Abstract
Reconstructing the physiology of extinct organisms is key to understanding mechanisms of selective extinction during biotic crises. Soft tissues of extinct organisms are rarely preserved and, therefore, a proxy for physiological aspects is needed. Here, we examine whether cephalopod conchs yield information about their physiology by assessing how the formation of chambers respond to external stimuli such as environmental changes. We measured chamber volume through ontogeny to detect differences in the pattern of chamber volume development in nautilids, coleoids, and ammonoids. Results reveal that the differences between ontogenetic trajectories of these cephalopods involve the presence or absence of abrupt decreases of chamber volume. Accepting the link between metabolic rate and growth, we assume that this difference is rooted in metabolic rates that differ between cephalopod clades. High metabolic rates combined with small hatching size in ammonoids as opposed to lower metabolic rates and much larger hatchlings in most nautilids may explain the selective extinction of ammonoids as a consequence of low food availability at the end of the Cretaceous.
Subject terms: Palaeontology, Palaeoecology
Introduction
The Ammonoidea is a group of ectocochleate cephalopods that were extant for more than 350 million years, during which time they played an essential ecological role in the world’s oceans as a result of their high abundance, wide distribution, and great diversity. Although they survived several of the most severe mass extinction events in the course of their evolution1–3, they perished at the end of the Cretaceous4,5. Despite extensive discussion on the selectivity of the K/Pg extinction, the actual mechanisms that led ammonoids to extinction and allowed nautilids to survive, have not yet been fully revealed, although both intrinsic (e.g., smaller embryonic sizes, larger geographical range, and microphagous feeding4,6,7) and extrinsic factors (e.g., surface ocean acidification and global cooling8,9) have been proposed. Details about intrinsic (anatomical and physiological) aspects such as the muscular system and metabolic rates are difficult to assess in extinct organisms because the soft tissue is rarely fossilized10. Thus, we need proxies for biological and physiological aspects to fully reveal the actual kill mechanism of ammonoids at the K/Pg boundary. In fact, such biological and physiological traits are apparently strongly linked to macroecology and macroevolution of organisms. For instance, Strotz et al.11 discovered a significant difference between basal metabolic rates of extinct and extant taxa. Additionally, Payne et al.12 demonstrated a new perspective on the evolution of bivalves and brachiopods by calculating their metabolic rates. Reconstructing the biological and physiological traits of extinct ammonoids may, therefore, be a key to understanding selective extinction13.
Most mollusk conchs contain a wealth of information about their development because the entire life history is recorded within the shell. In ectocochleate cephalopods (ammonoids and nautiloids), the conchs, which comprise the gas-filled phragmocone and the soft-tissue-bearing body chamber, have been studied with a focus on the external morphological characters such as ornamentation and coiling14,15. The internal structure of the conchs, however, has been studied much less frequently, largely due to technical difficulties of analyzing the often recrystallized and more or less sediment-filled conchs. Among other parameters, septal spacing of ammonoids, nautilids, and belemnites is of great interest because septa and chambers are constructed by the soft tissues of the animal, and may, therefore, provide information about key aspects of life history such as hatching, growth changes, and mode of life16–19. In addition to the conventional 2D-analyses of septal spacing through ontogeny (i.e., measuring septal rotational angles16,20–22), recent destructive and non-destructive methods to three-dimensionally reconstruct chamber volume have been developed23–26. Obtaining 2D-data is advantageous because of the simple preparation of fossils (grinding and polishing), requiring minimal lab time and post-processing; however, the changes of septal angle through ontogeny are sometimes very subtle, and thus this method may mask some important details. By contrast, although the 3D-method requires relatively complex technical set-ups to produce image stacks (e.g., high-energy beams for fossils in X-ray computed tomography, which is non-destructive or grinding tomography for low-contrast materials, which is destructive) and post-processing of image stacks is considerably time-consuming, the resulting volumetric data through ontogeny provide valuable information that might not be obtained from 2D-data. By plotting such 3D-measurements, we obtained curves that approximately conform to exponential functions, emphasizing subtle ontogenetic changes in septal spacing23–26 (see Naglik et al.24 and Hoffmann et al.27 for comparisons of 2D- and 3D-data). These studies reveal various patterns of ontogenetic change in septal spacing in several cephalopod taxa. However, the factors that determine these patterns and, particularly, the differences are hardly known. Some authors have suggested possible links between ecological changes (such as habitat changes) and abrupt changes in septal spacing, although such studies are still limited16,28,29. Determining the factors that control the pattern of septal spacing and growth of chamber volume can be of great relevance because they may be widely applicable to better understand environmental, ecological, and biological aspects of these organisms.
In this study, we depict volumetric growth trajectories of phragmocone chambers in various cephalopod taxa. We address the question of whether the development of chamber volume in cephalopod phragmocones conveys information about their physiology. We examine some specimens that bear various degrees of pathology to further discuss what controls the pattern of chamber volume development. We aim to answer the following questions:1) What are the typical patterns of chamber volume development in various cephalopod groups and how do they differ? 2) How do pathologies affect chamber volume development? 3) What are the factors that alter patterns of chamber volume development between different cephalopod groups? 4) What do these factors tell us about the ecology and extinction selectivity of cephalopods?
Methods
We studied 24 cephalopod conchs: 15 conchs of modern nautilids (2 with no pathology, 13 with pathology including 7 aquarium-reared individuals; Fig. 1), 3 specimens of the Cretaceous nautilid Eutrephoceras nebrascensis (1 specimens from the upper Campanian Baculites compressus Zone in Montana; 2 specimens from the B. compressus Zone in South Dakota), 4 specimens of Cretaceous ammonites (3 specimens of Tetragonites sp. and 1 specimen of Gaudryceras sp. from the Campanian of Hokkaido, Japan), 2 specimen of the modern coleoid Spirula spirula (see Table 1 for more detailed information). The specimens of the fossil nautilids and ammonites did not display any deformities or pathologies on the conchs with the exception of Tetragonites (NMA00803), where the shell dissolved during diagenesis30. In this study, we divide the degrees of pathology into ‘moderate’ and ‘fatal’. The former indicates that the animals still continued to grow and reached maturity in spite of the pathology. By contrast, the latter are those, which (most likely) continued to live for some time after the incident, but died before reaching maturity.
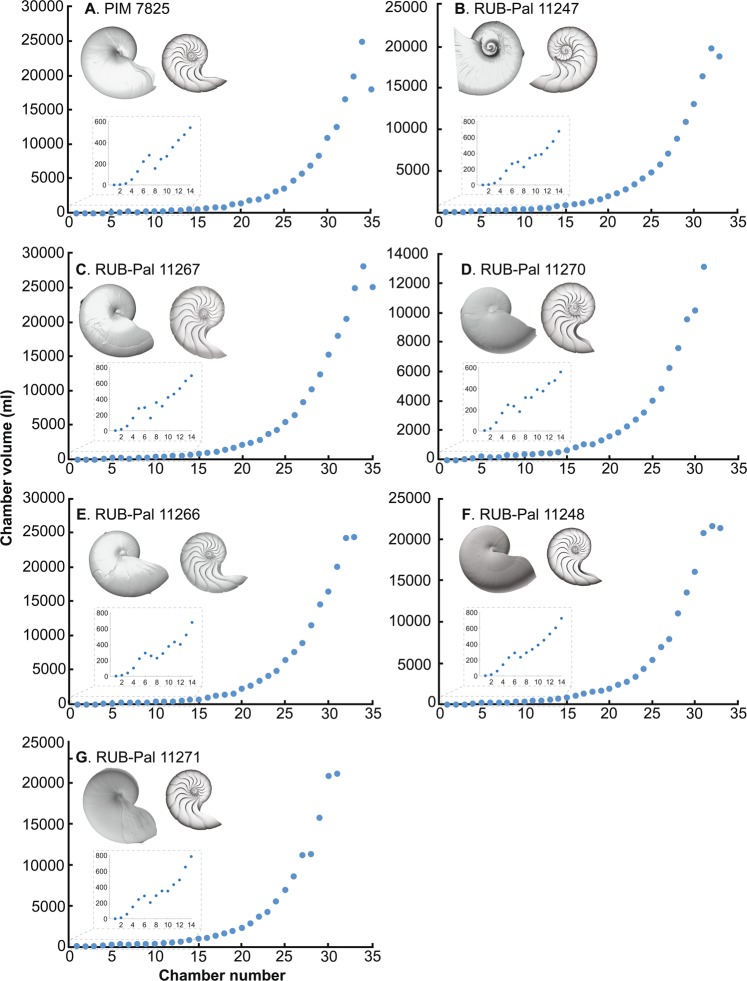
Figure 1.
Specimens of Nautilus pompilius with differing degrees of pathology examined in this study. (A) RUB-Pal 11248 (conch diameter = 180 mm) with a moderate pathology. (B) RUB-Pal 11267 (conch diameter = 187 mm) with a moderate pathology. (C) RUB-Pal 11270 (conch diameter = 148 mm) with a moderate pathology. (D) RUB-Pal 11268 (conch diameter = 83 mm) with a fatal pathology (pathology that led to premature death after phase of ill health). (E–H) AMNH FI 63303–63306 (conch diameters = 120, 110, 113, 132 mm, respectively), aquarium-reared specimens with a fatal pathology (pathology that led to premature death after a phase of ill health). RUB-Pal = Ruhr-University Bochum Palaeontology. AMNH FI = American Museum of Natural History Fossil Invertebrates.
Table 1.
Details of the examined specimens.
| Species | Specimen number | Age | Locality | Pathology | Conch diameter (mm) | 3D reconstruction method | Voxel size (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nautilid | Allonautilus scrobiculatus | RUB-Pal 11247 | Modern | unknown | no | 150? | computed tomography | 0.060*0.060*0.060 |
| Nautilus pompilius | PIM 7825 | no | 166 | 0.091*0.091*0.091 | ||||
| RUB-Pal 11248 | moderate | 180 | 0.089*0.089*0.089 | |||||
| RUB-Pal 11266 | moderate | 174 | 0.085*0.085*0.085 | |||||
| RUB-Pal 11267 | moderate | 187 | 0.099*0.099*0.099 | |||||
| RUB-Pal 11268 | fatal | 83 | 0.040*0.040*0.040* | |||||
| RUB-Pal 11270 | moderate | 148 | 0.079*0.079*0.079* | |||||
| RUB-Pal 11271 | moderate | 168 | 0.083*0.083*0.083 | |||||
| Zoo Arnhem, coll. AWI Bremerhaven; coll. no. Nehrke 01 | unknown (aquarium) | fatal | 136 | 0.087*0.087*0.087 | ||||
| Bochum Tierpark 01 | fatal | 148 | 0.087*0.087*0.087 | |||||
| Bochum Tierpark 02 | fatal | 164 | 0.088*0.088*0.088 | |||||
| AMNH FI 63303 | fatal | 120 | 0.053*0.053*0.053 | |||||
| AMNH FI 63304 | fatal | 110 | 0.053*0.053*0.053 | |||||
| AMNH FI 63305 | fatal | 113 | 0.053*0.053*0.053 | |||||
| AMNH FI 63306 | fatal | 132 | 0.060*0.060*0.060 | |||||
| Eutrephoceras nebrascensis | AMNH FI 102486 | Campanian | Pierre Shale, ?Montana | no | 12 | 0.010*0.010*0.010 | ||
| SD 002 | Pierre Shale, South Dakota | no | 37 | grinding tomography | 0.010*0.010*0.160 | |||
| SD 003 | no | 31 | grinding tomography | 0.010*0.010*0.160 | ||||
| ammonoid | Tetragonites sp. | NMA00803 | Campanian | Haborogawa Fm., Hokkaido | unknown | 36 | computed tomography | 0.020*0.020*0.020 |
| HKD TG 001 | no | 20 | grinding tomography | 0.010*0.010*0.070 | ||||
| HKD TG 002 | no | 25 | grinding tomography | 0.010*0.010*0.070 | ||||
| Gaudryceras sp. | HKD GC | no | 28 | grinding tomography | 0.010*0.010*0.070 | |||
| coleoid | Spirula spirula |
PIMUZ 017853 PIMUZ 37573 |
modern | unknown | no |
22 17 |
computed tomography |
0.018*0.018*0.018 0.033*0.033*0.033 |
RUB-Pal = Ruhr-University Bochum Palaeontology. AMNH FI = American Museum of Natural History Fossil Invertebrates. PIMUZ = Palaeontological Institute and Museum, University of Zurich. NMA = Nakagawa Museum of Natural History.
In order to extract chamber volume through ontogeny, we three-dimensionally reconstructed the conchs. To this end, computed tomography was applied to the modern nautilid specimens and one specimen each of Tetragonites sp. and Eutrephoceras sp., while grinding tomography was performed on the other fossils (for details of the procedure for grinding tomography, see Naglik et al. and Tajika et al.24,31). The images obtained with grinding tomography were sharpened and the contrast was enhanced. The image stacks obtained were segmented in Avizo 8.1 (Volume Graphics) to export the shell surface, which was then inverted in Meshlab (ISTI - CNR research center) to extract the phragmocone. The phragmocone was decomposed into individual chambers and the respective chamber volumes were measured using MATLAB (MathWorks). The chamber volumes measured were plotted against chamber number through ontogeny with chamber 1 as the first formed chamber after the protoconch. Because the first several chambers were not clearly visible due to insufficient contrast of our image stacks, the exact chamber number in ammonoids was unknown.
To examine the pattern of chamber volume development within a specimen, we calculated the chamber volume development rate (=volume of a chamber/volume of the proceeding chamber). If chamber volume increases, as expected from the allometric or isometric growth of cephalopods, the chamber volume development rate is higher than 1.0. The chamber volume development rates were also plotted through ontogeny.
Results
General trend of chamber volume development
Three-dimensionally reconstructed conchs and phragmocone chambers as well as phragmocone chamber volumes are shown in Figs. 2–4 (Supplementary Table 1). The chamber volume development rates in all the examined specimens are shown in Fig. 5 (Supplementary Table 1). In modern nautilids with and without pathology, chamber volumes show an increasing trend although individuals with a pathology leading to premature death often exhibit fluctuations. Such fluctuations appear to account for the difference in total phragmocone volume between individuals with no and moderate pathology and those with fatal pathologies (Figs. 2, 3, and Supplementary Table). Chamber volume in the embryonic and post-hatching stages (up to chamber 13) also fluctuates in nautilids. Although the earliest ontogenetic stages are missing, chamber volume in the ammonoids and the modern coleoid Spirula shows an increasing trend. The volumetric growth trajectories of the ammonoids and coleoid show abrupt decreases of chamber volume through ontogeny (Figs. 4D–F,H, 5C,E). In Spirula, chamber volume also decreases during the latest ontogeny (chambers 30–34). This decrease toward the end of ontogeny is probably related to the attainment of maturity22.
Figure 2.
Volumtric growth trajectories of modern nautilids with no and moderate pathology. (A), (C)-(O), Nautilus pompilius. (B) Allonautilus scrobiculatus. (A) PIM 7825, no pathology. (B) RUB-Pal 11247, no pathology. (C) RUB-Pal 11267, moderate pathology. (D) RUB-Pal 11270, moderate pathology. (E) RUB-Pal 11266, moderate pathology. (F) RUB-Pal 11248, moderate pathology. (G) RUB-Pal 11271, moderate pathology.
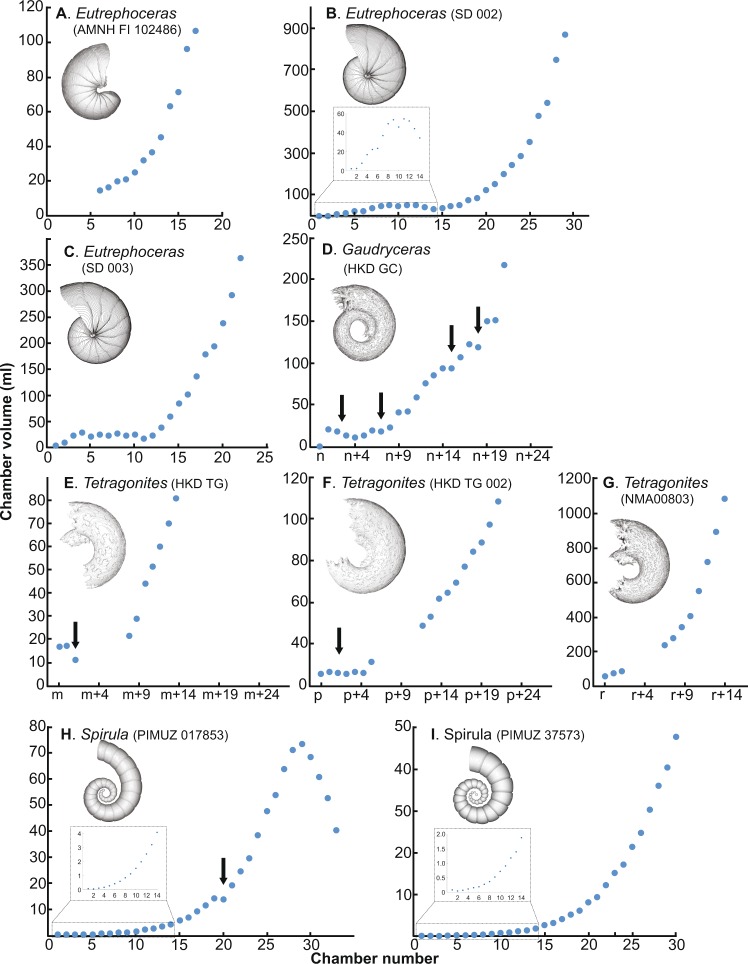
Figure 4.
Volumetric growth trajectories in Cretaceous nautilids (A–C), ammonites (D–G), and modern coleoid (H,I). (A) Eutrephoceras nebrascensis (AMNH FI 102486), (B) E. nebrascensis (SD 002). (C) E. nebrascensis (SD 003). (D) Gaudryceras sp. (HKD GC). (E) Tetragonites sp. (HKD TC 001), (F) Tetragonites sp. (HKD TC 002). (G) Tetragonites sp. (NMA00803). (H) Spirula spirula (PIMUZ 017853). (I) S. spirula (PIMUZ 37573). PIMUZ = Palaeontological Institute and Museum, University of Zurich. NMA = Nakagawa Museum of Natural History. Specimens (B–F) are no longer available due to destructive sampling.
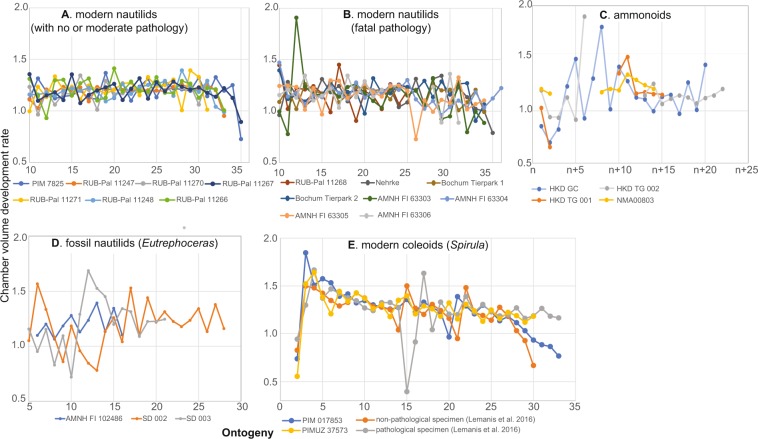
Figure 5.
Chamber volume development rates through ontogeny in nautilids, ammonoids, and coleoids. (A) Modern nautilids (Allonautilus scrobiculatus and Nautilus pompilius with no or moderate pathology). (B) Modern nautilids (Nautilus pompilius with fatal pathology: pathology that led to premature death). (C) Ammonoids (Tetragonites and Gaudryceras). Note that chamber volume in each specimen was not measured in the same ontogenetic stage. (D) Fossil nautilids (Eutrephoceras) (E) modern coleoid (Spirula spirula; data of two specimens (with and without pathology) from Lemanis et al. (2016).
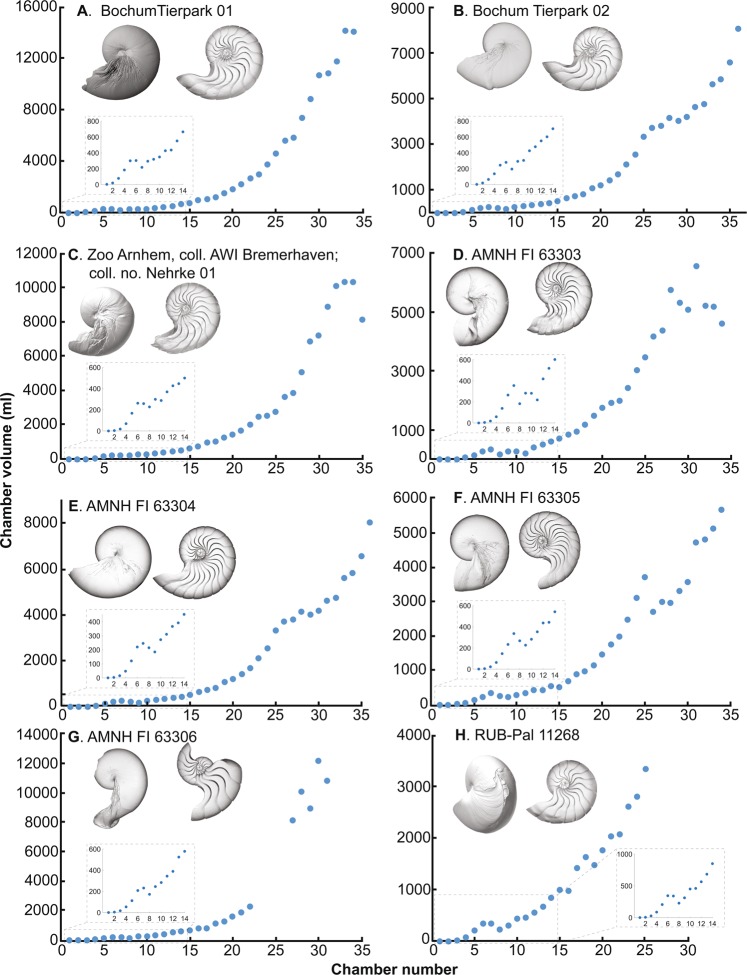
Figure 3.
Volumtric growth trajectories of modern nautilids (Nautilus pompilius) with fatal pathology (pathology that led to premature death). (A) Bochum Tierpark 01. (B) Bochum Tierpark 02. (C) Zoo Arnhem, coll. AWI Bremerhaven; coll. no. Nehrke 01. (D) AMNH FI 63303. (E) AMNH FI 63304. (F) AMNH FI 63305. (G) AMNH FI 63306. (H) RUB-Pal 11268.
Pattern of chamber volume development in modern nautilids
Fluctuations in chamber volume development appear to occur only in individuals with pathologies that led to premature death (Fig. 3) with the exception of embryonic, post-hatching, and mature stages, in which septal crowding in modern Nautilus is known23,25,32,33. The chamber volume development rate in non-pathological and moderately pathological individuals ranges mostly between 1.0–1.5 (Fig. 5). By contrast, the aquarium-reared individuals with pathologies that led to premature death often show abrupt decreases in volumetric growth trajectories (chamber volume development rates <1.0). These results are consistent with an experimental study on Nautilus by Keupp and Riedel29, in which they discovered that septal crowding occurs in aquarium-reared individuals as a reaction to adverse conditions rather than to the attainment of maturity. This illustrates the general pattern of chamber volume development in modern nautilids: only a pathology that leads to early death strongly affects the formation of chambers (Fig. 3) while slight pathologies (injuries, illnesses, adverse conditions) do not produce disharmonic chamber growth trajectories (Fig. 2). Considering that seven out of eight fatally pathological individuals are aquarium-reared, in which the ecological conditions significantly differ from that of nature (e.g., shallow water depth implying low hydrostatic pressure), it appears that the chamber volume development rate of modern nautilids in nature consistently increases even in cases where specimens display moderate pathologies. The consistent chamber volume development of Nautilus pompilius in nature was already reported by Tajika et al.25.
Pattern of chamber volume development in fossil nautilids
As in their modern relatives, the specimens of the Cretaceous nautilid Eutrephoceras show a similarly fluctuating pattern in early ontogeny (up to chamber 13; Figs. 4B,C, 5D). The changes of septal spacing at the embryonic stages in Eutrephoceras, which coincide with hatching, are well documented17,34. Later in ontogeny, the chamber volume increases relatively constantly at a rate between 1.0–1.5. This indicates that the Cretaceous nautilid Eutrephoceras and modern nautilids share a similar pattern of chamber volume development, in which both groups construct chambers with a consistently positive chamber volume development rate under normal natural conditions (i.e., when not excessively stressed). To date, no data on septal spacing in pathological fossil nautilids are available.
Pattern of chamber volume development in fossil ammonoids and coleoids
Due to insufficient contrast, resolution and preservation, the chambers formed during the earliest part of ontogeny could not be segmented with enough accuracy. Thus, our data on ammonoid chamber volume development were taken only from juvenile post-hatching growth stages (for the size of each specimen, see Table 1). Nevertheless, a difference in the pattern of chamber volume development appears to exist between ammonoids and nautilids. Although the studied ammonoid specimens HKD GC, HKD TG, and HKD TG 002 do not display any trace of pathology on the conchs, they show decreases in chamber volume development (distinct in Gaudryceras and Tetragonites in Fig. 4D,E, respectively; less conspicuous in Tetragonites in Fig. 4F). Naturally, these decreases are reflected in negative chamber volume development rates (Fig. 4B). In contrast, NMA00803 (Tetragonites) does not show such abrupt decreases during ontogeny (Fig. 4G). Naglik et al.24 published volumetric growth trajectories of two Devonian ammonoids (Diallagites and Fidelites) and one Carboniferous ammonoid (Goniatites). Although not discussed in that article, the graphs show high fluctuations during ontogeny. We calculated the chamber volume development rates for the ammonoid data of Naglik et al.24, which revealed that chamber volume decreases repeatedly at different ontogenetic stages (Supplementary Table) in the absence of distinct pathologies. Tajika et al.25 published volumetric data based on grinding tomography of two specimens of the Jurassic ammonoid Normannites. In their study, one of the specimens bears a syn vivo epizoan but does not show abrupt changes in chamber volume development, whereas an abrupt reduction of chamber volume occurred in the other specimen with no visible pathology or epizoan. Lemanis et al.23 studied one Carboniferous (Arnsbegites) and two Jurassic ammonoids (Cadoceras and Amauroceras), in which abrupt reductions of chamber volume also occurred. Our data and those of the previous studies confirm that abrupt changes of chamber volume (i.e., negative chamber volume development rates prior to maturity) are common among all ammonoids from the Devonian to the Cretaecous with few exceptions25 (Fig. 4G).
The modern coleoid Spirula spirula appears to have a pattern similar to that of ammonoids. In the ontogenetic trajectories of chamber volumes (Fig. 4H), an abrupt decrease occurs in the middle of ontogeny, which naturally corresponds to a negative chamber volume development rate in Fig. 5E. Lemanis et al.23 illustrated the volumetric trajectories in pathological and non-pathological specimens of Spirula spirula. The chamber volume development rate shows a negative value in both specimens, although the pathological specimen shows a higher rate (Fig. 5E). As in ammonoids, Spirula spirula displays abrupt changes in volumetric growth trajectories regardless of the presence or absence of pathologies with some exceptions (Fig. 4I).
Discussion
We discovered the following patterns of chamber volume development:
In modern and fossil nautilids, chamber volume usually increases constantly during ontogeny without abrupt drops under normal and natural environmental conditions. Abrupt drops in chamber volume occur only under extreme conditions (e.g., when individuals are reared in an aquarium); most of the examined nautilids collected from the wild do not show such irregular fluctuations in chamber volume.
In ammonoids and the modern coleoid Spirula, chamber volume development rate is roughly constant but it sometimes shows abrupt drops under natural ecological conditions during ontogeny. In Spirula, pathological individuals also show a higher rate of abrupt drops of chamber volume.
Although the mode of life (locomotion, migration, physiology) and ecological conditions (temperature, hydrostatic pressure, food availability, and chemical composition of the water) of these organisms cannot be fully reconstructed, we discuss possible factors that could explain these differences in the pattern of chamber volume development.
Change in mode of life: Changes in septal spacing in the earliest ontogeny of nautilids and Spirula correspond to hatching, which is also reflected in changes in carbon and oxygen isotopes of the conch17,22,35,36. In addition, Arai and Wani16 suggested that changes of septal spacing (two-dimensional rotational angles) in Late Cretaceous ammonoids from Japan, which occur at a shell diameter of less than 5 mm, may be linked to the change from a planktic to a more active nektic lifestyle. However, the abrupt decreases of chamber volume in our ammonoid data occur at much larger conch diameters (>10 mm), which suggests that these decreases cannot be explained only by a change of lifestyle.
Change in habitat (environmental conditions): Kraft et al.20 examined septal spacing of Carboniferous ammonoids from Algeria. They also documented abrupt changes in septal spacing (two-dimensional rotational angles). They concluded that these cases of septal crowding did not indicate maturity (because septal spacing normalized afterward) and was presumably caused by adverse ecological conditions such as low oxygen conditions, poor food availability or toxic chemical composition of the sea water. Some studies discovered positive correlations between ecological factors and lamellar (i.e., septal) spacing in the modern cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. For instance, Wiedmann and Boletzky28 documented that lamellar spacing in S. officinalis, which strongly correlates with growth rate, decreases in phases of very poor food availability. Also, some studies found that lamellar spacing in S. officinalis is controlled by temperature37,38. Gutowska et al.39 carried out an experimental study in which they found that cuttlebones of CO2- incubated Sepia officinalis individuals produce narrower lamellar spacing.
The abrupt changes of chamber volume, which occur in ammonoids and Spirula, may also be explained by disadvantageous environmental factors. Nevertheless, such adverse environmental conditions should also affect nautilids. Considering water temperature, it is known that modern Nautilus migrates diurnally from deep to shallow water environments between 100–700 m40, through which they traverse a temperature gradient. Additionally, as far as ecological conditions are concerned, Cretaceous Eutrephoceras presumably inhabited a shallow water environment ~70 m deep41, which was probably a higher-energy setting compared to the deep water habitat in which Spirula lives around 400–1000 m36. The habitat of the Cretaceous ammonoids examined is considered to be an outer shelf setting (near the continental slope), which was supposedly deeper than the habitat of Eutrephoceras. Thus, it is assumed that Eutrephoceras may have faced more environmental perturbations than the ammonoids and possibly Spirula. If temperature and/or environmental perturbations equally affect the septal spacing in nautilids, ammonoids, and coleoids, abrupt decreases of chamber volume should be visible in nautilids. Since our data on nautilids that lived under natural conditions show no fluctuations in volumetric growth trajectories, we suspect that environmental changes alone cannot explain the differences in the patterns of chamber volume development between nautilids, ammonoids, and coleoids.
Differences in metabolic rates (i.e., the minimum energy required to sustain life): The metabolic rate is known to be the rate of energy uptake, transformation, and allocation42. Acquisition and processing of energy are essential parts of animal physiology, which generate behavior (e.g., muscle contraction) and new biomass (e.g., growth and egg production43). Furthermore, most organisms display phenotypic plasticity in the expression of metabolism as a reflection of environmental differences42. For instance, Zeng et al.44 discovered that individuals with a high metabolic rate within a fish population experienced more mass loss during food deprivation.
As far as metabolic rates of cephalopods are concerned, the ‘live fast, die young’ strategy of many coleoids is well-known and some squids, octopuses, and cuttlefish are metabolically very active although variation in metabolic rate is also significant45–47. Modern Nautilus is known to live quite long (up to approximately ~20 years48), to have a low energy consumption, and to be able to maintain a low metabolic rate49–51. Although metabolic rates of Spirula spirula are not known, stable carbon isotopes of Spirula and Nautilus shells, which are considered to reflect metabolic rates in mollusks, suggest a lower δ13C value in S. spirula than in Nautilus52–54, and thus a higher metabolic rate. These facts and our new data suggest a possible link between metabolic rates and patterns of chamber volume development in cephalopods: abrupt drops in chamber volume occur in the modern coleoid Spirula with a higher metabolic rate, but not in nautilids with a lower metabolic rate.
Presumably, the high energy requirements of coleoids make them more susceptible to adverse ecological conditions, which, in turn, may affect the phenotype (chamber construction) since energy acquisition and processing are essential parts of growth and biomass production. This hypothesis is concordant with the abovementioned experiment by Wiedmann and Bolezky28. If this holds true for all phragmocone-bearing cephalopods, the fact that our ammonoid data show abrupt decreases in volumetric growth trajectories as in Spirula may suggest a metabolic rate in ammonoids higher than that in nautilids. Such a relatively high metabolic rate of ammonoids coincides with their supposedly relatively good locomotory capabilities and closer phylogenetic relationships to coleoids55–58. The actual environmental factors, which induced these abrupt changes, are difficult to detect.
At the end of the Cretaceous, ammonoids went extinct while nautilids survived4. After the asteroid impact and the Deccan trap-eruptions59, acidification of sea water occurred, which presumably caused a dramatic decrease in the abundance of primary producers and planktic animals8,60, thereby drastically cutting the food supply of ammonoids. It is likely that metabolic rate determined the degree to which the respective species could survive food-impoverished times. Assuming that ammonoids possessed a high metabolic rate, they required more energy input per time unit, and, in turn, were particularly susceptible to such adverse conditions. This prevented the soft body from growing and reduced the body chamber volume required for the soft parts, thus lowering shell secretion at the aperture. As a consequence, septal spacing was reduced and smaller chambers were constructed.
Reduced food availability implies a lower energy availability, which particularly affected young individuals, like hatchlings, because of their lower energy reservoirs. In contrast to small ammonoid hatchlings (<2 mm), larger nautilid hatchlings (>10 mm) could maintain their growth with their low metabolism (or by lowering their metabolic rate even more) and survive prolonged phases of low food-availability. Although there are other conceivable factors, which may have contributed to ammonoid extinction5, a high metabolic rate of ammonoids, in combination with their very small hatching size, was probably a fatal combination during times of low primary production. By contrast, nautilid hatchlings had larger reserves because they are an order of magnitude larger in diameter and accordingly have a body mass three orders of magnitude larger7,60,61. However, some coleoids, which most likely also had a high metabolic rate survived the K/Pg extinction. Although the exact reason for their survival is unclear, their greater range in fecundity, hatching size, locomotory capability, and macrophagous feeding strategy may have protected them from extinction6,55,62,63. In any case, belemnites, which also had rather small hatchlings, became extinct, while vampyromorph coleoids (ancestors of modern octopodids), which likely had larger hatchlings, survived63. Variation in embryonic size and metabolism in Mesozoic coleoids as well as the exact kill mechanism need further investigation.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We thank Kenji Ikuno (Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo) for providing the specimens for grinding tomography. Jamie Brezina (South Dakota School of Mines and Technology) kindly donated several Eutrephoceras specimens. We also acknowledge Christoph Zollikofer (University of Zurich) for permitting the use of his micro-CT scanner and for help with scanning. Kayla Irizarry (Penn State University) is thanked for proofreading the ms. Morgan Hill and Andrew Smith (American Museum of Natural History) helped us CT-scan some specimens of Nautilus. This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Project Numbers: 200020_169847 and 200021_149119) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author contributions
A.T., R.H., R.L., CI., and N.L. produced tomographic data. A.T., N.M., and R.L. segmented the tomographic data and measured chamber volume. A.T. and C.K. wrote the paper. All authors reviewed the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41598-020-59748-z.
References
- 1.Brayard A, et al. Good genes and good luck: ammonoid diversity and the end-Permian mass extinction. Science. 2009;325:1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.1174638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ward, P. Ammonoid extinction. In: Ammonoid paleobiology (eds. Landman, N. H., Tanabe, K. & Davis, R. A.). Springer (1996).
- 3.Wiedmann, J & Kullmann, J. Crises in ammonoid evolution. In: Ammonoid paleobiology (eds. Landman, N. H., Tanabe, K. & Davis, R. A.). Springer (1996).
- 4.Landman NH, et al. Ammonite extinction and nautilid survival at the end of the Cretaceous. Geology. 2014;42:707–710. doi: 10.1130/G35776.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Landman, N. H., Goolaerts, S., Jagt, J. W., Jagt-Yazykova, E. A., Machalski, M. Ammonites on the brink of extinction: Diversity, abundance, and ecology of the order Ammonoidea at the Cretaceous/Paleogene (K/Pg) boundary. In: Ammonoid Paleobiology: From macroevolution to paleogeography (eds Klug, C., Korn, D., De Baets, K., Kruta, I., Mapes, R. H.). Springer (2015).
- 6.Kruta I, Landman N, Rouget I, Cecca F, Tafforeau P. The role of ammonites in the Mesozoic marine food web revealed by jaw preservation. Science. 2011;331:70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1198793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Baets K, Klug C, Korn D, Landman NH. Early evolutionary trends in ammonoid embryonic development. Evolution. 2012;66:1788–1806. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tyrrell T, Merico A, McKay DIA. Severity of ocean acidification following the end-Cretaceous asteroid impact. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2015;112:6556–6561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418604112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kaiho K, et al. Global climate change driven by soot at the K-Pg boundary as the cause of the mass extinction. Scientific reports. 2016;6:28427. doi: 10.1038/srep28427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Klug, C. & Lehmann, J. Soft part anatomy of ammonoids: reconstructing the animal based on exceptionally preserved specimens and actualistic comparisons. In: Ammonoid Paleobiology: from anatomy to ecology (eds Klug, C., Korn, D., De Baets, K., Kruta, I., Mapes, R. H.). Springer (2015).
- 11.Strotz LC, Saupe EE, Kimmig J, Lieberman BS. Metabolic rates, climate and macroevolution: a case study using Neogene molluscs. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2018;285:20181292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Payne JL, Heim NA, Knope ML, McClain CR. Metabolic dominance of bivalves predates brachiopod diversity decline by more than 150 million years. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2014;281:20133122. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vermeij GJ. Paleophysiology: from fossils to the future. Trends in ecology & evolution. 2015;30:601–608. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2015.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bucher, H., Landman, N. H., Klofak, S. M. & Guex, J. Mode and rate of growth in ammonoids. In: Ammonoid paleobiology (eds Landman, N. H., Tanabe, K., Davis, R. A.). Springer (1996).
- 15.Klug, C. et al. Describing ammonoid conchs. In: Ammonoid Paleobiology: From anatomy to ecology (eds Klug, C., Korn, D., De Baets, K., Kruta, I., Mapes, R. H.). Springer (2015).
- 16.Arai K, Wani R. Variable growth modes in late cretaceous ammonoids: implications for diverse early life histories. Journal of Paleontology. 2012;86:258–267. doi: 10.1666/11-068.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Landman NH, Rye DM, Shelton KL. Early ontogeny of Eutrephoceras compared to Recent Nautilus and Mesozoic ammonites: evidence from shell morphology and light stable isotopes. Paleobiology. 1983;9:269–279. doi: 10.1017/S0094837300007685. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Davis, R. A. & Mohorter, W. Juvenile Nautilus from the Fiji Islands. Journal of Paleontology, 925–928 (1973).
- 19.Klug C. Life-cycles of Emsian and Eifelian ammonoids (Devonian) Lethaia. 2001;34:215–233. doi: 10.1080/002411601316981179. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kraft S, Korn D, Klug C. Patterns of ontogenetic septal spacing in Carboniferous ammonoids. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie-Abhandlungen. 2008;250:31–44. doi: 10.1127/0077-7749/2008/0250-0031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wani R, Tajika A, Ikuno K, Iwasaki T. Ontogenetic trajectories of septal spacing in Early Jurassic belemnites from Germany and France, and their palaeobiological implications. Palaeontology. 2018;61:77–88. doi: 10.1111/pala.12327. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yamaguchi A, Kumada Y, Alfaro AC, Wani R. Abrupt changes in distance between succeeding septa at the hatching time in modern coleoids Sepiella japonica and Spirula spirula. Swiss. Journal of Palaeontology. 2015;134:301–307. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lemanis R, Korn D, Zachow S, Rybacki E, Hoffmann R. The evolution and development of cephalopod chambers and their shape. PloS one. 2016;11:e0151404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Naglik C, et al. Growth trajectories of some major ammonoid sub‐clades revealed by serial grinding tomography data. Lethaia. 2015;48:29–46. doi: 10.1111/let.12085. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tajika A, Morimoto N, Wani R, Naglik C, Klug C. Intraspecific variation of phragmocone chamber volumes throughout ontogeny in the modern nautilid Nautilus and the Jurassic ammonite Normannites. PeerJ. 2015;3:e1306. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hoffmann R, et al. Non-invasive imaging methods applied to neo- and paleo-ontological cephalopod research. Biogeosciences. 2014;11:2721–2739. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-2721-2014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hoffmann R, Reinhoff D, Lemanis R. Non-invasive imaging techniques combined with morphometry: a case study from Spirula. Swiss Journal of Palaeontology. 2015;134:207–216. doi: 10.1007/s13358-015-0083-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wiedmann, J. & Boletzky, S. V. Wachstum und Differenzierung des Schulps von Sepia officinalis unter künstlichen Aufzuchtbedingungen-Grenzen der Anwendung um palökologischen Modell. E Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, 118–133 (1982).
- 29.Keupp H, Riedel F. Nautilus pompilius in captivity: a case study of abnormal shell growth. Berliner geowissenschaftliche Abhandlungen E. 1995;16:663–681. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Inoue S, Kondo S. Suture pattern formation in ammonites and the unknown rear mantle structure. Scientific reports. 2016;6:33689. doi: 10.1038/srep33689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tajika A, et al. Empirical 3D-model of the conch of the Middle Jurassic ammonite microconch Normannites: its buoyancy, the physical effects of its mature modifications and speculations on their function. Historical. Biology. 2015;27:181–191. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ward, P. D. The Natural History of Nautilus. Allen and Unwin (1987).
- 33.Collins, D. & Ward, P. D. Adolescent growth and maturity in Nautilus. In: Nautilus (eds). Springer (2010).
- 34.Wani R, Ayyasami K. Ontogenetic change and intra-specific variation of shell morphology in the Cretaceous nautiloid (Cephalopoda, Mollusca) Eutrephoceras clementinum (d’Orbigny, 1840) from the Ariyalur area, southern India. Journal of Paleontology. 2009;83:365–378. doi: 10.1666/08-119.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cochran JK, Rye DM, Landman NH. Growth rate and habitat of Nautilus pompilius inferred from radioactive and stable isotope studies. Paleobiology. 1981;7:469–480. doi: 10.1017/S0094837300025525. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lukeneder A, Harzhauser M, Müllegger S, Piller WE. Stable isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) in Spirula spirula shells from three major oceans indicate developmental changes paralleling depth distributions. Marine Biology. 2008;154:175–182. doi: 10.1007/s00227-008-0911-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Le Goff R, Gauvrit E, Du Sel GP, Daguzan J. Age group determination by analysis of the cuttlebone of the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis L. in reproduction in the Bay of Biscay. Journal of molluscan studies. 1998;64:183–193. doi: 10.1093/mollus/64.2.183. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hewitt RA, Stait B. Seasonal variation in septal spacing of Sepia officinalis and some Ordovician actinocerid nautiloids. Lethaia. 1988;21:383–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3931.1988.tb01767.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gutowska MA, Melzner F, Pörtner HO, Meier S. Cuttlebone calcification increases during exposure to elevated seawater ρCO2 in the cephalopod Sepia officinalis. Marine Biology. 2010;157:1653–1663. doi: 10.1007/s00227-010-1438-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dunstan AJ, Ward PD, Marshall NJ. Vertical distribution and migration patterns of Nautilus pompilius. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Landman NH, et al. Nautilid nurseries: hatchlings and juveniles of Eutrephoceras dekayi from the lower Maastrichtian (Upper Cretaceous) Pierre Shale of east‐central Montana. Lethaia. 2018;51:48–74. doi: 10.1111/let.12222. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology. 2004;85:1771–1789. doi: 10.1890/03-9000. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Biro PA, Stamps JA. Do consistent individual differences in metabolic rate promote consistent individual differences in behavior? Trends in ecology & evolution. 2010;25:653–659. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2010.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zeng L-Q, et al. Standard metabolic rate predicts growth trajectory of juvenile Chinese crucian carp (Carassius auratus) under changing food availability. Biology open. 2017;6:1305–1309. doi: 10.1242/bio.025452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.O’Dor RK, Shadwick R. Squid, the olympian cephalopods. Journal of Cephalopod Biology. 1989;1:33–55. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Seibel BA. On the depth and scale of metabolic rate variation: scaling of oxygen consumption rates and enzymatic activity in the Class Cephalopoda (Mollusca) Journal of Experimental Biology. 2007;210:1–11. doi: 10.1242/jeb.02588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Seibel BA, Childress JJ. Metabolism of benthic octopods (Cephalopoda) as a function of habitat depth and oxygen concentration. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 2000;47:1247–1260. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(99)00103-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Saunders WB. Nautilus growth and longevity: evidence from marked and recaptured animals. Science. 1984;224:990–992. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4652.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Boutilier R, et al. Nautilus and the art of metabolic maintenance. Nature. 1996;382:534. doi: 10.1038/382534a0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Boutilier R, et al. The protective effects of hypoxia-induced hypometabolism in the Nautilus. Journal of Comparative Physiology B. 2000;170:261–268. doi: 10.1007/s003600000096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.O’dor R, Forsythe J, Webber D, Wells J, Wells M. Activity levels of Nautilus in the wild. Nature. 1993;362:626. doi: 10.1038/362626a0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Price GD, Twitchett RJ, Smale C, Marks V. Isotopic analysis of the life history of the enigmatic squid Spirula spirula, with implications for studies of fossil cephalopods. Palaios. 2009;24:273–279. doi: 10.2110/palo.2008.p08-067r. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Auclair A-C, Lecuyer C, Bucher H, Sheppard SM. Carbon and oxygen isotope composition of Nautilus macromphalus: a record of thermocline waters off New Caledonia. Chemical Geology. 2004;207:91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.02.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ohno A, Miyaji T, Wani R. Inconsistent oxygen isotopic values between contemporary secreted septa and outer shell walls in modern Nautilus. Lethaia. 2015;48:332–340. doi: 10.1111/let.12109. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Naglik, C., Tajika, A., Chamberlain, J. & Klug, C. Ammonoid locomotion. In: Ammonoid Paleobiology: From anatomy to ecology (eds). Springer (2015).
- 56.Jacobs DK, Landman NH. Nautilus—a poor model for the function and behavior of ammonoids? Lethaia. 1993;26:101–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3931.1993.tb01799.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kröger B, Vinther J, Fuchs D. Cephalopod origin and evolution: a congruent picture emerging from fossils, development and molecules. Bioessays. 2011;33:602–613. doi: 10.1002/bies.201100001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Klug C, Korn D. The origin of ammonoid locomotion. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 2004;49:235–242. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hull PM, et al. On impact and volcanism across the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. Science. 2020;367:266–272. doi: 10.1126/science.aay5055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Tajika A, Nützel A, Klug C. The old and the new plankton: ecological replacement of associations of mollusc plankton and giant filter feeders after the Cretaceous? PeerJ. 2018;6:e4219. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Korn, D. & Klug, C. Conch form analysis, variability, morphological disparity, and mode of life of the Frasnian (Late Devonian) ammonoid Manticoceras from Coumiac (Montagne Noire, France). In: Cephalopods present and past: new insights and fresh perspectives (eds Landman, N. H., Davis, R. A. & Mapes, R. H.). Springer (2007).
- 62.Jenny D, et al. Predatory behaviour and taphonomy of a Jurassic belemnoid coleoid (Diplobelida, Cephalopoda) Scientific reports. 2019;9:7944. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44260-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fuchs, D., Laptikhovski, V., Nikolaeva, S., Alexei, I. & Rogov, M. Evolution of reproductive strategies in coleoid mollusks. Paleobiology, pp. 1–22 (2020).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.