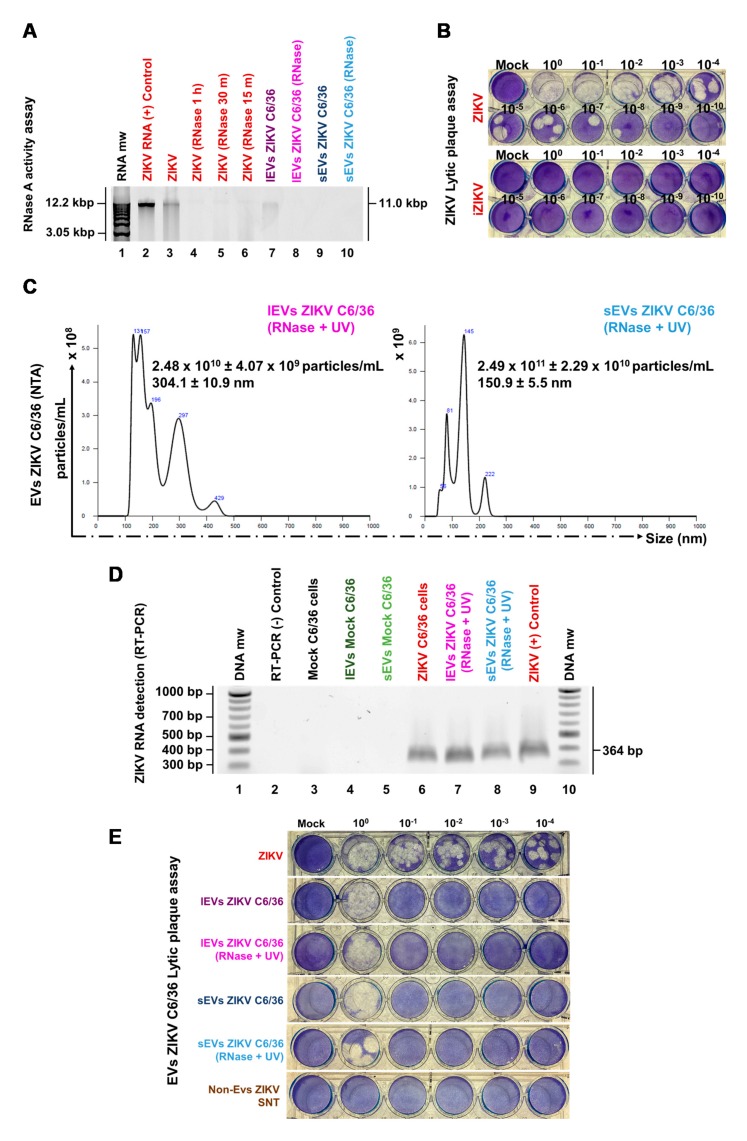
Figure 4.
EVs from ZIKV-infected C6/36 cells, after ZIKV inactivation by RNase A activity assay and UV radiation, carry viral RNA and favor the mammalian cell infection. (A) RNase A activity assay. RNase A (10 µg/mL) was added to the purified ZIKV RNA and incubated for 1 h, 30 min, and 15 min at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Additionally, the RNase A activity (1 h incubation) was evaluated in C6/36 EVs isolates. The RNA degradation pattern was visualized on 2% ethidium bromide-stained 1.2% agarose gel. (B) Inactivated ZIKV (iZIKV) titration by a lytic plaque assay. (C) NTA of the EV isolates (from ZIKV-infected cells) treated with RNase A and UV. Histograms are the representative mean ± SD of the nanoparticle’s concentration (particles/mL) and the size (nm) from three independent experiments. (D) ZIKV RNA detection (RT-PCR) in ZIKV-infected C6/36 EVs (RNase A + UV-treated) samples. The ZIKV amplicon (364 bp from E genome conserved region) was visualized on 2% ethidium bromide-stained 1.2% agarose gel. (E) Evaluation of the ZIKV-infected C6/36 EVs (RNase A + UV-treated and untreated samples) in the viral transmission to naïve Vero cells by a lytic plaque assay.