Abstract
Background
Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is a highly prevalent condition, characterised by excessive worry or anxiety about everyday events and problems. The effectiveness and comparative effectiveness of psychological therapies as a group has not yet been evaluated in the treatment of GAD.
Objectives
To examine the efficacy and acceptability of psychological therapies, categorised as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy and supportive therapy, compared with treatment as usual/waiting list (TAU/WL) and compared with one another, for patients with GAD.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Depression, Anxiety & Neurosis Group (CCDAN) Controlled Trials Register and conducted supplementary searches of MEDLINE, PsycInfo, EMBASE, LILACS and controlledtrials.com in February 2006. We searched reference lists of retrieved articles, and contacted trial authors and experts in the field for information on ongoing/completed trials.
Selection criteria
Randomised and quasi‐randomised controlled trials conducted in non‐inpatient settings, involving adults aged 18‐75 years with a primary diagnosis of GAD, assigned to a psychological therapy condition compared with TAU/WL or another psychological therapy.
Data collection and analysis
Data on patients, interventions and outcomes were extracted by two review authors independently, and the methodological quality of each study was assessed. The primary outcome was anxiety reduction, based on a dichotomous measure of clinical response, using relative risk (RR), and on a continuous measure of symptom reduction, using the standardised mean difference (SMD), with 95% confidence intervals.
Main results
Twenty five studies (1305 participants) were included in the review, of which 22 studies (1060 participants) contributed data to meta‐analyses. Based on thirteen studies, psychological therapies, all using a CBT approach, were more effective than TAU/WL in achieving clinical response at post‐treatment (RR 0.64, 95%CI 0.55 to 0.74), and also in reducing anxiety, worry and depression symptoms. No studies conducted longer‐term assessments of CBT against TAU/WL. Six studies compared CBT against supportive therapy (non‐directive therapy and attention‐placebo conditions). No significant difference in clinical response was indicated between CBT and supportive therapy at post‐treatment (RR 0.86, 95%CI 0.70 to 1.06), however, significant heterogeneity was indicated, which was partly explained by the number of therapy sessions.
Authors' conclusions
Psychological therapy based on CBT principles is effective in reducing anxiety symptoms for short‐term treatment of GAD. The body of evidence comparing CBT with other psychological therapies is small and heterogeneous, which precludes drawing conclusions about which psychological therapy is more effective. Further studies examining non‐CBT models are required to inform health care policy on the most appropriate forms of psychological therapy in treating GAD.
Keywords: Adult, Humans, Anxiety Disorders, Anxiety Disorders/therapy, Behavior Therapy, Behavior Therapy/methods, Psychotherapy, Psychotherapy/methods, Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic
Plain language summary
Psychological therapies for people with generalised anxiety disorder
Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is a very common condition, in which people suffer from excessive worry or anxiety about everyday events and problems. Psychological therapies are a popular form of treatment for anxiety disorders. This review aimed to find out whether psychological therapies are effective for GAD, and whether cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is more effective than other psychological therapy approaches, including psychodynamic and supportive therapies. The review included 25 studies, with a total of 1305 participants. All the studies used a CBT approach, and compared CBT against treatment as usual or waiting list (13 studies), or against another psychological therapy (12 studies). The review showed that people attending for psychological therapy based on a CBT approach were more likely to have reduced anxiety at the end of treatment than people who received treatment as usual or were on a waiting list for therapy. CBT was also very effective in reducing secondary symptoms of worry and depression. People who attended for group CBT and older people were more likely to drop out of therapy. None of the studies comparing CBT with treatment as usual or waiting list looked at the long‐term effectiveness of CBT. It is not clear whether people attending for CBT sessions were more likely to have reduced anxiety than people attending for psychodynamic therapy or supportive therapy, because only one study compared CBT with psychodynamic therapy, and the six studies that compared CBT with supportive therapy showed differing results. None of the studies included in the review reported on the possible side effects or acceptability of psychological therapies. More studies should be carried out to establish whether psychodynamic and supportive therapies are effective for GAD, and whether CBT is more helpful than other psychological therapy approaches in treating GAD.
Background
Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is a highly prevalent condition, characterised by excessive worry or anxiety about everyday events and problems to the point at which the individual experiences considerable distress and difficulty in performing day to day tasks. To meet Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV) criteria for GAD, anxiety and worry should be accompanied by autonomic hyperactivity (rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, dry mouth and dizziness), increased motor tension (fatigue, restlessness, trembling and muscle tension) and increased vigilance (impaired concentration and feeling tense) (APA 1994). The focus of the anxiety and worry is not confined to features of another Axis I disorder such as having a panic attack (as in panic disorder), being embarrassed in public (as in social anxiety disorder) or being contaminated (as in obsessive‐compulsive disorder). Symptoms should be experienced at least one day in two, for a period of six months or longer. The onset of GAD symptoms is usually gradual, although it may be precipitated by stressful life events. GAD tends to fluctuate in severity (Schweizer 1997) and is recurrent and chronic in presentation, with a low rate of remission and recovery (Tonks 2003, Yonkers 1996). It is frequently difficult to diagnose due to its diffuse clinical presentation, coupled with the common occurrence of comorbid medical or psychiatric conditions. Up to 90% of patients with GAD show concomitant symptoms of depression, dysthymia, somatisation, bipolar disorder or substance abuse (Kessler 1994).
In the general population, the lifetime prevalence of GAD is 5.1%, with a 12‐month prevalence measured at 3.1% (Kessler 1994). Within the primary care setting, the WHO collaborative study on Psychological Disorders in Primary Health Care study (Sartorius 1993) reported that GAD formed the second largest category of psychological disorders, with a prevalence of just under 7.9%. A survey of high utilisers of medical health care found a particularly high prevalence rate of GAD at 22% (Katon 1990), and the prevalence of GAD in patients visiting physicians' offices has been shown to be twice that found in the community (Schweizer 1997). Women have a higher prevalence rate for GAD than men (Kessler 1994), with the median age of onset occurring during the early 20s (Rickels 1990).
Individuals with GAD report subjective distress due to constant worry, and have difficulty in controlling the worry, resulting in impaired social functioning and quality of life. From a public health perspective, GAD is associated with increased reliance in public assistance, reduced work productivity, impaired social relationships and low ratings of life satisfaction (Massion 1993). It has been suggested that as an independent disorder, GAD has a disabling capacity comparable to that of major depression, and as such should be considered a major public health problem (Kessler 2000). In the UK, the Mental Health Foundation reports that of 91 million working days lost to mental ill health every year, approximately half of those days are lost due to anxiety and stress conditions (MHF 2003). Patients with GAD are more likely than other patients to make frequent medical appointments and to undergo extensive diagnostic testing, with associated cost implications. Direct and indirect costs of anxiety disorders were estimated to be as high as 40 to 50 billion dollars in 1990 in the United States alone (Greenberg 1999), representing approximately a third of all medical expenses incurred during the same period.
In the 1970s benzodiazepines were used extensively in the treatment of anxiety. However, due to their potential for the development of tolerance and dependence, clinical guidelines now recommend that benzodiazepines are prescribed for no longer than 2‐4 weeks in the treatment of GAD (NICE 2004). Azapirones, a form of 5‐HT1 anxiolytic that includes buspirone, are a preferred and reasonably effective alternative to benzodiazepines in treating GAD (Chessick 2006). Antidepressants have become a further pharmacological replacement for benzodiazepines in treating anxiety disorders, with the efficacy of imipramine, venlafaxine and paroxetine against placebo demonstrated in the clinical management of GAD in adults (Kapczinski 2003).
Surveys and opinion polls conducted over the last ten years have consistently indicated that the lay public and primary care attendees prefer psychological therapies to pharmacological treatments as a treatment modality for mental health disorders (Riedel‐Heller 2005, Churchill 2000, Priest 1996). A diverse range of manualised and non‐manualised psychological therapies are now available in treating common mental disorders (CMD), underpinned by cognitive (Beck 1979, Ellis 1962), behavioural (Watson 1924), psychodynamic (Freud 1949) and humanistic/non‐directive (Rogers 1951, Perls 1976) principles, as well as those that integrate components of different models, such as cognitive analytic therapy (Ryle 1990). There is a growing and demonstrable evidence base for the effectiveness of psychological therapies in treating CMD (Roth 2005). Cognitive therapy and behavioural interventions such as self‐control desensitisation, self‐monitoring and progressive muscle relaxation, used as stand‐alone treatments or combined within anxiety management programmes (Suinn 1971), appear to be effective compared with standard care for the treatment of GAD in adults (Fisher 1999, Gould 1997) and in the elderly (Wetherell 2005). These approaches seem to be well tolerated by patients with GAD, and the dropout rates in clinical trials appear to be low (Borkovec 2001). Other behavioural approaches such as exposure methods, commonly used in treating other anxiety disorders, may less applicable in GAD, due to the non‐specificity of external triggers (Deacon 2004).
Psychological therapies used in UK primary care practice remain predominantly Rogerian, psychodynamic and integrative in theoretical framework (Stiles 2006). Based on publications up to 1997/8, however, the Department of Health Treatment Choice in Psychological Therapies and Counselling Evidence‐based Clinical Practice Guideline (DoH 2001) concluded that while cognitive and behavioural therapies were effective in treating GAD, "other psychotherapeutic approaches have not yet been systematically reviewed/evaluated." Clinical guidelines now recommend cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a first‐line treatment for GAD (NICE 2004, Ballenger 2001), and a recent UK Government strategy paper has called for an additional 10,000 psychological therapists to be trained in CBT or other evidence‐based therapies to treat mental health disorders (Layard 2004). Nevertheless, the evidence‐base for the effectiveness and comparative effectiveness of non‐CBT approaches remains under‐investigated.
Previous reviews on psychological therapies for GAD have been limited to a single pooled outcome of clinically significant change (Fisher 1999), have summarised prevailing evidence on anxiety disorders/mental disorders narratively (Butler 2006, Roth 2005, Deacon 2004, DeRubeis 1998), or were published ten years ago (Gould 1997). Thus, an in‐depth and up to date comparative investigation of psychological therapy models in a GAD population using meta‐analytic techniques appears to be lacking. The current review aims to provide a comprehensive, updated summary and meta‐analysis on the effectiveness and comparative effectiveness of all psychological therapies for GAD.
Objectives
To examine the efficacy and acceptability of psychological therapies in comparison with treatment as usual/waiting list for patients with generalised anxiety disorder
To examine the efficacy and acceptability of cognitive behavioural therapy in comparison with psychodynamic and supportive therapy, for patients with generalised anxiety disorder
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials were eligible for inclusion in the review. Quasi‐randomised controlled trials, in which treatment assignment is decided through methods such as alternate days of the week, were also eligible for inclusion.
Trials that used a cross‐over design were eligible for inclusion in the review, using data from the first active treatment stage only.
Types of participants
Patient characteristics and setting Male and female adults, aged between 18‐75 years, treated in a primary, secondary or community setting, were eligible for inclusion. Studies conducted in an in‐patient setting were excluded.
Diagnosis The primary diagnosis comprised generalised anxiety disorder (GAD), including neurotic anxiety, but excluding social phobia, panic disorder, post‐traumatic stress disorder, simple phobias and obsessive‐compulsive disorder. Studies were required to use a formal standardised interview such as the Affective Disorders Interview Schedule (ADIS) (Di Nardo 1994) to diagnose GAD, based on ICD 9 and ICD‐10 criteria (WHO 1992) or DSM‐III (APA 1980), DSM‐IIIR (APA 1987) and DSM‐IV criteria (APA 1994), conducted by a qualified or trained psychiatric assessor. Studies using validated instruments to identify general anxiety symptoms were excluded.
Studies in which a minimum of 80% of participants had a primary diagnosis of GAD were eligible. Studies in which fewer than 80% of participants had a primary diagnosis of GAD were also included in the review if data limited to GAD participants were provided.
Comorbidity Since comorbidity is known to be a highly prevalent feature of GAD, studies involving participants with comorbid physical or common mental disorders were eligible for inclusion, as long as the comorbidity was secondary to the diagnosis of generalised anxiety disorder. However, studies involving patients with a comorbid psychiatric diagnosis of substance‐related disorder, schizophrenia or psychotic disorder were excluded.
Types of interventions
Psychological therapies included in the review Psychological therapies were classified into three principal categories, according to the theoretical underpinning described by trial authors, together with the references provided. The three categories were as follows:
1. Cognitive behavioural therapy First manualised as cognitive therapy (CT) (Beck 1979), cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) incorporates elements of both behavioural therapy (BT) and cognitive therapy approaches. CBT facilitates the identification of irrational, anxiety‐provoking thoughts, and challenges these negative automatic thoughts and dysfunctional underlying beliefs through collaborative 'hypothesis‐testing', using behavioural tasks of diary‐keeping and validity‐testing of beliefs between sessions, and skills training within sessions. For the purposes of this review, the CBT category included interventions developed and manualised in the treatment of anxiety disorders, including anxiety management training (Suinn 1977), cognitive restructuring, situational exposure and self‐control desensitisation (Borkovec 1988). Stand‐alone CT and BT interventions were included in the CBT category, and their comparative efficacy was also investigated separately (see Methods section).
Treatments developed for anxiety disorders often include relaxation techniques such as cue controlling, alternative self‐statements, relaxing imagery and meditational relaxation, which may also be manualised as stand‐alone applied interventions (Ost 1987, Berstein 1973). For this reason, whilst acknowledging that relaxation therapy/training (RT) is sometimes used as an attention‐placebo control comparison in psychological therapy trials, it was considered an active BT intervention, in line with previous reviews (Borkovec 2001, Gould 1997). 2. Psychodynamic therapy Grounded in psychoanalytic theory (Freud 1949), psychodynamic therapy (PD) uses the therapeutic relationship to explore and resolve unconscious conflict, with development of insight and circumscribed character change as therapeutic goals, and relief of symptomatology as an indirect outcome. Brief therapy models have been devised by Malan 1963, Balint 1972 and Mann 1973. More recently, psychodynamic therapies have been developed and manualised for the purposes of research evaluation, including short‐term anxiety‐provoking psychotherapy (STAPP), which is a focused, psychoanalytically oriented treatment, aiming at the resolution of oedipal, separation and grief problems (Sifneos 1992). 3. Supportive therapy Supportive therapy (ST) was categorised into active and inactive conditions. Active ST was included in the comparison of all psychological therapies versus treatment as usual/waiting list. STs were included as other psychological therapies in comparisons with CBT. Active supportive therapy Psychological therapies underpinned by humanistic principles were included in this category: a) Rogerian person‐centred therapy (Rogers 1951) is considered experiential in approach, and core conditions of empathy, acceptance and genuineness are utilised by the therapist within the therapeutic relationship to facilitate the client towards self‐awareness and self‐determination. In recent years, manualised versions of person‐centred therapy have been developed by researchers for use as a control condition in psychological therapy trials, and include non‐directive therapy (Svartberg 1998), non‐directive counselling (Blowers 1987) and supportive listening (Borkovec 2001). b) Gestalt therapy (Perls 1976) aims to heighten an individual's self‐awareness and perception of the moment, especially in terms of relationships with other people and with the environment. c) Transactional analysis (Berne 1961) is based on an understanding of the interactions (transactions) between patient and therapist, and between patient and others in the environment. It focuses primarily on ego states, principally the Parent, Adult, and Child. d) Counselling is a psychological treatment that draws predominantly from a range of humanistic or integrative approaches, and therefore was included in the supportive therapy category.
Inactive supportive therapy Interventions used in trials as attention‐placebo control conditions, and without a defined psychotherapeutic framework and appropriate supporting references, were placed in the inactive supportive therapy category. Examples of inactive attention‐placebo conditions included the use of discussion groups or 'holding' face‐to‐face sessions offering reassurance whilst on a waiting list for therapy. Modality of therapies The psychological intervention was required to be delivered face to face between the patient and therapist. Psychological therapies conducted on either an individual or on a group basis were eligible for inclusion. However, psychological therapies comprising couples therapy and family therapy were excluded, because these therapies work with patterns and dynamics of relating within and between systems, rather than focusing on the individual. Couples therapy for GAD and family therapy for GAD will be covered in separate reviews.
Control comparison The control comparison included treatment as usual (TAU) (also called standard care, usual care or no treatment) and waiting list (WL). In each study, the description of a TAU condition was scrutinised to ensure that it did not comprise an active supportive therapy treatment. Within the TAU condition, participants could receive any appropriate medical care during the course of the study on a naturalistic basis, including pharmacotherapy and/or psychological therapy, as deemed necessary by the clinician. Additional treatment(s) received by participants in both the control and active comparisons for each included study were carefully documented.
Combination treatment Combination treatments in which patients are randomised to receive psychological and pharmacological treatment concurrently were included in the review if the study of interest compared two psychological models and both groups were prescribed the same concomitant pharmacological/placebo intervention. However, combination treatment compared against a pharmacological or psychological treatment alone was excluded from this review, and will be investigated in a separate review. Main comparisons Where data were available, the following treatment comparisons were conducted to test the review hypotheses:
1. All psychological therapies versus treatment as usual/waiting list, stratified by psychological model: a) Cognitive behavioural therapy versus treatment as usual/waiting list b) Psychodynamic therapy versus treatment as usual/waiting list c) Supportive therapy versus treatment as usual/waiting list 2. Cognitive behavioural therapy versus psychodynamic therapy 3. Cognitive behavioural therapy versus supportive therapy, stratified by type of supportive therapy: a) Cognitive behavioural therapy versus active supportive therapy b) Cognitive behavioural therapy versus inactive supportive therapy 4. Psychodynamic therapy versus supportive therapy, stratified by type of supportive therapy: a) Psychodynamic therapy versus active supportive therapy b) Psychodynamic therapy versus inactive supportive therapy 5. Cognitive therapy versus behavioural therapy
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcome The primary outcome was reduction in anxiety, which was measured in the following two ways: 1. Treatment response, comprising the proportion of participants showing absence vs presence of symptoms or clinically significant change (treatment response/endpoint functioning) vs no significant change (Borkovec 1993) according to DSM‐III, DSM‐IV, ICD‐9 or ICD‐10 diagnostic criteria for GAD, or through use of a validated diagnostic measure such as the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM‐A) (Hamilton 1959) or a composite of validated measures, according to trialists' definition. Given the known chronicity of GAD, trialists commonly use a 20% reduction in anxiety symptoms as a definition of clinically significant change in this population, as set out by Barlow 1992. Where used in included studies, this definition was adopted as a measure of treatment response for the purposes of the current review. 2. Reduction in generalised anxiety symptoms measured using a validated continuous scale, either assessor‐rated, such as the Hamilton Anxiety Scale [HAM‐A] (Hamilton 1959) or self‐report, including the Trait subscale of the Spielberger State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI‐T) (Spielberger 1983), the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) (Beck 1988), Hospital Depression and Anxiety Scale (HADS) (anxiety subscale, Zigmond 1983), Leeds Anxiety Scale (Snaith 1976) and Zung Self‐Rating of Anxiety Scale (Zung 1975).
Secondary outcomes 1. Reduction in worry/fear symptoms, using validated scales such as the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ) (Meyer 1990) and Fear Questionnaire (Marks 1979). 2. Reduction in depression symptomatology, measured using validated observer‐rated scales such as the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) (Hamilton 1960) or self‐report scales, including the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) (Beck 1987) and Zung Depression Scale (ZDS) (Zung 1965) 3. Improvement in social functioning, measured using validated self‐report scales such as the Social Adjustment Scale (SAS) (Weissman 1974) 4. Quality of life, using measures such as the MOS 36‐Item Short Form Health Survey (SF‐36) or Short Form 12 (SF‐12) (Ware 1993) 5. Adherence to trial protocol (attrition), measured by the overall number of people dropping out post‐randomisation and during the course of trials 6. The number of participants reporting at least one adverse effect of psychological therapies, including increase in symptomatology levels or behavioural changes (eg increased use of alcohol) 7. Treatment acceptability, measured in the following ways: a) The number of participants dropping out of trials due to adverse effects of therapy b) Satisfaction with care/treatment based on self‐report scales 8. Cost‐effectiveness outcomes (days of work absence/ability to return to work, number of appointments with primary care physician, number of referrals to secondary services, use of additional treatments, hospitalisation for mental or physical health problems).
For studies comparing different psychological therapy categories, it was planned to examine the process of psychological therapy, using validated measures of the therapist/client relationship, such as the Relationship Inventory (Barrett‐Lennard 1986).
Outcomes were classified as post‐treatment, short term follow‐up (up to 6 months post‐treatment), medium term follow‐up (7‐12 months post‐treatment) and long term (longer than 12 months).
Search methods for identification of studies
See: Cochrane Collaboration Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis (CCDAN) Collaborative Review Group search strategy (http://web1.iop.kcl.ac.uk/IoP/ccdan/searches.htm)
1. Electronic databases
a) The two specialised CCDAN registers, CCDANCTR‐Studies and CCDANCTR‐References, were searched in February 2006 using the following search strategies:
CCDANCTR‐Studies Diagnosis = "Generalized Anxiety" or "Anxiety Neuros*" or "Neurotic Anxiety" and Intervention = *Therapy or Intervention and not "No Intervention" and not Age‐group = Child
CCDANCTR‐References Free‐text = "Generalized Anxiety" and Free‐text =*therapy or treatment
b) The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) was searched using the same terms as above.
c) MEDLINE (1966‐2006), PsycINFO (1966‐2006), EMBASE (1980 ‐2006) and LILACS (1982‐2003) were searched using the search strategy set out in Additional Table 1. A search of SciSearch was also conducted.
1. Search strategy used for MEDLINE, PsycInfo, EMBASE and LILACS.
| Search terms |
| #1 ANXIETY #2 ANXIETY‐DISORDERS* #3 ANXIOUS #4 EXP ANXIETY #5 EXP ANXIETY DISORDERS #6 EXP ANXIETY/ OR EXP ANXIETY DISORDERS #7 EXPLODE "ANXIETY‐DISORDERS" #8 GENERALISED ANXIETY #9 GENERALIZED ANXIETY #10 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 # 11 ALTERNATIVE‐THERAPY #12 BEHAVIOR‐THERAPY #13 BEHAV* THERAPY #14 BIOFEEDBACK #15 COGNITIVE‐BEHAVIOR‐THERAPY #16 COGNITIVE‐THERAPY #17 PSYCHOANALYTIC‐THERAPY #18 PSYCHOTHERAPY #19 PSYCHOTHERAP* #20 REHABILITATION #21 RELAXATION‐THERAPY #22 SOCIAL‐INTERVENTION #23 STRESS‐MANAGEMENT #24 THERAPY #25 PLACEBO #26 PLACEBO* #27 PLACEBO* AND ((EITHER OR ENTWEDER) OR (TREAT* OR BEHAND* OR UNTERSUCH*)) #28 PLACEBOS AND CONTROLS #29 SUPPORTIVE‐EXPRESSIVE THERAPY #30 THERAPEUTIC COMMUNITY #31 CONFRONTATIONAL INTERVENTIONS #32 GENERAL COUNSELING #33 SOCIAL SKILLS TRAINING #34 COPING SKILLS #35 #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 or #28 or #29 or #30 or #31 or #32 or #33 or #34 #36 ALEATORIS OR CASUAL OR ACASO OR AZAR #37 BLIND* #38 CLINIC* #39 CLINICAL TRIAL #40 CLINICAL‐ARTICLE #41CLINICALS AND TRIALS #42 COMPAR* #43 CONTROL* #44 CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL #45 EXP CLINICAL ARTICLE #46 EXP CLINICAL TRIALS #47 EXP MAJOR CLINICAL STUDY #48 EXP RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL #49 FOLLOW UP STUDIES #50 FOLLOW* AND UP #51 FOLLOW* UP #52 MASK* #53 RANDOM #54 RANDOM ALLOCATION #55 RANDOM* #56 RANDOM* AND (ALLOCAT* OR ASSIGN*) #57 RANDOMI* #58 RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS #59 RANDOMIZED‐CONTROLLED‐TRIAL #60 SINGL* #61 (SINGL* OR DOUBL* OR TRIPL* OR TREBL*) NEAR (BLIND* OR MASK*) #62 (SINGL*) NEAR (BLIND* OR MASK*) #63 SINGLE BLIND METHOD #64 SINGLE‐MASKED STUDY #65 STUDY #66 TRIAL* #67 #36 or #37 or #38 or #39 or #40 or #41 or #42 or #43 or #44 or #45 or #46 or #47 or #48 or #49 or #50 or #51 or #52 or #54 or #55 or #56 or #57 or #58 or #59 or #60 or #61 or #62 or #63 or #64 or #65 or #66 #68 #10 or #35 or #67 |
d) Ongoing studies controlledtrials.com was searched for information on trials in progress and recently completed.
2. Conference abstracts and book chapters Conference abstracts and book chapters were scrutinised for relevant references.
3. Personal Communication in order to ensure that as many as possible RCTs and CCTs were identified, authors of included studies and experts in the field were consulted to find out if they knew of any published or unpublished RCTs/ CCTs of psychological therapies for GAD, which had not been identified through electronic searches.
4. Reference checking Reference lists of all studies identified as potentially eligible for the review (both those included and those subsequently excluded following scrutiny of whole articles) were scrutinised to identify potential additional trials. Reference lists of previously published systematic reviews on the same topic were also scrutinised. 5. Handsearching The following journals will be handsearched for the next update of the review: Journal of Anxiety Disorders (1993 onwards) British Journal of Clinical Psychology (2000 onwards) Psychology and Psychotherapy (2000 onwards) Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy (2000 onwards)
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies Two review authors (VH and VAT) screened the abstracts of all publications obtained through the search strategy. For studies where psychological therapies were compared to a different type of psychological therapy or treatment as usual/waiting list, and were indicated to be an RCT or CCT, the full article was obtained and inspected to assess whether the review inclusion criteria were fully met. Any disagreement on the eligibility of a study was discussed with a third review author (RC), the decisions documented and, where necessary, the authors of the studies contacted for further information.
Data extraction and management Data were extracted independently by two review authors (VH and VAT), and entered into spreadsheets designed for the purposes of the review. Any disagreement was discussed with a third review author (MSL or RC), the decisions documented and, where necessary, the authors of the studies were contacted for further information. For each included study, information was recorded on the study population, interventions, randomisation and blinding procedures, sample size, outcome data, follow‐up and methods of statistical analysis.
Assessment of methodological quality of included studies In order to ensure that variation was not caused by systematic errors in the design of a study, the methodological quality of the selected trials was assessed by two review authors (VH and VT) independently. Any disagreement was discussed with a third review author, the decisions documented and, where necessary, the authors of the studies contacted for further information. Methodological quality was assessed according to the criteria set out in the Cochrane Handbook (Clarke 2002), based on evidence of a strong relationship between allocation concealment and potential for bias in the results (Schulz 1995). The criteria are defined below: A. Low risk of bias (adequate allocation concealment) B. Moderate risk of bias (unclear allocation concealment) C. High risk of bias (inadequate allocation concealment)
An additional quality assessment was performed using the Cochrane Collaboration Depression and Anxiety Group Quality Rating Scale (QRS) (Moncrieff 2001). The QRS consists of 23 items, including items on sample size, allocation, use of diagnostic criteria, compliance, attrition and statistical analysis. Total scores range from 0‐46. Quality rating scores were used for descriptive purposes and to categorise studies into high and low quality, for sensitivity analyses. Trial exclusions were not made based on these criteria (see Table 2).
2. Quality Rating Scale (QRS) overall scores for included studies.
| Study | QRS overall score |
| Ackkerman 2001 | 36 |
| Arntz 2003 | 27 |
| Barlow 1992 | 32 |
| Blowers 1987 | 20 |
| Bond 2002 | 25 |
| Borkovec 1987 | 27 |
| Borkovec 1993 | 30 |
| Butler 1991 | 29 |
| Dugas 2003 | 29 |
| Durham 1987 | 22 |
| Durham 1994 | 29 |
| Gath 1986 | 23 |
| Jannoun 1982 | 18 |
| Ladoucour 2000 | 26 |
| Lavallee 1993 | 14 |
| Linden 2002 | 31 |
| Lindsay 1987 | 14 |
| Mohlman 2003a | 24 |
| Mohlman 2003b | 24 |
| Ost 2000 | 27 |
| Stanley 1996 | 26 |
| Stanley 2003 | 21 |
| Wetherell 2003 | 31 |
| White 1992 | 22 |
| Woodward 1980 | 13 |
Data analysis Review Manager 4.0 software was used to organise and synthesise the data.
Measures of treatment effect Continuous outcomes: where studies used the same outcome measure for a comparison, data were pooled by calculating the weighted mean difference (WMD). Where different measures were used to assess the same outcome for a comparison, data were pooled by calculating the standardised mean difference (SMD), using 95% confidence intervals. Where continuous outcome data were skewed. It was planned not to use trials with skewed data, in which the standard deviation, when multiplied by 2, was higher than the mean (Altman 1996).
Dichotomous outcomes: dichotomous outcomes were analysed by calculating a pooled relative risk (RR) for each comparison, with the uncertainty in each result expressed using 95% confidence intervals (CIs). When overall results were significant, the number needed to treat (NNT) to produce one outcome was calculated by combining the overall relative risk with an estimate of the prevalence of the event in the control group of the trials.
Unit of analysis issues Where studies had two or more active treatment arms to be compared against TAU, data were managed as follows: Continuous data ‐ means, SDs and number of participants for each active treatment group were pooled across treatment arms as a function of the number of participants in each arm (Law 2003) to be compared against the control group. As an alternative strategy, the active comparison considered to be of greatest relevance was selected (eg CBT was selected in preference to CT or BT arms). Dichotomous data ‐ active treatment groups were collapsed into a single arm for comparison against the control group, or the control group was split equally into two.
Dealing with missing data Missing dichotomous data were managed through intention to treat (ITT) analysis, in which it was assumed that patients who dropped out after randomisation had a negative outcome, although it is acknowledged that categorising drop‐outs as treatment failures may have overestimated the number of patients with a poor outcome. Best/worse case scenarios were calculated for the clinical response outcome (comparisons 01, 02 and 03), in which it was assumed that dropouts in the active treatment group had positive outcomes and those in the control group had negative outcomes (best case scenario), and that dropouts in the active treatment group had negative outcomes and those in the control group had positive outcomes (worst case scenario), thus providing boundaries for the observed treatment effect.
Missing continuous data were either analysed on an endpoint basis, including only participants with a final assessment, or analysed using last observation carried forward to the final assessment (LOCF) if LOCF data were reported by the trial authors. Where SDs were missing, attempts were made to obtain these data through contacting trial authors. Where SDs were not available from trial authors, they were calculated from t‐values, confidence intervals or standard errors, where reported in articles (Deeks 1997). If these additional figures were not available or obtainable, the study data were not included in the comparison of interest.
For studies where the number of participants showing clinical response were not presented in the original articles, but means and standard deviations were reported for continuous symptomatology scales, the number of responders was calculated and imputed from continuous data using a validated statistical method (Furukawa 2005).
Data synthesis A fixed effect model was used in the first instance to combine data. Where there was evidence of statistical heterogeneity, results were recalculated using a random effects model, in order to obtain a more conservative estimate. Assessment of reporting biases Where sufficient numbers of trials allowed a meaningful presentation, funnel plots were constructed to establish the potential influence of publication bias.
Assessment of heterogeneity Statistical heterogeneity was formally tested using the natural approximate chi‐square test, which provides evidence of variation in effect estimates beyond that of chance. Since the chi‐squared test has low power to assess heterogeneity where a small number of participants or trials are included, the p‐value was conservatively set at 0.1. Heterogeneity was also tested using the I2 statistic, which calculates the percentage of variability due to heterogeneity rather than chance, with I2 values over 50% indicating strong heterogeneity (Higgins 2003).
Subgroup analyses and investigation of heterogeneity Clinical characteristics were examined in subgroup analyses to investigate their influence on the size of the treatment effect. Subgroup analyses were performed for: 1) type of control condition (treatment as usual vs waiting list) 2) modality of treatment (group therapy vs individual therapy) 3) number of psychological therapy sessions (up to and including 8 sessions vs more than 8 sessions) 4) age (adult vs elderly population) These subgroup analyses were also used to examine potential sources of clinical heterogeneity.
Where data become available in future updates of the review, further subgroup analyses will be conducted, as follows: 5) concomitant medication use (less than 25% use in sample and 25% or higher use) 6) severity/chronicity of GAD symptomatology at baseline 7) common mental disorder comorbidity (less than 50% comorbidity in sample and 50% or higher comorbidity) Sensitivity analyses Sensitivity analyses were conducted to test the robustness of the findings obtained by removing studies based on the following internal validity criteria: 1) overall quality rating on Quality Rating Scale (QRS) of 25 or lower 2) inadequate allocation concealment 3) use of less stringent diagnostic inclusion criteria These sensitivity analyses were also used to examine potential sources of methodological heterogeneity.
Where data become available in future updates of the review, further sensitivity analyses will be conducted, as follows: 4) dropout rate higher than 20% 5) lack of formal testing of fidelity to psychological therapy manual 6) psychological therapy allegiance of trialists.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
Electronic databases A search of CCDANCTR‐Studies and CCDANCTR‐References retrieved 85 references for 52 separate studies. Based on the information provided in each abstract, 22 studies were deemed not meet the broad inclusion criteria of the review. Full articles were obtained for 30 studies and screened for eligibility. A total of 23 published studies were deemed to meet full inclusion criteria for the review (Akkerman 2001, Arntz 2003, Barlow 1992, Blowers 1987, Bond 2002a, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Durham 1994a, Gath 1986, Ladouceur 2000, Lavallee 1993, Linden 2002, Lindsay 1987, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Ost 2000, Stanley 1996, Stanley 2003, Wetherell 2003a, White 1992, Woodward 1980).
The supplementary search conducted on MEDLINE, PsycINFO, EMBASE and LILACS in February 2006 retrieved five additional references for five further studies. Based on the information provided in the abstracts, full articles on the five studies were obtained, and one study was deemed to meet full inclusion criteria for the review (Durham 1987). Reference checking Scrutiny of reference lists of all included and excluded studies resulted in the identification of three additional trials for possible inclusion in the review. Full articles were obtained for each of these trials, of which one met inclusion criteria for the review (Jannoun 1982).
Personal communication Through personal contact with experts in the field, one recently completed trial was identified (Kitchiner 2006 in submission), however, it did not fully meet the inclusion criteria of the review and was excluded.
Included studies In total, the combined searches resulted in the identification of 25 completed studies that were eligible for inclusion in the review. Descriptive information on each individual study is presented in the Characteristics of Included Studies Table (Characteristics of included studies).
Design All the studies included in the review were described as randomised controlled trials, with randomisation at the patient (n=16) or patient and therapist level (n=9). The duration of trials ranged from four weeks (Lindsay 1987) to 24 months (Barlow 1992, Dugas 2003), with a mean overall duration of eight months.
Two studies reported obtaining ethical approval (Bond 2002a, Linden 2002), four studies stated that patient consent was obtained (Arntz 2003, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, White 1992), and the other nineteen studies did not provide any information.
Sample sizes The mean sample size of included studies was 54, ranging from a small pilot study of 12 participants (Stanley 2003) to a study of 119 participants in which psychological therapy was delivered in large groups of 23‐24 participants (White 1992). Studies used between two and five arms to conduct comparisons. Only one study (Linden 2002) reported using a power calculation to identify the required sample size prior to recruitment. Setting The studies were conducted in the US (n=9), Canada (n=3), UK (n=10) and other European countries (n=3). Two studies were conducted in a primary care setting (Lindsay 1987, Stanley 2003) and one study took place on a university campus (Borkovec 1987). A further two studies were conducted in specialist anxiety and stress clinics (Bond 2002a, Borkovec 1993). All other studies were conducted in out‐patient psychiatric or psychology department settings, or in community mental health settings. Participants The total number of participants included in the review was 1305. Seventeen studies provided full demographic information on their samples. A further six studies provided a few additional demographic details as well as age and gender, and two studies (Jannoun 1982, Lavallee 1993) provided little or no information on their participants. Nineteen studies recruited adult participants over the age of 17, and a further six studies were limited to elderly populations over the age of 55‐65 (Akkerman 2001, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 1996, Stanley 2003, Wetherell 2003a). Based on data reported in 23 out of the 25 studies, the weighted mean overall age of participants was 47.2 years, with a mean of 38.1 years in studies involving adult populations and a mean of 61.1 years in studies with elderly populations. From 19 studies reporting figures for gender, 68.6% of participants were female.
In 23 studies, all participants had a primary diagnosis of GAD. One study included all anxiety disorders for the purposes of recruitment and conducting the intervention, but patients with disorders other than GAD were excluded from analyses (White 1992). One further study recruited a anxiety disorders sample in which 82% of participants were diagnosed with GAD as a primary disorder (Gath 1986). Thirteen studies reported on the mean duration of GAD, which ranged from 30 months (Durham 1994a, Woodward 1980) to 20 years or longer (Ost 2000, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003a), demonstrating the striking chronicity of the disorder. Furthermore, in almost all studies, co‐morbidity was a key clinical feature, with the prevalence of one or more comorbid disorders ranging from 31% (Jannoun 1982) to 78% (Arntz 2003, Borkovec 1993).
In 22 studies, the diagnosis of GAD was made through a structured diagnostic interview in accordance with DSM‐III, DSM‐III‐R and DSM‐IV criteria, with the Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule‐Revised (ADIS‐R) most commonly employed as a diagnostic tool (9 studies). In nine studies, reliability checks were carried out for a proportion or all assessment interviews by a second clinician. Eleven studies additionally assessed GAD severity as a diagnostic inclusion criterion. In three other studies (Jannoun 1982, Lindsay 1987, Woodward 1980), a formal diagnosis of GAD was made by the referring clinician, but use of a standardised diagnostic interview was not specified. The extent to which bias may have been introduced through the inclusion of these three studies was examined in a sensitivity analysis.
Interventions Eight studies compared a CBT model of therapy against waiting list or treatment as usual (Akkerman 2001,Dugas 2003, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982; Ladouceur 2000; Mohlman 2003a; Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 2003), four further studies also incorporated a BT and/or CT arm for comparison against CBT (Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Lindsay 1987, Woodward 1980), and three studies conducted a comparison between CT and BT only (Arntz 2003, Durham 1987, Ost 2000). Six studies compared a CBT model against a supportive therapy condition (Blowers 1987, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003a), and two further studies compared CBT against non‐directive therapy in combination with medication (Bond 2002a, Lavallee 1993). One study compared CT with analytic therapy and BT (Durham 1994a) and one study conducted a comparison of CBT, CT, BT and placebo against a waiting list control (White 1992).
Sixteen studies (64%) used manuals for each psychological therapy, with five further studies using protocols (n=1), booklets (n=2) or 'a standardised approach' (n=2). In one study the CBT arm was manualised, but the BT arm was described as standardised and the analytic arm was non‐manualised (Durham 1994a). Three studies did not specify whether the psychological therapy interventions were manualised (Bond 2002a, Lavallee 1993, Lindsay 1987).
CBT interventions comprised a range of different CT and BT components. A total of 14 studies used a CBT model, with some investigators adapting the approach for application in elderly populations (Akkerman 2001, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 2003), as a specific approach for GAD (Dugas 2003) or for use in large groups (White 1992) . Seven studies used CT, as manualised by Beck 1979, and six studies used anxiety management training, manualised by Suinn 1971. Relaxation training was a key clinical intervention in almost all studies, either as a stand‐alone manualised treatment of progressive relaxation (Berstein 1973) or applied relaxation (Ost 1987), or as a component of the CBT treatment.
For supportive therapy (ST) conditions, five studies employed active non‐directive therapy, in which the therapist's role included reflective listening and acknowledgement of feelings, using empathy, warmth (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Blowers 1987), a non‐judgemental stance (Bond 2002a) and facilitation (Stanley 1996). An inactive attention placebo condition was used in two further studies, and comprised discussion group (Wetherell 2003a), in which expression of emotional content was explicitly discouraged by the group leaders (Wetherell, personal communication) and subconscious retraining (White 1992), in which participants listened to white noise and music with subliminal anti‐anxiety messages apparently embedded. One additional study used minimal therapeutic support for participants in the waiting list condition, which consisted of up to three face to face sessions to establish a treatment relationship, followed by monthly supportive reassurance provided face to face by members of the project team (Linden 2002). For the purposes of the current review,.this was categorised as inactive supportive therapy rather than waiting list control. Supportive therapy conditions were largely employed as a control comparison against active CBT, CT or BT approaches.
The standard care control conditions used in studies included waiting list (12 studies), usual care (one study) and no treatment (one study), in which participants were mostly offered weekly to 4‐weekly supportive telephone calls during the course of the trial.
The therapists employed to conduct psychological therapy treatments were predominantly qualified professionals, consisting of clinical psychologists (n=11), doctoral/senior/ advanced level CBT therapists (n=5) and experienced therapists/therapists (n=5). A small number of studies used graduates/advanced graduates (n=3). One study did not describe the therapists used to conduct the treatment (Lavallee 1993). Fidelity to treatment was reported at 79‐100% adherence, regardless of the psychological therapy approach under examination.
In five studies, therapists saw participants in small groups of 4‐7 participants (Akkerman 2001, Dugas 2003, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003a, Woodward 1980), and in one study large groups of 22‐24 participants were used (White 1992). In all other studies, therapists conducted treatment individually with participants. Intensity of treatment ranged from 4‐16 sessions, with sessions lasting from 45 minutes to 2 hours. Five studies offered booster sessions once initial therapy had been completed.
Concomitant prescribing of hypnotics, anti‐anxiolytics or antidepressants occurred in 16 studies, either in continued naturalistic prescribing in long‐term use (15 studies) or initiated during the course of trials (one study). The prevalence of concomitant pharmacotherapy ranged from 12% (Borkovec 1993) to 88% (Jannoun 1982). Two additional studies used pharmacotherapy arms in combination with CBT and supportive therapy within trial protocols, the drugs of interest comprising buspirone (Bond 2002a) and lorazepam (Lavallee 1993). One study included a stand‐alone benzodiazepines arm in addition to psychological therapy and TAU/WL arms (Lindsay 1987).
Outcomes All studies included in the review used validated outcome measures for the primary outcome of anxiety symptoms, and 21 studies used both clinician and self‐report scales.
Clinical response was measured in 16 studies. In ten studies (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Borkovec 1993, Dugas 2003, Ladouceur 2000, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 1996, Stanley 2003, Wetherell 2003a), investigators defined clinical response as a 20% reduction in symptom severity from pre to post treatment using an index outlined by Barlow 1992, and in three studies, investigators used Jacobson 1991 criteria (Durham 1994a, Lindsay 1987, Ost 2000). Three other studies used HAM‐D or STAI‐T cut‐off points for clinical improvement (Arntz 2003, Butler 1991, Linden 2002).
The most frequently used clinician‐rated outcome measure used for anxiety symptoms was the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM‐A) (13 studies), and the most commonly used self‐report scale was the Trait subscale of the Spielberger State‐Trait Inventory (STAI‐T) (16 studies). Ten studies used the Penn State Worry Questionnaire (PSWQ), nine studies used the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) and the Zung Anxiety Inventory (ZAI) was used in eight studies. To measure depression, ten studies used the clinician‐rated Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM‐D), and 14 studies used the self‐report Beck Depression Inventory (BDI). Quality of life was measured in three studies only.
Excluded studies A total of 14 studies were excluded from the review, 11 of which were identified through electronic searches, two through reference lists and one through personal communication with experts in the field. Of these 14 studies, seven included mixed anxiety disorders, with the proportion of participants diagnosed with GAD comprising less than 80% of the sample (van Boeijen 2005, Svartberg 1998, Barrowclough 2001, Borkovec 1988, Barlow 1984, Kitchiner 2006, Norton 2005), and one recruited students with state anxiety (Hutchings 1980). Two were dismantling studies of CBT/CT components (Borkovec 2002, Zuellig 2003). One study examined a psychological intervention with no face‐to‐face contact with participants (Bowman 1997) and one further study used an educational intervention without a psychological component (White 1995). One study examined an intervention to enable participants to taper off medication (Papp 1998), and one additional study compared the intensity of psychological therapies (Durham 1999). Further information is provided in the Characteristics of Excluded Studies Table (see .
Ongoing studies Three studies that meet the inclusion criteria for this review are currently in progress (Roemer 2004, personal communication; Wetherell 2005, personal communication; Borkovec 2003, personal communication), and it is hoped to include these studies in the first update of this review.
Studies awaiting assessment One study, an unpublished PhD dissertation conducted in the US, is awaiting assessment (Sachs 2005).
Risk of bias in included studies
The methodological quality of the 25 studies included in the review was classified according to the method of allocation concealment used, as specified in The Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook. One study was given an A classification (Akkerman 2001), 20 studies were classified as B, three studies as C (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Wetherell 2003a) and one study as D (White 1992).
Methodological quality was also assessed using the CCDAN Quality Rating Scale (QRS) (Moncrieff 2001). The overall QRS mean score for included studies was 24.8 (SD 5.84), ranging from 13 (Woodward 1980) to 36 (Akkerman 2001). A total of 13 studies (52%) had an overall QRS score of >25, although only five of those studies achieved a score of 30 or higher (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002, Wetherell 2003a). Studies that compared psychological therapies with TAU/WL were of lower methodological quality (mean QRS score of 24.6) than those comparing CBT with ST (28.3) and CT with BT (26.3). Aspects of methodological quality are considered below.
Allocation Although investigators for each study included in the review described the allocation of participants to groups as 'randomised', none specified their methods for assigning participants to groups or for concealing allocation. Therefore, all studies were initially classified as 'B' in the Table of included studies, and trial authors were contacted for further information. To date, four trialists (five studies) have responded with further details on the randomisation methods used. In the study by Akkerman 2001, the investigators employed adequate allocation methods, and the study was classified as 'A'. Borkovec 1987 and Wetherell 2003a used coin toss to assign participants to groups, and Borkovec 1993 used random selection of markers, each designating one of the three conditions. Group allocation was not concealed from the investigators, thus each of these studies were given a 'C' classification. In the study by White 1992, the investigators assigned participants to groups 'in batches', therefore, this design of this study was re‐categorised as a controlled clinical trial, with a 'D' classification. Given its original status as an RCT, the study remained eligible for inclusion in the review, but data were not included in the main meta‐analyses, and its inclusion was then tested in sensitivity analyses. Allocation concealment remained uncertain (B) for the other 20 studies.
All but one study conducted preliminary univariate analyses to check that randomisation had resulted in appropriate comparability of groups for demographic characteristics and/or baseline main outcomes. Four studies reported some significant differences between groups (Akkerman 2001, Arntz 2003, Durham 1994a, Mohlman 2003b), which were all controlled for by trial investigators in the main analyses. Blinding In line with all studies of psychological treatments, blinding of clinicians/therapists conducting the psychological therapy was not feasible. Blinding of participants was not achievable in studies where psychological therapy was compared against treatment as usual/waiting list, and was probably not achievable in comparative studies of psychological therapy approaches, given that clients attending for CBT are encouraged to access appropriate reading material on CBT methods. In the two combination therapy studies (Bond 2002a, Lavallee 1993), participants were indicated to be blind to the pharmacotherapy intervention.
Eighteen studies (72%) employed assessors who were blind to treatment allocation (Akkerman 2001,Barlow 1992, Blowers 1987, Bond 2002a, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Dugas 2003. Durham 1987, Durham 1994a, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982. Ladouceur 2000, Lavallee 1993, Linden 2002, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Wetherell 2003a). However, no trial investigators specified in articles whether a test of blind had been carried out. A further four studies employed research team members, but did not state whether they were blinded to treatment allocation (Arntz 2003, Ost 2000, Stanley 1996, Stanley 2003). Three studies used self‐report outcome measures only (Lindsay 1987, White 1992, Woodward 1980).
To assess treatment fidelity, four out of sixteen studies comparing differing psychological therapy approaches used evaluators who were blind to the psychological therapy under assessment (Barlow 1992, Blowers 1987, Wetherell 2003a, White 1992), and nine studies used independent assessors (Akkerman 2001, Borkovec 1993, Butler 1991, Linden 2002, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 1996) or graduates (Dugas 2003, Ladouceur 2000). In three further studies, audio‐tapes of therapy sessions were examined in weekly supervision meetings (Arntz 2003, Borkovec 1987, Gath 1986). No other studies reported on treatment fidelity. Follow‐up and exclusions Studies included in the review provided a paucity of follow‐up data for primary and secondary outcomes. For the first comparison of psychological therapies versus 'no treatment' control (14 studies), 12 studies used a waiting list condition and the two studies using treatment as usual/standard care did not have follow‐up assessments, therefore it was not possible to compare groups beyond that of post‐treatment assessment. For the second and third comparisons, in which differing psychological therapy models were compared (17 studies), only six studies provided data for six month follow‐up assessments (Arntz 2003, Borkovec 1993, Butler 1991, Durham 1994a, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003a), and three studies provided data at 12‐month follow‐up assessments (Borkovec 1993, Durham 1994a, Ost 2000).
The mean attrition rate from included studies between baseline and post‐treatment assessment was 15.6%. Five studies, all with small sample sizes of <40, reported a 0% attrition rate (Jannoun 1982, Ladouceur 2000, Lindsay 1987, Mohlman 2003a, Woodward 1980). In contrast, nine studies had a drop‐out rate of over 20% (Mohlman 2003b, Wetherell 2003a, Stanley 1996, Stanley 2003, Bond 2002a, Durham 1987, Borkovec 1993, Barlow 1992, Blowers 1987), with one study reporting an especially high overall dropout rate of 44% (Blowers 1987). One further study reported a dropout rate of 50% in the control group in contrast with that of only 24% in the treatment group (Barlow 1992). In 13 studies, reasons for participants' withdrawal were provided in full by the investigators.
Investigators in nine studies examined the influence of missing data caused by attrition from treatment in sensitivity analyses (Akkerman 2001, Arntz 2003, Barlow 1992, Bond 2002a, Borkovec 1993, Dugas 2003, Durham 1994a, Linden 2002, Wetherell 2003a) based on last observation carried forward (LOCF) for continuous data, and/or assuming a negative outcome for dichotomous data. Completers' data only were used in five studies. In one further study, dropouts (n=3) were replaced (Blowers 1987). As stated previously, five studies did not have any drop‐outs. In five studies, investigators did not clarify how missing data were managed.
Exclusion criteria used in studies were largely pragmatic, with investigators accepting the likely presence of comorbid disorders and ongoing prescribing of hypnotics, anxiolytics or antidepressants. Only one study excluded potential participants on the grounds of comorbidity (Linden 2002), and in doing so the investigators noted that to find one study patient, it was necessary to screen eight patients. A further 11 studies excluded patients with major depressive disorder or symptoms of severe depression. For drug treatments, seven studies excluded use of all anti‐anxiety medications (Akkerman 2001, Blowers 1987, Borkovec 1987, Linden 2002, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 1996), and two studies excluded the use of antidepressants only (Borkovec 1993, Butler 1991).
Selective reporting The vast majority of included studies did not report on the potential adverse effects of psychological therapies. Two studies examined 'relaxation‐induced anxiety' as a process measure (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993). In four additional studies, investigators reported that a small number of participants needed to be removed from active treatment due to worsening depression (Arntz 2003, Borkovec 1993, Butler 1991, Wetherell 2003a), however deterioration was not considered as an adverse effect of psychological therapy. In one study examining combination therapy, investigators limited consideration of adverse effects to pharmacotherapy (Bond 2002a).
Other potential sources of bias Adherence to therapy in ongoing treatment was rarely reported, with four studies only presenting mean attendance rates at psychological therapy sessions (Akkerman 2001, Borkovec 1987, Durham 1994a) or levels of adherence to homework assignments (Wetherell 2003a). The active treatment groups under examination in all studies were CBT‐based approaches. The 'non‐directive' control interventions used as comparators against the active CBT groups were largely underpinned theoretically by Rogerian therapeutic principles of empathy, warmth and non‐judgemental stance, which would be considered an active therapy approach by humanistic practitioners. However, non‐directive therapy was regarded as an inactive control comparison in some studies, suggesting potential allegiance towards CBT by those research teams.
Waiting list was used in almost all studies comparing psychological therapies against a no treatment control. Use of waiting list may have introduced bias in a positive or negative direction, as withholding treatment for a period of time could represent an implicit suggestion to participants not to get better until treatment began, or alternatively, might have been experienced by participants as a therapeutic 'holding' intervention.
Effects of interventions
Of 25 studies included in the review, 22 studies contributed to the meta‐analysis. Two studies had insufficient data for imputation (Blowers 1987, Lavallee 1993), and one study was excluded from the meta‐analysis (White 1992), due to its re‐classification as a controlled clinical trial.
Statistical heterogeneity was examined for each outcome, and where indicated to be statistically significant, chi2 and I2 figures were reported in the text, with reasons explored. The fixed effects model was used for all outcomes unless otherwise stated in the text. Findings from sub‐group analyses were reported in the text where outcome data from at least two studies were available for each sub‐group.
COMPARISON 01: ALL PSYCHOLOGICAL THERAPIES vs TREATMENT AS USUAL/WAITING LIST Thirteen studies contributed to Comparison 01 (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982, Ladouceur 2000, Lindsay 1987, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 2003, Wetherell 2003a, Woodward 1980). Psychological therapies were all underpinned by CBT principles.
No follow‐up data were available for primary or secondary outcomes. The study by Gath 1986 provided post‐treatment data for the secondary outcome of attrition only.
Primary outcome
1) Clinical response (Graph 01 01) Eight studies, with a total of 334 participants, contributed to the clinical response outcome at post‐treatment. Three studies used a clinician‐rated composite measure of anxiety severity to assess clinical response, and the other five studies used structured diagnostic interviews. A total of 46% of participants in the Psychological therapy group showed clinical response to treatment, in contrast with 14% in the treatment as usual/waiting list (TAU/WL) group. The difference between the two groups was highly significant (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.55 to 0.74). No statistical heterogeneity was indicated.
The best case scenario analysis showed a RR of 0.48 (95%CI 0.40 to 0.58), and the worst case scenario analysis showed a RR of 0.78 (95%CI 0.66 to 0.93) (see Additional Table 3), in favour of the psychological therapy group.
3. Comparisons 01‐03: Best/worst case scenarios for clinical response.
| COMPARISON | Best case scenario | Worst case scenario |
| All psychological therapies vs TAU/WL | RE, RR 0.48 (95%CI 0.32 to 0.71) | FE, RR 0.78 (95%CI 0.66 to 0.93) |
| Cognitive behavioural therapy vs psychodynamic therapy | FE, RR 0.53 (95%CI 0.41 to 0.68) | FE, RR 1.25 (95%CI 0.93 to 1.68) |
| Cognitive behavioural therapy vs supportive therapy | FE, RR 0.51 (95%CI 0.38 to 0.68) | FE, RR 1.34 (95%CI 0.88 to 2.03) |
2) Reduction in anxiety symptoms (Graph 01 02) Twelve studies, with a total of 330 participants, contributed to the anxiety symptoms outcome at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess anxiety symptoms comprised the SCID (three studies), ADIS (two studies), HAM‐A (five studies) and Zung Anxiety Inventory (two studies). The difference in anxiety symptom mean scores between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was highly significant, in favour of psychological therapies (SMD ‐1.00, 95%CI ‐1.24 to ‐0.77). No statistical heterogeneity was indicated. Secondary outcomes
1) Reduction in worry/fear symptoms (Graph 01 03) Nine studies, with a total of 256 participants, contributed to the outcome of reduction in worry/fear symptoms at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess worry/fear symptoms comprised the STAI‐T (three studies), PSWQ (five studies) and Fear Survey Questionnaire (one study). The difference in worry symptom mean scores between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was highly significant, in favour of psychological therapies (SMD ‐0.90, 95%CI ‐1.16 to ‐0.64).
2) Reduction in depression symptoms (Graph 01 04) Eleven studies, with a total of 317 participants, contributed to the outcome of reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess depression symptoms comprised the HAM‐D (one study), BDI (nine studies) and depression subscale of GHQ‐28 (one study). The difference in depression mean scores between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was highly significant, in favour of psychological therapies (SMD ‐0.96, 95%CI ‐1.20 to ‐0.72).
3) Improvement in social functioning (Graph 01 05) Three studies, with a total of 69 participants, contributed to the outcome of improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess improvement in social functioning comprised the social functioning subscale of the SF‐36 (two studies) and the extraversion subscale of the Eysenck Personality Inventory. Significant heterogeneity was indicated (Chi2=4.89, p=0.09, I2 =59%), and a random effects model was used. The difference in mean scores between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was significant, in favour of psychological therapies (SMD 1.01, 95%CI 0.00 to 2.03).
4) Improvement in quality of life (Graph 01 06) Three studies, with a total of 112 participants, contributed to the outcome of improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess improvement in quality of life included the SF‐36 (two studies) and the Quality of Life Inventory (one study). The difference in QoL mean scores between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was significant, in favour of psychological therapies (SMD 0.44, 95%CI 0.06 to 0.82).
5) Attrition for any reason (Graph 01 07) Thirteen studies reported attrition rates at post‐treatment. Five studies did not have any dropouts, therefore only eight studies contributed data, with a total of 509 participants. The attrition rate was 16.5% in the psychological therapies group and 13.3% in TAU/WL. The difference in attrition rate between the Psychological therapies group and the TAU/WL group was non‐significant (RR 1.00, 95%CI 0.65 to 1.54).
6) Adverse effects No studies contributed data on adverse effects experienced.
7) Treatment acceptability a) Dropout due to adverse effects No studies contributed data on dropouts due to adverse effects b) Satisfaction with care/therapy No studies contributed data on satisfaction with care/therapy.
8) Cost‐effectiveness outcomes No studies reported on cost‐effectiveness outcomes
Sub‐group analyses The figures for Comparison 01 sub‐group analyses are presented in Table 4.
4. Comparison 01: Sub‐group analyses.
| SUB‐GROUPS | Clinical response | Anxiety symptoms | Worry symptoms | Depression symptoms | Attrition |
| TAU vs Waiting list | TAU: RR 0.20 (0.03, 1.24) WL: RR 0.65 (0.57, 0.76) | TAU: SMD ‐0.82 (‐1.71, 0.07) WL: SMD ‐1.01 (‐1.26, ‐0.77) | TAU: SMD ‐0.62 (‐1.50, 0.27) WL: SMD ‐0.93 (‐1.20, ‐0.65) | TAU: SMD ‐0.93 (‐2.36, 0.50) WL: SMD ‐0.96 (‐1.20, ‐0.72) | TAU: RR 0.50 (0.06, 4.15) WL: RR 1.04 (0.67, 1.61) |
| Individual vs Group | Ind: RR 0.63 (0.51, 0.76) Grp: RR 0.66 (0.54, 0.82) | Ind: SMD ‐0.98 (‐1.32, ‐0.65) Grp: SMD ‐1.02 (‐1.35, ‐0.69) | Ind: SMD ‐0.92 (‐1.37, ‐0.48) Grp: SMD ‐0.66 (‐1.03, ‐0.29) | Ind: SMD ‐1.06 (‐1.39, ‐0.72) Grp: SMD ‐0.86 (‐1.20, ‐0.53) | Ind: RR 0.50 (0.28, 0.89) Grp: RR 2.68 (1.26, 5.73) |
| <8 vs >8 sessions | < 8: RR 0.49 (0.26, 0.91) > 8: RR 0.66 (0.57, 0.76) | < 8: SMD ‐1.00 (‐1.56, ‐0.44) > 8: SMD ‐1.00 (‐1.26, ‐0.74) | < 8: SMD ‐0.62 (‐1.50, 0.27) > 8: SMD ‐0.93 (‐1.20, ‐0.65) | < 8: SMD ‐1.35 (‐2.03, ‐0.66) > 8: SMD ‐0.91 (‐1.16, ‐0.65) | < 8: RR 0.50 (0.06, 4.15) > 8: RR 1.10 (0.71, 1.70) |
| Adults vs Elderly | Adt: RR 0.68 (0.55, 0.84) Eld: RR 0.62 (0.50, 0.75) | Adt: SMD ‐1.25 (‐1.57, ‐0.93) Eld: SMD ‐0.73 (‐1.07, ‐0.40) | Adt: SMD ‐.92 (‐1.33, ‐0.51) Eld: SMD ‐1.00 (‐1.38, ‐0.65) | Adt: SMD ‐1.20 (‐1.54, ‐0.87) Eld: SMD ‐0.72 (‐1.05, ‐0.38) | Adt: RR 0.52 (0.28, 0.97) Eld: RR 0.98 (1.04, 3.77) |
a) Treatment as usual vs waiting list Eleven studies used waiting list (WL) control as the control condition (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982, Ladouceur 2000, Lindsay 1987, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Wetherell 2003a). Two studies used a treatment as usual (TAU) control (Stanley 1996, Woodward 1980). Woodward 1980 contributed data to two outcomes of anxiety symptoms and worry symptoms only.
For the primary outcome of anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment, a non‐significant difference in effect was found between psychological therapies and TAU (SMD ‐0.82, 95%CI ‐1.71 to 0.07). In contrast, a significant difference in favour of psychological therapies was found when compared with WL, and the effect was shown to be of greater magnitude (SMD ‐0.96, 95%CI ‐1.20 to ‐0.72).
A similar finding was indicated for the worry symptoms outcome, with a non‐significant difference in effect between psychological therapies and TAU (SMD ‐0.62, 95%CI ‐1.50 to 0.27), and a significant difference in favour of psychological therapies when compared with WL, which was of greater magnitude (SMD ‐0.99, 95%CI ‐1.30 to ‐0.69).
b) Individual vs group therapy Nine studies used an individual therapy modality (Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982, Ladouceur 2000, Lindsay 1987, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 2003), and four studies used group therapy (Akkerman 2001, Dugas 2003, Wetherell 2003a, Woodward 1980).
For the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment, a highly significant difference in effect was shown for both individual and group therapy when compared with TAU/WL, and the effect was of similar magnitude for each modality.
For secondary outcomes of reduction in worry and depression at post‐treatment, a highly significant difference in effect was shown for individual and group therapy when compared with TAU/WL. Individual therapy showed a greater magnitude of effect than group therapy for both outcomes.
For post‐treatment attrition rates, a significant difference in effect was shown for individual and group therapy when compared with TAU/WL, however the direction of effect differed for the two sub‐groups. Individual therapy showed a significantly lower attrition rate (9.0%) than TAU/WL (15.0%) (RR 0.50, 95%CI 0.28 to 0.89), and in contrast, group therapy showed a significantly higher attrition rate (24.2%) than TAU/WL (8.2%) (RR 2.70, 95%CI 1.27 to 5.75).
c) 8 sessions or less vs >8 sessions Four studies used 8 or less psychological therapy sessions (Jannoun 1982, Lindsay 1987, Stanley 2003, Woodward 1980) and nine studies used more than 8 sessions (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Gath 1986, Ladouceur 2000, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Wetherell 2003a).
For the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms, a significant difference in effect was shown for8 or less sessions and more than 8 sessions when compared with TAU/WL, and the magnitude of effect was similar for both levels of contact.
For the secondary worry outcome at post‐treatment, a highly significant difference in effect was shown for more than 8 sessions when compared with TAU/WL, however, the difference was non‐significant for 8 sessions or less. The magnitude of effect was higher for more than 8 sessions than for 8 sessions or less. For the depression outcome at post‐treatment, a highly significant difference in effect was shown for both levels of contact, but the magnitude of effect was higher for 8 sessions or less than for more than 8 sessions.
d) Adults vs elderly Eight studies recruited adult participants (Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Gath 1986, Jannoun 1982, Ladouceur 2000, Lindsay 1987, Woodward 1980), and five studies were limited to elderly participants (Akkerman 2001, Mohlman 2003a, Mohlman 2003b, Stanley 2003, Wetherell 2003a).
For the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms, a significant difference in effect was shown for both adult and elderly groups when compared with TAU/WL. For clinical response, the magnitude of effect was similar for the two populations, however, for anxiety symptoms, adults showed a higher magnitude of effect than the elderly.
For secondary worry and depression outcomes, a significant difference in effect was shown for adults and elderly when compared with TAU/WL. The magnitude of effect for reduction of worry was similar for the two groups, but adults showed a higher magnitude of effect for reduction in depression than the elderly. For post‐treatment attrition rates, a significant difference was shown for adults and elderly when compared with TAU/WL, however, the direction of effect differed for the two sub‐groups. Adults had a significantly lower attrition rate (9.2%) than TAU/WL (13.8%) (RR 0.52, 95%CI 0.27 to 0.97), and the elderly had a significantly higher attrition rate (26.4%) than TAU/WL (8.2%) (RR 2.03, 95%CI 1.06 to 3.88). Sensitivity analyses The figures for Comparison 01 sensitivity analyses are presented in Additional Table 5.
5. Comparison 01: Sensitivity analyses.
| OUTCOMES | QRS: >25 | White 1992 included | Diagnostic criteria |
| Clinical response post‐treatment | FE, RR 0.67 (95%CI 0.57 to 0.79) | FE, RR 0.63 (95%CI 0.54 to 0.73) | FE, RR 0.63 (95%CI 0.54 to 0.73) |
| Reduction in anxiety symptoms post‐treatment | FE, SMD ‐1.21 (95%CI ‐1.51 to ‐0.90) | FE, SMD ‐0.97 (95%CI ‐1.19 to ‐0.75) | FE, SMD ‐0.99 (95%CI ‐1.24 to ‐0.74) |
| Reduction in worry symptoms post‐treatment | FE, SMD‐1.03 (95%CI ‐1.37 to ‐0.70) | FE, SMD ‐0.84 (95%CI ‐1.09 to ‐0.59) | FE, SMD ‐0.93 (95%CI ‐1.20 to ‐0.66) |
| Reduction in depression symptoms post‐treatment | FE, SMD‐1.00 (95%CI ‐1.30 to ‐0.70) | FE, SMD ‐0.92 (95%CI ‐1.16 to ‐0.68) | FE, SMD ‐0.89 (95%CI ‐1.16 to ‐0.62) |
| Improvement in social functioning post‐treatment | no data | FE, SMD ‐2.70 (95%CI ‐18.08 to 12.69) | FE, SMD ‐1.01 (95%CI 0.00 to 2.03) |
| Improvement in quality of life post‐treatment | no data | FE, SMD 0.44 (95%CI 0.06 to 0.82) | FE, SMD 0.44 (95%CI 0.06 to 0.82) |
| Attrition for any reason post‐treatment | FE, RR 0.99 (95%CI 0.59 to 1.66) | FE, RR 1.02 (95%CI 0.67 to 1.55) | FE, RR 0.98 (95%CI 0.64 to 1.49) |
Study quality Five studies were categorised as higher quality (QRS scores of >25) (Akkerman 2001, Barlow 1992, Butler 1991, Dugas 2003, Ladouceur 2000). For all outcomes, the direction of effect was unchanged when limited to higher quality studies, and the magnitude of effect was higher.
Inadequate allocation concealment Sensitivity analyses were conducted, including data from the study by White 1992 (CBT vs waiting list). The strength and direction of findings remained unchanged for all the post‐treatment outcomes.
Use of less stringent diagnostic inclusion criteria The studies by Jannoun 1982, Lindsay 1987 and Woodward 1980, each of which used less stringent diagnostic inclusion criteria, were removed in a sensitivity analysis. The strength and direction of all outcomes remained unchanged, and confidence intervals were slightly wider.
COMPARISON 02: COGNITIVE BEHAVIOURAL THERAPY vs PSYCHODYNAMIC THERAPY One study contributed to Comparison 02 (Durham 1994a). The study included CT, anxiety management (AM) and analytic psychotherapy (AP) arms, and examined high contact (16‐20 sessions) and low contact (8‐10 sessions) CT and AP over a six month period. For the purposes of this review, high contact and low contact interventions were entered as separate comparisons where data were provided. Data were also available at six months' follow‐up.
Primary outcome
1) Clinical response (Graph 02 01 and 02 08) Using Jacobson criteria based on the STAI‐T, 28% of participants in the combined high/low contact CT and AM groups showed a clinical response to treatment at post‐treatment, in comparison with 7% of participants in the combined high/low AP groups, based on a total of 110 participants. The difference between the two groups was significant, in favour of CT (RR 0.77, 95%CI 0.65 to 0.92). Best case scenario analysis showed an RR of 0.53 (95%CI 0.38 to 0.68). Worst case scenario analysis indicated a changed direction of effect, with an RR of 1.34 (95%CI 0.88 to 2.03).
At six month follow‐up, the difference between the two groups was smaller, with 39% of participants in the combined CT and AM groups showing clinical response in contrast with 23% of participants in the combined AP group, based on a total of 110 participants. The difference between the two groups was no longer significant (RR 0.79, 95%CI 0.62 to 1.01). 2) Reduction in anxiety symptoms (Graph 02 02 and 02 09) Using the HAM‐A to measure anxiety symptoms, based on a total of 64 participants, a significant difference in mean scores was indicated between the high/low contact CT groups and the high/low contact AP groups at post‐treatment, in favour of CT (WMD ‐6.85, 95%CI ‐11.20 to ‐2.50).
At six month follow‐up, based on a reduced number of 55 participants, a larger significant difference in HAM‐A mean scores was indicated between the high/low contact CT groups and the high/low contact AP groups, in favour of CT (WMD ‐13.41, 95%CI ‐19.09 to ‐7.74).
Secondary outcomes
1) Reduction in worry/fear symptoms No data were provided for worry/fear symptom outcomes.
2) Reduction in depression symptoms (Graph 02 04) Using the BDI to measure depression symptoms at post‐treatment, with a total of 64 participants, a highly significant difference in mean scores was indicated between the high/low contact CT groups and the high/low contact AP groups, in favour of CT (WMD ‐8.37, 95%CI ‐12.55 to ‐4.20).
3) Improvement in social functioning (Graph 02 05) Using the Dysfunctional Attitude Scale to measure improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment, with a total of 64 participants, a significant difference in mean scores was indicated between the high/low contact CT groups and the high/low contact AP groups, in favour of CT (WMD 14.28, 95%CI 1.82 to 26.75).
4) Improvement in quality of life No data were provided for quality of life outcomes.
5) Attrition for any reason (Graph 02 07) From an overall total of 110 participants, 14 participants (22%) dropped out of the combined high/low contact CT and AM groups during the course of the trial, and 22 participants (33%) dropped out of the combined high/low contact AP group. The difference in attrition rates between the two types of psychological therapy did not reach significance.
6) Adverse effects No data were provided for adverse effects. 7) Treatment acceptability a) Dropout due to adverse effects No studies contributed data on dropouts due to adverse effects
b) Satisfaction with care/therapy No studies contributed data on satisfaction with care/therapy. 8) Cost‐effectiveness outcomes No cost‐effectiveness outcomes were reported.
Subgroup analyses With only one study for inclusion in Comparison 02, it was not possible to conduct subgroup analyses.
Sensitivity analyses With only one study for inclusion in Comparison 02, it was not possible to conduct sensitivity analyses.
COMPARISON O3: COGNITIVE BEHAVIOURAL THERAPY vs SUPPORTIVE THERAPY Six studies (seven comparisons) contributed to Comparison 03 (Bond 2002a, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003b) at post‐treatment, with the study by Bond 2002a contributing two comparisons. Follow‐up data were also available at six months (Borkovec 1993, Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003b) and 12 months (Borkovec 1987).
Primary outcome 1) Clinical response (Graphs 03 01 and 03 08) At post‐treatment, six studies (seven comparisons), with a total of 332 participants, contributed clinical response data. Clinical response was assessed through use of a composite measure of anxiety severity (three studies) and HAM‐A (three studies). Statistical heterogeneity was indicated (chi2 =12.26, p=0.06, I2 =51.1%), with the studies by Borkovec 1993 and Linden 2002 indicated to be strongly in favour of CBT, and the studies by Bond 2002b and Stanley 1996 tending to favour ST, therefore a random effects model was used to combine data.
In the CBT group, 42% of participants responded to treatment, in contrast with 28% in the ST group. The difference in clinical response rates between the two groups was not significant (RR 0.86, 95%CI 0.70 to 1.06). Best case scenario analysis showed an RR of 0.51(95%CI 0.38 to 0.68). Worst case scenario analysis indicated a changed direction of effect, with an RR of 1.34 (95%CI 0.88 to 2.03). At six month follow‐up, three studies with a total of 158 participants contributed clinical response data. Statistical heterogeneity was no longer indicated, and a fixed effects model was used. Clinical response rates were increased in both the CT group (54%) and the ST group (41%). The difference in response rates between the two groups remained non‐significant (RR 0.79, 95%CI 0.59 to 1.06). 2) Reduction in anxiety symptoms (Graphs 03 02, 03 09 and 03 10) At post‐treatment, six studies, with a total of 235 participants, contributed data to the anxiety symptoms outcome. Anxiety symptoms were measured using HAM‐A (five studies) and the ADIS‐R (one study). In contrast with the clinical response outcome, the difference in anxiety symptom mean scores between the CBT and ST groups was highly significant, in favour of CBT (SMD ‐0.40, 95%CI ‐0.66 to ‐0.14). Statistical heterogeneity was not indicated.
At six month follow‐up, three studies, with a total of 97 participants, contributed data to the anxiety symptoms outcome. The difference in anxiety symptom mean scores between the CBT group and ST group remained significant (SMD ‐0.42, 95%CI ‐0.83 to ‐0.02).
At 12 month follow‐up, one study with 36 participants contributed data to the anxiety symptoms outcome. The difference in anxiety symptom mean scores between the CBT group and the ST group was no longer significant (SMD ‐0.57, 95%CI ‐1.24 to 0.10).
Secondary outcomes
1) Reduction in worry/fear symptoms (Graph 03 03) Four studies, with a total of 128 participants, contributed to the outcome of reduction in worry/fear symptoms at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess worry/fear symptoms comprised the PSWQ (2 studies), Fear Questionnaire (one study) and Fear Survey (one study). The difference in worry/fear symptom mean scores between the CBT and ST groups was highly significant, in favour of the CBT group (SMD ‐0.55, 95%CI ‐0.91 to ‐0.20).
2) Reduction in depression symptoms (Graph 03 04) Four studies, with a total of 128 participants, contributed to the outcome of reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess depression symptoms comprised the HAM‐D (2 studies) and the BDI (2 studies). The difference in depression mean scores between the CBT and ST groups was significant, in favour of the CBT group (SMD ‐0.37, 95%CI ‐0.72 to ‐0.02).
3) Improvement in social functioning (Graph 03 05) One study with 36 participants contributed to the outcome of improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment. The measure used to assess improvement in social functioning comprised the social functioning subscale of the SF‐36. The difference in mean scores between the CBT group and the ST group was non‐significant (SMD ‐2.70, 95%CI 18.08 to 12.68).
4) Improvement in quality of life (Graph 03 06) One study with 36 participants contributed to the outcome of improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment. The measure used to assess improvement in quality of life comprised the SF‐36. The difference in quality of life mean scores between the CBT and ST groups was non‐significant (SMD 0.30, 95%CI ‐10.77 to 11.37).
5) Attrition for any reason (Graph 03 07) Six studies (seven comparisons), with a total of 332 participants, reported attrition rates at post‐treatment. The attrition rate in the CBT group and in the ST group was equivalent, at 24% (RR 1.04, 95%CI 0.71 to 1.53).
6) Adverse effects In two studies (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993), a process measure of relaxation‐induced anxiety was completed after each session by participants receiving a psychological therapy that included applied relaxation. One of these studies (Borkovec 1987) reported that relaxation‐induced anxiety was significantly and negatively associated with changes on the HAM‐A and HAM‐D, with participants who became anxious during relaxation training showing less improvement in clinical response.
7) Treatment acceptability a) Dropout due to adverse effects No studies contributed data on dropouts due to adverse effects
b) Satisfaction with care/therapy No studies contributed data on satisfaction with care/therapy.
8) Cost‐effectiveness outcomes No studies reported on cost‐effectiveness outcomes. Subgroup analyses The figures for Comparison 03 subgroup analyses are presented in Additional Table 6.
6. Comparison 03: Sub‐group analyses.
| SUB‐GROUPS | Clinical response | Anxiety symptoms | Worry symptoms | Depression symptoms | Attrition |
| Active vs Inactive ST | Act: RR 0.90 (0.70, 1.16) Inact : RR 0.72 (0.54, 0.96) | Act: SMD ‐0.37 (‐0.72, ‐0.03) Inact: SMD ‐0.43 (‐0.83, ‐0.03) | Act: SMD ‐0.72 (‐1.15, ‐0.29) Inact: SMD ‐0.17 (‐0.82, ‐0.49) | Act: SMD ‐0.41 (‐0.83, 0.01) Inact: SMD ‐0.37 (‐0.72, ‐0.02) | Act: RR 1.03 (0.65, 1.62) Inact : RR 1.08 (0.55, 2.15) |
| Individual vs Group | Ind: RR 0.80 (0.62, 1.05) Grp: RR 1.07 (0.77, 1.49) | Ind: SMD ‐0.49 (‐0.80, ‐0.19) Grp: SMD ‐0.13 (‐0.64, 0.37) | Ind: SMD ‐1.00 (‐1.51, ‐0.49) Grp: SMD ‐0.13 (‐0.63, 0.37) | Ind: SMD ‐0.67 (‐1.16, ‐0.17) Grp: SMD ‐0.06 (‐0.57, 0.44) | Ind: RR 1.03 (0.62, 1.71) Grp: RR 1.07 (0.60, 1.89) |
| <8 vs >8 sessions | < 8: RR 1.08 (0.88, 1.32) > 8: RR 0.69 (0.56, 0.86) | < 8: SMD ‐0.10 (‐0.58, ‐0.37) > 8: SMD ‐0.52 (‐0.83, ‐0.21) | < 8: SMD ‐0.07 (‐0.86, 0.71) > 8: SMD ‐0.68 (‐1.09, ‐0.26) | < 8: SMD ‐0.24 (‐0.55, 0.03) > 8: SMD ‐0.52 (‐0.92, ‐0.13) | < 8: RR 1.00 (0.57, 1.75) > 8: RR 1.08 (0.64, 1.81) |
| Adults vs Elderly | Adt: RR 0.80 (0.62, 1.05) Eld: RR 1.07 (0.77, 1.49) | Adt: SMD ‐0.49 (‐0.80, ‐0.19) Eld: SMD ‐0.13 (‐0.64, ‐0.37) | Adt: SMD ‐1.00 (‐1.51, ‐0.49) Eld: SMD ‐0.13 (‐0.63, 0.37) | Adt: SMD ‐0.67 (‐1.16, ‐0.17) Eld: SMD ‐0.06 (‐0.57, 0.44) | Adt: RR 1.03 (0.62, 1.71) Eld: RR 1.07 (0.60, 1.89) |
Active ST vs non‐active ST Four studies (five comparisons) used active ST (non‐directive therapy) as a control condition against CBT (Bond 2002a, Bond 2002b, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Stanley 1996). Two studies used a non‐active attention placebo condition, comprising discussion group (Wetherell 2003b) and low contact support (Linden 2002). Linden 2002 contributed data to the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms and the secondary outcome of attrition only.
For the primary outcome of clinical response at post‐treatment, a non‐significant difference in effect was shown between CBT and active ST (RR 0.90, 95%CI, 0.70 to 1.16). In contrast, a significant difference in favour of CBT was shown when compared with inactive ST (RR 0.72, 95%CI 0.54 to 0.96). However, the magnitude of effect for CBT was higher compared with active ST than compared with inactive ST. Significant heterogeneity was observed in the active ST sub‐group (chi2 = 9.14, p=0.06, I2 = 56.2%).
For reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment, a significant difference was shown in favour of CBT when compared against active and inactive ST. The magnitude of treatment effect was similar for the two sub‐groups.
For attrition rates, a non‐significant difference in effect was found for active and inactive ST when compared with CBT, and the magnitude of attrition was similar for both sub‐groups. Individual vs group therapy Four studies (five comparisons) used an individual therapy modality (Bond 2002a, Bond 2002b, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993; Linden 2002) and two studies used a group therapy modality (Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003b).
For clinical response at post‐treatment, a non‐significant difference in effect was shown between CBT and ST for individual and group therapy, with the direction of effect favouring CBT for individual therapy, and favouring ST for group therapy. Significant heterogeneity was observed in the individual therapy sub‐group (chi2 =10.77, p=0.03, I2 =62.9%). For reduction in anxiety, worry and depression symptoms, a significant difference in effect was shown in favour of individual CBT compared with individual ST. In contrast, a non‐significant difference was shown between group CBT and group ST. The magnitude of effect was higher for individual CBT than for group CBT.
For attrition rates, a non‐significant difference in effect was found for individual and group CBT when compared with ST, and the magnitude of attrition was similar for both sub‐groups.
8 sessions or less vs more than 8 sessions Four studies used more than eight sessions to conduct CBT and ST (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002, Wetherell 2003b). Two studies (three comparisons) used eight sessions or less (Bond 2002a, Bond 2002b, Stanley 1996), of which Bond 2002a, Bond 2002b contributed data for the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms and the secondary outcome of attrition only.
For the primary outcome of clinical response and anxiety symptoms, a significant difference in effect was shown in favour of more than eight sessions of CBT compared with ST. In contrast the difference in effect between CBT and ST was non‐significant for eight sessions or less. For both anxiety outcomes, the treatment effect was in differing directions, with more than eight sessions favouring CBT and 8 sessions or less favouring ST. Heterogeneity was non‐significant in both sub‐groups.
For attrition rates, a non‐significant difference in effect was found for eight sessions or less and more than 8 sessions of CBT compared with ST, and the magnitude of attrition was similar for each sub‐group. Adults vs elderly Four studies (five comparisons) recruited adult participants (Bond 2002a, Bond 2002b, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002), and two studies were limited to elderly participants (Stanley 1996, Wetherell 2003b).
For clinical response at post‐treatment, a non‐significant difference in effect was shown between CBT and ST for adult participants and for elderly participants. Significant heterogeneity was observed in the adult sub‐group (chi2 =10.77, p=0.03, I2 =62.9%). The treatment effect was in differing directions, in favour of CBT for adults and in favour of ST for the elderly.
For reduction in anxiety, worry and depression symptoms at post‐treatment, a significant difference in effect was shown in favour of CBT when compared with ST for adults. In contrast, a non‐significant difference in effect was shown between CBT and ST for the elderly. The magnitude of effect was higher for adults than for the elderly
No significant difference in attrition rates was indicated between CBT and ST for either adult or elderly participants.
Sensitivity analyses The figures for Comparison 03 sensitivity analyses are presented in Additional Table 7.
7. Comparison 03: Sensitivity analyses.
| OUTCOMES | QRS: >25 | White 1992 included |
| Clinical response at post‐treatment | FE, RR 0.75 (95%CI 0.56 to 1.01) | RE, RR 0.86 (95%CI 0.70 to 1.06) |
| Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment | FE, SMD ‐0.49 (95%CI ‐0.81 to ‐0.16) | FE, SMD ‐0.38 (95%CI ‐0.62 to ‐0.13) |
| Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment | FE, SMD ‐0.72 (95%CI ‐1.15 to ‐0.29) | FE, SMD ‐0.49 (95%CI ‐0.81 to ‐0.17) |
| Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment | FE, SMD ‐0.41 (95%CI ‐0.83 to ‐0.01) | FE, SMD ‐0.36 (95%CI ‐0.68 to ‐0.05) |
| Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment | no data | FE, SMD ‐2.70 (95%CI ‐18.08 to 12.69) |
| Improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment | no data | FE, SMD 0.30 (95%CI ‐10.77 to 11.37) |
| Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment | FE, RR 1.13 (95%CI 0.67 to 1.90) | FE, RR 1.07 (95%CI 0.73 70 1.57) |
| Clinical response at 6 month follow‐up | no data | FE, RR 0.79 (95%CI 0.59 to 1.06) |
| Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up | no data | FE, SMD ‐0.42 (95%CI ‐.83 to ‐0.02) |
| Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 12 month follow‐up | no data | FE, SMD ‐0.57 (95%CI ‐1.24 to 0.10) |
Study quality (QRS) Four studies were rated as higher in quality, with Quality Rating Scale (QRS) scores of more than 25 ( Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Linden 2002, Stanley 1996).
A significant difference in clinical response was indicated between CBT (46% response) and ST (26% response), in favour of CBT (RR 0.75, 95%CI 0.56 to 1.01) and for anxiety symptoms, a significant difference in effect was shown in favour of CBT compared with ST (SMD ‐0.49, 95%CI ‐0.81 to ‐0.16).
For attrition, a non‐significant difference in effect was shown between CBT and ST groups.
Inadequate allocation concealment Inclusion of White 1992 data (CBT vs subconscious retraining attention placebo arms) in Comparison 03 did not alter the magnitude and direction of treatment effects, and the width of confidence intervals was slightly reduced for all outcomes.
COMPARISON O4: COGNITIVE THERAPY vs BEHAVIOURAL THERAPY Five studies contributed data to Comparison 04 (Arntz 2003, Barlow 1992, Durham 1987, Durham 1994a, Ost 2000). Follow‐up data were provided by three studies at six months (Arntz 2003, Durham 1987, Durham 1994a) and by two studies at 12 months (Durham 1994a, Ost 2000).
Primary outcome
1) Clinical response (Graphs 04 01 and 04 08) Five studies (220 participants) contributed towards the clinical response outcome at post‐treatment, based on Jacobson criteria (one study), a composite measure (one study) and HAM‐A/Zung/STAI‐T cut‐off (three studies). A significant difference in rate of clinical response was shown between the CT group and the BT group in favour of CT (RR 0.70, 95%CI, 0.56 to 0.87), with 50% of CT participants showing clinical response in contrast with 31% of BT participants.
At six month follow‐up, two studies, with a total of 105 participants, showed a significant difference between CT (58% clinical response) and BT (29% clinical response) in favour of CT (RR 0.56, 95%CI 0.40 to 0.79).
2) Reduction in anxiety symptoms (Graphs 04 02, 04 09 and 04 10) At post‐treatment, four studies with a total of 131 participants contributed to the anxiety symptom outcome. Measures used to assess anxiety levels consisted of STAI‐T (one study) and HAM‐A (three studies). No difference in mean anxiety scores was indicated between CT and BT (SMD ‐0.06, 95%CI ‐0.40 to 0.30).
At six month follow‐up, two studies with a total of 67 participants contributed to the anxiety symptom outcome. The difference between CT and BT was non‐significant (SMD ‐0.11, 95%CI ‐0.59 to 0.37).
At twelve month follow‐up, two studies with a total of 59 participants contributed to the anxiety symptom outcome. The difference between CT and BT was non‐significant (SMD 0.06, 95%CI ‐0.45 to 0.58).
Secondary outcomes
1) Reduction in worry/fear symptoms (Graph 04 03) One study with 20 participants contributed to the worry symptom outcome at post‐treatment, using the Fear Questionnaire to assess worry levels. The difference in worry symptom scores between the CT and BT group was non‐significant (SMD 0.24, 95%CI ‐0.66 to 1.14).
2) Reduction in depression symptoms (Graph 04 04) Three studies with a total of 89 participants contributed to the depression symptom outcome at post‐treatment. Measures used to assess depression levels consisted of the BDI (one study) and HAM‐D (two studies). The difference in depression scores between the CT group and BT group was significant, in favour of the CT group (SMD ‐0.58, 95%CI ‐1.01 to ‐1.15).
3) Improvement in social functioning No studies contributed data to the social functioning outcome at post‐treatment. 4) Improvement in quality of life No studies contributed data to the quality of life outcome at post‐treatment.
5) Attrition for any reason (Graph 04 07) Four studies with a total of 159 participants contributed to the attrition outcome at post‐treatment. The difference in attrition rates between CT and BT groups was non‐significant (RR 0.52, 95%CI 0.25 to 1.02).
6) Adverse effects No studies contributed data on adverse effects of therapy.
7) Treatment acceptability a) Dropout due to adverse effects No studies contributed data on dropouts due to adverse effects
b) Satisfaction with care/therapy No studies contributed data on satisfaction with care/therapy.
8) Cost‐effectiveness outcomes No studies reported cost‐effectiveness outcomes.
Subgroup analyses An insufficient number of studies were included in this comparisons to conduct sub‐group analyses.
Sensitivity analyses Removal of Durham 1987, a study of low methodological quality (QRS of 22), which contributed data to the first outcome of clinical response only, did not alter the direction of effect, but the magnitude of difference between the CT and BT groups was reduced (RR 0.79, 95%CI 0.63 to 0.99).
Consideration of publication bias Funnel plots were produced for the Comparison 01 primary outcome of clinical response (eight studies) and reduction of anxiety symptoms (12 studies) (see Additional Figures Figure 1 and Figure 2). Visual inspection of the funnel plot for clinical response (nine studies) indicated possible asymmetry, which might suggest that small trials with negative outcomes were not included in the review. Visual inspection of the funnel plot for anxiety symptom reduction (12 studies), suggested a more symmetrical spread. However, the small number of studies included in the two funnel plots limits further meaningful interpretation.
1.
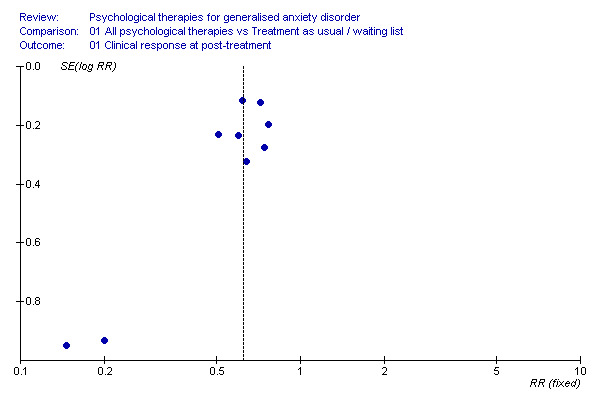
01 Clinical response.
2.
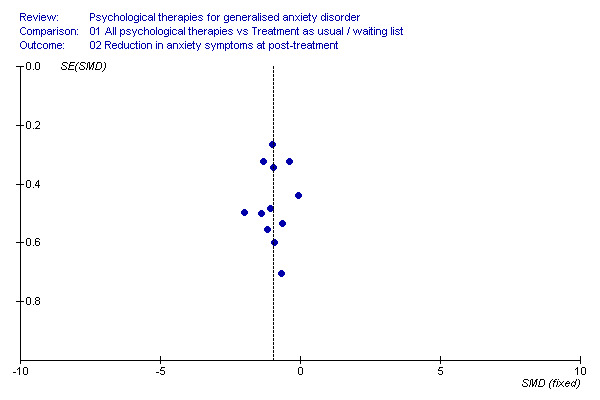
02 Anxiety symptoms.
Funnel plots were not produced for Comparisons 02, 03 and 04, due to the small number of studies (six or fewer) for inclusion in each outcome.
Additional comparisons in future updates of the review 1) The planned comparison of Psychodynamic therapy versus Supportive therapy was not conducted due to a lack of eligible studies. It is hoped to conduct this comparison in future updates of the review.
2) A dismantling investigation of CBT, CT and BT components lay beyond the scope of the stated objectives of this review. However, in future updates of the review, additional head to head comparisons are planned for CBT versus CT, CBT versus BT, CBT/CT versus BT and CBT/BT versus CT.
Discussion
Summary of main results
Comparison 01: All psychological therapies versus treatment as usual/waiting list Based on eight studies (334 participants), using best/worst case scenario analysis, this review provides robust evidence that patients with generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) assigned to cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) were more likely to achieve clinical response at post‐treatment than patients assigned to treatment as usual or waiting list control (TAU/WL). Based on 12 studies (330 participants), patients who completed CBT showed a greater reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment than patients in TAU/WL, together with a greater reduction in worry and depression symptoms. There was a lack of available evidence for the longer‐term effectiveness of CBT in treating GAD. Adverse effects of CBT were not examined. No studies examined the effectiveness of psychodynamic or supportive therapies for GAD.
Comparison 02: Cognitive behavioural therapy versus psychodynamic therapy The evidence is limited to a single study of 110 participants showing that patients receiving CBT were more likely to show clinical response and reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms than those receiving analytic therapy at post treatment and at six month follow‐up.
Comparison 03: Cognitive behavioural therapy versus supportive therapy Based on six studies (332 participants), using best/worst case scenario analysis, the review provides inconclusive evidence that patients assigned to CBT were more likely to achieve clinical response than those assigned to supportive therapy (ST). The difference between the two psychological therapy approaches was not significant at post‐treatment or at six month follow‐up. Statistical heterogeneity was indicated. Patients who completed CBT treatment showed a greater reduction in anxiety symptoms than those who completed ST, both at post‐treatment and at 6 month follow‐up, and also showed a greater reduction in worry and depression symptoms at post‐treatment than patients who completed ST treatment.
Comparison 04: Cognitive therapy versus behavioural therapy Based on five studies (220 participants), the review shows that patients assigned to CT were more likely to show clinical response than patients assigned to BT. However, a non‐significant difference in anxiety symptoms was shown between the two groups, which suggests some uncertainty in the findings. CT was more effective than BT in reducing depression symptoms.
Summary of additional findings Control comparators Patients assigned to a waiting list condition showed a smaller decrease in anxiety and worry symptoms than patients assigned to treatment as usual (TAU) when compared with psychological therapy. This finding may suggest that patients placed on a waiting list are less likely to improve whilst waiting for treatment to commence, although the inclusion of two small studies in the TAU subgroup limits interpretation of this finding.
Patients assigned to active ST and CBT showed equivalent clinical response. In contrast, patients assigned to inactive ST were less likely to show clinical response than those assigned to CBT. However, this finding is based on two studies only, in which differing placebo conditions were used and statistical heterogeneity was observed, which limits the ability to draw conclusions.
Modality of therapy Individual therapy and group therapy showed a similar treatment effect for all symptom outcomes at post‐treatment compared with TAU/WL. Patients assigned to individual psychological therapy were less likely to drop out of studies than TAU/WL patients, and in contrast, patients assigned to group therapy were more likely to drop out of studies than those in TAU/WL. Whilst this might suggest that individual therapy is a more popular modality of treatment, reasons for attrition were under‐reported in many study articles, and therefore it is uncertain to what extent dropout may have occurred because of low acceptability of group therapy.
Comparisons of CBT and ST approaches for modality of therapy were inconclusive for the primary outcome of clinical response, and significant heterogeneity was observed. Nevertheless, patients who completed individual CBT sessions showed a greater reduction in anxiety symptoms than patients completing individual ST sessions.
Number of therapy sessions Psychological therapy appeared of equivalent effectiveness for all symptom outcomes compared with TAU/WL, regardless of the number of sessions, suggesting that greater intensity of therapeutic contact did not result in a more enhanced effect. However, the four studies using eight or less sessions were all small and of very low methodological quality, which limits confidence in this finding.
A comparison of eight sessions or less and more than eight sessions between CBT and ST approaches showed consistent and homogeneous findings for all symptom outcomes, with greater benefit for CBT over ST where more than eight sessions were used. Although the small number of studies limits the ability to draw conclusions, it seems likely that the number of therapy sessions used in studies provides one explanation for the observed heterogeneity between studies in the main CBT vs ST comparison, and demonstrates the importance of providing an appropriate number of CBT sessions.
Participant age group Adults assigned to psychological therapies showed a greater magnitude of symptom reduction than elderly patients compared with TAU/WL across all outcomes at post‐treatment. For attrition rates, adult patients assigned to psychological therapies were less likely to drop out of studies than patients in the TAU/WL condition, and in contrast, elderly patients attending for psychological therapies were more likely to drop out of studies than patients in TAU/WL, suggesting some ambivalence by the elderly towards attendance for psychological therapy.
When comparing CBT and ST for studies of adult participants and those limited to elderly participants, the finding for the primary outcome of clinical response was inconclusive and heterogeneous. Whilst CBT appeared to confer greater benefit over ST for adult patients who completed therapy, no differences in anxiety, worry and depression symptoms were indicated between CBT and ST in elderly patients, suggesting that ST was as suitable for elderly patients as a psychological therapy based on CBT principles.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
Participants and settings Studies included in the review were reasonably well distributed internationally, with just under 50% of studies conducted in North America, 40% in the UK and the rest in other European countries. Given that studies were predominantly conducted in secondary care settings, it is possible that participants presented with more severe and chronic GAD symptoms than those in real world primary care settings, where the majority of GAD patients are likely to be treated. Certainly chronicity was a key clinical feature for participants in included studies. Nevertheless, the use of volunteers by 40% of studies may have resulted in the recruitment of less symptomatic participants than would be seen in usual out‐patient care.
When recruiting participants, 22 studies used diagnostic inclusion criteria conducted within a standardised clinical interview to identify potential participants with GAD, and the three remaining studies obtained a diagnosis of GAD through clinical assessment. Interviews were all conducted by qualified or trained health care professionals and in many studies a second clinician was employed to check the accuracy of diagnosis. Whilst potentially reducing the applicability of the findings through the use of such rigorous selection processes, this may be considered an important and necessary aspect of study design, given the inherent clinical difficulties of identifying GAD as a primary disorder (Borkovec 2001, Borkovec 1996). Furthermore, the pragmatic decision by all but one study to allow for the presence of secondary comorbidity, a highly prevalent feature of GAD, is likely to have increased the external validity of study findings to clinical practice.
Interventions The review provides a moderate body of evidence on psychological therapies underpinned by CBT principles. However, despite an exhaustive search of the literature, no trials examining the effectiveness of other psychological therapy models against no treatment control conditions were identified, and very few comparative studies between psychological therapy models were located. Since 79% of therapists and counsellors in UK primary care are person‐centred or integrative in theoretical orientation and CBT is only practiced by 10% of therapists (Stiles 2006), the evidence produced in this review could be regarded as of limited applicability. Furthermore, in the majority of studies, the therapists employed were highly qualified and experienced practitioners, who may not be representative of practitioners employed in real world clinical settings.
Outcomes Outcomes evaluated in studies were predominantly symptom focused, although the use of clinical response/improvement measures, regarded as a clinically relevant and applicable outcome, was reasonably wide‐spread. Adverse effects of psychological therapies were notably under‐reported in studies. Despite the fact that relaxation training involves the use of evoking anxiety in sessions in order to learn how to control symptoms, two studies only examined relaxation‐induced anxiety (Borkovec 1993, Borkovec 1987), and other possible harms such as increased depression or behavioural problems resulting from consideration of sensitive and difficult issues were only reported as a reason for participants to be removed from studies.
Acceptability of treatment, measured through dropout caused by adverse effects and satisfaction with treatment, was rarely reported in studies included in this review. Quality of life, social functioning and relationship changes were also under‐investigated. Cost‐effectiveness outcomes were not presented in any of the studies. Notably too, less than a third of studies included in the review investigated short or longer‐term outcomes of psychological therapies in controlled comparisons, therefore, the evidence for the sustained effect of CBT and other psychological therapy approaches remains very limited.
Quality of evidence For specific aspects of methodological quality, the majority of studies were rated well (QRS score of 2) for their descriptions of treatment, recruitment methods, diagnostic and exclusion criteria, withdrawal information and the outcome measures used, and almost all studies provided a declaration of interest. Aspects of methodological quality that were less well rated for most studies are considered below.
Randomisation procedure Although all studies included in this review described their assignment procedure as 'randomised', none provided any information in articles on the methods used. Four authors have very helpfully provided further information on their randomisation procedures (Akkerman 2001, Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993, Wetherell 2003a, White 1992), however allocation concealment in all other studies remains unknown. This lack of information increases uncertainty as to whether bias may have been introduced during the allocation process.
Blinding of assessors and participants Seventy‐two percent of studies in the review used blind assessors who were reported to be unaware of treatment assignment of participants. Notably, however, no studies reported whether intregity of blind was tested. Therefore, whilst the use of blind assessors in the majority of studies may be regarded as a methodological strength in this review, the extent to which detection bias may have occurred is unknown.
Sample size The studies included in the review were mostly small, with a mean sample size of 54, thus increasing the probability of type 1 and type 2 errors. Only one study, Linden 2002, reported carrying out a power calculation. Few of the studies comparing psychological therapies against TUA/WL are likely to have had sufficient power to detect true differences between groups. Studies in which two or more psychological therapies were compared would require even larger numbers of participants to detect a difference between models over and above a non‐specific treatment effect, and it seems highly unlikely, therefore, that any of these studies were adequately powered.
Fidelity to treatment protocols Because psychological therapy involves the application of complex techniques over a period of time, it is important from a methodological perspective that each intervention is operationally defined by detailed protocols (Borkovec 2001). One of the methodological strengths of studies included in this review was the use of manuals or protocols by the majority (76%) of investigators to standardise treatment approaches for CBT and for ST, together with the employment of therapists who were experienced in the psychological model under examination. Testing of therapists' fidelity to treatment manuals through the systematic or random checking of audiotapes by independent clinicians is an additional key methodological aspect of psychological therapy studies, especially when conducting comparative studies of psychological models, to ensure that any observed treatment effect can be attributed to specific components and characteristics of the model. However, given that only 52% of included studies tested therapists' treatment fidelity, there is no certainty in many studies that therapists were adhering to the required psychological model. Control comparators Waiting list was used in almost all studies comparing psychological therapies against a 'no treatment' control. Waiting list is frequently employed as an ethical 'no treatment' condition, to ensure that all participants eventually receive treatment for their condition. However sub‐group analyses in this review suggest that assignment to waiting list may have negatively influenced outcomes, with patients not expecting to improve until treatment began, and may have increased the difference in clinical response rate in favour of psychological therapies.
Researcher allegiance When examining the effectiveness of CBT, investigators used a diversity of ST control conditions as comparators against CBT. Notably, this group of studies continued to show statistical heterogeneity, even when subgrouped into active (non‐directive) and inactive (attention placebo) ST, with two studies favouring CBT (Borkovec 1987, Borkovec 1993), and two studies favouring ST (Bond 2002a, Stanley 1996). In the studies by Bond 2002a and Stanley 1996, non‐directive therapy was used as an active comparative approach to CBT, whereas in the studies by Borkovec 1987 and Borkovec 1993, non‐directive therapy was not considered 'the best available experiential treatment' and was used by investigators as a non‐specific attention control. These conceptual differences in control conditions between investigators might help to explain the differences between studies, and suggests the possibility of researcher allegiance, whilst acknowledging, nevertheless, that CBT and ST were managed equally across studies in terms of manualisation, fidelity checking and therapist qualifications/experience.
One study comparing CT with psychodynamic therapy (PD) (Durham 1994a) used a manual for the CT intervention, but did not manualise the PD intervention in a formal sense. The investigators acknowledged that patients with GAD would probably be excluded from brief dynamic therapy in clinical practice due to their 'poor prognosis'. This could again be perceived as researcher allegiance in terms of treatment expectations.
Use of concurrent medication Two thirds of studies allowed for concurrent naturalistic use of hypnotics, anti‐anxiolytics or antidepressants, either in ongoing use, as new courses during the trial period, or in follow‐up, and the possibility that reduction in primary and secondary symptom outcome was influenced by concurrent medication should not be discounted. Nevertheless, given the high prevalence of naturalistic prescribing in patients with GAD, it should be acknowledged that elimination of concurrent prescribing in studies would be likely to compromise the external validity of study findings .
Treatment adherence and attrition Adherence in ongoing treatment was reported in just four studies, which presented mean attendance rates at psychological therapy sessions (Akkerman 2001, Borkovec 1987, Durham 1994a) or adherence to homework assignments (Wetherell 2003a). Therefore, it is not known whether participants received the optimal intensity of therapy specified in treatment manuals, and to what extent low adherence may have impacted upon post‐treatment outcomes.
The overall attrition rate in studies was reasonably low at 15%. However, a small number of studies reported very high attrition rates, either across study arms, as in the study by Blowers 1987, or in one arm only, as in the study by Barlow 1992 where the dropout rate in active treatments was 24%, in contrast with the waiting list control condition, which had a dropout rate of 50%. Whilst 50% of studies reported reasons for attrition in full, it is not known for the remaining studies whether there were systematic differences between dropouts and completers that could have influenced treatment outcomes, leading to an underestimate or overestimate of effect. Nevertheless, through use of best/worst case scenarios for the three main comparisons, it was possible to set boundaries for the treatment effect, strengthening confidence in the findings.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews A number of reviews examining the effectiveness of psychological therapies for GAD have been published over the last ten years. The review by Fisher 1999 was limited to six studies examining clinical significant change through use of the STAI‐T. Mohlman 2004 conducted a narrative review limited to elderly populations. One review article examined 13 studies comparing CBT approaches against control conditions (Borkovec 2001), and one earlier systematic review and preliminary meta‐analysis examined studies comparing CBT against control conditions (13 studies) and pharmacotherapy (22 studies) for GAD (Gould 1997). Other reviews of psychological therapies have not been limited to GAD (DeRubeis 1998, Westen 2001, Roth 2005). None conducted meta‐analyses in accordance with the statistical methods used in Cochrane systematic reviews. The review and preliminary meta‐analysis by Gould 1997 remains the most widely cited summary of evidence on treatments for GAD. The authors acknowledged that some of the findings of their review were influenced by limitations of statistical power for some comparisons. The current review adds 12 more recently conducted studies, providing increased statistical power.
In this review, control conditions were examined as active and inactive ST or as a 'no treatment' condition (TAU or WL), together with an investigation of potential differences between the four control comparators. In the reviews by Gould 1997 and Borkovec 2001, the investigators categorised control conditions into two groups of non‐directive/attention placebo/pill placebo and wait‐list/no treatment conditions only. Both reviews were in agreement that for measurement of anxiety symptoms, the effect size for CBT compared with attention placebo conditions was smaller than that for waiting list/no treatment, findings that are broadly in line with those in the current review. However, neither review examined supportive psychotherapy or waiting list control conditions separately. Furthermore, although Gould 1997 stated that tests of heterogeneity were conducted, no findings were reported, and heterogeneity was not considered by Borkovec 2001, therefore the appropriateness of combining studies using such a diversity of control comparators remains unknown. In contrast, this review stratified control comparators, and investigated this as a potential source of heterogeneity.
In the review by Fisher 1999, STAI‐T data from six studies (404 participants) were re‐calculated using Jacobson criteria to identify recovery rates for participants assigned to psychological therapies. Their findings differed from the rates reported in the original studies, and showed an overall post‐treatment recovery rate of 32% with clinical improvement calculated at 23%. In the current review, clinical response data were based on the rates reported in the original studies, with a conservative estimate of response calculated through the use of ITT analysis, in which it was assumed that all dropouts were non‐responders, and ranged from 28% (supportive therapy) to 50% (CT). As Fisher 1999 state, response rates reported in the original studies was strongly influenced by the clinical response index used. Since the majority of studies in the current review used a standardised index (Barlow 1992) or Jacobson criteria (Jacobson 1991), it seems likely, nevertheless, that reasonable consistency was achieved across studies.
Two previous reviews have concluded that CBT is superior to BT in reducing anxiety symptoms (Borkovec 2001, Gould 1997). For the primary dichotomous outcome of clinical response, which was not examined in the two previous reviews, findings from this review indicated conflicting direction of effect between studies comparing CT and BT, although the small number of studies for inclusion in this comparison limits meaningful interpretation. Borkovec 2001 and Gould 1997 also concluded that CBT was successful in reducing comorbid depression symptoms at post‐treatment and in follow‐up. This review supports these conclusions, and provides increased statistical power to demonstrate a consistent effect in favour of CBT for reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment, compared with TAU/WL, psychodynamic therapy and non‐directive therapy.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
This review provides robust evidence that psychological therapy using a cognitive behavioural approach is effective in the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD). Forty six percent of patients assigned to cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) showed clinical response at post‐treatment, in contrast with 14% in waiting list/treatment as usual groups, and anxiety, worry and depression symptoms were also significantly reduced. There is a lack of evidence for longer‐term effectiveness of psychological therapy in treating GAD.
Whilst the overall attrition rate from psychological therapy using a CBT approach is reasonably low at 15%, this review suggests that patients who attended group therapy were more likely to drop out of treatment, and those attending individual therapy were more likely to persist with treatment. Attrition rates in the elderly were also significantly higher. Reasons for dropout were under‐reported in studies, and may not only have been due to low acceptability or effectiveness of psychological therapy.
Currently, this review is unable to provide evidence that demonstrates the effectiveness of non‐CBT approaches in treating GAD, whilst emphasising strongly that lack of available evidence does not imply that non‐CBT approaches are ineffective.
Evidence on differences of effect between psychological therapy models is limited to a small number of studies comparing CBT with supportive therapy and a single study comparing CBT with psychodynamic therapy. Comparisons between CBT and supportive therapy show inconsistent differences between approaches. The heterogeneity of findings, in part explained by the number of sessions used and possible researcher allegiance, together with the small number of studies included in this comparison, precludes the ability to draw conclusions on the comparative superiority of CBT for treating patients with the primary symptoms of GAD.
Implications for research.
Whilst clinical guidelines in the UK and US recommend cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) as a first‐line treatment for GAD (NICE 2004, Ballenger 2001), psychological therapies used in UK primary care practice are predominantly Rogerian, psychodynamic and integrative in theoretical framework (Stiles 2006), which, as demonstrated in this review, lack an evidence base supporting their use. A recent UK Government strategy paper has called for an additional 10,000 psychological therapists to be trained in CBT or other evidence‐based therapies to treat mental health disorders (Layard 2004). In order to inform future health care policy on the use of psychological therapies for GAD, and the training of psychological therapists, as recommended in the Layard strategy paper, it seems of key importance to conduct further randomised controlled trials that examine the effectiveness of non‐CBT models, and the comparative effectiveness of CBT and non‐CBT models for GAD.
The studies included in this review demonstrated a number of methodological strengths, including the use of structured diagnostic interviews checked by a second independent clinician, the use of independent assessors and the manualisation and fidelity checking of psychological therapies. Further specific recommendations to enhance the internal validity of future studies include the recruitment of larger appropriately powered samples, the use of treatment as usual control conditions rather than waiting list, adequate allocation concealment, testing of blind for assessors, measurement of treatment adherence and measurement of adverse effects/acceptability. To increase the applicability of the findings, future studies should include long‐term follow‐up assessments, cost‐effectiveness outcomes, quality of life outcomes and process outcomes such as strength of therapeutic alliance. Use of concurrent medication may be a necessary feature of future trials, to ensure generalisability and applicability of the findings, however, studies should ensure that all prescribing is recorded in detail and that prescribing rates are comparable across groups or controlled for in analyses.
As a chronic and diffuse disorder, GAD is difficult to treat successfully, and indeed, it is notable that less than 50% of participants from studies included in this review showed clinical response to CBT. Other psychological therapy models such as cognitive analytic therapy or interpersonal therapy may be of added value in the treatment of GAD, and would be worthy of examination in RCTs. One study currently in progress is evaluating an interpersonal and emotional processing therapy approach as an additional component to CBT in treating GAD (Borkovec 2003), and it is hoped to include the findings in a future update of this review.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 March 2010 | Amended | Two previously missing tables inserted into review and hyperlinked to text. Contact author's email address updated. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 4, 1999 Review first published: Issue 1, 2007
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 November 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. |
| 2 April 2007 | Amended | Minor update |
| 1 August 2006 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Substantive amendment |
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the authors of the original published version of the protocol ‐ F Kapczinski, JS Souza, A Cunha, C Gale and R Schmitt ‐ for their initial work on the review.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of experts in the field who provided us with information about ongoing trials: Jonathan Bisson, University Hospital of Wales, UK Thomas Borkovec, Pennsylvania State University, US Steve Wood, Cardiff & Vale NHS Trust, UK Lizabeth Roemer, University of Massachusetts at Boston, US Julie Wetherell, University of California, US
We would like to thank the trial investigators who responded to our request for further information on their studies: Thomas Borkovec, Pennsylvania State University, US Jean‐Phillipe Boulenger, Montpelier University Hospital, France Dennis Lepage, University of Sherbrooke, Canada Lizabeth Roemer, University of Massachusetts at Boston, US Melinda Stanley, University of Texas, US Julie Wetherell, University of California, US Jim White, Lanarkshire Healthcare NHS Trust, UK
We are most grateful to Dr John Cape, Head of Psychology, Camden and Islington Mental Health and Social Care Trust, and to Dr Judith Anzures‐Cabrera, MRC Biostatistics Unit, University of Cambridge, for their very helpful comments on the first draft of this review.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment | 8 | 334 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.55, 0.74] |
| 1.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 8 | 334 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.55, 0.74] |
| 1.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 1.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment | 12 | 330 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.00 [‐1.24, ‐0.77] |
| 2.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 12 | 330 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.00 [‐1.24, ‐0.77] |
| 2.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment | 9 | 256 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.90 [‐1.16, ‐0.64] |
| 3.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 9 | 256 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.90 [‐1.16, ‐0.64] |
| 3.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment | 11 | 317 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.96 [‐1.20, ‐0.72] |
| 4.1 cognitive behavioural therapy | 11 | 317 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.96 [‐1.20, ‐0.72] |
| 4.2 psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.3 supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment | 3 | 69 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.01 [‐0.00, 2.03] |
| 5.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 3 | 69 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.01 [‐0.00, 2.03] |
| 5.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6 Improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment | 3 | 112 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.06, 0.82] |
| 6.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 3 | 112 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.06, 0.82] |
| 6.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment | 13 | 483 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.65, 1.54] |
| 7.1 Cognitive behavioural therapy | 13 | 483 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.65, 1.54] |
| 7.2 Psychodynamic therapy | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7.3 Supportive therapy | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
1.1. Analysis.
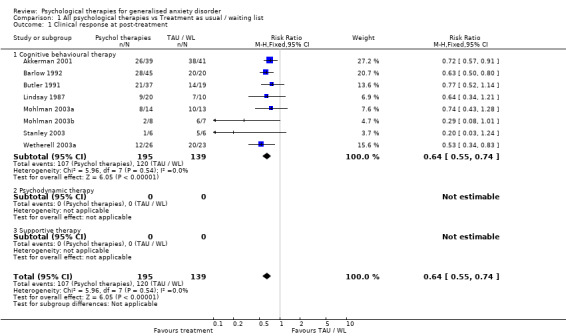
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment.
1.2. Analysis.
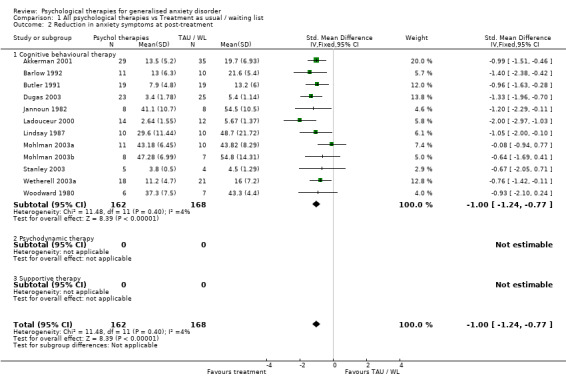
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment.
1.3. Analysis.
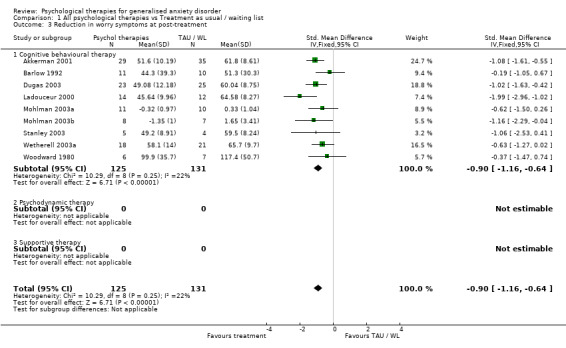
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment.
1.4. Analysis.
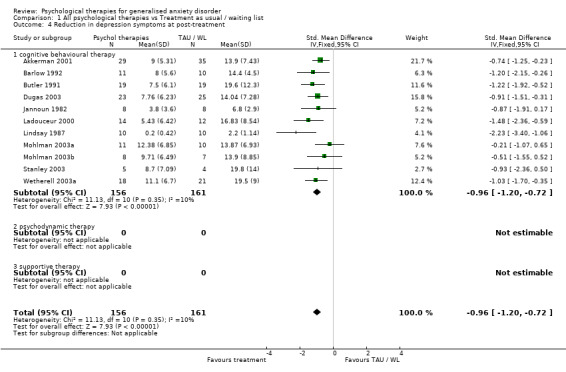
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment.
1.5. Analysis.
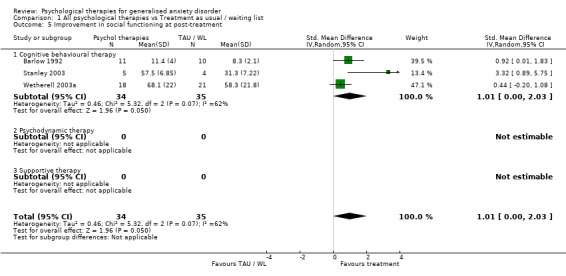
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment.
1.6. Analysis.
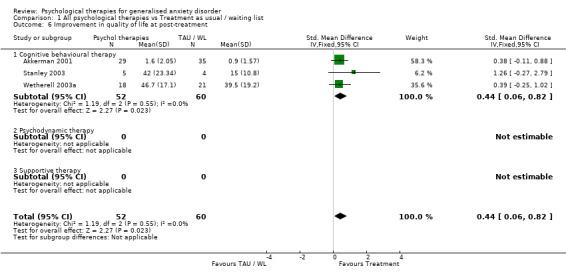
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 6 Improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment.
1.7. Analysis.
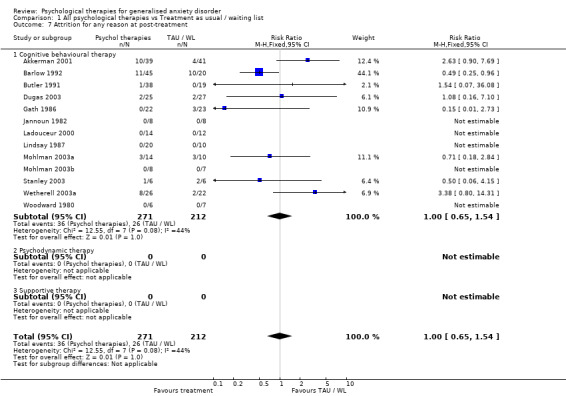
Comparison 1 All psychological therapies vs Treatment as usual / waiting list, Outcome 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment.
Comparison 2. Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.65, 0.92] |
| 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment | 2 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐6.85 [‐11.20, ‐2.50] |
| 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment | 2 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐8.37 [‐12.55, ‐4.20] |
| 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment | 2 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 14.28 [1.82, 26.75] |
| 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.35, 1.20] |
| 8 Clinical response at 6 month follow‐up | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.62, 1.01] |
| 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up | 2 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐13.41 [‐19.09, ‐7.74] |
2.1. Analysis.
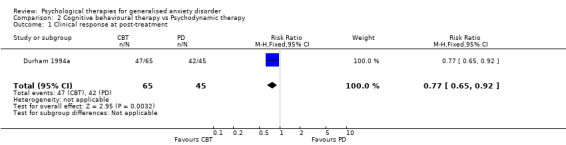
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment.
2.2. Analysis.
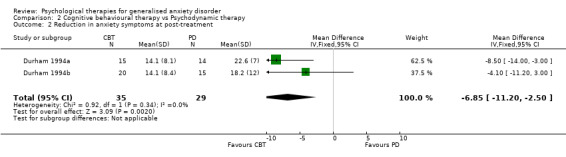
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment.
2.4. Analysis.
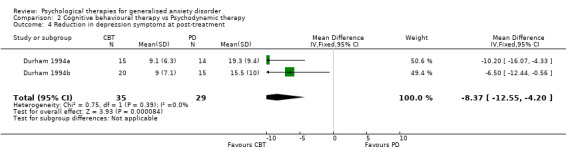
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment.
2.5. Analysis.
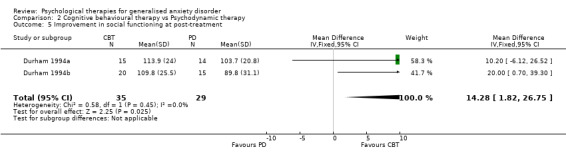
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment.
2.7. Analysis.
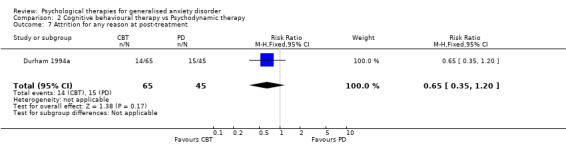
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment.
2.8. Analysis.
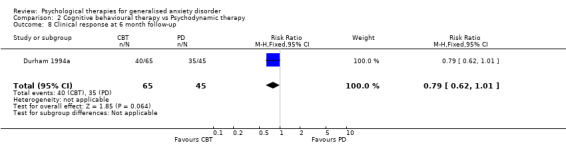
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 8 Clinical response at 6 month follow‐up.
2.9. Analysis.
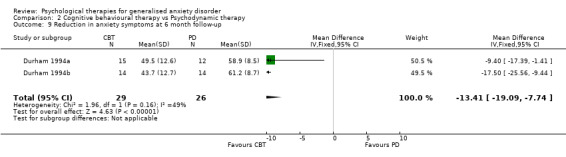
Comparison 2 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Psychodynamic therapy, Outcome 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up.
Comparison 3. Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment | 7 | 332 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.70, 1.06] |
| 1.1 Active ST | 5 | 208 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.70, 1.16] |
| 1.2 Inactive ST | 2 | 124 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.54, 0.96] |
| 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment | 7 | 235 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.40 [‐0.66, ‐0.14] |
| 2.1 Active ST | 5 | 136 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.37 [‐0.72, ‐0.03] |
| 2.2 Inactive ST | 2 | 99 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.43 [‐0.83, ‐0.03] |
| 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment | 4 | 128 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.55 [‐0.91, ‐0.20] |
| 3.1 Active ST | 3 | 92 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.72 [‐1.15, ‐0.29] |
| 3.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 36 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.17 [‐0.82, 0.49] |
| 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment | 4 | 128 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.37 [‐0.72, ‐0.02] |
| 4.1 Active ST | 3 | 92 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 4.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 36 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐0.93, 0.39] |
| 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.70 [‐18.08, 12.68] |
| 5.1 Active ST | 0 | 0 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.70 [‐18.08, 12.68] |
| 6 Improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [‐10.77, 11.37] |
| 6.1 Active ST | 0 | 0 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [‐10.77, 11.37] |
| 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment | 7 | 332 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.71, 1.53] |
| 7.1 Active ST | 5 | 208 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.65, 1.62] |
| 7.2 Inactive ST | 2 | 124 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.55, 2.15] |
| 8 Treatment response at 6 month follow‐up | 3 | 158 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.59, 1.06] |
| 8.1 Active ST | 2 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.54, 1.13] |
| 8.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 52 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.50, 1.33] |
| 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up | 3 | 97 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.42 [‐0.83, ‐0.02] |
| 9.1 Active ST | 2 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.39 [‐0.90, 0.11] |
| 9.2 Inactive ST | 1 | 35 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.47 [‐1.14, 0.20] |
| 10 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 12 month follow‐up | 1 | 36 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.57 [‐1.24, 0.10] |
| 10.1 Active ST | 1 | 36 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.57 [‐1.24, 0.10] |
| 10.2 Inactive ST | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
3.1. Analysis.
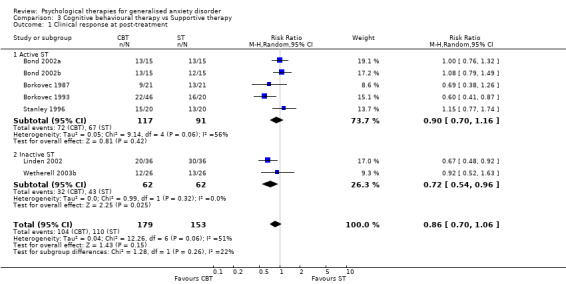
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment.
3.2. Analysis.
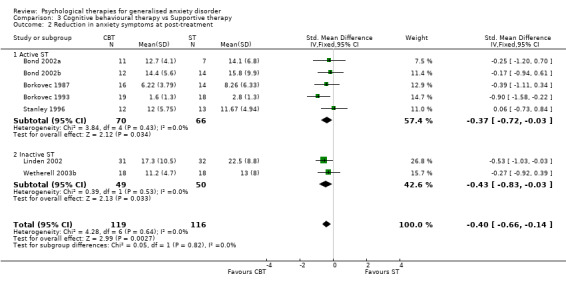
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment.
3.3. Analysis.
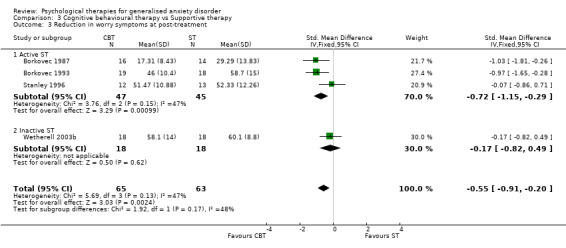
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment.
3.4. Analysis.
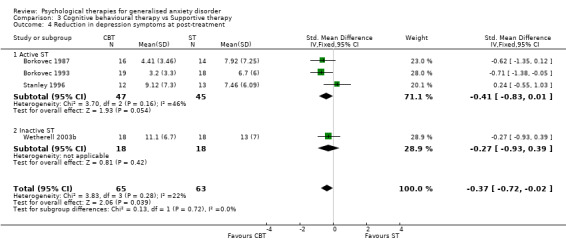
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment.
3.5. Analysis.
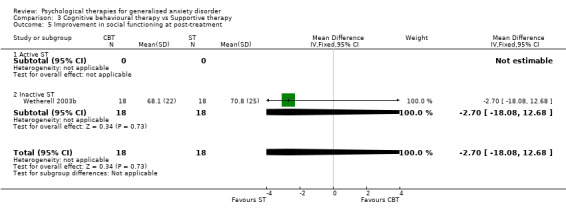
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 5 Improvement in social functioning at post‐treatment.
3.6. Analysis.
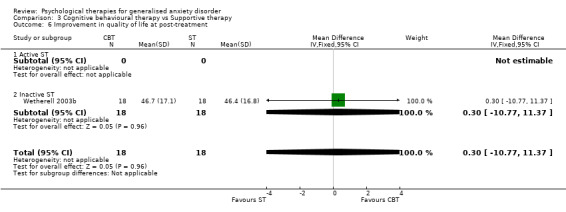
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 6 Improvement in quality of life at post‐treatment.
3.7. Analysis.
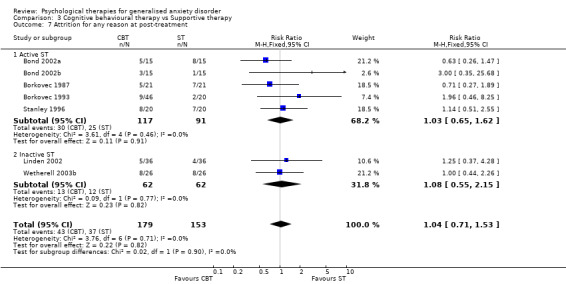
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment.
3.8. Analysis.
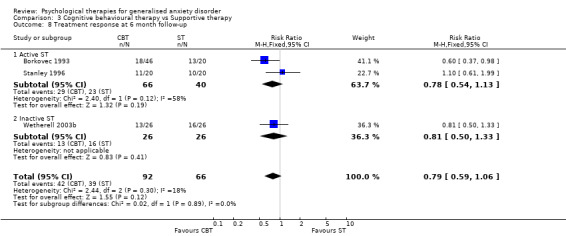
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 8 Treatment response at 6 month follow‐up.
3.9. Analysis.
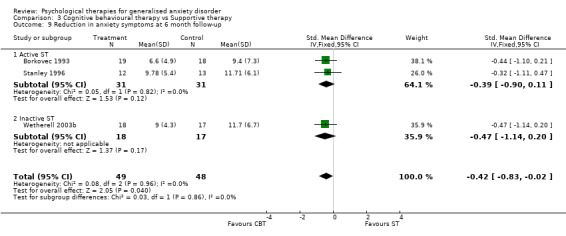
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up.
3.10. Analysis.
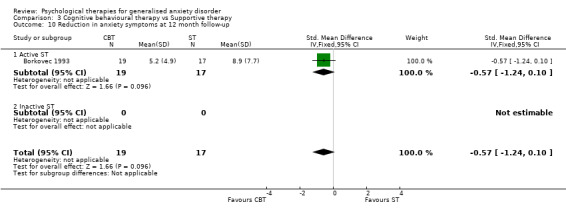
Comparison 3 Cognitive behavioural therapy vs Supportive therapy, Outcome 10 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 12 month follow‐up.
Comparison 4. Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment | 5 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.56, 0.87] |
| 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment | 4 | 131 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.40, 0.30] |
| 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment | 1 | 20 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.24 [‐0.66, 1.14] |
| 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment | 3 | 89 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.58 [‐1.01, ‐0.15] |
| 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment | 4 | 159 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.52 [0.25, 1.07] |
| 8 Treatment response at 6 month follow‐up | 2 | 105 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.40, 0.79] |
| 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up | 2 | 67 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.59, 0.37] |
| 10 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 12 month follow‐up | 2 | 59 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [‐0.45, 0.58] |
4.1. Analysis.
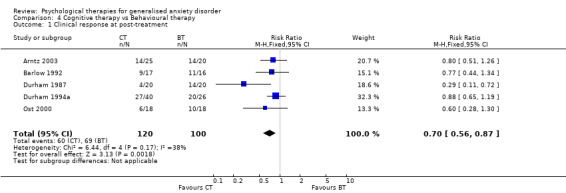
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 1 Clinical response at post‐treatment.
4.2. Analysis.
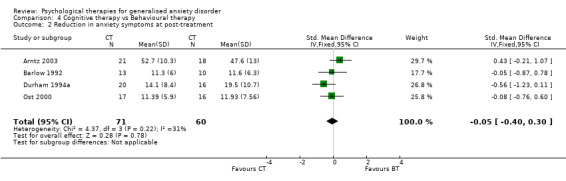
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 2 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at post‐treatment.
4.3. Analysis.
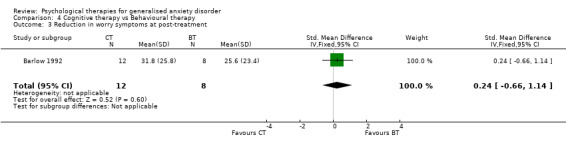
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 3 Reduction in worry symptoms at post‐treatment.
4.4. Analysis.
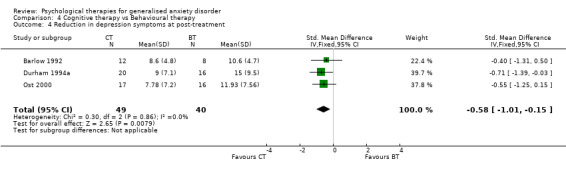
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 4 Reduction in depression symptoms at post‐treatment.
4.7. Analysis.
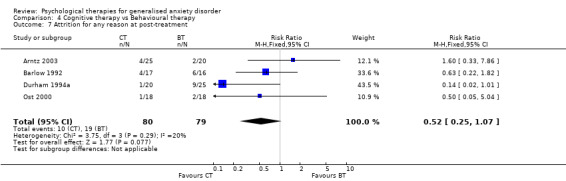
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 7 Attrition for any reason at post‐treatment.
4.8. Analysis.
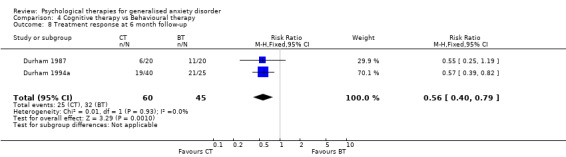
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 8 Treatment response at 6 month follow‐up.
4.9. Analysis.
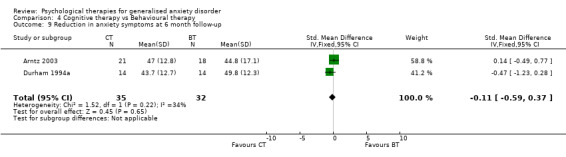
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 9 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 6 month follow‐up.
4.10. Analysis.
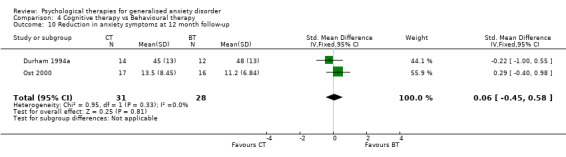
Comparison 4 Cognitive therapy vs Behavioural therapy, Outcome 10 Reduction in anxiety symptoms at 12 month follow‐up.
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Akkerman 2001.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ allocation concealed Blinding: independent assessors Trial duration: 15 weeks Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Setting: academic clinical psychology dept Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 85 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of Moderate‐severe GAD through diagnostic interview using ADIS‐IV. Comorbidity: 65% of sample had at least one co‐existent MH diagnosis | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. minimal contact waiting list control Modality: group Intensity: 15 1.5‐hour sessions over 15 weeks Manualised: Yes Treatment fidelity: tested through videotape examination of 20% of sessions | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: HAMA, HAM‐D, composite measure of severity Self‐report: PSWQ, Worry Scale, STAI‐T, BDI, Geriatric Depression Scale, Fear Questionnaire, QoLI, Life Satisfaction Index‐Z. | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 36 Overall dropout rate: 16.5% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Arntz 2003.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: 9 months | |
| Participants | Setting: community mental health centre Population: adult clinic attendees Sample size: 45 Diagnosis: presence of GAD symptoms according to DSM‐III‐R, using Dutch version of SCID (SDM‐III‐R or SDM‐IV) Comorbidity: 78% had secondary diagnoses | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. Applied relaxation Modality: individual Intensity: 12 weekly 1‐hour sessions Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested through weekly supervision meetings | |
| Outcomes | Self‐report: STAI‐T, SCL‐90, FQ, Bouman Depression Inventory (Dutch BDI) | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 27 Overall dropout rate: 17.7% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Barlow 1992.
| Methods | Allocation: randomly assigned to treatment condition and to available therapists Blinding: assessors blind to treatment condition Trial duration: 15 weeks Follow‐up: 2 years | |
| Participants | Setting: academic specialist centre Population: adults referred by health professionals, community agencies or self‐referral Sample size: 65 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of GAD based on DSM‐III‐R crieria, using ADIS‐R clinical interview Comorbidity: not excluded on basis of comorbidity but prevalence not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Combined relaxation and cognitive restructuring 2. Cognitive restructuring 3. Applied progressive muscle relaxation 4. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 15 1‐hour sessions over 15 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested through periodic spot‐checks of audio‐tapes, conducted by raters blind to treatment condition | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: HAMA, HAM‐D, composite measure of severity Self report: STAI‐T, Cognitive‐Somatic Anxiety Questionnaire, Fear Questionnaire, BDI, EPI, Subjective Symptoms Scale, credibility scale. | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 32 Overall dropout rate: 32.3% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Blowers 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessors blind to condition and therapist Trial duration: 10 weeks Follow‐up: 8.5 months | |
| Participants | Setting: community mental health Population: adults referred by GP Sample size: 66 Diagnosis: main complaint of GAD based on DSM‐III criteria Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Anxiety management training 2. Non‐directive counselling 3. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 8 45‐min sessions over 10 weeks Manualised: patients given booklet (both therapies) Treatment fidelity: tested through assessment of 20 audio‐recorded sessions by blind assessor | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: Clinical Anxiety Scale (Snaith 1982), SAS, Panic and Problem ratings Self report: HADS, STAI‐T, St George's Anxiety Questionnaire | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 20 Overall dropout rate: 44.4% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Bond 2002a.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level using randomisation code ‐ patients blind to medication Blinding: assessor blind to treatment group Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: O/P anxiety disorders clinic Population: adult clinic attendees Sample size: 60 Diagnosis: GAD according to DSM‐III‐R criteria through structured interview Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Anxiety management training + buspirone 2. Anxiety management training + placebo 3. Non‐directive therapy + buspirone 4. Non‐directive therapy + placebo Modality: individual Intensity: 7 45‐min sessions over 8 weeks Manualised: not reported Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, composite measure of severity Self‐report: HADS, Zung, GHQ, Cognitive Checklist, Mood Rating Scale, severity/interference in life for key symptoms | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 25 Overall dropout rate: 26.6% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Bond 2002b.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level using randomisation code ‐ patients blind to medication Blinding: assessor blind to treatment group Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: O/P anxiety disorders clinic Population: adult clinic attendees Sample size: 60 Diagnosis: GAD according to DSM‐III‐R criteria through structured interview Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Anxiety management training + buspirone 2. Anxiety management training + placebo 3. Non‐directive therapy + buspirone 4. Non‐directive therapy + placebo Modality: individual Intensity: 7 45‐min sessions over 8 weeks Manualised: not reported Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, composite measure of severity Self‐report: HADS, Zung, GHQ, Cognitive Checklist, Mood Rating Scale, severity/interference in life for key symptoms | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 25 Overall dropout rate: 26.6% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Borkovec 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised in 3 waves at patient and therapist level ‐ no further information reported Blinding: assessors blind to therapy‐condition assignment. Trial duration: 6 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: university campus Population: young adult volunteers Sample size: 42 Diagnosis: GAD, using Anxiety Disorder Interview Schedule (ADIS) Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Cognitive therapy + relaxation training 2. Non‐directive therapy + relaxation training Modality: individual Intensity: 12 60‐105 min sessions twice a week over 6 weeks Manualised: both therapies manualised Treatment fidelity: tested through examination of audio‐tapes in weekly supervision | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, HAM‐D, composite measure of severity, four SDM‐III GAD characteristics Self‐report: Zung, STAI‐T, Fear Questionnaire, Reactions to Relaxation/ Arousal Questionnaire Process measures: relaxation‐induced anxiety, frequency of home practice | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 27 Overall dropout rate: 28.5% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
Borkovec 1993.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised within each wave of 3 clients at the client level ‐ no further information reported Blinding: assessors unaware of treatment condition Trial duration: 6 weeks Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Setting: academic clinical psychology dept (Stress & Anxiety Centre) Population: adult volunteers Sample size: 66 Diagnosis: Principal diagnosis of GAD according to diagnostic interview using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: 78.2% received at least one additional diagnosis | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Applied relaxation (AR) 3. Non‐directive therapy (ND) Modality: individual Intensity: 12 1‐hour sessions twice a week over 6 weeks Manualised: all therapies manualised Treatment fidelity: tested through examination of audiotapes from 20% of sessions by clinical graduate students (CT and AR) and by specialist (ND) | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, HAM‐D, composite measure of severity. Self‐report: STAI‐T, Zung, PSWQ, BDI, Reaction to Relaxation and Arousal Questionnaire, credibility and expectation scales, Relationship Inventory | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 30 Overall dropout rate: 8.3% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
Butler 1991.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: independent assessor who was not aware of random allocation to group or to therapist Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: adult attendees referred by GP or psychiatric hospital sources Sample size: 57 Diagnosis: GAD as defined by DSM‐III‐R, using structured interview based on ADIS Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. BT 3. Waiting list (WL) Modality: individual Intensity: Up to 12 1‐hour 12 sessions, with additional post‐treatment booster sessions at 2, 4 and 6 weeks Manualised: 'standardised procedures' Treatment fidelity: 3 random samples of tapes from beginning, middle and end of the study independently rated by 2 sets of clinical psychologists | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, anxiety/ depression based on 9‐pt scale Self‐report: Leeds Scale, STAI‐T, BAI, BDI, 9‐pt anxiety/ depression rating scale, Dysfunctional Attitude Scale, Cognition Checklist, Fear of Negative Evaluation Scale, Expectations of treatment | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 29 Overall dropout rate: 5.2% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Dugas 2003.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessor uninformed of group assignment Trial duration: 14 weeks Follow‐up: 2 years | |
| Participants | Setting: academic clinical psychology dept Population: adult volunteers Sample size: 52 Diagnosis: primary diagnosis of GAD, according to structured diagnostic interview, using ADIS‐IV. Comorbidity: 35 participants had one or more additional comorbid diagnoses | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Waiting list Modality: group Intensity: 14 2‐hour sessions over 14 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: randomly selected audiotapes examined by advanced graduate student using checklists to assess treatment integrity | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: ADIS Symptom Severity Scale (9 pt) Self‐report: PSWQ, Worry and Anxiety Questionnaire, Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale, BAI, BDI, SAS | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 29 Overall dropout rate: 7.7% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Durham 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessors blind to treatment condition Trial duration: 4‐6 months Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: consecutive adult attendees referred by psychiatrist or GP Sample size: 51 Diagnosis: main problem of generalized anxiety according to structured interview assessment using Zung Anxiety Status Inventory Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. Applied relaxation Modality: individual Intensity: 16 hours of therapy over a maximum of 6 months ‐ for most patients, treatment was weekly and 1 hour in length Manualised: protocol used Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician: Zung Anxiety Status Inventory Self‐report: Modified Somatic Perception Questionnaire, BDI, Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire, DAQ, Zung Anxiety Scale, expectation and satisfaction with treatment scale GP ‐ no of visits and additional medication prescribed | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 22 Overall dropout rate: 7.7% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Durham 1994a.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessor was blind to therapist and treatment Trial duration: 6 months Follow‐up: 1 year | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: adults referred by psychiatrist or GP Sample size: 110 Diagnosis: Primary diagnosis of GAD as defined by DSM‐III‐R, using ADIS‐R. Comorbidity: 46% had co‐existing personality disorders | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. Analytic psychotherapy 3. Anxiety management training Modality: individual Intensity: high contact CT/AP ‐16‐20 sessions, low contact CT/AP/AMT ‐8‐10 sessions. All sessions 1 hr in length over 6 months Manualised: CT ‐manualised, AP‐non‐ manualised, AMT‐ structured Treatment fidelity: not checked | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, composite measure of severity Self‐report: Brief Symptom Inventory, STAI‐T, BDI, BAI, Self‐Esteem Scale, SAS, DAS, treatment expectations | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 29 Overall dropout rate: 27.2% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Durham 1994b.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessor was blind to therapist and treatment Trial duration: 6 months Follow‐up: 1 year | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: adults referred by psychiatrist or GP Sample size: 110 Diagnosis: primary diagnosis of GAD as defined by DSM‐III‐R, using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: 46% had co‐existing personality disorders | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. Analytic psychotherapy 3. Anxiety management training Modality: individual Intensity: high contact CT/AP ‐16‐20 sessions, low contact CT/AP/AMT ‐8‐10 sessions. All sessions 1 hr in length over 6 months Manualised: CT ‐manualised, AP‐non‐ manualised, AMT‐ structured Treatment fidelity: not checked | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, composite measure of severity Self‐report: Brief Symptom Inventory, STAI‐T, BDI, BAI, Self‐Esteem Scale, SAS, Dysfunctional Attitude Scale, treatment expectations | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 29 Overall dropout rate: 27.2% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | D ‐ Not used |
Gath 1986.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient and therapist level ‐ method not reported Blinding: Assessors blinded to treatment condition Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: whole sample only | |
| Participants | Setting: O/P psychology dept Population: adults referred by psychiatrist or GP Sample size: 45 Diagnosis: GAD according to Research Diagnostic Criteria (82% had primary diagnosis of GAD) Comorbidity: 44% had minor depression and 47% had recurrent panic attacks | |
| Interventions | 1. Anxiety management 2. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 4‐12 1‐hour sessions ‐ booster sessions 2 and 6 weeks after end of treatment Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested through examination of tape‐recorded sample of sessions at regular meetings | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: 9‐point scale (Watson 1971), HAMA, HAM‐D, PSE Self‐report: Leeds Scale, 9‐point rating scale, STAI, GHQ, expectations of treatment/suitability of treatment | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 23 Overall dropout rate: 6.6% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Jannoun 1982.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: psychiatric assessor blind to treatment conditions Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: referred adult attendees Sample size: 26 Diagnosis: main complaint of generalised anxiety Comorbidity: 8 patients had agoraphobic symptoms | |
| Interventions | 1. Anxiety management training 2. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 5 30‐45 min sessions over 6 weeks, and one booster session 6 weeks after end of treatment Manualised: standardised procedures Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, HAM‐D Self‐report: Leeds Anxiety Scale, Leeds Depression Scale, STAI‐T, Eysenck Personality Inventory | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 18 Overall dropout rate: 0% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Ladouceur 2000.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 16 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: psychology treatment centre Population: adult volunteers Sample size: 26 Diagnosis: primary diagnosis of GAD based on structured diagnostic interview, using ADIS‐IV Comorbidity: specific phobia, social phobia, panic, MDD, OCD, trichotillomania | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 16 weekly 1‐hour sessions over 16 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: ADIS‐IV Symptom Severity Scale (9 pt) Self‐report: PSWQ, Worry and Anxiety Questionnaire, Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale, BAI, BDI Significant Other Rating Scale ‐GAD assessed by person close to patient | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 26 Overall dropout rate: 0% | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Lavallee 1993.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessor blind to treatment conditions Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: 1 year | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: volunteers Sample size: 60 Diagnosis: GAD, according to DSM‐III criteria Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1.CBT+lorazepam 2. CBT+placebo 3. Support therapy+lorazepam 4. Supportive therapy+placebo Modality: individual Intensity: conducted over 8 weeks ‐ number and duration of sessions not reported Manualised: not reported Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, HCL‐90 self‐report: Zung Anxiety Scale | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 14 Overall dropout rate: not reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Linden 2002.
| Methods | Allocation: 'simple randomisation' at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: independent assessors Trial duration: 14 weeks for comparison of CBT vs WL ‐ 8 months altogether Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: psychiatric O/P dept Population: adults referred by GPs and anxiety call centre Sample size: 72 Diagnosis: pure GAD, according to DSM‐IV criteria, using MINI interview Comorbidity: no ‐ pure GAD only (1/8 patients screened) | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 25 50‐min sessions over 44.8 weeks ‐ but comparison with WL took place after immediate treatment which was after 14 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested by audiotaping sessions, with subsample of 147 sessions evaluated by trained independent assessors | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: HAMA, CGIS Self‐report: STAI‐T | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 31 Overall dropout rate: 12.5 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Lindsay 1987.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported (outcome measures all self‐report) Trial duration: 4 weeks Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Setting: primary care Population: adults referred by GPs Sample size: 40 Diagnosis: primary problem of anxiety ‐ anxiety scores of 4 or higher on GHQ, high scores in Fear Survey Schedule, and high score on Zung Anxiety Scale Comorbidity: screened by GP for specific phobia | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Anxiety management training 3. Benzodiazepines (not included in review) 4. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 8 1‐hour sessions held twice weekly Manualised: not reported Treatment fidelity: no formal assessment | |
| Outcomes | Self‐report: GHQ‐28 (anxiety, depression, general health, social skills), Zung Anxiety Scale, Autonomic Perception Questionnaire, CAQ | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 14 Overall dropout rate: 0 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Mohlman 2003a.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessors unaware of treatment condition Trial duration: 13 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: mental health clinic Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 27 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of GAD, according to DSM‐IV criteria comorbidity: 14 (58%) | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Waiting list Modality: individual Intensity: 13 50‐min weekly sessions, followed by monthly booster sessions for 6 months Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested by independent clinician who rated 10 randomly selected session tapes | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: SCLD interview, DRS Self‐report: BAI, BDI, STAI‐T, PSWQ, Revised Hopkins Symptom Checklist‐90 | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 24 Overall dropout rate: 22.2 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Mohlman 2003b.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: assessors unaware of treatment condition Trial duration: 13 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: mental health clinic Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 15 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of GAD, according to DSM‐IV criteria Comorbidity: 8 (57%) | |
| Interventions | 1. Enhanced CBT Modality: individual Intensity: 13 50‐min weekly sessions, followed by monthly booster sessions for 6 months Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested by independent clinician who rated 10 randomly selected session tapes | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: SCLD interview, DRS Self‐report: BAI, BDI, STAI‐T, PSWQ, Revised Hopkins Symptom Checklist‐90 | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 24 Overall dropout rate: 9 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Ost 2000.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: independent assessors Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Setting: O/P psychology dept Population: adult volunteers and referred by GP Sample size: 36 Diagnosis: GAD, according to DSM‐III‐R criteria Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. Applied relaxation Modality: individual Intensity: 12 50‐60 minute sessions over 12 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: ADIS‐R, HAM‐A and HRSD Self‐report: BAI, STAI‐T, PSWQ, BDI, Cognitive Somatic Anxiety Questionnaire | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 27 Overall dropout rate: 8.3 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Stanley 1996.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level in groups of 4‐6 ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 14 weeks Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Setting: university health sciences centre Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 48 Diagnosis: primary diagnosis of GAD, based on diagnostic interview using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: 58% had secondary MH diagnoses | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Non‐directive supportive therapy Modality: group Intensity: 14 weekly 90‐min sessions over 14 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: tested by clinical psychologist who assessed videotapes using a checklist | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: ADIS‐R, HAMA, HAMD Self‐report: Worry Scale, PSWQ, STAI, BDI, FQ | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 26 Overall dropout rate: 31.2 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Stanley 2003.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: university health sciences centre Population: elderly identified through waiting‐room screens, referred by physician or volunteers Sample size: 12 Diagnosis: GAD according to Structured Diagnostic Interview for DSM‐IV Comorbidity: 67% had secondary MH diagnoses | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Treatment as usual Modality: individual Intensity: 8 weekly sessions, with 2 additional sessions as required Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Clinician‐rated: GAD section of SCID Self‐report: PSWQ, BAI, BDI, QOL Inventory, SF‐36, CSQ, Expectancy Rating Scale. | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 21 Overall dropout rate: 25 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Wetherell 2003a.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level in three's using coin toss Blinding: assessors unaware of treatment condition assignation Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Setting: university dept of psychiatry Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 75 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of GAD, according to DSM‐IV criteria, using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: 52% had a comorbid psychiatric diagnosis and the majority had physicial comorbidity | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Discussion group 3. Waiting list Modality: group (4‐6 in each group) Intensity: 12 90 minute weekly sessions over 12 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: rater unaware of study hypotheses coded three randomly selected tapes from each group using a codebook and form | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: ADIS‐IV, HAMA, HAM‐D Self‐report: PSWQ, BAI, BDI, SF‐36 | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 31 Overall dropout rate: 24 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
Wetherell 2003b.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level in three's using coin toss Blinding: assessors unaware of treatment condition assignation Trial duration: 12 weeks Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Setting: university dept of psychiatry Population: elderly volunteers Sample size: 75 Diagnosis: principal diagnosis of GAD, according to DSM‐IV criteria, using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: 52% had a comorbid psychiatric diagnosis and the majority had physicial comorbidity | |
| Interventions | 1. CBT 2. Discussion group 3. Waiting list Modality: group (4‐6 in each group) Intensity: 12 90 minute weekly sessions over 12 weeks Manualised: yes Treatment fidelity: rater unaware of study hypotheses coded three randomly selected tapes from each group using a codebook and form | |
| Outcomes | Clinician rated: ADIS‐IV, HAMA, HAM‐D Self‐report: PSWQ, BAI, BDI, SF‐36 | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 31 Overall dropout rate: 24 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
White 1992.
| Methods | Allocation: randomised at patient level into groups Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 6 weeks Follow‐up: 6 months, 2 years | |
| Participants | Setting: clinical psychology primary care service Population: adults referred by local GPs Sample size: 141 Diagnosis: Primary diagnosis of GAD according to DSM‐III criteria, using ADIS‐R Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. CT 2. BT 3. CBT 4. Placebo‐subconscious retraining 5. waiting lis Modality: group (20‐24 in each group) Intensity: 6 2‐hour weekly sessions over 6 weeks Manualised: yes (booklets) Treatment fidelity: sessions audiotaped ‐ 2 session tapes randomly selected from each of the 4 conditions and given to 'blind' CBT‐trained clinical psychologists | |
| Outcomes | Self‐report: STAI‐T, DAS, BDI, Fear Survey Schedule, Modified Somatic Perception Questionnaire, global ratings of anxiety and coping, credibility/expectation ratings GP rating ‐ number of consultations over 6 months pre/post treatment and number of benzodiazepine prescriptions | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 22 Overall dropout rate: 10.7 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | D ‐ Not used |
Woodward 1980.
| Methods | Allocation: simple randomisation process at patient level into groups ‐ method not reported Blinding: not reported Trial duration: 8 weeks Follow‐up: none | |
| Participants | Setting: hospital clinical psychology dept Population: adult clinic attendees Sample size: 27 Diagnosis: General anxiety defined as neurotic anxiety in the absence of a specific phobia made by psychologist in dept Comorbidity: not reported | |
| Interventions | 1. Modified symptomatic desensitization 2. Cognitive restructuring 3. Combined cognitive behaviour modification 4. No treatment Modality: group (6‐7 in each group) Intensity: 8 weekly 75‐minute sessions over 8 weeks Manualised: based on Meichenbaum 1974 manual Treatment fidelity: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Self‐report: Zung anxiety scale, Fear thermometer, What can I do? Form, cognitive anxiety measure, Fear Survey Schedule, Internal/External Control Scale | |
| Notes | QRS total score: 13 Overall dropout rate: 0 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Key for scale acronyms (see outcomes): ADIS‐IV ‐ Anxiety Disorders Inventory Schedule, BDI ‐ Beck Depression Inventory; CAQ ‐ Cognitive Anxiety Questionnaire; CGIS ‐ Clinical Global Inventory Schedule: DAQ ‐ Dysfunctional Attitude Questionnaire; HAMA ‐ Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety; HADS ‐ Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; DIS‐R ‐ Diagnostic Interview Schedule ‐ Revised; EPI ‐ Eysenck Personality Inventory; FQ ‐ Fear Questionnaire; GAF ‐ Global Assessment of Functioning scale; HAM‐D ‐ Hamilton Depression Scale; PSWQ ‐ Penn State Worry Questionnaire; SAS ‐ Social Adjustment Scale; STAI‐T ‐ Trait subscale of State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory; SF‐36 ‐ Quality of Life Short Form‐36; CSQ‐Client Satisfaction Questionnaire
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Barlow 1984 | 50% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| Barrowclough 2001 | 81% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| Borkovec 1988 | 40% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| Borkovec 2002 | Dismantling study examining differing components of cognitive therapy |
| Bowman 1997 | Intervention was a 45‐page booklet on anxiety management, Contact with research staff was limited to a weekly 5 minute telephone call, with no therapy provided. |
| Durham 1999 | Study compared differing intensity of CBT over a six month period (10 versus 20 sessions) |
| Hutchings 1980 | Students were screened for general anxiety state ‐ no diagnostic interview conducted by clinicians |
| Kitchiner 2006 | <80% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| Norton 2005 | 57% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| Papp 1998 | Primary aim of study was reduction/tapering in anxiolytics, therefore all participants were on prescribed medication that altered in dosage over the course of the study |
| Svartberg 1998 | 85% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| van Boeijen 2005 | 68% of sample had anxiety disorders other than GAD as a primary diagnosis |
| White 1995 | The psychological intervention was limited to bibliotherapy ('Stresspac'), and the face‐to‐face intervention ('Advice Only') did not include a psychological component. |
| Zuellig 2003 | Study examined differing CT components |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Borkovec 2003.
| Trial name or title | Cognitive behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder with integrations from interpersonal and experiential therapies |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Patients with generalized anxiety disorder |
| Interventions | CBT plus Interpersonal and Emotional Processing Therapy versus CBT plus Reflective Listening Control |
| Outcomes | |
| Starting date | Data collection has been completed and analyses are being conducted |
| Contact information | Thomas D Borkovec Penn State University tdb@psu.edu |
| Notes |
Roemer 2004.
| Trial name or title | Acceptance based treatment for generalized anxiety disorder |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Patients over the age of 18 with generalised anxiety disorder |
| Interventions | Intervention: Acceptance and mindfulness‐based strategies+CBT vs no treatment |
| Outcomes | anxiety and depression outcomes |
| Starting date | Data collection has been completed and preliminary analyses are being conducted |
| Contact information | Dr Lizabeth Roemer University of Massachusetts lizabeth.roemer@umb.edu |
| Notes |
Wetherell 2005.
| Trial name or title | The CALM study: Controlling Anxiety in Later‐life Medical Patients |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Patients over the age of 60 diagnosed with diffuse anxiety (GAD, anxiety NOS, mixed anxiety/depression) |
| Interventions | Intervention: a psychological therapy tailored for the elderly ‐ 12 individual sessions of skills training on coping with anxiety, problem‐solving and pain management, together with a life review Control: usual care |
| Outcomes | STAI‐T, BDI, PSWI, SF‐36 |
| Starting date | Data collection has been completed |
| Contact information | Julie Loebach Wetherell PhD University of California jwetherell@ucsd.edu |
| Notes | Lead investigator has reported that 80% of participants have a primary diagnosis of GAD |
Contributions of authors
April 2003: VT submitted an amended version of the published protocol under the supervision of MSdL. Nov 2005: VT submitted an initial draft of the review, under the supervision of MSdL, with 8 studies included Feb 2006: VH made changes to the protocol in response to editorial feedback received on the updated version of the published protocol, RC provided comments on the revised version of the updated protocol. July 2006: VH and RC selected an additional 17 studies for inclusion, VH extracted data for all 25 studies Aug 2006: VH entered data for all studies and conducted meta‐analyses Sept 2006: VT checked selection of additional studies, VT and RC extracted data from 17 additional studies, VH interpreted and wrote up results Oct 2006: VH wrote up discussion, RC provided comments on revised/updated draft review
Sources of support
Internal sources
Institute of Psychiatry, UK.
Universidade Federal de Pelotas, Brazil.
External sources
Department of Health, UK.
Declarations of interest
MSL took up a position with Eli Lilly in 2003.
Please note that the current version of this review contravenes Cochrane's commercial sponsorship policy (revised 2014). The protocol for this review is being re‐written and publication of the new review is scheduled for 2016/17.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Akkerman 2001 {published data only}
- Akkerman RL, Stanley MA, Averill PM, Novy DM, Snyder AG, Diefenbach GJ. Recruiting older adults with generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Mental Health and Aging 2001;7(4):385‐94. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley MA, Beck JG, Novy DM, Averill PM, Swann AC, Diefenbach GJ, & Hopko DR. Cognitive‐behavioral treatment of late‐life generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;71(2):309‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley MA, Novy DM, Bourland SL, Beck JG, Averill PM. Assessing older adults with generalized anxiety: a replication and extension. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2001;39(2):221‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Arntz 2003 {published data only}
- Arntz A. Cognitive therapy versus applied relaxation as treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Behav Res Ther 2003 Jun;41(6):633‐46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barlow 1992 {published data only}
- Barlow DH, Rapee RM, Brown TA. Behavioral treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Behavior Therapy 1992;23:551‐70. [Google Scholar]
Blowers 1987 {published data only}
- Blowers C, Cobb J, Mathews A. Generalised anxiety: a controlled treatment study. Behavioural Research and Therapy 1987;25(6):493‐502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bond 2002a {published data only}
- Bond A, Wingrove J. A controlled trial of buspirone and anxiety management training in the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1992;15(1 Pt B):618. [Google Scholar]
- Bond A, Wingrove J, Lader M. Combined treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. WPA Thematic Conference Jerusalem November 1997.
- Bond AJ, Wingrove J, Curran HV, Lader MH. Treatment of generalised anxiety disorder with a short course of psychological therapy, combined with buspirone or placebo. Journal of Affective Disorders 2002;72:267‐271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bond 2002b {published data only}
- Bond A, Wingrove J. A controlled trial of buspirone and anxiety management training in the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1992;15(1 Pt B):618. [Google Scholar]
- Bond A, Wingrove J, Lader M. Combined treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. WPA Thematic Conference Jerusalem November 1997.
- Bond AJ, Wingrove J, Curran HV, Lader MH. Treatment of generalised anxiety disorder with a short course of psychological therapy, combined with buspirone or placebo. Journal of Affective Disorders 2002;72:267‐271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 1987 {published data only}
- Borkovec TD, Mathews AM, Chambers A, Ebrahimi S, Lytle R, Nelson R. The effects of relaxation training with cognitive or nondirective therapy and the role of relaxation‐induced anxiety in the treatment of generalized anxiety. J Consult Clin Psychol 1987 Dec;55(6):883‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson RA, Borkovec TD. Relationship of client participation to psychotherapy. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry 1989;20(2):155‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 1993 {published data only}
- Borkovec TD, Abel JL, Newman H. Effects of psychotherapy on comorbid conditions in generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1993;63(3):479‐83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovec TD, Costello E. Efficacy of applied relaxation and cognitive‐behavioral therapy in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1993 Aug;61(4):611‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Butler 1991 {published data only}
- Butler G. Predicting outcome after treatment for generalised anxiety disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1993;31(2):211‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G, Fennell M, Robson P, Gelder M. Comparison of behavior therapy and cognitive behavior therapy in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 1991 Feb;59(1):167‐75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dugas 2003 {published data only}
- Belanger L, Morin CM, Langlois F, Ladouceur R. Insomnia and generalized anxiety disorder: effects of cognitive behavior therapy for GAD on insomnia symptoms. Journal of Anxiety Disorders 2004;18(4):561‐71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugas MJ, Ladouceur R, Leger E, Freeston MH, Langlois F, Provencher MD, Boisvert JM. Group cognitive‐behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: treatment outcome and long‐term follow‐up. J Consult Clin Psychol 2003 Aug;71(4):821‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Durham 1987 {published data only}
- Durham RC, Turvey AA. Cognitive therapy vs behaviour therapy in the treatment of chronic general anxiety. Behavioural Research and Therapy 1987;25(3):229‐34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Durham 1994a {published data only}
- Durham RC, Allan T, Hackett CA. On predicting improvement and relapse in generalized anxiety disorder following psychotherapy. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1997;36(Pt 1):101‐19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Chambers JA, MacDonald RR, Power KG, Major K. Does cognitive‐behavioural therapy influence the long‐term outcome of generalized anxiety disorder? An 8‐14 year follow‐up of two clinical trials. Psychological Medicine 2003;33(3):499‐509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Fisher PL, Treliving LR, Hau CM, Richard K, Stewart JB. One year follow‐up of cognitive therapy, analytic psychotherapy and anxiety management training for generalized anxiety disorder: symptom change, medication usage and attitudes to treatment.. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 1999;27(1):19‐35. [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Murphy T, Allan T, Richard K, Treliving LR, Fenton GW. Cognitive therapy, analytic psychotherapy and anxiety management training for generalised anxiety disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994 Sep;165(3):315‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Durham 1994b {published data only}
- Durham RC, Allan T, Hackett CA. On predicting improvement and relapse in generalized anxiety disorder following psychotherapy. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1997;36(Pt 1):101‐19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Chambers JA, MacDonald RR, Power KG, Major K. Does cognitive‐behavioural therapy influence the long‐term outcome of generalized anxiety disorder? An 8‐14 year follow‐up of two clinical trials. Psychological Medicine 2003;33(3):499‐509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Fisher PL, Treliving LR, Hau CM, Richard K, Stewart JB. One year follow‐up of cognitive therapy, analytic psychotherapy and anxiety management training for generalized anxiety disorder: symptom change, medication usage and attitudes to treatment. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 1999;27(1):19‐35. [Google Scholar]
- Durham RC, Murphy T, Allan T, Richard K, Treliving LR, Fenton GW. Cognitive therapy, analytic psychotherapy and anxiety management training for generalised anxiety disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994 Sept;165(3):315‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gath 1986 {published data only}
- Butler G, Anastasiades P. Predicting response to anxiety management in patients with generalised anxiety disorders. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1988;26(6):531‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gath D, Catalan J. The treatment of emotional disorders in general practice: psychological methods versus medication. Journal of Psychosomatic Research 1986;30(3):381‐386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jannoun 1982 {published data only}
- Jannoun L, Oppenheimer C, Gelder M. A self‐help treatment program for anxiety state patients. Behavior Therapy 1982;13:103‐111. [Google Scholar]
Ladouceur 2000 {published data only}
- Ladouceur R, Dugas MJ, Freeston MH, Leger E, Gagnon F, Thibodeau N. Efficacy of a cognitive‐behavioral treatment for generalized anxiety disorder: evaluation in a controlled clinical trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2000 Dec;68(6):957‐64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lavallee 1993 {published data only}
- Lavallee YJ, Jolicoeur FB, Lepage D, Boulenger JP. Are benzodiazepines useful in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorders?. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1993;3(3):364. [Google Scholar]
Linden 2002 {published data only}
- Linden M, Bar T, Zubragel D, Ahrens B, Schlattmann P. Effectiveness of the cognitive behavior therapy in the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorders ‐ Results of the Berlin GAD‐KVT‐study. Verhaltenstherapie 2002;12(3):173‐81. [Google Scholar]
- Linden M, Zubraegel D, Baer T, Franke U, Schlattmann P. Efficacy of cognitive behaviour therapy in generalized anxiety disorders. Results of a controlled clinical trial (Berlin CBT‐GAD Study). Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2005;74(1):36‐42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lindsay 1987 {published data only}
- Lindsay WR, Gamsu CV, McLaughlin E, Hood EM, Espie CA. A controlled trial of treatments for generalized anxiety. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1987;26:3‐15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mohlman 2003a {published data only}
- Mohlman J, Gorenstein EE, Kleber M, Jesus M, Gorman JM, Papp LA. Standard and enhanced cognitive‐behavior therapy for late‐life generalized anxiety disorder: two pilot investigations. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003 Jan‐Feb;11(1):24‐32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mohlman 2003b {published data only}
- Mohlman J, Gorenstein EE, Kleber M, Jesus M, Gorman JM, Papp LA. Standard and enhanced cognitive‐behavior therapy for late‐life generalized anxiety disorder: two pilot investigations. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003 Jan‐Feb;11(1):24‐32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ost 2000 {published data only}
- Ost LG, Breitholtz E. Applied relaxation vs. cognitive therapy in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2000;38:777‐790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stanley 1996 {published data only}
- Stanley MA, Beck JG, Glassco JD. Treatment of generalized anxiety in older adults: a preliminary comparison of cognitive‐behavioral and supportive approaches. Behavior Therapy 1996;27:565‐581. [Google Scholar]
Stanley 2003 {published data only}
- Stanley MA, Hopko DR, Diefenbach GJ, Bourland SL, Rodriguez H, Wagener P. Cognitive‐behavior therapy for late‐life generalized anxiety disorder in primary care: preliminary findings. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;11:92‐96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetherell 2003a {published data only}
- Wetherell JL, Gatz M, Craske MG. Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder in older adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2003;71:31‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wetherell 2003b {published data only}
- Wetherell JL, Gatz M, Craske MG. Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder in older adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2003;71:31‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
White 1992 {published data only}
- White J, Brooks N, Keenan M. Stress control: a controlled comparative investigation of large group therapy for generalized anxiety disorder: process of change. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy 1995;2(2):86‐97. [Google Scholar]
- White J, Keenan M, Brooks N. Stress control: a controlled comparative investigation of large group therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. Behavioural Psychotherapy 1992;20:97‐114. [Google Scholar]
Woodward 1980 {published data only}
- Woodward R, Jones RB. Cognitive restructuring treatment: a controlled trial with anxious patients. Behavior Research and Therapy 1980;18:401‐407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Barlow 1984 {published data only}
- Barlow DH. Panic and generalized anxiety disorders: Nature and treatment. Behavior Therapy 1984;15:431‐449. [Google Scholar]
Barrowclough 2001 {published data only}
- Barrowclough C, King P, Coville J, Russell E, Burns A, Tarrier N. A randomized trial of the effectiveness of cognitive‐bheavioral therapy and supportive counseling for anxiety symptoms in older adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;69:756‐762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 1988 {published data only}
- Borkovec TD, Mathews AM. Treatment of nonphobic anxiety disorders: a comparison of nondirective, cognitive and copying desensitization therapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56:877‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 2002 {published data only}
- Borkovec TD, Newman MG, Pincus AL, Lytle R. A component analysis of cognitive‐behavioural therapy for generalized anxiety disorder and the role of interpersonal problems. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56:877‐884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bowman 1997 {published data only}
- Bowman D, Scogin F, Floyd M, Patton E, Gist L. Efficacy of self‐examination therapy in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Counseling Psychology 1997;3:267‐273. [Google Scholar]
Durham 1999 {unpublished data only}
- Durham RC. Doubling the intensity of standard cognitive‐behavioural therapy for poor prognosis outpatients with generalised anxiety disorder: Is it effective?. National Research Register 1999.
Hutchings 1980 {published data only}
- Hutchings DF, Denney DR, Basgall J, Houston BK. Anxiety management and applied relaxation in reducing general anxiety. Behavioral Research and Therapy 1980;18:181‐190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kitchiner 2006 {unpublished data only}
- Kitchiner NJ, Bisson JI, Edwards D, Wood S, Sainsbury S, Hewin P, Burnard P. A Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing an Adult Education Class Using Cognitive Behavioural Therapy ('Stress Control'), Anxiety Management Group Treatment and a Waiting List for Anxiety Disorders. Journal of Mental Health in submission.
Norton 2005 {published data only}
- Norton PJ, Hope DA. Preliminary evaluation of a broad‐spectrum cognitive‐behavioral group therapy for anxiety. Journal of Behavior Therapy 2005;36:79‐97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Papp 1998 {published data only}
- Papp, LA. Psychosocial treatment in late‐life anxiety. 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, Ontario, Canada. 30th May ‐ 4th June. 1998.
Svartberg 1998 {published data only}
- Svartberg M, Seltzer M, Stiles TC. The effects of common and specific factors in short‐term anxiety‐provoking psychotherapy: a pilot process‐outcome study. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1998;186:691‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van Boeijen 2005 {published data only}
- Boeigen CA, Oppen P, Balkom AJLM, Visser S, Kempe PT, Blankenstein N, Dyck R. Treatment of anxiety disorders in primary care practice: a randomised controlled trial. British Journal of General Practice 2005;55:763‐769. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
White 1995 {published data only}
- White J. "Stresspac": three‐year follow‐up of a controlled trial of a self‐help package for the anxiety disorders. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 1998;26:133‐141. [Google Scholar]
Zuellig 2003 {unpublished data only}
- Zuellig AR. A comparison of the effect of three therapies on generalized anxiety disordered adults' self‐reported internal working models of attachment. Dissertation Abstract 2003.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Sachs 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Sachs AD. Integrating aceptance with imaginal exposure to core schema: Process and outcome in generalized anxiety disorder. Dissertation Abstracts International 2005; Vol. Section B: The Sciences and Engineering, issue 65(9‐B):4850.
References to ongoing studies
Borkovec 2003 {unpublished data only}
- Borcovec TD, Newman MG, Castonguay LG. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder with integrations from interpersonal and experiential therapies. CNS Spectrums 2003;8(5):382‐389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Roemer 2004 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Roemer L. Developing a new therapy for GAD: acceptance‐based CBT. ClinicalTrials.gov 2004.
Wetherell 2005 {published and unpublished data}
- Wetherell JL, Sorrell JT, Thorp SR, Patterson TL. Psychological interventions for late‐life anxiety: a review and early lessons from the CALM Study. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology 2005;18:72‐82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Altman 1996
- Altman DG, Bland JM. Detecting skewness from summary information. BMJ 1996;313(7066):1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
APA 1980
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III). 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press, 1980. [Google Scholar]
APA 1987
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III‐R). 3rd Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987. [Google Scholar]
APA 1994
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994. [Google Scholar]
Balint 1972
- Balint M, Ornstien PO, Balint E. Focal Psychotherapy. London: Tavistock, 1972. [Google Scholar]
Ballenger 2001
- Ballenger JC, Davidson JR, Lecrubier Y, Nutt DJ, Borkovec TD, Rickels K, et al. Consensus statement on generalized anxiety disorder from the International Consensus Group on Depression and Anxiety. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2001;62:53‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barrett‐Lennard 1986
- Barrett‐Lennard GT. The relationship inventory now: Issues and advances in theory, method and use. In: Greenberg LS, Pinsof W editor(s). The Psychotherapeutic Process: A Research Handbook. New York, NY: Guildford Press, 1986:439‐76. [Google Scholar]
Beck 1979
- Beck AT, Rush AJ, Shaw BF, Emery G. Cognitive Therapy of Depression. New York, NY: Guildford Press, 1979. [Google Scholar]
Beck 1987
- Beck AT, Steer R. Beck Depression Inventory: Manual. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation, 1987. [Google Scholar]
Beck 1988
- Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: Psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56:893‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berne 1961
- Berne E. Transactional Analysis in Psychotherapy. New York, NY: Grove Press, 1961. [Google Scholar]
Berstein 1973
- Bernstein DA, Borkovec TD. Progressive relaxation training. Champaign, IL: Research Press, 1973. [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 1996
- Borkovec TD, Whisman MA. Psychosocial treatments for generalized anxiety disorder. In M. Mavissakalian & R Prien (Eds.), Long‐term treatment of anxiety disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1996. [Google Scholar]
Borkovec 2001
- Borkovec TD, Ruscio AM. Psychotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2001;62 Suppl 11:15‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Butler 2006
- Butler AC, Chapman JE, Forman EM, Beck AT. The empirical status of cognitive‐behavioral therapy: a review of meta‐analyses. Clinical Psychology Review 2006;26:17‐31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chessick 2006
- Chessick C, Allen M, Thase M, Batista Miralha da Cunha A, Kapczinski F, Lima M, et al. Azapirones for generalized anxiety disorder. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006115] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Churchill 2000
- Churchill R, Khaira M. Gretton V, Chilvers C, Dewey M, Duggan C, et al. Treating depression in general practice: factors affecting patients' treatment preferences. British Journal of General Practice 2000;50:905‐6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Clarke 2002
- Clarke M, Oxman AD, editors. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.1.5. Oxford: Update Software, 2002. [Google Scholar]
Deacon 2004
- Deacon BJ, Abramowitz JS. Cognitive and behavioral treatments for anxiety disorders: a review of meta‐analytic findings. Journal of Clinical Psychology 2004;60:429‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deeks 1997
- Deeks J. Are you sure that's a standard deviation? (part 1). Cochrane News 1997;10:11‐2. [Google Scholar]
DeRubeis 1998
- DeRubeis RJ, Crits‐Christoph P. Empirically supported individual and group psychological treatments for adult mental disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;1:37‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Di Nardo 1994
- Nardo PA, Brown TA, Barlow DH. Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule for DSM‐IV (ADIS‐IV). San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation, 1994. [Google Scholar]
DoH 2001
- British Psychological Society Centre for Outcomes Research and Effectiveness. Treatment choice in psychological therapies and counselling: evidence based clinical practice guideline. Department of Health Publications. London: Department of Health, 2001.
Ellis 1962
- Ellis A. Reason and emotion in psychotherapy. New York, NY: Lyle Stuart, 1962. [Google Scholar]
Fisher 1999
- Fisher PL, Durham RC. Recovery rates in generalized anxiety disorder following psychological therapy: an analysis of clinically significant change in the STAI‐T across outcome studies since 1990. Psychological Medicine 1999;29:1425‐34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Freud 1949
- Freud S. An Outline of Psychoanalysis. London: Hogarth Press, 1949. [Google Scholar]
Furukawa 2005
- Furukawa TA, Cipriani A, Barbui C, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing response rates from means and standard deviations in meta‐analyses. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2005;1:49‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gould 1997
- Gould RA, Otto MW. Pollack MH, Yap L. Cognitive behavioural and pharmacological treatment of generalized anxiety disorders: a preliminary meta‐analysis. Behaviour Therapy 1997;28(2):285‐305. [Google Scholar]
Greenberg 1999
- Greenberg PE, Sisitsky T, Kessler RC, Finkelstein SN, Berndt ER, Davidson JR, et al. The economic burden of anxiety disorders in the 1990s. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1999;60(7):427‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hamilton 1959
- Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. British Journal of Medical Psychology 1959;32:50‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hamilton 1960
- Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1960;23:56‐62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. BMJ 2003;327(6):557‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jacobson 1991
- Jacobson NS, Truax P. Methods for defining and determining the clinical significance of treatment effects in mental health reserach: current status, new applications and future directions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1991;59:12‐19. [Google Scholar]
Kapczinski 2003
- Kapczinski F, Lima MS, Souza JS, Cunha A, Schmitt R. Antidepressants for generalised anxiety disorder. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003592] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Katon 1990
- Katon W, Korff M, Lin E, Lipscomb P, Russo J, Wagner E, et al. Distressed high utilizers of medical care. DSM‐III‐R diagnoses and treatment needs. General Hospital Psychiatry 1990;12:355‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kessler 1994
- Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zao S, Nelson CB, Hughes M, Eshleman S, et al. Lifetime and 12‐ month prevalence of DSM‐III‐R psychiatry disorders in the United States. Archives of General Psychiatry 1994;51(1):8‐19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kessler 2000
- Kessler RC. The epidemiology of pure and comorbid generalized anxiety disorder: a review and evaluation of recent research. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. Supplementum 2000;406:7‐13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Law 2003
- Law J, Garrett Z, Nye C. Speech and language therapy interventions for children with primary speech and language delay or disorder. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004110] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Layard 2004
- Layard, Lord R. Mental health: Britain's biggest social problem?. http://www.strategy.gov.uk/downloads/files/hm_layard.pdf 2004.
Malan 1963
- Malan DH. A Study of Brief Psychotherapy. London: Plenum, 1963. [Google Scholar]
Mann 1973
- Mann J. Time‐Limited Psychotherapy. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1973. [Google Scholar]
Marks 1979
- Marks IM, Mathews AM. Brief standard self‐rating for phobic patients. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1979;17:263‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Massion 1993
- Massion AO, Warshaw MG, Keller MB. Quality of life and psychiatric morbidity in panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry 1993;150(4):600‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meyer 1990
- Meyer TJ, Miller ML, Metzger RL, Borkovec TD. Development and validation of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1990;28:487‐95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
MHF 2003
- Annual Report. Mental Health Foundation: 2003.
Mohlman 2004
- Mohlman J. Psychosocial treatment of late‐life generalized anxiety disorder: current status and future directions. Clinical Psychology Review 2004;24:149‐169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moncrieff 2001
- Moncrieff J, Churchill R, Drummond C, McGuire H. Development of a quality assessment instrument for trials of treatments for depression and neurosis. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 2001;10:126‐33. [Google Scholar]
NICE 2004
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Management of anxiety in adults in primary, secondary and community care: Clinical Guideline 22. London: National Institute for Clinical Excellence, December 2004. [Google Scholar]
Ost 1987
- Ost LG. Applied relaxation: description of a coping technique and review of controlled studies. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1987;25:397‐409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perls 1976
- Perls F. The Gestalt Approach & Eye Witness to Therapy. New York, NY: Bantam Books, 1976. [Google Scholar]
Priest 1996
- Priest RG, Vize C, Roberts A, Roberts M, Tylee A. Lay people's attitudes to treatment of depression: results of opinion poll for Defeat Depression Campaign just before its launch. BMJ 1996;313:858‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rickels 1990
- Rickels K, Schweizer E. The clinical course and long‐term management of generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1990;10 3 Suppl:101S‐110S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Riedel‐Heller 2005
- Ridel‐Heller SG, Matschinger H, Angermeyer MC. Mental disorders ‐ who and what might help? Help‐seeking and treatment preferences of the lay public. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 2005;40:167‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rogers 1951
- Rogers C. Client‐Centered Therapy. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 1951. [Google Scholar]
Roth 2005
- Roth A, Fonagy P. What Works for Whom. 2nd Edition. London: Guildford Press, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Ryle 1990
- Ryle, A. Cognitive‐analytic therapy: Active participation in chanrge, a new integration in brief psychotherapy. Chichester: Wiley, 1990. [Google Scholar]
Sartorius 1993
- Sartorius N, Ustun TB, Costa e Silva JA, Goldberg D, Lecrubier Y, Ormel J, et al. An international study of psychological problems in primary care. Preliminary report from the World Health Organization Collaborative Project on 'Psychological Problems in General Health Care'. Archives of General Psychiatry 1993;50:819‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schulz 1995
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman D. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schweizer 1997
- Schweizer E, Rickels K. Strategies for treatment of generalized anxiety in the primary care setting. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58 Suppl 3:27‐31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sifneos 1992
- Sifneos PE. Short‐term Anxiety‐Provoking Psychotherapy: A Treatment Manual. New York, NY: Plenum, 1992. [Google Scholar]
Snaith 1976
- Snaith RP, Bridge GWK, Hamilton M. The Leeds scales for the self assessment of anxiety and depression. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;128:156‐65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Spielberger 1983
- Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene R, Vagg PR, Jacobs GA. Manual for the State‐Trait Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, 1983. [Google Scholar]
Stiles 2006
- Stiles BW, Barkham M, Twigg E, Mellor‐Clark J, Cooper M. Effectiveness of cognitive‐behavioural, personal‐centred and psychodynamic therapies as practised in UK National Health Service settings. Psychological Medicine 2006;36:555‐566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Suinn 1971
- Suinn RM, Richardson F. Anxiety Management Training: a nonspecific behavior therapy program for anxiety control. Behavior Therapy 1971;2:498‐510. [Google Scholar]
Suinn 1977
- Suinn RM. Manual: Anxiety Management Training. Fort Collins, CO: Rocky Mountain Behavioral Institute, 1977. [Google Scholar]
Tonks 2003
- Tonks A. Extracts from "Best Treatments": treating generalized anxiety disorder. BMJ 2003;326:700‐2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ware 1993
- Ware JE, Snow KK, Kosinski, Gandek B. SF‐36 Health Survey: Manual and 1993 Interpretation Guide.. Boston, MA: New England Medical Center, Health Institute, 1993. [Google Scholar]
Watson 1924
- Watson JB. Behaviorism. New York: Norton, 1924. [Google Scholar]
Weissman 1974
- Weissman MM, Paykel ES. The Depressed Woman: A Study of Social Relationships. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 1974. [Google Scholar]
Westen 2001
- Westen D, Morrison K. A multidimensional meta‐analysis of treatments for depression, panic and generalized anxiety disorder: an empirical examination of the status of empirically supported therapies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2001;69:875‐899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
WHO 1992
- World Health Organisation. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. Geneva: WHO, 1992. [Google Scholar]
Yonkers 1996
- Yonkers KA, Warshaw MG, Massion AO, Keller MB. Phenomenology and course of generalized anxiety disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry 1996;168:308‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zigmond 1983
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67:361‐70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zung 1965
- Zung WW. A self rating depression rating scale. Archives of General Psychiatry 1965;12:63‐70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zung 1975
- Zung WW. A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics 1975;12:371‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


