Abstract
In the Anthropocene, marine ecosystems are rapidly shifting to new ecological states. Achieving effective conservation of marine biodiversity has become a fast‐moving target because of both global climate change and continuous shifts in marine policies. How prepared are we to deal with this crisis? We examined EU Member States Programs of Measures designed for the implementation of EU marine environmental policies, as well as recent European Marine Spatial Plans, and discovered that climate change is rarely considered operationally. Further, our analysis revealed that monitoring programs in marine protected areas are often insufficient to clearly distinguish between impacts of local and global stressors. Finally, we suggest that while the novel global Blue Growth approach may jeopardize previous marine conservation efforts, it can also provide new conservation opportunities. Adaptive management is the way forward (e.g., preserving ecosystem functions in climate change hotspots, and identifying and targeting climate refugia areas for protection) using Marine Spatial Planning as a framework for action, especially given the push for Blue Growth.
Keywords: adaptive management, Blue Growth, climate change, marine protected areas, marine special planning, marine strategy framework directive, Mediterranean Sea, policy
Introduction
Current local and global stressors continue to alter marine ecosystems at alarming rates (Halpern et al. 2008, 2015, Hoegh‐Guldberg and Bruno 2010, Poloczanska et al. 2013), despite considerable intentions in the past few decades to turn the tide. Marine protected areas (MPAs), and especially no‐take marine reserves, are considered one of the main instruments for achieving the objectives of marine conservation (Halpern et al. 2010). Several decades of studies have indeed shown that, when well managed and enforced, MPAs can maintain and restore biodiversity and ecosystem functions (Edgar et al. 2014, Sala and Giakoumi 2017). A decade ago, Parties of the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to protect 10% of their marine waters by 2020 (Aichi Target 11). Nonetheless, recent assessments showed that, so far, only about 2% of the global ocean is included in fully or highly protected areas (Lubchenco and Grorud‐Colvert 2015, Claudet and Pendleton 2018), the two classes of MPAs unambiguously providing high ecological benefits (Zupan et al. 2018b). The rest of the designated MPAs either allow significant extractive activities that undermine biodiversity conservation objectives (Giakoumi et al. 2017) or are “paper parks” with little positive impact on marine ecosystems (Lubchenco and Grorud‐Colvert 2015, Sala et al. 2018). During the 2014 World Parks Congress it was stressed that the current 10% target, recently reached in European waters (European Environment Agency 2018), will not be sufficient to achieve conservation goals, and that 30% protection or more for each marine habitat could be required (O'Leary et al. 2016). In this already problematic arena, two looming challenges could further jeopardize the contribution of MPAs to achieving conservation goals.
The first fast‐unfolding challenge is global climate change, which modifies the marine environment at alarming rates, with severe impacts on marine ecosystems (Hoegh‐Guldberg and Bruno 2010, Poloczanska et al. 2013, IPCC 2014, 2018, Gattuso et al. 2015). Recently, it was shown that the ocean is warming even faster than previously thought (Cheng et al. 2019). In areas where climate change is rapidly altering the ocean physicochemical conditions, local populations of species are collapsing or expanding with changes in assemblage configurations inevitably leading to changes in community interactions and possibly also in ecosystem functioning. Under the threat of climate change, preserving marine ecosystems and local biodiversity is an increasingly difficult challenge and potentially unachievable target, even within effectively managed MPAs.
The second challenge is the ratchet‐like adoption of new marine policies. Their implementation, while promoting jobs and innovation in the short term, could have antagonistic objectives difficult to reconcile and potentially conducive to new sources of disturbance, undermining the essential functions of MPAs that are intended to be very long term. Most notable is the recent push toward policies supporting Blue Growth that was initiated in 2012 by the 4th United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development Rio + 20, and was strongly supported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Blue Growth is clearly reflected in the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal no. 14 for 2030 that aims to “conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources” (UN 2015). The concept of Blue Growth is young and it has no generally agreed definition (Eikeset et al. 2018). This leads to many problems in its interpretation (Voyer et al. 2018) and shifts back from a pure conservation perspective to a utilitarian sustainable use perspective. Still, sustainability in a Blue Growth context has been only vaguely defined and, if misused, can be a slippery slope of compromises to permanent harm. The global shift from sectorial management to Marine Spatial Planning (MSP; Ehler and Douvere 2009) has the potential to further restrict the space for biodiversity conservation in the ocean if conservation targets are not explicitly included in plans. These situations may increase the risk that the main motivation of stakeholders and managers of marine resources will be monetary and not based on conservation goals. Under the imperative of exploiting marine resources to support Blue Growth, also included in the goal no. 14 of the United Nations Sustainable Development goals (UN 2015), countries can be driven to plan new uses at sea primarily by economic motivations, overlooking environmental conservation goals, as well as social equity, the other two pillars of sustainable development (Gee 2019). This increases the risk that stakeholders and managers of marine resources overlook hidden ecosystem benefits and costs if only commercial revenues and costs are considered (Börger et al. 2014) at the expenses of multiple environmental, social, and economic benefits and ecosystem services arising from healthy, productive, and resilient ecosystems (Cavanagh et al. 2016).
Faced with these two unfolding challenges, effective marine conservation becomes a fast‐moving target such that policymakers, managers, and scientists have to adjust their expectations and strategies constantly for conservation planning. Here, we aim to address the challenge of achieving conservation targets under shifting conditions, specifically (1) global environmental change and (2) policy shift from pure focus on biodiversity conservation to sustainable use of the oceans, and within it the specific change in management strategies, from designating single MPAs to networks of MPAs within an overarching MSP framework. The European Union (EU) is used here as a case study to examine how these challenges are tackled by a large coordinated group of developed countries with well‐developed environmental policies. In particular, we reviewed European programs of measures for achieving good environmental status in European seas, existing marine spatial plans, and monitoring schemes in MPAs to investigate whether climate change is sufficiently accounted for and whether conservation objectives that largely mirror the need for Blue Growth initiatives are embedded into the revised policy toolbox. We also propose strategies and possible solutions to address the impacts of global change and improve the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Global Change Can Strongly Disrupt Current Conservation Efforts
Current and expected climate change impacts, even under the most optimistic Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change scenarios (IPCC 2018) pose a tremendous challenge to marine conservation (Pressey et al. 2007). The geographic distribution of species pools is altering rapidly in many regions in part reflecting shifts in ocean isotherms (Pinsky et al. 2013, Burrows et al. 2014, Molinos et al. 2015), and because native species are often replaced by thermophilic invaders (Rilov 2016, Rilov et al. 2018). Heat waves cause mass mortalities (Garrabou et al. 2009) while “dead zones” are expanding along with episodic phenomena that cause large‐scale hypoxia events (Bakun 2017). As a consequence of such complex processes, major ecological shifts, including local or even regional collapse of entire ecosystems such as coral reefs (Hughes et al. 2017) or macroalgal forests (Vergés et al. 2016, Wernberg et al. 2016), are increasingly observed. Deep‐sea biodiversity can also be vulnerable to global climate change (Danovaro et al. 2017b). Synergistic effects among stressors are increasingly documented and predicted as well (Mora et al. 2013, Boero et al. 2018). In such dynamic conditions, even the largest and best managed MPAs cannot be expected to achieve their conservation goals, especially in global change hotspots where both environmental conditions and ecological communities are shifting rapidly.
Recently, Roberts et al. (2017) listed some ecological pathways in which well‐managed MPAs can actually aid in mitigation and adaptation to many aspects of climate change. However, empirical evidence for mitigation or adaptation is still rare, and some climate effects are surely unavoidable inside MPAs. Bruno et al. (2018) have recently observed that the thermal ranges of marine communities will be crossed in the tropics by 2050, and further stated that climate change severely threatens many of the world's MPAs, especially at low latitudes. Undoubtedly, local population collapses of native species that are sensitive to ocean warming cannot be realistically mitigated even by the most effectively protected MPAs. For example, in the southeastern Mediterranean Sea, where coastal waters have warmed by 2–3°C in the past few decades, sea urchin populations totally collapsed along the entire coastline (Yeruham et al. 2015, Rilov 2016), including within the only well‐enforced marine reserve that has been protected for over two decades (Rilov 2016, Rilov et al. 2018). At the same time, MPAs cannot prevent the establishment of spreading thermophilic (often alien) species, unless they specifically facilitate native populations of strong competitors or predators (Giakoumi et al. 2019). In this situation, the chances of maintaining existing species and communities are most probably very low even under the most stringent management regimes. Should we then insist on targeting the protection of the established native biodiversity only, or perhaps accept the new situation and set fresh criteria for a healthy ecosystem state under a shifting ocean climate? In other words, in climate change hotspots, should managers give up their attempts to preserve native communities (a main statutory conservation goal) and shift their attention to other areas, or should they rather shift their expectations and adjust their conservation targets to better suit the new situation imposed by global stressors? We address some of these questions below.
The Policy Shift From Pure Conservation Targets to Sustainable Ocean Use
The global consensus to protect marine ecosystems dates back to the 1950s when the Geneva Convention on the Law of the Sea was adopted. After that period, in the 1970s several other conventions (e.g., Ramsar, World Heritage) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) were launched. More recently, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) came into force (in 1982 and 1993, respectively), highlighting and strengthening the role of MPAs. Global efforts to implement the CBD led to a substantial increase of MPAs worldwide and to the establishment of important networks of protected areas, such as the Natura 2000 network in Europe, which includes 3,957 marine sites, covering 11.7% of EU Member States’ territorial waters (Mazaris et al. 2018).
In the last decade, meanwhile, the oceans have been conceptualized as spaces that offer development opportunities for a so‐called blue economy (UN 2012, Voyer et al. 2018). Some consider oceans to be a modern economic frontier (OECD 2016), to respond to global challenges such as food security, medical care, and renewable energy. Emerging ocean‐based industries for the support of Blue Growth often include coastal tourism, aquaculture, offshore wind farms, marine biotechnology, and seabed mining (e.g., EC 2012).
In principle, “blue economy” aims to support and improve human welfare and social stability, while at the same time to reduce environmental risks and ecological losses (UNEP et al. 2012), which is essentially in line with the aim of MPAs as tools for achieving conservation objectives. Even heavily impacting activities like seabed mining may offer a strong leverage for marine conservation through the expansion of networks of offshore MPAs to protect the deep sea (Mazaris et al. 2018). For example, because of the evidence that deep‐sea areas that host high biodiversity coincide with ferro‐manganese crusts, and thus are rich in nodules and seamounts, the EU is supporting the creation of networks of offshore MPAs to protect unique deep ecosystems and pose restrictions to mining activities based on strategic environmental assessments (EU 2017). The momentum created by several G7 and G20 States for the exploration and possible exploitation of mineral resources in the deep Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and in the Mediterranean Sea is pushing the international scientific community to investigate the potential consequences and, eventually, to propose the establishment of different forms of marine protection in the deep sea (Danovaro et al. 2017a).
Coastal tourism can also offer opportunities for marine conservation. Worldwide, MPAs often failed to achieve their conservation objectives due to lack of funding, while, with the right policies and governance, the development of coastal tourism can offer economic support to the viability of MPAs (Depondt and Green 2006). Bioeconomic models have shown that marine reserves can represent a tool for Blue Growth, as in the medium term they increase the benefits for the local economy offsetting management and opportunity costs (Roncin et al. 2008, Sala et al. 2013). Protected areas associated with socioeconomic benefits for local people are more likely to produce positive conservation outcomes (Oldekop et al. 2016, Pascual et al. 2016), and can have higher acceptance and support by stakeholders, which is a prerequisite for their effectiveness (Gleason et al. 2010, Di Franco et al. 2016, Christie et al. 2017). Overall, then, MPAs are not per se in conflict with Blue Growth.
However, in practice, there is always the risk that a policy with negative implications for conservation will be greenwashed with the application of a “Blue Growth” label (Howard 2018). A tendency of designating remote and isolated areas for conservation, residual to commercial use and therefore not yet heavily exploited, is acknowledged in the literature (Devillers et al. 2015), with the result of aiding a country's progress toward the Aichi target, while missing the representativeness and effectiveness of conservation (Jones and De Santo 2016). For example, the continental shelf of Australia, where most activities potentially harmful to marine biodiversity are concentrated, is scarcely covered by MPAs (Barr and Possingham 2013), and in some cases, this was due to “a deliberate avoidance of areas with high fishing value and mineral resources” (Edgar et al. 2008; Spalding et al. 2013, Devillers et al. 2015, Bax et al. 2016). Such “tactics” should certainly be avoided.
The Policy Shift From Single MPAs to MPA Networks, and Finally to Conservation Through Marine Spatial Plans
Initially, MPAs were designated on a case‐by‐case basis but soon the vision of moving from single MPAs to MPA networks gained momentum (Sala et al. 2002, Boero et al. 2016) (Grorud‐Colvert et al. 2014). Conservation and ecological networks of MPAs are not ad hoc aggregations of independently designed MPAs but a system of MPAs in a given area aimed at protecting conservation priority sites and/or connected by the movement and dispersal of larvae, juveniles, or adults (Grorud‐Colvert et al. 2014). Networks of MPAs have important ecological benefits, such as adequate representation of marine biodiversity, protection of all stages of life cycles, provision of stepping stones of genetic, demographic, and ecological connectivity, and better overall resilience to climate change impacts (Olsen et al. 2013). Over time, MPA networks have been incorporated within the wider concept of ecosystem‐based marine spatial management, which recognizes the full array of interactions within an ecosystem, including human uses (Katsanevakis et al. 2011).
In parallel with the growth of the idea of MPA networks, the need for more holistic marine planning processes has been recognized and developed by different nations. Marine spatial plans are considered as such a holistic tool aimed to support ecosystem‐based management of the oceans (Ansong et al. 2017, UNEP 2017). Marine spatial planning is a “public process of analyzing and allocating the spatial and temporal distribution of human activities in marine areas to achieve ecological, economic, and social objectives that are usually specified through a political process” (Ehler and Douvere 2009). MSP has its roots in marine conservation, and the original zoning plan of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Australia is considered to be the initiator of MSP globally (Jay et al. 2013). In 2017, nearly 27% of the world's exclusive economic zones (EEZs) were managed by enforcing marine spatial plans in 22 countries, and about 26% more will be managed in the near future due to the ongoing MSP processes in 44 additional countries (Frazao Santos et al. 2019). However, since its inception, the conservation focus of marine spatial plans seems to have weakened with an increasing focus on managing disputes for marine space among different users of the sea (Merrie and Olsson 2014).
If MSP is applied, as it should be, through an ecosystem‐based approach, it has the potential to substantially benefit marine conservation (Fraschetti et al. 2018). Nevertheless, there are several concerns regarding the different interpretations of the sustainability concept between marine spatial plans and marine environmental policies (Qiu and Jones 2013). Under the Integrated Maritime Policy (EC 2007), the European Union conceived environmental protection and sustainable development as two pillars of the same strategy, by issuing two distinct Directives, the Marine Strategy Framework Directive 2008/56/EC (EC, 2008), and the Maritime Spatial Planning Framework Directive 2014/89/EC (EC 2014). However, they addressed contradictory policy goals (Gee 2019), compounded by the linguistic choice of “maritime” instead of “marine” spatial planning. Very recently, the new “MSP Global” initiative, a joint roadmap to accelerate “Maritime/Marine Spatial Planning” processes worldwide was launched by UNESCO‐IOC and the European Commission to specifically focus on priority actions related, among others, to implementing Ecosystem‐based MSP in practice (MSP‐Roadmap, 2017). Indeed, the way countries will operationalize sustainable development between the power‐play of maritime activities and uses in their national MSP initiatives will potentially bring both threats and opportunities for conservation and human wellbeing.
Is Climate Change Sufficiently Addressed in Marine Conservation Planning and Policy Implementation? The European Case
We utilized the European seas as a case study to test how climate change considerations are integrated into policies and legislation related to marine conservation and planning. The EU has issued a number of legislative acts that directly address marine conservation (Fraschetti et al. 2018). The most recent (but already in place for a decade) is the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD, Council Directive 2008/56/EC; amended by the Commission Directive 2017/845). The MSFD is of direct relevance to the Birds (Council Directive 79/409/EEC) and Habitats (Council Directive 92/43/EEC) Directives, which are the EU legislative instruments that set out the rules for the establishment of the Natura 2000 network of marine and terrestrial protected areas. The basic goal of the network is to ensure the long‐term maintenance of Europe's endangered species and habitats at a “favourable conservation status” (Fraschetti et al. 2018). The MSFD aims at achieving good environmental status (GES) of the EU's marine waters and fosters the use of MPAs (inclusive of the Natura 2000 network) as an important tool to fulfill this objective. The MSFD requires EU Member States to develop strategies to achieve GES. In this regard, EU Member States have published their Programmes of Measures (PoM) that identify those actions needed to be taken in order to achieve or maintain GES. However, GES can be put at significant risk by climate change, which exerts its influence on a broader scale and with less predictable trends and patterns than any local human activity. This is acknowledged in the preamble of the MSFD, which states that “in view of the dynamic nature of marine ecosystems and their natural variability, […] and the impact of climate change, it is essential to recognize that the determination of good environmental status may have to be adapted over time.”
To examine how the issue of climate change is being treated in practice, we scanned the recently published PoMs by the 23 coastal EU Member States to assess if and how climate change is being addressed in their current implementation of MSFD. The results showed that climate change was not mentioned at all in four PoMs (Denmark, Greece, Ireland, and Latvia). In eight countries (Spain, France, United Kingdom, Germany, Croatia, Estonia, Romania, and Finland) specific measures and objectives address climate change (see Appendix S1: Table S1 in Supporting Information for further details). In the PoMs of the 11 remaining countries, climate change was only mentioned in general statements but no specific measures were foreseen (Fig. 1). Climate change is considered in these PoMs as an interaction influencing other environmental and human components, such as biodiversity, fisheries and sea‐level rise. Nonetheless, some of the countries have published national strategies specifically to address adaptation to climate change, for example Portugal, Italy, and Croatia (UNEP 2015; Resolution of the Council of Ministers no. 56/2015; Galluccio et al. 2017).
Figure 1.

How climate change (CC) is addressed in the Programmes of Measures (PoMs) for the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) by the Coastal EU Member States. Information was taken and categorized from the text and summarized in Appendix S1: Table S1, where it was possible to review the details of the sections dedicated to CC of each PoM. The figure shows, as follows: CC not mentioned (orange), CC simply mentioned (yellow), and CC addressed within objectives and measures (green). Since the MSFD is focused on the marine environment, the colored areas represent the national jurisdiction defined under the United Nation Convention of the Law of the Sea (1982), including also the Ecological Protection Zone (EPZ) of Italy (Decree of the President of the Republic 209/2011) and the Ecological and Fishery Protection Zone of Croatia (ZERP; Law 331/2003) where coastal states have the right to enforce their jurisdiction for the preservation of the marine environment.
The Natura 2000 network potentially offers a solid basis for EU Member States to satisfy many of the criteria required for determining GES, including the establishment of systematic monitoring schemes and thus the production of comparable outcomes across countries. However, what is missing is a clear direction toward integrating and utilizing the collected information on species, habitats, and threats with comprehensive, flexible, and consistent site‐based assessments (including long‐term monitoring) that also address possible impacts of climate change (Rilov et al. 2019). The lack of criteria and practical rules for translating the knowledge collected in the Natura 2000 sites into GES assessments and thus to conservation recommendations and priorities is problematic.
We also scanned the marine spatial plans published by different European countries (some are not published yet) to assess how they address climate change. We found that climate change is considered mainly as a challenge in the general planning framework of marine spatial plans (Figs. 2, 3, Appendix S1: Table S2). Only three countries (UK, Netherlands, and Sweden) considered adaptation and mitigation to climate change in the marine environment as an objective of their plan, for which specific actions are put in place. All other countries ignore this threat entirely in their plans. Interestingly, the British and Dutch plans also include climate change as a management concern in the plan's monitoring phase, in order to get new knowledge about the effects and the response of the marine environment and of human uses to climate change along with the implementation of the plan. The fact that climate change as a threat and challenge is basically absent in the PoMs and MSP documents of most EU Member States clearly indicates that in practice present and future climate change impacts are largely ignored by marine and maritime managers.
Figure 2.
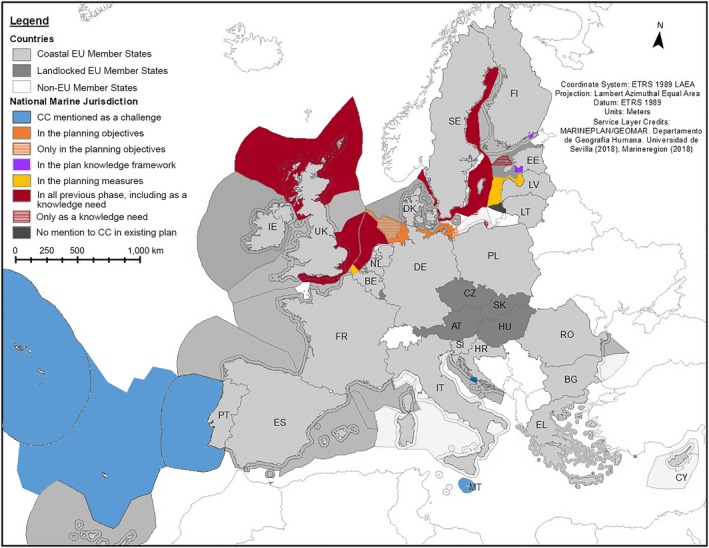
How climate change (CC) is addressed in marine spatial plans in EU marine waters. Colors in the map represent the phase(s) in the planning where climate change is considered/mentioned in marine spatial plans. Phases of the plans are a synthesis from Ehler and Douvere (2009). Gray shows the countries that are in the process of preparing their marine plans according to the EU Directive 2014/89/EU and do not have an approved plan yet. Dark gray shows the marine waters of Lithuania, where the existing marine spatial plan does not mention CC.
Figure 3.
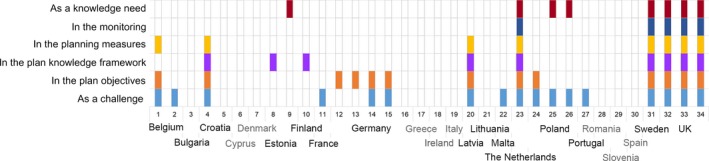
Marine spatial plans in the EU and the phase(s) in the planning where climate change is considered/mentioned. Phases of the plans are a synthesis from Ehler and Douvere (2009). Countries with gray font show that they are in the process of preparing their marine spatial plans according to EU Directive 2014/89/EU and do not have an approved plan yet. The marine spatial planning initiatives are the following: (1) Marine Spatial Plan for the Belgian part of the North Sea, 2014, (2) Belgian Vision for the North Sea 2050, Think Tank North Sea, 2017, (3) no plan, analysis for planning, (4) Coastal Plan for the Šibenik‐Knin County, 2016, (5) Zadar County Integrated Sea Use and Management Plan, 2001, 2015, (6) no plan, preplanning, (7) no plan, preplanning, (8) Pärnu Bay area pilot, 2017, (9) Hiiu Island MSP# Pilot Plan, 2016, (10) Regional Land Use Plan for the Sea, Kymenlaakso Region, 2013, (11) No plan, National Strategy for the Sea and Coastlines, 2014, preplanning, (12) Maritime Spatial Plan for the German EEZ in the Baltic Sea, 2009, (13) Maritime Spatial Plan for the German EEZ in the North Sea, 2009, (14) State Development Plan for Schleswig‐Holstein, 2010, 2015, (15) Spatial Development Programme of Mecklenburg‐Vorpommer, 2005, 2016, (16) Spatial Planning Programme of Lower Saxony, 1994, 2008, 2017, (17) no plan, preplanning, (18) no plan, analysis for planning, (19) no plan, preplanning, (20) Maritime spatial plan for the internal marine waters, territorial waters and exclusive economic zone of the Republic of Latvia, 2016, (21) Comprehensive Plan of the Republic of Lithuania (and its part “Maritime territories “), 2015, (22) Strategic Plan for the Environment and Development, 2017, 23. Policy Document on the North Sea 2016–2021, (24) Pilot Maritime Spatial Plan for the Western part of the Gulf of Gdańsk, 2003, 2008, (25) Pilot Maritime Spatial Plan for Pomeranian Bight/Arkona Basin, 2012, (26) Pilot Maritime Spatial Plan for Southern Middle Bank, 2012, (27) Situation Plan of Maritime Spatial Planning (PSOEM) in preparation, (28) no plan, national plan in preparation, (29) no plan, national plan in preparation, (30) no plan, preplanning, (31) Swedish marine spatial plans for three planning areas, published for consultation, (32) South Inshore and Offshore Plan, 2018, (33) East Inshore and Offshore Marine plan, 2014, (34) Scotland's National Marine Plan, 2015.
Can Existing MPA Monitoring Schemes Help to Detect Climate Change Impacts?
In order to distinguish between the effects of local stressors (e.g., fishing or recreational activities) that occur with varying intensity inside or outside MPAs (Zupan et al. 2018a), and global stressors occurring both inside and outside (e.g., warming), the best monitoring design would include time series from both inside and outside MPAs, before and after the establishment of the MPA (Benedetti‐Cecchi 2001, Thiault et al. 2017). To test if the information gathered from ecological studies carried out in MPAs would allow for the detection of climate change impacts through long‐term monitoring, we carried out a systematic scientific literature review (that is, not including reports and gray literature; details in Appendix S1: Table S3) to evaluate the existence of time series longer than two years across Mediterranean nationally designated MPAs and EU Natura 2000 sites (treated jointly as MPAs hereafter). For this analysis, we focused on the Mediterranean Sea as it represents a major hotspot of climate change with strong impacts already acting on its ecological communities (Lejeusne et al. 2010, Marbà et al. 2015) and where marine ecological research has a long tradition. Overall, we examined 89 scientific publications covering 35 different protected areas including 24 nationally designated MPAs, 10 EU Natura 2000 sites, and one international sanctuary (Fig. 4, Appendix S1: Table S3). Our analysis shows that most research efforts were concentrated in the western Mediterranean (Spain, Italy, and France), with only a few studies showing coordinated activities in more than one of these countries (e.g., study ID 22, 43‐46, 85, 86 in Appendix S1: Table S3). The majority of the studies were largely fragmented, covered a time span shorter than 10 years and very few exceeded 10 successive sampling dates (e.g., study ID 19, 30, 46, 61, 87). The most recent literature reporting time series does not provide data beyond 2014 (with the exception of Mazaris et al. 2017 on sea turtles), and 75 out of the 89 published time series were completed before 2010. Interestingly, most long‐term time series were carried out with the support of regional, national, or European research projects, and were only occasionally totally or partially financed by the MPA's management body as part of a continuous monitoring plan (16 studies; e.g., study ID 5, 12, 33, 51, 65). Few studies benefited from private or university funding (e.g., study ID 30, 34, 46, 87).
Figure 4.
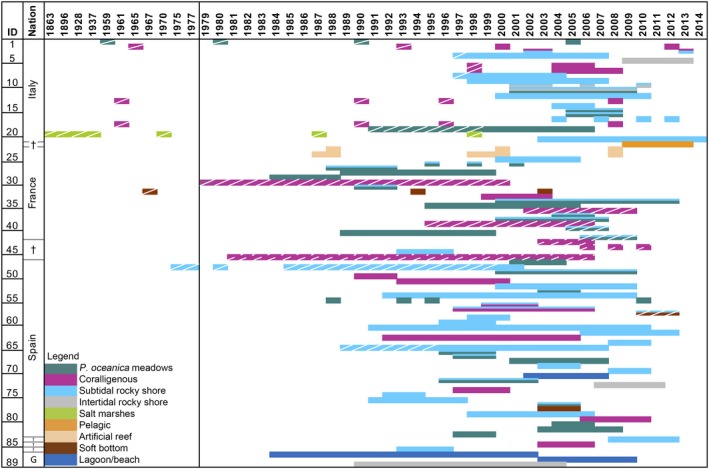
Duration of long‐term monitoring or repeated samplings in marine protected areas. Each horizontal bar shows the years of sampling for the corresponding article. The geographic area of the study is also indicated (G, Greece; †, international study: ID 22 Italy and France, ID 43‐46 France and Spain, ID 84 Italy and Croatia, ID 85 Italy and Spain, ID 86 Italy, France, and Spain). Different colors specify the habitat sampled; white stripes in the bars indicate years of sampling before the institution of the protection regime, intermittent white stripes represent studies investigating several marine protected areas (MPAs), some before and some after the institution of protection regime.
The focus of the monitoring programs was either on a single species (37 studies, for a total of 14 different species; e.g., study ID 39, 60, 89) or, more generally, on a guild of species or the entire assemblage (52 studies; e.g., study ID 21, 41, 80). The most explored habitats were subtidal rocky reefs and seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows, followed by coralligenous formations. Different response variables were investigated, including density or cover (e.g., study ID 35), abundance (e.g., study ID 12), biomass (e.g., study ID 34), diversity (e.g., study ID 29), age and sex of the organisms (e.g., study ID 4, 19), life‐history traits (e.g., study ID 39), behavior (e.g., study ID 60), biochemistry (e.g., study ID 74), variables utilized as proxies of the effect of natural or anthropogenic stressors (e.g., study ID 19), and catch effort for fish assemblages (e.g., study ID 4; Fig. 5). Overall, only 32.6% of studies adopted a sampling design allowing a comparison between areas with different protection regimes (fully protected vs. partially protected or unprotected zones) or estimated the effect of protection in MPAs by comparing data acquired before and after the protection started (e.g., study ID 4, 27, 54). Few studies (~20%) considered the effects of global climate change, either correlating one or more environmental variables to the biotic response variable as a proxy of change (8 studies out of 18) or suggesting the potential influence of climate change in the discussion of the article. The most cited process influencing natural assemblages was global warming (e.g., study ID 43, 68), followed by extreme events (e.g., study ID 61, 80), variation in the rainfall regime, variations in the North Atlantic Ocean Index (representing different phases of the jet‐stream that affect weather patterns; e.g., study ID 32), and introduction of invasive species (e.g., study ID 35, 62). However, no study citing climate change adopted a sampling design comparing protected and nonprotected areas in an attempt to disentangle the potential effects of protection from the effects of climate change, thus lacking the means to separate the effects of local and global stressors. Practical constraints often limit the potential to adopt rigorous experimental designs in contexts like this one; nonetheless, so far, in most of the cases, heat stress events reported within MPAs have been linked to climate change. We stress that applying rigorous experimental designs using MPAs to assess one of the most important processes occurring at basin scale should be a priority.
Figure 5.
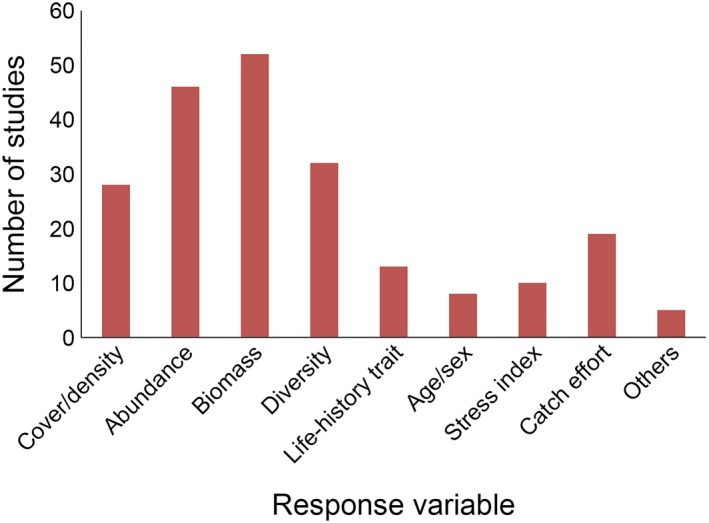
Number of monitoring studies reporting different types of response variables.
In summary, the lack of long‐term monitoring data poses serious limits to our potential to assess the role of MPAs in reaching GES, including their ability to help in assessing or mitigating the effects of climate change impacts (as suggested by Roberts et al. 2017). This result is of particular concern considering the tremendous impacts described in the previous sections, and shows that we are substantially ill equipped to handle the consequences of climate change, even in those areas that can be considered sentinel observatories of the impacts of ocean warming and more broadly to the state of the marine environment as a whole.
Adaptive Conservation Strategies to Address the Impacts of Global Change
Although dealing with global climate change is a huge challenge, changes in perception, and adaptive and creative thinking may offer some plausible courses of action. Here we list some ideas on how to deal with this problem.
Shifting the focus from species to functions in climate change hotspots
It is quite certain that, in the long run, we will not be able to protect species sensitive to warming in climate change hotspots, namely areas where climate is changing the most, e.g., where heatwaves are most frequent or intense (Holbrook et al. 2019, Smale et al. 2019). Therefore, a possible solution might be to adapt to the new situation by focusing on maintaining ecosystem functions (support of processes) and services that might otherwise be impacted by changes in species occurrences (Worm et al. 2006). A possible criterion could be that, as long as the main ecosystem functions are maintained in a region, regardless of the origin of the species involved, the system is in a good status and protection goals are met. That is, if a native species sensitive to warming has been functionally replaced by an alien or range‐expanding species, a good status has been maintained. As a consequence, monitoring should also focus on assessing critical ecosystem functions in the evaluation of conservation targets, using indirect methods such as biological traits analysis (Bremner et al. 2006) and, where possible, direct measurements of ecosystem functions and processes (such as habitat provisioning, community productivity, food web structure, nutrient cycling, metabolic functions). The use of global standardized measures for monitoring, such as Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBVs; Pereira et al. 2013) and the more recent, marine‐focused Essential Ocean Variables (EOVs; Miloslavich et al. 2018), might provide common standards for some of these components. SMART conservation objectives (and adequate indicators) are needed for effective evaluation of management performance (ICES 2005), i.e., (1) specific, clearly identifying the state to be achieved; (2) measurable, referring to measurable properties of ecosystem functioning, so that the development of indicators and reference points is feasible; (3) achievable, being possible to achieve (e.g., not including conflicting objectives, properly accounting for global change); (4) realistic, being feasible to achieve with the available resources for monitoring and management; and (5) time bound, having a clear time scale for their achievement.
Adaptive conservation planning in marine spatial planning
The implementation of MSP provides not only challenges but also a series of opportunities for conservation globally. For example, if systematic conservation planning is applied and implemented in the framework of MSP, advances can be made in marine conservation by extending MPAs, in particular fully protected areas or zones, and by creating MPA networks that are coherent, representative, and more robust at multiple spatial scales. Effective design of networks will rely on advances made in mapping population connectivity, by combining genetic and oceanographic data and models (Hodgson et al. 2009, Andrello et al. 2013, Coleman et al. 2017, Padrón et al. 2018). Systematic conservation planning puts operational targets for all ecological components but also accounts for the distribution of human activities and thus can settle disputes among sectors and balance conservation and economic activities (Gissi et al. 2018). A basic requirement of MSP (but not commonly applied in practice) is adaptive management, in which decisions can be modified based on new knowledge acquired on the system, environmental change, and assessment of the effectiveness of previous decisions and management actions (Parma 1998, Katsanevakis et al. 2011). It is in the light of such knowledge that new policies should be formulated rather than the ad hoc, short‐term, and static manner that happens today.
Ideally, marine spatial plans will be revised taking account of monitoring results and evaluation of their effectiveness to achieve the established planning objectives (Ehler 2014, Gissi et al. 2019). The assessment of the coherence with (potentially adaptive) conservation targets and sustainability of the actions and measures proposed through the marine spatial plans can be performed in relation to conservation policies and targets. It is the sustainability achieved through implementing the marine spatial plans that must be assessed over time, such plans (ideally) being instruments to achieve both Blue Growth and conservation targets in the changing ocean. However, the temporal framework of the planning revisions might not be able to detect shifts that take place at different temporal scales (Kidd and Ellis 2012), as dramatic changes over months or days can also occur (Hein et al. 2016). The implementation of dynamic ocean management (Maxwell et al. 2015) within marine spatial plans can constitute an opportunity to adapt to ecological shifts, by acting in real time. In this context, working to incorporate change in marine spatial plans is crucial, since currently only a few studies on marine spatial plans incorporate climate change in MSP processes (Gissi et al. 2019). Finally, long‐term monitoring will be of paramount importance to assess the effects of climate change and to disentangle global and human‐induced changes in marine ecosystems contrasting time series of data collected inside and outside MPAs (McQuatters‐Gollop 2012).
Targeting refugia from global climate change
Where relevant, marine spatial plans should include a climate‐ready response strategy that contains areas that can serve as potential climate refugia. Climate refugia are areas where climate‐induced physical and biological changes are slower or those that are significantly colder (e.g., upwelling areas or deeper waters) than surrounding areas, especially in fast‐warming regions (Keppel and Wardell‐Johnson 2012, Keppel et al. 2012). Including refugia habitats in conservation plans (e.g., Smythe and McCann 2018) is a promising approach to help mitigate for climate change implications (Keppel et al. 2015, Jones et al. 2016), especially when these refugia are assembled as a well‐connected network or a series of “stepping stones” (Hannah et al. 2014). Strategies for the detection and operationalization of refugia include the use of climate forecasts (in both mean and extreme conditions) to prioritize areas where climate change will not have a considerable effect (Levy and Ban 2013), identifying where current and future species distributions overlap (Terribile et al. 2012), and using historical or current climatic factors (Hermoso et al. 2013). Some countries are already thinking along these lines; for example, Sweden is considering the incorporation of climate refugia in its marine spatial plan in order to identify new MPAs within the planning framework.
Assisted (evolution) adaptation
Another increasingly discussed approach of dealing with the climate change challenge is harnessing nature's innate ability for rapid adaptation through transgenerational plasticity, epigenetics, and natural selection (Calosi et al. 2016). For some sensitive native species that are critical for local ecosystem functions, or those that have great economic value, “assisted evolution” has been suggested as at least a partial solution. Webster et al. (2017) recently argued that instead of trying to predict which species will be winners under climate change or create potential winners through assisted evolution, we should adopt a “diverse portfolio” strategy to promote climate adaptation. It should be driven by designing actions to facilitate different opportunities for selection across environmental conditions through diverse networks of protected areas, which goes back to developing proper MSP initiatives while taking these aspects into consideration. Since there is no single solution, the adoption of different tools to enhance the resilience of marine habitats should be the way to go, and MPAs might also benefit from local restoration actions using heat resistant lineages. In this framework, large‐scale interventions still seem to be challenging but a solid in‐depth knowledge of both the selected species and the system to be restored, together with the development of appropriate techniques might become another possibility to address the effects of climate change in the coming decades.
Conclusions
Despite the increasing impact of global climate change on marine biodiversity, and some rudimentary efforts to deal with it in nature conservation, it seems that we still mostly plan for the present, i.e., in a business‐as‐usual scenario, and not for the future, as there is an evident lack of consideration of climate change issues in actual marine management practice. Part of the problem is that the strongest tool that should allow us to distinguish between local and global stressors (mainly climate change), long‐term ecological monitoring inside and outside properly managed MPAs, is still rarely conducted. These problems translate into the difficulty in setting conservation priorities through an MSP process, although MPAs are considered among the strongest tools for ecosystem‐based management in a MSP context (Katsanevakis et al. 2011). We suggest that stakeholders need to more fully acknowledge the fact that marine conservation is becoming a fast‐moving target because of climate change and ongoing unrelated shifts in policies; and we need to address them accordingly. Then, in our efforts to establish networks of effective MPAs we should focus on (1) making sure we do the science right by continuing (where present) or starting and then maintaining well designed physical and ecological monitoring programs in MPAs; (2) finding the way to deal with climate change hotspots where change is fast and inevitable (i.e., frequency of marine heat waves is increasing and mass mortalities occur or are approaching), and identifying and considering potential refugia areas (where safety margins are large) in conservation plans; (3) thinking about how to set different targets or criteria for the health of the system in climate hotspots (for example, focus on maintaining functions); (4) counting on safety in numbers and habitat diversity by ensuring that protection networks reflect different environmental conditions to allow for climate adaptation; and (5) taking account of these issues when formulating new policies. With eyes wide open, in the framework of both marine spatial plans and Blue Growth, we still have to solve the potentially growing conflicts between protection and increasing human uses, first of all by facing the challenge to define precisely what is ecologically sustainable in the fast‐changing ocean we see today.
Supporting information
Acknowledgments
Author contributions: G. Rilov conceived the idea for the study, S. Fraschetti, E. Gissi, E. Menini, and L. Tamburello performed the analysis; G. Rilov, S. Fraschetti, S. Katsanevakis, C. Pipitone, F. Badalamenti, E. Gissi, E. Menini, and L. Tamburello wrote the first draft of the manuscript and all authors contributed to later stages of the manuscript. This article is based upon ideas developed in two workshops in Naples in November 2017 and November 2018 organized as part of the COST Action 15121 ‘Advancing marine conservation in the European and contiguous seas (MarCons; http://www.marcons-cost.eu; Katsanevakis et al. 2017) supported by COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology, CA15121). It is also partly supported by an Israel Science Foundation grant to GR (grant no. 1982/16).
Rilov, G. , Fraschetti S., Gissi E., Pipitone C., Badalamenti F., Tamburello L., Menini E., Goriup P., Mazaris A. D., Garrabou J., Benedetti‐Cecchi L., Danovaro R., Loiseau C., Claudet J., and Katsanevakis S.. 2020. A fast‐moving target: achieving marine conservation goals under shifting climate and policies. Ecological Applications 30(1):e02009 10.1002/eap.2009
Corresponding editor: Eric J. Ward.
Literature Cited
- Andrello, M. , Mouillot D., Beuvier J., Albouy C., Thuiller W., and Manel S.. 2013. Low connectivity between Mediterranean marine protected areas: a biophysical modeling approach for the dusky grouper Epinephelus marginatus . PLoS ONE 8:e68564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansong, J. , Gissi E., and Calado H.. 2017. An approach to ecosystem‐based management in maritime spatial planning process. Ocean & Coastal Management 141:65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bakun, A. 2017. Climate change and ocean deoxygenation within intensified surface‐driven upwelling circulations. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences 375:20160327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr, L. M. , and Possingham H. P.. 2013. Are outcomes matching policy commitments in Australian marine conservation planning? Marine Policy 42:39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bax, N. J. , Cleary J., Donnelly B., Dunn D. C., Dunstan P. K., Fuller M., and Halpin P. N.. 2016. Results of efforts by the convention on biological diversity to describe ecologically or biologically significant marine areas. Conservation Biology 30:571–581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti‐Cecchi, L. 2001. Beyond Baci: Optimization of environmental sampling designs through monitoring and simulation. Ecological Applications 11:783–799. [Google Scholar]
- Boero, F. , Foglini F., Fraschetti S., Goriup P., Macpherson E., Planes S., Soukissian T., and C. Consortium . 2016. CoCoNet: towards coast to coast networks of marine protected areas (from the shore to the high and deep sea), coupled with sea‐based wind energy potential. SCIRES‐IT‐SCIentific RESearch and Information Technology 6:1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Boero, F. , Danovaro R., and Orombelli G.. 2018. Changes and crises in the Mediterranean sea: current problems. Rendiconti Lincei. Scienze Fisiche e Naturali 29:511–513. [Google Scholar]
- Börger, T. , Beaumont N. J., Pendleton L., Boyle K. J., Cooper P., Fletcher S., Haab T., Hanemann M., Hooper T. L., and Hussain S. S.. 2014. Incorporating ecosystem services in marine planning: the role of valuation. Marine Policy 46:161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J. , Rogers S. I., and Frid C. L. J.. 2006. Methods for describing ecological functioning of marine benthic assemblages using biological traits analysis (BTA). Ecological Indicators 6:609–622. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, J. F. , Bates A. E., Cacciapaglia C., Pike E. P., Amstrup S. C., van Hooidonk R., Henson S. A., and Aronson R. B.. 2018. Climate change threatens the world's marine protected areas. Nature Climate Change 8:499–503. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, M. T. , et al. 2014. Geographical limits to species‐range shifts are suggested by climate velocity. Nature 507:492–495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calosi, P. , De Wit P., Thor P., and Dupont S.. 2016. Will life find a way? Evolution of marine species under global change. Evolutionary Applications 9:1035–1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, R. D. , Broszeit S., Pilling G. M., Grant S. M., Murphy E. J., and Austen M. C.. 2016. Valuing biodiversity and ecosystem services: a useful way to manage and conserve marine resources? Proceedings of the Royal Society B 283:20161635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L. , Abraham J., Hausfather Z., and Trenberth K. E.. 2019. How fast are the oceans warming? Science 363:128–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie, P. , Bennett N. J., Gray N. J., Wilhelm T. A., Lewis N. A., Parks J., Ban N. C., Gruby R. L., Gordon L., and Day J.. 2017. Why people matter in ocean governance: Incorporating human dimensions into large‐scale marine protected areas. Marine Policy 84:273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Claudet, J. , and Pendleton H. E. L.. 2018. Six conditions under which MPAs might not appear effective (when they are). ICES Journal of Marine Science 75:1172–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M. A. , Cetina‐Heredia P., Roughan M., Feng M., van Sebille E., and Kelaher B. P.. 2017. Anticipating changes to future connectivity within a network of marine protected areas. Global Change Biology 23:3533–3542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R. , Aguzzi J., Fanelli E., Billett D., Gjerde K., Jamieson A., Ramirez‐Llodra E., Smith C., Snelgrove P., and Thomsen L.. 2017a. An ecosystem‐based deep‐ocean strategy. Science 355:452–454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R. , Corinaldesi C., Dell'Anno A., and Snelgrove P. V.. 2017b. The deep‐sea under global change. Current Biology 27:R461–R465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depondt, F. , and Green E.. 2006. Diving user fees and the financial sustainability of marine protected areas: Opportunities and impediments. Ocean & Coastal Management 49:188–202. [Google Scholar]
- Devillers, R. , Pressey R. L., Grech A., Kittinger J. N., Edgar G. J., Ward T., and Watson R.. 2015. Reinventing residual reserves in the sea: are we favouring ease of establishment over need for protection? Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 25:480–504. [Google Scholar]
- Di Franco, A. , et al. 2016. Five key attributes can increase marine protected areas performance for small‐scale fisheries management. Scientific Reports 6:38135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EC . 2007. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions—an integrated maritime policy for the European Union. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52007DC0575
- EC . 2008. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). European Union, Brussels, Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- EC . 2012. Communication from the Commission: Blue growth opportunities for marine and maritime sustainable growth. European Union, Brussels, Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- EC . 2014. Directive 2014/89/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 23 July 2014 establishing a framework for maritime spatial planning. European Union, Brussels, Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, G. J. , Langhammer P. F., Allen G., Brooks T. M., Brodie J., Crosse W., De Silva N., Fishpool L. D., Foster M. N., and Knox D. H.. 2008. Key biodiversity areas as globally significant target sites for the conservation of marine biological diversity. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:969–983. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, G. J. , Stuart‐Smith R. D., Willis T. J., Kininmonth S., Baker S. C., Banks S., Barrett N. S., Becerro M. A., Bernard A. T., and Berkhout J.. 2014. Global conservation outcomes depend on marine protected areas with five key features. Nature 506:216–220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehler, C. 2014. A IOC manuals guide; guide to evaluating marine spatial plans. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Paris, France. p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Ehler, C. , and Douvere F.. 2009. Marine Spatial Planning: a step‐by‐step approach toward ecosystem‐based management. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission and Man and the Biosphere Programme, Paris, France. [Google Scholar]
- Eikeset, A. M. , Mazzarella A. B., Davíðsdóttir B., Klinger D. H., Levin S. A., Rovenskaya E., and Stenseth N. C.. 2018. What is blue growth? The semantics of “Sustainable Development” of marine environments. Marine Policy 87:177–179. [Google Scholar]
- EU . 2017. Report on the Blue Growth strategy towards more sustainable growth and jobs in the blue economy. Commission staff working document, SWD(2017) 128 final. European Union, Brussels, Belgium. p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency . 2018. EU reaches the Aichi target of protecting ten percent of Europe's seas. https://www.eea.europa.eu/highlights/eu-reaches-the-aichi-target
- Fraschetti, S. , et al. 2018. Light and shade in marine conservation across European and Contiguous Seas. Frontiers in Marine Science 5:420. [Google Scholar]
- Frazao Santos, C. , Crowder L. B., Orbach M., and Ehler C. N.. 2019. Marine spatial planning Page 660 in Sheppard C., editor. World seas: an environmental evaluation: volume III: ecological issues and environmental impacts. Elsevier Academic Press, London, UK. [Google Scholar]
- Galluccio, G. , Mereu V., Bacciu V., Bosello F., Marras S., Mercogliano P., Mysiak J., Navarra A., and Vinci V.. 2017. Supporto tecnico‐scientifico per il Ministero dell'Ambiente e della Tutela del Territorio e del Mare (MATTM) ai fini dell'Elaborazione del Piano Nazionale di Adattamento ai Cambiamenti Climatici (PNACC). Centro Euro‐Mediterraneo sui Cambiamenti Climatici, Lecce, Italy, p. 392. [Google Scholar]
- Garrabou, J. , et al. 2009. Mass mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: effects of the 2003 heat wave. Global Change Biology 15:1090–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Gattuso, J.‐P. , Magnan A., Billé R., Cheung W., Howes E., Joos F., Allemand D., Bopp L., Cooley S., and Eakin C.. 2015. Contrasting futures for ocean and society from different anthropogenic CO2 emissions scenarios. Science 349:4722‐4721–4722‐4710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee, K. 2019. The ocean perspective Pages 23–45 in Zaucha J. and Gee K., editors. Maritime spatial planning. Springer, Palgrave Macmillan, Cham, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Giakoumi, S. , Scianna C., Plass‐Johnson J., Micheli F., Grorud‐Colvert K., Thiriet P., Claudet J., Di Carlo G., Di Franco A., and Gaines S. D.. 2017. Ecological effects of full and partial protection in the crowded Mediterranean Sea: a regional meta‐analysis. Scientific Reports 7:8940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giakoumi, S. , Pey A., Di Franco A., Francour P., Kizilkaya Z., Arda Y., Raybaud V., and Guidetti P.. 2019. Exploring the relationships between marine protected areas and invasive fish in the world's most invaded sea. Ecological Applications 29:e01809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissi, E. , McGowan J., Venier C., Di Carlo D., Musco F., Menegon S., Mackelworth P., Agardy T., and Possingham H.. 2018. Addressing transboundary conservation challenges through marine spatial prioritization. Conservation Biology 32:1107–1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissi, E. , Fraschetti S., and Micheli F.. 2019. Incorporating change in marine spatial planning: A review. Environmental Science & Policy 92:191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, M. , McCreary S., Miller‐Henson M., Ugoretz J., Fox E., Merrifield M., McClintock W., Serpa P., and Hoffman K.. 2010. Science‐based and stakeholder‐driven marine protected area network planning: a successful case study from north central California. Ocean & Coastal Management 53:52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Grorud‐Colvert, K. , Claudet J., Tissot B. N., Caselle J. E., Carr M. H., Day J. C., Friedlander A. M., Lester S. E., De Loma T. L., and Malone D.. 2014. Marine protected area networks: assessing whether the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. PLoS ONE 9:e102298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B. S. , et al. 2008. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 319:948–952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B. S. , Lester S. E., and McLeod K. L.. 2010. Placing marine protected areas onto the ecosystem‐based management seascape. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 107:18312–18317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B. S. , Frazier M., Potapenko J., Casey K. S., Koenig K., Longo C., Lowndes J. S., Rockwood R. C., Selig E. R., and Selkoe K. A.. 2015. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world's ocean. Nature Communications 6:7615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah, L. , Flint L., Syphard A. D., Moritz M. A., Buckley L. B., and McCullough I. M.. 2014. Fine‐grain modeling of species’ response to climate change: holdouts, stepping‐stones, and microrefugia. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 29:390–397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein, L. , van Koppen C. K., van Ierland E. C., and Leidekker J.. 2016. Temporal scales, ecosystem dynamics, stakeholders and the valuation of ecosystems services. Ecosystem Services 21:109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hermoso, V. , Ward D. P., and Kennard M. J.. 2013. Prioritizing refugia for freshwater biodiversity conservation in highly seasonal ecosystems. Diversity and Distributions 19:1031–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, J. A. , Thomas C. D., Wintle B. A., and Moilanen A.. 2009. Climate change, connectivity and conservation decision making: back to basics. Journal of Applied Ecology 46:964–969. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegh‐Guldberg, O. , and Bruno J. F.. 2010. The impact of climate change on the world's marine ecosystems. Science 328:1523–1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook, N. J. , et al. 2019. A global assessment of marine heatwaves and their drivers. Nature Communications 10:2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard, B. C. 2018. Blue growth: stakeholder perspectives. Marine Policy 87:375–377. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T. P. , Barnes M. L., Bellwood D. R., Cinner J. E., Cumming G. S., Jackson J. B., Kleypas J., Van De Leemput I. A., Lough J. M., and Morrison T. H.. 2017. Coral reefs in the Anthropocene. Nature 546:82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ICES . 2005. Guidance on the Application of the Ecosystem Approach to Management of Human Activities in the European Marine Environment. ICES Cooperative Research Report 273. The Council, Copenhagen, Denmark. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC . 2014. Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability Page 151 in Core Writing Team , Pachauri R. K., and Meyer L. A., editors. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC . 2018. Summary for policymakers In Global warming of 1.5°C. Page 32 in Masson‐Delmotte V., Zhai P., Pörtner H. O., Roberts D., Skea J., Shukla P. R., Pirani A., Moufouma‐Okia W., Pćan C., Pidcock R., Connors S., Matthews J. B. R., Chen Y., Zhou X., Gomis M. I., Lonnoy E., Maycock T., Tignor M., and Waterfield T., editors. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre‐industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, S. , et al. 2013. International progress in marine spatial planning Pages 171–212 in Chircop A., Coffen‐Smout S., and McConnell M., editors. Ocean yearbook 27. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P. J. , and De Santo E.. 2016. Viewpoint–Is the race for remote, very large marine protected areas (VLMPAs) taking us down the wrong track? Marine Policy 73:231–234. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K. R. , Watson J. E., Possingham H. P., and Klein C. J.. 2016. Incorporating climate change into spatial conservation prioritisation: A review. Biological Conservation 194:121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanevakis, S. , Stelzenmüller V., South A., Sørensen T. K., Jones P. J., Kerr S., Badalamenti F., Anagnostou C., Breen P., and Chust G.. 2011. Ecosystem‐based marine spatial management: review of concepts, policies, tools, and critical issues. Ocean & Coastal Management 54:807–820. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanevakis, S. , Mackelworth P., Coll M., Fraschetti S., Mačić V., Giakoumi S., Jones P., Levin N., Albano P., and Badalamenti F.. 2017. Advancing marine conservation in European and contiguous seas with the MarCons Action. Research Ideas and Outcomes 3:381–409. [Google Scholar]
- Keppel, G. , and Wardell‐Johnson G. W.. 2012. Refugia: keys to climate change management. Global Change Biology 18:2389–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Keppel, G. , Van Niel K. P., Wardell‐Johnson G. W., Yates C. J., Byrne M., Mucina L., Schut A. G., Hopper S. D., and Franklin S. E.. 2012. Refugia: identifying and understanding safe havens for biodiversity under climate change. Global Ecology and Biogeography 21:393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Keppel, G. , Mokany K., Wardell‐Johnson G. W., Phillips B. L., Welbergen J. A., and Reside A. E.. 2015. The capacity of refugia for conservation planning under climate change. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 13:106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, S. , and Ellis G.. 2012. From the land to sea and back again? Using terrestrial planning to understand the process of marine spatial planning. Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning 14:49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lejeusne, C. , Chevaldonné P., Pergent‐Martini C., Boudouresque C. F., and Pérez T.. 2010. Climate change effects on a miniature ocean: the highly diverse, highly impacted Mediterranean Sea. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 25:250–260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J. S. , and Ban N. C.. 2013. A method for incorporating climate change modelling into marine conservation planning: An Indo‐west Pacific example. Marine Policy 38:16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lubchenco, J. , and Grorud‐Colvert K.. 2015. Making waves: The science and politics of ocean protection. Science 350:382–383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbà, N. , Jorda G., Agusti S., Girard C., and Duarte C. M.. 2015. Footprints of climate change on Mediterranean Sea biota. Frontiers in Marine Science 2:56. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, S. M. , Hazen E. L., Lewison R. L., Dunn D. C., Bailey H., Bograd S. J., Briscoe D. K., Fossette S., Hobday A. J., and Bennett M.. 2015. Dynamic ocean management: Defining and conceptualizing real‐time management of the ocean. Marine Policy 58:42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Mazaris, A. D. , Schofield G., Gazinou C., Almpanidou V., and Hays G. C.. 2017. Global sea turtle conservation successes. Science Advances 3:e1600730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazaris, A. D. , Almpanidou V., Giakoumi S., and Katsanevakis S.. 2018. Gaps and challenges of the European network of protected sites in the marine realm. ICES Journal of Marine Science 75:190–198. [Google Scholar]
- McQuatters‐Gollop, A. 2012. Challenges for implementing the Marine Strategy Framework Directive in a climate of macroecological change. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences 370:5636–5655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrie, A. , and Olsson P.. 2014. An innovation and agency perspective on the emergence and spread of marine spatial planning. Marine Policy 44:366–374. [Google Scholar]
- Miloslavich, P. , Bax N. J., Simmons S. E., Klein E., Appeltans W., Aburto‐Oropeza O., Andersen Garcia M., Batten S. D., Benedetti‐Cecchi L., and Checkley D. M. Jr. 2018. Essential ocean variables for global sustained observations of biodiversity and ecosystem changes. Global Change Biology 24:2416–2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinos, J. G. , Halpern B. S., Schoeman D. S., Brown C. J., Kiessling W., Moore P. J., Pandolfi J. M., Poloczanska E. S., Richardson A. J., and Burrows M. T.. 2015. Climate velocity and the future global redistribution of marine biodiversity. Nature Climate Change 6:83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, C. , Wei C.‐L., Rollo A., Amaro T., Baco A. R., Billett D., Bopp L., Chen Q., Collier M., and Danovaro R.. 2013. Biotic and human vulnerability to projected changes in ocean biogeochemistry over the 21st century. PLoS Biology 11:e1001682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MSP‐Roadmap . 2017. Joint Roadmap to accelerate Maritime/Marine Spatial Planning processes worldwide (MSP). 2nd International Conference on Marine/Maritime Spatial Planning, Paris, March 15–17 2017. http://www.mspglobal2030.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Joint_Roadmap_MSP.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- OECD . 2016. The ocean economy in 2030. OECD Publishing, Paris, France: 10.1787/9789264251724-en [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Oldekop, J. A. , Holmes G., Harris W. E., and Evans K. L.. 2016. A global assessment of the social and conservation outcomes of protected areas. Conservation Biology in Practice 30:133–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary, B. C. , Winther‐Janson M., Bainbridge J. M., Aitken J., Hawkins J. P., and Roberts C. M.. 2016. Effective coverage targets for ocean protection. Conservation Letters 9:398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, E. , et al. 2013. Achieving ecologically coherent MPA networks in Europe: science needs and priorities In Larkin K. and McDonough N., editors. Europe: science needs and priorities. Marine Board Position Paper 18. European Marine Board, Ostend, Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- Padrón, M. , Costantini F., Bramanti L., Guizien K., and Abbiati M.. 2018. Genetic connectivity supports recovery of gorgonian populations affected by climate change. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 28:776–787. [Google Scholar]
- Parma, A. M. 1998. What can adaptive management do for our fish, forests, food, and biodiversity? Integrative Biology: Issues, News, and Reviews 1:16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, M. , Rossetto M., Ojea E., Milchakova N., Giakoumi S., Kark S., Korolesova D., and Melia P.. 2016. Socioeconomic impacts of marine protected areas in the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Ocean & Coastal Management 133:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, H. M. , Ferrier S., Walters M., Geller G. N., Jongman R., Scholes R. J., Bruford M. W., Brummitt N., Butchart S., and Cardoso A.. 2013. Essential biodiversity variables. Science 339:277–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky, M. L. , Worm B., Fogarty M. J., Sarmiento J. L., and Levin S. A.. 2013. Marine taxa track local climate velocities. Science 341:1239–1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poloczanska, E. S. , Brown C. J., Sydeman W. J., Kiessling W., Schoeman D. S., Moore P. J., Brander K., Bruno J. F., Buckley L. B., and Burrows M. T.. 2013. Global imprint of climate change on marine life. Nature Climate Change 3:919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Pressey, R. L. , Cabeza M., Watts M. E., Cowling R. M., and Wilson K. A.. 2007. Conservation planning in a changing world. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 22:583–592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W. , and Jones P. J.. 2013. The emerging policy landscape for marine spatial planning in Europe. Marine Policy 39:182–190. [Google Scholar]
- Rilov, G. 2016. Multi‐species collapses at the warm edge of a warming sea. Scientific Reports 6:36897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilov, G. , Peleg O., Yeruham E., Garval T., Vichik A., and Raveh O.. 2018. Alien turf: overfishing, overgrazing and invader domination in southeastern Levant reef ecosystems. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 28:351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Rilov, G. , Mazaris A. D., Stelzenmüller V., Helmuth B., Wahl M., Guy‐Haim T., Mieszkowska N., Ledoux J.‐B., and Katsanevakis S.. 2019. Adaptive marine conservation planning in the face of climate change: What can we learn from physiological, ecological and genetic studies? Global Ecology and Conservation 17:e00566. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, C. M. , O'Leary B. C., McCauley D. J., Cury P. M., Duarte C. M., Lubchenco J., Pauly D., Sáenz‐Arroyo A., Sumaila U. R., and Wilson R. W.. 2017. Marine reserves can mitigate and promote adaptation to climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 114:6167–6175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncin, N. , Alban F., Charbonnel E., Crec'hriou R., De La Cruz Modino R., Culioli J.‐M., Dimech M., Goñi R., Guala I., and Higgins R.. 2008. Uses of ecosystem services provided by MPAs: How much do they impact the local economy? A southern Europe perspective Journal for Nature Conservation 16:256–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, E. , and Giakoumi S.. 2017. No‐take marine reserves are the most effective protected areas in the ocean. ICES Journal of Marine Science 75:1166–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, E. , Aburto‐Oropeza O., Paredes G., Parra I., Barrera J. C., and Dayton P. K.. 2002. A general model for designing networks of marine reserves. Science 298:1991–1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala, E. , Costello C., Dougherty D., Heal G., Kelleher K., Murray J. H., Rosenberg A. A., and Sumaila R.. 2013. A general business model for marine reserves. PLoS ONE 8:e58799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala, E. , Lubchenco J., Grorud‐Colvert K., Novelli C., Roberts C., and Sumaila U. R.. 2018. Assessing real progress towards effective ocean protection. Marine Policy 91:11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Smale, D. A. , Wernberg T., Oliver E. C., Thomsen M., Harvey B. P., Straub S. C., Burrows M. T., Alexander L. V., Benthuysen J. A., and Donat M. G.. 2019. Marine heatwaves threaten global biodiversity and the provision of ecosystem services. Nature Climate Change 9:306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Smythe, T. C. , and McCann J.. 2018. Lessons learned in marine governance: Case studies of marine spatial planning practice in the US. Marine Policy 94:227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, M. D. , Meliane I., Milam A., and Fitzgerald C.. 2013. Protecting marine space: global targets and changing approaches. Ocean YB 27:213–248. [Google Scholar]
- Terribile, L. C. , Lima‐Ribeiro M. S., Araújo M. B., Bizão N., Collevatt R. G., Dobrovolski R., Franco A. A., Guilhaumon F., Lima J. D. S., and Murakami D. M.. 2012. Areas of climate stability of species ranges in the Brazilian Cerrado: disentangling uncertainties through time. Brazilian Journal of Nature Conservation 10:152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Thiault, L. , Kernaléguen L., Osenberg C. W., and Claudet J.. 2017. Progressive‐Change BACIPS: a flexible approach for environmental impact assessment. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 8:288–296. [Google Scholar]
- UN . 2015. Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. UNGA Resolution A/RES/70/1. Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015. United Nations, General Assembly, New York. [Google Scholar]
- UN . 2012. Blue Economy Concept Paper: Rio + 20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development. United Nations, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP , FAO , IMO , UNDP , IUCN , W. F. Center , and GRIDArendal . 2012. Green Economy in a Blue World—synthesis report.
- UNEP . 2015. United Nations Environmental Programme annual report, UNEP, Nairobi, Kenya. pp. 55. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP . 2017. Taking steps toward marine and coastal ecosystem‐based management: An introductory guide. UNEP, Nairobi, Kenya. [Google Scholar]
- Vergés, A. , Doropoulos C., Malcolm H. A., Skye M., Garcia‐Pizá M., Marzinelli E. M., Campbell A. H., Ballesteros E., Hoey A. S., and Vila‐Concejo A.. 2016. Long‐term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 113:13791–13796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyer, M. , Quirk G., McIlgorm A., and Azmi K.. 2018. Shades of blue: what do competing interpretations of the Blue Economy mean for oceans governance? Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning 20:595–616. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, M. S. , Colton M. A., Darling E. S., Armstrong J., Pinsky M. L., Knowlton N., and Schindler D. E.. 2017. Who should pick the winners of climate change? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 32:167–173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernberg, T. , et al. 2016. Climate‐driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science 353:169–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worm, B. , et al. 2006. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 314:787–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeruham, E. , Rilov G., Shpigel M., and Abelson A.. 2015. Collapse of the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus populations in the Eastern Mediterranean—result of climate change? Scientific Reports 5:13479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zupan, M. , et al. 2018a. How good is your marine protected area at curbing threats? Biological Conservation 221:237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zupan, M. , Fragkopoulou E., Claudet J., Erzini K., Horta e Costa B., and Gonçalves E. J.. 2018b. Marine partially protected areas: drivers of ecological effectiveness. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 16:381–387. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials


