Abstract
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a syndrome leading to chronic intermittent hypoxia, and the up-regulation of toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and 6 on peripheral blood cells has been reported. We hypothesized that DNA methylation in TLR2 and TLR6 genes may play a role in the development of OSA and its excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) phenotype. DNA methylation over 28 cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) sites of the TLR2 promoter region and 3 CpG sites of the TLR6 gene body, and their protein expressions were measured by using pyrosequencing and ELISA methods in 18 heathy subjects (HS) and 58 patients with severe OSA (divided into 18 non-EDS and 40 EDS group). Patients with severe OSA had higher DNA methylation levels over five CpG sites (#1, #2, #3, #25 and #28) and lower DNA methylation levels over CpG site #18 of the TLR2 promoter region, higher DNA methylation levels over two CpG sites (#1 and #3) of the TLR6 gene body, and higher protein expressions of TLR6 than HS. The CpG site #2 of the TLR6 gene body was hypermethylated in severe OSA patients with EDS. Both DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1 of the TLR6 gene body and protein expressions of TLR6 were reduced after more than 6 months of nasal CPAP treatment in seven selected patients. Aberrant DNA methylation of the TLR2 promoter region and TLR6 gene body are associated with the consequence of severe OSA and its EDS phenotype.
Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a syndrome characterized by repetitive upper airway collapse during sleep, leading to chronic intermittent hypoxia, sleep fragmentation, oxidative stress and the damage similar to that caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury [1, 2]. Indeed, intermittent hypoxia (IH) activates a number of signaling pathways that are involved in oxygen sensing, oxidative stress, metabolism, catecholamine biosynthesis, and immune responsiveness. The cumulative effect of these processes over time can undermine cell integrity and lead to a decline in its function, cell injury and cell death [3]. These consequences not only result in excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and impaired cognitive function, but are also correlated with cardiovascular morbidities such as stroke, ischemic heart disease (IHD), congestive heart failure (CHF), and arrhythmias [4–7].
DNA methylation is a heritable, tissue-specific, and reversible gene regulatory process that is highly modified in response to environmental factors, including intermittent hypoxia [8, 9]. DNA methylation occurs at position 5 of the pyrimidine ring of cytosines in the context of the cytosine followed by guanine dinucleotide sequence (CpG) forming the basis of epigenetic mechanisms modulating gene expressions by inhibition of the binding of transcription factors (TF) at the promoter regions. The negative correlation between gene expression and the DNA methylation at the promoter regions is well-established, whereas recent studies have proven that DNA methylation status in the gene body shows a positive correlation with gene expression through alternative splicing [10–14]. DNA methylation does not only affect TF binding leading to de-regulated gene expression. More importantly, there is a crosstalk between DNA methylation and histone modifications which directly affects transcriptional gene activity.
Although aberrant DNA methylation in the promoter regions of several inflammation-related genes such as IL1R2 (interleukin 1 receptor 2), AR (androgen receptor), NPR2 (natriuretic peptide receptor 2), and SP140 (speckled protein 140) genes have been reported in patients with OSA [15], little is known about the role of DNA methylation over the TLR genes in the development of OSA and its clinical phenotypes. In our previous study, we found co-upregulation of TLR 2 and 6 on peripheral blood neutrophils and mononuclear cells in patients with OSA, and these changes could be reversed after continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment [16, 17]. It has been demonstrated that hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α coordinates selective induction of both TLR2 and TLR6 during persistent hypoxia [18], and the intermittent hypoxia led to greater than two fold upregulation of the TLR2 in healthy volunteers has also reported[19]. The down-regulation of TLR2 expressions through aberrant DNA methylation of certain CpG sites over TLR2 promoter region has been demonstrated in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) disease and cystic fibrosis [20]. In this study, we hypothesized that DNA methylation in the promoter region of TLR2 and in the TLR6 gene body might play a role in the development of severe OSA and the EDS phenotype.
Materials and methods
Subjects
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan (certificate number: 102-3887B). The participants were recruited from both Sleep and Health Examination Centers of Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital from February 2014 through February 2017. Informed consent was obtained from each subject participating in the study. Adults (aged 20 to 65 years) who were diagnosed as healthy subject (HS) with primary snoring (defined as Apnea-hypopnea index(AHI) < 5 and were free of other sleep disorder) or severe OSA (defined as AHI >30) after full-night polysomnographic studies in our sleep laboratory were included. The exclusion criteria were ongoing infections, autoimmune disease, use of immunosuppressive agent in the past 6 months, narcolepsy, severe obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥ 35 kg/m2), and those with a BMI < 21 kg/m2. Patients with severe OSA were further divided into two subgroups according to the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS): OSA with ESS≦10 (non-EDS group) and OSA with ESS>10 (EDS group). Seven patients with severe OSA who had been under nasal CPAP management at least 4 hours per night for more than 6 months were included for further comparison.
Polysomnography
Body height, body weight, and BMI were measured prior to the overnight polysomnographic study. Subjective sleepiness was assessed using the ESS, a 24-point questionnaire comprised of 8 questions, each with a 0–3 scale that assesses a subject’s tendency to fall asleep during various situations, where a higher score indicates increased sleepiness[21, 22]. The completed polysomnography examination, including electroencephalography, electrooculography, chin and anterior tibial electromyography, respiratory effort detectors, nasal/oral flow sensors, and pulse oximetry, was performed using a standardized commercial device (Sandman SD32+TM Digital Amplifier [Embla, Colorado, U.S.A.]).
All subjects completed their polysomnographic study with at least 4 hours of total sleep time as indicated by electroencephalography. Sleep stage scoring was done at 30-second intervals by experienced technicians according to the standard criteria [23]. Obstructive apnea was defined as a cessation of airflow for at least 10 seconds with the subject making an effort to breathe during apnea. Obstructive hypopnea was defined as an abnormal respiratory event with at least a 30% reduction in thoraco-abdominal movement or airflow as compared to baseline, lasting for at least 10 seconds, with a greater than 4% oxygen desaturation. The AHI was defined as the total number of apneas and hypopneas per hour of electroencephalographic sleep. An AHI of at least five events per hour of sleep established the diagnosis of OSA (primary snoring, AHI <5; mild OSA, AHI = 5.0–14.9; moderate OSA, AHI = 15.0–29.9; severe OSA, AHI≥30.0). The CPAP-treated patients had undergone a CPAP titration study with a manually titrated machine (GoodKnight 420E, Nellcor Puritan Bennett, California, U.S.A.) to get an optimal pressure before starting their treatment with either fixed or auto-adjusted positive airway pressure machines at home.
Measurement of DNA methylation levels over the TLR2 promoter region and TLR6 gene body by bisulfite pyrosequencing method
Twenty milliliters of venous blood were withdrawn from healthy subjects and patients with severe OSA at around 07:30–08:30AM after overnight fast and sleep. The venous blood (20 ml) was also obtained before and after 6-month CPAP management in 7 patients with severe OSA who had been under CPAP therapy.
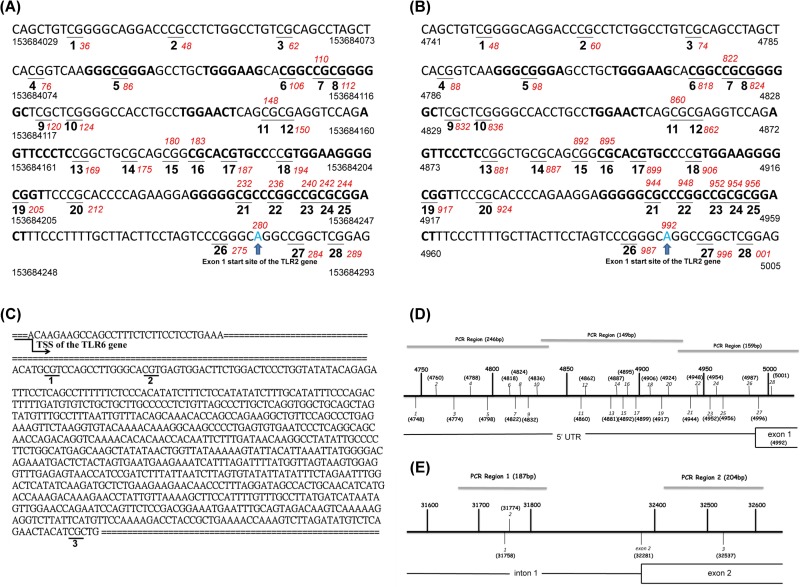
Genomic DNA was isolated from whole blood using a genomic DNA purification kit (Puregene). Three regions of the TLR2 promoter element (NCBI Reference Sequence: NC_000004.12 and NG_016229.1), including 28 CpG sites, were amplified (Figs 1 and S1–S2). Two regions of the TLR6 gene body, including 3 CpG sites (NCBI Reference Sequence: NG_028087.1) were analyzed (CpG site #1 and #2 were in the intron 1, and #3 was in the exon 2 of the gene body) (Figs 1 and S3–S4). Sodium bisulfate treatment was performed using EZ DNA MethylationTM Kit (ZYMO RESEARCH, USA) and PCR amplification was performed using PyroMark PCR Kit (Qiagen, Germany). The PCR condition was 45 cycles of 95°C for 20 s, 50°C for 20 s, and 72°C for 20 s, followed by 72°C for 5 min. Primer sequences used for PCR amplification and pyrosequencing are listed in S1 Table. The biotin-labeled PCR product was captured by Streptavidin SepharoseTM High Performance (GE Healthcare, Germany). Quantitation of cytosine methylation was done using the PyroMark Q24 system (Qiagen, Germany). The amount of C relative to the sum of the amounts of C and T at each CpG site was calculated as percentage. Representative pyrograms of CpG di-nucleotides assayed are presented in S5 Fig.
Fig 1. Diagrams showing CpG site locations of the TLR2 and TLR6 genes (genome build “GRCh38.p13”).
(A)~(B): A zoom of the 28 CpG sites assayed in the TLR2 gene and their genomic sequences based on NCBI Reference Sequence (NC_000004.12 and NG_016229.1). (C): A zoom of the 3 CpG sites assayed in the TLR6 gene and their genomic sequences based on NCBI Reference Sequence (NG_028087.1). (C): Diagram showing CpG site locations of the TLR2 gene. The CpG site #27 and #28 were in the exon 1 of the gene body, and the others were in the promoter regions. (D): Diagram showing CpG site locations of the TLR6 gene. CpG site #1 and #2 were in the intron 1, and #3 was in the exon 2 of the gene body.
Measurement of TLR2 and TLR6 total protein expression by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
TLR2 and TLR6 protein expression were measured by using TLR2 and TLR6 Human ELISA Protocol Kit (USCN Life Science Inc, USA)
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Independent samples t-test or Mann–Whitney U test was used for comparing continuous variables. Categorical variables were analyzed using Chi-square test. ANOVA model followed by post-hoc Bonferroni analysis was performed to analyze the differences in continuous variables among HS, non-EDS and EDS groups. Paired samples t-test was used to compare the change in the levels of DNA methylation and protein expressions before and after CPAP management. Multivariate linear regression with hierarchical comparison was performed in two steps with all potential co-variables (age, body mass index<BMI>, gender, diabetes mellitus<DM>, hypertension, stroke, valvular heart disease <VHD>, ischemic heart disease <IHD>, congestive heart failure<CHF>, arrhythmia, rhinitis, obstructive airway disease<OAD>, malignancy, renal failure and gastroesophageal reflux disease<GERD> were entered in the first step, and the OSA or EDS were entered in the second step) to determine independent factors contributing to the DNA methylation of the TLR2 promoter region and the TLR6 gene body, and their protein expressions in patients. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS for Windows, version 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). To assist in the interpretation of p-values given the number of statistical tests performed, q-values (false discovery rate) were calculated separately for multiple comparisons of the DNA methylation and protein expression levels by Benjamini-Hochberg test using R Console software, version 3.4.0. (2017 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing). A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, so up to 10% of declared discoveries should be expected to be false.
Results
Demography
A total of 18 healthy subjects (HS) and 58 patients with severe OSA were included in the study. Patients with OSA were older (37.72±9.20 vs. 49.43±10.07, p < .001) and more obese (BMI 24.54±3.58 vs. 29.06±5.23, p = .001). Male gender and prevalent hypertension were also more frequently noted in patients with severe OSA (Table 1).
Table 1. Demographic characteristics between healthy subjects and patients with severe OSA.
| HS(n = 18) | OSA (n = 58) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 37.72±9.20 | 49.43±10.07 | < .001 |
| BMI | 24.54±3.58 | 29.06±5.23 | .001 |
| Gender(M/F) | 10(55.6%)/8(44.4%) | 54(93.1%)/6(10.3%) | .001 |
| DM | 0(0%) | 8(13.8%) | .187 |
| Hypertension | 0(0%) | 22(37.9%) | .002 |
| Stroke | 0(0%) | 1(1.7%) | 1.00 |
| VHD | 1(5.6%) | 10(17.2%) | .441 |
| IHD | 0(0%) | 3(5.1%) | 1.00 |
| CHF | 0(0%) | 2(3.4%) | 1.00 |
| Arrhythmia | 0(0%) | 1(1.7%) | 1.00 |
| Rhinitis | 3(16.7%) | 13(22.4%) | .75 |
| OAD | 0(0%) | 7(12.1%) | .192 |
| Malignancy | 0(0%) | 4(6.9%) | .57 |
| Renal failure | 2(11.1%) | 6(10.3%) | 1.00 |
| GERD | 1(5.6%) | 15(25.9%) | .10 |
| WBC | 6.32±1.52 | 6.84±1.99 | .351 |
| TSH | 1.44±.73 | 1.88±1.40 | .30 |
| Chol | 187.93±33.36 | 190.96±35.01 | .76 |
| TG | 111.80±58.65 | 165.45±109.11 | .07 |
| HbA1c | 5.39±.31 | 8.96±16.76 | .48 |
DNA methylation and protein expression levels in OSA and healthy subjects
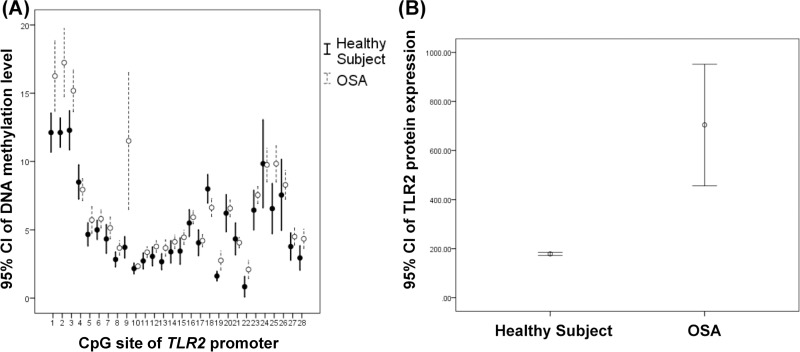
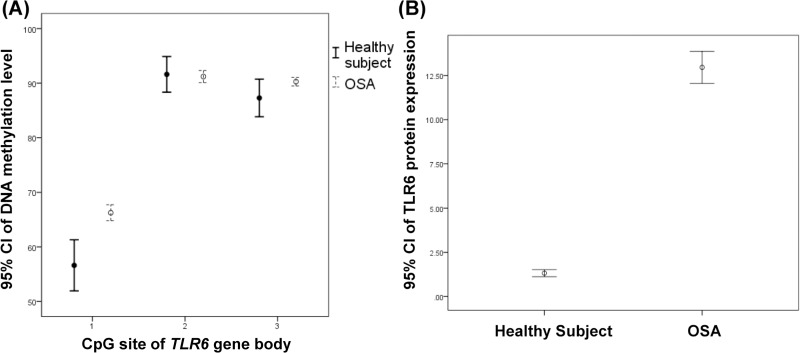
DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1, #2, #3, #8, #9, #13, #19, #22, #25 and #28 of the TLR2 promoter region and TLR2 protein expression were all increased in patients with severe OSA as compared with HS, while DNA methylation levels over CpG site #18 of the TLR2 promoter region was decreased (Fig 2 and S2 Table). Both DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1 of the TLR6 gene body and TLR6 protein expressions were significantly increased in patients with severe OSA versus HS (Fig 3 and S2 Table).
Fig 2. Comparisons of DNA methylation levels over the TLR2 promoter region and TLR2 protein expressions.
(A)DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1, #2, #3, #8, #9, #13, #19, #22, #25 and #28 of the TLR2 promoter region were increased (p = .006, < .001, .006, .027, .003, .018, .004, .013, .005, and .015 respectively ), while DNA methylation levels over CpG site #18 of the TLR2 promoter region was decreased (p = .027). (B)TLR2 protein expression were increased in patients with severe OSA (p < .001).
Fig 3. Comparisons of DNA methylation levels of the TLR6 gene body and TLR6 protein expression.
(A)DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1 of TLR6 gene body and (B)TLR6 protein expressions were increased in patients with severe OSA (p < .001 and < .001 respectively).
Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that OSA was the independent factor of DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1, #2, #3, #18, #25 and #28 of the TLR2 promoter region, CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body, and protein expressions of TLR6 (Tables 2 and S3). Apnea-Hypopnea index (AHI) or oxygen de-saturation index (ODI) were also independent factors of DNA methylation levels of the TLR2 promoter region, TLR6 gene body, and protein expressions of TLR6 (S4 and S5 Tables). These results remained statistically significant in DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body after correction for multiple comparisons with all q values <0.1. (Tables 2 and S6–S8). In addition, the DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1 and #3 were significant correlated to protein expressions of TLR6 after the analysis using Pearson correlation (p < .001 and p = .028 respectively).
Table 2. Summary of results of multivariate linear regression and multiple comparison: OSA is the independent risk factor of DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1, #2, #3, #18, #25 and #28 of the TLR2 promoter region, CpG site #1 and #3 of TLR6 gene body, and protein expression of TLR6.
(The complete data was presented at S6 Table).
| Multivariate linear regression | Multiple comparisons | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| △F | p | △R2 | β | t | pr2 | q | ||
| TLR2 promoter region | CpG#1 | 4.546 | .037 | .051 | .327 | 2.132 | .071 | .153 |
| CpG#2 | 5.202 | .026 | .055 | .339 | 2.281 | .081 | .123 | |
| CpG#3 | 5.293 | .025 | .053 | .335 | 2.301 | .082 | .123 | |
| CpG#18 | 4.333 | .042 | .056 | -.342 | -2.082 | .069 | .154 | |
| CpG#25 | 6.221 | .015 | .072 | .389 | 2.494 | .095 | .123 | |
| CpG#28 | 5.856 | .019 | .070 | .383 | 2.420 | .090 | .123 | |
| TLR6 gene body | CpG#1 | 20.736 | < .001 | .192 | .635 | 4.554 | .260 | < .001 |
| CpG#3 | 9.421 | .003 | .120 | .502 | 3.069 | .138 | .033 | |
| Protein expression | TLR6 | 97.805 | < .001 | .325 | .825 | 9.890 | .645 | < .001 |
DNA methylation and protein expression levels in OSA with and without excessive daytime sleepiness
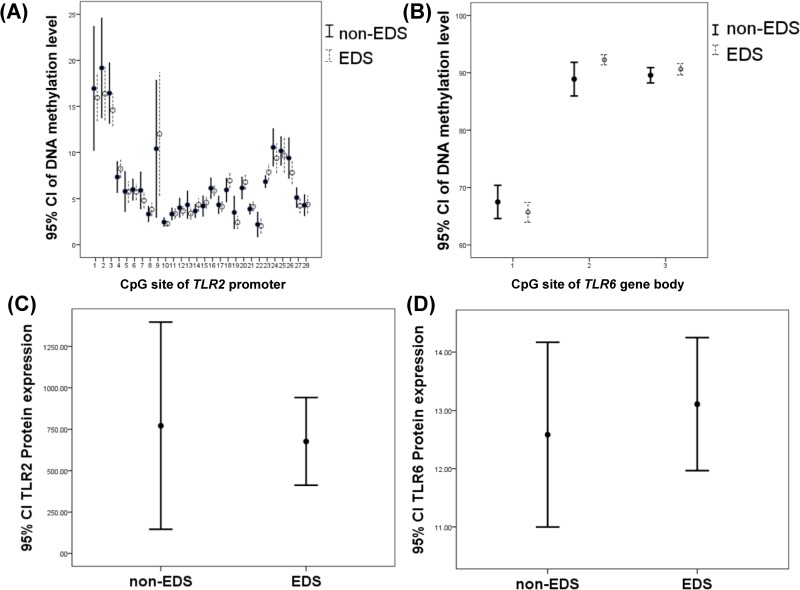
All the severe OSA patients were divided into two groups based on Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS): 18 patients with ESS less than or equal to 10 (non-EDS group) and 40 patients with ESS more than 10 (EDS group). Using ANOVA model followed by post-hoc Bonferroni correction analysis among the HS, non-EDS and EDS groups, we found that the demographic characteristics were not significantly different between non-EDS and EDS groups, but these two groups had significantly older age, were more obese and had a larger proportion of prevalent hypertension than did the HS group (Table 3). DNA hypermethylation over CpG site #2 of the TLR6 gene body was noted in the EDS group versus non-EDS group (Fig 4 and S9 Table). EDS was the independent factor of the DNA methylation level over CpG site #2 of the TLR6 gene body after multivariate linear regression analysis and multiple comparisons. (S10 and S11 Tables).
Table 3. Demographic characteristics between healthy subjects, non-EDS and EDS patients.
| HS(n = 18) | Non-EDS(n = 18) | EDS(n = 40) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 37.72±9.20 | 49.16±7.79 | 49.56±11.06 | < .001* |
| BMI | 24.54±3.58 | 28.74±5.67 | 29.21±5.09 | .004** |
| Gender(M/F) | 10(55.6%)/8(44.4%) | 14(77.8%)/4(22.2%) | 38(95%)/2(5%) | .001@ |
| DM | 0(0%) | 3(16.7%) | 5(12.5%) | .247 |
| Hypertension | 0(0%) | 7(38.9%) | 15(37.5%) | .009@@ |
| Stroke | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 1(2.5%) | .643 |
| VHD | 1(5.6%) | 4(22.2%) | 6(15%) | .406 |
| IHD | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 3(7.5%) | .252 |
| CHF | 0(0%) | 1(5.6%) | 1(2.5%) | .607 |
| Arrhythmia | 0(0%) | 1(5.6%) | 0(0%) | .214 |
| Rhinitis | 3(16.7%) | 4(22.2%) | 9(22.5%) | .200 |
| OAD | 0(0%) | 1(5.6%) | 6(15%) | .161 |
| Malignancy | 0(0%) | 3(16.7%) | 1(2.5%) | .049 |
| Renal failure | 2(11.1%) | 1(5.6%) | 5(12.5%) | .714 |
| GERD | 1(5.6%) | 3(16.7%) | 12(30%) | .099 |
| WBC | 6.32±1.52 | 6.85±1.79 | 6.82±2.09 | .648 |
| TSH | 1.44±.73 | 2.09±1.96 | 1.79±1.10 | .441 |
| Chol | 187.93±33.36 | 196.10±38.45 | 188.39±33.40 | .702 |
| TG | 111.80±58.65 | 141.62±78.89 | 177.36±120.63 | .091 |
| HbA1c | 5.39±.31 | 10.91±20.99 | 8.07±14.64 | .638 |
* p = .002 and p < .001were noted in HS versus Non-EDS and EDS group respectively; ** p = .035 and p = .004 were noted in HS versus Non-EDS and EDS group respectively;
@ p = .148 and p = .001 were noted in HS versus Non-EDS and EDS group respectively;
@@ p = .034 and p = .011 were noted in HS versus Non-EDS and EDS group respectively.
Fig 4. Comparisons of DNA methylation levels over the TLR2 promoter region, TLR6 gene body, and protein expressions of TLR2 and TLR6 between non-EDS and EDS groups.
(A)~(D) The DNA methylation levels over the TLR2 promoter region, and protein expressions of TLR2 and TLR6 were not significantly different except that CpG site #2 of the TLR6 gene body was hypermethylated significantly in the EDS group (p = .032).
DNA methylation and protein expression levels after CPAP management
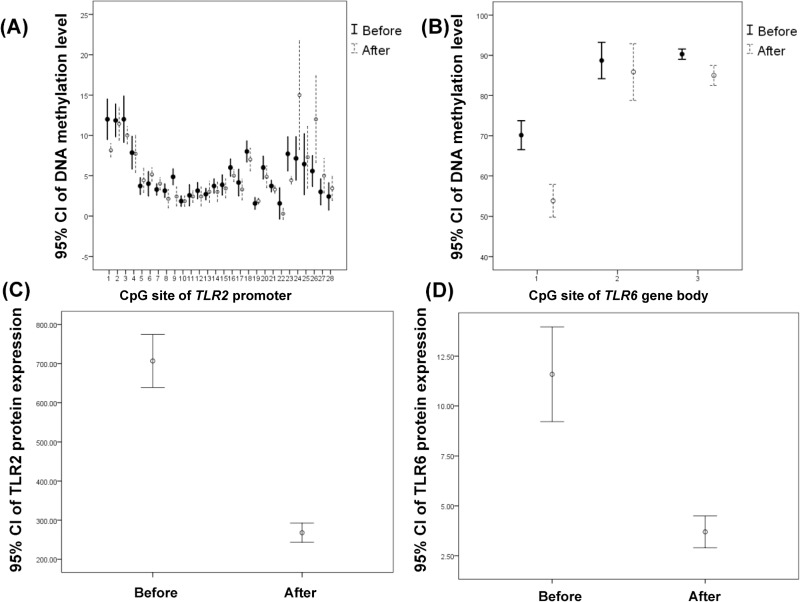
In seven patients with severe OSA who had received more than 6 months of CPAP treatment, DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1, #9 and #23 of the TLR2 promoter region, CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body, and TLR2 and TLR6 protein expressions were all reduced, and DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #24 and #26 of the TLR2 promoter region were both elevated (Fig 5 and S12 Table). After multiple comparison corrections with the Benjamini and Hochberg method, CPAP management was still an independent factor for the changes in the DNA methylation levels of CpG sites #1, #9, and #23 of the TLR2 promoter region, and CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body (S13 Table)
Fig 5. Changes in DNA methylation and protein expression levels of the TLR2 promoter region and TLR6 gene body in 7 selected severe OSA patients before and after more than 6-month CPAP treatment.
(A) DNA methylation levels over CpG site #1, #9 and #23 of TLR2 promoter region were decreased (p = .018, .015 and .006 respectively) and DNA methylation levels over CpG site #24 and #26 of TLR2 promoter region were increased (p = .028 and .042 respectively). (B)~(D) DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body, and TLR2 and TLR6 protein expressions were reduced (p < .001, p = .003, p < .001 and < .001 respectively).
Discussion
The main findings of our study are summarized as follows(Tables 4 and 5):
Table 4. The summarized results of multivariate linear regression and multiple comparisons in DNA methylation levels of TLR2 promoter region, TLR6 gene body, and protein expressions of TLR2 and TLR6 between healthy subjects and patients with severe OSA.
The DNA methylation levels over CpG#1, #2, #3, #18, #25, and #28 of TLR2, and CpG#1 and CpG#3 of TLR6 were significant differently between HS and OSA after multivariate linear regression. However, only the CpG#1 and CpG#3 of TLR6 were increased significantly in OSA after multiple comparisons. The TLR6 expression was also increased significantly in OSA.
| HS (n = 18) | OSA(n = 58) | p | q | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 promoter region | CpG#1 | cg153684036 | 12.11±2.888 | 16.25±9.822 | .037 | 0.1526250 |
| CpG#2 | cg153684048 | 12.11±2.166 | 17.24±9.528 | .026 | 0.1225714 | |
| CpG#3 | cg153684062 | 12.28±2.886 | 15.18±5.823 | .025 | 0.1225714 | |
| CpG#18 | cg153684194 | 8.00±2.086 | 6.63±2.492 | .042 | 0.1540000 | |
| CpG#25 | cg153684244 | 6.56±3.698 | 9.83±5.016 | .015 | 0.1225714 | |
| CpG#28 | cg153688942 | 2.94±1.798 | 4.34±2.686 | .019 | 0.1225714 | |
| TLR6 gene body | CpG#1 | cg13006575 | 56.61±9.432 | 66.26±5.565 | < .001 | 0.0004455 |
| CpG#3 | cg25769980 | 87.28±6.952 | 90.28±2.996 | .003 | 0.0330000 | |
| Protein expression | TLR6 | 1.3219±.40024 | 12.9591±3.29140 | < .001 | na |
Table 5. The summarized results of multivariate linear regression and multiple comparisons in DNA methylation levels of TLR2 promoter region, TLR6 gene body, and protein expressions of TLR2 and TLR6 in OSA before and after CPAP management.
(genome build “GRCh38.p13”). The DNA methylation levels over CpG#1, #9, #23, #24, and #26 of TLR2, and CpG#1 and CpG#3 of TLR6 were significant differently in multivariate linear regression. After CPAP management, only the CpG#1 and CpG#3 of TLR6 were decreased significantly in multiple comparisons. The TLR2 and TLR6 expression was also decreased significantly after CPAP management.
| Before | After | Difference | p | q | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 promoter region | CpG#1 | cg153684036 | 12.00±2.70 | 8.142±.89 | 3.85±3.18 | .018 | 0.08485714 |
| CpG#9 | cg153684120 | 4.86±1.06 | 2.42±1.27 | 2.42±1.90 | .015 | 0.08250000 | |
| CpG#23 | cg153684240 | 7.71±2.28 | 4.42±.53 | 3.28±2.05 | .006 | 0.03960000 | |
| CpG#24 | cg153684242 | 7.14±2.91 | 15.00±7.30 | -7.85±7.22 | .028 | 0.11550000 | |
| CpG#26 | cg153684275 | 5.57±2.07 | 12.00±5.83 | -6.42±6.60 | .042 | 0.15400000 | |
| TLR6 gene body | CpG#1 | cg13006575 | 70.14±3.89 | 53.86±4.38 | 16.29±3.45 | < .001 | 0.00026400 |
| CpG#3 | cg25769980 | 90.29±1.38 | 85.00±2.71 | 5.29±2.93 | .003 | 0.02475000 | |
| Protein expression | TLR2 | 706.53±73.29 | 268.04±26.62 | 438.49±69.84 | < .001 | na | |
| TLR6 | 11.59±2.57 | 3.70±.86 | 7.89±1.84 | < .001 | na |
Both DNA methylation levels of the TLR6 gene body over CpG site #1 and #3, and protein expressions of TLR6 were significant correlated, and increased in patients with severe OSA.
Aberrant DNA methylation levels of the TLR2 promoter region, hypermethylated TLR6 gene body, and increased protein expressions of TLR6 were all independently associated with higher AHI and ODI.
DNA methylation levels of the TLR6 gene body over CpG site #2 were increased in OSA with EDS phenotype.
The altered DNA methylation levels over CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body as well as TLR2 and TLR6 protein expressions were reversed after nasal CPAP management.
These results provide evidence for the first time that aberrant DNA methylation of the TLR2 promoter region and TLR6 gene body might be involved in the consequence of OSA and its clinical phenotypes.
Persistent hypoxia can induce hypermethylation or demethylation of specific genes [24–26], while the impact of chronic intermittent hypoxia on DNA methylation remains uncertain. Previous studies [15, 27] have found aberrant DNA methylations in several genes and might constitute an important determinant of disease severity and vulnerability to EDS in OSA. In addition, both TLR2/6 co-expressions on neutrophil and monocyte were increased either in OSA patients or with intermittent hypoxia with re-oxygenation treatment in vitro [16]. The cause-and-effect relationship between hypermethylation or demethylation of these genes and the consequences of OSA are still unclear, and we speculated that chronic intermittent hypoxia might contribute to systemic inflammation and adverse consequences through inducing aberrant DNA methylation. However, it is equally possible that these epigenetic changes might occur in the prenatal period or early life and predispose subjects to an epigenotype and subsequently a phenotype with more frequent hypoxic events during sleep in adulthood.
Toll-like receptors play central roles in the innate immune response by recognizing conserved structural patterns in diverse microbial molecules [28]. They are key mediators of innate immunity in both vertebrates and invertebrates, respond to various pathogen-associated stimuli, and transduce the complex signaling responses that are required for inflammation and for the subsequent development of adaptive immunity [29]. TLR2 has been shown to sense bacterial lipopeptides: it heterodimerizes either with TLR1 to recognize tri-acylated lipopeptides or with TLR6 to recognize di-acylated lipopeptides [30]. Intermittent hypoxia induces several inflammatory cascades, including the production of reactive O2 species, HIF-1 activation, and activated TLRs [3].
Our results emphasize the role of TLR6 in association with its epigenetic change in OSA. Aberrant DNA methylation levels of the TLR2 promoter region and TLR6 gene body as well as protein expressions of TLR6 were all independently associated with AHI and ODI. The reversion of the DNA methylation levels of the TLR2 promoter region, TLR6 gene body and protein expression of TLR2/TLR6 after CPAP management were also observed in seven selected patients. These results suggest that chronic intermittent hypoxia during sleep would induce the changes in the epigenesis of TLR2/TLR6 genes and the downstream protein expressions, especially TLR6. TLR6 might well serve as a biomarker in the diagnosis, disease severity, or evaluation of management in serial follow-up in OSA, but further investigation is warranted.
Although DNA methylation levels over several CpG sites in the TLR2 promoter region were increased in OSA patients, hypomethylated CpG site #18 in association with increased TLR2 protein expression was noted. In our previous study [20], we showed hyper-methylated CpG site #18 was in association with decreased TLR protein expression in active pulmonary TB patients. Thus, we speculated that CpG#18 methylation status may have a major effect on TLR2 gene expression under chronic intermittent hypoxic stimuli in OSA. Given the hypermethylated CpG sites #1 and #3 of the TLR6 gene body are in association with increased TLR6 protein expressions, we speculated that heterodimerization between TLR2 and TLR6 might be enhanced through aberrant DNA methylation of these two genes as well as through hypermethylation of the AKT1 and LY86 genes, both of which are involved in the activation of TLR signaling [31–34].
EDS is one of the prominent symptoms of OSA [35], and in particular, it is known to be a predisposing factor for accidents, interpersonal (communicative) problems, and reduced productivity [36–38]. EDS is also correlated with the severity of OSA [39] and might be a useful clinical marker to identify patients at risk of metabolic syndrome, hypertension and low-grade inflammation [40–42], which might all be linked to cardiometabolic morbidity and mortality. Nocturnal hypoxemia is a major determinant of EDS in Chinese OSA patients [39]. In our patients, hypertension was more prevalent in OSA but not significantly different between non-EDS and EDS groups. Increased DNA methylation over CpG site #2 of the TLR6 gene body was noted in the EDS group. This finding suggests that hypermethylation of the TLR6 gene body might also participate in the development of the EDS phenotype, but further investigation in a larger cohort of patients is necessary.
The limitations of our study should be acknowledged. Firstly, we enrolled only patients with severe OSA in order to avoid the potential confounding variables emanating from low severity of OSA. Secondly, this was a small population and cross-sectional case-control study, but we had direct comparison before and after CPAP treatment in some selected OSA patients. Further studies with sufficiently large sample sizes are required for internal and external validity and reliability of the results. Thirdly, although the difference of DNA methylation level between HS and OSA patients in statistically, it is insufficient for indicating the regulation of TLR2 and TLR6 expression. The further investigation by performing luciferase assay should be considered. Fourthly, the mechanisms of regulation of gene expression by DNA methylation of promoter region are thought that highly methylated DNA region inhibit for binding of transcription factor to their binding motif. However, we did not check what of the region of TLR2 promoter highly methylated in patient contains transcription factor binding motif. Fifthly, to assess the compliance and adherence of CPAP management by using CPAP >4 hours per night for 6 months might be insufficient. Further reassessment of compliance and adherence of CPAP management by using residual AHI (eg, "effective AHI [43]) is warranted. Sixthly, further in vitro study is needed to establish the cause-and-effect relationship between intermittent hypoxia and aberrant DNA methylation of the TLR2 and TLR6 genes. Seventhly, these particular methylation may have biological significance but additional support from epigenetic atlases and/or multiple site tests should be warranted.
Conclusions
This study provides a novel finding of aberrant DNA methylation in OSA. Hyper-methylated TLR6 gene bodies are associated with the consequence of severe OSA and its EDS phenotype. Increased protein expressions of TLR6 might serve as a biomarker for OSA. CPAP management partly reversed the altered DNA methylation levels and protein expressions of TLR2 and TLR6. Further verification and investigation of underlying mechanisms are warranted.
Supporting information
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
The pyrograms of the TLR2 and TLR6 genes: A representative pyrogram showing the percentage of methylation at CpG sites of TLR2 gene (A~C) and TLR6 gene (D~E) in a patient with severe OSA.
(TIF)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 2 would be significant.
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 7 would be significant.
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 11 would be significant.
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries.
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 5 would be significant.
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical support provided by the Genomic and Proteomic Core Laboratory, and Internal Medicine Core Facility of the Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. The authors wish to thank Ms. Shu-Jun Kong, Ms. Lian-Rong Liu, and Mr. Wei-Zhe Liu for manual scoring of all PSG.
Abbreviations
- OSA
Obstructive sleep apnea
- TLR
Toll-like receptors
- EDS
Excessive daytime sleepiness
- IH
Intermittent hypoxia
- IHD
Ischemic heart disease
- CHF
Congestive heart failure
- CpG
Guanine dinucleotide sequence
- IL1R2
Interleukin 1 receptor 2
- AR
Androgen receptor
- NPR2
Natriuretic peptide receptor 2
- SP140
Speckled protein 140
- CPAP
Continuous positive airway pressure
- HIF
Hypoxia inducible factor
- TB
Tuberculosis
- HS
Healthy subjects
- BMI
Body mass index
- DM
Diabetes mellitus
- VHD
Valvular heart disease
- OAD
Obstructive airway disease
- GERDm
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- AHI
Apnea-Hypopnea index
- ODI
Oxygen de-saturation index
- ESS
Epworth sleepiness scale
- na
not available
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This research was funded by grants from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPG 8C1181/1182/1183 to M.C. Lin), Taiwan, and by grants (NMRPG8F6071-6073/105-2314-B-182A-092-MY3 to M.C. Lin) from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Arnardottir ES, Mackiewicz M, Gislason T, Teff KL, Pack AI. Molecular signatures of obstructive sleep apnea in adults: a review and perspective. Sleep. 2009;32(4):447–70. 10.1093/sleep/32.4.447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lavie L. Oxidative stress in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia—revisited—the bad ugly and good: implications to the heart and brain. Sleep medicine reviews. 2015;20:27–45. 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.07.003 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Douglas RM, Haddad GG. Can O2 dysregulation induce premature aging? Physiology. 2008;23:333–49. 10.1152/physiol.00023.2008 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gottlieb DJ, Yenokyan G, Newman AB, O'Connor GT, Punjabi NM, Quan SF, et al. Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: the sleep heart health study. Circulation. 2010;122(4):352–60. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wolk R, Kara T, Somers VK. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2003;108(1):9–12. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000072346.56728.E4 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;353(19):2034–41. 10.1056/NEJMoa043104 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bradley TD, Floras JS. Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet. 2009;373(9657):82–93. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61622-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nanduri J, Makarenko V, Reddy VD, Yuan G, Pawar A, Wang N, et al. Epigenetic regulation of hypoxic sensing disrupts cardiorespiratory homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(7):2515–20. 10.1073/pnas.1120600109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ma Q, Xiong F, Zhang L. Gestational hypoxia and epigenetic programming of brain development disorders. Drug discovery today. 2014;19(12):1883–96. 10.1016/j.drudis.2014.09.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lev Maor G, Yearim A, Ast G. The alternative role of DNA methylation in splicing regulation. Trends in genetics: TIG. 2015;31(5):274–80. 10.1016/j.tig.2015.03.002 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kulis M, Queiros AC, Beekman R, Martin-Subero JI. Intragenic DNA methylation in transcriptional regulation, normal differentiation and cancer. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2013;1829(11):1161–74. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jjingo D, Conley AB, Yi SV, Lunyak VV, Jordan IK. On the presence and role of human gene-body DNA methylation. Oncotarget. 2012;3(4):462–74. 10.18632/oncotarget.497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Maunakea AK, Nagarajan RP, Bilenky M, Ballinger TJ, D'Souza C, Fouse SD, et al. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature. 2010;466(7303):253–7. 10.1038/nature09165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jones PA. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nature reviews Genetics. 2012;13(7):484–92. 10.1038/nrg3230 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen YC, Chen TW, Su MC, Chen CJ, Chen KD, Liou CW, et al. Whole Genome DNA Methylation Analysis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: IL1R2, NPR2, AR, SP140 Methylation and Clinical Phenotype. Sleep. 2016;39(4):743–55. 10.5665/sleep.5620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen YC, Su MC, Liou CW, Liu SF, Chen CJ, Lin HC, et al. Co-upregulation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 on peripheral blood cells in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep & breathing. 2015;19(3):873–82. 10.1007/s11325-014-1116-4 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Akinnusi M, Jaoude P, Kufel T, El-Solh AA. Toll-like receptor activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep & breathing. 2013;17(3):1009–16. 10.1007/s11325-012-0791-2 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kuhlicke J, Frick JS, Morote-Garcia JC, Rosenberger P, Eltzschig HK. Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1 coordinates induction of Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR6 during hypoxia. PloS one. 2007;2(12):e1364 10.1371/journal.pone.0001364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Polotsky VY, Bevans-Fonti S, Grigoryev DN, Punjabi NM. Intermittent Hypoxia Alters Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Healthy Volunteers. PloS one. 2015;10(12):e0144725 10.1371/journal.pone.0144725 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen YC, Hsiao CC, Chen CJ, Chao TY, Leung SY, Liu SF, et al. Aberrant Toll-like receptor 2 promoter methylation in blood cells from patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. The Journal of infection. 2014;69(6):546–57. 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.08.014 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991;14(6):540–5. 10.1093/sleep/14.6.540 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chen NH, Johns MW, Li HY, Chu CC, Liang SC, Shu YH, et al. Validation of a Chinese version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Quality of life research: an international journal of quality of life aspects of treatment, care and rehabilitation. 2002;11(8):817–21. 10.1023/a:1020818417949 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kales A, Rechtschaffen A, University of California LA, Brain Information S, National Institute of Neurological D, Blindness A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office; 1968. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Watson JA, Watson CJ, McCann A, Baugh J. Epigenetics, the epicenter of the hypoxic response. Epigenetics. 2010;5(4):293–6. 10.4161/epi.5.4.11684 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee JS, Kim Y, Kim IS, Kim B, Choi HJ, Lee JM, et al. Negative regulation of hypoxic responses via induced Reptin methylation. Molecular cell. 2010;39(1):71–85. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.06.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tausendschon M, Dehne N, Brune B. Hypoxia causes epigenetic gene regulation in macrophages by attenuating Jumonji histone demethylase activity. Cytokine. 2011;53(2):256–62. 10.1016/j.cyto.2010.11.002 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim J, Bhattacharjee R, Khalyfa A, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Capdevila OS, Wang Y, et al. DNA methylation in inflammatory genes among children with obstructive sleep apnea. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2012;185(3):330–8. 10.1164/rccm.201106-1026OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jin MS, Lee JO. Structures of the toll-like receptor family and its ligand complexes. Immunity. 2008;29(2):182–91. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.07.007 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gay NJ, Gangloff M, Weber AN. Toll-like receptors as molecular switches. Nature reviews Immunology. 2006;6(9):693–8. 10.1038/nri1916 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.O'Neill LA, Golenbock D, Bowie AG. The history of Toll-like receptors—redefining innate immunity. Nature reviews Immunology. 2013;13(6):453–60. 10.1038/nri3446 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Karper JC, Ewing MM, de Vries MR, de Jager SC, Peters EA, de Boer HC, et al. TLR accessory molecule RP105 (CD180) is involved in post-interventional vascular remodeling and soluble RP105 modulates neointima formation. PloS one. 2013;8(7):e67923 10.1371/journal.pone.0067923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wagner NM, Bierhansl L, Noldge-Schomburg G, Vollmar B, Roesner JP. Toll-like receptor 2-blocking antibodies promote angiogenesis and induce ERK1/2 and AKT signaling via CXCR4 in endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2013;33(8):1943–51. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301783 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Manoharan I, Hong Y, Suryawanshi A, Angus-Hill ML, Sun Z, Mellor AL, et al. TLR2-dependent activation of beta-catenin pathway in dendritic cells induces regulatory responses and attenuates autoimmune inflammation. Journal of immunology. 2014;193(8):4203–13. 10.4049/jimmunol.1400614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu B, Zhang N, Liu Z, Fu Y, Feng S, Wang S, et al. RP105 involved in activation of mouse macrophages via TLR2 and TLR4 signaling. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. 2013;378(1–2):183–93. 10.1007/s11010-013-1609-7 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Verstraeten E, Cluydts R, Pevernagie D, Hoffmann G. Executive function in sleep apnea: controlling for attentional capacity in assessing executive attention. Sleep. 2004;27(4):685–93. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Barbe, Pericas J, Munoz A, Findley L, Anto JM, Agusti AG. Automobile accidents in patients with sleep apnea syndrome. An epidemiological and mechanistic study. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 1998;158(1):18–22. 10.1164/ajrccm.158.1.9709135 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gami AS, Howard DE, Olson EJ, Somers VK. Day-night pattern of sudden death in obstructive sleep apnea. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352(12):1206–14. 10.1056/NEJMoa041832 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Garbarino S, Durando P, Guglielmi O, Dini G, Bersi F, Fornarino S, et al. Sleep Apnea, Sleep Debt and Daytime Sleepiness Are Independently Associated with Road Accidents. A Cross-Sectional Study on Truck Drivers. PloS one. 2016;11(11):e0166262 10.1371/journal.pone.0166262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen R, Xiong KP, Lian YX, Huang JY, Zhao MY, Li JX, et al. Daytime sleepiness and its determining factors in Chinese obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep & breathing. 2011;15(1):129–35. 10.1007/s11325-010-0337-4 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang JF, Chen LD, Lin QC, Chen GP, Yu YH, Huang JC, et al. The relationship between excessive daytime sleepiness and metabolic syndrome in severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. The clinical respiratory journal. 2016;10(6):714–21. 10.1111/crj.12276 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Feng J, He QY, Zhang XL, Chen BY, Sleep Breath Disorder Group SoRM. Epworth Sleepiness Scale may be an indicator for blood pressure profile and prevalence of coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep & breathing. 2012;16(1):31–40. 10.1007/s11325-011-0481-5 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li Y, Vgontzas AN, Fernandez-Mendoza J, Kritikou I, Basta M, Pejovic S, et al. Objective, but Not Subjective, Sleepiness is Associated with Inflammation in Sleep Apnea. Sleep. 2016. . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Boyd SB, Upender R, Walters AS, Goodpaster RL, Stanley JJ, Wang L, et al. Effective Apnea-Hypopnea Index ("Effective AHI"): A New Measure of Effectiveness for Positive Airway Pressure Therapy. Sleep. 2016;39(11):1961–72. 10.5665/sleep.6224 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
(TIF)
The pyrograms of the TLR2 and TLR6 genes: A representative pyrogram showing the percentage of methylation at CpG sites of TLR2 gene (A~C) and TLR6 gene (D~E) in a patient with severe OSA.
(TIF)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 2 would be significant.
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 7 would be significant.
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 11 would be significant.
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries.
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
A q value threshold of 0.1 was selected to separate false from true discoveries, and the first 5 would be significant.
(DOCX)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.