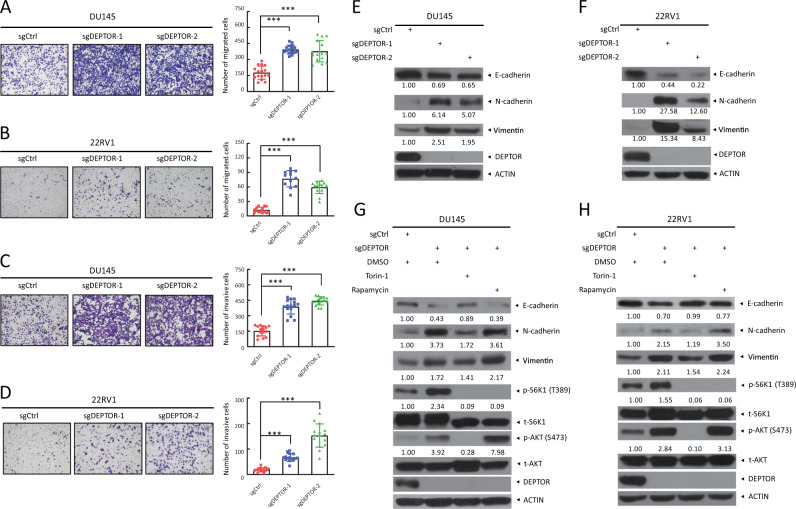
Fig. 4.
DEPTOR knockout enhances cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells, and Torin-1 abrogates the alterations of EMT markers upon DEPTOR depletion. a, b DEPTOR knockout promotes the migration of prostate cancer cells. DU145 (a) and 22RV1 cells (b) were transfected with the indicated sgRNA and then subjected to transwell migration assays. Representative images of migratory cells at 12–24 h are shown (left, a and b). The number of migratory cells was counted in five random fields per chamber insert (right, a and b). The mean ± SEM from three independent experiments are shown; n = 3; ***p < 0.001. c, d DEPTOR knockout promotes the invasion of prostate cancer cells. Cells were seeded into a 24-well plate chamber insert with Matrigel matrix and incubated for 12–24 h, followed by imaging (left). The invasive cells in five random fields per chamber insert were counted (right). The mean ± SEM from three independent experiments are shown; n = 3; ***p < 0.001. e, f DEPTOR knockout induces EMT in prostate cancer cells. DU145 (e) and 22RV1 (f) cells transfected with the indicated sgRNA were subjected to western blotting using the indicated antibodies. g, h Torin-1, but not rapamycin rescues the alterations of EMT markers upon DEPTOR depletion. DU145 (g) and 22RV1 (h) cells were treated with Torin-1 or rapamycin for 12 h and then subjected to western blotting using the indicated antibodies. The band density was quantified and expressed as the relative gray value (compared with the control), by arbitrarily setting the control value as 1