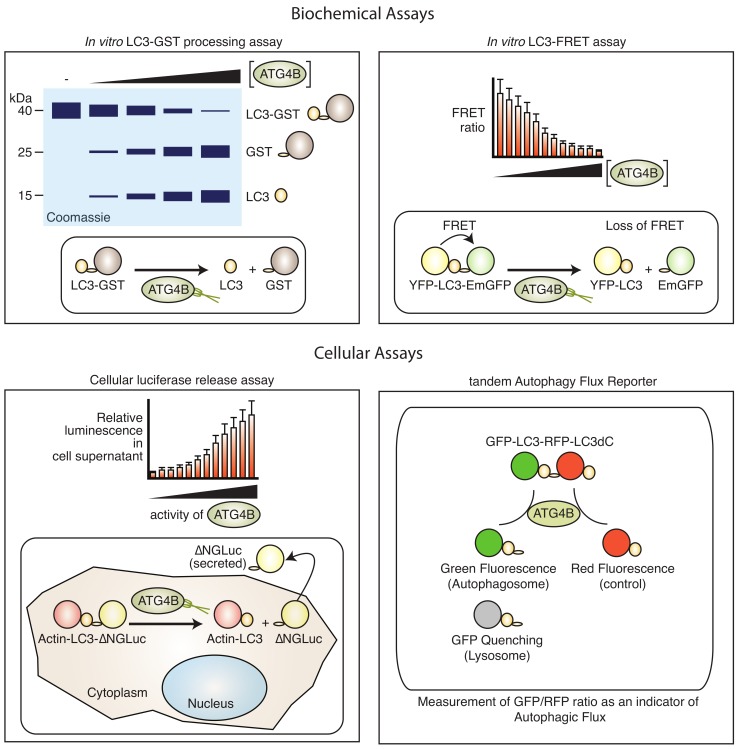
Figure 3.
Biochemical and cell-based assays to monitor ATG4B activity. Biochemical assays such as the in vitro GST–LC3 processing assay (top left) that relies on poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis are often used to monitor cleavage of a LC3–GST pseudo-substrate, but are not suitable for high-throughput screening applications. The LC3–FRET assay (top right) has been used in large-scale screening applications in vitro. The luciferase release assay (bottom left) that relies on ATG4B-dependent release of an N-termially truncated Gaussia luciferase (ΔNGLuc) enzyme and export into supernatants of cells is suitable for cell-based high-throughput screening. The tandem autophagy flux reporter (bottom right) that monitors ATG4B-dependent cleavage of a tandem GFP–LC3–RFP–LC3dC (C-terminal truncation) is suitable for cell-based high-content screening and in vivo. For more detail on each assay see text.