Abstract
Organ failure manifests severe symptoms affecting the whole body that may cause death. However, the number of organ donors is not enough for patients requiring transplantation worldwide. Illegal transplantation is also sometimes conducted. To help address this concern, primary hepatocytes are clinically transplanted in the liver. However, donor shortage and host rejection via instant blood-mediated inflammatory reactions are worrisome. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells have been developed as an alternative treatment. Recently, organoid technology has been developed to investigate the pathology and mechanism of organoids in cultures. Organoids can be transplanted with vascularization and connected to host blood vessels, and functionally mature better in vivo than in vitro. Hepatic organoids improve pathology in liver disease models. In this review, we introduce induced pluripotent stem cell- and organoid-based therapies against liver diseases considering present and future perspectives.
Keywords: Stem cell therapy, liver regeneration
Introduction
Liver tissues can regenerate on being injured. Acute liver failure has different etiologies, including drug overdose, viral infection, ischemia, etc., and has a high mortality rate1. In contrast, chronic liver injury results from viral infection, alcoholism, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, autoimmune disorders, metabolic diseases, and promotes liver fibrosis2. Although the liver has considerable regenerative potential, it cannot regenerate when there is chronic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Early fibrosis can be reversible, whereas cirrhosis is irreversible. In 2012, cirrhosis was the 14th leading cause of death worldwide3. Moreover, it can cause hepatocellular carcinoma, which is the most common metastatic liver cancer. Organ transplantation is the only treatment option for both acute liver failure and end-stage liver disease. Transplantation increases the chance of survival in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ALF) grades 2 and 34. Another report showed that the hospital survival rate of patients with ALF who underwent transplantation increased from 16.7% to 62.2%5.
Progress of Organ Transplantation
Organ transplantation is the only treatment option for the heart, kidney, and liver at the terminal state of organ failure. Although the number of patients on the waiting list for organ transplantation continues to increase, the supply of transplantable organs cannot sufficiently meet the demand. Illegal transplantation may be performed in 10% of all patients to satisfy a large demand 6. One reason is that many deceased organs are not transplantable because the donors are high risk. For example, the donor was declared dead based on cardiovascular criteria, as opposed to brainstem death donors, or the donor was elderly with multiple comorbidities (extended criteria donors)7. In addition, over about 30 years, there has been no advancement in the methods of organ preservation. Organs are usually stored in an icebox, called static cold storage (SCS), to slow down the metabolism. However, when the organ is transplanted, ischemia-reperfusion generates reactive oxygen species, which damage the transplanted organ. To resolve this, machine perfusion was developed, and the first randomized controlled trial was performed7,8. This novel technique increases the duration of organ storage and maintains the physiological function of the organ7,9,10. Compared with SCS, machine perfusion increases the storage life of transplantable organs. Moreover, an inadequate number of donors is predicted even by using machine perfusion.
Hepatocyte Transplantation
An alternative approach to organ transplantation is transplantation of hepatocytes. Hepatocytes are transplanted because they can repair and replace the host liver. They are obtained via patients autopsy then cryoprotected11–16. Transplantation of hepatocytes is optimal for liver tissue; however, donor shortages and instant blood-mediated inflammatory reaction (IBMIR) are difficulties faced by medical professionals during hepatocyte transplantation17,18. IBMIR recognizes transplanted hepatocytes and rejects them through the activation of both complement and coagulation pathways18. Moreover, hepatocytes have low viability and little proliferation capability in cultures despite recent improvement in culture methods19. Cryopreservation tends to be deleterious in viability, attachment, and engraftment20. Despite their functionality, hepatocytes show low engraftment and are difficult to preserve, which is a matter of concern.
Somatic Stem Cell Transplantation
As an alternative cell transplantation, several types of stem cells have been reported as resources to restore liver functions21. Bone marrow-derived cells differentiate into hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs)22. Several studies have proven the feasibility of HSCs, MSCs, and EPCs in restoring hepatic functions in liver injury models23–26. MSCs are beneficial for transplantation. They can be obtained from many tissues including bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, and placenta, and are easily cultured ex vivo 27. Moreover, they have immunomodulatory properties28–30. In fact, the safety and short-term efficacy of transplantation of bone marrow-derived MSCs was reported to significantly improve Child–Pugh and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scores in 20 patients31. In total, 40 registered trials targeting liver cirrhosis or acute liver diseases have used different types of MSCs32. However, the results of most of these trials showed only temporary effects and need to be further investigated with large cohorts31. Furthermore, MSCs cannot reconstitute the host liver.
Pluripotent Stem Cell Transplantation
Embryonic stem (ES) cells are pluripotent and can differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. They demonstrate mature hepatocyte-like properties31. ES cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells contribute to liver repair by cell replacement33,34. The generation of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by Takahashi and Yamanaka35 has resulted in the expansion of iPS cell-based research. Diverse types of cells in the body are differentiated from iPS cells, and each cell shows specific morphology and gene and protein marker expressions and functions36.
Research in clinical applications such as cell replacement, disease model or disease-specific iPS cell model (genetic mutation), and drug screening is progressing. Autologous transplantation of iPS cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium was performed for treating neovascular age-related macular degeneration in the eyes, and no serious side effect was reported at 25 months of follow-up in one patient37. Moreover, a clinical trial was started for Parkinson’s disease. In 2018, Kikuchi et al. implanted 2.4 million dopamine precursor cells into the brain of a patient with Parkinson’s disease. They reported that the transplanted dopamine precursor cells were functional in the primate brain model of Parkinson’s disease38. iPS-based clinical application has progressed to confirm its safety and efficacy.
In a basic research study, transplantation of human iPS cell-derived hepatocyte-like cell sheets was reported39. This sheet was made using temperature-responsive culture dishes, which is a scaffoldless technology with clinical applications39,40. Sheet transplantation ameliorates the lethal acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice39. Furthermore, recently, iPS cells have been reported to generate liver-specific endothelial (sinusoidal) cells and stellate cells41. Moreover, liver parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells can be induced from iPS cells in two-dimensional cultures. The differentiation of ES or iPS cells to hepatocytes in vitro is successful and iPS-hepatocyte like cells show therapeutic effect in vivo 39. However, two-dimensional hepatocytes cannot be produced in sufficient numbers, and are not sufficient to reconstitute the liver, which is a complex and large tissue with different cell types.
Functional Three-Dimensional Organoids
The liver is a complex tissue mainly composed of hepatocytes, liver sinusoidal cells, stellate cells, and Kupffer cells and has different functions, such as the production of bile, albumin, cholesterol, and immune factors; glucose storage and release; processing of hemoglobin; and clearance of ammonia and bilirubin. The other organs also have several functions. Therefore, to generate multifunctional tissues, such as liver tissues, three-dimensional (3D) sphere or organoid technology has been developed.
Recent advances show the self-organization of neural cells into multiple layers in the eyes and brain42,43. This suggests that complex tissues can be reproduced using organoids. However, these organoids are similar to fetal organs but not to adult organs44. Functional and mature organoids are preferable for organ replacement. Novel techniques permit expansion of hepatocytes in long-term culture embedded in Matrigel. Some growth factors or TNF-α enable proliferation of hepatocyte organoids in vitro and the repopulation of human hepatocytes after engraftment into a liver injury mouse model45,46.
Another interesting topic of research is organ-on-a-chip technology. This technology enables moderate perfusion and organ–organ interactions in a microfluidic device47. Primary human hepatocytes form microtissues with hepatic functions such as albumin secretion and metabolic activity48.
To create a complex organ system, researchers have tried to combine organoids with different organs, such as vasculature and nerves49,50. One of the breakthroughs is the generation of vascularized organoids. Takebe et al. created the vascularized and functional human liver bud (LB) from human iPS cells50–52. iPS cell-derived hepatic cells self-organize into 3D iPS-LB by recapitulating interactions during organogenesis with endothelial (human umbilical vein endothelial) and mesenchymal (mesenchymal stem) cells. In 2017, three types of cells, hepatic endoderm, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells, were successfully differentiated from iPS cells and self-organized into LB52. Human endothelial cells in iPS-LB become functional blood vessels when connected to the host vessels. Although iPS-LB resembles fetal liver tissue in vivo, LB matures after in vivo transplantation and blood perfusion into LB to escape hypoxia50,52,53. Moreover, gene expressions in 3D culture are different to those in 2D culture, and gene expressions in the former are similar to those in fetal hepatocytes53. A mouse model with lethal liver failure could be treated by transplanting iPS-LB50. This demonstrates the generation of a functional human organ-like tissue from iPS cells. Its effects have spread further. This organ bud formation is also driven by mesenchymal cells from other organs such as intestines, lungs, heart, kidneys, and brain, and even cancer cells51. Therefore, this universal technology is useful for investigating the pathology and mechanism of various diseases in each organ. The organ bud is also a potential therapeutic option against some diseases. Moreover, the culture system is continuously advancing, thus progressing from cells to complex organoids (Table 1)44. Specially, organoid technology is progressed by modifying the medium, scaffold, and types of mixed cells. Liver organoid growth is desired in vitro because the liver is a large tissue in the body. Many researchers have partially achieved in vitro growth of hepatocytes since 197645,46,50,54. Advances in organoid culture could lead to ex vivo hepatocyte growth, which may be sufficient for the replacement of a host liver. However, there are some hurdles such as low engraftment and high costs to accomplish clinical applications55.
Table 1.
Comparison of culture and transplantation properties of each discussed method to produce liver tissue.
| Cell | Cell sheet | Organ-on-chip | 3D organoid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation method | Obtained from donor; culture and/or differentiation on coating dish | Differentiation on temperature-responsive culture dishes | Cultured in chambers | Cultured in or on Matrigel or matrix-free |
| Cell proliferation and expansion | Almost none | Almost none | Proliferate but limited in size | Proliferate and expand |
| Maturation | High | High | Low maturation | Low but mature in vivo |
| Technical accessibility | Easy | Easy | Hard | Relatively easy |
| Vascularization | Absent | Absent | Present | Present |
| Perfusion | Absent | Absent | Present | Absent |
| Transplantation | Easy | Easy | Hard (or impossible) | Relatively easy |
3D: three dimensional.
Conclusion and Perspectives
iPS cell-based research and organoid technology have rapidly advanced and aimed at the reconstitution of organs in the past decade (Figure 1). Most recently, several types of organoids have been transplanted to mature or to create a disease model in vivo, even if they are not intended for therapy56–58. Organoid technology is a powerful tool for the establishment of disease models and drug screening. In addition, iPS cell-derived hepatocytes and hepatic organoids are beneficial in the field of regenerative medicine50,52,59. An organoid is particularly expected to become a functional organ in the host tissue because it is more complex and functional than a single cell population. In the liver, mass production of organoids is essential for treating chronic fibrosis and cirrhosis because most liver tissues cannot regenerate under these conditions, although the recent iPS-LB transplantation method can treat acute liver injury. Perhaps one of the solutions to generating a more functional organoid in vitro is the combination of organoid technologies and perfusion by organs-on-a-chip to reveal the complex pathology and mechanisms60. Some technologies can concertedly accelerate organoid growth and maturation for clinical applications.
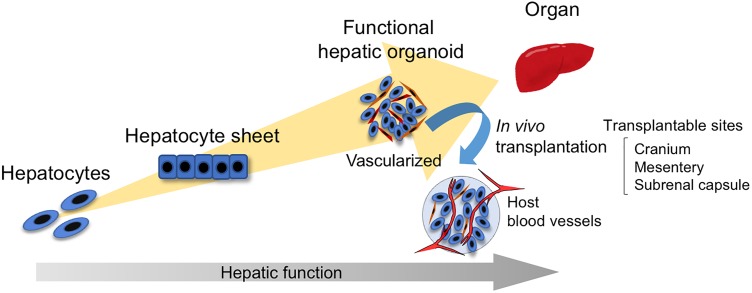
Figure 1.
Overview of the culture process from cell to organ. In two-dimensional cultures, primary hepatocytes, embryonic stem (ES), or induced-pluripotent stem (iPS)-hepatocyte-like cells and iPS-hepatocyte-like cell sheets are developed. In three-dimensional cultures, the functional and vascularized organoid is advanced, and transplantation helps achieve maturation in vivo by blood perfusion.
Footnotes
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was partly supported by Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under Grant Number 18bm0304002h0006.
ORCID iD: Yoshiki Kuse  https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8484-7265
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8484-7265
References
- 1. O’Grady JG. Acute liver failure. Postgrad Med J. 2005;81(953):148–154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Canbay A, Friedman S, Gores GJ. Apoptosis: the nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology. 2004;39(2):273–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Arroyo V, Moreau R, Kamath PS, Jalan R, Ginès P, Nevens F, Fernández J, To U, García-Tsao G, Schnabl B. Acute-on-chronic liver failure in cirrhosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2:16041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bernal W, Hyyrylainen A, Gera A, Audimoolam VK, McPhail MJW, Auzinger G, Rela M, Heaton N, O’Grady JG, Wendon J, Williams R. Lessons from look-back in acute liver failure? A single centre experience of 3300 patients. J Hepatol. 2013;59(1):74–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Delmonico FL. The implications of Istanbul Declaration on organ trafficking and transplant tourism. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009;14(2):116–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Nasralla D, Coussios CC, Mergental H, Akhtar MZ, Butler AJ, Ceresa CDL, Chiocchia V, Dutton SJ, García-Valdecasas JC, Heaton N, Imber C, et al. A randomized trial of normothermic preservation in liver transplantation. Nature. 2018;557(7703):50–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Ravikumar R, Jassem W, Mergental H, Heaton N, Mirza D, Perera MTPR, Quaglia A, Holroyd D, Vogel T, Coussios CC, Friend PJ. Liver transplantation after ex vivo normothermic machine preservation: a phase 1 (First-in-Man) Clinical Trial. Am J Transplant. 2016;16(6):1779–1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Xu H, Berendsen T, Kim K, Soto-Gutiérrez A, Bertheium F, Yarmush ML, Hertl M. Excorporeal normothermic machine perfusion resuscitates pig DCD livers with extended warm ischemia. J Surg Res. 2012;173(2):e83–e88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Brockmann J, Reddy S, Coussios C, Pigott D, Guirriero D, Hughes D, Morovat A, Roy D, Winter L, Friend PJ. Normothermic perfusion: a new paradigm for organ preservation. Ann Surg. 2009;250(1):1–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Katenz E, Vondran FWR, Schwartlander R, Pless G, Gong X, Cheng X, Neuhaus P, Sauer IM. Cryopreservation of primary human hepatocytes: the benefit of trehalose as an additional cryoprotective agent. Liver Transplant. 2007;13(1):38–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Fausto N, Campbell JS, Riehle KJ. Liver regeneration. Hepatology. 2006;43(2 Suppl 1):S45–S53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Theise ND, Nimmakayalu M, Gardner R, Illei PB, Morgan G, Teperman L, Henegariu O, Krause DS. Liver from bone marrow in humans. Hepatology. 2000;32(1):11–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Alison MR, Poulsom R, Jeffery R, Dhillon AP, Quaglia A, Jacob J, Novelli M, Prentice G, Williamson J, Wright NA. Hepatocytes from non-hepatic adult stem cells. Nature. 2000;406(6793):257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. Liver regeneration. Science. 1997;276(5309):60–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Gramignoli R, Vosough M, Kannisto K, Srinivasan RC, Strom SC. Clinical hepatocyte transplantation: practical limits and possible solutions. Eur Surg Res. 2015;54(3–4):162–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Baptista PM, Moran E, Vyas D, Shupe T, Soker S. Liver regeneration and bioengineering In: Orlando G, Lerut JP, Soker S, Stratta RJ, eds. Regenerative Medicine Applications in Organ Transplantation. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier; 2014:391–400. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Squires RH, Fox IJ, Soltys KA, Squires JE, Strom SC, McKiernan P, Soto-Gutierrez A. Clinical hepatocyte transplantation: what is next? Curr Transplant Reports. 2017;4(4):280–289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Levy G, Bomze D, Heinz S, Ramachandran SD, Noerenberg A, Cohen M, Shibolet O, Sklan E, Braspenning J, Nahmias Y. Long-term culture and expansion of primary human hepatocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(12):1264–1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Terry C, Bailey M, Mitry RR, Lehec SC, Dhawan A, Hughes RD. Analysis of the effects of cryopreservation on rat hepatocytes using SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Cell Transplant. 2006;15(1):35–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Zhang Z, Wang FS. Stem cell therapies for liver failure and cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2013;59(1):183–185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kwak KA, Cho HJ, Yang JY, Park YS. Current perspectives regarding stem cell-based therapy for liver cirrhosis. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;2018:1–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Nakamura T, Torimura T, Sakamoto M, Hashimoto O, Taniguchi E, Inoue K, Sakata R, Kumashiro R, Murohara T, Ueno T, Sata M. Significance and therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation in a cirrhotic liver rat model. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(1):91–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fang B, Shi M, Liao L, Yang S, Liu Y, Zhao RC. Systemic infusion of FLK1(+) mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Transplantation. 2004;78(1):83–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Abdel Aziz MT, Atta HM, Mahfouz S, Fouad HH, Roshdy NK, Ahmed HH, Rashed LA, Sabry D, Hassouna AA, Hasan NM. Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental liver fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2007;40(12):893–899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Sakaida I, Terai S, Yamamoto N, Aoyama K, Ishikawa T, Nishina H, Okita K. Transplantation of bone marrow cells reduces CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1304–1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Klimczak A, Kozlowska U. Mesenchymal stromal cells and tissue-specific progenitor cells: their role in tissue homeostasis. Stem Cells Int. 2016:4285215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, Giunti D, Cappiello V, Cazzanti F, Risso M, Gualandi F, Mancardi GL, Pistoia V, Uccelli A. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367–372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Zhang B, Liu R, Shi D, Liu X, Chen Y, Dou X, Zhu X, Lu C, Liang W, Liao L, Zenke M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce mature dendritic cells into a novel Jagged-2-dependent regulatory dendritic cell population. Blood. 2009;113(1):46–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815–1822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Amer MEM, El-Sayed SZ, El-Kheir WA, Gabr H, Gomaa AA, El-Noomani N, Hegazy M. Clinical and laboratory evaluation of patients with end-stage liver cell failure injected with bone marrow-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(10):936–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kojima Y, Kawata Y, Tsuchiya A, Ikarashi S, Seino S, Terai S, Watanabe Y. Clinical trials using mesenchymal stem cells in liver diseases and inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Regen. 2017;37:16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Tolosa L, Caron J, Hannoun Z, Antoni M, López S, Burks D, Castell JV, Weber A, Gomez-Lechon M-J, Dubart-Kupperschmitt A. Transplantation of hESC-derived hepatocytes protects mice from liver injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Woo DH, Kim SK, Lim HJ, Heo J, Park HS, Kang GY, Kim SE, You HJ, Hoeppner DJ, Kim Y, Kwon H, et al. Direct and indirect contribution of human embryonic stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells to liver repair in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(3):602–611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663–676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Nishikawa S, Goldstein RA, Nierras CR. The promise of human induced pluripotent stem cells for research and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(9):725–729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Mandai M, Kurimoto Y, Takahashi M. Autologous induced stem-cell-derived retinal cells for macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(8):792–793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Kikuchi T, Morizane A, Doi D, Magotani H, Onoe H, Hayashi T, Mizuma H, Takara S, Takahashi R, Inoue H, Morita S, et al. Human iPS cell-derived dopaminergic neurons function in a primate Parkinson’s disease model. Nature. 2017;548(7669):592–596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Okamoto R, Nagamoto Y, Takayama K, Mizuguchi H, Sakurai F, Kawabata K, Tachibana M, Ohashi K. Transplantation of a human iPSC-derived hepatocyte sheet increases survival in mice with acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2016;64(5):1068–1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Elloumi-Hannachi I, Yamato M, Okano T. Cell sheet engineering: a unique nanotechnology for scaffold-free tissue reconstruction with clinical applications in regenerative medicine. J Intern Med. 2010;267(1):54–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Koui Y, Kido T, Ito T, Oyama H, Chen SW, Katou Y, Shirahige K, Miyajima A. An in vitro human liver model by iPSC-derived parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9(2):490–498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Eiraku M, Takata N, Ishibashi H, Kawada M, Sakakura E, Okuda S, Sekiguchi K, Adachi T, Sasai Y. Self-organizing optic-cup morphogenesis in three-dimensional culture. Nature. 2011;472(7341):51–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Kang E, Christian KM, Hadiono C, Chickering M, Hammack C, Ogden SC, Zhang C, Maher BJ, Jeang W, Ming G, Berg DA, et al. Brain-region-specific organoids using mini-bioreactors for modeling ZIKV exposure. Cell. 2016;165(5):1238–1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Liu C, Oikonomopoulos A, Sayed N, Wu JC. Modeling human diseases with induced pluripotent stem cells: from 2D to 3D and beyond. Development. 2018;145(5):dev156166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Peng WC, Logan CY, Fish M, Anbarchian T, Aguisanda F, Álvarez-Varela A, Wu P, Jin Y, Zhu J, Li B, Grompe M, et al. Inflammatory cytokine TNFα promotes the long-term expansion of primary hepatocytes in 3D culture. Cell. 2018;175(6):1607–1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Hu H, Gehart H, Artegiani B, LÖpez-Iglesias C, Dekkers F, Basak O, van Es J, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Begthel H, Korving J, et al. Long-term expansion of functional mouse and human hepatocytes as 3D organoids. Cell. 2018;175(6):1591–1606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, Wheeler S, Taylor DL, Stolz DB, Griffith L, Wells A. Liver organ on a chip. Exp Cell Res. 2018;363(1):15–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Schepers A, Li C, Chhabra A, Seney BT, Bhatia S. Engineering a perfusable 3D human liver platform from iPS cells. Lab Chip. 2016;16(14):2644–2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Workman MJ, Mahe MM, Trisno S, Poling HM, Watson CL, Sundaram N, Chang C, Schiesser J, Aubert P, Stanley EG, Elefanty AG, et al. Engineered human pluripotent-stem-cell-derived intestinal tissues with a functional enteric nervous system. Nat Med. 2017;23(1):49–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Takebe T, Sekine K, Enomura M, Koike H, Kimura M, Ogaeri T, Zhang R-R, Ueno Y, Zheng Y-W, Koike N, Aoyama S, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013;499(7459):481–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Takebe T, Enomura M, Yoshizawa E, Kimura M, Koike H, Ueno Y, Matsuzaki T, Yamazaki T, Toyohara T, Osafune K, Nakauchi H, et al. Vascularized and complex organ buds from diverse tissues via mesenchymal cell-driven condensation. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(5):556–565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Takebe T, Sekine K, Kimura M, Yoshizawa E, Ayano S, Koido M, Funayama S, Nakanishi N, Hisai T, Kobayashi T, Kasai T, et al. Massive and reproducible production of liver buds entirely from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017;21(10):2661–2670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Camp JG, Sekine K, Gerber T, Loeffler-Wirth H, Binder H, Gac M, Kanton S, Kageyama J, Damm G, Seehofer D, Belicova L, et al. Multilineage communication regulates human liver bud development from pluripotency. Nature. 2017;546(7659):533–538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Mitaka T. The current status of primary hepatocyte culture. Int J Exp Pathol. 1998;79:393–409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Huch M, Knoblich JA, Lutolf MP, Martinez-Arias A. The hope and the hype of organoid research. Development. 2017;144(6):938–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Daviaud N, Friedel RH, Zou H. Vascularization and engraftment of transplanted human cerebral organoids in mouse cortex. eNeuro. 2018;5(6). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Wimmer RA, Leopoldi A, Aichinger M, Wick N, Hantusch B, Novatchkova M, Taubenschmid J, Hämmerle M, Esk C, Bagley JA, Lindenhofer D, et al. Human blood vessel organoids as a model of diabetic vasculopathy. Nature. 2019;565(7740):505–510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Mansour AA, Gonçalves JT, Bloyd CW, Li H, Fernandes S, Quang D, Johnston S, Parylak SL, Jin X, Gage FH. An in vivo model of functional and vascularized human brain organoids. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36(5):432–441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Nie YZ, Zheng YW, Ogawa M, Miyagi E, Taniguchi H. Human liver organoids generated with single donor-derived multiple cells rescue mice from acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Takebe T, Zhang B, Radisic M. Synergistic engineering: organoids meet organs-on-a-chip. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(3):297–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]