Abstract
Background
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-obligate precursor of invasive breast carcinoma and presents a potential risk of over or undertreatment. Finding molecular biomarkers of disease progression could allow for more adequate patient treatment. We aimed to identify potential biomarkers that can predict invasiveness risk.
Methods
In this epithelial cell-based study archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded blocks from six patients diagnosed with invasive lesions (pure invasive ductal carcinoma), six with in-situ lesions (pure ductal carcinoma in situ), six with synchronous lesions (invasive ductal carcinoma with an in-situ component) and three non-neoplastic breast epithelium tissues were analyzed by gene expression profiling of 770 genes, using the nCounter® PanCancer Pathways panel of NanoString Technologies.
Results
The results showed that in comparison with non-neoplastic tissue the pure ductal carcinoma in situ was one with the most altered gene expression profile. Comparing pure ductal carcinoma in situ and in-situ component six differentially expressed genes were found, three of them (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1), play a role in cell invasiveness. Importantly, these genes were also differentially expressed between invasive and noninvasive groups and were negatively regulated in later stages of carcinogenesis.
Conclusions
We propose these three genes (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1) as potential biomarkers of ductal carcinoma in situ progression, suggesting that their downregulation may be involved in the transition of stationary to migrating invasive epithelial cells.
Keywords: Ductal carcinoma in situ, Tumor progression, FGF2, GAS1, SFRP1
Background
Breast cancer (BC) begins as premalignant lesions, progressing to the preinvasive stage of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and culminating as invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) [1, 2]. DCIS represents 20–25% of newly diagnosed BC and up to 40% can progress to IDC [3]. Gene expression profiling-based studies have shown that distinct stages of progression are evolutionary products of same clonal origin and that genes conferring invasive growth are disrupted during preinvasive stages [4–8]. Differences among these stages are not clear and there is no consensus as to how gene activation or inactivation alters the course of BC progression.
DCIS is a form of BC where epithelial cells restricted to the ducts exhibit an atypical phenotype [8]. Interestingly, some DCIS lesions progress to IDCs, while others remain unchanged [9]. Finding gene expression patterns that could predict invasive progression would allow us to personalize DCIS treatment to each patient’s real needs.
In this study, gene expression profiling was performed in non-neoplastic breast epithelium, pure DCIS, mixed lesions (DCIS-IDC) (IDC with an in-situ component) and pure IDCs, aiming to identify molecular predictors of invasive disease risk.
Materials and methods
Study population
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) breast blocks of 3 healthy women were selected as non-neoplastic breast epithelium. Specimens with pathological lesions (IDC, DCIS, DCIS-IDC) were obtained from the Department of Pathology of Barretos Cancer Hospital-Sao Paulo, Brazil. Archival FFPE blocks from 6 patients diagnosed with IDC, 6 with DCIS and 6 with IDC with in-situ (DCIS-IDC) component were selected (Table 1). Cases of IDC and DCIS-IDC were chosen considering the molecular subtype, according to St. Gallen consensus [13]. Pathological staging was defined by current edition in 2015 of TNM classification [10]. Histological grade was determined as Lakhani et al. [12]. Myriad’s hereditary cancer tests were done by Myriad Genetic Laboratories, Inc. (Salt Lake City, Utah, USA) through observations of deleterious mutations, as published by Frank et al. [11]. Selected patients had a mean age of 55 years and were not under risk of hereditary BC, they did not present metastasis and did not receive any treatment prior surgery.
Table 1.
Patients characteristics
| Case ID | Age range (years) | Invasive type | Molecular subtype | Histological type | Histological grade | Invasive nuclear grade | DCIS Nuclear grade |
DCIS type | ERf in DCIS | PRg in DCIS | Size (mm) | Th stage | Ni stage | Pathological clinical stage | Myriad test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1P1 | 50–60 | IDCa | Luminal B Her negativo | IDC | 3 | 3 | N | N | N | N | 31 | T2 | N0 | IIa | N > 50 |
| G1P2 | 50–60 | IDC | TNd | IDC | 3 | 3 | N | N | N | N | 10 | T1b | N0 | I | N > 50 |
| G1P3 | 60–70 | IDC | HER2 | IDC | 3 | 3 | N | N | N | N | 33 | T2 | N1 | IIb | N > 50 |
| G1P4 | 60–70 | IDC | Luminal A | IDC | 2 | 2 | N | N | N | N | 20 | T1c | N0 | I | N > 50 |
| G1P5 | 40–50 | IDC | Luminal B Her positivo | IDC | 1 | 1 | N | N | N | N | 40 | T2 | N0 | IIa | N < 50 |
| G1P6 | 40–50 | IDC | Luminal B Her negativo | IDC | 2 | 2 | N | N | N | N | 20 | T1c | N0 | I | N < 50 |
| G2P1 | 70–80 | Nb | N | DCISe | N | N | 3 | S, C, M, Co | ++++ | +++ | 105 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N > 50 |
| G2P2 | 40–50 | N | N | DCIS | N | N | 3 | S, C, M | – | – | 50 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N < 50 |
| G2P3 | 40–50 | N | N | DCIS | N | N | 3 | S, Co, C, M | +++ | +++ | 18 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N < 50 |
| G2P4 | 50–60 | N | N | DCIS | N | N | 3 | S, Co | ++++ | ++ | 30 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N > 50 |
| G2P5 | 50–60 | N | N | DCIS | N | N | 3 | C, M, Co | + | + | 60 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N > 50 |
| G2P6 | 50–60 | N | N | DCIS | N | N | 3 | S, M, Co | + | – | 20 | Tis | N0 | 0 | N > 50 |
| G3P1 | 50–60 | *IDCc | TN | DCIS-IDC | 3 | 3 | 3 | S, C, Co | – | – | 30 | T1c | N0 | I | N > 50 |
| G3P2 | 60–70 | *IDC | Her2 | DCIS-IDC | 3 | 3 | 3 | S, A, M, Co | – | – | 100 | T2 | N1 | IIb | N > 50 |
| G3P3 | 50–60 | *IDC | Luminal B Her negativo | DCIS-IDC | 3 | 3 | 3 | S, C, Co | ++++ | ++ | 65 | T1c | N0 | I | N > 50 |
| G3P4 | 60–70 | *IDC | Her2 | DCIS-IDC | 2 | 2 | 3 | S, C | – | – | 36 | T1a | N1 | IIa | N > 50 |
| G3P5 | 30–40 | *IDC | Luminal B Her negativo | DCIS-IDC | 2 | 2 | 2 | S, C | ++++ | + | 29 | T1a | N1 | IIa | N > 50 |
| G3P6 | 50–60 | *IDC | Luminal B Her positivo | DCIS-IDC | 3 | 3 | N | S, C, Co | ++++ | + | N | T1a | N0 | I | N > 50 |
DCIS type: S – solid; M – micropapillary; C – cribriform; A – adherent; Co – comedocarcinoma
Clinical stage as defined by TNM staging [10] metastases have always been absent, so the clinical stage is only extrapolated from T and N
Myriad’s hereditary cancer tests were made according Frank et al. [11] - N < 50 (family history of hereditary cancer absent and breast cancer diagnosed before 50 years of age) and > 50 (family history of hereditary cancer absent and breast cancer diagnosed after 50 years of age)
Histological grade was obtained according Lakhani et al. [12]. For ER and PR: stained slides were examined as follows: “negative” (−) - absence of brown precipitate in cells; the positive samples were labeled as (+) [if there were a few (< 10%) scattered cells with precipitate]; (++) [for large areas (10–50%) of positivity] and (+++) [designated 50 to 100% positivity]
IDC invasive ductal carcinoma
N not available or absent
DCIS-IDC IDC with in-situ component
TN triple negative
DCIS ductal carcinoma in situ
ER estrogen receptor
PR- progesterone receptor
T tumor
N regional lymph node
RNA extraction
Manual microdissection of epithelial cells was performed isolating the area with, at least, 70% of tumor cells. The DCIS-IDC samples were microdissected for both tissues.
Sample naming is as follows: non-neoplastic breast epithelium - control; pure IDC - IDCpure; pure DCIS - DCISpure; IDC of DCIS-IDC group - IDCcomp and DCIS of DCIS-IDC group - DCIScomp.
RNA was isolated by RecoverAll™ Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit (Ambion/Life Sciences, Carlsbad, California, USA), according to manufacturer’s protocols. RNAs were quantified using NanoDrop (ThermoFisher, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) and Qubit RNA HS Assay kit (ThermoFisher).
Gene expression analysis
Multiplex gene expression analyses were performed at the Molecular Oncology Research Center-Barretos Cancer Hospital by nCounter® PanCancer Pathways panel (NanoString Technologies™, Seattle, Washington, USA), which allows the evaluation of 770 genes (730 cancer-related human genes, being 124 driver genes and 606 genes from 13 cancer-associated canonical pathways, and 40 as internal reference loci). An average of 100 ng of RNA was used for hybridization. The system analyses for gene expression digital quantification used was the nCounter® SPRINT Profiler (NanoString Technologies™).
Data analysis
Raw counts expression was analyzed using the nSolver™ Analysis Software (NanoString Technologies™). Two-by-two comparisons were performed and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were selected using expression levels p-value ≤0.01. Comparisons between the noninvasive group (control and DCISpure), and the invasive group (IDCpure, DCIScomp, and IDCcomp) were performed. A heatmap comparing the 3 tissues (control, DCISpure, and IDCpure) was made in nSolver™, and a Venn diagram was constructed to select genes of interest. Gene enrichment analyses were performed by FunRich Functional Enrichment Analysis Tool [14], using the Gene Ontology database. Interaction network analyses were also performed at the FunRich using FunRich database. The UALCAN [15] was used to evaluate gene expression in BC stages available at The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database.
Results
Putative genes involved in DCIS progression
Eleven comparisons were made two-by-two to obtain the DEGs (p-value ≤0.01) (see Additional file 1: Tables S1-S11). Between control and tumor tissues, the greatest differential expression was observed between DCISpure and control (123 DEGs - 72 downregulated), and the lowest, between control and IDCpure (66 DEGs - 46 downregulated).
Additional file 2 Figure S1. shows the comparison of gene expression between control, DCISpure, and IDCpure. Statistically, the invasive tissue exhibited a more similar profile to control than to the in-situ lesions. DCIScomp gene expression retains more similarities with IDCpure (2 DEGs), than with DCISpure (6 DEGs) and has a lower similarity with the control (104 DEGs) (see Additional file 2: Figure S1 and Additional file 1: Tables S5, S6, and S8), which suggests progressive molecular alterations from DCISpure to the IDC passing through DCIScomp.
Among the 6 DEGs found between DCISpure and DCIScomp (FGF2, GAS1, IBSP, LAMC3, MAP3K8, and SFRP1), only IBSP is downregulated in noninvasive lesions (Table 2).
Table 2.
DEGs between DCISpure and DCIScomp and between invasive and noninvasive groups
| DEGs | Gene | t statistic | p value | FCa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCISpure vs DCIScomp | Downregulated in DCISpure | IBSP | −3.86 | 8,00E-03 | −3.4 |
| Upregulated in DCISpure | FGF2 | 4.16 | 4,00E-03 | 1.5 | |
| GAS1 | 3.6 | 7,00E-03 | 2.67 | ||
| LAMC3 | 4.11 | 2,00E-03 | 2.06 | ||
| MAP3K8 | 3.49 | 8,00E-03 | 1.91 | ||
| SFRP1 | 4.75 | 1,00E-03 | 2,61 | ||
| Noninvasive vs invasive group | Downregulated in noninvasive group | ARID2 | −3.42 | 4,00E-03 | −1.52 |
| BCL2L1 | −3.17 | 6,00E-03 | −1.7 | ||
| BMP8A | −4.11 | 4,00E-04 | −2.28 | ||
| CCNB1 | −3.12 | 5,00E-03 | −1.95 | ||
| CDC25C | −3.16 | 4,00E-03 | −1.91 | ||
| OSM | −3.11 | 5,00E-03 | −2.23 | ||
| UTY | −3.1 | 5,00E-03 | −1.97 | ||
| WHSC1 | −3.26 | 6,00E-03 | −1.46 | ||
| Upregulated in noninvasive group | AXIN2 | 3 | 8,00E-03 | 2.14 | |
| CNTFR | 2.95 | 9,00E-03 | 2.4 | ||
| COL6A6 | 3.26 | 7,00E-03 | 3.75 | ||
| DKK1 | 2.79 | 1,00E-02 | 2.02 | ||
| DTX1 | 2.82 | 9,00E-03 | 1.76 | ||
| EFNA5 | 3.21 | 4,00E-03 | 1.71 | ||
| FGF10 | 3.26 | 3,00E-03 | 3.03 | ||
| FGF2 | 3.73 | 2,00E-03 | 2.91 | ||
| FGF7 | 3.71 | 1,00E-03 | 2.72 | ||
| FOS | 2.8 | 1,00E-02 | 2.6 | ||
| FZD7 | 3.3 | 4,00E-03 | 2.09 | ||
| GAS1 | 3.67 | 1,00E-03 | 2.5 | ||
| GLI3 | 3.11 | 5,00E-03 | 1.73 | ||
| GRIA3 | 3.7 | 2,00E-03 | 2.88 | ||
| IGF1 | 4.25 | 3,00E-04 | 2.72 | ||
| IRS1 | 3.28 | 6,00E-03 | 2.05 | ||
| ITGA9 | 3.55 | 2,00E-03 | 2.04 | ||
| ITGB8 | 3.47 | 2,00E-03 | 2.83 | ||
| JAK1 | 4.45 | 1,00E-04 | 1.32 | ||
| JUN | 3.19 | 7,00E-03 | 2.51 | ||
| KLF4 | 3.78 | 1,00E-03 | 2.4 | ||
| LAMB3 | 2.9 | 1,00E-02 | 2.47 | ||
| LAMC2 | 2.9 | 1,00E-02 | 2.14 | ||
| LEPR | 4.43 | 3,00E-04 | 3.08 | ||
| LIFR | 3 | 7,00E-03 | 2.16 | ||
| MAP3K8 | 2.98 | 8,00E-03 | 1.56 | ||
| MET | 4.09 | 4,00E-04 | 1.99 | ||
| NGFR | 3.48 | 2,00E-03 | 2.49 | ||
| NTRK2 | 3.32 | 4,00E-03 | 4.17 | ||
| PDGFRA | 3.85 | 1,00E-03 | 2.01 | ||
| PLD1 | 4.14 | 3,00E-04 | 1.81 | ||
| PRKCA | 3.7 | 1,00E-03 | 1.89 | ||
| PROM1 | 2.89 | 9,00E-03 | 3.68 | ||
| RELN | 3.05 | 9,00E-03 | 3.25 | ||
| SFRP1 | 4.01 | 5,00E-04 | 5.79 | ||
| SOX17 | 3.84 | 8,00E-04 | 2.41 | ||
| SOX9 | 3.01 | 6,00E-03 | 2.63 | ||
| SRPY1 | 3.73 | 1,00E-03 | 2.15 | ||
| SRPY2 | 3.47 | 3,00E-03 | 2.16 | ||
| TCF7L1 | 3.23 | 4,00E-03 | 2.15 | ||
| TGFBR2 | 3.9 | 7,00E-04 | 2.24 | ||
| THEM4 | 2.86 | 9,00E-03 | 1.6 | ||
| TNN | 3.47 | 2,00E-03 | 2.64 | ||
| TSC1 | 2.83 | 9,00E-03 | 1.35 | ||
| TSPAN7 | 3.61 | 1,00E-03 | 2.4 | ||
In bold are the genes potentially involved in DCIS progression
FC fold change
DEGs differentially expressed genes
DCIScomp DCIS as component
DCISpure pure DCIS
To verify which genes would have the greatest potential in the acquisition of invasive capacity, a Venn diagram was constructed (Fig. 1). FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1 are intersected between DCISpure vs DCIScomp and control vs DCIScomp and not present in the comparison control vs DCISpure, possibly acting in the acquisition of the invasive capacity of DCISpure.
Fig. 1.
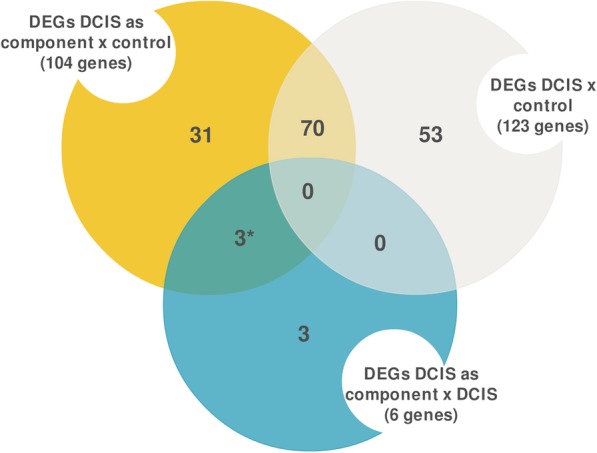
Putative genes involved in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) progression. Venn diagram depicting the common and distinct genes in each comparison. Genes most likely involved in invasive capacity of pure DCIS are marked with an asterisk. DEGs - Differentially expressed genes
The comparison between invasive and noninvasive groups shows 53 DEGs, being 8 upregulated and 45 downregulated in the invasive group (Table 2). Four of the downregulated genes in the invasive group were also differentially expressed between DCISpure and DCIScomp and the genes most probably involved in the DCIS progression are among them (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1) (Table 2).
Gene functional analysis
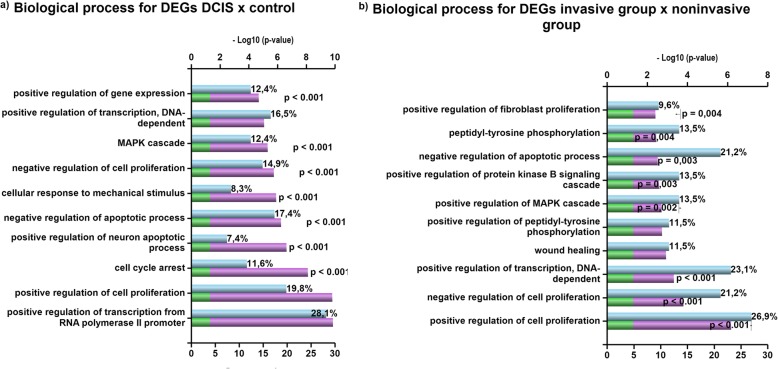
Enrichment analysis showed that the main biological processes altered between control and DCISpure (adjusted p-value ≤0.01) are related to gene expression regulation, cell proliferation and cell cycle arrest (Fig. 2a). Comparing invasive and noninvasive groups, the largest changes were seen in cell proliferation and transcription regulation (adjusted p-value ≤0.01) (Fig. 2b). To verify differences between genes potentially involved in DCIS progression (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1) and other 3 DEGs of DCISpure vs DCIScomp (LAMC3, MAP3K8, and IBSP), enrichment was done separately. In the first analysis, the most altered processes were regulation of angiogenesis, somatic stem cell maintenance, growth factor-dependent regulation of satellite cell proliferation and positive regulation of cell fate (p-value ≤0.01) (see Additional file 3: Table S12). For the latter ones, there were more changes in the extracellular matrix organization, differentiation cell morphogenesis and cell adhesion (p-value ≤ 0.01) (see Additional file 3: Table S12).
Fig. 2.
Top 10 Biological Processes for differentially expressed genes. Comparisons are between: a Control vs DCIS and b noninvasive vs invasive groups. Gene enrichment analyses were performed by FunRich Functional Enrichment Analysis Tool, using the Gene Ontology database
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks of the 6 DEGs of DCISpure vs DCIScomp are shown in Additional file 4: Figure S2. In Additional file 4: Figure S2a, all interactions are shown and in Additional file 4: Figure S2b only the 107 statistically significant interactions were left in the PPI snapshot, showing 3 out of 6 genes (p-value ≤0.01).
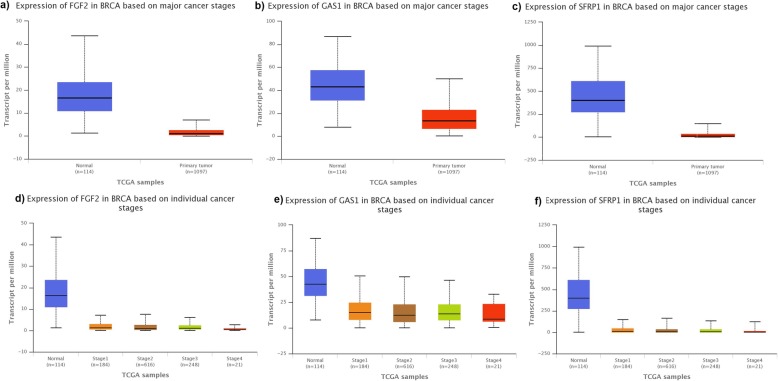
Evaluation of gene expression in normal tissue and BC stages was made for 3 genes potentially involved in DCIS progression (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1) using the TCGA database (Fig. 3). The downregulation correlate with earlier stages, which corroborates our results when comparing DCISpure vs DCIScomp.
Fig. 3.
Comparisons of FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1 expressions. Comparisons are made between normal tissue and primary tumor (first tumor in the body) and among breast cancer (BC) progression stages (Stages 1–4). This data was generated online in UALCAN website based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database (TCGA). a Expression of FGF2 in normal tissue and primary tumor. b Expression of GAS1 in normal tissue and primary tumor. c Expression of SFRP1 in normal tissue and primary tumor. d Expression of FGF2 in BC stages. e Expression of GAS1 in BC stages. f Expression of SFRP1 in BC stages
Discussion
Six DEGs were found in DCISpure vs DCIScomp, being 3 of them also differentially expressed between control and DCIScomp, but not between control and DCISpure. The same 3 genes (FGF2, GAS1, and SFRP1) showed distinct gene expression profiles between noninvasive and invasive groups. Thus, suggesting their involvement in DCIS progression.
Interestingly, the in-situ stage (DCISpure) has more molecular differences with control than the invasive stage (IDCpure). However, considering that IDC is the most advanced stage in progression and morphology, we expected greater molecular changes in reference to non-neoplastic tissue. Our result is probably due to early acquisition of tumor enabling features, which are later followed by minor ones [4].
DCIScomp and IDCcomp of patients with DCIS-IDC do not have DEGs between them and are more like IDCpure than control. Initial gene expression changes may remain necessary in DCIS-IDC since acquisition of invasive potential has not yet been completed in all cells. Also, as suggested by Muggerud et al. [16] and Hu et al. [17] many processes involved in DCIS progression may be expression changes in the tumor microenvironment, and not only in tumor cells [18].
The 3 DEGs more likely involved in DCIS progression were FGF2, GAS1, and SFPR1, all downregulated in DCIScomp. This fact suggests that progression from DCISpure to DCIScomp may use silencing mechanisms more often than activating ones.
When comparing DEGs between control and DCISpure, 31% are driver genes, whereas none of the genes that may be involved in DCIS progression or DEGs between DCISpure and IDCpure is driver genes, suggesting that major alterations occur at the beginning of carcinogenesis and not at the end.
In the analysis of invasive vs noninvasive groups, FGF2, GAS1, and SFPR1 were downregulated in the invasive group. Epigenetic alterations may contribute to BC progression by transcriptionally silencing specific tumor suppressor genes [19, 20], which could explain the loss of expression that we observed.
The expression of FGF2 was lower in BC when compared to normal tissues [21]. In vitro assays have demonstrated a potent inhibitory effect of FGF2 on BC cells, possibly involving MAPK cascade and cell cycle G1/S transition [22–24]. Enrichment analysis has shown statistically significant interactions between FGF2 and MAPK pathway genes and other components of the FGF family. UALCAN analysis has shown an upregulation of FGF2 in normal tissues, in comparison to primary BC and FGF2 downregulation is associated with tumor progression.
According to TCGA database GAS1 is downregulated in primary breast tumors. Hedgehog (Hh) signaling has been suggested as a critical determinant of tumor progression [25–28]. A progressive increase of Hh expression and Hh pathway activation has been observed from control, DCIS, DCIS with microinvasion and to IDC [29, 30]. GAS1 protein binds Sonic hedgehog (SHH), one of three Hh proteins, and may inhibit Hh signaling [31, 32]. The interaction of GAS1 with SHH was observed but was not statistically significant.
SFRP1 gene is a negative regulator of the Wnt pathway, which is aberrantly activated in BC [33–35]. Statistically significant interactions of SFRP1 with Wnt pathway genes were seen and enrichment analysis showed a negative regulation of canonical Wnt receptor signaling pathway. SFRP1 was downregulated in primary BC in comparison to normal tissue and in invasive lesions.
Functional analyses of FGF2, GAS1 and SFRP1 suggests a role in DCIS progression, being negative regulators of cell cycle G1/S transition, Hh signaling, and the Wnt pathway, respectively. We propose that downregulation favors DCIS progression. Unfortunately, our samples could not be divided into high and low-grade DCIS, nor could we study samples according to cancer molecular subtypes. Studying these groups separately may reveal important events in the DCIS progression.
Conclusions
Understanding BC progression will enable the design of effective strategies for diagnosis and treatment. Progression biomarkers should be able to predict DCIS cases destined to become invasive tumors, therefore allowing for proper monitoring and avoiding overtreatment. Here, we identified 3 progression-specific candidate genes namely FGF2, GAS1, SFRP1, downregulated in tissues with invasive capacity. The progression from DCIS to invasive BC is a complex process, being possible that DCIS of distinct molecular phenotypes progress to invasive BC through the acquisition of distinct genetic or epigenetic hits.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Comparison between control and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S2. Comparison between control and pure ductal carcinoma in situ. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S3. Comparison between pure carcinoma ductal in situ and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S4. Comparison between invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S5. Comparison between ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S6. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ and ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S7. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S8. Comparison between control and ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S9. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S10. Comparison between control and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S11. Comparison between noninvasive and invasive groups. Differentially expressed genes are in bold.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Hierarchical clustering of 730 genes and its gene expressions. Genes of nCounter® PanCancer Pathways panel. Gene expressions are in non-neoplastic (control), ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) tissues. Agglomerative clustering was made in nSolver™ Analysis Software. Individual genes are arranged in rows and samples’ groups in columns. The color scale is shown above the figure.
Additional file 3: Table S12. Top 10 biological process of DEGs between DCIScomp and DCISpure and comparisons with control tissue.
Additional file 4: Figure S2. Snapshot of protein-protein interaction networks. Networks are made with the 6 differentially expressed genes between ductal carcinoma in situ as component (DCIScomp) and pure DCIS (DCISpure). Interaction diagram was generated using FunRich Functional Enrichment Analysis Tool and FunRich database. a) Network diagram with all annotated interactions. b) Network diagram illustrating the 107 statistically significant interactions (p-value ≤0.01).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Lucienne B. Oliveira, Histotechnical Laboratory technique in Federal University of Espirito Santo for the aid in the preparation of some slides with mammoplasties material; Ana Paula S. Louro, pathologist in immunohistochemistry laboratory of the Death Verification Service-Vitoria-Espirito Santo, for help in the selection of elective mammoplasties to be used as control; Adriane F. Evangelista, bioinformatician of Barretos Cancer Hospital, for help in delineating the bioinformatics analysis at the project beginning; Sabina B. Aleixo, oncologist at the Evangelical Hospital of Cachoeiro de Itapemirim-Espirito Santo, for aid in the initial sampling design and Adriana C. Carloni, biologist of Barretos Cancer Hospital, for help in molecular analysis.
Abbreviations
- BC
Breast cancer
- DCIS
Ductal carcinoma in situ
- DEG
Differently expressed gene
- FFPE
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
- Hh
Hedgehog
- IDC
Invasive ductal carcinoma
- PPI
Protein-protein interaction
- QC
Quality Control
- SHH
Sonic hedgehog
- TCGA
The cancer genome atlas
Authors’ contributions
RSD has made the design of the work; acquisition of the patient’s data; analysis; interpretation of the data and drafted the work. ES has made the design of the work; acquisition of the patient’s data; molecular analysis; interpretation of the data and revised the work. ACL has acquired the patient’s data; molecular analysis and revised the work. RACV has made the design of the work; acquisition of the patient’s data making data available from your services as an oncologist; histological analysis; interpretation of the data and revised the work. MMCM has acquired the patient’s data; histological analysis and revised the work. IVVS has acquired the patient’s data; histological analysis and revised the work. JZP has acquired the patient’s data making data available from your services as an oncologist and revised the work. LFR has acquired the patient’s data and histological analysis. NJP has acquired the patient’s data and revised the work. LPA has made the design of the work and acquisition of the patient’s data. RSR has interpreted the data and revised the work. EVWS revised the work. LNRA has acquired the patient’s data. FMG has acquired the patient’s data. JAS has acquired the patient’s data. DPV has acquired the patient’s data. RMR has acquired the patient’s data; molecular analysis; made its infrastructure available for molecular analysis; interpretation of the data and revised the work. IDL has made the design of the work; analysis; interpretation of the data and revised the work. All authors have read and approved this manuscript.
Funding
R.S.D. has received a scholarship by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Espirito Santo-Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (FAPES-CAPES) (number 0698/2015). ES has received a scholarship by FAPES (number 66141494/2014). LPA has received a scholarship by FAPES (number 66271126/2014). These scholarships made it possible for these 3 students to dedicate themselves to the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript. This study was supported by FAPES (number 0468/2015) and this financing enabled the purchase of all reagents used in the analyzes and the trips to the partner hospitals for sample collection and to the Barretos Cancer Hospital where molecular analyzes were performed.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed were following the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study complies with the laws of the country. It was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Integrated Center of Health Attention-CIAS/UNIMED VITORIA by protocol number 2.337.052 and the patients signed the informed consent form including authorization for publication of research data. This study also was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Barretos Cancer Hospital by protocol number 1505/2017. This ethics committee regularly authorized the dispensation of consent form.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Raquel Spinassé Dettogni and Elaine Stur contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12885-020-6608-y.
References
- 1.Wellings SR, Jensen HM. On the origin and progression of ductal carcinoma in the human breast. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;50(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allred DC, Mohsin SK, Fuqua SA. Endocrinol. Relat Cancer. 2001;8:47–61. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0080047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCormick B, Winter K, Hudis C, Kuerer HM, Rakovitch E, Smith BL, Sneige N, Moughan J, Shah A, Germain, et al. RTOG 9804: a prospective randomized trial for goodrisk ductal carcinoma in situ comparing radiotherapy with observation. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:709–715. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ma XJ, Salunga R, Tuggle JT, Gaudet J, Enright E, McQuary P, Payette T, Pistone M, Stecker K, Zhang BM, et al. Gene expression profiles of human breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:5974–5979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0931261100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schuetz CS, Bonin M, Clare SE, Nieselt K, Sotlar K, Walter M, Fehm T, Solomayer E, Riess O, Walwiener D, et al. Progression-specific genes identified by expression profiling of matched ductal carcinomas in situ and invasive breast tumors, combining laser capture microdissection and oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5278–5286. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Castro NP, Osorio CA, Torres C, Bastos EP, Mourao-Neto M, Soares FA, Brentani HP, Carraro DM. Evidence that molecular changes in cells occur before morphological alterations during the progression of breast ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:R87. doi: 10.1186/bcr2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ma XJ, Dahiya S, Richardson E, Erlander M, Sgroi DC. Gene expression profiling of the tumor microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11:R7. doi: 10.1186/bcr2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parikh U, Chhor CM, Mercado CL. Ductal carcinoma in situ: the whole truth. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018;210:246–255. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Carraro DM, Elias EV, Andrade VP. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: morphological and molecular features implicated in progression. Biosci Rep. 2014;34(1):e00090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7. New York (NY): Springer; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frank TS, Deffenbaugh AM, Reid JE, Hulick M, Ward BE, Lingenfelter B, Grumpper KL, Scholl T, Taytigian SV, Pruss DR, et al. Clinical characteristics of individuals with Germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2: analysis of 10,000 individuals. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1480–1490. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.6.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ. WHO classification of Tumours of the breast. 4. Lyon (LY): IARC; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ. Panel menbers. Strategies for subtypes—dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–1747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Chisanga D, Alessandro R, Ang CS, Askenase P, Batagov AO, Benito-Martin A, Camussi G, Clayton A, et al. A novel community driven software for functional enrichment analysis of extracellular vesicles data. J Extracellular Vesicles. 2017;1:1321455. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2017.1321455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Rodriguez IP, Chakravarthi BVSK, Varambally S. UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 2017;19:649–658. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Muggerud A, Hallett M, Johnsen H, Kleivia K, Zhouf W, Tahmasebpoorg S, Amini RM, Botling J, Borresen-Dale AL, Sorlie T, et al. Molecular diversity in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and early invasive breast câncer. Mol Oncol. 2010;4:357–368. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hu M, Yao J, Cai L, Bachman KE, van den Brule F, Velculescu V, Polyak K. Distinct epigenetic changes in the stromal cells of breast cancers. Nat Genet. 2005;37:899–905. doi: 10.1038/ng1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gorringe KL, Fox SB. Ductal carcinoma in situ biology, biomarkers, and diagnosis. Front Oncol. 2017;7:248. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Widschwendter M, Jones PA. DNA methylation and breast carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2002;21:5462–5482. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fazzari MJ, Greally JM. Epigenomics: beyond CpG islands. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:446–455. doi: 10.1038/nrg1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Korah RM, Sysounthone V, Golowa Y, Wieder R. Basic fibroblast growth factor confers a less malignant phenotype in MDA-MB- 231 human breast Cancer Cells1. Cancer Res. 2000;60:733–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang JK. Gao 0, Goldfarb M. fibroblast growth factor receptors have different signaling and mitogenic potentials. Mol Cel Biol. 1994;14:181–188. doi: 10.1128/MCB.14.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fenig E, Wieder R, Paglin S, Wang H, Persaud R, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z, Yahalom J. Basic fibroblast growth factor confers growth inhibition and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang H, Rubin M, Fenig E, DeBlasio A, Mendelsohn J, Yahalom J, Wieder R. Basic fibroblast growth factor causes growth arrest in MCF-7 human breast Cancer cells while inducing both Mitogenic and inhibitory G1 events. Cancer Res. 1997;7:1750–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mullor JL, Sanchez P, Ruiz I, Altaba A. Pathways and consequences: hedgehog signaling in human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:562–569. doi: 10.1016/S0962-8924(02)02405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2454–2472. doi: 10.1101/gad.1693608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ng JM, Curran T. The Hedgehog’s tale: developing strategies for targeting cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;11:493–501. doi: 10.1038/nrc3079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abidi A. Hedgehog signaling pathway: a novel target for cancer therapy: Vismodegib, a promising therapeutic option in treatment of basal cell carcinomas. Indian J Pharmacol. 2014;46:3–12. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.124884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.O’Toole SA, Machalek DA, Shearer RF, Millar EK, Nair R, Schofield P, McLeod D, Cooper CL, McNeil CM, McFarland A, et al. Hedgehog overexpression is associated with stromal interactions and predicts for poor outcome in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4002–4014. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xuan Y, Lin Z. Expression of Indian hedgehog signaling molecules in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:235–240. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Allen BL, Tenzen T, McMahon AP. The hedgehog-binding proteins Gas1 and Cdo cooperate to positively regulate Shh signaling during mouse development. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1244–1257. doi: 10.1101/gad.1543607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Beachy PA, Hymowitz SG, Lazarus RA, Leahy DJ, Siebold C. Interactions between hedgehog proteins and their binding partners come into view. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2001–2012. doi: 10.1101/gad.1951710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Veeck J, Niederacher D, An H, Klopocki E, Wiesmann F, Betz B, Galm O, Camara O, Durst M, Kristiansen G, et al. Aberrant methylation of the Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in breast cancer is associated with unfavourable prognosis. Oncogene. 2006;25:3479–3488. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Klopocki E, Kristiansen G, Wild PJ, Klaman I, Castanos-Velez E, Singer G, Stohr R, Simon R, Sauter G, Leibiger H, et al. Loss of SFRP1 is associated with breast cancer progression and poor prognosis in early stage tumors. Int J Oncol. 2004;25:641–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huth L, Rose M, Kloubert V, Winkens W, Schlensog M, Hartmann A, Knuchel R, Dahl E. BDNF is associated with SFRP1 expression in luminal and basal-like breast Cancer cell lines and primary breast Cancer tissues: a novel role in tumor suppression? PLoS One. 2014;9:e102558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Comparison between control and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S2. Comparison between control and pure ductal carcinoma in situ. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S3. Comparison between pure carcinoma ductal in situ and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S4. Comparison between invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S5. Comparison between ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions and pure invasive ductal carcinoma. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S6. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ and ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S7. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S8. Comparison between control and ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S9. Comparison between pure ductal carcinoma in situ of mixed lesions and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S10. Comparison between control and invasive ductal carcinoma of mixed lesions. Differentially expressed genes are in bold. Table S11. Comparison between noninvasive and invasive groups. Differentially expressed genes are in bold.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Hierarchical clustering of 730 genes and its gene expressions. Genes of nCounter® PanCancer Pathways panel. Gene expressions are in non-neoplastic (control), ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) tissues. Agglomerative clustering was made in nSolver™ Analysis Software. Individual genes are arranged in rows and samples’ groups in columns. The color scale is shown above the figure.
Additional file 3: Table S12. Top 10 biological process of DEGs between DCIScomp and DCISpure and comparisons with control tissue.
Additional file 4: Figure S2. Snapshot of protein-protein interaction networks. Networks are made with the 6 differentially expressed genes between ductal carcinoma in situ as component (DCIScomp) and pure DCIS (DCISpure). Interaction diagram was generated using FunRich Functional Enrichment Analysis Tool and FunRich database. a) Network diagram with all annotated interactions. b) Network diagram illustrating the 107 statistically significant interactions (p-value ≤0.01).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].