Figure 8.
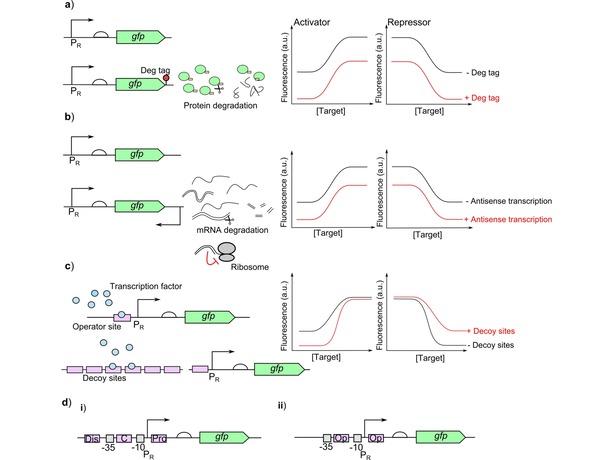
Approaches to reduce leaky expression: a) Degradation tags (Deg tags) can be used for post‐translational reduction of leaky expression. Degradation tags increase the degradation of the reporter protein and reduce the levels within the cells. The strength of the degradation tag will determine the reduction in the levels of the reporter protein.8, 61 The two curves show the change in the response curve with a degradation tag (+ Deg tag) or without (− Deg tag) for activators and repressors. b) A downstream promoter placed on the non‐coding strand can be used to produce a complementary RNA to the mRNA to generate a double stranded complex which is degraded or blocks the ribosome to prevent translation. The level of mRNA prevented from being used in translation is controlled by the level of complementary RNA which can be altered by changing the strength of the promoter used to express the complementary RNA.66 The two curves show the change in the response curve with antisense transcription (+ Antisense transcription) or without (− Antisense transcription) for activators and repressors. c) Decoy sites titrate the binding of the transcription factor away from the responsive promoter (PR). For activator systems this can reduce leakiness by preventing binding of the transcription factor in the absence of target.8, 67 Whilst for repressors this can be used to reduce the amount of effective repressor. The two curves show the change in the response curve with decoy sites (+ Decoy sites) or without (− Decoy sites) for activators and repressors. d) For repressors the position and number of operator sites can be altered to improve the efficiency of the repressor to reduce leaky expression. i) There are three possible sites for the where the operator can be. First the core site (C) is most efficient and its efficiency is increased when the binding site overlaps with either the −35 or −10 regions.59 Second is the proximal site (Pro) downstream of the transcription start site where the repressor can act as a physical block to the polymerase followed by the distal site (Dis).68 ii) If the initial operator site (Op) cannot provide enough repression then an additional site can be added downstream to act as a physical ‘roadblock’.69
