Abstract
Accumulating studies have revealed gender differences in many aspects of schizophrenia (SZ), including obesity and cognitive function. The relationship between obesity and cognitive impairment in SZ has been studied before; however, the results are inconsistent. This study was designed to examine the sex differences in the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and cognitive deficits in Chinese patients with chronic SZ, which have not been investigated yet. 176 chronic patients with SZ (male/female = 108/68) and 200 controls (male/female = 120/80) were enrolled to compare the sex differences in cognitive functions measured by the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS), BMI, and their associations. The clinical symptoms were evaluated using the positive and negative syndrome scales (PANSS). Our results showed that male patients had lower BMI and more negative symptoms but fewer positive symptoms than female patients (all p < 0.05). However, there was no significant sex difference in RBANS scores. In male patients, BMI was correlated with age of onset, PANSS general psychopathology, total score, negative symptom, together with RBANS language, visuospatial/construction, and attention. Further regression analysis showed that in male patients, BMI was significantly associated with RBANS language, PANSS general psychopathology, PANSS total score, and age of onset, with adjusted R2 = 0.22. These findings revealed significant sex differences in BMI, cognitive dysfunctions and their association in SZ. Nonetheless, these results should only be considered as preliminary because of the cross-sectional design, which will deserve further replication in first-episode patients using a prospective longitudinal design.
Subject terms: Psychiatric disorders, Pathogenesis
Introduction
A growing body of studies have reported sex differences in almost all features of schizophrenia (SZ) from prevalence, incidence, prodromal symptoms, onset age, clinical manifestation, illness course, response to treatment, side effects, as well as long-term outcome, and social functions1–4. For example, the incidence of male SZ approximates 1.4 times of female patients2. Recent reviews reported that men had disadvantages over women in their earlier onset age and poorer response to antipsychotic treatments and poorer functioning1,5,6. Moreover, male patients displayed more clinical symptoms, especially negative symptoms7. The results suggest that men have a more severe form of SZ than women, which may be related to sex hormones8. However, several literatures reported no sex differences or even opposite results in some clinical presentations9.
Some researchers have specially examined sex differences in cognitive impairments of patients with SZ1,10,11. Previous studies showed that female patients showed better performance on executive functioning, verbal and language memory, and attention than male patients10,12. However, the results of sex differences in cognitive dysfunctions were inconsistent9,13, especially for those first-episode patients3,4.
SZ is related to a significantly high incidence of obesity14–16, and ~45–55% of patients with SZ were found to be obese17–19. One important cause for the increased rate of obesity among SZ patients is antipsychotic treatment, notably with olanzapine and clozapine15,20–22. Many studies have investigated sex differences in obesity as well as metabolic syndrome in SZ14,23. Some studies reported higher prevalence of obesity and metabolic symptoms in females than males24–26, with inconsistent results27–29.
Interestingly, recent studies have shown that obesity may produce negative effect on cognitive performance among healthy population30,31. Moreover, there is even increasing interest in examining the influence of obesity on cognitive deficits in SZ32. Only two recent studies explored their relationship. For example, one study reported that obesity was associated with poorer cognitive performance in Chinese SZ patients28. However, another study found no significant difference in cognitive dysfunction in SZ patients with and without obesity33. The real relationship between obesity and cognitive dysfunction in patients with SZ warrants further investigation.
In view of the high prevalence of obesity and cognitive impairments in SZ34, and significant sex differences in many aspects including obesity and cognitive deficits, it would be of great interest to examine whether there would be sex difference in the relationship of BMI and cognitive deficits in SZ, which has not been investigated in patients with SZ. Thus, this study was intended to explore whether there would be significant difference in the relationship of body mass index (BMI) with cognitive deficits in Chinese chronic SZ patients. We speculated that sex differences may occur in cognitive performance, BMI and their correlation in SZ.
Methods
Subjects
176 inpatients were randomly recruited from Beijing Hui-Long-Guan Hospital, a Beijing-city-owned psychiatric hospital. The hospital has 29 wards and the daily outpatient visits are about 500 patients. The inclusion criteria were: (1) aged 25–65 years, Han Chinese; (2) met the DSM-IV diagnosis of SZ, which was confirmed by 2 psychiatrists according to the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID), without any patients with schizoaffective disorder; (3) at least 2 years of illness. The exclusion criteria were: (1) pregnancy or lactation; (2) major medical abnormalities; (3) alcohol or drug abuse or dependence; (4) subjects with ongoing infections, allergies or past history of autoimmune disorders; (5) subjects that took immunosuppressive drugs; (6) subjects with physical diseases or cerebral pathologies including multiple sclerosis seizure, dementia, epilepsy, Huntington’s disease, brain tumor, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, severe headache for unknown reasons, cardiovascular diseases; (7) education level less than 5 years by subject report. We had initially recruited 199 patients from Beijing Hui-Long-Guan Hospital. After screening, 5 individuals were excluded due to the inability to comprehend consent procedures, 10 patients were excluded for their severe medical abnormalities and 8 patients were excluded for being unable to perform cognitive tests. The excluded patients were not different from those included in the study in any demographic parameters. Thus, a total of 176 patients were randomly enrolled in the present study.
Research psychiatrists obtained social-demographic characteristics, smoking behavior and medical status using the questionnaires. Moreover, they collected a complete physical examination, laboratory tests and medical history for each subject. All patients had been receiving stable doses of oral antipsychotic drugs for at least six months before entry into the study. Antipsychotic drug treatment consisted mainly of drug monotherapy including clozapine (n = 80), risperidone (n = 38), chlorpromazine (n = 12), sulpiride (n = 9), perphenazine (n = 9), quetiapine (n = 7), haloperidol (n = 6), aripirazole (n = 5), and others (n = 10).
Since admission, all subjects received three balanced meals directly from the hospital canteen every day and took 60 min of physical exercise a day. The diet of all patients was similar. During hospitalization, their friends or family occasionally brought some snacks or fruits as a supplement.
Two hundred healthy controls (120 males and 80 females) were recruited by advertisements at the local community. A research psychiatrist ruled out a personal or family history of psychiatric disorder among healthy controls by direct psychiatric interview. Any subjects with medical illnesses or drug and alcohol abuse/dependence were excluded. The patients and healthy controls had a similar socioeconomic status and dietary patterns. Neither the patients nor the healthy controls had any history of alcohol or substance dependence (aside from tobacco). The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB). Psychiatrists carefully explained the protocol to those potential subjects. Each participant consented to join in the study.
Clinical measurement and cognitive assessment
Four psychiatrists, who had simultaneously attended a training session in the use of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) before the study began, assessed the patient’s psychopathology using the PANSS. After training, repeated assessment showed that these psychiatrists maintained an interobserver correlation coefficient greater than 0.8 for the PANSS total score.
Cognitive functioning was evaluated using the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS, Form A)35. The RBANS is comprised of 5 age-adjusted index scores and a total score. Test indices are immediate memory (comprising List Learning and Story Memory tasks); visuospatial/constructional (comprising Figure Copy and Line Orientation tasks); language (comprising Picture Naming and Semantic Fluency tasks); attention (comprising Digit Span and Coding tasks); and delayed memory (comprising List Recall, Story Recall, Figure Recall, and List Recognition tasks). Our group previously translated RBANS into Chinese and the clinical validity and its test-retest reliability were established among healthy controls and SZ patients36. The total and 5 index scores reported in this study were the standard scores.
Assessment of anthropometric variables
Height and weight were measured and BMI was calculated. Participants in light indoor clothes were weighted by electronic scales. Height was measured to the closest millimeter and participants stood barefoot.
Data analysis
Kolmogorov–Smirnov one-sample test was performed for normality. Continuous variables between groups were compared by analysis of variance and categorical variables by chi-square test (X2). To adjust the influence of age and education on cognitive function, analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was further performed between groups. Then, we performed ANCOVA to compare the clinical characteristics between male and female patients. Associations of demographic, clinical characteristics, cognitive functions, and BMI were assessed by Pearson correlation coefficients in female and male patients separately. Logistic regression analyses were performed to explore which characteristics were related to BMI. Adjusting for multiple testing, the Bonferroni corrections were used. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS (version 20.0) and significance levels of p-values were set at 0.05.
Results
Sample characteristics in patients and controls grouped by sex
Table 1 shows that smoking was more common in male patients and male controls than female counterparts. Further, male patients smoked more than male controls (77.1% vs 59.2%); however, female patients smoked fewer than female controls (7.4% vs 25.0%) (all p < 0.01). Therefore, smoking was controlled in the following analyses.
Table 1.
Demographics and cognitive function in SZ and healthy controls.
| SZ | Healthy control | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n = 108) | Female (n = 68) | Male (n = 120) | Female (n = 80) | Diagnose F (p-value)a | Sex F (p-value)a | Diagnose × Sex F (p-value) | |
| Age (years) | 51.5 ± 9.1 | 48.3 ± 11.7 | 49.9 ± 9.6 | 48.7 ± 10.0 | 0.30 (0.58) | 4.62 (0.03) | 0.93 (0.34) |
| Education (years) | 9.6 ± 2.5 | 10.4 ± 2.6 | 9.5 ± 3.0 | 9.9 ± 2.7 | 1.14 (0.29) | 4.73 (0.03) | 0.59 (0.44) |
| Body mass index (BMI) | 24.2 ± 4.7 | 25.6 ± 4.3 | 25.7 ± 3.3 | 24.2 ± 3.1 | 0.03 (0.87) | 0.26 (0.61) | 8.49 (0.004) |
| Smoker (n%) | 83/76.9% | 5/7.4% | 71/59.2% | 20/25.0% | 0.96 (0.45) | 93.0 (0.000) | 90.4 (0.000) |
| RBANS | |||||||
| Immediate memory | 62.9 ± 17.9 | 66.3 ± 19.8 | 72.8 ± 16.8 | 75.7 ± 17.7 | 17.46 (<0.0001) | 1.88 (0.17) | 0.02 (0.90) |
| Visuospatial/constructional | 82.6 ± 18.3 | 84.8 ± 20.1 | 81.0 ± 15.0 | 80.8 ± 14.8 | 1.74 (0.19) | 0.24 (0.63) | 0.32 (0.57) |
| Language | 85.7 ± 13.0 | 86.7 ± 14.6 | 95.3 ± 10.5 | 94.8 ± 12.2 | 31.3 (<0.001) | 0.03 (0.87) | 0.20 (0.66) |
| Attention | 81.9 ± 15.0 | 82.3 ± 15.0 | 86.7 ± 17.0 | 84.4 ± 19.7 | 2.42 (0.12) | 0.19 (0.66) | 0.34 (0.56) |
| Delayed memory | 69.2 ± 19.6 | 73.5 ± 22.1 | 85.7 ± 15.5 | 87.3 ± 14.0 | 46.0 (<0.001) | 1.78 (0.18) | 0.37 (0.55) |
| Total score | 69.6 ± 16.5 | 73.5 ± 17.8 | 79.5 ± 13.2 | 79.7 ± 15.0 | 16.7 (<0.001) | 1.16 (0.28) | 0.90 (0.34) |
aThe p-values for RBANS and BMI were adjusted for age and education as covariates.
There was a significant diagnosis × sex interaction on BMI. Further analysis showed that male patients had lower BMI than females (F = 4.19, df = 1, 175, p = 0.042), while male controls had significantly higher BMI than female controls (F = 8.87, df = 1, 198, p = 0.002).
As shown in Table 2, male patients had older age, younger age of onset, poorer education, together with more negative symptoms but less positive symptoms compared to female patients (all p < 0.05).
Table 2.
Characteristics of male and female patients with SZ.
| Male | Female | F or X2 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 51.5 ± 9.1 | 48.3 ± 11.7 | 4.4 | 0.04 |
| Education (years) | 9.6 ± 2.5 | 10.4 ± 2.6 | 4.6 | 0.032 |
| Age of onset (years) | 23.9 ± 5.5 | 26.0 ± 7.2 | 4.75 | 0.031 |
| Antipsychotic types (typicals/atypicals) | 24/83 | 13/56 | 0.33 | 0.57 |
| Antipsychotic dose (CPZ equivalents) | 411.2 ± 193.8 | 437.6 ± 251.9 | −0.76 | 0.45 |
| Duration of current antipsychotic treatment | 66.6 ± 68.5 | 46.3 ± 68.3 | 1.75 | 0.08 |
| Duration of current antipsychotic treatment | 66.6 ± 68.5 | 46.3 ± 68.3 | 1.75 | 0.08 |
| Number of hospitalizations | 3.9 ± 3.7 | 3.5 ± 2.4 | 0.73 | 0.46 |
| PANSS | ||||
| Positive symptom scale | 12.0 ± 4.7 | 14.6 ± 6.2 | −3.20 | 0.002 |
| Negative symptom scale | 23.0 ± 6.8 | 20.4 ± 9.0 | 2.05 | 0.04 |
| General psychopathology scale | 27.3 ± 4.9 | 27.9 ± 6.0 | −0.66 | 0.51 |
| Total score | 62.3 ± 12.3 | 62.9 ± 15.3 | −0.50 | 0.62 |
Mean ± SD.
CPZ chlorpromazine, PANSS the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale.
Cognitive function performance in SZ and controls grouped by sex
Although female patients appeared to show higher scores on RBANS total score, delayed memory and immediate memory scores, as compared to male patients, these differences were not statistically significant (all p > 0.05). Also, there was no sex difference in cognitive function performance in controls (all p > 0.05) (Table 1).
Sex differences in the associations between BMI and clinical symptoms and cognitive measures
For all patients, BMI was correlated with age of onset (r = 0.15, df = 177, p = 0.041), Language (r = 0.26, df = 111, df = 0.006, df = 111), Visuospatial/construction (r = 0.19, df = 111, p = 0.04), negative symptom (r = −0.20, df = 173, p = 0.009), general psychopathology (r = −0.23, df = 173, p = 0.002), and PANSS total score (r = −0.24, df = 173, p = 0.002).
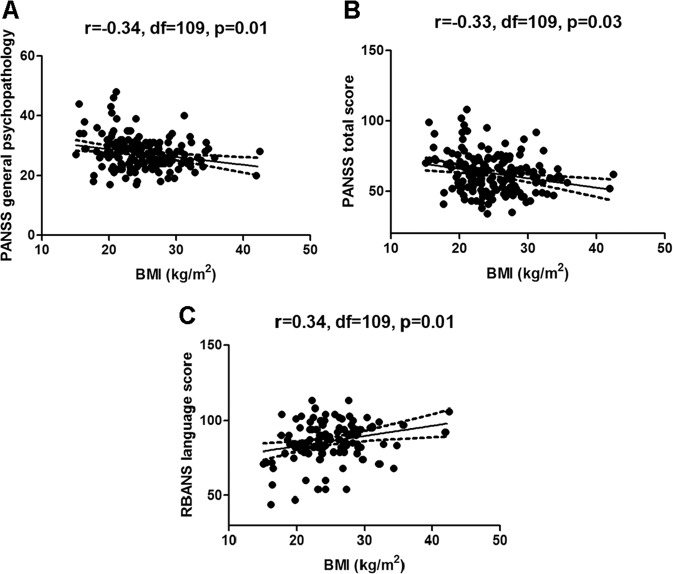
As shown in Table 3, BMI was related to the following characteristics: onset age (r = 0.21, df = 109, p = 0.03), PANSS general psychopathology (r = −0.34, df = 109, p < 0.001), total score (r = −0.33, df = 109, p < 0.001), negative symptom (r = −0.23, df = 109, p = 0.02), together with RBANS language (r = 0.34, df = 109, p < 0.001), visuospatial/construction (r = 0.27, df = 109, p = 0.01) and attention (r = 0.25, df = 109, p = 0.02) in male SZ subjects. Further stepwise regression analysis indicated that BMI was significantly associated with RBANS language (beta = 0.11, t = 2.65, p = 0.01), PANSS general psychopathology (beta = −0.27, t = −2.64, p = 0.01) and PANSS total score (beta = −0.09, t = −2.21, p = 0.03), with adjusted R2 = 0.22 (Fig. 1).
Table 3.
Correlations between BMI and clinical variables or cognitive performance measures in male and female patients with SZa.
| Male (n = 108) | Female (n = 68) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | −0.08 (0.42) | 0.10 (0.41) |
| Education (years) | −0.01 (0.93) | −0.01 (0.93) |
| Age of onset (years) | 0.21 (0.03) | 0.08 (0.50) |
| PANSS | ||
| Positive | −0.14 (0.16) | −0.04 (0.75) |
| Negative | −0.23 (0.02) | −0.12 (0.35) |
| General psychopathology | −0.34 (<0.001) | −0.10 (0.41) |
| Total | −0.32 (<0.01) | −0.15 (0.23) |
| RBANS | ||
| Immediate memory | 0.11 (0.30) | −0.18 (0.36) |
| Visuospatial/constructional | 0.27 (0.01) | −0.07 (0.71) |
| Language | 0.34 (0.001) | −0.01 (0.95) |
| Attention | 0.25 (0.02) | −0.16 (0.41) |
| Delayed memory | 0.13 (0.25) | −0.11 (0.59) |
| Total score | 0.19 (0.09) | −0.13 (0.50) |
aValues are shown as r (p).
Fig. 1.
There were significant negative relationships between body mass index (BMI) and PANSS general psychopathology (r = −0.34, df = 108, p = 0.01, (a) and total score (r = −0.33, df = 108, p = 0.03, (b), as well as a positive relationship between BMI and RBANS language score (r = 0.34, df = 108, p = 0.01, (c) in male schizophrenia patients.
Nonetheless, no statistically significant correlation between BMI and clinical and cognitive parameters was found in the female patients (all p > 0.05). Furthermore, no correlation between BMI and cognitive domains was found across the entire healthy subjects or when analyzed by sex group (all p > 0.05).
Discussion
In our present study, significant sex differences were found in many aspects of SZ, showing that male patients had older age, younger age of onset, poorer education, together with more negative symptoms but less positive symptoms compared to female patients. Although female patients appeared to show high scores on RBANS immediate memory, delayed memory and total scores compared with males, there was no statistically significant sex difference in the RBANS scores. Notably, we did find negative associations of BMI with negative symptom, general psychopathology, and PANSS total score, as well as positive associations between BMI and age of illness onset, RBANS language, visuospatial/construction, and attention in SZ patients. More importantly, we found that these significant associations were largely driven by the male patients, suggesting that the influence of BMI on cognitive performance and clinical symptoms may be mainly present in male patients with SZ.
In this present study, we found that female patients had higher education level and later age of onset than male patients, which was consistent with previous reports showing that women with SZ received better education3,37,38. However, some reports did not find sex difference in onset age of SZ39,40. Also, we found that male patients had severer negative symptoms and less positive symptoms than female patients, which confirmed other studies3,39,41–43. However, there are some conflicting results in the investigation of sex differences in clinical manifestations of SZ9. These discrepant results may be due to different stages of disease (first episode vs. chronic), sample representation (community vs. outpatients vs. inpatients), exposure for antipsychotics, or the different ethnic population3.
Interestingly, we found that female patients exhibited higher BMI than male patients, which is accordant with previous studies26,44. However, a recent study reported the contrast result in a Chinese population28. We scrutinized their methods and found that the subjects in their study were much younger compared to the subjects in our current study (around 30 years vs. 50 years). Moreover, their subjects had much shorter duration of illness than ours (about 2.2 years vs 25 years). Thus, our patients had taken antipsychotic medicines much longer and may have had more side effects related to the change of sex hormones caused by long-term antipsychotic treatment. Moreover, recent studies reported that the hormonal changes during menopause increased abdominal obesity, insulin resistance and hyperplasia markedly45–47. Also, a previous study showed that menopausal women developed much more obesity and other metabolic abnormalities than non-menopausal women48. Our female patients had an average age of 48.3 years and most of them were either postmenopausal or perimenopausal. Taken together, our finding of higher BMI in female patients may be related with older age and possible hormone alterations due to long-term antipsychotic treatment as well as postmenopause or perimenopause. However, this is only our speculation. The relationship between gender and BMI deserves further investigation in large-scale follow-up studies.
Furthermore, we found significantly inverse associations between BMI and clinical symptoms, accordant to some prior studies49–51. This association may be caused by treatments with antipsychotics, since the antipsychotic treatments may improve the psychopathological symptoms of SZ patients and simultaneously cause the increase in weight due to their side effects49. Previous studies found that antipsychotic treatment, such as clozapine, olanzapine, and haloperidol decreased the psychological symptoms accompanying weight gain49,52–56. In particular, our current study revealed that BMI was positively related to onset age of SZ, suggesting a protective factor for the onset of SZ. Taken together, these findings suggest that high BMI or increased bodyweight during antipsychotic treatment may be beneficial to the clinical symptoms of SZ patients.
Another interesting finding was that BMI showed significantly positive association with cognitive performance on Language and visuospatial/construction domains. Gunstad et al. demonstrated that elevated BMI was associated with better performance on psychomotor speed, visuospatial skills, and attention57, which is similar to our finding. Moreover, higher BMI was found to be associated with better cognition in older adults among the general population, but low BMI or weight loss preceded dementia58,59. However, our finding is in disagreement with two recent studies reporting no association of high BMI or obesity with cognitive performance33 or even an inverse association between higher BMI and lower scores on some cognitive performance in SZ patients28. Such a discrepancy of the relationship between BMI and cognitive functioning due to the complicated inter-relationships between BMI/obesity and cognition warrants further exploration in future studies.
More importantly, we found significant associations between BMI and age of onset, clinical symptoms and cognitive function in SZ only in men, but not in women. Further scrutiny on all p-values for associations of BMI with clinical and cognitive parameters in whole patients and in males, it indicated that almost all p-values were increased in males compared to those in all patients, further suggesting that high BMI may produce stronger impacts on clinical and cognitive parameters only in male patients. The finding of a relationship between sex and cognitive function in SZ patients may be explained by sex hormones. Prior researches showed significant correlations of sex hormones with anthropometric parameters60,61. For example, a recent literature demonstrated that serum levels of testosterone were inversely related to all anthropometric measures including leptin, waist-to-hip-ratio, and BMI in men, while in women, testosterone was positively correlated with BMI61. On the other hand, basic and clinical studies demonstrated that hypoandrogenism was associated with cognitive impairment. For example, some animal studies found a relationship between the decrease of androgens including dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate (DHEA-S) as well as testosterone and memory impairment during aging62,63. Therefore, some animal studies showed that the administration of these hormones improved the performance of cognitive tasks64. In the brain, these androgens promote neuroprotection, neurite growth, neurogenesis, neuronal survival, and catecholamine synthesis and release, and they modulate physiological functions, such as sexual behavior, diet, emotion, and cognition64,65. Furthermore, testosterone was found to be positive with the execution of spatial, semantic, working, and verbal episodic memory in elderly subjects66,67. Taken together, androgen was closely correlated with both BMI and cognitive performance. Therefore, the finding of a positive relationship between BMI and some cognitive domains including language, visuospatial/construction and attention only in male patients may be associated with high levels of androgen hormone. However, it is worth mentioning that no sex difference was observed in the association between BMI and cognitive function in controls. Currently, it is unclear why sex difference in association between BMI and cognition was only observed in SZ patients, while not in controls. In addition, we could not explain the findings that BMI was only associated with some cognitive domains, but not with others such as immediate or delayed memories.
We have several limitations in this present study. First, it is only a cross-sectional study, which does not allow us to make causal inferences on the relationship between BMI and cognition in men and women with SZ. Second, the sample size is relatively small, which may explain the negative result in the relationships between BMI and cognition in female patients. Moreover, the ratio of males vs. females was unbalanced in patient group, which may lead to the statistical basis. Third, the age of the patients ranged from 25–65 years, and the effect of the age heterogeneity on cognitive performance is obvious. Fourth, all patients were of chronic types and on long-term different medications. Since the antipsychotic drugs such as atypical antipsychotics have more metabolic side effects and different effects on cognitive function in SZ patients compared to typical antipsychotics, we could not rule out totally the differential influences of different antipsychotic medications on BMI and cognition, as well as on their association, although we controlled for antipsychotic treatment as a confounding factor in the statistical analyses. Fifth, in this study, we utilized RBANS for cognition, rather than the Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia (BACS) or Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia (MATRICS) that represent the gold standard for cognition in schizophrenia. This is because when we carried out this study, we did not have BACS or MATRICS at that time. Sixth, only one hospital in China was included in this survey. Therefore, the findings could not be generalized to other settings.
In summary, sex difference was found in many aspects of SZ patients in our current study. Moreover, we observed significantly negative associations between BMI and clinical symptoms including PANSS general psychopathology, negative symptom, and total score, but positive associations between BMI and age of illness onset, or some cognitive performance including RBANS language, visuospatial/construction and attention. More importantly, these significant associations were largely driven by the male patients. These sexually differential associations between BMI and cognition may be related to sex hormones particularly testosterone, since the androgens were found to be associated with both anthropometric measures and with cognitive functioning. However, we did not find these sexually differential associations in healthy controls.
Considering the limitations of the current study, our results should be preliminary and should be verified using a longitudinal study of the first-episode patients with SZ.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Chang Wei Wei, Ying Qi Chen
Contributor Information
Mei Hong Xiu, Email: xiumeihong97@163.com.
Xiang Yang Zhang, Email: zhangxy@psych.ac.cn.
References
- 1.Mendrek A, Mancini-Marie A. Sex/gender differences in the brain and cognition in schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 2016;67:57–78. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abel KM, Drake R, Goldstein JM. Sex differences in schizophrenia. Int Rev. Psychiatry. 2010;22:417–28. doi: 10.3109/09540261.2010.515205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang XY, et al. Gender differences in never-medicated first-episode schizophrenia and medicated chronic schizophrenia patients. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2012;73:1025–33. doi: 10.4088/JCP.11m07422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Talonen S, Vaananen J, Kaltiala-Heino R. Gender differences in first onset Schizophrenia spectrum psychoses. Nord J. Psychiatry. 2017;71:131–8. doi: 10.1080/08039488.2016.1245783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Seeman MV. Does gender influence outcome in schizophrenia? Psychiatr. Q. 2019;90:173–84. doi: 10.1007/s11126-018-9619-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McGregor C, Riordan A, Thornton J. Estrogens and the cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia: Possible neuroprotective mechanisms. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2017;47:19–33. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2017.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Esterberg ML, et al. The impact of a family history of psychosis on age-at-onset and positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2010;120:121–30. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goldstein JM, et al. Hypothalamic abnormalities in schizophrenia: sex effects and genetic vulnerability. Biol. Psychiatry. 2007;61:935–45. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ayesa-Arriola R, et al. No sex differences in neuropsychological performance in first episode psychosis patients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2014;48:149–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamson DK, Roes MM, Galea LA. Sex hormones and cognition: neuroendocrine influences on memory and learning. Compr. Physiol. 2016;6:1295–337. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Leger M, Neill JC. A systematic review comparing sex differences in cognitive function in schizophrenia and in rodent models for schizophrenia, implications for improved therapeutic strategies. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 2016;68:979–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goldstein JM, et al. Are there sex differences in neuropsychological functions among patients with schizophrenia? Am. J. Psychiatry. 1998;155:1358–64. doi: 10.1176/ajp.155.10.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Navarra-Ventura G, et al. Gender differences in social cognition: a cross-sectional pilot study of recently diagnosed patients with schizophrenia and healthy subjects. Can. J. Psychiatry. 2018;63:538–46. doi: 10.1177/0706743717746661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li Q, et al. Sex differences in body mass index and obesity in chinese patients with chronic schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2016;36:643–8. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Annamalai A, Kosir U, Tek C. Prevalence of obesity and diabetes in patients with schizophrenia. World J. Diabetes. 2017;8:390–6. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i8.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cameron IM, Hamilton RJ, Fernie G, MacGillivray SA. Obesity in individuals with schizophrenia: a case controlled study in Scotland. BJPsych Open. 2017;3:254–6. doi: 10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.003640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.D.E.H. M, Schreurs V, Vancampfort D, V.A.N.W. R. Metabolic syndrome in people with schizophrenia: a review. World Psychiatry. 2009;8:15–22. doi: 10.1002/j.2051-5545.2009.tb00199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Finucane MM, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–67. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Manu P, et al. Weight gain and obesity in schizophrenia: epidemiology, pathobiology, and management. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015;132:97–108. doi: 10.1111/acps.12445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.De Hert M, et al. Typical and atypical antipsychotics differentially affect long-term incidence rates of the metabolic syndrome in first-episode patients with schizophrenia: a retrospective chart review. Schizophr. Res. 2008;101:295–303. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2008.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rojo LE, et al. Metabolic syndrome and obesity among users of second generation antipsychotics: a global challenge for modern psychopharmacology. Pharm. Res. 2015;101:74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hirsch L, et al. Second-generation antipsychotics and metabolic side effects: a systematic review of population-based studies. Drug Saf. 2017;40:771–81. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0543-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang F, et al. Sex difference in the association of body mass index and BDNF levels in Chinese patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol. (Berl.) 2019;236:753–62. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McEvoy JP, et al. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia: baseline results from the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) schizophrenia trial and comparison with national estimates from NHANES III. Schizophr. Res. 2005;80:19–32. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2005.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boke O, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among inpatients with schizophrenia. Int J. Psychiatry Med. 2008;38:103–12. doi: 10.2190/PM.38.1.j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li Q, et al. The prevalence, risk factors and clinical correlates of obesity in Chinese patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017;251:131–6. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bobes J, et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic risk in outpatients with schizoaffective disorder treated with antipsychotics: results from the CLAMORS study. Eur. Psychiatry. 2012;27:267–74. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guo X, et al. The relationship between obesity and neurocognitive function in Chinese patients with schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Susilova L, et al. Changes in BMI in hospitalized patients during treatment with antipsychotics, depending on gender and other factors. Int J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2017;21:112–7. doi: 10.1080/13651501.2017.1291818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fagundo AB, et al. Executive functions profile in extreme eating/weight conditions: from anorexia nervosa to obesity. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e43382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Restivo MR, et al. Effect of obesity on cognition in adults with and without a mood disorder: study design and methods. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e009347. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bora E, Akdede BB, Alptekin K. The relationship between cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2017;47:1030–40. doi: 10.1017/S0033291716003366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Depp CA, et al. Association of obesity and treated hypertension and diabetes with cognitive ability in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord. 2014;16:422–31. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lang X, et al. FOXP2 contributes to the cognitive impairment in chronic patients with schizophrenia. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:6440–8. doi: 10.18632/aging.102198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Randolph C, Tierney MC, Mohr E, Chase TN. The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1998;20:310–9. doi: 10.1076/jcen.20.3.310.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang BH, Zhang WF, Wang ZR. Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) as a screening test in Chinese: reliability and validity. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2009;28:865–9. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hafner H. Gender differences in schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2003;28(Suppl 2):17–54. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4530(02)00125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grossman LS, et al. Sex differences in schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders: a 20-year longitudinal study of psychosis and recovery. Compr. Psychiatry. 2008;49:523–9. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gangadhar BN, Panner Selvan C, Subbakrishna DK, Janakiramaiah N. Age-at-onset and schizophrenia: reversed gender effect. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2002;105:317–9. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.1153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thorup A, et al. Gender differences in young adults with first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorders at baseline in the Danish OPUS study. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2007;195:396–405. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000253784.59708.dd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gur RE, Petty RG, Turetsky BI, Gur RC. Schizophrenia throughout life: sex differences in severity and profile of symptoms. Schizophr. Res. 1996;21:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(96)00023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tang YL, et al. Gender differences in 542 Chinese inpatients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2007;97:88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Theodoropoulou S, et al. Cytokine serum levels, autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction and surface marker analysis in never medicated and chronically medicated schizophrenic patients. Schizophr. Res. 2001;47:13–25. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(00)00007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Subramaniam M, et al. Body mass index, obesity, and psychopathology in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2014;34:40–6. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Holcomb VB, Hong J, Nunez NP. Exogenous estrogen protects mice from the consequences of obesity and alcohol. Menopause. 2012;19:680–90. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e31823cf6ee. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Davis SR, et al. Understanding weight gain at menopause. Climacteric. 2012;15:419–29. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2012.707385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Norbeck LA, Sheridan MA. An in vitro model for evaluating peripheral regulation of growth in fish: effects of 17beta-estradiol and testosterone on the expression of growth hormone receptors, insulin-like growth factors, and insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011;173:270–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Eshtiaghi R, Esteghamati A, Nakhjavani M. Menopause is an independent predictor of metabolic syndrome in Iranian women. Maturitas. 2010;65:262–6. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Meltzer HY, Perry E, Jayathilake K. Clozapine-induced weight gain predicts improvement in psychopathology. Schizophr. Res. 2003;59:19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(01)00326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hermes E, et al. The association between weight change and symptom reduction in the CATIE schizophrenia trial. Schizophr. Res. 2011;128:166–70. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2011.01.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hui CL, et al. Examining gender difference in adult-onset psychosis in Hong Kong. Early Inter. Psychiatry. 2016;10:324–33. doi: 10.1111/eip.12167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ascher-Svanum H, Stensland M, Zhao Z, Kinon BJ. Acute weight gain, gender, and therapeutic response to antipsychotics in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry. 2005;5:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-5-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ascher-Svanum H, Stensland MD, Kinon BJ, Tollefson GD. Weight gain as a prognostic indicator of therapeutic improvement during acute treatment of schizophrenia with placebo or active antipsychotic. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005;19:110–7. doi: 10.1177/0269881105058978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Basson BR, et al. Factors influencing acute weight change in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine, haloperidol, or risperidone. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001;62:231–8. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v62n0404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kemp DE, et al. Associations among obesity, acute weight gain, and response to treatment with olanzapine in adolescent schizophrenia. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2013;23:522–30. doi: 10.1089/cap.2012.0099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kang SH, Lee JI. Metabolic disturbances independent of body mass in patients with schizophrenia taking atypical antipsychotics. Psychiatry Investig. 2015;12:242–8. doi: 10.4306/pi.2015.12.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gunstad J, et al. Longitudinal examination of obesity and cognitive function: results from the Baltimore longitudinal study of aging. Neuroepidemiology. 2010;34:222–9. doi: 10.1159/000297742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Barrett-Connor E. Rethinking estrogen and the brain. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1998;46:918–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stewart R, et al. A 32-year prospective study of change in body weight and incident dementia: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Arch. Neurol. 2005;62:55–60. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Vaidya D, et al. Association of baseline sex hormone levels with baseline and longitudinal changes in waist-to-hip ratio: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Int J. Obes. (Lond.) 2012;36:1578–84. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2012.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Seyfart T, et al. Association of sex hormones with physical, laboratory, and imaging markers of anthropometry in men and women from the general population. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0189042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hawley WR, et al. Reactivation of an aversive memory modulates learning strategy preference in male rats. Stress. 2013;16:73–86. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2012.683466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Locklear MN, Kritzer MF. Assessment of the effects of sex and sex hormones on spatial cognition in adult rats using the Barnes maze. Horm. Behav. 2014;66:298–308. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jimenez-Rubio G, Herrera-Perez JJ, Hernandez-Hernandez OT, Martinez-Mota L. Relationship between androgen deficiency and memory impairment in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2017;45:227–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Melcangi RC, Mensah-Nyagan AG. Neurosteroids: measurement and pathophysiologic relevance. Neurochem Int. 2008;52:503–5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Matousek RH, Sherwin BB. A randomized controlled trial of add-back estrogen or placebo on cognition in men with prostate cancer receiving an antiandrogen and a gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010;35:215–25. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Panizzon MS, et al. Interaction of APOE genotype and testosterone on episodic memory in middle-aged men. Neurobiol. Aging. 2014;35:1778 e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.12.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]