Abstract
Ca2Fe2O5 (CFO) is a potentially viable material for alternate energy applications. Incorporation of nitrogen in Ca2Fe2O5 (CFO-N) lattice modifies the optical and electronic properties to its advantage. Here, the electronic band structures of CFO and CFO-N were probed using Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and UV-Visible spectroscopy. The optical bandgap of CFO reduces from 2.21 eV to 2.07 eV on post N incorporation along with a clear shift in the valence band of CFO indicating the occupation of N 2p levels over O 2p in the valence band. Similar effect is also observed in the bandgap of CFO, which is tailored upto 1.43 eV by N+ ion implantation. The theoretical bandgaps of CFO and CFO-N were also determined by using the Density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The photoactivity of these CFO and CFO-N was explored by organic effluent degradation under sunlight. The feasibility of utilizing CFO and CFO-N samples for energy storage applications were also investigated through specific capacitance measurements. The specific capacitance of CFO is found to increase to 224.67 Fg−1 upon N incorporation. CFO-N is thus found to exhibit superior optical, catalytic as well as supercapacitor properties over CFO expanding the scope of brownmillerites in energy and environmental applications.
Subject terms: Energy science and technology, Materials science, Nanoscience and technology, Physics
Introduction
Multifunctional brownmillerite Ca2Fe2O5 is a promising material for energy and environmental applications such as fuel cells, supercapacitors, batteries, H2 production and CO2 capture, attributed mostly to its multifaceted property like those in catalysis and mixed ionic electronic conduction (MIEC)1–5. Presence of a visible region bandgap along with its catalytic activity also enables it as a photoactive material and most importantly as material for textile waste water remediation. There is a huge need for industrial waste water purification of the effluents from the textile industries before releasing it to water bodies. A lower cost and energy requirement pushes us to explore more efficient materials which can absorb a larger percentage of incident natural sunlight and make their impact felt on the environment6–10. Well known wide band gap semiconductors, such as TiO2 and ZnO (bandgap > 3 eV), cannot perfectly match the broad ranges of solar radiation emphasizing the need to investigate new materials/composites with narrow bandgap11. Quite recently perovskite metal oxides, such as PbTiO3 (2.75 eV), AgNbO3 (2.86 eV), SrNbO3 (1.9 eV), BiFeO3 (2.1 eV), LaFeO3 (2.4 eV), LaNiO3 (2.42 eV) have been found to possess reasonable catalytic efficiency12–19. This encourages us to work with novel materials like oxygen deficient perovskites for sunlight-driven photocatalysis.
To meet the above objectives, it is desirable to modify such structures with transition metal-Nx active sites to enhance the charge transport features and hence the catalytic activity towards remediation of industrial wastewater20,21. Recently, Nitrogen-doped layered perovskite K2La2Ti3O10 was shown to exhibit enhanced photocatalytic activity over Degussa P25 while degrading organic effluents under visible light22. Both LaNiO3 and double perovskite-structured rGO-NdBa0.5Sr0.5Co1.5Fe0.5O5+δ have also shown enhanced catalytic performance with N-doping23.
An efficient way to improve photocatalytic performance lies in reducing the electron-hole recombination24. Oxygen defects present in the photocatalysts act as photoinduced charge traps providing adsorption sites and transferring the charge to the adsorbed compounds, thus preventing the recombination of photogenerated charge carriers. The process results in an overall improvement of the photocatalytic performance. A perfect example is that of oxygen deficient perovskite showing an enhanced catalytic efficiency for H2 production as well as photocatalytic activity25–27. This makes it evident that the catalyst system incorporating the advantageous features of oxides with substantial oxygen vacancies and transition metal-N interaction in a single stable structure will have desirable enhanced catalytic activity. Ca2Fe2O5 (CFO) possesses a significant combination of oxygen vacancies as well as a narrow bandgap ~1.8 to 2.2 eV (falling under visible region of solar spectrum). Both perovskites and brownmillerites exhibit photocatalytic activity due to the existence of active FeO6 octahedra in the crystal structure. CFO composites and metal-supported brownmillerites have already been used for water-splitting and as well as for oxidizing CO28,29. Though these reports tend to reveal the photodegrading ability of CFO, the photodegradation rate is much slower. An efficient way to enhance the photocatalytic performance of brownmillerite CFO is by incorporating N for efficient wastewater treatment. Since CFO is a mixed ionic-electronic conductor (MIEC), it has a strong potential to be used for supercapacitor applications2,30,31. N incorporation in metal-oxides can enhance the electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance as well as stabilty. Some of these properties are desirable for supercapacitor applications32,33. Detailed investigation on the feasibility of using nitrogen incorporated CFO (CFO-N) for solar energy utilization as well supercapacitor applications is the focus of this work.
Experimental
Polycrystalline single phase Ca2Fe2O5 was synthesized by chemical route5. High pure chemicals of Ca, Fe nitrates were dissolved in water and proportionate amount of citric acid (CA) was added and stirred at room temperature. Ammonia solution was then added to maintain the pH ~ 6–7 and temperature of hot plate was increased to 80 °C. Once the solution turns viscous, ethylene glycol (EG) was added to the suspension to maintain the ratio of EG/CA as 1.2. The product was then heated at 300 °C to obtain a dry mass which was calcined at 700 °C for 6 h in box furnace to obtain nanostructured CFO. To enable N incorporation, as synthesized CFO was heated at 700 °C for 6 h in NH3 gas flow with a constant flow rate. The as-prepared powder sample was calcined at 500 °C for 4 h to avoid surface absorbed OH species and to obtain single phase nitrogen incorporated CFO (CFO-N).
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) of these samples were performed by a Bruker D2 X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation. The microstructure and elemental mapping of as-synthesized samples were recorded using scanning electron microscope (SEM, Jeol, 20KV) and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) respectively. The High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images were recorded using a field emission transmission electron microscope (JEOL) at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. The UV–visible absorption spectra of the samples were recorded on a UV–visible spectroscope (Jasco V-730). The chemical states present in CFO and CFO-N samples were analyzed using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) with Al Kα source from SPECS (XR 50) at the experimental station of angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES), Indus-2, India. To obtain atomically clean surface, the samples were sputtered with Argon ions at 1 keV for 10 min. C 1s (284.6 eV) was used to calibrate the peak position of the core levels. In order to investigate the valence band of CFO and CFO-N, the excitation energy of monochromatic He-1 line from SPECS (UVS 300) was used. The photoemission data was recorded with a SPECS Phoibos 150 electron energy analyzer and the base vacuum during the measurement was 7 × 10−11 mbar. Cyclic voltammetry and charge-discharge studies were investigated using Electrochemical workstation using Autolab (PGSTAT 204 FRA32M).
Results and Discussions
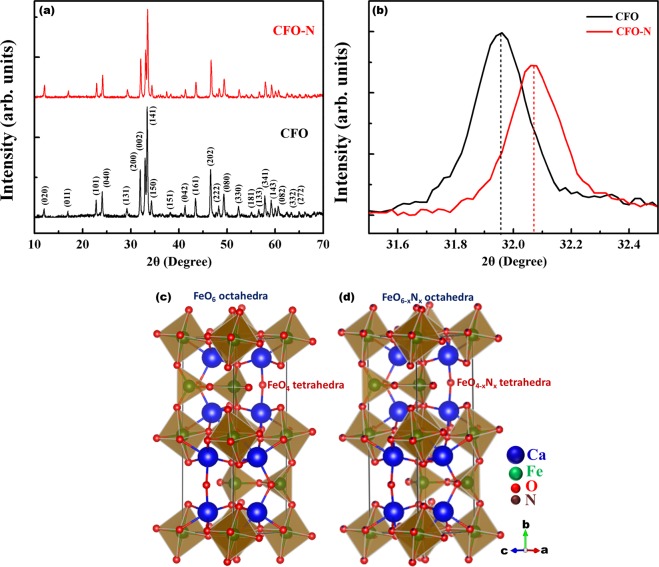
X-ray diffraction patterns of both CFO and CFO-N are shown in figure 1a are in good agreement with the orthorhombic crystal system. Figure 1b shows a shift in peak position for (200) in CFO-N towards higher 2θ values implying the N incorporation34,35. Figures 1(c,d) show the crystal structure of CFO and CFO-N. The oxygen sites of FeO6 octahedra and FeO4 tetrahedra are partially replaced with N atoms, leading to the formation of FeO6−xNx and FeO4−xNx in CFO-N.
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns for CFO and CFO-N (b) Magnified view of (200) plane in XRD showing a shift towards higher 2θ (c) Crystal structure of CFO with alternative layers of FeO6 octahedra and FeO4 tetrahedra (d) Crystal structure of CFO-N with partial incorporation of N in O sites.
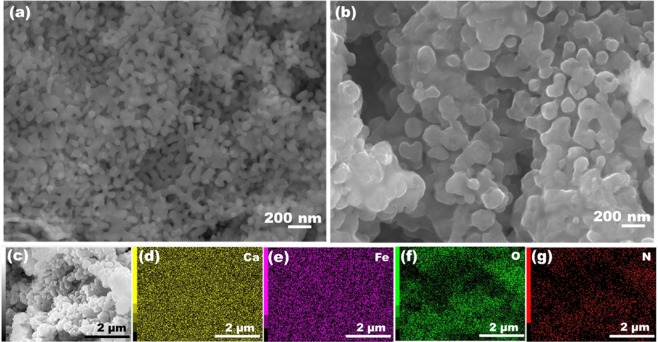
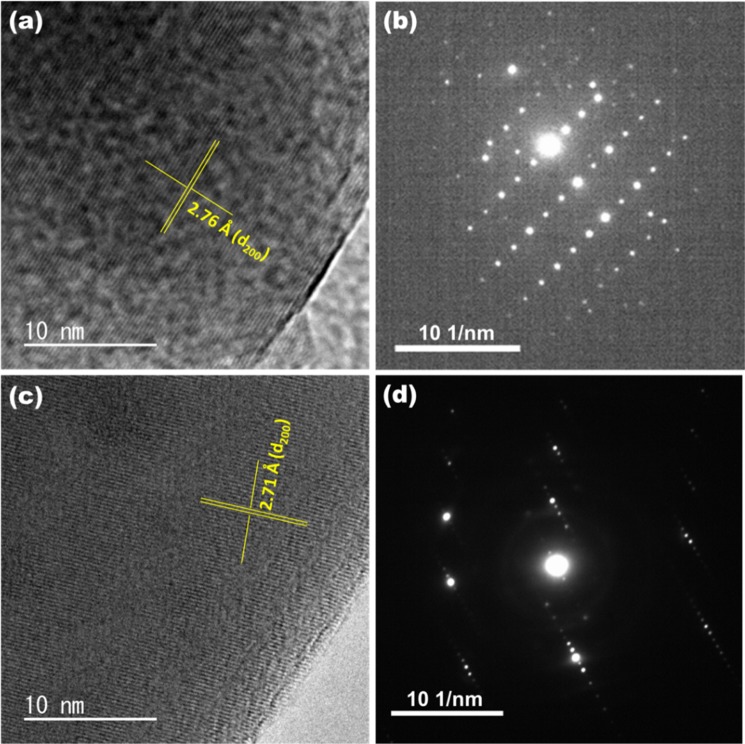
Figure 2a,b do not reveal any appreciable change in morphology upon N incorporation. EDX mapping of CFO-N (Fig. 2(c–g)) reveal the presence and uniform distribution of Ca, Fe, O and N elements throughout the compound. The EDX elemental mapping and spectra of CFO and CFO-N are shown in Figs. S1 and S2. EDX elemental mapping of CFO-N revealed that 3.36% atomic percentage of N was incorporated in CFO. Figure 3(a–d) show HRTEM and SAED micrographs of CFO and CFO-N samples having clear resolved crystalline domains corresponding to (200) lattice plane. The lattice spacing corresponding to (200) plane in CFO-N (2.71 Å) is found to be smaller than that of CFO (2.76 Å), which is also consistent with the small shift observed in XRD. The SAED pattern also establishes the crystalline nature of CFO and CFO-N samples.
Figure 2.
SEM images corresponding to (a and b) CFO and CFO-N (c–g) EDX mapping images of CFO-N sample showing uniform distribution of Ca, Fe, O and N elements.
Figure 3.
HRTEM and SAED images corresponding to (a,b) CFO and (c,d) CFO-N.
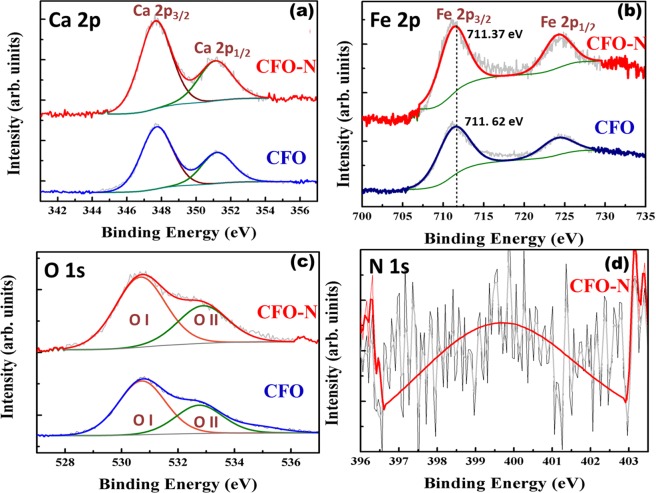
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements of CFO and CFO-N confirm the valence states of constituent elements, simultaneously pointing towards the presence of nitrogen in CFO-N. XPS spectra corresponding to Ca 2p of CFO and CFO-N (Fig. 4(a)) reveal a split into doublet due to spin-orbit coupling of Ca 2p3/2 and Ca 2p1/2 with binding energy difference ~3.42 eV and ~3.41 eV respectively. The split points toward the existence of Ca in 2+ oxidation state in both these samples. Similarly for Fe, the Fe2p splits into two spin orbits Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 peaks (Fig. 4(b)). The positions of Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2 spin orbits at 711.62 eV and 724.40 eV respectively for CFO confirms the existence of Fe in Fe3+ valence state36. A small shift in Fe 2p towards lower binding energy in CFO-N arises due to the replacement of O in Fe-O sites by N. Since N has lower electronegativity as compared to O, it leads to lower binding energy of Fe 2p in CFO-N by forming Fe-Nx sites37. The XPS spectra of O1s for CFO and CFO-N (Fig. 4(c)) were deconvoluted into two components at 530.72 eV (OI) and 532.75 eV (OII) for CFO and at 530.66 eV (OI) and 532.88 eV (OII) for CFO-N respectively. The OI component arises from the lattice oxygen, whereas OII is typical of hydroxyl and carbonate groups indicating possible chemisorption of oxygen species from the atmosphere31. The N 1s component appears at 399.5 eV (Fig. 4(d)) confirming the presence of nitrogen in CFO-N.
Figure 4.
X-ray photoelectron spectra and the corresponding fits belonging to CFO and CFO-N samples: (a) Ca 2p, (b) Fe 2p, and (c) O 1s, (d) N 1s.
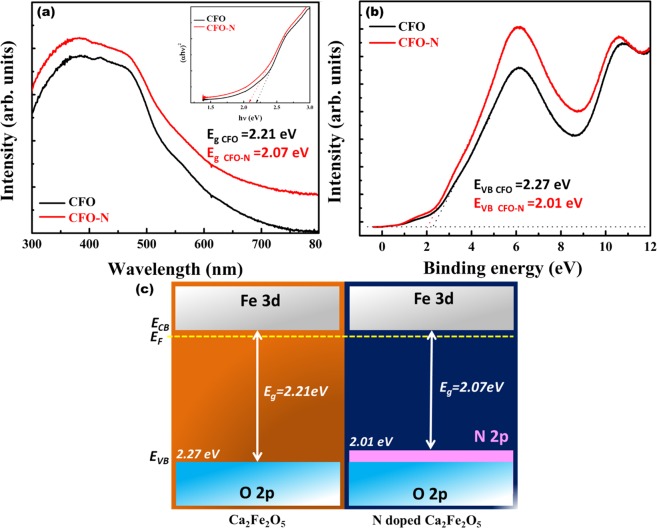
The electronic structures of CFO and CFO-N were probed by ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS) measurements. It is a well-established fact that the valence band maximum (VBM) calculation can be performed by considering the cutoff for the lowest binding energy. A clear decrease in VBM is observed in CFO-N (2.01 eV) compared with CFO (2.27 eV) shown in Fig. 5b. This points towards occupation of N 2p levels over O 2p levels in valence band leading to an effective reduction in bandgap due to the lower electronegativity of N and creation of Fe-Nx active sites in CFO-N. Figure 5(a) illustrates the UV-visible absorption spectra corresponding to CFO and CFO-N. The absorption edge of CFO-N shifts towards higher wavelength indicating a significant reduction in bandgap for CFO-N (2.07 eV) over CFO (2.21 eV) (inset Fig. 5a). The corresponding energy band diagrams of CFO and CFO-N are shown in Fig. 5(c).
Figure 5.
(a) UV-vis absorption spectra (inset shows corresponding Tauc plot) (b) Ultraviolet photoelectron spectra (c) Energy band diagram corresponding to CFO and CFO-N.
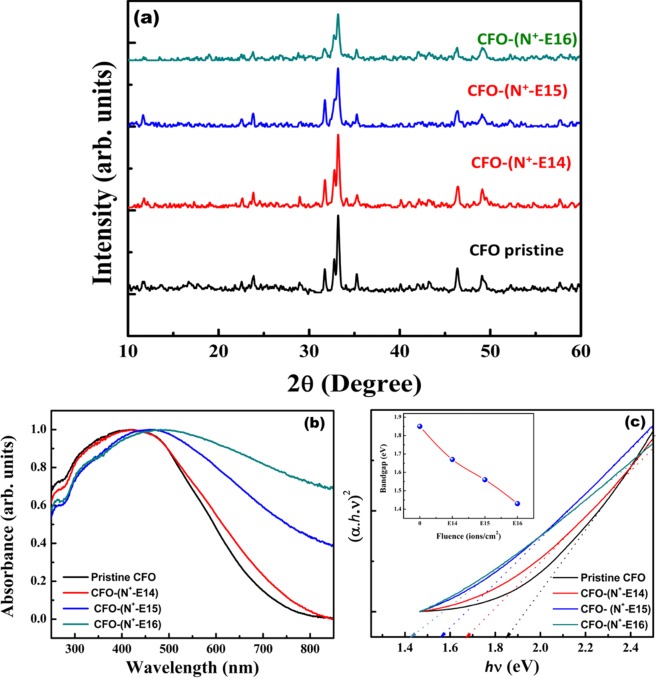
The bandgap of CFO could also be tailored by N+ ion implantation unlike conventional doping. In order to implant the N+ ions, Ca2Fe2O5 bulk films were fabricated on glass substrates using Doctor blade method. These CFO films were then implanted with 1 MeV of N+ ion beam with a beam current of 1 µA using low energy ion beam facility (LEIBF). The implantation was performed at three ion fluencies 1014, 1015 and 1016 ions per cm2, which were named as CFO-N+--E14, CFO-N+-E15 and CFO-N+-E16 respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were performed to investigate the effect of N ion implantation on the crystal structure and the nature of crystallinity of CFO films. Figure 6(a) shows the XRD patterns of pristine CFO and N implanted CFO films. No additional diffraction peaks corresponding to other phases are detected.
Figure 6.
(a) XRD pattern of pristine CFO, N ion implanted CFO films with fluencies of 1014, 1015 and 1016 ions/cm2. (b) UV-Vis absorption spectra of pristine CFO, N ion implanted CFO films (c) corresponding Tauc plot to measure band gap (inset bandgap reduction plot by increasing fluence).
Nitrogen (N) incorporation in CFO by implantation is also expected to change the optical properties by narrowing its bandgap due to reasons mentioned above. In the present case too, N+ ion implanted films showed modified optical properties as compared to pristine CFO (see Fig. 6(b)). Figure 6(c) shows the corresponding Tauc plot. The bandgap values were found to be 1.85, 1.67, 1.56 and 1.43 eV for pristine CFO, CFO-N+-E14, CFO-N+-E15 and CFO-N+-E16 respectively. These studies corroborate the effective reduction in bandgap of CFO due to N incorporation.
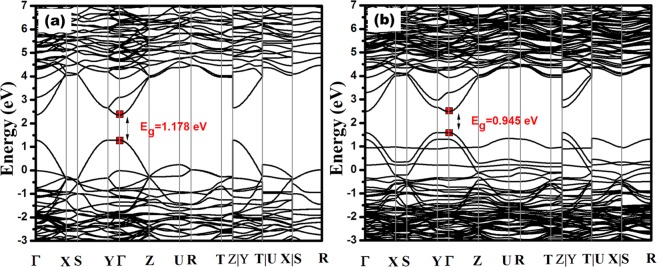
The electronic structures of CFO and CFO-N were also investigated theoretically by density functional theory (DFT) calculations, as shown in Fig. 7(a,b). These calculations were performed by sampling the Brillouin zone with a set of high symmetry k-points. The effect of Nitrogen incorporation in CFO was analyzed theoretically and the bandgap of CFO was found to be 1.17 eV. Upon replacement of few O atoms with N atoms in a unit cell of CFO, the bandgap reduces to 0.94 eV, strongly supporting the experimental trend. The computationally predicted bandgap values are lower than the experimental values. It is a well-known fact that density functional theory (DFT) calculations underestimate the actual values38,39 (Detailed computational procedure is discussed in supplementary information).
Figure 7.
Computationally calculated band structures of (a) CFO and (b) CFO-N.
CFO and CFO-N have excellent optical and catalytic properties. To explore the use of CFO and CFO-N in environmental remediation applications, we have investigated sunlight driven photocatalytic degradation of organic effluent Mythylene blue (MB). The photodegradation experiments were carried out under natural sunlight at a latitude of 13.0087°N and longitude of 80.2371°E (Chennai, India). The initial dye (MB) concentration was kept at Co: 1 × 10−5 mol/L. Then 50 mg/100 ml catalyst loaded dye solution was ultrasonicated vigorously under the dark condition and allowed to rest in dark for 10 min to ensure good adsorption. The catalyst loaded dye solution was then kept in sunlight and the sample was collected at regular time intervals. Simultaneous light intensity measurements were also carried out using lux meter. For the whole duration of experiment (50 min) the incident intensity of sunlight was almost constant with an average intensity of about 105.40 klux. The degradation efficiency and first-order reaction kinetics are calculated using the following equations.
| 1 |
| 2 |
where Co and C are the concentrations of MB at 0 min and at time interval t respectively. k is the degradation rate constant.
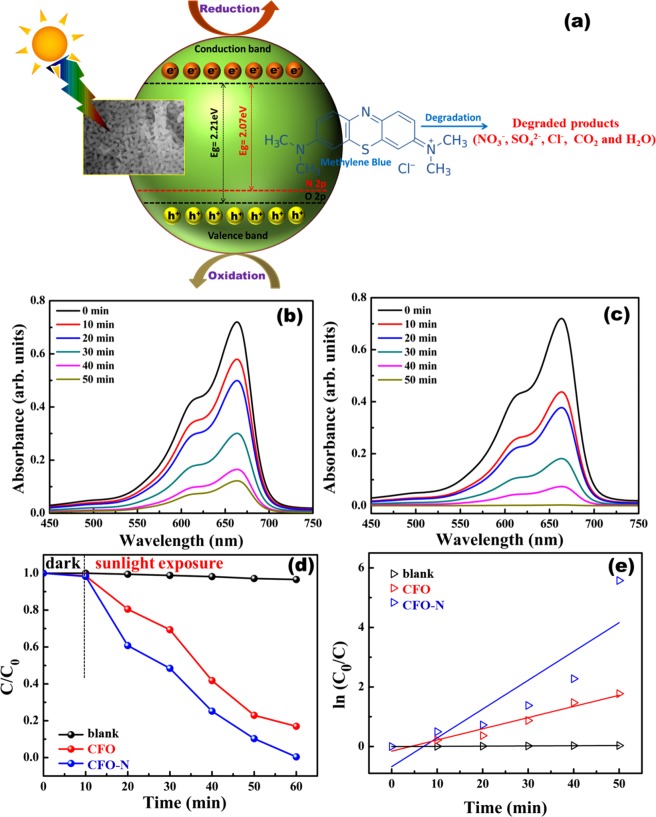
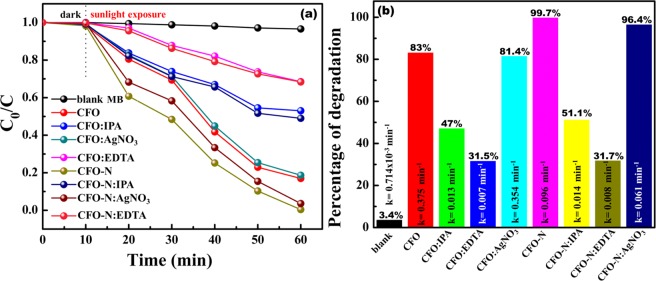
The schematic representation of photodegradation process, along with degradation profile, efficiency and first-order reaction kinetics of CFO andCFO-N are shown in Fig. 8(a–e). The degradation efficiencies of bare MB, CFO and CFO-N are found to be 3.5%, 83% and 99.7% respectively and the first order rate constants of CFO and CFO-N are found to be 0.0375 min−1 and 0.096 min−1 respectively. CFO-N shows superior photocatalytic performance compared to CFO due to a relatively smaller bandgap as well as the presence of Fe-Nx active sites. Adsorption curves of MB and photodegradation performance CFO and CFO-N over different photocatalysts are discussed in supporting information.
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic representation of sunlight driven photodegradation mechanism of MB (b) degradation profile of MB by CFO (c) degradation profile of MB by CFO-N (d) C/Co for MB under natural sunlight (e) First order photocatalytic reaction kinetics.
The major active species involved in the photodegradation mechanism of MB was determined by the active species trapping experiments. The trapping experiment results are shown in Fig. 9(a,b). We have used various scavengers such as AgNO3 (1 mmol) as electron (e−) scavenger, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, 1 mmol) as a hole scavenger (h+) and Isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 1 mmol) as the OH− radical trapping agent. The trapping agents were added to dye-catalyst solution and degradation experiments were performed under sunlight. In absence of trapping agents, the MB could be degraded by 83% and 99.7% of its initial concentration with the presence of CFO and CFO-N respectively. Upon addition of AgNO3 as an e− scavenger to CFO and CFO-N dye solution the photodegradation efficiencies were found to be 81.4% and 96.4% respectively. No significant change in photodegradation performance leads us to infer that electrons (e−) are not involved in photodegradation mechanism of MB by both CFO and CFO-N. With the presence of EDTA as h+ scavenger photodegradation efficiencies of CFO and CFO-N were reduced to 31.5% and 31.7% respectively, confirming that photodegradation of MB using CFO and CFO-N are governed by holes. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as .O2, ·OH, singlet oxygen (1O2), peroxyl (RO2.), and alkoxyl (RO−) are highly active in photochemical reactions such as photodegradation of organic pollutants40. Among the all ROS, superoxide (O2.) and hydroxyl(·OH) radicals are the most possible generated ROS in photodegradation of organic pollutants. In the present case, it is evident from e- and h+ trapping experiments, that photodegrading phenomena are governed by holes (h+) and there is no participation of e− in photodegradation process. Hence, the generation of -O2. species is limited. This is, because -O2. can be generated upon reduction of O2 by e− 41. In the present photochemical reaction, ·OH is one of the major ROS, which is generated by oxidation of H2O/OH− by holes (h+). Since ·OH has high tendency to degrade organic pollutants42, ·OH species trapping experiment was conducted by addition of IPA; as a result of which the photodegradation efficiencies of CFO and CFO-N were reduced to 47% and 51.1% respectively. Hence, the active species trapping experiments suggest that, photodegradations of MB by CFO and CFO-N are attributed to the holes(h+) and ·OH active species.
Figure 9.
(a,b) Comparisons of photocatalytic activities of CFO and CFO-N for the degradation of MB with or without adding trapping agents.
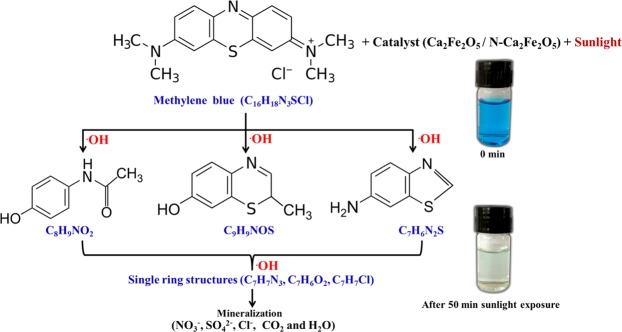
Figure 10 shows a possible MB photodegradation pathway in the presence of catalyst. During the photocatalytic degradation process, active species such as holes(h+) and hydroxyl radicals (·OH) are generated which are responsible for mineralization of MB into unstable organic byproducts Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO2, and H2O36,43. MB degradation process is initiated by active species breaking the S-Cl bonds and then Cl− ions being separated from MB core structure. Several intermediate molecules such as C8H9NO2, C9H9NOS and C7H6N2S are generated by breaking N-CH3 bonds, (which are connected to terminal of MB core structure). The active species further oxidizes the –CH3 groups. It also gives rise to single ring structures (C7H7N3, C7H6O2 and C7H7Cl). These reactions continue until the MB mineralizes into Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO2, and H2O.
Figure 10.
Possible photodegration pathway of MB in the presence of catalyst.
Ca2Fe2O5, by virtue of its unique properties as mentioned above, could also be used for energy harvesting applications such a supercapacitors, batteries and fuel cells etc. In this regard,we have explored the feasibility of CFO and CFO-N for supercapacitor applications. Electrochemical studies have been performed on CFO and CFO-N using three electrode system with 0.5 M Na2SO4 aqueous solution as the electrolyte. These techniques are employed for investigating the redox behavior, stability and supercapacitor properties. The working electrodes are prepared on FTO plates with ethanol as solvent using a doctor blade method.
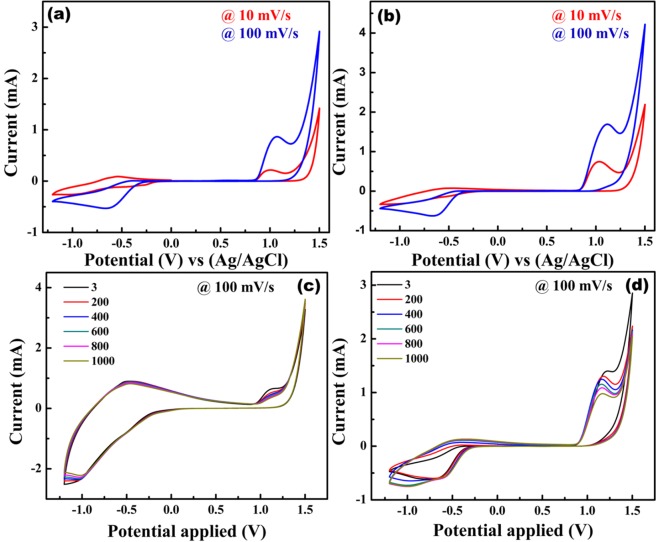
Figure 11(a,b) shows the cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves of CFO and CFO-N at different scan rates (10 mV/s and 100 mV/s). CV curves reveal the presence of redox peaks for both the samples, demonstrating the pseudocapacitive nature of both CFO and CFO-N. A notable difference in the peak current was observed for both samples at low and high scan rates of 10 mV/s and 100 mV/s respectively, which can be attributed to diffusion-controlled reaction kinetics as well as faster electronic and ionic transport in the electrode/electrolyte interface. CFO-N sample shows well defined anodic and cathodic peaks even after 1000 cycles (Fig. 11c,d), which is attributed to a higher stability than CFO. Hence, it delivers a higher specific capacitance with good cycling stability due to the presence of Fe-Nx active sites. Specific capacitance values were calculated from CV curves using the expressions (3) and (4) shown below.
| 3 |
where denotes the integral area of CV curve, denotes the potential window (V), m is mass of the active material (g), and S is the scan rate (mVs−1). The calculated specific capacitance (Csp) values are 175.07 Fg−1 and 224.67 Fg−1 for CFO and CFO-N respectively for third cycle.
| 4 |
where ∆V denotes the potential window (V), m denotes the mass of active material (mg), I (A) is the discharge current density and ∆t (s) denotes the discharge time. The specific capacitances from charge-discharge curves are calculated to be 75 Fg−1 and 165 Fg−1 for CFO and CFO-N respectively. CFO-N exhibits higher Csp and longer discharge time than CFO. Both CV and charge-dicharge curves point towards improved capacitive properties of CFO-N over CFO.
Figure 11.
Cyclic voltammetric curves of (a) CFO at high and low scan rates 10 mV/s and 100 mV/s (b) CFO-N at high and low scan rates 10 mV/s and 100 mV/s (c,d) Cyclic stability of CFO for 1000 cycles (d) Cyclic stability of CFO-N for 1000 cycles.
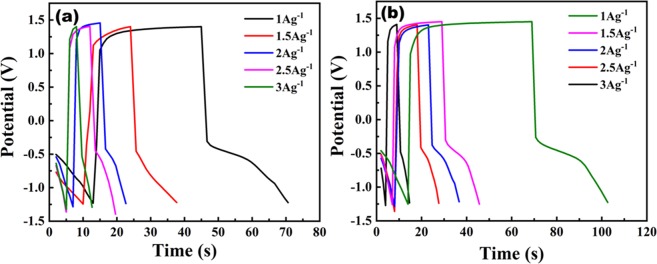
The Galvanostatic charge discharge (GCD) studies of CFO and CFO-N are shown in Fig. 12. GCD studies are carried out using chrono-potentiometric analysis at a current density of 1 Ag−1, which revealed the capacitive behavior of CFO and CFO-N. The GCD studies are consistent with the CV curves. A non-linear discharging behavior is observed with various current densities. The curvature in charge and discharge profile indicates the capacitive behavior of material, which is influenced by both redox reactions (pseudocapacitor) and electrical double layer (EDLC) response, is similar to reported trends44–47. The specific capacitance values were calculated using the expression below (4)
| 5 |
Figure 12.
GCD curves of (a) CFO (b) CFO-N.
CFO-N achieved a high specific capacitance of 160.73 Fg−1 at 1 Ag−1 with a large potential window of 2.6 V whereas CFO achieved only 109.19 Fg−1. A higher potential window implies high energy density of the electrode material. CFO-N exhibits higher Csp and longer charge discharge time as compared to CFO. Both CV and GCD curves point towards improved capacitive properties of CFO-N over CFO. The stability of both materials at various current densities (using GCD plots) are discussed in detail in the supporting information.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were carried out for both samples (Fig. 13). From the impedance plot, it is observed that CFO and CFO-N offer negligible series resistance (Rs) at high frequencies. Both the samples exhibit the same trend exhibiting high-frequency semicircular arc followed by a straight line at lower frequencies. These studies reveal that both are promising candidates for capacitive applications. However, CFO-N is found to be a better candidate than CFO as it offers lower charge transfer resistance. Electrochemical studies revealed better capacitive behavior for CFO-N as compared to CFO. Hence nitrogen doped brownmillerites can be promising materials for energy and environmental applications.
Figure 13.
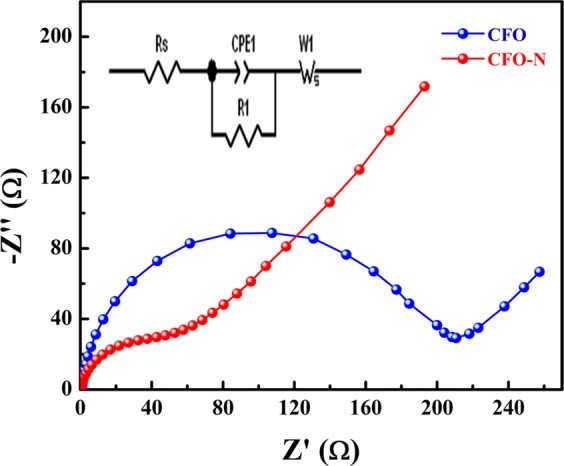
Electrochemical impedance spectra of CFO and CFO-N (inset shows an equivalent circuit).
Conclusion
CFO and CFO-N nanoparticles were synthesized using a chemical route followed by thermoammonolysis. The effect of N incorporation on the bandgap and photocatalytic properties of brownmillerite CFO has been examined. The incorporation of N into CFO significantly decreases the band gap by occupying N 2p energy levels over the O 2p level in the valence band. The electronic band structures of CFO and CFO-N were demonstrated using UPS and UV-vis spectroscopy and the trend was supported by DFT studies. Photodegradation of methylene blue under sunlight revealed superior photocatalytic performance of CFO-N over undoped CFO. Electrochemical studies revealed the feasibility for supercapacitor applications, where CFO-N showed better specific capacitance over CFO. Hence, sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of MB and supercapacitor properties expand the scope of utilization of CFO and CFO-N for energy and environmental applications.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
S Singh would like to acknowledge UGC-FRP scheme, DST SERB (EMR/2017/000794),DST Solar EnergyHarnessingCenter-DST/TMD/SERI/HUB/1(C) and Durga Sankar would like to acknowledge Japan Student Services Organization (JASSO) and Shibaura Institute of Technology (SIT) for the fellowship under the Top Global University Project, Designed by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science & Technology in Japan. Authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Tapas Ganguli, RRCAT for extending his support for accessing XPS and UPS facilities.
Author contributions
Durga Sankar conceived and planned the present idea of work. Sankar developed the material and performed the experimental work as well as analyzed its structural, optical and catalytic studies. Shubra Singh supervised the findings of this work and helped shape the manuscript. Shubra Singh encouraged to investigate the energy and environmental applications of as developed materials. Electronic structure investigations on as developed materials using UPS and XPS were performed under the guidance of Soma Banik. Raja Gopal and Muthuraaman performed the cyclic voltammetry studies and analyzed its supercapacitive properties. Muralidhar, Murakami and Klimkowicz contributed to the microstructural studies using SEM and TEM. Ion implantation experiments were carried out under the supervision of Asokan. He also provided critical feedback. Durga Sankar, M.S. Ramachandra Rao and Shubra Singh contributed to the design and implementation of the research, analysis of the results and writing of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41598-020-59454-w.
References
- 1.Baijnath, Tiwari P, Basu S. Cobalt and molybdenum co-doped Ca2Fe2O5 cathode for solid oxide fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2019;44:10059–10070. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.164. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dhankhar S, Menon SS, Gupta B, Baskar K, Singh S. Electrochemical performance of brownmillerite calcium ferrite for application as supercapacitor. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2017;1832:080050. doi: 10.1063/1.4980510. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dhankhar S, Tiwari P, Baskar K, Basu S, Singh S. Effect of low Cobalt doping on morphology and properties of calcium ferrite and its application as cathode in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell. Current Applied Physics. 2017;17:467–473. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2017.01.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ismail M, Liu W, Chan MSC, Dunstan MT, Scott SA. Synthesis, Application, and Carbonation Behavior of Ca2Fe2O5 for Chemical Looping H2 Production. Energy & Fuels. 2016;30:6220–6232. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00631. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gupta K, Singh S, Ramachandra Rao MSF. reversible CO2 capture in nanostructured Brownmillerite CaFeO2.5. Nano Energy. 2015;11:146–153. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.10.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemann DW. Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis. Chemical Reviews. 1995;95:69–96. doi: 10.1021/cr00033a004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen X, Shen S, Guo L, Mao SS. Semiconductor-based Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation. Chemical Reviews. 2010;110:6503–6570. doi: 10.1021/cr1001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen C, Ma W, Zhao J. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation. Chemical Society Reviews. 2010;39:4206–4219. doi: 10.1039/b921692h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kubacka A, Fernández-García M, Colón G. Advanced Nanoarchitectures for Solar Photocatalytic Applications. Chemical Reviews. 2012;112:1555–1614. doi: 10.1021/cr100454n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wen F, Li C. Hybrid Artificial Photosynthetic Systems Comprising Semiconductors as Light Harvesters and Biomimetic Complexes as Molecular Cocatalysts. Accounts of Chemical Research. 2013;46:2355–2364. doi: 10.1021/ar300224u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang Z, et al. Progress on extending the light absorption spectra of photocatalysts. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2014;16:2758–2774. doi: 10.1039/c3cp53817f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Arney D, Watkins T, Maggard PA. Effects of Particle Surface Areas and Microstructures on Photocatalytic H2 and O2 Production over PbTiO3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 2011;94:1483–1489. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04262.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shu H, et al. Structural characterization and photocatalytic activity of NiO/AgNbO3. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2010;496:633–637. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.02.148. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xu X, Randorn C, Efstathiou P, Irvine JTS. A red metallic oxide photocatalyst. Nature Materials. 2012;11:595–598. doi: 10.1038/nmat3312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gao F, et al. Visible-Light Photocatalytic Properties of Weak Magnetic BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. Advanced Materials. 2007;19:2889–2892. doi: 10.1002/adma.200602377. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sankar, V. D. & Singh, S. Optical Properties of Fe Based Perovskite and Oxygen Deficient Perovskite Structured Compounds: A Comparison.). Springer International Publishing (2019).
- 17.Vavilapalli DS, et al. Multifunctional brownmillerite KBiFe2O5: Structural, magneto-dielectric, optical, photoelectrochemical studies and enhanced photocatalytic activity over perovskite BiFeO3. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells. 2019;200:109940. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.109940. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li L, Wang X, Zhang Y. Enhanced visible light-responsive photocatalytic activity of LnFeO3 (Ln=La, Sm) nanoparticles by synergistic catalysis. Materials Research Bulletin. 2014;50:18–22. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.10.027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Li Y, Yao S, Wen W, Xue L, Yan Y. Sol–gel combustion synthesis and visible-light-driven photocatalytic property of perovskite LaNiO3. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2010;491:560–564. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.10.269. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen Z, Higgins D, Yu A, Zhang L, Zhang J. A review on non-precious metal electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells. Energy & Environmental Science. 2011;4:3167–3192. doi: 10.1039/c0ee00558d. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu J, Li E, Ruan M, Song P, Xu W. Recent Progress on Fe/N/C Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Fuel Cells. Catalysts. 2015;5:1167–1192. doi: 10.3390/catal5031167. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang Y, et al. Photocatalytic property of nitrogen-doped layered perovskite K2La2Ti3O10. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells. 2010;94:761–766. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2009.12.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang J, et al. Nitrogen-Doped Perovskite as a Bifunctional Cathode Catalyst for Rechargeable Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2018;10:5543–5550. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b17289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kim N-I, et al. Highly active and durable nitrogen doped-reduced graphene oxide/double perovskite bifunctional hybrid catalysts. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 2017;5:13019–13031. doi: 10.1039/C7TA02283B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tan H, et al. Oxygen Vacancy Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Pervoskite SrTiO3. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2014;6:19184–19190. doi: 10.1021/am5051907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yang Y, Cao Z, Jiang Y, Liu L, Sun Y. Photoinduced structural transformation of SrFeO3 and Ca2Fe2O5 during photodegradation of methyl orange. Materials Science and Engineering: B. 2006;132:311–314. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2006.03.031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xu X, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Ca2Fe2O5 nanofibers photocatalyst by sol-gel assisted electrospinning at low-temperature. Materials Letters. 2015;143:75–79. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.12.065. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang Y, Wang Y, Gao Y. Photocatalytic H2 evolution from water in the presence of carbon dioxide over NiO/Ca2Fe2O5. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis. 2010;99:485–491. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Penkala B, et al. In situ generated catalyst: copper(ii) oxide and copper(i) supported on Ca2Fe2O5 for CO oxidation. Catalysis Science & Technology. 2018;8:5236–5243. doi: 10.1039/C8CY00806J. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Malti A, et al. An Organic Mixed Ion–Electron Conductor for Power Electronics. Advanced Science. 2016;3:1500305. doi: 10.1002/advs.201500305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rivnay J, et al. Structural control of mixed ionic and electronic transport in conducting polymers. Nature Communications. 2016;7:11287. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Deng Y, Xie Y, Zou K, Ji X. Review on recent advances in nitrogen-doped carbons: preparations and applications in supercapacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 2016;4:1144–1173. doi: 10.1039/C5TA08620E. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ramesh S, Karuppasamy K, Kim H-S, Kim HS, Kim J-H. Hierarchical Flowerlike 3D nanostructure of Co3O4@MnO2/N-doped Graphene oxide (NGO) hybrid composite for a high-performance supercapacitor. Scientific Reports. 2018;8:16543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34905-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mapa M, Gopinath CS. Combustion Synthesis of Triangular and Multifunctional ZnO1−xNx (x ≤ 0.15) Materials. Chemistry of Materials. 2009;21:351–359. doi: 10.1021/cm803048h. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Barnes TM, Olson K, Wolden CA. On the formation and stability of p-type conductivity in nitrogen-doped zinc oxide. Applied Physics Letters. 2005;86:112112. doi: 10.1063/1.1884747. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vavilapalli DS, et al. Photoactive Brownmillerite Multiferroic KBiFe2O5 and Its Potential Application in Sunlight-Driven Photocatalysis. ACS Omega. 2018;3:16643–16650. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jijil CP, et al. Nitrogen Doping in Oxygen-Deficient Ca2Fe2O5: A Strategy for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Oxide Catalysts. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2016;8:34387–34395. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b11718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hohenberg P, Kohn W. Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Physical Review. 1964;136:B864–B871. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.136.B864. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kohn W, Sham LJ. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Physical Review. 1965;140:A1133–A1138. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang H, et al. Macroscopic Polarization Enhancement Promoting Photo- and Piezoelectric-Induced Charge Separation and Molecular Oxygen Activation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2017;56:11860–11864. doi: 10.1002/anie.201706549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huang H, et al. Anionic Group Self-Doping as a Promising Strategy: Band-Gap Engineering and Multi-Functional Applications of High-Performance CO32–-Doped Bi2O2CO3. ACS Catalysis. 2015;5:4094–4103. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00444. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huang H, et al. In situ assembly of BiOI@Bi12O17Cl2 p-n junction: charge induced unique front-lateral surfaces coupling heterostructure with high exposure of BiOI {001} active facets for robust and nonselective photocatalysis. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2016;199:75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Si Y, et al. Photocatalytic Performance of a Novel MOF/BiFeO3 Composite. Materials. 2017;10:1161. doi: 10.3390/ma10101161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Park HW, Na B-K, Cho BW, Park S-M, Roh KC. Influence of vanadium doping on the electrochemical performance of nickel oxide in supercapacitors. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2013;15:17626–17635. doi: 10.1039/c3cp52498a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dar FI, Moonoosawmy KR, Es-Souni M. Morphology and property control of NiO nanostructures for supercapacitor applications. Nanoscale Research Letters. 2013;8:363. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Thiagarajan K, et al. Synthesis of Ni3V2O8@graphene oxide nanocomposite as an efficient electrode material for supercapacitor applications. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry. 2018;22:527–536. doi: 10.1007/s10008-017-3788-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Theerthagiri, J. et al. Synthesis of hierarchical structured rare earth metal–doped Co3O4 by polymer combustion method for high performance electrochemical supercapacitor electrode materials. Ionics (2019).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.