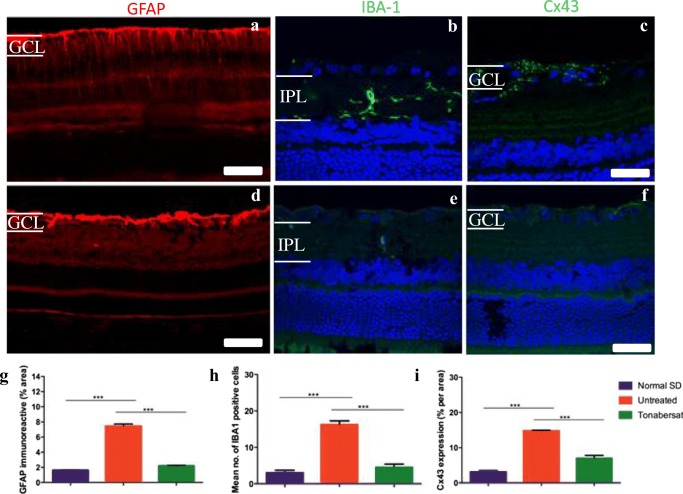
Fig. 10.
Immunohistochemical labelling in tonabersat-treated and vehicle-treated hyperglycemic rats at 8 weeks of age. GFAP labelling was intense in the GCL, in which astrocytes are resent in areas around microaneurysms in the hyperglycemic rat retina, extending from the nerve fiber layer to the ONL indicating Müller cell activation (a). There was abnormally high Iba-1 labelling in the hyperglycemic retina (b) in the IPL in which cells with enlarged soma and numerous elongated branches were present and Connexin43 labelling was abnormally high in the GCL of the untreated animals (c). Hyperglycemic rats that had been fed daily with tonabersat for 14 days had reduced inflammation as evident by labelling of all three markers (d-f). Quantification of the results in g-i shows that all three markers, GFAP, Connexin43 and Iba-1 were significantly higher in vehicle-treated rats compared to undamaged control retina and tonabersat treatment resulted in significantly reduced labeling at 8 weeks, and significantly less than untreated rat retina levels. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Significant values in comparison with results from the untreated group are indicated with asterisks: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Scale bars = 100 μm