Abstract
Background
Schistosomiasis is a neglected tropical disease that infects over 200 million people worldwide. Control measures can benefit from improved surveillance methods in freshwaters, with environmental DNA (eDNA) surveys having the potential to offer effective and rapid detection of schistosomes. However, sampling eDNA directly from natural water bodies can lead to inaccurate estimation of infection risk if schistosome eDNA is rare in the environment. Here we report a xenomonitoring method that allows schistosome infections of host snail species to be determined from eDNA in water used to house those snails.
Methods
Host snail species were collected and placed in containers of water and allowed to shed cercariae, and then water samples were filtered and tested using qPCR assays specific to the African species Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma haematobium. We evaluated this “eDNA-based xenomonitoring” approach by experimentally comparing the results to those obtained from direct qPCR screening of tissue sourced from the snails in the experiment.
Results
We found that our method accurately diagnosed the presence of S. mansoni-infected snails in all tests, and S. haematobium-infected snails in 92% of tests. Moreover, we found that the abundance of Schistosoma eDNA in experiments was directly dependent on the number and biomass of infected snails.
Conclusions
These results provide a strong indication that this surveillance method combining the utility of eDNA-based monitoring with the reliability of traditional xenomonitoring approaches could be used to accurately assay the presence of Schistosoma species in natural habitats. This approach may be well-suited for epidemiological studies and monitoring in endemic areas, where it can assist schistosomiasis control by indicating infection risk from freshwaters and guiding necessary interventions to eliminate the disease.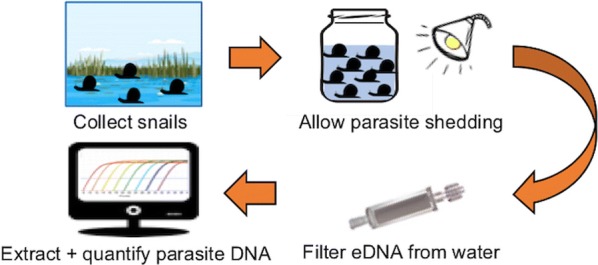
Keywords: Schistosomatidae, Freshwater eDNA, African freshwater body, Detection and quantification level
Background
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever or bilharzia, affects an estimated 207 million people in over 67 countries worldwide, and there are over 779 million further people at risk of infection [1]. The disease is considered a major cause of disability impeding socioeconomic development in regions of the world where it is endemic [2]. It is listed as a ‘neglected tropical disease’ and has been recognised by the World Health Assembly as a disease that should be targeted by control programmes and elimination campaigns where appropriate [3]. The disease is caused by parasitic trematodes that as adults are present in the blood vessels surrounding the urogenital or gastrointestinal tracts of human hosts. Eggs are then released into freshwaters via urine and faeces, miracidia hatch from eggs and infect snail hosts. Infected snails later release cercariae into the water, and the disease is acquired by humans when they encounter the cercariae [2]. While the disease can be treated in humans using anthelmintic medication, a key factor in elimination of the disease will be the prevention of reinfection after treatment [3–6]. This could be achieved by reducing exposure of the human population to free-swimming schistosome cercariae, either by treating or manipulating freshwater habitats to eliminate snail hosts [7], or by alerting local human populations to the infection risk associated with use of freshwater environments. Both strategies will require an appropriate surveillance framework for the presence of schistosomes in freshwaters [8]. Moreover, expansion of areas suitable for transmission under climate change requires pro-active monitoring of new at-risk areas [9].
Conventionally, environmental monitoring for Schistosoma spp. has primarily focused on snail-based surveys in which snails are collected and exposed to light to induce cercarial shedding. Microscopical examination of schistosome cercariae is then used to determine the infection status of snails [10–12], and the method requires considerable time, effort and expertise in the taxonomic identification of schistosome cercariae using microscopy. Alternatively, it is possible to test infection status of individual snails using molecular xenomonitoring tests for the presence of Schistosoma DNA in snail tissue using conventional end-point PCR [13–16] or quantitative PCR [17, 18]. While these methods requiring testing of individual snails have been very effective, they are limited by the need to test large numbers, as often only a small proportion of a total snail population are infected [19, 20]. Thus, without extensive testing using conventional methods it is possible for a schistosomiasis-endemic area with a low parasite burden to appear free of the infection risk, but transmission may continue with the potential to expand in future [20].
Movement towards tests that can rapidly and reliably assess infection risk from trematode parasites in natural water bodies has been achieved through “cercariometry” (the collection and molecular testing of free-swimming cercariae) [21, 22], or testing of environmental DNA (eDNA) sampled directly from freshwaters [23, 24]. Methods sampling “environmental DNA” are varied, but from a parasitological perspective, the term eDNA has been defined as “DNA extracted from environmental or organismal matrices, in other words from the environment or host organism” [25]. Because environmental samples are inherently heterogeneous, it is therefore appropriate from this parasitological standpoint to define any DNA from microscopic organisms present within environmental samples to be eDNA, irrespective of whether the DNA sampled originated from whole microscopic organisms, cellular debris, chemically bound DNA, or DNA in solution.
For schistosome surveillance, eDNA methods that rely on screening water samples collected directly from natural environment are promising, given the relative ease of field sampling, and the absence of any firm requirements to directly sample living organisms. However, the use of eDNA from such samples still needs evaluation, particularly in cases where infected snails are rare and Schistosoma DNA is consequently below the limits of detection. Assays could yield false negatives if the water is turbid and adequate water volumes cannot be filtered, if turbid water contains PCR inhibitors, or if water movement transports eDNA away from a sampling site. Moreover, where Schistosoma eDNA is detected in areas where no snails were found during manual searches [24], it can be uncertain if infected snails are present but went undetected, or if parasite material has been transported to the sampling site from elsewhere. It is also possible that the local environment contains schistosome material released as miracidia from infected mammalian hosts, but the infectious cercarial stage is absent [24].
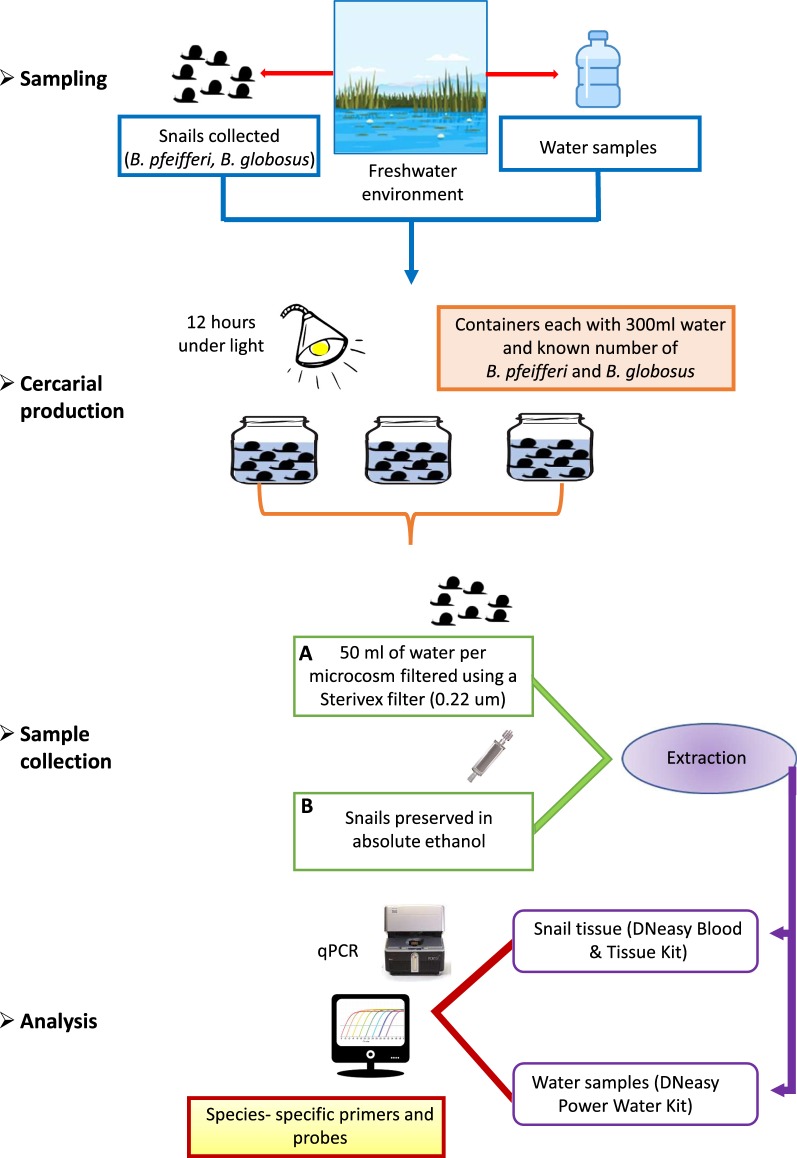
Given the potential limitations of testing for the presence of Schistosoma species using eDNA collected directly from the sampling site, particularly the risk of false negatives in cases of low schistosome density, it would be beneficial to design a protocol that enables the schistosome eDNA originating from cercariae shed by snail hosts to be concentrated prior to molecular testing. In this study, we report an approach where snails are collected and housed in experimental containers to allow them to shed cercariae, before eDNA in the water - from whole cercariae, cellular debris, or DNA chemically bound or in solution - is collected and its abundance measured using quantitative PCR (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Overview of steps in the eDNA-based xenomonitoring assay, from sampling to analysis. Validation of the assay is conducted using qPCR analysis of tissue from preserved snails
Methods
Site description
Tanzania is a country with high schistosomiasis endemism, where primary intermediate hosts include the freshwater snails Biomphalaria pfeifferi for S. mansoni and Bulinus globosus for S. haematobium. On 16th September 2018, potential schistosome host snails were collected from two proximate locations in the Mpemba River in the Lake Rukwa catchment. At the time of the sampling, Site 1 (9.242°S, 32.841°E) was slowly flowing, and shallow (1.0 m maximum depth), with a temperature of 23.3 °C, pH 8.15, and conductivity 300 μS. Site 2 (9.265°S, 32.841°E) was not flowing, shallow (0.5 m maximum depth) with a temperature of 27.5 °C, pH 8.67, and conductivity 430 μS. At both sites the schistosome host snails B. pfeifferi and B. globosus were present, and snails were collected by scooping along 50 m of river. These sites were chosen as they are within an endemic area of S. haematobium and S. mansoni, and our pilot work had indicated that both species were present in the river. Moreover, both sites are near towns, and at the time of sampling there was clear evidence that the river was being used by the local population regularly for bathing, fishing, washing clothes, washing vehicles and collection of water for household activities.
Experimental design and sample collection
All field-collected snails were taken back to the laboratory and identified to the species level based on shell morphology [26]. At the start of the experiment the infection status of individual snails was not known. The experiment included five different treatments (A–E) that differed in the number of snails kept in each container and used river water collected from Site 1 (Table 1). The design aimed to achieve the objective of a range of infected snail numbers and infected snail biomass across containers in the experiment as a whole. Specifically, Treatment A included a median of 20 B. pfeifferi and 3 B. globosus, Treatment B included a median of 20 B. pfeifferi and 6 B. globosus, Treatment C included a median of 10 B. pfeifferi and 3 B. globosus, Treatment D included a median of 10 B. pfeifferi and 6 B. globosus, and Treatment E was a negative control of river water that contained no snails (Table 1). In addition, Treatment F was a negative control treatment of tap water that contained no snails.
Table 1.
Summary of the number of replicates in each treatment, and the numbers of snails in used in each of the treatments A-D (that were all housed in water from Site 1)
| Treatment | No. of replicates | No. of B. pfeifferi Median (range) |
Location source of B. pfeifferi | No. of B. globosus Median (range) |
Location source of B. globosus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 6 | 20 (19–21) | Site 1 | 3 (2–3) | Site 1 |
| B | 6 | 20 (19–21) | Site 1 | 6 (3–6) | Site 1 |
| C | 6 | 10 (10–11) | Site 1 | 3 (3–3) | Site 2 |
| D | 6 | 10 (10–11) | Site 1 | 6 (5–6) | Site 2 |
| Ea | 6 | – | – | – | – |
| Fb | 2 | – | – | – | – |
aTreatment E was a negative control (using water from Site 1)
bTreatment F was a negative control (using tap water)
Notes: There is some slight variation in the numbers of snails in each replicate, as on inspection after the experiment some snails used were found to be empty shells containing only sediment, while some small snails had tucked into shells of larger snails
Each of the six replicates within each of the river water treatments (A–E) included the use of one clear plastic sealable container (bottle with lid) filled with 300 ml of water collected from Site 1 approximately 12 h prior to the start of the experiment. Although it is possible that trace eDNA was present in this river water, it was necessary to use water from the natural environment to reduce the likelihood that snails and schistosomes would be negatively affected by substantive changes to the physio-chemical parameters of the water. Treatment F comprised two replicates each with one clear plastic sealable container (bottle with lid) filled with 300 ml of tap water.
After snails were introduced to containers, they were placed under artificial light, to induce cercarial shedding. After a period of 12 h, one 50 ml water sample was taken from each container using a sterile 50 ml syringe and filtered using a Sterivex filter with a pore size 0.22 µm and a polyethersulfone membrane (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). To preserve the samples, absolute ethanol was passed through the filter with a sterile syringe. Post-filtering, Whirl-Pak bags (118 ml capacity; Nasco, Fort Atkinson, USA) were used to keep each filter separate and reduce potential contamination. After filtering the water, snails were preserved in absolute ethanol; each group in one bag. All field-collected samples (eDNA and snails) were kept as cool as possible in the field, and transported to the UK where they were stored at − 20 °C until DNA extraction. This eDNA-based method will potentially collect DNA from whole schistosomes, chemically bound or free DNA in solution in the environment, or DNA within cellular debris in the environment. In practical terms, however, the result is a measure of parasite DNA present in the immediate environment of the snail host, following augmentation by stimulation of cercarial release.
DNA extraction from Sterivex filters
eDNA from filter samples was extracted individually using the DNeasy Power Water Kit (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Before the extraction process, the laboratory bench was cleaned with 10% bleach, then with 70% ethanol, and finally UV light was used to eliminate residual DNA. All tools used for cutting and handling the filter, including blades, tweezers and scissors were wiped with 10% bleach then washed with 70% ethanol to avoid sample cross-contamination. Used gloves were exchanged for new at each step of the extraction process. Extraction of eDNA and DNA from tissue samples was carried out in different laboratories.
DNA extraction from molluscs
Prior to extractions, snails were separated, and individual snails were washed with distilled water. The length (mm) and wet weight (g) of each snail was then measured. A small sample of tissue (no more than 20 mg), and DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kits (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
eDNA assay of samples
DNA quantification of eDNA samples used a qPCR approach based on the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene of S. mansoni and S. haematobium. Reactions were performed in a 5 µl final volume, containing 1 µl DNA template, 2.5 µl Master Mix (PrimeTime Gene Expression Master Mix; Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA), 1.25 µl molecular grade water (VWR International, Leicestershire, UK) and 0.25 µl of the primer/probe premix. The primer/probe premix was prepared with 4 µl of each primer (100 µM, Integrated DNA Technologies), 2 µl of probe (100 µM, Integrated DNA Technologies), and 40 µl of molecular grade water. The species-specific forward and reverse primers and probes are shown in Table 2. The qPCR conditions were as follows: 3 min at 95 °C for initial denaturation, followed by 45 cycles of 95 °C for 0.05 s and 60 °C for 30 s. Each sample was run in triplicate (technical replicates) and each plate of samples quantified with a 7-fold serial dilution of a control positive DNA sample (ranging from 1,000,000 copies/μl to 1 copy/μl), and a no-template negative control. The reactions were run on a Eco48 thermal cycler machine (PCRMax, Staffordshire, UK) in 48-well plates with ROX normalisation. DNA detection was expressed by quantification cycle threshold (Cq) values. We report the theoretical limits of detections as estimated as the number of copies at which there was a 95% probability of amplification in any one PCR of a sample (termed LODI) and the 95% probability of amplification in any one of three PCRs of a sample (termed LODIII), using the standard dilution series, and fitting logistic models [27] using CurveExpert Basic 2.1.0 (Hyams Development). The theoretical limit of quantification (LOQ) was estimated as the minimum dilution in which 90% of standards amplified reliably [28].
Table 2.
Details of species-specific assays for S. mansoni and S. haematobium
| Species | Primer or probe | Sequence (5′-3′) | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. mansoni | Forward primer | CTGCTCAGTGAAGAAGTTTGTTT | 104 |
| Probe | AGCCGCGATTATTTATCGTGCTAAGGT | ||
| Reverse primer | CCTCATTGAACCATTCACAAGTC | ||
| S. haematobium | Forward primer | AATGAACATGAATGGCCGCA | 143 |
| Probe | TGGAGACTTGTGAATGGTCGAACG | ||
| Reverse primer | ATGGGTTCCTCACCACTTAAACT |
Notes: Probes were designed with a dual labelled 5(6)-carboxy-fluorescein (FAM) fluorescent tag at the 5′ end and with a black hole quencher 1 (BHQ1) at the 3′-end
Tests for the presence of S. mansoni and S. haematobium within the tissue samples of B. pfeifferi and B. globosus were also conducted using the same qPCR approach as described above. However, in these tests only the presence or absence of amplification was recorded for samples, alongside positive and no-template negative controls, and DNA was not formally quantified using a dilution series.
Data analysis
Cq values, DNA concentrations and the qPCR quantification parameters r2 and percent efficiency were calculated using EcoStudy version 5.2.16 (PCRMax) using the default settings. Data for each assay (S. haematobium and Bulinus; S. mansoni and Biomphalaria) were analysed separately using linear models in R 3.6.0 (R Core Team, 2019). Each model included the eDNA quantity as the response variable (measured as the mean number of eDNA copies across the technical replicates). The predictor variables were either the number of infected host snail individuals or the total infected host snail biomass in experimental replicates, as determined from the qPCR assays of snail tissue.
Results
The qPCR efficiency of S. mansoni eDNA assay was 103% across the four dilution series assays (range 91.55–110.86%) with a mean r2 value of 0.99 (range 0.97–0.99). For S. mansoni the LODI was 32.36 copies/μl, the LODIII was 1.49 copies/μl, and the LOQ was 100 copies/µl. No amplifications were observed in the no-template qPCR controls, the negative control samples of water collected from the natural water body, or from the local tap water controls. The tests revealed the presence of S. mansoni eDNA in water from all 24 containers with Biomphalaria host snails, with all 72 qPCR replicates showing positive amplifications (Additional file 1: Table S1). In total S. mansoni was present in 145 of 364 Biomphalaria individuals from the experiment that had their tissue tested. There was complete congruence between the presence of S. mansoni in the eDNA assay and the presence of S. mansoni in the tissue of the Biomphalaria host snails (Table 3).
Table 3.
Results of S. mansoni and S. haematobium DNA experimental analyses
| Treatment | Replicate code | S. mansoni | S. haematobium | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eDNA amplification success | eDNA Cq (mean) | eDNA copies/µl (mean) | n/N | Infected snail biomass (g) | eDNA amplification success | eDNA Cq (mean) | eDNA copies/µl (mean) | n/N | Infected snail biomass (g) | ||
| A | 1 | 3/3 | 32.47 | 211.48 | 8/21 | 1.49 | 3/3 | 32.88 | 20.14 | 3/3 | 1.38 |
| 2 | 3/3 | 35.13 | 35.62 | 10/21 | 1.71 | 3/3 | 34.53 | 6.35 | 3/3 | 1.44 | |
| 3 | 3/3 | 33.92 | 72.73 | 6/19 | 0.83 | 2/3 | 36.11 | 2.64 | 2/3 | 1.03 | |
| 4 | 3/3 | 37.11 | 6.71 | 5/20 | 0.59 | 3/3 | 32.36 | 29.30 | 2/3 | 0.76 | |
| 5 | 3/3 | 38.59 | 2.57 | 12/21 | 1.91 | 0/3 | – | 0 | 1/2 | 0.38 | |
| 6 | 3/3 | 38.48 | 2.45 | 3/20 | 0.37 | 2/3 | 37.28 | 1.03 | 0/3 | 0 | |
| B | 7 | 3/3 | 36.55 | 10.20 | 9/20 | 0.56 | 3/3 | 28.91 | 325.97 | 4/6 | 2.07 |
| 8 | 3/3 | 34.47 | 52.78 | 6/20 | 1.07 | 2/3 | 36.28 | 1.95 | 1/3 | 0.33 | |
| 9 | 3/3 | 35.03 | 33.27 | 11/20 | 1.72 | 3/3 | 33.10 | 19.53 | 6/6 | 2.48 | |
| 10 | 3/3 | 33.85 | 77.28 | 7/19 | 0.84 | 3/3 | 29.56 | 222.73 | 4/6 | 1.68 | |
| 11 | 3/3 | 31.47 | 435.27 | 11/21 | 1.2 | 3/3 | 30.07 | 160.39 | 3/6 | 1.17 | |
| 12 | 3/3 | 33.59 | 94.77 | 6/20 | 0.76 | 3/3 | 33.10 | 19.50 | 1/6 | 0.49 | |
| C | 13 | 3/3 | 36.14 | 18.16 | 4/10 | 0.64 | 3/3 | 34.86 | 8.01 | 2/3 | 0.53 |
| 14 | 3/3 | 34.81 | 40.36 | 3/10 | 0.39 | 0/3 | – | 0 | 2/3 | 0.64 | |
| 15 | 3/3 | 39.68 | 1.09 | 4/10 | 0.30 | 3/3 | 37.09 | 1.48 | 3/3 | 0.78 | |
| 16 | 3/3 | 34.05 | 67.49 | 2/11 | 0.14 | 3/3 | 35.05 | 4.95 | 2/3 | 0.59 | |
| 17 | 3/3 | 36.21 | 22.03 | 3/10 | 0.37 | 3/3 | 24.17 | 8445.25 | 3/3 | 0.48 | |
| 18 | 3/3 | 36.03 | 20.46 | 5/10 | 0.54 | 3/3 | 28.77 | 342.91 | 3/3 | 1.20 | |
| D | 19 | 3/3 | 35.03 | 43.35 | 4/10 | 0.66 | 3/3 | 34.29 | 7.61 | 5/5 | 1.23 |
| 20 | 3/3 | 35.89 | 26.35 | 4/10 | 1.13 | 3/3 | 29.65 | 180.51 | 6/6 | 1.44 | |
| 21 | 3/3 | 37.26 | 12.39 | 7/10 | 0.97 | 3/3 | 31.49 | 49.80 | 5/5 | 1.07 | |
| 22 | 3/3 | 35.63 | 27.94 | 6/11 | 1.27 | 3/3 | 27.90 | 611.29 | 6/6 | 1.79 | |
| 23 | 3/3 | 37.95 | 5.25 | 4/10 | 0.58 | 3/3 | 35.36 | 3.49 | 6/6 | 1.44 | |
| 24 | 3/3 | 36.04 | 21.65 | 5/10 | 0.44 | 3/3 | 31.36 | 53.09 | 6/6 | 1.34 | |
| E | 25 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – |
| 26 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
| 27 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
| 28 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
| 29 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
| 30 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
| F | 31 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – |
| 32 | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | 0/3 | – | – | – | – | |
Note: The table includes the results from eDNA monitoring and the results of the qPCR tests of host snail infection
Key: –, no amplification was observed
Abbreviations: n, number of infected snails; N, number of all host snails in the assay
The qPCR efficiency of S. haematobium assay was 101% across the four dilution series assays (range 91.7–102.33%) with a mean r2 value of 0.99 (range 0.98–0.99). For S. haematobium the LODI was 1.33 copies/μl, LODIII was ≤ 1 copy/μl while the LOQ was 100 copies/μl. Again, no amplifications were observed in the no-template qPCR controls, the negative control samples of water collected from the natural water body, or from local tap water controls. The results also revealed the presence of S. haematobium eDNA in water from 22 of the 24 experimental containers with Bulinus host snails, with 61 of 72 eDNA qPCR replicates showing positive amplifications (Additional file 1: Table S1). In total, S. haematobium was present in 79 out of 102 Bulinus individuals that had their tissue tested. There was a strong congruence between the presence of S. haematobium in the eDNA assay and the presence of S. haematobium in the tissue of the Bulinus host snails, with only three exceptions. Two experimental containers negative for S. haematobium eDNA contained B. globosus snails positive for S. haematobium in tissue assays, and one experimental container that was positive for S. haematobium eDNA contained B. globosus found negative for S. haematobium in the tissue assay (Table 3).
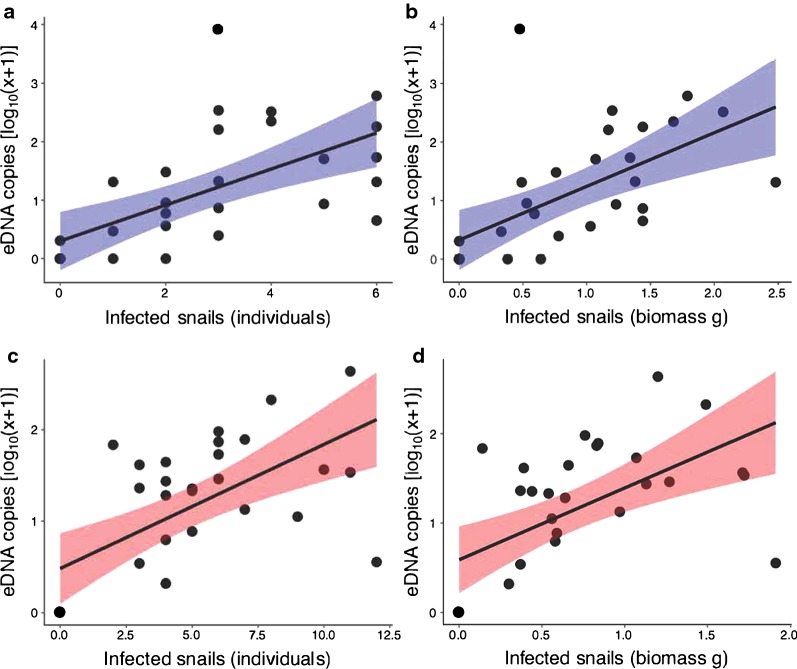
There were strong associations between the number of infected snails and eDNA copy number; as the number of infected snails in an experiment increased, the number of eDNA copies increased (Fig. 2, Table 4). We also found strong associations between the infected biomass of host snails and eDNA abundance in the experimental containers, measured using eDNA copies. As the infected snail biomass increased, eDNA copy number increased (Table 4).
Fig. 2.
Associations between eDNA copies and infected snails in experimental containers. aSchistosoma haematobium copies and number of infected host snail individuals. bS. haematobium copies and biomass of infected host snail individuals. cS. mansoni copies and number of infected host snail individuals. dS. mansoni copies and biomass of infected host snail individuals. Lines illustrate linear models of associations between the variables, with 95% confidence intervals
Table 4.
Summary linear models, predicting the number of eDNA copies/µl (log10 transformed)
| Assay | Predictor variable | Estimate (SE) | F(1, 28) | r2 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. haematobium | Infected host individuals | 0.308 (0.073) | 4.220 | 0.389 | < 0.001 |
| Infected host biomass | 0.916 (0.230) | 3.980 | 0.361 | < 0.001 | |
| S. mansoni | Infected host individuals | 0.136 (0.032) | 4.257 | 0.393 | < 0.001 |
| Infected host biomass | 0.804 (0.209) | 3.854 | 0.347 | < 0.001 |
Abbreviations: SE, standard error
Discussion
Our results confirmed a strong association between the detection of DNA in the experimental chamber and the presence of infected snails for both S. haematobium and S. mansoni assays. One experimental replicate detected S. haematobium eDNA, but no S. haematobium in the tissue. This may be explained by schistosome life-cycle stages being absent from the specific sub-sample of tissue used, or alternatively it may be linked to PCR inhibition given potential for polysaccharides in mollusc tissue to act as PCR inhibitors [29]. Additionally, two experimental replicates failed to detect S. haematobium eDNA, but did detect S. haematobium in the tissue. This may be explained by the parasite DNA concentration in water sample being below the estimated level of detection with three qPCR technical replicates, or because of a failed DNA extraction, or perhaps cercariae were not shed into the surrounding water. We did not measure the number of snails actively shedding cercariae, but they can be absent if infection is prepatent [30–32], or if cercariae are affected by environmental factors such as interactions with other organisms. For example, rotifers can limit cercarial motility and infectivity, which may influence detectability [33, 34]. Nevertheless, despite these modest inconsistencies in results of the two testing methods, we clearly demonstrated that both numbers and biomass of infected host snails were significantly positively related to eDNA abundance, thus demonstrating that it is possible to use eDNA abundance to predict the number of infected host snails within containers used in the assay.
The results presented show for the first time that standardised eDNA-based xenomonitoring assays using consistent conditions can provide quantitative information on infection prevalence within snail populations sampled in the field, and therefore if coupled with snail abundance information it may be possible to quantify transmission risk. In principle, this method could be more consistent and reliable than direct eDNA sampling of water, which may depend on extrinsic factors, such as water flow, temperature and light regime in the days prior to sampling. Moreover, it would also be less labour-intensive than testing individual snails in order to quantify the prevalence of infection by conventional microscope-based identification of emerging cercariae [10–12]. Our method would also overcome potential taxonomic complications due to the sympatric coexistence of human and non-human schistosome species with morphologically similar cercariae [35, 36]. Additionally, it may be preferable to the PCR-based approaches on snail tissue (either end-point PCR [15] or qPCR as in this study), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) on snail tissue [37], given the time-consuming nature of DNA extraction from multiple individual snails, and the potential presence of polysaccharide PCR inhibitors in mollusc tissue [29]. More specifically, this eDNA-based xenomonitoring method that requires only one eDNA extraction from the water in each experimental chamber could replace the need to extract DNA individually from potentially hundreds of snails, thus providing significant savings in cost and time. In comparison to the subsampling and homogenising of large numbers of snails prior to DNA extraction, water sampling with enclosed filters can also represent an advantage in the laboratory in terms of speed, cost, and reduced likelihood of cross-contamination.
A practical challenge faced during the collection of eDNA samples is rapid blocking of filters from the turbid water that is typical of Schistosoma transmission sites. Typically, it is necessary to use fine small pore sizes (0.22 μm) [24, 38] and this can mean that it is only practical to sample 500 ml of water, or often much less, per filter. However, we note that large pore size units (350 μm) for pre-filtering water samples have been used successfully [24]. Nevertheless, the xenomonitoring method we used overcame these difficulties as it allowed sediment to settle prior to sampling. It also required only smaller (50 ml) volumes of water, as schistosome eDNA would have been more concentrated in our experimental containers than it would be in the natural environment. In principle, it would also be possible to precipitate eDNA directly from water samples, therefore foregoing the need to use filters [39, 40].
One of the key advantages of eDNA sampling directly from the environment is that it does not require collection or analysis of snails. By contrast, eDNA-based xenomonitoring, like conventional tests of the presence of cercariae, requires both sampling of snails and housing them in controlled conditions for the duration of an experiment. In practice, where snail infection is low, it may be necessary to collect and test several hundred snails to reach detectable levels of infection, but this could be readily achieved within experimental containers if sufficient numbers can be collected from the natural environment. Further research will be required to determine the relative power of different analytical approaches for detecting and quantifying schistosome prevalence across natural densities of snails and across differing intensities of snail infection. Specifically, it would be useful to compare the detection probabilities using directly sampled eDNA, to both conventional and eDNA-based xenomonitoring methods where estimates of schistosome abundance require snail density estimates from searches and tests of snail infection status.
It might not be possible to reliably quantify snail infection rates if snails are not readily shedding cercariae [12, 33], and although we succeeded in using the eDNA-based xenomonitoring method with the schistosome hosts B. pfeifferi and B. globosus, the effectiveness for other host species, perhaps with specific habitat requirements, is unknown. For example, in Lake Malawi the endemic Bulinus nyassanus, a host of S. haematobium, is found in the upper 2–3 cm of the sediment on open sandy shorelines [41–43]. Additionally, the eDNA testing of Schistosoma species may be compromised by hybridization among species, as observed between the closely related S. mansoni and S. rodhaini [36]. Previous work has demonstrated that hybridization can result in sharing of mitochondrial haplotypes, and distinguishing between the two species at some locations would therefore be intractable using any methods that rely exclusively on amplification of targeted fragments of the mitochondrial genome. A final consideration is the evidence of some cross-species amplification within assays, so in some situations where closely related schistosome species coexist then primers and probes may need to be considered carefully, and potentially with bespoke designs.
In 2012, the World Health Assembly resolved to continue efforts to eliminate schistosomiasis through control and surveillance measures. It is widely recognized that there are multiple required facets to an integrated control programme, focused on both treatment of existing human infections with chemotherapy in synergy with intervention techniques focused on the life stages of the intermediate gastropod host [2, 6]. Physical measures to reduce habitat for snail populations could be used more widely, for example cementing irrigation canals, draining wetlands, or aiming to eliminate snail populations by applying molluscicides (such as new niclosamide formulations) and biological control (including intentional introductions of competitor snails or snail predators). However, in practice such snail control methods may not be practical or ethical in many environmental circumstances. Regardless, the surveillance of freshwaters can enable an early warning of infection risk, and may prove increasingly critical for prevention of reinfection during the elimination phase of control programmes [20, 23], as well as the early detection and elimination of new foci of infection resulting from environmental change [44].
A key consideration for further development of the methods outlined in this study would be to evaluate their effectiveness across different host gastropod species and in different environments. We may expect, for example, that the rate of schistosome cercarial production would vary among sites dependent upon the environmental conditions, for example the temperature and light regimes of assay containers. Therefore, to evaluate potential for effective application, the method needs to be refined enabling robust and systematically consistent results. Moreover, the method would not necessarily be appropriate where snails are rare or hard to sample, and instead in those circumstances eDNA sampling of water collected directly from the natural environment may be more appropriate. Additionally, consideration should be given to the need to standardise training and materials typically available for sampling and analysis in endemic areas [20, 45].
Conclusions
Here we provide evidence that eDNA-based assays can determine the presence of schistosomes in intermediate host snail species. We suggest that the methods may be appropriate for epidemiological studies and large-scale monitoring in some endemic areas. They could prove useful, alongside other surveillance methods, to inform schistosomiasis control programmes by highlighting freshwater bodies where there is a risk of schistosomiasis transmission. However, further comparative investigations are needed to evaluate the power and practicality of this method in the field, alongside the range of other diagnostic and surveillance methods available.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Results of S. mansoni and S. haematobium qPCR experiments, including Cq scores and eDNA copies for all replicates in the experiment.
Acknowledgements
We thank staff from the Tanzania Fisheries Research Institute for contributions to fieldwork. The Tanzania Commission for Science and Technology (COSTECH) provided fieldwork permits, while the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries permitted export of materials. We thank BEI Resources Repository of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases for the provision of material. We thank Richard Wall for his support.
Abbreviations
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- eDNA
Environmental DNA
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- qPCR
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- Cq
Quantification cycle
- LOD
Limit of detection
- LOQ
Limit of quantification
- LAMP
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Authors’ contributions
HA, MJG, EAM and RAC performed the study design. HA, MJG, AS, BPN and RAC implemented the study and collected the data. HA and MJG performed sample and study analysis and interpretations. HA, MJG and RAC drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
HA was funded by the Saudi Arabia Cultural Bureau in London and Prince Nourah Bin Abdulrahman University. MJG and BPN were supported by the Royal Society-Leverhulme Trust Africa Award AA130107. MJG and RAC were supported by Global Challenges Research Fund pump priming project “Aquatic environmental DNA for enhanced health and food security in Tanzania”. The authors also acknowledge UKRI GCRF QR funding from Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article and its additional files.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Hind Alzaylaee, Email: ha15695@bristol.ac.uk.
Rupert A. Collins, Email: rc16041@bristol.ac.uk
Asilatu Shechonge, Email: ashechonge@yahoo.com.
Benjamin P. Ngatunga, Email: bpngatunga@yahoo.com
Eric R. Morgan, Email: Eric.Morgan@qub.ac.uk
Martin J. Genner, Email: m.genner@bristol.ac.uk
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s13071-020-3941-6.
References
- 1.Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:411–425. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Colley DG, Bustinduy AL, Secor WE, King CH. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet. 2014;383:2253–2264. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61949-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fenwick A, Jourdan P. Schistosomiasis elimination by 2020 or 2030? Int J Parasitol. 2016;46:385–388. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.King CH, Sturrock RF, Kariuki HC, Hamburger J. Transmission control for schistosomiasis—why it matters now. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:575–582. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2006.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sokolow SH, Wood CL, Jones IJ, Swartz SJ, Lopez M, Hsieh MH, et al. Global assessment of schistosomiasis control over the past century shows targeting the snail intermediate host works best. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0004794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sokolow SH, Wood CL, Jones IJ, Lafferty KD, Kuris AM, Hsieh MH, et al. To reduce the global burden of human schistosomiasis, use ‘old fashioned’ snail control. Trends Parasitol. 2018;34:23–40. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2017.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kariuki HC, Madsen H, Ouma JH, Butterworth AE, Dunne DW, Booth M, et al. Long term study on the effect of mollusciciding with niclosamide in stream habitats on the transmission of Schistosomiasis mansoni after community-based chemotherapy in Makueni District, Kenya. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:107. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stothard JR, Campbell SJ, Osei-Atweneboana MY, Durant T, Stanton MC, Biritwum NK, et al. Towards interruption of schistosomiasis transmission in sub-Saharan Africa: developing an appropriate environmental surveillance framework to guide and to support ‘end game’interventions. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017;6:10. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0215-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McCreesh N, Nikulin G, Booth M. Predicting the effects of climate change on Schistosoma mansoni transmission in eastern Africa. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:4. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0617-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Loy C, Haas W. Prevalence of cercariae from Lymnaea stagnalis snails in a pond system in southern Germany. Parasitol Res. 2001;87:878–882. doi: 10.1007/s004360100462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wolmarans CT, De Kock KN, Strauss HD, Bornman M. Daily emergence of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium cercariae from naturally infected snails under field conditions. J Helminthologia. 2002;76:273–277. doi: 10.1079/JOH2002122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kariuki HC, Clennon JA, Brady MS, Kitron U, Sturrock RF, Ouma JH, et al. Distribution patterns and cercarial shedding of Bulinus nasutus and other snails in the Msambweni area, Coast Province, Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:449–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Melo FL, Gomes AL, Barbosa CS, Werkhauser RP, Abath FG. Development of molecular approaches for the identification of transmission sites of schistosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2006;100:1049–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Farghaly A, Saleh AA, Mahdy S, El-Khalik DA, El-Aal NF, Abdel-Rahman SA, et al. Molecular approach for detecting early prepatent Schistosoma mansoni infection in Biomphalaria alexandrina snail host. J Parasit Dis. 2016;40:805–812. doi: 10.1007/s12639-014-0583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bakuza JS, Gillespie R, Nkwengulila G, Adam A, Kilbride E, Mable BK. Assessing S. mansoni prevalence in Biomphalaria snails in the Gombe ecosystem of western Tanzania: the importance of DNA sequence data for clarifying species identification. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:584. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2525-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chua JC, Tabios IK, Tamayo PG, Fontanilla IK, Fornillos RJ, De Chavez ER, et al. Genetic comparison of Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi (Mollendorf, 1895) (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae), the intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in the Philippines, based on 16S ribosomal RNA sequence. Sci Diliman. 2017;29:32–50. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thanchomnang T, Intapan P, Sri-Aroon P, Lulitanond V, Janwan P, Sanpool O, et al. Molecular detection of Schistosoma japonicum in infected snails and mouse faeces using a real-time PCR assay with FRET hybridisation probes. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011;106:831–836. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762011000700008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kane RA, Stothard JR, Rollinson D, Leclipteux T, Evraerts J, Standley CJ, et al. Detection and quantification of schistosome DNA in freshwater snails using either fluorescent probes in real-time PCR or oligochromatographic dipstick assays targeting the ribosomal intergenic spacer. Acta Trop. 2013;128:241–249. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Angelo T, Shahada F, Kassuku A, Mazigo H, Kariuki C, Gouvras A, et al. Population abundance and disease transmission potential of snail intermediate hosts of human schistosomiasis in fishing communities of Mwanza region, north-western, Tanzania. Int J Sci Res. 2014;3:1230–1236. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weerakoon K, Gordon C, McManus D. DNA diagnostics for schistosomiasis control. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018;3:81. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed3030081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hung YW, Remais J. Quantitative detection of Schistosoma japonicum cercariae in water by real-time PCR. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2008;2:e337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Worrell C, Xiao N, Vidal JE, Chen L, Zhong B, Remais J. Field detection of Schistosoma japonicum cercariae in environmental water samples by quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:2192–2195. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01561-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sato MO, Rafalimanantsoa A, Ramarokoto C, Rahetilahy AM, Ravoniarimbinina P, Kawai S, et al. Usefulness of environmental DNA for detecting Schistosoma mansoni occurrence sites in Madagascar. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;76:130–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sengupta ME, Hellstrom M, Kariuki HC, Olsen A, Thomsen PF, Mejer H, et al. Environmental DNA for improved detection and environmental surveillance of schistosomiasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:8931–8940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815046116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bass D, Stentiford GD, Littlewood DTJ, Hartikainen H. Diverse applications of environmental DNA methods in parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2015;31:499–513. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brown DS. Freshwater snails of Africa and their medical importance. London: Taylor and Francis; 1994. pp. 1–487. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Forootan A, Sjoback R, Bjorkman J, Sjogreen B, Linz L, Kubista M. Methods to determine limit of detection and limit of quantification in quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) Biomol Detect Quantif. 2017;12:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bdq.2017.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klymus KE, Richter CA, Chapman DC, Paukert C. Quantification of eDNA shedding rates from invasive bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis and silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Biol Cons. 2015;183:77–84. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schrader C, Schielke A, Ellerbroek L, Johne R. PCR inhibitors—occurrence, properties and removal. J Appl Microbiol. 2012;113:1014–1026. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Muhoho ND, Katsumata T, Kimura E, Migwi DK, Mutua WR, Kiliku FM, et al. Cercarial density in the river of an endemic area of schistosomiasis haematobia in Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:162–167. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1997.57.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aoki Y, Sato K, Muhoho ND, Noda SI, Kimura E. Cercariometry for detection of transmission sites for schistosomiasis. Parasitol Int. 2003;52:403–408. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5769(03)00057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Opisa S, Odiere MR, Jura WG, Karanja DM, Mwinzi PN. Malacological survey and geographical distribution of vector snails for schistosomiasis within informal settlements of Kisumu City, western Kenya. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:226. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stirewalt M, Lewis FA. Schistosoma mansoni: effect of rotifers on cercarial output, motility and infect1vity. Int J Parasitol. 1981;11:301–308. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(81)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gao J, Yang N, Lewis FA, Yau P, Collins JJ, Sweedler JV, et al. A rotifer-derived paralytic compound prevents transmission of schistosomiasis to a mammalian host. PloS Biol. 2019;17:e3000485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Norton A, Rollinson D, Richards L, Webster J. Simultaneous infection of Schistosoma mansoni and S. rodhaini in Biomphalaria glabrata: impact on chronobiology and cercarial behaviour. Parasit Vectors. 2008;1:43. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-1-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Leger E, Webster JP. Hybridizations within the genus Schistosoma: implications for evolution, epidemiology and control. Parasitology. 2017;144:65–80. doi: 10.1017/S0031182016001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gandasegui J, Fernández-Soto P, Hernández-Goenaga J, López-Abán J, Vicente B, Muro A. Biompha-LAMP: a new rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Schistosoma mansoni in Biomphalaria glabrata snail host. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0005225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spens J, Evans AR, Halfmaerten D, Knudsen SW, Sengupta ME, Mak SS, et al. Comparison of capture and storage methods for aqueous macrobial eDNA using an optimized extraction protocol: advantage of enclosed filter. Methods Ecol Evol. 2017;8:635–645. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ficetola GF, Miaud C, Pompanon F, Taberlet P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol Lett. 2008;4:423–425. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2008.0118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eichmiller JJ, Miller LM, Sorensen PW. Optimizing techniques to capture and extract environmental DNA for detection and quantification of fish. Mol Ecol Resour. 2016;16:56–68. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Madsen HR, Stauffer JR, Jr, Bloch P, Konings A, McKaye KR, Likongwe JS. Schistosomiasis transmission in Lake Malawi. Afr J Aquat Sci. 2004;29:117–119. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Madsen H, Bloch P, Makaula P, Phiri H, Furu P, Stauffer JR. Schistosomiasis in Lake Malawi villages. EcoHealth. 2011;8:163–176. doi: 10.1007/s10393-011-0687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Madsen H, Stauffer JR., Jr The burrowing behaviour of Bulinus nyassanus, intermediate host of Schistosoma haematobium, in Lake Malawi. Afr J Aquat Sci. 2012;37:113–116. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Booth M, Clements A. Neglected tropical disease control: the case for adaptive, location-specific solutions. Trends Parasitol. 2018;34:272–282. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2018.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Xu J, Duan ZL, Guan ZX, Wang YY, Lin C, Zhang TT, et al. Early detection of circulating DNA of Schistosoma japonicum in sentinel mice models. Exp Parasitol. 2017;176:82–88. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2016.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Results of S. mansoni and S. haematobium qPCR experiments, including Cq scores and eDNA copies for all replicates in the experiment.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article and its additional files.