Abstract
Background
Zotepine is a relatively new antipsychotic often used for the treatment of people with schizophrenia. It is claimed to be particularly effective for negative symptoms.
Objectives
To determine the effects of zotepine compared with placebo, typical and other atypical antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia and related psychoses.
Search methods
For the 2006 update we searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's register of trials.
Selection criteria
We included all randomised clinical trials comparing zotepine with other treatments for people with schizophrenia or other psychoses.
Data collection and analysis
We independently inspected citations and abstracts, ordered papers, re‐inspected these and assessed their quality. For homogenous dichotomous data we calculated the relative risk (RR), 95% confidence intervals (CI) and, where appropriate, numbers needed to treat/harm (NNT/H) on an intention‐to‐treat basis. For continuous data, we calculated weighted mean differences (WMD). We inspected all data for heterogeneity.
Main results
The review currently includes 11 studies with 966 participants. Most outcomes were short term (4‐12 weeks). We found no data for outcomes such as relapse, time in hospital, satisfaction with care and day‐to‐day functioning. Compared with placebo, mental state ratings favoured zotepine (n=106, 1 RCT, RR No 20% decrease in BPRS 0.44 CI 0.3 to 0.7, NNT 3 CI 2 to 6) using the last observation carried forward method. For the comparison with typical drugs, limited data suggest that zotepine may be as effective as these older medications. Mental state measures of 'no clinically important improvement' favour zotepine when compared with other active drugs (n=356, 4 RCTs, RR 0.77 CI 0.7 to 0.9, NNT 7 CI 4 to 22). About one third of people in both the zotepine and control groups left the studies before trial completion. Zotepine may result in less movement disorder adverse effects than typical antipsychotic drugs. Trials have not highlighted clear differences between zotepine and other atypical drugs.
Authors' conclusions
Zotepine may be a valuable addition to the class of atypical antipsychotic drugs. However, more data from existing studies is urgently needed to increase confidence in the findings of this review. In addition to this, new data from well planned, conducted and reported long term pragmatic randomised trials are needed. Otherwise clinical use of zotepine will be based upon speculation of short explanatory trials for everyday practice.
Plain language summary
Zotepine for schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic, relapsing mental illness and has a worldwide lifetime prevalence of about 1% irrespective of culture, social class and race. Schizophrenia is characterised by positive symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions and negative symptoms such as emotional numbness and withdrawal. One quarter of those who have experienced an episode of schizophrenia recover and the illness does not recur. Another 25% experience an unremitting illness. Half of those diagnosed do have a recurrent illness but with long episodes of considerable recovery from the positive symptoms. Current medication is effective in reducing positive symptoms, but negative symptoms are fairly resistant to treatment. In addition, drug treatments are associated with adverse effects and the overall cost of the illness to the individual, their carers and the community is considerable.
Antipsychotic medications are categorised as typical antipsychotics (i.e. first generation: chlorpromazine, haloperidol, etc) and atypical antipsychotics (i.e. second generation: amisulpiride; olanzapine; risperidone etc) and both are the mainstay of treatment for people with schizophrenia. Zotepine is an atypical antipsychotic and the atypicals are thought to have a different adverse effects profile to typicals; in particular they are thought less likely to cause movement disorders.
We sought all relevant randomised controlled trials comparing zotepine with placebo and other antipsychotics but found very few. Zotepine may well be a useful drug, but currently data are sparse, and importantly this data emanates from a company with an interest in showing zotepine to be effective and safe.
Background
Typical antipsychotic drugs, such as haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and trifluoperazine, are widely used as the first line treatment for people with schizophrenia, in both the acute and chronic stages of the illness (APA 1997, Silverstone 1995). However, the atypical class of antipsychotic drugs, most of which have been formulated relatively recently, are making important inroads into this approach (Wood Mackenzie 1998, Adams 1999). Atypical is a widely used term used to describe second generation antipsychotics which have a low propensity to produce movement disorders, sedation and raised serum prolactin (Kerwin 1994).The pharmacological profiles of the atypical drugs have been described as either clozapine‐like or risperidone‐like, but with the inclusion of compounds such as sulpiride and zotepine this dichotomy becomes simplistic (Kerwin 1996). There is some suggestion that the different adverse effect profiles of the atypical antipsychotic group make them more acceptable to people with schizophrenia (Casey 1997). Certainly, the adverse effects of the typical drugs, such as movement disorders and sedation, are problematic and can result in poor compliance with treatment (CWG 1998).
The positive symptoms of schizophrenia (delusions, hallucinations, and disordered thinking) seem more responsive to the typical antipsychotic drugs than negative symptoms (poverty of speech, lack of motivation, apathy and inability to express emotions (Carpenter 1994)). These can be very disabling and may respond better to the atypical antipsychotic drugs (APA 1997, Silverstone 1995), although this has not yet been adequately established (Kane 1996). Atypical antipsychotics are more expensive than conventional drugs (Meltzer 1996), but it has been suggested that if they do indeed reduce a person's need for inpatient services their use would result in a net reduction of costs (Buckley 1997, Glazer 1997).
In treating people with schizophrenia, choosing the most appropriate, effective and tolerable antipsychotic drug is a key to maximising the usefulness of medication. According to recent treatment guidelines, both conventional/typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs may be reasonable choices in the treatment of schizophrenia (APA 1997, Geddes 1999).
Technical background Zotepine is a dopamine D1, D2 and 5‐HT antagonist with particular effects on the noradrenergic system and it is claimed to be particularly effective in negative symptoms (www.psychotropics.dk).
Objectives
To review the effects of zotepine compared with placebo, other antipsychotics drugs (typicals and other atypicals) for people with schizophrenia or related psychoses.
As secondary objectives, we proposed to investigate: 1. Whether people with schizophrenia described as 'treatment resistant' differed in their response from those whose illness was not designated as such; 2. Whether people having predominantly positive or negative symptoms of schizophrenia were more responsive to zotepine than those without this designation; and 3. Whether people experiencing their first episode of schizophrenia differed in their response from those at a later stage of their illness.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We sought all relevant randomised controlled trials. Where a trial was described as 'double‐blind', but it was only implied that the study was randomised, we included these trials in a sensitivity analysis. If there was no substantive difference within primary outcomes (see types of outcome measures) when these 'implied randomisation' studies were added, then we added them into the final analysis. If there was a substantive difference, then we only used clearly randomised trials and the results of the sensitivity analysis were described in the text. We excluded quasi‐randomised studies, such as those allocating by using alternate days of the week.
Types of participants
We included people with schizophrenia and other types of schizophrenia‐like psychoses (schizophreniform and schizoaffective disorders) however diagnosed. There is no clear evidence that the schizophrenia‐like psychoses are caused by fundamentally different disease processes or require different treatment approaches (Carpenter 1994). If possible, we excluded people with dementing illnesses, depression and primary problems associated with substance misuse.
Types of interventions
1. Zotepine: any dose. 2. Placebo. 3. Any other antipsychotic agent, divided into the typical and the atypical antipsychotics (amisulpiride, clozapine, loxapine, molindone, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, sertindole, sulpiride, ziprasidone).
Types of outcome measures
All outcomes were reported for the short term (up to six weeks), medium term (7‐26 weeks) and long term (over 26 weeks).
Primary outcomes
1. Global state 1.1 Relapse
Secondary outcomes
1. Death ‐ suicide and natural causes
2. Global state 2.1 No clinically important change in global state (as defined by individual studies) 2.2 Average endpoint global state score 2.3 Average change in global state scores
3. Service outcomes 3.1 Hospitalisation 3.2 Time to hospitalisation
4. Mental state (with particular reference to the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia) 4.1 No clinically important change in general mental state 4.2 Average endpoint general mental state score 4.3 Average change in general mental state scores 4.4 No clinically important change in specific symptoms (positive symptoms of schizophrenia, negative symptoms of schizophrenia, depression, mania) 4.5 Average endpoint specific symptom score 4.6 Average change in specific symptom scores
5. General functioning 5.1 No clinically important change in general functioning 5.2 Average endpoint general functioning score 5.3 Average change in general functioning scores 5.4 No clinically important change in specific aspects of functioning, such as social or life skills 5.5 Average endpoint specific aspects of functioning, such as social or life skills 5.6 Average change in specific aspects of functioning, such as social or life skills
6. Behaviour 6.1 No clinically important change in general behaviour 6.2 Average endpoint general behaviour score 6.3 Average change in general behaviour scores 6.4 No clinically important change in specific aspects of behaviour 6.5 Average endpoint specific aspects of behaviour 6.6 Average change in specific aspects of behaviour
7. Adverse effects ‐ general and specific (particularly movement disorders) 7.1 Clinically important general adverse effects 7.2 Average endpoint general adverse effect score 7.3 Average change in general adverse effect scores 7.4 Clinically important specific adverse effects 7.5 Average endpoint specific adverse effects 7.6 Average change in specific adverse effects
8. Engagement with services
9. Satisfaction with treatment 9.1 Leaving the studies early 9.2 Recipient of care not satisfied with treatment 9.3 Recipient of care average satisfaction score 9.4 Recipient of care average change in satisfaction scores 9.5 Carer not satisfied with treatment 9.6 Carer average satisfaction score 9.7 Carer average change in satisfaction scores
10. Quality of life 10.1 No clinically important change in quality of life 10.2 Average endpoint quality of life score 10.3 Average change in quality of life scores 10.4 No clinically important change in specific aspects of quality of life 10.5 Average endpoint specific aspects of quality of life 10.6 Average change in specific aspects of quality of life
11. Economic outcomes 11.1 Direct costs 11.2 Indirect costs
12. Cognitive functioning 12.1 No clinically important change in cognitive functioning 12.2 Average endpoint cognitive functioning score 12.3 Average change in cognitive functioning scores 12.4 No clinically important change in specific aspects of cognitive functioning 12.5 Average endpoint specific aspects of cognitive functioning 12.6 Average change in specific aspects of cognitive functioning
13. Leaving the study early
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
1. Electronic search for the 2006 review update We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register (December 2005) using the phrase:
[(*zotepine* or *lodopin* or *nipolept* or *zopite* or *setous* or *majorpin* in REFERENCE title, abstract or index fields) OR (*zotepine* or *lodopin* or *nipolept* or *zopite* or *setous* or *majorpin* in STUDY intervention field)]
This register is compiled by systematic searches of major databases, hand searches and conference proceedings (see Group Module).
2. Details of previous searches
2.1. We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Register (January 1999) using the phrase:
[zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin or #42 = 138]
(#42 is the field within this register that contains the intervention code and 138 is zotepine)
2.2. We searched Biological Abstracts (January 1980 ‐ January 1999) using the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's phrase for both randomised controlled trials and schizophrenia (see Group search strategy) combined with the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin)]
2.3. We searched the Cochrane Library (Issue 1, 1999) using the phrase:
[zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin]
2.4. We searched CINAHL (1982 ‐ April 1999) using the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's phrase for both randomised controlled trials and schizophrenia (see Group search strategy) combined with the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin)]
2.5. We searched EMBASE (January 1980 ‐ January 1999) using the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's phrase for both randomised controlled trials and schizophrenia (see Group search strategy) combined with the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin or explode "ZOTEPINE"/ all subheadings)]
2.6. We searched MEDLINE (January 1966 ‐ March 1999) using the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's phrase for both randomised controlled trials and schizophrenia (see Group search strategy) combined with the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin)]
2.7. We searched PsycLIT (January 1974 ‐ January 1999) using the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's phrase for both randomised controlled trials and schizophrenia (see Group search strategy) combined with the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin)]
2.8. We undertook specific searches for randomised trials of zotepine in the following databases:
Pharmaceutical databases available on the Dialog Corporation Datastar service:
ADIS Inpharma; ADIS LMS drug alerts; IDIS Drug File; PharmLine; Pharma Marketing Service
using the following schizophrenia search terms: schizo$ psychotic$ psychoses psychosis ((chronic$ or sever$) near2 mental$) near2 (ill$ or disorder$)
combined with the following randomised trial search terms: trial$ random$ (singl$ or doubl$ or trebl$ or tripl$) near (blind$ or mask$) placebo or standard adj treatment study or studies rct$ crossover$ control or controlled or controls
and the phrase:
[and (zotepine or lodopin or nipolept or zopite or setous or majorpin)]
Searching other resources
1. Reference lists We searched all references of articles selected for further relevant trials.
2. Authors of studies We contacted the first authors of studies when necessary to clarify data, and asked for additional studies.
3. Pharmaceutical company We contacted Knoll Pharmaceuticals to obtain data on unpublished trials.
Data collection and analysis
1. Selection of trials We (MF, SM and AMB) inspected the citations identified from the search independently. We indentified potentially relevant abstracts and ordered full papers and reassessed these for inclusion and methodological quality. We discussed and reported any disagreements. For the 2006 update we (MF and JR) independently inspected and selected citations from the search results. We obtained full reports and reassessed these for inclusion and rated them according to their methodological quality.
2. Assessment of methodological quality We assessed the methodological quality of included trials in this review using the criteria described in the Cochrane Handbook (Higgins 2005) and the Jadad Scale (Jadad 1996). The former is based on the evidence of a strong relationship between allocation concealment and direction of effect (Schulz 1995). The categories are defined below:
A. Low risk of bias (adequate allocation concealment) B. Moderate risk of bias (some doubt about the results) C. High risk of bias (inadequate allocation concealment). For the purpose of the analysis in this review, we included trials if they met the Cochrane Handbook criteria A or B.
The Jadad Scale measures a wider range of factors that impact on the quality of a trial. The scale includes three items: 1. Was the study described as randomised? 2. Was the study described as double‐blind? 3. Was there a description of withdrawals and drop outs?
Each item receives one point if the answer is positive. In addition, a point can be deducted if either the randomisation or the blinding/masking procedures described are inadequate. For this review we used a cut‐off of two points on the Jadad scale to check the assessment made by the Handbook criteria. However, we did not use the Jadad Scale to exclude trials.
3. Data management 3.1 Data extraction We (MF, SM, PD, AMB, GG) independently extracted data and, where further clarification was needed, the authors' of trials were contacted to provide missing data. For the 2006 update we (MF and JR) independently extracted data and contacted authors of trials for missing data.
3.2 Intention to treat analysis We excluded data from studies where more than 50% of data for any given outcome were lost to follow up. In studies with less than 50% dropout rate, we considered people leaving early to have had the negative outcome, except for the event of death. We analysed the impact of including studies with high attrition rates (25‐50%) in a sensitivity analysis. If inclusion of data from this latter group did result in a substantive change in the estimate of effect we did not add their data to trials with less attrition, but presented the data separately.
4. Data analysis 4.1 Binary data For binary outcomes we calculated the relative risk (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI). We also calculated the number needed to treat statistic (NNT) and number needed to harm (NNH). If heterogeneity was found (see section 5) we used a random effects model.
4.2 Continuous data 4.2.1 Normal distribution: Continuous data on outcomes in trials relevant to mental health issues are often not normally distributed. To avoid the pitfall of applying parametric tests to non‐parametric data we applied the following standards to continuous endpoint data before inclusion: i. standard deviations and means were reported in the paper or were obtainable from the authors; ii when a scale started from zero, the standard deviation, when multiplied by two, should be less than the mean (otherwise the mean is unlikely to be an appropriate measure of the centre of the distribution, Altman 1996); In cases with data that are greater than the mean they were entered into 'Other data' table as skewed data.
Endpoint scores on scales often have a finite start and endpoint and this rule can be applied to them. However, when continuous data are presented on a scale which includes a possibility of negative values (such as change on a scale) it is impossible to tell whether data are non‐normally distributed (skewed) or not. It is thus preferable to use scale endpoint data, which typically cannot have negative values. If endpoint data were not available, we used change data, because the statistics used in Metaview are rather robust towards skewness. If a scale starts from a positive value (such as PANSS, which can have values from 30 to 210) the calculation described above in (b) should be modified to take the scale starting point into account. In these cases skewness is present if 2SD>(S‐Smin), where S is the mean score and Smin is the minimum score.
4.2.2 Summary statistic: For continuous outcomes we estimated the weighted mean difference (WMD) between groups. Again, if heterogeneity was found (see section 5) we used a random effects model.
4.2.3 Valid scales: Continuous data from rating scales were included only if the measuring instrument had been described in a peer‐reviewed journal and the instrument was either a self report or completed by an independent rater or relative (not the therapist). However, as it was expected that therapists would frequently also be the rater, we presented such data, but with a comment that they would likely be 'prone to bias'.
4.2.4 Endpoint versus change data Where possible we presented endpoint data and if both endpoint and change data were available for the same outcomes then we only reported endpoint data.
4.2.5 Cluster trials: studies increasingly employ 'cluster randomisation' (such as randomisation by clinician or practice) but analysis and pooling of clustered data poses problems. Firstly, authors often fail to account for intra class correlation in clustered studies, leading to a 'unit of analysis' error (Divine 1992) whereby p values are spuriously low, confidence intervals unduly narrow and statistical significance overestimated. This causes type I errors (Bland 1997; Gulliford 1999).
Where clustering was not accounted for in primary studies, we presented the data in a table, with a (*) symbol to indicate the presence of a probable unit of analysis error. In subsequent versions of this review we will seek to contact first authors of studies to obtain intra class correlation co‐efficients of their clustered data and to adjust for this by using accepted methods (Gulliford 1999). Where clustering has been incorporated into the analysis of primary studies, we will also present these data as if from a non‐cluster randomised study, but adjusted for the clustering effect.
We have sought statistical advice and have been advised that the binary data as presented in a report should be divided by a 'design effect'. This is calculated using the mean number of participants per cluster (m) and the intra‐class correlation co‐efficient (ICC) Design effect = 1+(m‐1)*ICC (Donner 2002). If the ICC was not reported it was assumed to be 0.1 (Ukoumunne 1999).
5. Test for heterogeneity Firstly, we considered all the included studies within any comparison to judge clinical heterogeneity. Then we visually inspected graphs to investigate the possibility of statistical heterogeneity. This was supplemented, primarily, by employing the I‐squared statistic. This provides an estimate of the percentage of inconsistency thought to be due to chance. Where the I‐squared estimate was equal to, or greater than 75%, this was interpreted as evidence of high levels of heterogeneity (Higgins 2003). In such cases, we sought to remove outlying trial(s) and perform and report sensitivity analyses both with and without these outlying trials. Where no obvious outlying trial(s) could be identified we analysed and reported the result using a random effects model, which takes into account that the effects being estimated are not identical.
6. Addressing publication bias We entered data from all included studies into a funnel graph (trial effect against trial size) in an attempt to investigate the likelihood of overt publication bias (Egger 1997).
7. Sensitivity analyses The effect of including studies with high attrition rates was analysed in a sensitivity analysis. We also hoped to investigate whether there were differences between: i. People with schizophrenia described as 'treatment resistant' and those whose illness was not designated as such; ii. People having predominantly positive or negative symptoms of schizophrenia and those without this designation; and iii. People experiencing their first episode of schizophrenia and those at a later stage of their illness.
8. General Where possible, we entered data in such a way that the area to the left of the line of no effect indicated a favourable outcome for zotepine.
Results
Description of studies
For substantive descriptions of studies please see Included and Excluded Studies table.
1. Excluded studies We excluded fourteen studies, mostly because they were reviews or non‐randomised clinical studies. One study was an animal investigation and two other papers studied the physiological effects of zotepine on healthy volunteers. Three studies did not provide any usable outcome data.
2. Awaiting assessment Despite considerable efforts we are still awaiting assessment of three Japanese studies. We are waiting for two studies to be translated and are still seeking one study.
3. Ongoing studies We are not aware of any ongoing studies.
4. Included studies We included 11 studies with 966 participants. All included studies were randomised and double blind. One was sponsored by Klinge Pharma, five had company employees from Knoll Pharmaceuticals as named authors and one appeared to be undertaken by independent researchers (Sarai 1987).
4.1 Length of trials Most studies were of very short duration, lasting between six and eight weeks. Cooper 1999b lasted 26 weeks but only met inclusion criteria for the outcome of leaving the study early.
4.2 Participants Ten studies employed operationalised diagnoses of schizophrenia either by Diagnostic and Statistical Manual or International Classification of Diseases criteria. Cooper 1999a used inclusion criteria of a baseline score of 4 on the Clinical Global Impression scale (CGI), and Cooper 1999b a baseline of 3 on the CGI with a history of recurrence of illness within the last 18 months. Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 only included those who had previously not responded to at least three weeks of treatment with two conventional antipsychotics in effective doses. Petit 1996 included those with a baseline score of 4 on the CGI. Sarai 1987 included those who were 'overshadowed by lack of spontaneity' and excluded people in advanced stages of schizophrenia, psychomotor excitement, in sedative states, hallucinating, deluded or with sleep disturbances. Moller 2004 included stable participants who had primarily negative symptoms. Fleischhacker 1989 included people with DSM III diagnosis of acute paranoid schizophrenia.
4.3 Setting Most participants in the included studies were in hospital, and all of those in the Barnas 1987 and Petit 1996 trials were also hospitalised. Small proportions of those in the other studies were attending outpatient departments.
4.4 Study size Klieser 1996 was the largest study with 180 participants followed by Cooper 1999a with 159 and Petit 1996 with 126. Cooper 1999a, Cooper 1999b and Petit 1996 reported power calculations, rarely seen in schizophrenia trials. Petit 1996 stated: 'so that a difference between treatment groups of 8.2 points could be detected in the change from baseline to endpoint in the BPRS total scores'; Cooper 1999a used an 8.8 change in mean BPRS total scores and Cooper 1999b a difference in recurrence rates between groups from 20% to 50% could be detected with 90% power and 5% significance, although why so an exact 8.2 and 8.8 change is not mentioned. Dieterle 1991 had 40 participants, Sarai 1987, 94, Moller 2004, 85, Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 randomised 50, Fleischhacker 1989, 40, Barnas 1987, 30 and Wetzel 199141.
4.5 Interventions Doses of zotepine in these trials ranged from 75‐600 mg/day. We identified three placebo controlled trials (Cooper 1999a, Cooper 1999b, Moller 2004). When an active comparison was used the choice of drug varied. Haloperidol was used in low doses in Barnas 1987 (means 4.2 mg/day) but Fleischhacker 1989, Petit 1996 used doses above 10 mg/day. Cooper 1999a compared zotepine with up to 600 mg/day of chlorpromazine, whilst perazine was the comparator drug for Dieterle 1991(348 mg/day) and Wetzel 1991(150‐900 mg/day). Sarai 1987 used thiothixene as control drug at 15‐60 mg/day. Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 compared zotepine to clozapine (150‐450 mg/day). Klieser 1996 randomised to six groups; zotepine was compared to two doses of risperidone (4 mg/day or 8 mg/day), one of clozapine (400 mg/day), one of remoxipride (400 mg/day) and one of haloperidol (15 mg/day).
4.6 Outcomes 4.6.1 Improvement: Definition of improvement varied. It consisted of an analysis of variance of BPRS or CGI scores in two studies (Fleischhacker 1989, Meyer‐Lindberg 1996). Kaplan‐Meir survival analysis of time to recurrence was used in Cooper 1999b, whilst Cooper 1999a used mean change in BPRS scores, although endpoint scores were supplied by the trialists. Klieser 1996 and Wetzel 1991 both gave endpoint BPRS scores, but it is unclear how Dieterle 1991 defined improvement. The latter study made extensive use of graphs from which it is not possible to extract data. Barnas 1987 and Sarai 1987, however, provided a binary report of 'improved or not' from their measurement of BPRS and CGI. Petit 1996 used a 50% improvement in BPRS scores as a measure of improvement. Moller 2004 provided binary CGI data.
4.6.2 Missing outcomes: As most participants were hospitalised only Moller 2004 reported on hospital admission. Such short trials were also not focusing on clinically relevant outcomes such as quality of daily functioning, 'employed', 'trouble with the police', satisfaction with care. Unfortunately no cost data were reported. Just Moller 2004 reported on mortality.
4.6.3 Continuous data: Details of the scales that supplied usable data for this review are shown below. Reasons for exclusion of data from other instruments are given under 'outcomes' in the 'included studies' table.
4.6.3.1 Global state 4.6.3.1.1 Clinical Global Impression Scale ‐ CGI Scale (Guy 1976) The CGI is a three‐item scale commonly used in studies on schizophrenia that enables clinicians to quantify severity of illness and overall clinical improvement. The items are: severity of illness; global improvement and efficacy index. A seven‐point scoring system is usually used with low scores indicating decreased severity and/or greater recovery. Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a and Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.2 Mental state 4.6.3.2.1 Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale ‐ BPRS (Overall 1962) This is used to assess the severity of abnormal mental state. The original scale has 16 items, but a revised 18‐item scale is commonly used. Each item is defined on a seven‐point scale varying from 'not present' to 'extremely severe', scoring from 0‐6 or 1‐7. Scores can range from 0 to 126, with high scores indicating more severe symptoms. All studies in this review used a seven point scoring system. Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a, Klieser 1996 and Wetzel 1991 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.2.2 Positive and Negative Symptom Scale ‐ PANSS (Kay 1986) The Positive and Negative Symptom Scale was developed from the BPRS and the Psychopathology Rating Scale. It is used as a method for evaluating positive, negative and other symptom dimensions in schizophrenia. The scale has 30 items and each item can be defined on a seven‐point scoring system varying from 1 =absent to 7 =extreme. This scale can be divided into three sub‐scales for measuring the severity of general psychopathology, positive symptoms (PANSS‐P) and negative symptoms (PANSS‐N). A low score indicates low levels of symptoms. Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.2.3 Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms ‐ SANS (Andreasen 1984) This six‐point scale gives a global rating of the following negative symptoms: alogia; affective blunting; avolition‐apathy; anhedonia‐asociality and attention impairment. Higher scores indicate more symptoms. Cooper 1999a and Klieser 1996 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.2.4 Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale ‐ MADRS (Montgomery 1979) A 65‐item comprehensive psychopathology scale was used to identify the 17 most commonly occurring symptoms in primary depressive illness. Ratings are based on 10 items, with higher scores indicating more symptoms. Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.3 Adverse effects 4.6.3.3.1 Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ‐ AIMS (Guy 1976) The Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale has been used to assess abnormal involuntary movements associated with antipsychotic drugs, such as tardive dyskinesia and chronic akathisia, as well as 'spontaneous' motor disturbance related to the illness itself. Tardive dyskinesia is a long‐term, drug‐induced movement disorder. However, using this scale in short‐term trials may also be helpful to assess some rapidly occurring abnormal movement disorders such as tremor. Scoring consists of rating movement severity in the anatomical areas (facial/oral, extremities, and trunk) on a five point scale (0‐4). A low score indicates low levels of dyskinetic movements. Cooper 1999a reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.3.2 Tardive Dyskinesia Rating Scale ‐ TDRS (Simpson 1979) The TDRS exists under several names including: Simpson abbreviated dyskinesia rating scale, abbreviated dyskinesia scale, tardive dyskinesia scale. Thirty‐four items are included in the scale rated in six steps of severity (1‐6). There is also the possibility of writing in idiosyncratic signs so that no symptom (head, neck, extremities, body) is forgotten. The scale has been demonstrated to have good reliability and validity, and its sensitivity to change has been established. It is recommended as a suitable instrument for describing the breadth of tardive dyskinesia syndrome and also for quantifying the disorder. Higher scores indicate more tardive dyskinesia signs. Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.3.3 Simpson and Angus Scale ‐ SAS (Simpson 1970) The SAS is a 10‐item scale, used to evaluate the presence and severity of drug‐induced parkinsonian symptomatology. The ten items focus on rigidity rather than bradykinesia, and do not assess subjective rigidity or slowness. The scale comprises of a 10‐item rating scale, each item rated on a five‐point scale with zero meaning the complete absence of the condition and four meaning an extreme presence of the condition. A low score indicates low levels of parkinsonism. Cooper 1999a, Klieser 1996 and Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.3.4 Dosage Record and Treatment Emergent Symptoms Scale ‐ DOTES (German Version NIMH 1981) This side effect tool seems less of a scale, where the degree and severity of a symptom is recorded, and more of a checklist. The DOTES seems to record the presence or absence of a list of side effects. These dichotomous outcomes are then easily and usefully employed within a systematic review. Barnas 1987 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.3.5 COSTART Terms (COSTART 1990) This is a list drawn up by the US Food and Drug Administration in order to help consistent description of adverse reactions. As far as the reviewers understand, it is not a scoring system. Cooper 1999a reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.4 Cognition 4.6.3.4.1 Syndrome Short Test (Syndrome‐Kurtz‐Test) ‐ SKT (Erzigkeit 1986) Descriptions of this published short scale were not available even in the studies that employed it. Klieser 1996 reported usable data from this scale.
4.6.3.5 Quality of life 4.6.3.5.1 Social Functioning Scale 36 SF36 (Jenkinson 1997) The SF‐36 is a multi‐purpose, short‐form health survey with 36 questions. The SF‐36 includes one multi‐item scale that assesses eight health concepts: 1) limitations in physical activities because of health problems; 2) limitations in social activities because of physical or emotional problems; 3) limitations in usual role activities because of physical health problems; 4) bodily pain; 5) general mental health (psychological distress and well‐being); 6) limitations in usual role activities because of emotional problems; 7) vitality (energy and fatigue); and 8) general health perceptions. The survey was constructed for self‐administration by persons 14 years of age and older, and for administration by a trained interviewer in person or by telephone. The score range is between 0 and 100, with higher scores indicating better health status. Moller 2004 reported usable data from this scale.
Risk of bias in included studies
1. Randomisation Four studies, Cooper 1999a, Cooper 1999b, Moller 2004 and Sarai 1987, fall into quality category A (adequate concealment of allocation). The others were all category B as it was not clear exactly how randomisation had been conducted. The reader, therefore, is not assured that the introduction of biases were minimised at this crucial stage. It has been shown that poor reporting of randomisation increases the odds of presenting 'significant' outcomes (Chalmers 1983, Schulz 1995).
2. Blinding to interventions and outcomes Nine studies of the 11 included studies clearly described adequate precautions for blinding of treatment (Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a, Cooper 1999b, Dieterle 1991, Fleischhacker 1989, Moller 2004, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987, Wetzel 1991). No included trial tested the adequacy of the blindness of those rating outcomes.
3. Follow‐up In the placebo studies 48% of people left early. In comparison with typical antipsychotics, about one third of people left before completion (see Results). In comparisons with other atypicals, it was only possible to ascertain from one study how many left before study completion (Meyer‐Lindberg 1996). In this study there was 34% attrition which resulted in randomisation being broken and matched pairs being reported on. In Cooper 1999b and Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 attrition was over 50% so only data for the outcome of 'leaving the study early' was entered into this review (see Methods). Reasons for leaving early were given in Cooper 1999b but exactly why people decided to leave or were excluded from other studies was not made explicit. Once participants leave a study, unless the trialists continue to follow and collect data, assumptions have to be made about outcome. In ten studies data was analysed on an intention‐to‐treat basis using the last observation carried forward. This practice may well overestimate the effects of treatment effect. Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 used controlled, matched pairs and only reported on those pairs remaining in the study. Fleischhacker 1989 only reported on outcomes which reached statistical significance. In this review those leaving the studies early were considered to have had a 'bad outcome' and analysed accordingly (except for the outcome of death). Whatever the management of lost data, interpretation of results with large degrees of attrition must be undertaken with caution.
The barely adequate reporting of randomisation, possible lack of double blindness for these outcomes and unclear reasons for loss to follow up would suggest that all estimates of effect of the experimental intervention are prone to exaggeration (Moher 1998).
Effects of interventions
Please see Table of comparisons for more detailed data.
1. Search For the update search (2006) we found ten references. We were able to include one additional study (Moller 2004) and one further report of the Fleischhacker 1989 study.
2. COMPARISON 1. ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO Only three studies compared zotepine against placebo. Cooper 1999b only contributes to the outcome of 'leaving the study early' as this study had greater than 50% loss to follow up. 2.1 Death Only Moller 2004 explicitly reported on the outcome of death, with no deaths occurring during eight weeks of participation.
2.2 Global state 2.2.1 Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative drugs Moller 2004 found that the need for additional medications were similar for both the zotepine and placebo group with no significant differences found by eight weeks (n=85, RR 0.74 CI 0.48 to 1.14).
2.2.2 Not improved/worse (CGI scale) Moller 2004 also found no significant differences between zotepine and placebo over eight weeks of treatment (n=85, RR 0.59 CI 0.3 to 1.1).
2.2.3 Mean endpoint scores (CGI scale) Cooper 1999a reports continuous results for the CGI scale by eight weeks. Using the last observation carried forward method we found the results favoured zotepine (n=106, MD ‐1.0 CI ‐1.5 to ‐0.5).
2.2.4 Hospitalisation The numbers of people requiring hospitalisation in the Moller 2004 study were low: zotepine (0/39) and placebo (1/46) and we found no statistically significant differences.
2.3 Mental state 2.3.1 No important clinical response (BPRS) Using last observation carried forward at eight weeks, we found Cooper 1999a to be statistically significant in a 20% mean reduction in BPRS endpoint scores in favour of zotepine over placebo (n=106, RR 0.44 CI 0.3 to 0.7, NNT 3 CI 2 to 6).
2.3.2 Average total scores Cooper 1999a reports BPRS endpoint scores by eight weeks which we found to be statistically significant favouring zotepine over placebo (n=105, MD ‐11.6, CI ‐18.3 to ‐4.9). Moller 2004 reported PANSS change scores that were not clearly significant (n=79, MD ‐4.9 CI ‐12.36 to 2.56).
2.3.3 Average negative symptom scores Cooper 1999a reports continuous data at eight eight weeks from the Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms. We found the zotepine group did have significantly lower scores for negative symptoms than placebo using the last observation carried forward (n=105, MD ‐12.5 CI ‐22.7 to ‐2.3). However, again Moller 2004, using PANSS change scores, found no difference between groups (n=79, MD ‐0.9 CI ‐3.49 to 1.69).
2.3.4 Average positive symptom change score (PANSS) Only Moller 2004 reported on positive symptoms, and change scores around eight weeks were not significant when compared with placebo.
2.3.5 Average general pathology change score Again Moller 2004 reported change scores for the PANSS on general pathology and found no difference between groups.
2.3.6 Average depression change score (MADRS) Moller 2004 found the Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores by eight weeks to significantly favour zotepine (n=79, MD ‐3.00 CI ‐5.7 to ‐0.3) compared with placebo using the LOCF method.
2.4 Behaviour changes For the outcomes of agitation, hostility and nervousness, we found that data from a study of 106 people (Cooper 1999a) did not reach statistical significance, although all data did tend to favour those taking zotepine.
2.5 Leaving the study early 2.5.1 Any reason ‐ by 8‐26 weeks We found significantly fewer people in the zotepine group (43%, 67/155) left the study early (n=312, 3 RCTs, RR 0.78 CI 0.6 to 1.0, NNT 9 CI 6 to 48) compared with placebo (53%, 83/157).
2.5.2 Due to lack of efficacy ‐ by 8‐26 weeks We found significantly fewer participants given zotepine were withdrawn or withdrew from the studies due to 'lack of efficacy' (n=312, 3 RCTs, RR 0.4 CI 0.2 to 0.7, NNT 10 CI 8 to 22) compared with placebo.
2.5.3 Due to adverse effects ‐ by eight weeks We found the data from Moller 2004 to be equivocal for people leaving the study early due to adverse effects. 2.6. Adverse effects 2.6.1 Any adverse event Adverse events were found to be similar in both zotepine and placebo group with no statistical significant difference (n=191, 2 RCTs, RR 1.38 CI 0.8 to 2.5) using a random effects model (I‐squared statistic=88%).
2.6.2 Cardiovascular problems ‐ pulse rate We found no differences in pulse rates between the zotepine and placebo group.
2.6.3 Gastrointestinal problems Fewer people taking zotepine suffered constipation than those on placebo but the result does not reach statistical significance.
2.6.4 Metabolic problems We found no statistical differences for weight gain, or weight changes between zotepine and placebo from data reported by Cooper 1999a.
2.6.5 Movement disorders For the outcomes of akathisia, dyskinesia and needing antiparkinson medication we found no clear differences between those allocated to zotepine and those randomised to placebo. Continuous ratings were also reported and skewed data showed no clear differences between groups. Movement disorders evaluated by Moller 2004 with The Tardive Dyskinsia Rating Scale also did not reveal any significant differences between zotepine and placebo. Extrapyramidal symptoms measured, by Moller 2004 using the Simpson and Angus scale, were equivocal.
2.6.6 Sleep problems More people taking zotepine experienced somnolence than those allocated to placebo (n=106, 1 RCT, RR 1.5 CI 1.1 to 2.1, NNH 4 CI 3 to 29). We did not find rates of Insomnia to be statistically different, but the zotepine group did have lower rates of insomnia which almost reached statistical significance (p=0.06).
2.6.7 Others On the outcomes of asthenia, increased salivation, liver function abnormalities and pain, we found no clear differences between zotepine and placebo.
2.7 Quality of life Moller 2004 reported on quality of life change scores using the Social Functioning 36 scale (SF‐36). We found no significant differences on physical functioning, physical pain, perception of general health status, vitality, social functioning, emotional role function and psychological well being. Physical role functions (n=72, MD 20.6 CI 2.7 to 38.6) did significantly favour zotepine. The physical component scale of the SF36 almost reached significance.
3. COMPARISON 2. ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
3.1 Global state 3.1.1 Not improved (CGI) Barnas 1987 dichotomised data from the Clinical Global Impression to produce an outcome of 'not improved'. We found no clear difference between zotepine and haloperidol (4 mg/day), but total numbers were small (n=30) and clear differences are unlikely to emerge.
3.1.2 Average endpoint score (CGI) Barnas 1987 and Cooper 1999a reported Clinical Global Impression endpoint scores. When pooled these data significantly favoured zotepine compared with haloperidol and chlorpromazine (n=135, WMD ‐0.61 CI ‐1.0 to ‐0.2).
3.1.3 Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative medication We found that no more people allocated zotepine were in need of additional antipsychotics or sedative drugs than those on 15‐60 mg of thiothixene or 150‐900 mg or perazine per day (n=175, 3 RCTs, RR 1.03 CI 0.8 to 1.4).
3.2 Mental state 3.2.1 No important clinical response (BPRS) Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987 pre‐stated a cut‐off point on the overall BPRS change score that they considered to be clinically important. We found the data favoured zotepine when compared with other active drugs (n=356, RR 0.77 CI 0.7 to 0.9, NNT 7 CI 4 to 22).
3.2.2 Average total endpoint score (BPRS) We found data favoured zotepine (n=234, 4 RCTs, WMD ‐6.92 CI ‐11.0 to ‐2.8) compared with typical antipsychotics.
3.2.3 Average negative symptom endpoint sores (SANS) We found that negative symptoms scores at endpoint (Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a) were significantly different in favour of zotepine (n=132, WMD ‐8.7 CI ‐16.9 to ‐0.4) when compared with those allocated typical antipsychotics.
3.3 Behaviour changes Petit 1996, Sarai 1987 reported on anxiety, with or without irritability, as an adverse effect. We found no clear differences between groups (n=220, RR 0.92 CI 0.7 to 1.3). Cooper 1999a reports on hostility and nervousness as adverse effects, but again we found no clear differences between zotepine and the comparator group allocated to chlorpromazine.
3.4 Leaving the study early ‐ any reason The numbers of people leaving studies early were not significantly different 32% (77/239) in the zotepine group and 40% (93/238) in the comparator group. A funnel plot of these data shows no sign of asymmetry (n=477, 7 RCTs, RR 0.83 CI 0.65 to 1.04).
3.5 Cognition: No improvement (Syndrome Short Test) We found that more people on zotepine exhibited an improved cognition as measured by the Syndrome Short Test, than people on haloperidol (outcome = not improvement, n=65, RR 0.32 CI 0.1 to 0.8, NNT 3 CI 2 to 9). 3.6. Adverse events 3.6.1 Any adverse event Dieterle 1991, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987 reporting on outcomes "any adverse event" found no significant difference between zotepine and haloperidol and thiothixene (n=160, RR 0.98 CI 0.9 to 1.1).
3.6.2 Cardiovascular problems We found two studies reporting abnormal ECG results for those taking zotepine (Petit 1996, Sarai 1987) although only Sarai 1987 reported specific data which were not significant (n=94, RR 1.44, CI 0.3 to 8.2). Sarai 1987 reporting on tachycardia (n=94, RR 3.83 CI 0.9 to 17.1) with non‐significant results. Cooper 1999a reported pulse rates which we found were not significantly different between zotepine and chlorpromazine. 3.6.3 Gastrointestinal problems Limited data do not suggest differences between zotepine and haloperidol or thiothixene for the outcomes of anorexia, constipation, or nausea.
3.6.4 Metabolic problems ‐ weight increase We found mean weight change (Cooper 1999a) in the zotepine and control group (chlorpromazine) were not significantly different. Petit 1996 did report on weight gain in those taking zotepine, but did not report its variance.
3.6.5 Movement disorders Zotepine did produce less akathisia (n=396, 5 RCTs, RR 0.73 CI 0.6 to 0.9, NNH 8 CI 5 to 34), dystonia (n=70, 2 RCTs, RR 0.47 CI 0.2 to 0.9, NNH 4 CI 2 to 56) and rigidity (n=164, 3 RCTs, RR 0.63 CI 0.4 to 1.0, NNH 7 CI 4 to 360) than other drugs. We found that rates of dyskinesia, gait disturbance, parkinsonism and restlessness gave no suggestion of a differential effect of zotepine and the drugs of comparison. Rates of tremor were less in the zotepine group, although this did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (n=290, 4 RCTs, RR 0.69 CI 0.5 to 1.1). The suggestion that zotepine causes less movement disorders than typical drugs is supported by the data for use of additional anticholinergic medication. We found pooled results from Barnas 1987, Klieser 1996 and Petit 1996 favoured zotepine (n=221, RR 0.65 CI 0.5 to 0.8, NNH 4 CI 3 to 8). Continuous ratings (skewed data) from the AIMS scale and the Simpson and Angus Scale did not produce any clear difference between groups.
3.6.6 Sleep problems We found no clear differences between zotepine and chlorpromazine, haloperidol or thiothixene for the outcomes of insomnia, lassitude, sleepiness or somnolence. Data are consistent with zotepine being a sedating drug, at least as much as chlorpromazine.
3.6.7 Other adverse effects We found asthenia, dry mouth or an increase in salivation, dizziness, headache, hyperhidrosis, nasal congestion and pain are equally prevalent in zotepine and control groups. Six studies reported the incidence of abnormal liver function tests. None of these abnormalities were stated to be serious and were no more common in the zotepine group than the control groups (n=430, RR 1.15 CI 0.9 to 1.4).
3.7 Missing outcomes No studies reported on the medium to long term effects of zotepine. Data on service utilisation, economic outcomes, quality of life and satisfaction with care were not reported.
4. COMPARISON 3. ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
4.1 Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 compared zotepine with clozapine in a group of people who were moderately unresponsive to antipsychotics. The Klieser 1996 study compared two doses of risperidone, clozapine, remoxipride and haloperidol with zotepine. For this section of the review, haloperidol is excluded, and for continuous outcomes only data from the risperidone 8 mg/day intervention is compared with zotepine.
4.2 Mental state (BPRS endpoint scores) We found one study (Klieser 1996) reporting BPRS endpoint scores with no significant differences (n=40, MD ‐1.30 CI ‐13.0 to 10.4) between zotepine and risperidone.
4.3 Leaving the study early: Any reason Limited data were reported by Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 (n=50) and we found similar numbers of people leaving the study early between zotepine and clozapine, with no suggestion that either drug offers advantages over the other (n=50, RR 1.43 CI 0.7 to 3.2 in terms of treatment acceptability for people whose illness is moderately resistant to drug treatments.
4.4 Cognition: No improvement We found no clear differences between zotepine and other atypicals (Klieser 1996) when cognition was measured using the Syndrome Short Test.
4.5 Adverse effects: Movement disorders ‐ needing additional anticholinergic medication Klieser 1996 reported that those allocated to zotepine needed anticholinergic medication more frequently than the atypicals group. We found data to be significant, although little were used in either group (n=135, RR 2.88 CI 1.2 to 6.8, NNH 3 CI 1 to 10).
5. Sensitivity analysis and publication bias It was not possible to undertake the proposed funnel graph for publication bias or sensitivity analysis for people with schizophrenia described as 'treatment resistant', people having predominantly positive or negative symptoms of schizophrenia and people experiencing their first episode of schizophrenia.
Discussion
1. Applicability Most studies were set in Europe and randomised people with operationally diagnosed disorders uncomplicated by co‐morbidity. Sarai 1987, however, was undertaken in Japan. This study had such strict inclusion criteria that its results must be of limited generalisability. Other studies set in Japan await assessment. At this point it is unclear if these will add much to the data that has already been presented. We are collaborating with the Medical Information department of Orion Pharmaceuticals in order to acquire these data for a future update of this review.
2. Limited data The review may be subject to several biases. Most trials from which data have been extracted are supported by the company that will profit most from zotepine being shown to be successful. Those studies are likely to have results favouring the experimental compound (Montgomery 2004, Heres 2006).
Data were often inadequately reported and rendered many outcomes unusable. In addition, only six to twelve week outcomes are reported in most of the trials. Cooper 1999b was over 26 weeks but the rate of attrition was over 50%, so we were only able to include data on 'leaving the study early'. Dieterle 1991 had exactly 50% loss of data and we included the study. Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 focused on cognitive functioning, but the only usable data we found were 'leaving the study early' as the trialists decided to break randomisation and manufacture matched pairs as the rate of attrition threaten the results. Two of the most recent studies (Meyer‐Lindberg 1996, Petit 1996), were published in the year of the CONSORT statement (Begg 1996), which encourages high standards of trial reporting yet these trials only achieve a quality rating of 'B' (poor). Sarai 1987 published nearly a decade before the CONSORT guidelines scored a quality rating of 'A'. Cooper 1999a, and Cooper 1999b were unpublished manuscripts and authors provided additional methodological data, which enabled us to assign a quality rating of 'A'. No studies reported on service utilisation, economic outcomes, or on satisfaction with care. Fleischhacker 1989 used the BPRS and CGI scales but no usable data were available and no further information has been made available.
3. COMPARISON 1. ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO
3.1 Death No deaths occurred in the zotepine or placebo group during eight weeks of treatment. Unfortunately, only one study (Moller 2004) reported this important outcome.
3.2 Global state The need for additional antipsychotic drugs or sedatives did not reveal any obvious differences between zotepine and placebo, which is surprising given the placebo group were without treatment. People taking zotepine showed greater improvement than those in the placebo group, when measured as continuous CGI scores, although what an average shift of one point means in clinical terms is difficult to say. However, CGI scores that were dichotomised to 'not improved/worse' were equivocal (n=85). The result did show a trend in favour of zotepine and perhaps a larger sized study would have rendered this outcome significant. Participants requiring hospitalisation were only reported by Moller 2004 who found just one person from the placebo group required hospitalisation. Participants in this study were reported as being stable with primarily negative symptoms.
3.3 Mental state All BPRS data are consistent and derived from one study (n=106, duration 12 weeks, Cooper 1999a). Trialists took the last observation and carried it forward, but this trial had considerable attrition which undermines the validity of the result, as it is difficult to say exactly where the best estimate of effect is. For the binary outcome of a 20% mean reduction in BPRS endpoint scores the result favoured zotepine over placebo (NNT 3 CI 2 to 6). Cooper 1999a reported a statistically significant result in favour of zotepine for the BPRS endpoint scores (11.6 difference between groups). Again this is encouraging but difficult to interpret into clinically meaningful terms and in the light of the considerable loss to follow up. The measure of negative symptoms (SANS) also demonstrated a statistically significant difference in favour of zotepine (12.5 difference in endpoint results), again using last observation carried forward. These data need to be strengthened by replication and use of more complete data sets, if possible avoiding the assumptions of the last observation carried forward. PANSS change scores were reported by Moller 2004 with all outcomes (total score, PANSS+ve, PANSS ‐ve and general psychopathology) being not significantly different between groups. Zotepine did significantly lower depression scores (MADRS scale) compared with the placebo group, and longer term follow up with a larger sample would have been useful to see if this effect is sustained.
3.4 Behaviour Zotepine caused no greater improvement in occurrence of agitation, hostility and nervousness than placebo. This may be an indication that the study had insufficient power to detect real change.
3.5 Leaving the study early Significantly fewer people taking zotepine left the study early (43%) for any reason than those on placebo (53%) from the three studies with an NNT of about nine. More people left the study early due to lack of efficacy in the placebo group, suggesting that zotepine is a more acceptable and efficacious form of treatment than placebo. Cooper 1999b reported the highest dropout rate of 76% but did have the longest trial duration 26 weeks. The numbers of people leaving early due to adverse events was similar for both the zotepine and placebo groups. Long term follow up and larger trials are needed to determine if this is a reliable result. 3.6 Adverse effects We found no differences in the number of any adverse event occurring between zotepine and placebo. This was surprising given the known adverse event profile of antipsychotics. Data from the two included studies were heterogeneous and were analysed using a random effects model, and Moller 2004 shifted the Cooper 1999a result towards the equivocal. Cooper 1999a suggested that zotepine did cause more adverse events than placebo with an NNH of about three, but adverse events were only recorded if they occurred five times. This means of recording may result in rare, but important, events being unreported. Pulse rates did not appear to be affected in the Cooper 1999a study and zotepine did not cause constipation any more frequently than placebo. Zotepine may also increase in weight. However, the will to undertake an intention‐to‐treat analysis masks this finding in the data presented in this review. As more people from the placebo group were lost to follow up and the 'Methods' of this review state that those who leave early were to be attributed the negative outcome, the five in the zotepine group who were reported to have a gain in weight were masked by the assumed gain in weight in the placebo group. Rather surprisingly high proportions of those taking placebo needed anticholinergics and modest movement disorders were common in both groups, although using intention to treat analyses may have increased this. Continuous data measuring movement disorders (TDRS, SAS) were equivocal. Data from Cooper 1999a suggests that zotepine may have an adverse effect of sedation (NNH 4). Other reported adverse events, asthenia, liver function, pain and salivation were similar for both the zotepine and placebo groups.
3.7 Quality of Life Moller 2004 used the SF‐36 scale to record quality of life with most components from the scale being equivocal. The component 'physical role functions' was significantly in favour of zotepine, although confidence intervals were wide and conclusions problematic.
4. COMPARISON 2. ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
4.1 Global state The Clinical Global Impression scores were reported in ten trials, but only two reported the standard deviation (Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a), and therefore in a form that is useful for this review. The CGI continuous data did significantly favour zotepine, although binary outcomes 'not improved' were equivocal. It is unfortunate that other studies did not produce a binary outcome from this simple scale. Although there is a suggestion of improvement from CGI ratings, perhaps the overall improvement in global state or functioning is not great since the zotepine group did require similar additional antipsychotics to the control group on 15‐60 mg of thiothixene, or 150‐900 mg perazine per day.
4.2 Mental state Whereas most studies did not report binary outcomes for global improvement they did for mental state (4 RCTs). All findings tend to favour zotepine. For the outcome of 'no important improvement in mental state' the number needed to treat is seven (n=356). Overall, what data there are suggests that zotepine is as effective as the typical drugs for mental state outcomes.
Four studies reported scores on the BPRS, whilst two (Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a) also presented data from a measure of negative symptoms (SANS). The results statistically significantly favoured zotepine for the general mental state score (BPRS), with only a seven point average difference between groups. The SANS averaged a nine point difference between groups in favour of zotepine which is intriguing. Neither the BPRS or the SANS are 'interval' scales where a ten point decline for someone starting with a score of 90 means the same as the same decline for a person whose initial rating was 20. It is therefore difficult to interpret this finding for clinical use. Two other studies (Meyer‐Lindberg 1996, Petit 1996) claimed superiority for zotepine in treating negative symptoms, but did not demonstrate this by reporting data. Much larger studies are needed to replicate these mental state findings.
4.3 Behaviour changes We found two studies reporting the mental state outcome of anxiety ‐ with or without irritability (Petit 1996, Sarai 1987) as an adverse effect. No clear differences were found between groups (n=220, RR 0.92 CI 0.7 to 1.3). We are unclear where to present these findings as they relate to mental state but are labelled by trialists as adverse effects who did not state whether they considered zotepine had failed to control the natural anxiety of the study participants or whether the experimental compound caused the anxiety. Cooper 1999a reports on hostility and nervousness as adverse effects. Again these are presented within this outcome. Zotepine is not different to chlorpromazine for these effects.
4.4 Leaving the study early As a proxy measure of study acceptability, seven of the nine trials provided data on leaving the study early (Barnas 1987, Cooper 1999a, Dieterle 1991, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987, Fleischhacker 1989, Wetzel 1991). Leaving the study early zotepine (32%) and typicals (39%) were not significantly different. The figure of about 32% is likely to be higher than that seen in clinical practice due to the need to rigorously adhere to trial protocols. Although this may improve internal validity, it can decrease the generalisability (external validity) of the results. That a funnel plot of these data shows no sign of asymmetry may suggest that there is no overt identification of studies that present potentially biased data.
4.5 Cognition Measures of cognition using the Syndrome Short Test did significantly favour the zotepine group when dichotomised to not improved. Despite efforts we have been unable to find good data on what this may mean from the clinical perspective. Nevertheless, with the increasing emphasis on the cognitive decline associated with schizophrenia (Pantelis 1997) this is an interesting finding, worthy of replication with zotepine and other compounds.
4.6 Adverse effects Only three studies report data in a usable format for any adverse event (Dieterle 1991, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987). No differences were found between zotepine when compared to haloperidol, perazine and thiothixene. It is difficult to understand what this outcome means in the clinical situation and other data are needed to provide more useful information.
Studies report abnormal ECG results for those taking zotepine (Cooper 1999a, Petit 1996, Sarai 1987). Petit 1996 and Cooper 1999a reported that ECG abnormalities were found in both groups but gave no data. Only Sarai 1987 presents usable data and neither the incidence of ECG abnormalities nor tachycardia differ between zotepine and thiothixene. Cooper 1999a also found equivocal results for changes in pulse rates. An intention‐to‐treat analysis is used in this review. Those who dropped out of the studies are added into the numbers of those who experience adverse side effects, which could give an overly pessimistic incidence. However, with only 94 randomised in the Sarai 1987 trial, and both results suggesting the negative outcome for zotepine, these findings are in urgent need of replication with clear reporting of findings.
There were no clear differences between zotepine and chlorpromazine, haloperidol or thiothixene for the outcomes of anorexia, constipation, or nausea. Forty percent of those on zotepine complained of constipation. Cooper 1999a reported weight increase and found no clear difference between zotepine and chlorpromazine. Petit 1996 also reported a mean increase in weight gain of those taking zotepine, but did not provide a standard deviation. This important adverse effect is consistently poorly or under‐reported (Duggan 1999).
Zotepine does seem to produce less movement disorders than the comparison drugs. There are clearly lower rates of akathisia, dystonia and rigidity and tremors are somewhat less prevalent. Rates of dyskinesia, gait disturbance, parkinsonism and restlessness, however, gave no suggestion of a differential effect of zotepine and the control drugs. The suggestion that zotepine causes less movement disorders than typical drugs is supported by the data on use of additional anticholinergic medication and this is even the case when the dose of control drug is low (Barnas 1987).
Zotepine is not clearly more sedating than haloperidol or thiothixene. The data, however, do consistently fall on the relevant sides of the line of no effect for the outcomes of insomnia and sedation to suggest that it does have some moderate sedating properties. Other effects such as dry mouth, dizziness, headache, hyperhidrosis and nasal congestion are equally prevalent in both groups, although the latter did look more common in the zotepine group. Six studies reported the incidence of abnormal liver function tests. None of these abnormalities were stated to be serious and were equally prevalent in both experimental and control groups.
4.7 Missing outcomes In these short‐term explanatory studies data on service utilisation, economic outcomes, quality of life and satisfaction with care were not recorded. The medium or long term effects of zotepine are currently unknown and are in urgent need of investigation.
5. COMPARISON 3. ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
5.1 General If zotepine is to make inroads into an increasingly competitive atypical antipsychotic market it will have to be compared more frequently to its close sibling compounds. Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 (n=50) compared it to clozapine in a moderately treatment resistant population and Klieser 1996 (n=135) compared it with risperidone, clozapine and remoxipride. Very little satisfactory data were available.
5.2 Mental state Endpoint mental state scores (BPRS) between zotepine and 8 mg/day of risperidone did not reveal any clear difference (n=40), although larger sample sizes would have provided more confidence of any treatment effects being detected.
5.3 Leaving the study early Limited data show no differences between clozapine and zotepine for leaving the study early.
5.4 Cognition Cognitive testing data were also equivocal.
5.5 Adverse events Interestingly, the control groups experienced significantly less movement disorders than those on zotepine (NNH 3). These small trials are in urgent need of replication.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
1. For people with schizophrenia All data for this compound relate to a treatment period of six to twelve weeks. Zotepine seems more effective than placebo and is at least as effective and acceptable as other drugs prescribed for those with schizophrenia. Zotepine may have an effect on the negative symptoms of schizophrenia and it is less likely to cause movement disorders than typical drugs such as haloperidol and chlorpromazine although its sedative properties may be similar. Data from studies comparing zotepine with other atypical drugs is currently too sparse to be informative.
2. Clinicians Further studies are needed using pragmatic and clinically meaningful trial methods that cover longer periods before clear clinical recommendations can be made regarding the use of zotepine. Zotepine does show some advantage when compared with typical antipsychotics when measured by the BPRS and SANS and in avoiding movement disorders.
3. Managers or policy makers No data relating to service utilisation, functioning in society and economics were reported. If zotepine is to gain wide acceptance future studies should address these important outcomes.
Implications for research.
1. General Clear and strict adherence to the CONSORT statement (Moher 2001) for all outcomes would have resulted in this review being more informative. Denominator data were not always clearly presented and some results were described as 'significant' or not, but numbers were not reported (Fleischhacker 1989, Meyer‐Lindberg 1996). Authors should present raw data. If p‐values are used, the exact value and specific test should be reported.
2. Specific Better planned, conducted and reported randomised controlled trials of longer duration are needed to address clinically relevant outcomes. Data relating to mental state and behaviour need replication and expansion. High quality trial‐derived data relating to hospital admission, satisfaction with care, social functioning, family burden and employment would be of interest (Table 4).
1. Suggested design for future study.
| Methods | Participants | Interventions | Outcomes | Notes |
| Allocation: randomised ‐ clearly described generation of sequence and concealment of allocation. Blinding: double ‐ described and tested. Duration: 6‐12 months minimum. | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (operational or clinical criteria). N=450.* Age: any. Sex: both. History: any. | 1. Zotepine: dose ˜ 150‐200 mg/day (clinician's and patent's preference). N=150. 2. Risperidone: dose ˜ 4‐6mg/day. N=150. 3. Perphenazine: dose ˜ 8‐32 mg/day. N=150. | Healthy: time.** Leaving study early. Service outcomes: hopsitalised, time in hospital, attending out patient clinics. Global impression: relapse, CGI.*** Mental state: BPRS, SANS. Adverse events: DOTES. Quality of life. QoL, employment, family satisfaction, patient satisfaction. | * power calculation suggested 150/group would allow good chance of showing a 20% difference between groups for primary outcome. ** Primary outcome *** All scale‐derived outcomes would have clinically meaningful binary cut off points defined before trial commences. |
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 18 January 2012 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 3, 1999 Review first published: Issue 1, 2000
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 August 2009 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
| 31 October 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. |
Notes
Cochrane Schizophrenia Group internal peer review complete (see Module). External peer review scheduled.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Maria Leitner for work undertaken at the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, York, assisting in applying for funding for a series of reviews on the atypical antipsychotics, and input into the selection of studies. Thank you also to Daniela Domler and Melanie Rösch for help with translation.
We would like to thank Anne‐Marie Bagnall, Gert Gammelin, Susan Morriss, Maria Leitner and Steve Cooper for their contribution in previous versions of this review.
Thanks are made to Dr Martyn Corby from Orion Pharmaceuticals and Dr Chris Reynolds, Clinical Research Manager, CNS Clinical Development from Knoll/BASF.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Death | 1 | 85 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Global state: 1. Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative drugs | 1 | 85 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.48, 1.14] |
| 3 Global state: 2. Not improved or worse (CGI) | 1 | 85 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.59 [0.31, 1.10] |
| 4 Global state: 3. Average endpoint score (CGI, higher scores=poor) at 8 weeks | 1 | 106 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐1.50, ‐0.50] |
| 5 Global state: 4. Hospitalisation | 1 | 85 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.02, 9.35] |
| 6 Mental state: 1. No important clinical response ‐ by 4‐12 weeks (20% reduction in BPRS from baseline) | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.27, 0.72] |
| 7 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, higher scores=poor) | 1 | 105 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐11.60 [‐18.32, ‐4.88] |
| 8 Mental state: 2b. Average total change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐4.9 [‐12.36, 2.56] |
| 9 Mental state: 3a. Average negative symptom change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.90 [‐3.49, 1.69] |
| 10 Mental state: 3b. Average negative symptom endpoint score (SANS, higher scores=poor) | 1 | 105 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐12.5 [‐22.68, ‐2.32] |
| 11 Mental state: 4. Average positive symptom change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐2.63, 0.63] |
| 12 Mental state: 5. Average general psychopathology change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.1 [‐7.15, 0.95] |
| 13 Mental state: 6. Average depression change score (MADRS, higher scores=poor, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.0 [‐5.72, ‐0.28] |
| 14 Behaviour: Specific behaviour changes | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 14.1 agitation | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.48, 1.14] |
| 14.2 hostility | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.48, 1.14] |
| 14.3 nervousness | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.52, 1.18] |
| 15 Leaving the study early | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 15.1 any reason by 8‐26 weeks | 3 | 312 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.63, 0.96] |
| 15.2 due to lack of efficacy by 8‐26 weeks | 3 | 312 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.37 [0.19, 0.73] |
| 15.3 due to adverse events by 8 weeks | 1 | 85 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.59 [0.11, 3.05] |
| 16 Adverse events: 1. Any adverse event | 2 | 191 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.38 [0.76, 2.52] |
| 17 Adverse events: 2. Cardiovascular problems ‐ pulse rate | 1 | 106 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.91, 5.71] |
| 18 Adverse events: 3. Gastrointestinal problems ‐ constipation | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.52, 1.24] |
| 19 Adverse events: 4a. Metabolic problems ‐ weight gain | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.64, 1.45] |
| 20 Adverse events: 4b. Metabolic problems ‐ weight change | 1 | 106 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.70 [‐3.54, 6.94] |
| 21 Adverse events: 5a. Movement disorders ‐ specific problems | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 21.1 akathisia | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.48, 1.14] |
| 21.2 dyskinesia | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.55, 1.17] |
| 21.3 needing additional anticholinergic medication | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.55, 1.22] |
| 22 Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia (AIMS, higher scores=poor, skewed data) | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 23 Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, reduction=good, skewed data) | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 24 Adverse events: 5d. Movement disorders ‐ change scores by 8 wks (Simpson‐Angus Scale, reduction=good, LOCF) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.03 [‐0.12, 0.06] |
| 25 Adverse events: 5e. Movement disorders ‐change score by 8 wks(Tardive Dyskinesia Rating Scale, reduction=good) | 1 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.2 [‐2.87, 0.47] |
| 26 Adverse events: 6. Sleep problems | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 26.2 insomnia | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.68 [0.45, 1.01] |
| 26.5 somnolence | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [1.06, 2.07] |
| 27 Adverse events: 7. Others | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 27.1 asthenia | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.60, 1.32] |
| 27.2 liver function abnormalities | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.56, 1.29] |
| 27.3 pain | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.62, 1.38] |
| 27.4 saliva increase | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.57, 1.35] |
| 28 Quality of life: Average change score by 8 weeks (SF‐36, high score=better) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 28.1 physical functioning | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.90 [‐1.93, 15.73] |
| 28.2 physical role functions | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 20.6 [2.65, 38.55] |
| 28.3 physical pain | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.1 [‐6.20, 22.40] |
| 28.4 perception of general health status | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.40 [‐2.75, 11.55] |
| 28.5 vitality | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.5 [‐10.79, 5.79] |
| 28.6 social functioning | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐8.5 [‐18.02, 1.02] |
| 28.7 emotional role function | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 15.10 [‐1.96, 32.16] |
| 28.8 psychological well being | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.3 [‐1.28, 9.88] |
| 28.9 physical component scale | 1 | 72 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.60 [‐0.07, 7.27] |
1.1. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 1 Death.
1.2. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 2 Global state: 1. Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative drugs.
1.3. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 3 Global state: 2. Not improved or worse (CGI).
1.4. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 4 Global state: 3. Average endpoint score (CGI, higher scores=poor) at 8 weeks.
1.5. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 5 Global state: 4. Hospitalisation.
1.6. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 6 Mental state: 1. No important clinical response ‐ by 4‐12 weeks (20% reduction in BPRS from baseline).
1.7. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 7 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, higher scores=poor).
1.8. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 8 Mental state: 2b. Average total change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF).
1.9. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 9 Mental state: 3a. Average negative symptom change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF).
1.10. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 10 Mental state: 3b. Average negative symptom endpoint score (SANS, higher scores=poor).
1.11. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 11 Mental state: 4. Average positive symptom change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF).
1.12. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 12 Mental state: 5. Average general psychopathology change scores by 8 weeks (PANSS, higher scores=poor, LOCF).
1.13. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 13 Mental state: 6. Average depression change score (MADRS, higher scores=poor, LOCF).
1.14. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 14 Behaviour: Specific behaviour changes.
1.15. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 15 Leaving the study early.
1.16. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 16 Adverse events: 1. Any adverse event.
1.17. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 17 Adverse events: 2. Cardiovascular problems ‐ pulse rate.
1.18. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 18 Adverse events: 3. Gastrointestinal problems ‐ constipation.
1.19. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 19 Adverse events: 4a. Metabolic problems ‐ weight gain.
1.20. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 20 Adverse events: 4b. Metabolic problems ‐ weight change.
1.21. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 21 Adverse events: 5a. Movement disorders ‐ specific problems.
1.22. Analysis.
Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 22 Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia (AIMS, higher scores=poor, skewed data).
| Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia (AIMS, higher scores=poor, skewed data) | |
|---|---|
| Study | |
| Cooper 1999a | 1. Zotepine group: mean 2.5, SD 3.6. 2. Placebo group: mean 2.8, SD 4.3. |
1.23. Analysis.
Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 23 Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, reduction=good, skewed data).
| Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, reduction=good, skewed data) | |
|---|---|
| Study | |
| Cooper 1999a | 1. Zotepine group: mean 3.9, SD 4.4. 2. Placebo group: mean 2.9, SD 4.4. |
1.24. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 24 Adverse events: 5d. Movement disorders ‐ change scores by 8 wks (Simpson‐Angus Scale, reduction=good, LOCF).
1.25. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 25 Adverse events: 5e. Movement disorders ‐change score by 8 wks(Tardive Dyskinesia Rating Scale, reduction=good).
1.26. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 26 Adverse events: 6. Sleep problems.
1.27. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 27 Adverse events: 7. Others.
1.28. Analysis.

Comparison 1 ZOTEPINE versus PLACEBO, Outcome 28 Quality of life: Average change score by 8 weeks (SF‐36, high score=better).
Comparison 2. ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Global state: 1. Not improved (CGI) | 1 | 30 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.11, 2.33] |
| 2 Global state: 3. Average endpoint score (CGI, high=poor) | 2 | 135 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.61 [‐1.01, ‐0.21] |
| 3 Global state: 2. Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative drugs | 3 | 175 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.77, 1.39] |
| 4 Mental state: 1. No important clinical response ‐ by 4‐12 weeks | 4 | 356 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.65, 0.92] |
| 5 Mental state: 2. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, high=poor) | 4 | 234 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐6.92 [‐11.02, ‐2.83] |
| 6 Mental state: 3. Average negative symptom endpoint score (SANS, high=poor) | 2 | 132 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐8.66 [‐16.93, ‐0.39] |
| 7 Behaviour: Specific behaviour changes | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 7.1 anxiety +/‐ irritation | 2 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.67, 1.27] |
| 7.2 hostility | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.51, 1.25] |
| 7.3 nervousness | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.52, 1.18] |
| 8 Leaving the study early: Any reason | 7 | 477 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.65, 1.04] |
| 9 Cognition: Not improved (Syndrome Short Test) | 1 | 65 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.13, 0.80] |
| 10 Adverse events: 1. Any adverse event | 3 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.85, 1.13] |
| 11 Adverse events: 2a. Cardiovascular problems | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 11.1 ECG abnormalities | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.44 [0.25, 8.21] |
| 11.2 tachycardia | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.83 [0.86, 17.11] |
| 12 Adverse events: 2b. Cardiovascular problems ‐ pulse rate | 1 | 105 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.30 [‐5.38, 2.78] |
| 13 Adverse events: 3. Gastrointestinal problems | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 13.1 anorexia | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.44 [0.65, 3.19] |
| 13.2 constipation | 3 | 326 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.73, 1.23] |
| 13.3 nausea | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.20 [0.52, 2.77] |
| 14 Adverse events: 4. Metabolic problems ‐ weight change | 1 | 105 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.30 [‐6.26, 3.66] |
| 15 Adverse events: 5a. Movement disorders ‐ specific problems | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 15.1 akathisia | 5 | 396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.73 [0.58, 0.93] |
| 15.2 dyskinesia | 2 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.55, 1.13] |
| 15.3 dystonia | 2 | 70 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.24, 0.93] |
| 15.4 gait disturbance | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.30, 3.09] |
| 15.5 needing additional anticholinergic medication | 3 | 221 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.54, 0.77] |
| 15.6 parkinsonism | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.34 [0.46, 3.93] |
| 15.7 restlessness | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.31 [0.67, 2.54] |
| 15.8 rigidity | 3 | 164 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.40, 0.98] |
| 15.9 tremor | 4 | 290 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.46, 1.05] |
| 16 Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia ‐ endpoint scores (AIMS, high=poor, skewed data) | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 17 Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, high=poor, skewed data) | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 18 Adverse events: 6. Sleep problems | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 18.1 insomnia | 3 | 326 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.66, 1.01] |
| 18.2 lassitude | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.13 [0.57, 2.27] |
| 18.3 sleepiness | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.71, 3.41] |
| 18.4 somnolence | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.94, 1.76] |
| 19 Adverse events: 7. Others | 5 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 19.1 asthenia | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.58, 1.27] |
| 19.2 dry mouth | 3 | 250 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.76, 1.42] |
| 19.3 dizzyness | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.30, 2.26] |
| 19.4 headache | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.34 [0.46, 3.93] |
| 19.5 hyperhydrosis | 1 | 30 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.43, 1.80] |
| 19.6 liver function abnormalities | 5 | 396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.87, 1.38] |
| 19.7 nasal congestion/obstruction | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.35 [0.73, 15.31] |
| 19.8 pain | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.60, 1.32] |
| 19.9 salivation increased | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.52, 1.18] |
| 19.10 slight alterations in EEG | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.78 [0.18, 17.80] |
2.1. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 1 Global state: 1. Not improved (CGI).
2.2. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 2 Global state: 3. Average endpoint score (CGI, high=poor).
2.3. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 3 Global state: 2. Needing additional antipsychotic/sedative drugs.
2.4. Analysis.
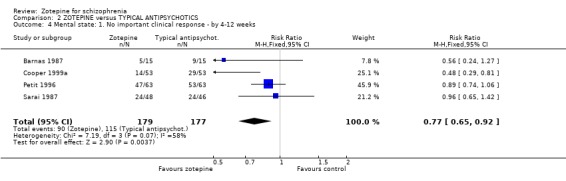
Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 4 Mental state: 1. No important clinical response ‐ by 4‐12 weeks.
2.5. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 5 Mental state: 2. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, high=poor).
2.6. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 6 Mental state: 3. Average negative symptom endpoint score (SANS, high=poor).
2.7. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 7 Behaviour: Specific behaviour changes.
2.8. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 8 Leaving the study early: Any reason.
2.9. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 9 Cognition: Not improved (Syndrome Short Test).
2.10. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 10 Adverse events: 1. Any adverse event.
2.11. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 11 Adverse events: 2a. Cardiovascular problems.
2.12. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 12 Adverse events: 2b. Cardiovascular problems ‐ pulse rate.
2.13. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 13 Adverse events: 3. Gastrointestinal problems.
2.14. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 14 Adverse events: 4. Metabolic problems ‐ weight change.
2.15. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 15 Adverse events: 5a. Movement disorders ‐ specific problems.
2.16. Analysis.
Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 16 Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia ‐ endpoint scores (AIMS, high=poor, skewed data).
| Adverse events: 5b. Movement disorders ‐ dyskinesia ‐ endpoint scores (AIMS, high=poor, skewed data) | |
|---|---|
| Study | |
| Cooper 1999a | 1. Zotepine group: mean 2.5. SD 3.6. N=53. 2. Chlorpromazine group: mean 2.9, SD 4.2. N=52. |
2.17. Analysis.
Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 17 Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, high=poor, skewed data).
| Adverse events: 5c. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale, high=poor, skewed data) | |
|---|---|
| Study | |
| Cooper 1999a | 1. Zotepine group: mean 3.9, SD 4.4. 2. Chlorpromazine group: mean 4.3, SD 5.5. |
| Klieser 1996 | 1. Zotepine: mean 2.6, SD 5.3. N=20. 2. Haloperidol: mean 5.5, SD 5.7. N=45. |
2.18. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 18 Adverse events: 6. Sleep problems.
2.19. Analysis.

Comparison 2 ZOTEPINE versus TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 19 Adverse events: 7. Others.
Comparison 3. ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Mental state: 1. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, high=poor) | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.30 [‐12.95, 10.35] |
| 2 Leaving the study early: Any reason | 1 | 50 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.43 [0.65, 3.15] |
| 3 Cognition: Not improved (Syndrome Short Test) | 1 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.28, 1.75] |
| 4 Adverse events: 1a. Movement disorders ‐ needing additional anticholinergic medication | 1 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.88 [1.22, 6.78] |
| 5 Adverse events: 1b. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale endpoint, high=poor, data skewed) | Other data | No numeric data |
3.1. Analysis.

Comparison 3 ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 1 Mental state: 1. Average total endpoint score (BPRS, high=poor).
3.2. Analysis.

Comparison 3 ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 2 Leaving the study early: Any reason.
3.3. Analysis.

Comparison 3 ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 3 Cognition: Not improved (Syndrome Short Test).
3.4. Analysis.

Comparison 3 ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 4 Adverse events: 1a. Movement disorders ‐ needing additional anticholinergic medication.
3.5. Analysis.
Comparison 3 ZOTEPINE versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS, Outcome 5 Adverse events: 1b. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale endpoint, high=poor, data skewed).
| Adverse events: 1b. Movement disorders ‐ parkinsonism (Simpson‐Angus Scale endpoint, high=poor, data skewed) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Intervention | mean | SD | N |
| Klieser 1996 | Zotepine | 2.6 | 5.3 | 20 |
| Klieser 1996 | Risperidone 8mg group | 0.1 | 2.4 | 20 |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Barnas 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further information. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets. Duration: 7 weeks ‐ preceded by washout ‐ 7 day for oral, 3 months for depot. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: last observation carried forward. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM‐III‐R). N=30. Age: mean ˜34 years. Sex: 20 M, 10 F. History: duration ill 6 months ‐ >5 years. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose mean ˜ 94 mg/day (SD˜29). N=15. 2. Haloperidol: dose mean ˜ 4 mg/day (SD˜1). N=15. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving study early.
Global impression: CGI.
Mental state: BPRS, SANS.
Adverse events: DOTES. Unable to use ‐ ECG and EEG (no data). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Cooper 1999a.
| Methods | Allocation: blocks of 6, randomisation undertaken by drug company. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets, double dummy technique. Duration: 8 weeks ‐ preceded by 1 dose interval for depot. Intention to treat analysis: last observation carried forward. Power calculation: able to detect a change of 8.8 from baseline (BPRS total score). | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia, acute exacerbation (DSM‐III‐R). Inclusion criteria: baseline CGI > 4, not physically ill, no substance abuse. N=159. Age: 18‐65, mean ˜ 40 years. Sex: 115 M, 44 F. History: mostly inpatients, duration ill, range 6‐440 months. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose titrated 150 mg/day ‐ 300 mg/day over first 7 days. N=53. 2. Chlorpromazine: dose titrated 200 mg/day ‐ 600 mg/day over first 7 days. N=53. 3. Placebo. N=53. Other treatments as required. Decreased dose if intolerant of higher dose, withdrawn if intolerant of lower dose. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving the study early.
Mental state: BPRS, SANS.
Side effects: AIMS, SAS, adverse events using COSTART terms ‐ only used if reported 5+ times.
Weight.
Pulse. Unable to use ‐ Global impression: CGI (no data). Benzodiazepine use (no data). Blood pressure (no SD). Discharge from inpatient status (N unclear). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Cooper 1999b.
| Methods | Allocation: block randomisation, code held by drug company. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets, double dummy technique. Duration: 26 weeks ‐ preceded by 1 dose interval for depot. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: last observation carried forward. Power calculation: able to detect 30% change between groups with 90% power, 5% significance. Setting: participants recruited from 6 European countries. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia, chronic (DSM‐III‐R). Inclusion criteria: baseline CGI >2, reoccurrence in last 18 months, currently maintained on antipsychotics, not physically ill, no substance abuse. N=121*. Age: range 20‐65, mean ˜42 years. Sex: 82 M, 37 F. History: mostly outpatients, duration ill, mean ˜13 years. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose titrated 150 mg/day ‐ 300 mg/day over first 4 days. N=63. 2. Placebo. N=58. Decreased to 150 mg/day if intolerant of higher dose, withdrawn if unable to tolerate lower dose. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving the study early. Unable to use ‐ Global impression: CGI (>50% attrition). Mental state: BPRS, SANS (>50% attrition). Adverse events: AIMS, SAS (50% attrition). Use of benzodiazepines and night sedation (>50% attrition). Physiological measures (>50% attrition). |
|
| Notes | Loss to follow 76%. *2 participants refused baseline measurements and were not included after randomisation. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Dieterle 1991.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further information. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets. Duration: 28 days ‐ preceded by washout of 3‐5 days for oral, 14 days for depot. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (ICD 9). N=40. Age: mean ˜34 years. Sex: 13 M, 27 F. History: inpatients, chronic illness. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose mean 241 mg/day (SD˜70). N=20. 2. Perazine: dose mean 348 mg/day (SD˜98). N=20. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving study early. Unable to use ‐ Global impression: CGI (no mean). Mental state: BPRS, SANS (no usable data). Adverse events: Webster and SAS, AMDP Lab tests (no usable data). Physiological measures: EEG, ECG (no usable data). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Fleischhacker 1989.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further details. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets. Duration: 6 weeks. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: last observation carried forward. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia acute paranoid (DSM‐III). N=40. Age: mean ˜33 years. Sex: 29 M, 11 F. History: ill 3 months to > 5 years. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose mean 309 mg/day. N=20. 2. Haloperidol: dose mean 14.5 mg/day. N=20. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving the study early.
Adverse events: Laboratory tests. Unable to use ‐ Global effect: CGI (no usable data). Mental state: BPRS (no SD). Adverse events: DOTES (no mean). ECG (outcomes not reported). |
|
| Notes | Written to authors for further data. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Klieser 1996.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further details. Blinding: double ‐ no further details. Duration: 4 weeks. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (ICD 9), acute, paranoid hallucinatory psychoses. N=180. Age: mean ˜ 33 years. Sex: 84 M, 96 F. History: duration ill, mean ˜3 years. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose 75 mg/tid. N=20. 2. Risperidone: increased to 4 mg/day over first 7 days. N=20. 3. Risperidone: increased to 8 mg/day over first 7 days. N=20. 4. Clozapine: increased to 400 mg/day over first 7 days. N=37.* 5. Remoxipride: increased to 400 mg/day over first 7 days. N=38.* 6. Haloperidol: 15 mg/day. N=45. Biperiden, diazepam and choloral hydrate as required. |
|
| Outcomes | Global impression: CGI.
Mental state: BPRS.
Adverse events: SAS, Laboratory tests.
Cognition: SKT. Unable to use ‐ Physiological tests: ECG, EEG (no data). |
|
| Notes | * Only data from the zotepine, risperidone 8 mg/day and the haloperidol group used for continuos outcomes. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Meyer‐Lindberg 1996.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further details. Blinding: double ‐ no further details. Duration: 6 weeks. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM‐III‐R). N=50. Age: mean ˜ 33 years (SD˜10). Sex: 18 M, 8 F* History: unresponsive to > 3 weeks of 2 typical antipsychotics in effective doses, BPRS >39. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose 150‐450 mg/day. N=25 2. Clozapine: dose 150‐450 mg/day. N=25. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving the study early. Unable to use ‐ Global function: CGI (no mean). Mental state: BPRS, SANS (no mean). Behaviour: CIPS, NOSIE (no mean) Adverse events: UKU (data presented only for matched pairs). Cognitive function: maze tests (no mean). ECG (no data). Weight gain (no data). |
|
| Notes | * Data only provided on a sub‐set of 26 participants 13 from each arm. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Moller 2004.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised (in blocks of four). Blinding: double blind ‐ identical capsules. Duration: 8 weeks. Setting: hospital and community, multicentre. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (ICD 10). N=85. Age: range 81‐65 years, mean 41 years. Sex: male and female ˜ equal numbers. History: stable participants with primarily negative symptoms. Exclusion criteria: drug and alcohol abuse; acute drug or alcohol intoxication (ICD 10), presence of any other psychiatric diagnosis, suicidal tendency suspected or suicide attempted in the prior 12 months. Inclusion criteria: residual schizophrenia (ICD 10), presenting with stable primary negative symptoms; minimum score >3 on 3 items PANSS ‐ve; maximum two items > 3 on PANSS +ve. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose 25 mg or 50 mg/day (max. 225 mg/day). N=39. 2. Placebo. N=46. Concomitant medication benzodiazepines, hypnotics, promethazine. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving the study early.
Death.
Hospitalisation.
Mental state: PANSS, MADRS.
Global impression: CGI.
Adverse events: EPS, TDRS.
Qualtiy of life: SF‐36. Unable to use ‐ Quality of life: SF‐36 ‐psychic component (not listed as part of the SF‐36 scale) |
|
| Notes | Last observation carried forward. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Petit 1996.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further details.* Blinding: double ‐ identical and dummy capsules. Duration: 8 weeks ‐ preceded by omission of last depot. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: last observation carried forward. Setting: 13 French hospitals. Power calculation: able to demonstrate an 8.2 difference between treatment groups on BPRS. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM‐III‐R). Inclusion criteria: 4+ on CGI, not physically ill, no substance abuse. N=126. Age: range 18‐68 years, mean ˜39. Sex: 63 M, 63 F.* History: currently acutely ill, in hospital, overall duration ill 6 months to 41 years. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose 150‐300 mg/day. N=63. 2. Haloperidol: dose 10‐20 mg/day. N=63. |
|
| Outcomes | Mental state (50% reduction in BPRS).
Leaving the study early.
Adverse events. Unable to use ‐ Global improvement (CGI ‐ no mean). Mental state (SANS ‐ no mean). Adverse events: (AIMS, SAS ‐ no SD). ECG (no data). Pulse (no SD). |
|
| Notes | * Haloperidol group had twice as many women as zotepine group. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Sarai 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised, tablets in identical boxes and given a random number kept by pharmacist, stratified by hospital. Blinding: double ‐ identical tablets. Raters: trained in use of BPRS. Duration: 8 weeks. Setting: multicentre, Japan. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia.* N=94. Age: range 29‐>50 years. Sex: 47 M, 47 F. History: 82/94 in hospital, ill 3 ‐10 years. Exclusion criteria: if "in an advanced stage of schizophrenia, severe psychomotor excitement, in sedative state, sleep disturbance, hallucinating or deluded, fixed delusions, pregnant or physically ill". | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose 75‐300 mg/day. N=48. 2. Thiothixene: dose 15‐60 mg/day. N=46. |
|
| Outcomes | Mental state: BPRS.
Excluded/leaving the study early.
Adverse events.
Use of additional medication.
Laboratory results. Unable to use ‐ Mental state: BPRS (continuous data, no mean). |
|
| Notes | * Mainly people 'overshadowed by lack of spontaneity'. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Wetzel 1991.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised ‐ no further information. Blinding: double ‐ identical capsules. Duration: 28 days ‐ no washout. Setting: inpatient. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (paranoid, hallucinatory type) (ICD 9). N=41. Age: range 18‐68 years. Sex: 16 M, 25 F. History: acute phase. | |
| Interventions | 1. Zotepine: dose range 100‐600 mg/day, mean 250 mg/day. N=20. 2. Perazine: dose range 150‐900 mg/day, mean 500 mg/day. N=21. |
|
| Outcomes | Leaving study early.
Mental state: BPRS.
Use of additional medication. Unable to use ‐ Global impression: CGI (no usable data). Mental state: SANS (no usable data). Adverse events: Webster and Simpson scale, AMDP, Lab tests (no usable data). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Diagnostic tools ‐ DSM III ‐ Diagnostic Statistical Manual, version 3 DSM III‐R and DSM‐IV ‐ Diagnostic Statistical Manual version 3 Revised, and version 4 ICD 9 ‐ International Classification of Diseases
Behaviour scales ‐ NOSIE ‐ Nurses Observational Scale of Inpatients Evaluation CIPS ‐ Collegium Internationale Psychiatriae Scalarum
Global rating scales ‐ CGI ‐ Clinical Global Impressions
Mental state scales ‐ BPRS ‐ Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale SANS ‐ Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms MADRS ‐ Mongomery and Asberg Depression Rating Scale
Side effects scales ‐ AIMS ‐ Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale AMDP ‐ Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Methodik und Dokumentation in der Psychiatrie COSTART ‐ Coding Symbols for Thesaurus of Adverse Reaction Terms DOTES ‐ Dosage Record & Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale SAS ‐ Simpson‐Angus Index ‐ for neurological side effects TDRS‐ Tardive Dyskinesia Rating Scale UKU ‐ Side Effects Rating Scale
Cognition scales ‐ SKT ‐ The Short Cognitive Performance Test
Quality of Life ‐ SF‐36 ‐ Short Form 36
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Faulkner 1997 | Allocation: randomised, two way crossover study. Participants: healthy volunteers, not people with schizophrenia. |
| Fleischhacker 1998 | Allocation: not randomised, review article. |
| Fukahori 1995 | Allocation: none randomised study of single drug sultopride hydrochloride. |
| Hada 1985 | Allocation: not randomised. |
| Harada 1991 | Allocation: not randomised, case series. |
| Hen 1987 | Allocation: not randomised, evaluation of Chinese Classification of Mental Diseases scale. |
| Komada 1987 | Allocation: not randomised. |
| Naber 1997 | Allocation: randomised, open label. Participants: people with schizophrenia. Interventions: zotepine versus olanzapine versus risperidone. Outcomes: no usable data, authors contacted May 2006, no further data supplied. |
| Needham 1996 | Allocation: not randomised, animal study. |
| Nishizono 1994 | Allocation: not reported. Participants: people with schizophrenia. Interventions: zotepine versus chlorpromazine versus haloperidol. Outcomes: no usable data ‐ wrote to author on 8/05/2006 no reply. |
| Ohhara 1988 | Allocation: not randomised. |
| Prakash 1998 | Allocation: not randomised, review article. |
| Saletu 1987 | Allocation: latin square design. Participants: healthy volunteers, not people with schizophrenia. |
| Takashina 1986 | Allocation: randomised, crossover design. Participants: people with schizophrenia. Interventions: immediate switch to zotepine, phasing in of zotepine, phasing out of usual care, phasing in of zotepine while maintaining usual care, and 2 others. Outcomes: key symptom change, no data available for end of first stage before crossover. |
| Welch BPI1201‐USA | Allocation: not randomised, review article. |
Contributions of authors
John Rathbone ‐ selected and acquired studies, extracted data and inputted data, summated data, wrote report (2006 update).
Mark Fenton ‐ prepared protocol, undertook searches, selected and acquired studies, extracted data, summated data, produced report.
Susan Morris ‐ prepared protocol, undertook searches, selected and acquired studies, extracted data, summated data, produced report.
Prasanna DeSilva ‐ prepared protocol, extracted data, produced report.
Anne‐Marie Bagnall ‐ prepared protocol, undertook searches, selected and acquired studies, extracted data, summated data, produced report.
Stephen Cooper ‐ provided comments on final version of the review.
Gert Gammelin ‐ translation of German studies, data extraction, report writing.
Maria Leitner ‐ finding funding, initial input into the protocol and searches.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, UK.
South Tees Community and Mental Health Services Trust, UK.
The Queen's University of Belfast, UK.
Cochrane Schizophrenia Group, UK.
External sources
NHS‐R&D Health Technology Assessment Programme, UK.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, UK.
Declarations of interest
Mark Fenton has lead Jansen, Lilly and Zeneca sponsored workshops for clinicians.
Prasanna De‐Silva has received financial assistance to attend various scientific meetings and conferences world‐wide.
Stephen Cooper has undertaken trials of zotepine with employees of Knoll Pharmaceuticals.
The Cochrane Schizophrenia Group has received general support funding from Eli Lilly during the years 1996‐8 (see Group Module). This, along with some funds from other pharmaceutical companies, is used to support any ongoing work of the editorial base and is not linked to any particular review (annual report available on request).
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Barnas 1987 {published data only}
- Barnas C, Stuppack CH, Miller C, Haring C, Sperner‐Unterweger B, Fleischhacker WW. Zotepine in the treatment of schizophrenic patients with prevailingly negative symptoms: A double blind trial vs. haloperidol. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1992;7:23‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnas C, Stuppack CH, Miller C, Haring C, Sperner‐Unterweger B, Fleischhacker WW. Zotepine: treatment of schizophrenic patients with predominantly negative symptoms. A double‐blind study vs. haloperidol] [Zotepin: Die Behandlung schizophrener Patienten mit vorherrschender Negativsymptomatik. Eine Doppelblindstudie vs. Haloperidol]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:36‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cooper 1999a {unpublished data only}
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Welch CP. Zotepine in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. 10 th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress, Vienna, Austria. 1997.
- Cooper SJ, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a comparison versus chlorpromazine and placebo. XX th Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum, Melbourne, Australia. 1996.
- Cooper SJ, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Butler A, Welch C. A placebo controlled comparison of zotepine versus chlorpromazine in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2000;101(3):218‐25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper SJ, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. A placebo‐controlled comparison of zotepine versus chlorpromazine in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Unpublished manuscript 1999. [PubMed]
- Cooper SJ, Welch CP. A Comparison of zotepine and chlorpromazine on BPRS sub‐scores. 10 th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress, Vienna, Austria. 1997.
Cooper 1999b {unpublished data only}
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in the prevention of relapse. Biological Psychiatry 1997;42:41S. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Raniwalla J, Welch C. Zotepine in the prevention of relapse. Sixth World Congress of Biological Psychiatry, Nice, France. 1997.
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed J, Welch C, Raniwalla J. Zotepine in the prevention of reoccurrence: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study for chronic schizophrenia. Unpublished manuscript 1999. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed JA, Welch CP, Wighton AJ, Appleby P, Reynolds CW, Ruck A. Zotepine is effective in preventing recurrence in patients with chronic schizophrenia. 11 th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress Oct 31 ‐ Nov 4, Paris, France. 1998.
- Cooper SJ, Butler A, Tweed JA, Welch CP, Wighton AJ, Appleby P, Reynolds CW, Ruck A. Zotepine is effective in preventing recurrence in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):207‐8. [Google Scholar]
Dieterle 1991 {published data only}
- Dieterle DM, Muller Spahn F, Ackenheil M. Effectiveness and tolerance of zotepine in a double‐blind comparison with perazine in schizophrenic patients [Wirksamkeit und vertraglichkeit von zotepin im doppelblindvergleich mit perazin bei schizophrenen patienten]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:18‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller Spahn F, Dieterle D, Ackenheil M. Clinical effectiveness of zotepine in treatment of negative schizophrenic symptoms. Results of an open and a double‐blind controlled trial [Klinische wirksamkeit von zotepin in der behandlung schizophrener minussymptomatik. Ergebnisse einer offenen und einer doppelblind‐ kontrollierten studie]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:30‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fleischhacker 1989 {published data only}
- Fleischhacker WW, Barnas C, Stuppack CH, Sperner‐Unterweger B, Miller C, Hinterhuber H. Zotepine vs. haloperidol in paranoid schizophrenia: a double‐blind study [Zotepin vs. haloperidol bei paranoider schizophrenie: eine doppelblindstudie]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:10‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischhacker WW, Barnas C, Stuppack CH, Unterweger B, Miller C, Hinterhuber H. Zotepine vs. haloperidol in paranoid schizophrenia: a double‐blind trial. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989;25:97‐100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuppäck H, Barnas B, Unterweger B, Fleischhacker WW. Zotepine vs. Haloperidol in acute schizophrenia: a double blind trial. Schizophrenia Research 1998;1(2‐3):200‐1. [Google Scholar]
Klieser 1996 {published data only}
- Klieser E, Lehmann E, Heinrich K. Risperidone in Comparison with various treatments of schizophrenia. In: Kane JM, Möller HJ editor(s). Medical Psychiatry. Vol. 3, New York: Marcel Dekker, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Klieser E, Lehmann E, Tegeler J. Double‐blind comparison of 3 x 75 mg zotepine und 3 x 4 mg haloperidol in acute schizophrenic patients [Doppelblindvergleich von 3 x 75 mg zotepin und 3 x 4 mg haloperidol bei akut schizophrenen patienten]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:14‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meyer‐Lindberg 1996 {published data only}
- Gallhofer B, Gruppe H, Bauer U. Zotepine versus clozapine: A comparison of the impact on the cognitive dysfunction syndrome in schizophrenia (a double blind trial). Pharmacopsychiatry 1995;28:179. [11th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology [CD‐ROM]: Conifer, Excerpta Medica Medical Communications BV, 1998 P6037] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer‐Lindenberg A, Gruppe H, Bauer U, Lis S, Krieger S, Gallhofer B. Improvement of cognitive function in schizophrenic patients receiving clozapine or zotepine: results from a double‐blind study. Pharmacopsychiatry 1997;30:35‐42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moller 2004 {published data only}
- Moller HJ, Riedel M, Muller N, Fischer W, Kohnen R. Zotepine versus placebo in the treatment of schizophrenic patients with stable primary negative symptoms: a randomized double‐blind multicenter trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2004;37(6):270‐8. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE: 2004519196] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Petit 1996 {published data only}
- Petit M, Raniwalla J, Leutenegger E, Tweed J, Kelly F. Double‐blind study of zotepine vs haloperidol in schizophrenia. 8th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1995 Sep 30 ‐ Oct 4; Venice, Italy. 1995.
- Petit M, Raniwalla J, Tweed J, Leutenegger E, Dollfus S, Kelly F. A comparison of an atypical and typical antipsychotic, zotepine versus haloperidol in patients with acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a parallel‐group double‐blind trial. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32:81‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sarai 1987 {published data only}
- Sarai K, Okada M. Comparison of efficacy of zotepine and thiothixene in schizophrenia in a double‐blind study. Pharmacopsychiatry 1987;20:38‐46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetzel 1991 {published data only}
- Wetzel H, Bardeleben U, Holsboer F, Benkert O. Zotepine versus perazine in patients with paranoid schizophrenia: a double‐blind controlled trial of its effectiveness [Zotepin versus perazin bei patienten mit paranoider schizophrenie: eine doppelblind‐kontrollierte wirksamkeitsprufung]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:23‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Faulkner 1997 {published data only}
- Faulkner RD, Hinson J, Leone MB, Moult J, Ghani S, Velagapudi RB. Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of zotepine and norzotepine in healthy subjects. 10th ECNP (European College of Neuropsychopharmacology) Congress, Vienna, Austria. Sep 13 ‐ 17, 1997.
Fleischhacker 1998 {published data only}
- Fleischhacker WW. Problems in evaluating new antipsychotic drugs [Zur problematik der beurteilung neuer antipsychotika]. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 1998;148:266‐72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fukahori 1995 {published data only}
- Fukahori M, Inanaga K, Suetsugu M. Clinical evaluation of sultopride hydrochloride on outpatients with schizophrenia. Japanese Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1995;23:267‐80. [Google Scholar]
Hada 1985 {published data only}
- Hada Y. Clinical effects of zotepine in outpatients with schizophrenia. Shinryo to Shin'yaku 1985;22(2):435‐44. [Google Scholar]
Harada 1991 {published data only}
- Harada T, Otsuki S, Fujiwara Y. Effectiveness of zotepine in therapy‐refractory psychoses. An open, multicenter study in eight psychiatric clinics [Wirksamkeit von ztepin bei therapieresistenten pychosen. Eine offene, multizentrische sudie in acht psychiatrischen kiniken]. Fortschritte der Neurologie Psychiatrie 1991;59:41‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T, Sato M, Omori B, Hirata J, Fujimoto A, Nishioka H, Takahashi Y, Oshimo T, Suemaru K. Effectiveness of zotepine in refractory psychoses. Shin'yaku to Rinsho 1987;36(9):1447‐59. [Google Scholar]
Hen 1987 {published data only}
- Hen LS. Controlled clinical trial of zotepine in schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Nervous and Mental Disorders 1987;1392:87. [Google Scholar]
Komada 1987 {published data only}
- Komada A, Kishimoto A, Tanaka K, Fukuma E, Kunimoto N. Effects of zotepine in acute treatment and maintenance therapy of schizophrenic out‐patients. Igaku to Yakugaku 1987;18(4):1175‐87. [Google Scholar]
Naber 1997 {published data only}
- Briken P, Nika E, Moritz S, Haasen C, Perro C, Yagdiran O, Naber D, Krausz M. Effect of zotepine, olanzapine and rispiridone on hostility in schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Research 2002;57:311‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber D. Evidence of efficacy of neuroleptics in effective versus negative symptoms. 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress (ECNP ), Vienna, Austria. September 13‐17, 1997.
Needham 1996 {published data only}
- Needham PL, Atkinson J, Skill M J, Heal DJ. Zotepine: preclinical tests predict antipsychotic efficacy and an atypical profile. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32:123‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nishizono 1994 {published data only}
- Nishizono M. A comparative trial of zotepine, chlorpromazine and haloperidol in schizophrenic patients. Shinkei Seishin Yakuri 1994;10(2):30. [Google Scholar]
Ohhara 1988 {published data only}
- Ohhara K, Suzuki Y, Kawaguchi K, et al. Effects of zotepine on chronic schizophrenics with a mean disease duration of 19.9 years. Shinryo to Shinyaku 1988;25(6):1205‐11. [Google Scholar]
Prakash 1998 {published data only}
- Prakash A, Lamb HM. Zotepine: A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in the management of schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 1998;9:153‐75. [Google Scholar]
Saletu 1987 {published data only}
- Saletu B, Grunberger J, Linzmayer L, Anderer P. Comparative placebo‐controlled pharmacodynamic studies with zotepine and clozapine utilizing pharmaco‐EEG and psychometry. Pharmacopsychiatry 1987;20:12‐27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Takashina 1986 {published data only}
- Takashina K, Yasuda T, Terada H, Yoshida H, Okuda J. Clinical use of zotepine (Lodopin) for schizophrenia and mania. Shinryo to Shin'yaku 1986;23(9):2043‐69. [Google Scholar]
Welch BPI1201‐USA {published data only}
- Welch CP, Kilpatrick AT, Butler A, Tweed JA. The efficacy of zotepine in reducing negative symptoms. Knoll Pharmacueticals Advertising Material 1999.
- Welch CP, Kilpatrick AT, Butler A, Tweed JA. The efficacy of zotepine in reducing negative symptoms. Knoll Pharmacueticals Advertising Material 1999.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Imai 1982 {published data only}
- Imai H, Ohtani W, Kondo H. Comparison of efficacy of zotepine and perphenazine in schizophrenia by double‐blind, controlled study. Japanese Journal Neuropsychopharmacology 1982;2:61. [Google Scholar]
Iwanaga 1980 {published data only}
- Owanaga M, Okada I, Ichinomiya Y. Clinical evaluation of zotepine in chronic schizophrenia. A multi‐institutional double‐blind study in comparison with propericiazine. Yakuri To Chiryo 1980;9:121. [Google Scholar]
Okada 1980 {published data only}
- Okada M, Sarai K, Hamano H. Comparison of efficacy of zotepine and tiotixene in schizophrenia by double‐blind study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1980;22(9):947‐65. [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Adams 1999
- Adams CE, Gray R, Daniels J, Thornley B, Philpott H, Wahlbeck K. A survey of UK consultant psychiatrists first and second choice drug treatments for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Trials Meeting, Stratford upon Avon. 5‐7th May, 1999.
Altman 1996
- Altman DG, Bland JM. Detecting skewness from summary information. BMJ 1996;313:1200. [ZOT020600] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Andreasen 1984
- Andreasen NC. Scale for the assessment of negative symptoms (SANS). Iowa City: University of Iowa, 1984. [Google Scholar]
APA 1997
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154(4):1‐63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Begg 1996
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, Pitkin R, Rennie D, Schulz KF, Simel D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement.. JAMA 1996;8:637‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bland 1997
- Bland JM. Statistics notes. Trials randomised in clusters. BMJ 1997;315:600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Buckley 1997
- Buckley PF. New dimensions in the pharmacologic treatment of schizophrenia and related psychoses. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1997;37:363‐78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carpenter 1994
- Carpenter WT Jr, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Casey 1997
- Casey DE. The relationship of pharmacology to side effects. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58(10):55‐62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chalmers 1983
- Chalmers TC, Celano P, Sacks HS, Smith H Jr. Bias in treatment assignment in controlled clinical trials. New Englans Journal of Medicine 1983;309(22):1358‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
COSTART 1990
- US Food, Drug Administration. COSTART coding sysmbols for thesaurus of adverse reaction terms. 2. Rockville, MD: Food and Drug Administration, 1990. [Google Scholar]
CWG 1998
- Collaborative Working Group on Clinical Trial Evaluations. Adverse effects of the atypical antipsychotics. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59:17‐22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Divine 1992
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donner 2002
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Duggan 1999
- Duggan L, Fenton M, Dardennes RM, El‐Dosoky A, Indran S. Olanzapine for schizophrenia. The Cochrane Library 1999, Issue 2. [Google Scholar]
Egger 1997
- Egger M, Davey‐Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta‐analysis detected by a simple graphical test. BMJ 1997;315:629‐34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Erzigkeit 1986
- Erzigkeit H. Manual zum syndrom Kurztest (SKT). Vaterstetten: Vless‐Verlag, 1986. [Google Scholar]
Geddes 1999
- Geddes J. Clinical Guidelines. Schizophrenia Trials Meeting, Stratford‐upon‐Avon. 5‐7th May, 1999.
Glazer 1997
- Glazer WM, Johnstone BM. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of antipsychotic therapy for schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58(10):50‐4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gulliford 1999
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guy 1976
- Guy W. Early clinical drug evaluation (ECDEU) assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Washington DC: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976:217‐22. [Publication No.76‐338] [Google Scholar]
Heres 2006
- Heres S, Davis J, Maino K, Jetzinger E, Kissling W, Leucht S. Why Olanzapine Beats Risperidone, Risperidone Beats Quetiapine, and Quetiapine Beats Olanzapine: An Exploratory Analysis of Head‐to‐Head Comparison Studies of Second‐Generation Antipsychotics. American Journal of Psychiatry 2006;163(2):185‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. BMJ 2003;327:557‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2005
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). The Cochrane Library. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2005. [Google Scholar]
Jadad 1996
- Jadad AR, Moore A, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds JM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jenkinson 1997
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Lawrence K. Development and testing of the SF‐36 summary scale scores in the United Kingdom: Results from a large scale survey and a clinical trial. Medical Care 1997;35:410‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kane 1996
- Kane JM. Factors which can make patients difficult to treat. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;169(31):10‐4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kay 1986
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986. [Google Scholar]
Kerwin 1994
- Kerwin RW. The new atypical antipsychotics. A lack of extrapyramidal side‐effects and new routes in schizophrenia research. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994;164:141‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kerwin 1996
- Kerwin R, Taylor D. New antipsychotics. A review of their current status and clinical potential. CNS Drugs 1996;6:71‐82. [Google Scholar]
Meltzer 1996
- Meltzer HY. Cost‐effectiveness of clozapine treatment. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry ‐ Monograph Series 1996;14:16‐7. [Google Scholar]
Moher 1998
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, Tugwell P, Klassen TP. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352:609‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moher 2001
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Montgomery 1979
- Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Montgomery 2004
- Montgomery JH, Byerly M, Carmody T, Li B, Miller DR, Varghese F, Holland R. An analysis of the effect of funding source in randomized clinical trials of second generation antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Controlled Clinical Trials 2004;25 (Dec)(6):598‐612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NIMH 1981
- National Institue of Mental Health. Dosage record and treatment emergent symptom scale (DOTES). Collegium Internationale Psychiatriae Scalarum: Internationale Skalen fur Psychiatrie. Weinheim: Beltz Test, 1981. [Google Scholar]
Overall 1962
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812. [Google Scholar]
Pantelis 1997
- Pantelis C, Barnes TRE, Nelson HE, Tanner S, Weatherley L, Owen AM, Robbins TW. Frontal‐striatal cognitive deficits in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Brain 1997;120(10):1823‐43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schulz 1995
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Silverstone 1995
- Silverstone T, Turner P. Drug treatment in psychiatry. 5th Edition. Cornwall: TJ Press, 1995. [Google Scholar]
Simpson 1970
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;212:11‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Simpson 1979
- Simpson GM, Lee JH, Zoubouk B, Gardos G. A rating scale for tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 1979;64:171‐79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ukoumunne 1999
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organistation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wood Mackenzie 1998
- Wood Mackenzie. Review of the Global Schizophrenia Market. PharmaForum 1998;39:9. [Google Scholar]
www.psychotropics.dk
- Psychotropics. www.psychotropics.dk/default.asp.
References to other published versions of this review
Fenton 2000
- Fenton M, Morris S, De‐Silva P, Bagnall A, Cooper SJ, Gammelin G, Leitner M. Zotepine for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Systematic Reviews 2000, Issue 2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


