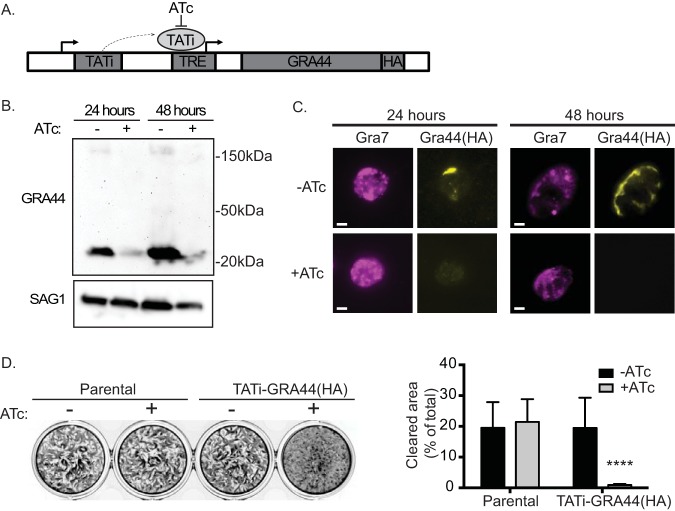
FIG 4.
Knockdown of GRA44 disrupts parasite propagation. To determine the function of GRA44, we applied a tetracycline (Tet)-repressible system to establish a conditional GRA44 knockdown strain. (A) Diagram of the strategy used to generate the conditional knockdown of GRA44, as outlined in the Materials and Methods section. Sel marker, selective marker. (B) Quantitative Western blot of the TATi-GRA44(HA) parasite strain grown for either 24 or 48 h in the absence (lanes −) or the presence (lanes +) of ATc probed with HA to detect GRA44 and SAG1 as a loading control. (C) The reduction in GRA44 expression in the presence of ATc was confirmed by IFA of intracellular parasites of the TATi-GRA44(HA) strain grown with and without ATc for 24 or 48 h and probed with anti-HA antibodies. Bars = 2 μm. (D) Plaque assays were performed with the GRA44(HA) parasites (parental) or the TATi-GRA44(HA) parasites grown without (−) or with (+) ATc for 5 days. (Left) Representative results of a plaque assay. (Right) The results were quantitated based on the percentage of the cell monolayer cleared by the parasite (cleared area) and the average for biological and experimental triplicates (n = 3; mean ± SD; P < 0.0001, unpaired t test).