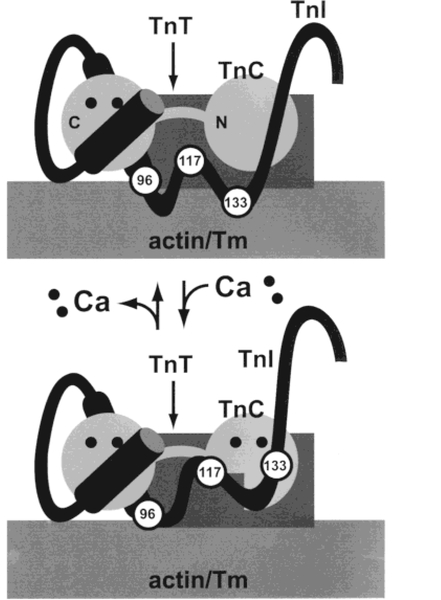
Figure 4:
Structural changes in TnI upon binding of Ca2+ to the regulatory sites of TnC. Schematic drawing illustrating a proposed Ca2+-sensitive “hinge” near the middle of the TnI polypeptide chain. In the absence of Ca2+ (top), the inhibitory region (residues 96–117) and a second actin-binding site (region near residue 133) of TnI interact with actin–Tm. Binding of Ca2+ to the N-terminal, regulatory sites of TnC (bottom) exposes a hydrophobic pocket in TnC’s N-terminal domain. TnI residues 117–133 interact with the newly exposed hydrophobic pocket of TnC, moving the C-terminal part of TnI away from actin–Tm. The environment of the AEDANS label on TnI residue 96 does not change significantly when Ca2+ binds to the regulatory sites of TnC, but the side chain of the AEDANS label on TnI residue 117 becomes less flexible as it moves toward the hydrophobic pocket of TnC.