 s after intubation. | Length of stay in PACU | |||
| The details of the VCM were not described | ||||
| Whalen 2006 [25] | n = 20, BMI > 40 kg m-2 | VCV: FiO2 = 50%, RR = 8 irpm; VC = 8 ml/kg; PEEP = 4 cmH2O; I:E = 1:2. | ARM (n = 10): progressive increase of PEEP to 4, 10, 15 for three cycles and after more 20 cmH2O of PEEP for 10 cycles. | Pulmonary mechanics |
| Intraoperative and postoperative Respiratory complications | ||||
| The number of ARM depended of the PaO2. After ARM the PEEP was keep in 12 cmH2O. |
Legends: BMI: Body Mass Index; NPPV: noninvasive positive pressure ventilation; VCM: vital capacity maneuvers; VCV: volume-controlled ventilation; PCV: Pressure-controlled ventilation; FiO2: inspired fraction of oxygen; RR: respiratory rate; Vt: tidal volume; PEEP: positive end-expiratory pressure; ZEEP: zero end-expiratory pressure; I:E: inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio; ARM: alveolar recruitment maneuvers; ETCO2: end-tidal CO2; VCM: viral capacity maneuver; PIP: peak inspiratory pressure
Risk of bias in included studies
Random sequence generation and allocation concealment were correctly described in seven studies [14, 17, 19, 20, 22, 24, 25]. In the blinding of participants and personnel domain all the studies were classified as high risk as the personnel could not be blinded. Four studies [7, 13, 17, 25] adequately described the blinding of outcome assessment. Eleven studies [7, 14–21, 24, 25] did not describe losses or exclusions which could cause imbalance between the groups. Only two studies [17, 21] employed selective reporting and while two studies [17, 25] presented other sources of bias Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
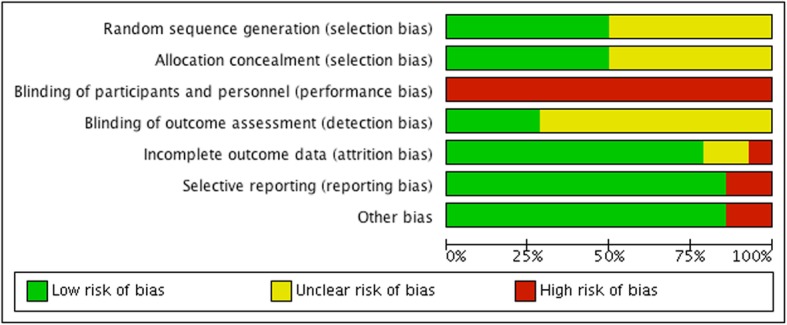
Risk of bias graph: review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies
Effects of interventions
Alveolar recruitment maneuvers versus PEEP only
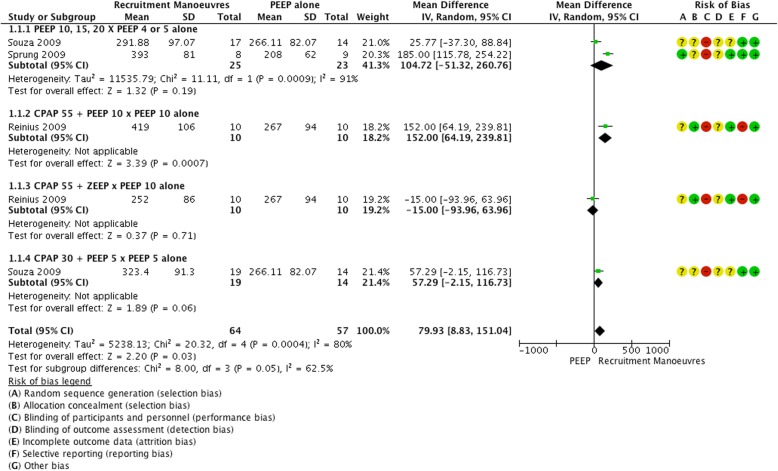
Three studies [21, 23, 24] compared alveolar recruitment maneuvers (RM) versus PEEP to evaluate intra operative gas exchange, with the mean PaO2/FiO2 ratio found to be greater in the groups that underwent RM, p = 0.03, (MD 79.93, 95% CI 8.83 to 151.04; participants = 121; studies = 5; I2 = 80%,). Figure 3 shows the comparison of three different studies, separate in four subgroups, where the best results were in favor of RM Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
Forest plot of recruitment manoeuvres x PEEP: Intra operative gas exchange - PaO2/FiO2
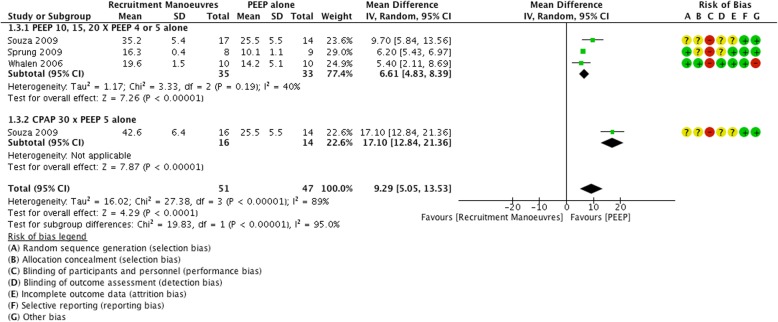
Three studies [23–25] evaluated mean airway pressures by comparing RM with progressive PEEP of 10, 15 and 20 cmH2O versus Peep of 4 or 5 cmH2O only and found that the use of PEEP without RM led to lower airway pressure, p < 0.001 (MD 9.29, 95% CI 5.05 to 13.53; participants = 98; studies = 4; I2 = 89%). Figure 4 shows the comparison of three different studies, separate in two subgroups, where the best results were in favor of PEEP when airway pressure was measured. Figure 4.
Fig. 4.
Forest plot of recruitment manoeuvres x PEEP: Mean airway pressure (cmH2O)
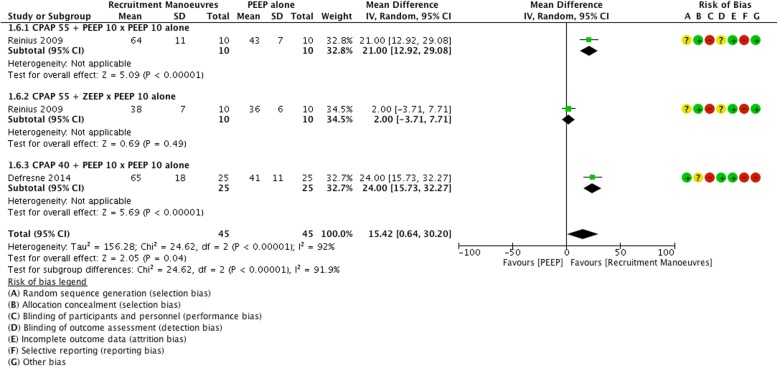
Two studies [17, 21] evaluated compliance by comparing RM with PEEP. The study by Reinius et al. [21] compared RM with 55 cmH2O CPAP plus 10 cmH2O PEEP versus 10 cmH2O of PEEP only, and identified greater compliance when using RM plus PEEP, p < 0.00001 (MD 21.00, 95% CI 12.92 to 29.08; participants = 20; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). The same study by Reinius et al. [21] also compared RM with CPAP 55 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus PEEP with 10 cmH2O, only and found no difference between the groups for compliance, p = 0.49 (MD 2.00, 95% CI − 3.71 to 7.71; participants = 20; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). The study by Defresne et al. [17] compared RM with CPAP of 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 10 cmH2O versus 10 cmH2O of PEEP only and found greater compliance when using RM plus PEEP, P < 0.00001 (MD 24.00, 95% CI 15.73 to 32.27; participants = 50; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). When all the studies were taken together, the groups receiving RM exhibited better pulmonary compliance, p < 0.04, (MD 15.42, 95% CI 0.64 to 30.20; participants = 90; studies = 3; I2 = 92%,). Figure 5 shows the comparison of two different studies, separate in three subgroups, where the best results were in favor of RM when pulmonary compliance was measured. Figure 5.
Fig. 5.
Forest plot of recruitment manoeuvres x PEEP: Compliance (ml cmH2O− 1)
Four studies [15, 19, 21, 22] evaluated mean arterial pressure. The studies by Chalhoub et al. [15]; Futier et al. [19] and Reinius et al. [21] compared RM with CPAP of 40 or 55 cmH2O versus 8 or 10 cmH2O of PEEP only and found no difference between the groups, p = 0,84, (MD 0.87, 95% CI − 3.77 to 5.52; participants = 116; studies = 3; I2 = 0%). The study by Remístico et al. [22] compared a group with RM combined with inspiratory pressure of 15 cmH2O and 30 cmH2O of PEEP versus PEEP of 5 cmH2O only, and found no difference between the mean arterial pressure of the groups, p = 0.41, (MD 4.00, 95% CI − 5.45 to 13.45; participants = 30; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). The study by Reinius et al. [21] compared a group receiving RM with CPAP of 55 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus 10 cmH2O PEEP only, and also found no difference between the mean arterial pressure of the groups, p = 0.74, (MD 2.00, 95% CI − 9.69 to 13.69; participants = 20; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). When all the studies were grouped there was no difference in mean arterial pressure between RM versus the use of PEEP without RM, p = 0.44, (MD 1.54, 95% CI − 2.39 to 5.47; participants = 166; studies = 5; I2 = 0%).
Pressure control ventilation versus volume control ventilation
Of the two included studies that evaluated this comparison [14, 16], only the study by Cadi et al. [14] evaluated the PaO2/FiO2 ratio, finding that the PCV mode achieved greater oxygenation than the VCV mode, p = 0.007, (MD 82.00, 95% CI 21.90 to 142.10; participants = 36; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). The study by De Baerdemaeker et al. [16] did not identify differences in the variables analyzed.
No differences were found between the VCV and PCV modes in the evaluation of mean airway pressure, plateau pressure, lung compliance, lung resistance and arterial pressure.
Alveolar recruitment maneuver plus ZEEP versus the same RM plus 5 or 10 cmH2O of PEEP
The study by Reinius et al. [21] compared RM with 55 cmH2O CPAP plus ZEEP versus the same RM plus 10 cmH2O of PEEP and found an improvement in oxygenation in the group with RM plus PEEP 10 cmH2O p = 0.001, (MD 167.00, 95% CI 82.40 to 251.60; participants = 20; studies = 1; I2 = 0%) and in compliance p < 0.00001, (MD 26.00, 95% CI 17.92 to 34.08; participants = 20; studies = 1; I2 = 0%) when PEEP of 10 cmH2O was used.
The study by Talab et al. [7] evaluated the length of stay (LOS) in the post- anesthesia care unit (PACU), comparing the RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O followed by PEEP 10 cmH2O and found a shorter LOS in the PACU in the RM plus PEEP group, p = 0.02, (MD -21.05, 95% CI − 38.90 to − 3.20; participants = 39; studies = 1; I2 = 0%), The same authors compared RM with 40 cmH2O CPAP plus ZEEP versus ARM with 40 cmH2O CPAP plus 5 cmH2O PEEP and found no difference between the LOS in PACU of the groups, p = 0.26, (MD -10.45, 95% CI − 28.78 to 7.88; participants = 38; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). When the two comparisons were pooled the shortest LOS in the PACU was found in the group that received RM plus PEEP, p = 0.01, (MD -15.89, 95% CI − 28.68 to − 3.10; participants = 77; studies = 2; I2 = 0%).
The study by Talab et al. [7] compared RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 10 cmH2O and found fewer patients with lamellar atelectasis in the group that received RM plus ZEEP, p = 0.007, (RR 5.22, 95% CI 1.33 to 20.55; participants = 39; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). The same author Talab et al. [7] compared RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 5 cmH2O and found no difference in lamellar atelectasis between the groups, p = 0.38, (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.41 to 9.65; participants = 38; studies = 1; I2 = 0%). When the two comparisons were pooled there was a smaller proportion of lamellar atelectasis in the group that underwent RM plus ZEEP, p = 0.03, (RR 3.45, 95% CI 1.23 to 9.71; participants = 77; studies = 2; I2 = 0%). When Talab et al. [7] evaluated RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus ZEEP versus RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 10 cmH2O, fewer patients with segmental atelectasis were found in the group that received RM plus 10 cmH2O PEEP, p = 0.009, (RR 0.29, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.74; participants = 39; studies = 1; I2 = 0%).
Talab et al. [7] also compared RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 5 cmH2O versus RM with CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 10 cmH2O and found a difference between the groups, with a lower number of patients with Lamellar atelectasis in the RM plus PEEP 5 cmH2O group, p = 0.05, (RR 2.61, 95% CI 1.00 to 6.80; participants = 39; studies = 1; I2 = 0%).
CPAP 40 plus PEEP10 versus CPAP 40 plus PEEP15
El-Sayed et al. [18] compared CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 10 cmH2O versus CPAP 40 cmH2O plus PEEP 15 cmH2O and found that CPAP plus PEEP 15 cmH2O achieved a greater PaO2/FiO2 ratio, p = 0.003, (MD 36.00, 95% CI 12.10 to 59.90; participants = 38; studies = 1; I2 = 0%) and greater lung compliance cmH2O, p = 0.0003, (MD 3.00, 95% CI 1.38 to 4.62; participants = 38; studies = 1; I2 = 0%).
Alveolar recruitment maneuver plus PEEP 10, 15 and 20 versus CPAP 30
The study by Souza et al. [23] compared the use of RM with progressive PEEP of 10, 15 and 20 cmH2O versus CPAP 30 cmH2O and found that the RM with progressive PEEP obtained lower mean airway pressures, p = 0.0003, (MD -7.40, 95% CI − 11.45 to − 3.35; participants = 33; studies = 1; I2 = 0%).
PEEP 10 versus PEEP 5
The study by Baltieri et al. [13] compared the use of PEEP 10 cmH2O versus PEEP 5 cmH2O and found no difference between the groups in LOS in the PACU, p = 0.21, (MD 36.00, 95% CI − 20.16 to 92.16; participants = 30; studies = 1; I2 = 0%).
I:E 1:1 ratio versus I:E 1:2 ratio
The study by Mousa et al. [20] evaluated the I:E 1:1 ratio versus the I:E 1:2 ratio and found that the I:E 1:1 ratio group achieved greater lung compliance than the group with a I:E 1:2 ratio, p = 0.01, (MD 4.67, 95% CI 1.06 to 8.28; participants = 30; studies = 1; I2 = 0%, low-quality evidence).
Discussion
The present systematic review evaluated different ventilatory strategies for obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery, such as: comparison between PCV and VCV; comparison of different forms of RM, different PEEP levels and comparison between I:E 1:1 ratio and I:E 2:2. Fourteen studies with a total of 574 participants were included.
Significant variability in interventions were found. This demonstrates the lack of consensus on how to ventilate obese patients undergoing surgery, corroborating a review published by Aldenkortt et al. [8]
The main finding of the present study is the evidence that obese patients receiving mechanical ventilation benefit from RM, especially when combined with PEEP, as evidenced by improvements in oxygenation and respiratory compliance. While it was observed in this systematic review that the isolated use of PEEP was more effective when higher values were used, however the best result was the combination of the RM with higher levels of PEEP. In addition to these findings, no difference was found between VCV and PCV modes of ventilation in all analyzed outcomes, corroborating another study by Aldenkortt et al. [8]. No respiratory complications or major adverse events were reported in the studies included in this review. Such findings are similar to those found by Aldenkortt et al. [8]. and Hu et al. [26]. Recent guidelines regarding mechanical ventilation of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have shown that the incidence of complications associated with diferent mechanical ventilation strategies is low [27].
There is insufficient evidence to support differences between VCV and PCV in the evaluated outcomes. While the study by Cadi et al. [14]. Showed that the pressure controlled mode led to a higher PaO2/FiO2 ratio than the volume controlled mode, the study by De Baerdemaeker et al. [16]. Did not identify a difference in PaO2 between the two modes.
Three studies [17, 24, 25] included in this review describe the performance of more than one alveolar recruitment maneuver. There is no consensus on the ideal number of alveolar recruitment maneuvers regarding frequency and repetitions, however, the use of various maneuvers with patients with ARDS is associated with decreased pulmonary shunt and increased compliance [27].
Despite the wide variety of interventions and outcomes evaluated, the present review provides some evidence that the use of PEEP effectively improves oxygenation and compliance of the respiratory system. Better results seem to be achieved, however, when it is combined with alveolar recruitment maneuvers, and the absence of adverse effects shows that it is an effective and safe strategy for obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Briel et al. [28] published a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the use of high versus low PEEP values for ARDS patients, and concluded that the use of high levels of PEEP was associated with lower hospital mortality in this group of patients. The American Thoracic Society also currently recommends the use of high levels of PEEP for patients with ARDS [27].
One study compared I:E 1:1 ratio with I:E 1:2 ratio and found that only the 1:1 ratio only improved lung compliance [20]. Few studies evaluated the use of the I:E 1:1 ratio, while some studies evaluated different inverted ratios in patients with ARDS, with conflicting results regarding its effectiveness [29–31].
Limitations
Important methodological limitations of the studies included reduced the certainty of the evidence offered by most of the included trials. Many of the trials were small and included different outcome measures, and selective outcome reporting was occasionally an issue.
The paucity of long-term follow-up data, the small sample sizes, and the heterogeneous nature of the measured outcomes limit the generalizability of the results.
Conclusions
There is evidence that alveolar recruitment maneuvers plus PEEP improve gas exchange with an increase in respiratory system compliance. The quality of such evidence is low, however.
There is no evidence to support that there is a difference between the volume and pressure controlled modes.
The various interventions assessed were shown to be safe with no major adverse events reported.
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by governmental foundation Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). We are grateful to Universidade Estadual de Ciências da Saúde de Alagoas (UNCISAL) for the institutional support. We are thankful to our colleague Dr. Alvaro Atallah who provided expertise that greatly assisted this systematic review.
Abbreviations
- ARM
Alveolar recruitment maneuvers
- BMI
Body mass index
- CI
Confidence intervals
- CPAP
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
- I:E
Inspiratory:Expiratory ratio
- ICU
Intensive care unit
- LOS
Length of stay
- MD
Mean difference
- PACU
Post-anesthesia care unit
- PCV
Pressure control ventilation
- PEEP
Positive end-expiratory pressure
- PICO
Problem, intervention, control, outcome
- RCTs
Randomized controlled trials
- RM
Recruitment maneuvers
- UNIFESP
Universidade Federal de São Paulo
- VCV
Volume control ventilation
- ZEEP
Zero end-expiratory pressure
Authors’ contributions
GMCS - corresponding author and major reseacher. GMS – statistician expert. SAZ - second researcher for data extraction. TM - methodology expert. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by governmental foundation Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) which is a government agency. The funding was used for articles translation to Portuguese. Theare were no role of the funding body in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable. All data from this systematic review were extracted from primary studies. The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research was approved by the ethics committee of the federal university of São Paulo - Unifesp - CAAE: 57099216.0.0000.5505.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
George Márcio Costa Souza, Email: georgemarcioft@gmail.com.
Gianni Mara Santos, Email: gsantos@unifesp.br.
Sandra Adriana Zimpel, Email: sandrazimpel@uol.com.br.
Tamara Melnik, Email: tameln@terra.com.br.
References
- 1.Mathus-Vliegen L, Toouli J, Fried M, Khan AG, Garisch J, Hunt R, et al. World gastroenterology organization global guidelines on obesity. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46(7):555–561. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318259bd04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Peeters A, Barendregt JJ, Willekens F, Mackenbach JP, Al Mamun A, Bonneux L, NEDCOM The Netherlands epidemiology and demography compression of morbidity research group. Obesity in adulthood and its consequences for life expectancy: a life-table analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(1):24–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-138-1-200301070-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Prospective Studies Collaboration Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet. 2009;373:1083–1096. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60318-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, et al. Bariatric surgery. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–1737. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.14.1724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Salihoglu T, Salihoglu Z, Zengin AK, Taskin M, Colakoglu N, Babazade R. The impacts of super obesity versus morbid obesity on respiratory mechanics and simple hemodynamic parameters during bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2013;23(3):279–283. doi: 10.1007/s11695-012-0783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pelosi P, Croci M, Ravagnan I, Tredici S, Pedoto A, Lissoni A, Gattinoni L. The effects of body mass on lung volumes, respiratory mechanics, and gas exchange during general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1998;87(3):654–660. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199809000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Talab HF, Zebani IA, Abdelrahman HS, Bukhari WL, Mamoun I, Ashour MA, et al. Intraoperative ventilatory strategies for prevention of pulmonar atelectasis in obese patients undergoing laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Anesth Analg. 2009;109(5):1511–1516. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181ba7945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Aldenkortt M, Lysakowski C, Elia N, Brochard L, Tramèr MR. Ventilation strategies in obese patients undergoing surgery: a quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2012;109(4):493–502. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
- 10.American Society for Matabolic and Bariatric Surgery{https://asmbs.org}. Bariatric Surgery in ClassI Obesity {accessed 21 March 2020}. Avaliable from http://asmbs.org/resources/bariatric-surgery-in-class-i-obesity.
- 11.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Higgins JPT AD, Sterne, JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: In: Higgins JPT GSe, editor: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org
- 13.Baltieri L, Santos LA, Rasera I, Montebelo MIL, Forti EMP. Use of positive pressure in pre and intraoperative of bariatric surgery and its effect on the time of extubation. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2015;65(2):130–135. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2013.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cadi P, Guenoun T, Journois D, Chevallier JM, Diehl JL, Satran D. Pressure-controlled ventilation improves oxygenation during laparoscopic obesity surgery compared with volume- controlled ventilation. Br J Anaesth. 2008;100(5):709–716. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chalhoub V, Yazigi A, Sleilaty G, Haddad F, Noun R. Madi- Jebara S, et al. effect of vital capacity manoeuves on arterial oxygenation in morbidly obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007;24(3):283–288. doi: 10.1017/S0265021506001529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Baerdemaeker LE, Van Der Herten C, Gillardin JM, Patty P, Mortier EP, Szegendi LL. Comparison of volume- controlled and pressure-controlled ventilation during laparoscopic gastric banding in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2008;18(5):680–685. doi: 10.1007/s11695-007-9376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Defresne AA, Hans GA, Goffin PJ, Bindelle SP, Amabili PJ, DeRoover AM, Poirrier JF, Brichant JF, Joris JL. Recruitment of lung volume during surgery neither affects the postoperative spirometry nor the risk of hypoxaemia after laparoscopic gastric bypass in morbidly obese patients: a randomized controlled study. Bristsh J Anaesth. 2014;113(4):501–507. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.El-Sayed KM, Tawfeek MM. Perioperative ventilatory strategies for improving arterial oxygenation and respiratory mechanics in morbidly obese patients undergoing laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Egyption J Anaesth. 2012;28:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.egja.2011.09.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Futier E, Constantin JM, Pelosi P, Chanques G, Massone A, Petit A, Kwiatkowski F, Bazin JE, Jaber S. Noninvasive ventilation and alveolar recruitment maneuver improve respiratory function during and after intubation of morbidly obese patients. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:1354–1363. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31821811ba. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mousa WF. Equal ratio ventilation (1:1) improves arterial oxygenation during laparoscopic bariatric surgery: a crossover study. Saudi J Anaesth. 2013;7(1):9–13. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.109559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Reinius H, Jonsson L, Gustafsson S, Sundbom M, Duvemoy O, Oelosi P, et al. Prevention of atelectasis in morbidly obese oatients during general anestesia and paralysis: a computerized tomography study. Anesthesiology. 2009;111(5):979–987. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181b87edb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Remístico PPJ, Araújo S, Figueiredo LC, Aquim EE, Gomes LM, Sombrio ML, Ambiel SDF. Impact of alveolar recruitment maneuver in the postoperative period of Videolaparoscopic bariatric surgery. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2011;61(2):163–176. doi: 10.1016/S0034-7094(11)70021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Souza AP, Buschpigel M, Mathias LAST, Malheiros CA, Alves VLS. Analysis of the effects of the alveolar recruitment maneuver on blood oxygenation during bariatric surgery. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2009;59(2):177–186. doi: 10.1590/S0034-70942009000200005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sprung J, Whalen FX, Comfere T, Bosnjak ZJ, Bajzer Z, Gajic O, Sarr MG, Schroeder DR, Liedl LM, Offord CP, Warner DO. Alveolar recruitment and arterial Desflurance concentration during bariatric surgery. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:120–127. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31818db6c7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Whalen FX, Gajic O, Thompson GB, Kenfrick ML, Que FL, Williams BA, et al. The effects of the alveolar recruitment maneuver and positive end-expiratory pressure on arterial oxygenation during laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Anesth Analg. 2006;102(1):298–305. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000183655.57275.7a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hu XY. Effective ventilation strategies for obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery a literature review: a literature review. AANA J. 2016;84(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fan E, Del Sorbo L, Goligher EC, Hodgson CL, Munshi L, Walkey AJ, Adhikari NKJ, Amato MBP, Branson R, Brower RG e col. An official American Thoracic Society/European Society of Intensive Care Medicine/Society of Critical Care Medicine clinical practice guideline: mechanical ventilation in adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med; 2017 195(9): 1253–1263. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Briel M, Meade M, Mercat A, Brower RG, Talmor D, Walter SD, Slutsky AS, Pullenayegum E, Zhou Q, Cook D, et al. Higher vs lower positive end-expiratory pressure in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010;303:865–873. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lessard MR, Guérot E, Lorino H, Lemaire F, Brochard L. Effects of pressure-controlled with different I:E ratios versus volume-controlled ventilation on respiratory mechanics, gas exchange, and hemodynamics in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesıology. 1994;80:983–991. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199405000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang CC, Shih MJ, Tsai YH, Chang YC, Tsao TC, Hsu KH. Effects of inverse ratio ventilation versus positive end- expiratory pressure on gas exchange and gastric intramucosal PCO2 and pH under constant mean airway pressure in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesiology. 2001;95:1182–1188. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200111000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gurevitch MJ, Van Dyke J, Young ES, Jackson K. Improved oxygenation and lower peak airway pressure in severe adult respiratory distress syndrome: treatment with inverse ratio ventilation. Chest. 1986;89:211. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable. All data from this systematic review were extracted from primary studies. The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.