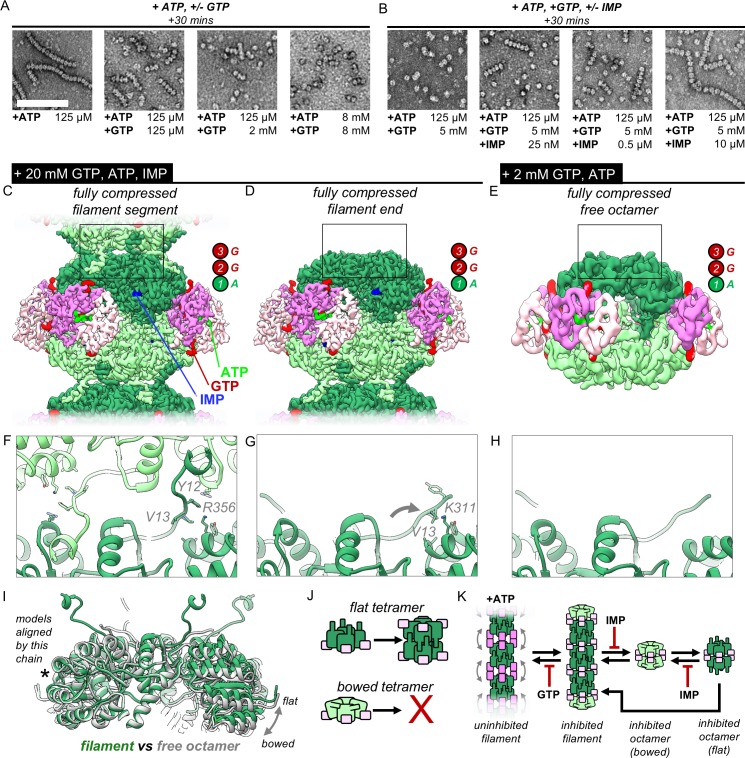
Figure 4. IMP and GTP allosterically modulate filament assembly and disassembly.
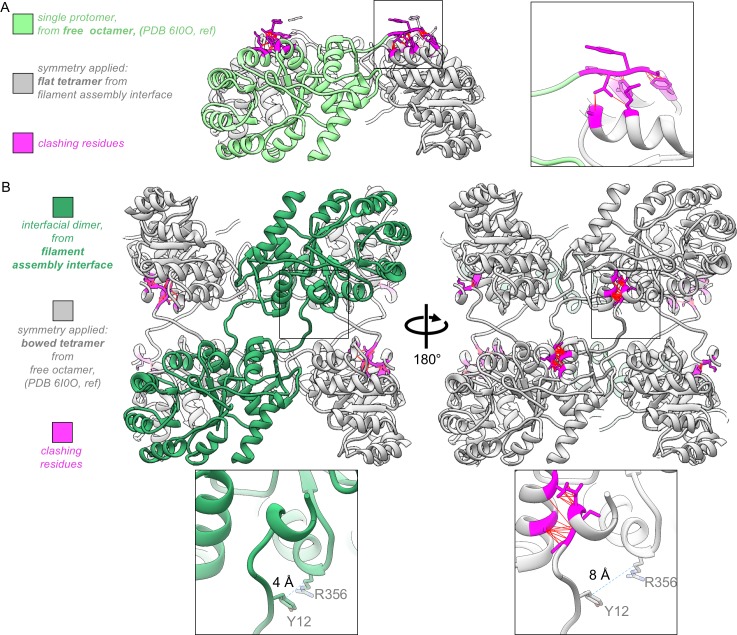
(A) Roughly 2 mM GTP inhibits filament assembly of IMPDH by ATP. Negative stain EM, protein concentration 2 uM. Scale bar 100 nm. Final nucleotide concentrations for each EM grid were as indicated below each image. (B) Roughly 10 uM IMP inhibits filament assembly by GTP. Final nucleotide concentrations for each EM grid were as indicated below each image. (C) Composite cryo-EM density of the GTP/ATP/IMP filament assembly interface and fully compressed filament segment maps (20 mM GTP, 0.5 mM ATP, 1 mM IMP). (D) Cryo-EM density of the fully compressed filament end map. (E) Cryo-EM density of the GTP/ATP non-filament fully compressed free octamer map (2 mM GTP, 2 mM ATP). (F–H) Close-up ribbon views of the assembled and unassembled filament interfaces the maps in A-C. (I) Comparison between the tetramer conformations of the ‘flat’ assembled filament interface (green) and the ‘bowed’ unassembled free octamer (gray). (J) Cartoon of the relationship between tetramer bowing and filament assembly. (K) Model of the regulation of filament assembly by GTP and IMP.
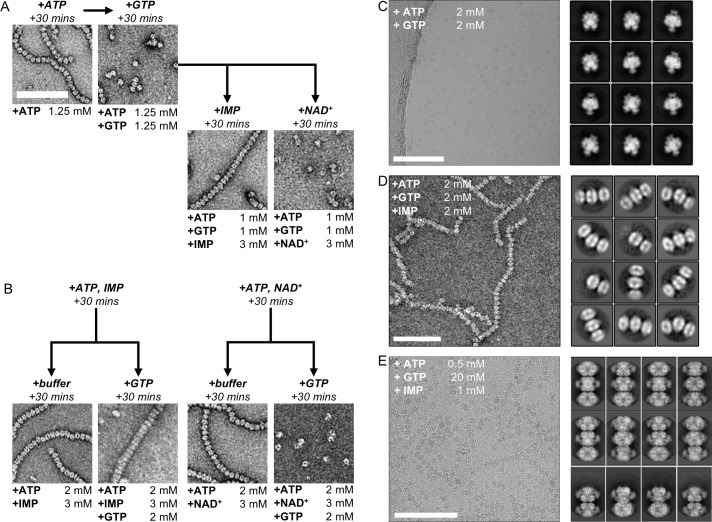
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Electron microscopy of human IMPDH2 treated with ATP, GTP, IMP, and NAD+.
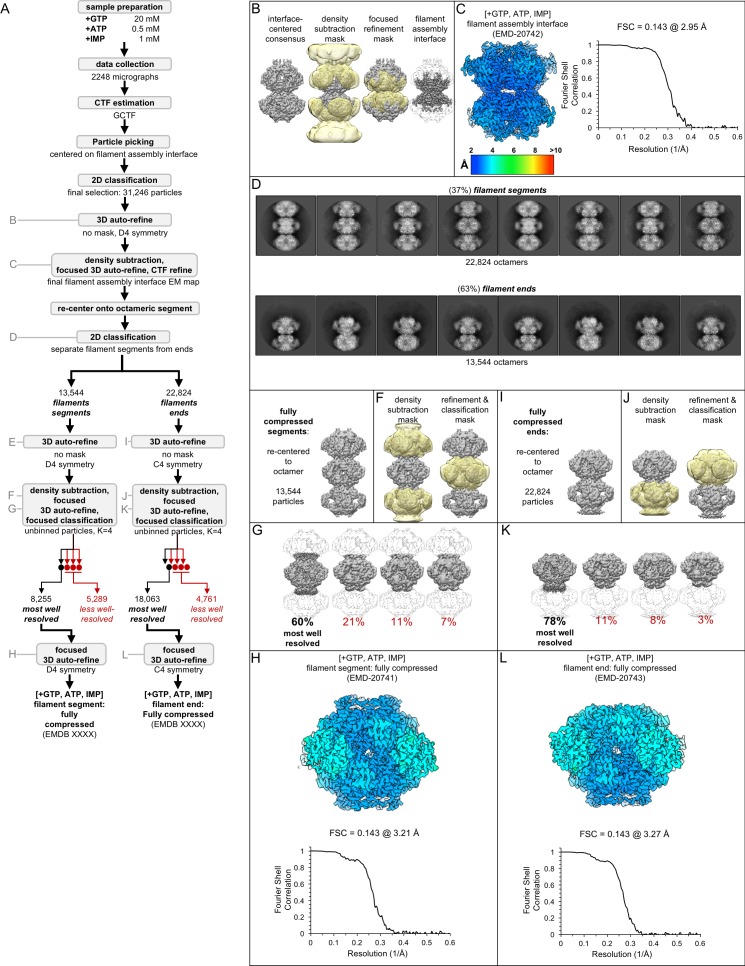
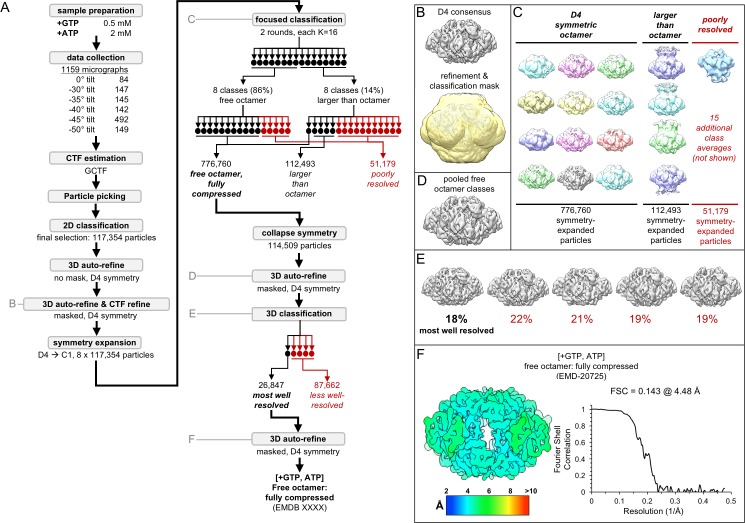
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Image processing of the IMPDH2 +ATP, IMP, 20 mM GTP cryo-EM dataset.
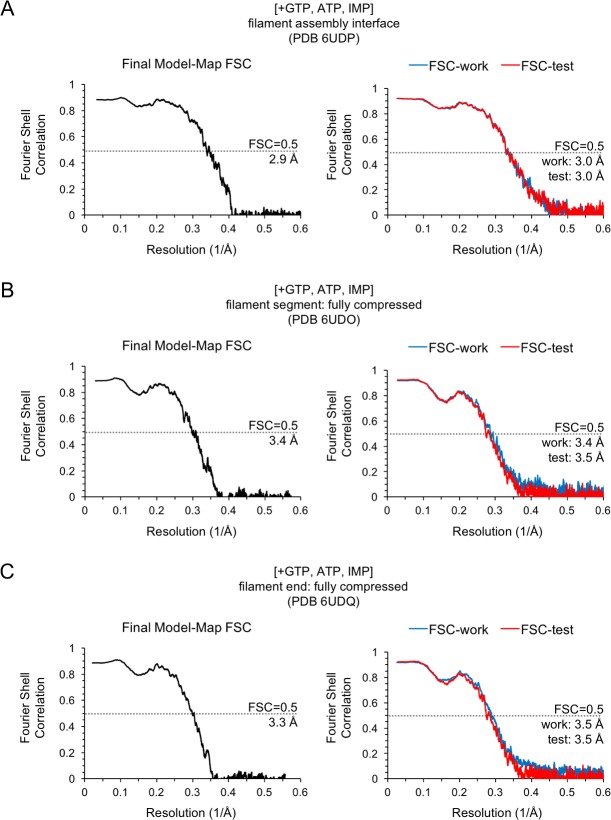
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. Model/Map FSC curves for the IMPDH2 +ATP, IMP, 20 mM GTP cryo-EM dataset.
Figure 4—figure supplement 4. Image processing of the IMPDH2 +ATP, 2 mM GTP cryo-EM dataset.
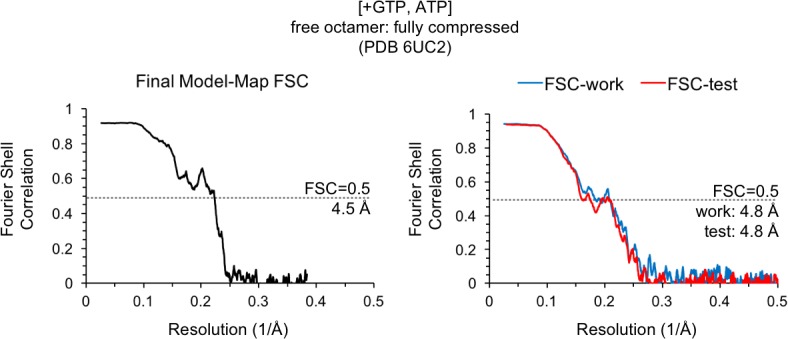
Figure 4—figure supplement 5. Model/Map FSC curves for the IMPDH2 +ATP, 2 mM GTP cryo-EM dataset.