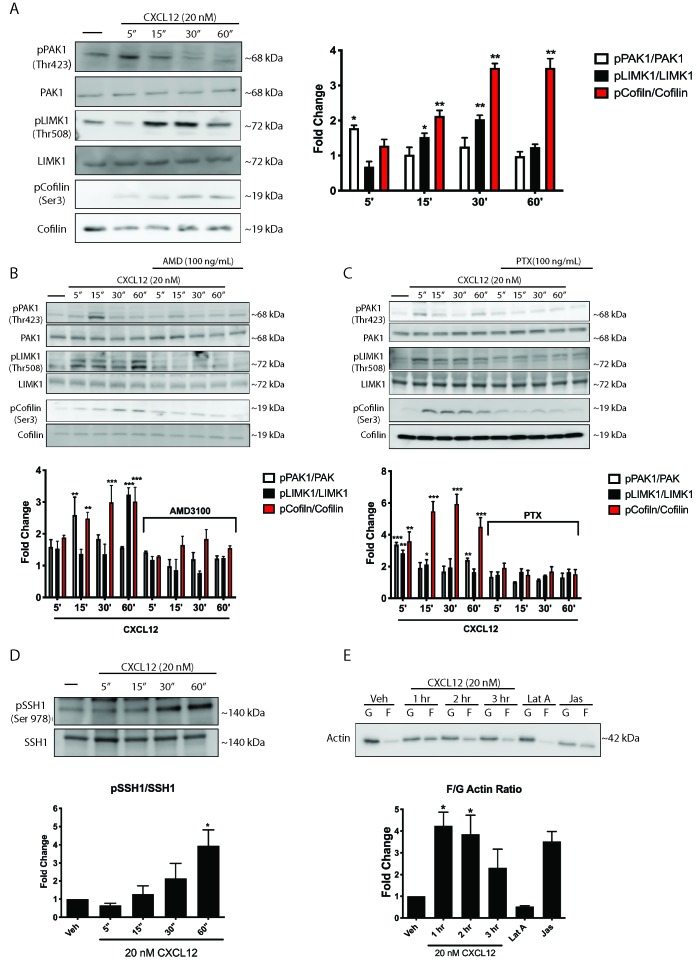
Figure 5. CXCL12 phosphorylates downstream mediators of the Rac1 pathway and results in changes to actin polymerization in cortical neurons.
(A) Cultured cortical neurons (21 DIV) were exposed to CXCL12 (20 nM) for the indicated time points and the phosphorylation status of PAK1, LIMK1, and cofilin was examined. CXCL12 treatment resulted in a time-dependent increase in the phosphorylation of all three proteins. N = 3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B) Pretreatment with AMD3100 (100 ng/mL; 20 min) blocked CXCL12-induced phosphorylation of Rac1 downstream mediators. N = 3, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (C) Inhibition of Gαi signaling (via PTX) blocked the ability of CXCL12 to phosphorylate Rac1 downstream mediators. N = 3, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (D) Following treatment with CXCL12, the protein phosphatase SSH1 is phosphorylated (and inactivated) in a time-dependent manner. N = 3, *p<0.05. (E) Separation of F and G-actin in cortical neurons revealed a shift in favor of F-actin following CXCL12 treatment. Latrunculin A (5 μM, 2 hr), a potent actin polymerization inhibitor, and jaspakinolide (5 μM, 2 hr), an inducer of actin polymerization, were used as internal controls for the assay. N = 3; *p<0.05.