Correction to: Scientific Reports 10.1038/s41598-019-46203-x, published online 18 July 2019
This Article contains errors in Figures 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 where the white backgrounds have been erroneously changed to black. The correct Figures 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 appear below as Figures 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
Figure 1.
Bax translocation to mitochondria in cerebral ischemia-induced apoptosis. Bax was immuno-stained with anti-Bax34, and the mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker (green). The merged image indicates colocalization of Bax on mitochondria. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *P < 0.01 compared to sham, @P < 0.001 compare to MCAO + vehicle.
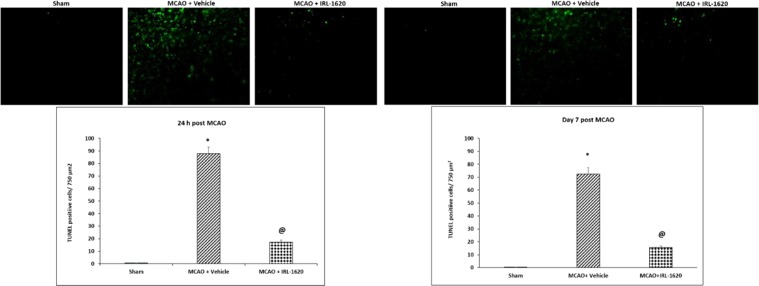
Figure 2.
TUNEL positive cells per 750 μm2 in the ischemic region were detected by TUNEL staining 24 h and day 7 after MCAO. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.0001 compared to sham; @p < 0.001 compared to vehicle.
Figure 3.
Effect of IRL-1620 on cerebral blood flow before, after and day 7 post MCAO in rat brains. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.001 compared to sham; @P < 0.05 compared to MCAO + vehicle; $P < 0.0001 compared to IRL-1620 1 h post MCAO.
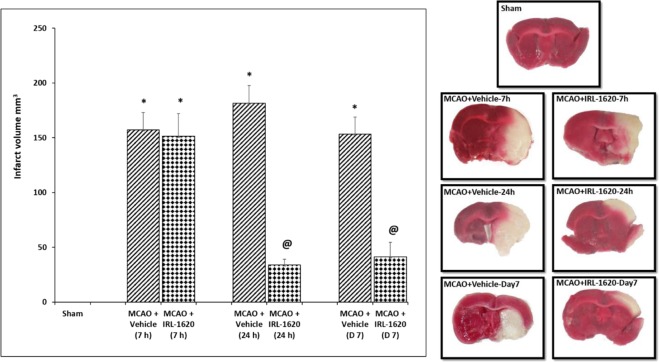
Figure 4.
Effect of IRL-1620 on infarct volume in MCAO rats. 2 mm coronal sections of brains stained with TTC to visualize the infarct area 7 h, 24 h and day 7 post MCAO (red indicates normal tissue and white indicates infarct tissue). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.001 compared to sham; @P < 0.05 compared to MCAO + vehicle.
Figure 5.
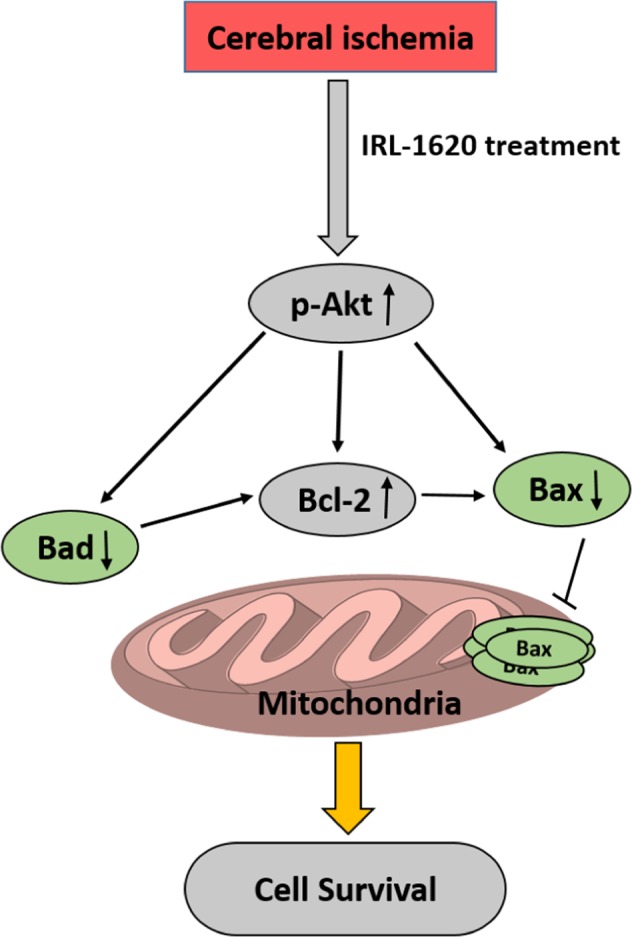
Stimulation of ETB receptors by IRL-1620 can stimulate apoptotic signaling pathways which may be implicated in its neuroprotective effect.