Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) and neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) are two prominent antiangiogenic targets. They are highly expressed on vascular endothelial cells and some tumor cells. Therefore, targeting VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 may be a potential antiangiogenic and antitumor strategy. A7R, a peptide with sequence of Ala-Thr-Trp-Leu-Pro-Pro-Arg that was found by phage display of peptide libraries, can preferentially target VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 and destroy the binding between vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165) and VEGFR-2 or NRP-1. This peptide is a new potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis and a targeting ligand for cancer therapy. This review describes the discovery, function and mechanism of the action of A7R, and further introduces the applications of A7R in antitumor angiogenic treatments, tumor angiogenesis imaging and targeted drug delivery systems. In this review, strategies to deliver different drugs by A7R-modified liposomes and nanoparticles are highlighted. A7R, a new dual targeting ligand of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, is expected to have efficient therapeutic or targeting roles in tumor drug delivery.
Keywords: A7R, Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, Neuropilin-1, Antiangiogenesis, Tumor angiogenesis imaging, Drug delivery
Graphical abstract
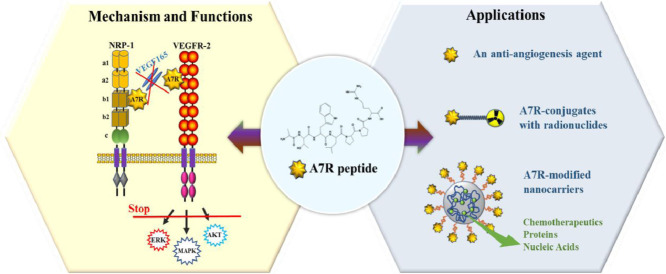
A7R, a new dual targeting ligand for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) and neuropilin-1(NRP-1), has been applied in the field of antiangiogenesis, tumor angiogenesis imaging and targeted drug delivery systems.
1. Introduction
In 1971, Folkman speculated that tumors could not grow beyond 1 mm in diameter without developing their own blood supply by angiogenesis [1]. Thus, angiogenesis was first proposed as a therapeutic target for tumors. Blood vessels in solid tumors are composed of endothelial cells and tumor cells. Research has revealed that angiogenesis is required for tumor cells to grow beyond a certain size, break away from an established solid tumor, enter blood vessels, implant, and initiate the growth of a secondary tumor at a distant site, i.e., tumor metastasis [2].
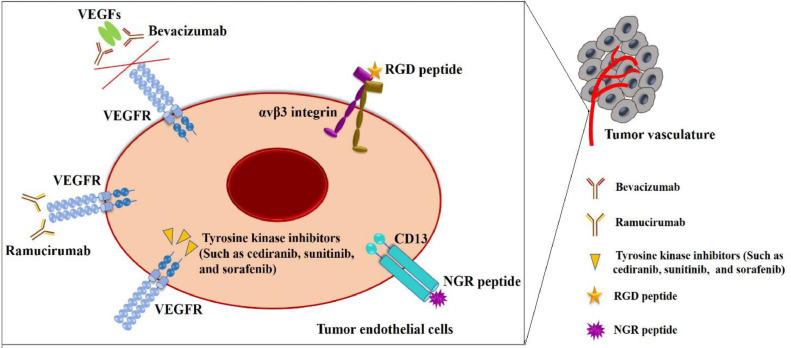
During the past decades, a series of strategies have emerged to target tumor endothelial cells, and many angiogenesis inhibitors have also been developed [3]. Tumor endothelial cells and cancer cells show abnormal surface expression of numerous molecular markers, such as endothelial cell growth factor receptors, integrins and cell surface proteoglycans, which differ from those expressed by normal cells [4]. Thus, targeting tumor cells and tumor vasculature is important for effective cancer treatment. During tumor growth, many proangiogenic factors are stimulated and upregulated. Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs), which regulate angiogenesis through binding VEGF receptors (VEGFRs), are regarded as major regulators of tumor angiogenesis [5]. Thus, antiangiogenic strategies can be achieved through targeting VEGF or VEGFR (Fig. 1). Bevacizumab (a humanitzed monoclonal antibody) and aflibercept (a recombinant fusion protein) are the most popular antiangiogenesis drugs. These VEGF-targeted drugs can inhibit VEGF activity though binding to VEGFs [6]. Antiangiogenic therapies also involve targeting VEGFR. Ramucirumab can block signaling activation through binding VEGFR. In addition, cediranib, sunitinib, and sorafenib are tyrosine kinase inhibitors that suppress the kinase activity of VEGFR [7]. The above treatment methods have been clinically used for colorectal cancer, breast cancer and advanced gastric cancer. However, current antiangiogenic targeted therapies have many drawbacks [3]. For example, VEGF-targeted blockers are generally nonselective, show poor tissue penetration in normal vascular tissue and are always associated with acquired resistance and severe side effects, including hypertension, proteinuria and stroke. The high cost of the production and purification of monoclonal antibodies further limits their clinical applications [8].
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of other targeted strategies to tumor vasculature.
To overcome the shortcomings of the above agents, scientists and clinicians have investigated peptides as therapeutics. Peptides with high specificity and low immune responses in hosts may overcome some of the limitations of other inhibitors and may be promising vascular-targeting diagnostic and therapeutic agents [9], [10].
The selection of phage display libraries allows us to discover and acquire numerous peptides targeting tumor angiogenesis due to their high specificity and affinity for molecular markers and vascular receptors on the endothelial cell surface [11]. To date, the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) and arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptides (Fig. 1) are the two most studied vascular-homing peptides screened from phage display libraries [12]. Aminopeptidase-N (CD13) is a zinc-dependent transmembrane ectopeptidase that is mainly overexpressed on tumor vascular cells and some tumor cells compared with normal blood vessels [13]. CD13 can promote the proliferation, invasion and migration of tumor endothelial cells. The NGR peptide and NGR-containing peptides can recognize and bind to CD13 expressed on the surface of endothelial cells of tumor blood vessels via the arginine and asparagine residues [14].
Integrins are heterodimeric membrane glycoproteins composed of noncovalently associated α- and β- subunits. Different subunit combinations comprise various types of heterodimers that determine the affinity of extracellular domains in integrins to diverse extracellular matrix (ECM) ligands (e.g., proteins, growth factors, immunoglobulin, cytokines) [15]. As cell adhesion receptors, these integrins regulate multiple intracellular signal transduction pathways by binding different ECM ligands. Among various integrins, αvβ3 integrin, which is overexpressed in endothelial cells and tumor cells, is regarded as the strongest regulator of tumor angiogenesis [16]. Researchers have discovered that the RGD sequence exhibits a high affinity for the active sites present in the αvβ3 integrin, and later, a wide variety of synthetic RGD-based peptides were designed as targeting ligands for the αvβ3 integrin receptor [17]. The two peptides have been successfully used to deliver various antiangiogenic and antitumor drugs, including chemotherapeutic drugs, therapeutic proteins, cytokines, nucleic acids and nanoparticles, for cancer therapy. In addition, after these molecules are coupled with different dyes or radiolabeled agents, they can be highly efficient imaging probes for molecular imaging studies in the diagnosis of various cancers or other angiogenic diseases [15]. In addition to NGR and RGD peptides, other vascular-homing peptides have been shown to target tumor angiogenesis. For example, the CAGALCY cyclic peptide exhibited a high-affinity interaction with the endothelium of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) [11]. The GX1 (CGNSNPKSC) peptide, a cyclic 9-mer peptide, displayed efficient targeting of the gastric tumor vasculature; the TCP-1 (CTPSPFSHC) peptide showed a high affinity for the blood vessels of orthotopic colorectal cancer; and SP5-52 (SVSVGMKPSPRP) showed selective recognition of tumor blood vessels, not normal vessels, and was used as a targeting ligand for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) [12]. Although these vasculature-homing peptides have been proven to be useful and potential targeting agents in tumor-targeted diagnosis and therapy, only preclinical studies and a few clinical trials have been conducted to date. Notably, the exact mechanisms underlying the interactions of the tumor vasculature with most vasculature-homing peptides, such as NGR, are undefined, and the receptors of some peptides have not yet been identified. Moreover, because some known molecular markers are present in both tumor vasculature and ordinary inflammatory vasculature, many peptides, such as NGR and RGD, have shown low selectivity to tumor vasculature under some specific inflammatory pathologic conditions. In addition, more studies should be carried out on the structural stability, toxicity, immunogenicity and biodistribution of these vasculature-homing peptides. Hence, development of new vasculature-homing peptides that have definite receptors and highly selective targets on the tumor vasculature should be carried out.
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2/KDR) and neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) are two important markers that contribute to the high proliferation and migration of endothelial cells [4]. Blocking VEGFR-2 or NRP-1 may be an effective therapeutic strategy for antitumor angiogenesis and drug delivery. ATWLPPR (A7R) was identified by a phage display peptide library [18] and was shown to simultaneously inhibit VEGF binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 with high specificity and to decrease tumor angiogenesis and growth. Subsequently, scientists found that A7R could also induce endothelial cell and tumor cell apoptosis [19]; decrease vascular permeability, brain hemorrhage and BBB disruption [20]; and reduce early retinal damage by preserving vascular integrity [21]. Based on these results, A7R may become a new potent dual inhibitor of both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 and a targeting peptide for tumor angiogenesis in cancer therapy.
To help understand and use A7R in disease treatment and diagnosis, in this review, we first introduce the discovery and mechanisms of action of A7R and then summarize the research progress in the applications of A7R and A7R-based strategies, including the use of A7R as an antiangiogenic and anticancer agent, radiolabeled A7R in imaging, and the grafting of A7R as a targeting ligand on the surface of nanocarriers. Finally, we provide our opinions on the future research and development of A7R.
2. A7R peptide and its mechanism of action
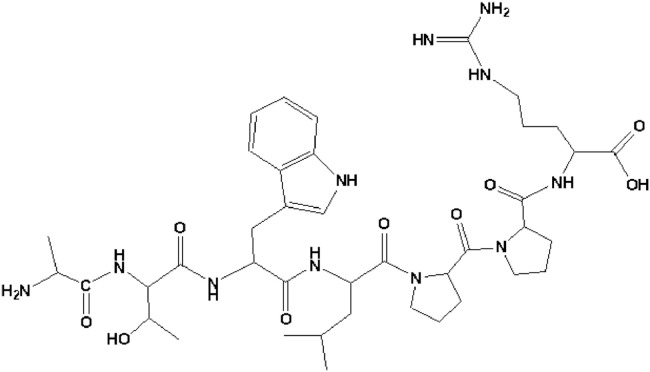
Screening peptides from phage display peptide libraries is a powerful technique for identifying agonists or antagonists according to their ability to bind to the desired targets [22]. With the assistance of this technique, a new heptapeptide, ATWLPPR (A7R) (Fig. 2), with the ability to selectively inhibit human endothelial cell proliferation in vitro, was identified [18]. A7R has been extensively studied by researchers because is a specific ligand for VEGFR-2 and NRP-1. The identification of A7R and its mechanism of action were closely related to the regulatory roles of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 in angiogenesis.
Fig. 2.
Structure of the A7R sequence.
2.1. The regulatory roles of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 in angiogenesis
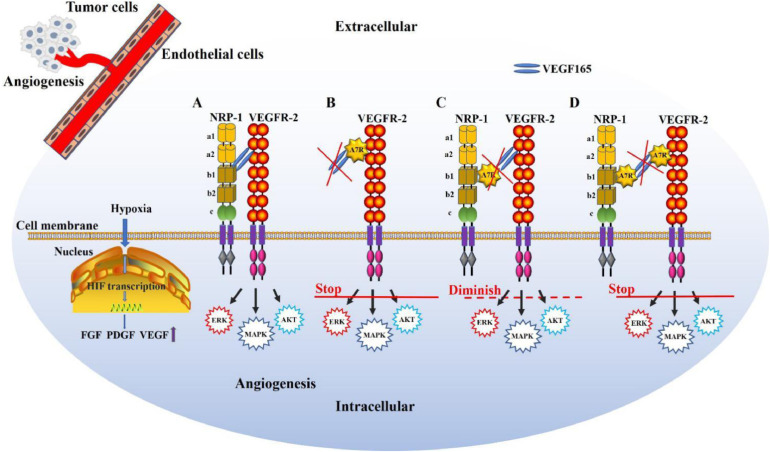
The delicate balance between inducers (proangiogenic factors) and inhibitors (antiangiogenic factors) is critical for physiological homeostasis of tumor angiogenesis [23]. Triggered by signals such as metabolic stress (low pH, low oxygen pressure), mechanical stress, genetic mutations, etc., tumors often activate angiogenesis by shifting the balance towards proangiogenic conditions. For example (Fig. 3), hypoxia increases cellular hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) transcription, leading to the upregulation of various proangiogenic factors, such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), angiopoietins, and VEGF [24]. Among these factors, the signaling pathway initiated by VEGFs and their receptors plays determinant roles in angiogenesis [25].
Fig. 3.
Roles of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 in angiogenesis and the antiangiogenic mechanism of action of A7R. Hypoxia increases cellular hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) transcription, leading to the upregulation of FGF, PDGF, and VEGF expression in endothelial cells. (A) NRP-1 functioning as a coreceptor binds to VEGF165 and enhances VEGF165-VEGFR-2 intracellular trafficking, facilitating angiogenesis. (B) A7R can target and compete with VEGF165 to bind VEGFR-2 and suppress the downstream signal transduction of VEGFR-2. (C) A7R can bind to the b1 domain of NRP-1, inhibit VEGF165 binding to NRP-1 and diminish VEGF165-VEGFR-2 intracellular trafficking. (D) A7R can bind preferentially to both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 simultaneously and suppress the signal transduction downstream of VEGFR-2, displaying the strongest antiangiogenic activity.
Among the VEGF family, VEGF165 (one isoform of VEGF-A) shows varied binding abilities with its receptors. In the tumor endothelium, VEGF165 interacts with VEGFR-2 and then induces capillary growth, which fulfills the increased tumor demand for oxygen and nutrients, contributing to tumor metastasis [26]. Studies have shown that VEGFR-2 may be the most important receptor in VEGF-induced endothelial cell mitogenesis and permeability [27]. NRP-1, a cell-surface glycoprotein that lacks intrinsic kinase sequences, was found to contribute to the high migration of endothelial cells [28]. As a type I transmembrane receptor, NRP-1 was primarily identified as an axonal adhesion protein, a receptor for semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) [29]. Researchers have proved that NRP-1 is a coreceptor that binds to VEGF165 and enhances the binding of VEGF165 to VEGFR-2 [30].
In addition to the highly conserved short cytoplasmic domain, NRP-1 possesses five discrete extracellular domains for ligand binding, two domains with homology to complement components C1r and C1s (CUB domains, a1 and a2), two coagulation factor V/VIII domains (CF V/VIII, b1 and b2), and one C-terminal MAM (meprin, A5, µ-phosphatase) domain (c) [30]. Thus, with a core conserved binding pocket formed by the b1 coagulation factor loops, NRP-1 binds to VEGF165, forming a VEGF165-NRP-1 complex [31]. This complex then enhances VEGF165-VEGFR-2 intracellular trafficking, activating receptor kinase activity that leads to receptor autophosphorylation. The phosphorylated receptors then recruit interacting proteins, such as Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing proteins, and induce the activation of signaling pathways that involve another second messenger, thereby activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway, which promotes endothelial cell survival; the Src-FAK pathway, which mediates endothelial cell migration and vascular permeability [26]; and the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway, which induces endothelial cell proliferation and network formation, facilitating angiogenesis (Fig. 3A) [32].
In addition to binding to VEGF, NRP-1 can also interact with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor (PDGFR), which promotes the proliferation of endothelial cells and blood vessel formation [29]. Furthermore, studies have shown that NRP-1 can regulate angiogenesis in a VEGFR-2-independent manner [33,34]. As an adhesion molecule, NRP-1 interacts with integrins and promotes endothelial cell adhesion to the ECM. Then, the cytoplasmic domain of NRP-1 forms a complex with the intracellular kinase ABL1 and promotes endothelial cell migration in response to integrin ligand-mediated angiogenesis [34].
Due to the close relationship of VEGF165, VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, interrupting the formation of the VEGF165/NRP-1/VEGFR-2 complex or specifically inhibiting VEGFR-2 or NRP-1 will inhibit tumor angiogenesis. Although A7R has been verified to interrupt the VEGF165/NRP-1/VEGFR-2 pathway and display antiangiogenic effects, different strategies for interrupting the pathway have been proposed (Fig. 3).
2.2. The mechanism underlying A7R peptide function
2.2.1. Binding to VEGFR-2
In 2000, Tournaire et al. found that A7R could completely abolish VEGF binding to VEGFR-2. The researchers used two different strategies to identify peptides blocking the binding between VEGF and VEGFR-2 [18]. First, they selected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells that expressed recombinant VEGFR-2 at the membrane surface to test the binding ability of different peptides to VEGFR-2. After screening, seven peptides (K1–K7) were chosen. However, these peptides showed low affinity to VEGFR-2 in ELISAs. Then, the researchers screened the peptides by an anti-VEGF antibody binding test. Another seven peptides (V1–V7) with no consensus motifs were selected, and all of them showed strong affinity for VEGFR-2. Among these peptides, V1 (ATWLPPR) and V6 (LPPNPTK), which both had an LPP motif, showed the best reactivity. Interestingly, only V1 (ATWLPPR) competed with VEGF for binding to VEGFR-2, inhibited human endothelial cell proliferation in vitro and abolished VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vivo. Subsequently, Perret et al. also proposed that this heptapeptide (A7R) might target VEGFR-2 since it could suppress [125I]-VEGF binding to endothelial cells [35]. In a 2005 report, Barr et al. observed that 5-(6)-carboxyfluorescein-labeled A7R could interact with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) expressing VEGFR-2, as shown by confocal microscopy in vitro [19]. All these studies demonstrated that A7R could target VEGFR-2 and potentially inhibit tumor angiogenesis (Fig. 3B).
2.2.2. Binding to NRP-1
In 2004, Perret labeled A7R with 99mTc to explore whether it could target NRP-1 or NRP-2. Interestingly, the researchers found that 99mTc-labeled A7R could bind NRP-1 but not NRP-2. Incubation of 99mTc-labeled A7R with recombinant NRP-1 protein resulted in a visual monophasic binding curve [36]. Subsequently, Starzec et al. proved that A7R could inhibit the binding of VEGF165 to recombinant NRP-1 protein and NRP-1-expressing MDA-MB-231 cells but could not inhibit the binding between VEGF165 and recombinant VEGFR-2 protein or VEGFR-2-expressing porcine aortic endothelial (PAE) cells. The researchers also found that A7R could form a specific complex with recombinant NRP-1 by affinity crosslinking experiments (Fig. 3C) [37].
In 2007, the above mentioned laboratory performed a structural characterization of A7R. According to their research, the interface between NRP-1 and VEGF165 is predominantly stabilized by a network of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges based on analysis of the complex crystal structure of NRP-1-VEGF165 [38]. VEGF165 contributes two separate principal regions to the heterodimeric interactions: the exon 8 region, including the C-terminal arginine, is essential for the high affinity of VEGF165 for NRP-1; and the electronegative residues of the exon 7 region form additional interactions with the L1 loop of NRP-1. In addition, the C-terminal tail (residues 160–165, CDKPRR) of VEGF165 is the binding site for NRP-1 [39,40]
Based on the NRP-1 structure (PDB ID: 2ORZ), a molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of the NRP-1-A7R complex was performed [38]. The complex structure showed that the hydrogen bonds between the terminal amino acid Arg7 of A7R and NRP-1 played a key role in stabilization of the complex, which was the same as the structural basis for the interaction between VEGF165 and NRP-1 mentioned before. The guanidinium group of Arg7 of A7R (donor) formed hydrogen bonds with the side-chain carboxylic group of Asp320 in NRP-1 (acceptor). The hydroxyl groups of Ser346, Thr349 and Tyr353 (donor) formed hydrogen bonds with the C-terminal carboxylic group of Arg7 in A7R (acceptor). Interestingly, the C-terminal tails of both VEGF165 and A7R possess a CendR sequence (C-terminal arginine), which was confirmed to be essential for the interaction with the b1 domain of NRP-1. The cell binding and internalization abilities were lost when the C-terminal arginine was mutated to alanine, thus confirming the presumed hydrogen bonding network between Arg7 and NRP-1 [41]. In addition, based on alanine scanning (mutation of each amino acid to alanine) or amino acid deletion, the C-terminal LPPR sequence is important for A7R activity; mutation of both Pro5 and Pro6 to alanine in A7R significantly reduced the inhibitory effect. Thus, A7R contains a CendR sequence targeting NRP-1: the C-terminal arginine is optimally accommodated at the binding pocket in the b1 domain of NRP-1 by a hydrogen bond network, and the two internal proline residues in the LXXR motif may be responsible for stabilization of the NRP-1-peptide complex. In 2009, Tuttle further studied the dynamic behavior of A7R through a hybrid quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) method, which may contribute to revealing its conformation [42].
In summary, A7R may mimic the C-terminal tail of VEGF165, simulate the interaction with the b1 domain of NRP-1 and thus generate steric hindrance between NRP-1 and VEGF165. A7R competes with VEGF165 for binding to NRP-1, which can disrupt the VEGFR-2-NRP-1 complex, thereby interrupting VEGFR-2-mediated angiogenesis through NRP-1. These results provide useful information for future studies aimed at designing new peptide inhibitors of angiogenesis.
2.2.3. Binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1
Although some recent studies showed that A7R targeted NRP-1 but not VEGFR-2, Ying et al. [43], [44]. proved that this peptide specifically bound to both NRP-1 and VEGFR-2 (Fig. 3D). Molecular docking and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analyses were conducted to explore the interactions of A7R with its receptors.
In the molecular docking study, A7R was shown to be deeply docked at two domains of VEGFR-2, among which the Arg could form ionic interactions with Asp1054 of VEGFR-2, while the indole fragment of Trp could form hydrophobic interactions with Phe1045, Phe916, Ala864 and Leu1033 of VEGFR-2. In addition, the Leu and Pro of A7R could permeate into the binding pocket through hydrophobic interactions. The binding mode between A7R and NRP-1 showed that A7R localized in the head of the b1 domain of NRP-1, and ionic interactions between Arg of A7R and Asp320 of NRP-1, as well as the Pro and Leu residues of the peptide and the Tyr297 and Trp301 residues of NRP-1, were observed and were consistent with previous mechanistic research [44]. In the SPR assay, A7R displayed a similar high binding affinity to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 with an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 9.29 and 6.62 nM, respectively [43]. In conclusion, all these results confirmed the binding affinity of A7R to both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1.
Based on the above findings, although A7R was originally thought to target VEGFR-2 and display antiangiogenic activity, the hypothesis that A7R directly targets NRP-1 and thus blocks the binding between VEGF165 and NRP-1 has the most support. Nevertheless, the latest studies by Ying et al. showed that this peptide might exhibit specific dual binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, suggesting that the antiangiogenic effects of A7R may be caused by blocking both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 instead of only one receptor. Certainly, the underlying mechanisms need to be elucidated, which will be indispensable for applications of this peptide.
3. The applications of A7R
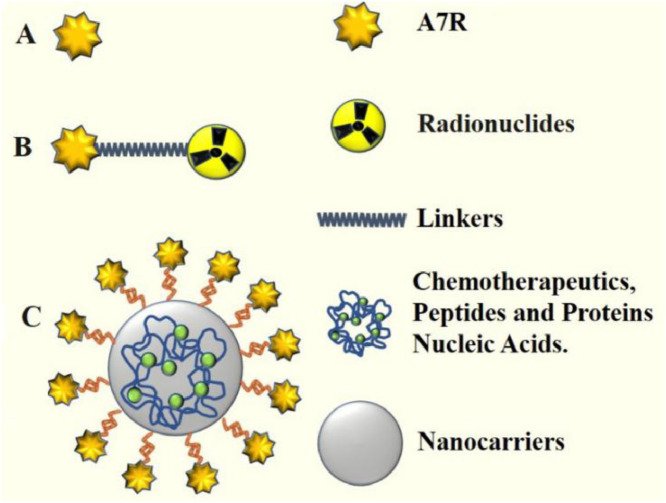
Although the mechanism underlying A7R targeting of VEGFR-2 or NRP-1 is still controversial, applications of A7R based on its inhibitory effects on tumor angiogenesis have been extensively examined in recent years. A7R has several advantages for scientific research and practical applications. First, owing to its ability to target VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, which are highly expressed on tumor neovasculature, A7R can be preferentially recognized and taken up by the endothelial system. Second, modified A7R (N-to-C cyclization or the retro-inverso isomer of A7R) showed enhanced proteolytic and thermal stability against proteolytic degradation and retained comparable binding affinities to the receptors (VEGFR-2 and NRP-1), and A7R conjugates could show increased accumulation in tumor tissue. Third, A7R, which consists of only seven amino acids and is much smaller than monoclonal antibodies, has a lower risk of immunoreactivity than therapeutic antibodies and is easy to produce. Based on the merits of A7R mentioned above, we primarily examined three applications of A7R: A7R used as an antiangiogenic and anticancer agent, radiolabeled A7R for tumor imaging and diagnostics, and A7R-mediated targeted delivery systems (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
The applications of A7R. (A) A7R was used as an antiangiogenic and anticancer agent. (B) Radiolabeled A7R. The A7R peptide is covalently conjugated to radionuclides. (C) A7R peptides or peptidomimetics are grafted at the nanocarrier surface (liposomes, nanoparticles, etc.). These nanocarriers are loaded with various drugs, such as anticancer therapeutic drugs, peptides, proteins, or nucleic acids.
3.1. A7R as an antiangiogenic and anticancer agent
3.1.1. Inhibiting tumor and ocular angiogenesis
Tournaire et al. discovered that A7R could completely abolish VEGF binding to VEGFR-2 expressed by CHO cells [18]. In vitro, the proliferation of bovine pulmonary endothelial cells was reduced by 60% by A7R, and the mitogenic activity of HUVECs was inhibited by A7R in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, A7R could significantly suppress neovascularization stimulated by VEGF in a rabbit corneal model. Rodrigues et al. found that A7R (200 µM) efficiently suppressed the angiogenic response stimulated by VEGF in a chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay and capillary formation of HUVECs plated on Matrigel [45].
Anna et al. also confirmed that A7R diminished VEGF-induced proliferation of HUVECs in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 450 µM. In HUVECs cocultured with human fibroblasts, tubule length and the density of branching junctions formed by endothelial cells were decreased by A7R. In vivo, the intratumor vessel density decreased by 22% compared to that of the control group after A7R treatment in a nude mouse model harboring MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell-derived xenografts expressing NRP-1 [37]. In summary, A7R can be used as a potent therapeutic agent to treat angiogenic diseases.
3.1.2. Reducing vascular permeability
Upon activation by VEGF, VEGFR-2, which is highly expressed on retinal and cerebral endothelial cells, adopts an activated form and stimulates downstream pathways, such as the Src-FAK pathway. The signal transduction induced by VEGFR-2 weakens endothelial tight junctions and increases vascular permeability [46]. Moreover, this signal transduction induced by VEGFR-2 is strengthened by NRP-1 binding to VEGF165 [33]. Different studies have proven that A7R can reduce vascular permeability in diseases characterized by BBB and blood-retinal barrier (BRB) disruption [20], [21].
Vascular permeability dysfunction is an indispensable factor in BBB disruption [47]. CD8 T cells that have a close relationship with central nervous system (CNS) vascular permeability can promote BBB disruption [48]. In 2012, Suidan's group built a murine model of CD8 T cell-initiated BBB disruption [20]. By blocking VEGF signal transduction with the NRP-1 inhibitor A7R, researchers reduced vascular permeability, brain hemorrhage and mortality in this murine model. The VEGFR-2 expression level was also decreased in this BBB disruption model. This research demonstrated that A7R effectively suppressed NRP-1 to protect against neuroinflammatory diseases, including BBB dysfunction and brain hemorrhage.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a cause of blindness, and BRB disruption is a prominent sign of DR [49]. In 2015, Wang et al. [21] evaluated the effects of A7R on the early stages of DR. The researchers established an experimental diabetic mouse model and treated it with A7R at a dosage of 400 µg/kg once daily for one week. The results showed that A7R not only noticeably decreased diabetes-induced leucocyte attachment, oxidative stress, and the expression of inflammation-associated proteins but also prevented occludin degradation and extravasation of albumin. Occludin proteins play irreplaceable roles in tight junctions formed by vascular endothelial cells in the BRB. VEGF autocrine signaling and occludin degradation in DR can be induced by glucose conditions [50]. Li et al. found that A7R (100 µM) significantly prevented occludin downregulation under high-glucose conditions in rhesus monkey retinal fovea vascular endothelial (RF/6A) cells, which suggested that A7R could reduce vascular permeability in DR [51]. All these results indicated that A7R may prevent the early retinal damage induced by diabetes and preserve vascular integrity. Furthermore, this study proposes a new strategy to treat DR with A7R.
3.1.3. Inducing apoptosis of endothelial cells
In addition to inducing the proliferation and differentiation of endothelial cells, Barr et al. studied the effects of A7R on the apoptosis of endothelial cells. Confocal microscopy showed that A7R labeled with 5-(6)-carboxyfluorescein bound to HUVECs expressing functional VEGFR-2. Treatment with A7R resulted in a significant increase in apoptosis of the HUVECs. Therefore, A7R may be an effective apoptosis-inducing peptide in antiangiogenic strategies [19].
3.1.4. Inhibiting tumor growth and angiogenesis with A7R-containing peptides
As described above, A7R has been used as an independent antitumor angiogenic agent. In 2010, Wu et al. connected A7R to NLLMAAS via a flexible linker, Ala-Ala, and obtained the novel peptide ATWLPPRAANLLMAAS [52]. AANLLMAAS was screened from a phage display peptide library and suppressed the binding of angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) and angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) to endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinase (Tie-2) and further inhibit angiogenesis [53]. The researchers tested the novel peptide on sarcoma S180- and hepatoma H22-bearing BALB/c nude mouse models. After subcutaneous injection for 7 days, the conjugated peptide showed potent antitumor activity in reducing tumor weight, volume, and microvessel density (MD) without significant side effects on normal tissue compared with A7R and AANLLMAAS. Thus, these results showed that the conjugated peptide could be an effective inhibitor of tumor growth and angiogenesis.
3.2. Tumor imaging and diagnosis with radiolabeled A7R
Radiolabeled receptor-binding peptides have been extensively investigated as potential molecular imaging probes and diagnostic agents [54,55]. Due to the affinity of A7R to NRP-1 and VEGFR-2 overexpressed in the tumor vasculature, A7R can be used for tumor angiogenesis imaging.
The peptide A7R was labeled with 99mTc (a benzoyl mercaptoacetyl group was added to the peptide N-terminus in order to allow the formation of an SNNN tetradentate 99mTc complex), and a stable radiolabeled peptide was obtained. In vitro 99mTc-labeled A7R showed high binding to recombinant NRP-1. After intravenous injection, high-level radioactive biodistribution of 99mTc-labeled A7R was observed in the digestive tract of mice and rats rather than in the tumor region. The rapid elimination and low tumor accumulation of this molecule in vivo may result in low tumor uptake and rapid dissociation from tumors, which indicates that improved labeling methods are needed to obtain better imaging results [36].
Integrins are essential cell adhesion receptors and play important roles in mediating adhesive events, tumor angiogenesis and metastasis [56]. αvβ3 integrins are some of the most important integrins because they facilitate endothelial cell migration. High expression of these molecules on tumor cells is stimulated by proangiogenic factors. The RGD peptide, a cell adhesion motif, shows high affinity for αvβ3 integrins. Given that both NRP-1 and αvβ3 integrins are overexpressed in gliomas, Wu et al. [57] and Ma et al. [58] synthesized a conjugated RGD-ATWLPPR peptide that was labeled with fluorine-18 (18F-RGD-A7R) and evaluated the receptor-binding properties and tumor-targeting efficacy. Cell uptake experiments in vitro showed that 18F-RGD-A7R had a higher cell uptake rate than 18F-RGD or 18F-A7R at the 2 h time point, and the uptake of 18F-RGD-A7R was completely inhibited in the presence of both RGD and A7R. In static micro-PET/CT scans of the U87MG glioma cell-derived xenograft model in vivo, conspicuous accumulation of 18F-RGD-A7R was observed in the tumor compared with normal organs and blood. All these results demonstrated that the 18F-labeled RGD-A7R peptide exhibited improved in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetics and superior imaging quality [57], [58].
Ultrasound molecular imaging has been widely used in early disease detection and disease progression monitoring [59]. In 2015, Zhang et al. conjugated A7R onto the surface of lipid microbubbles (A7R-MBs) to evaluate the molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis in a breast cancer model. In vitro, the MBs modified with 1 mol% A7R bound to NRP-1-expressing primary prostate carcinoma-1 (PPC-1) cells at a 17.6 times higher rate than non-modified MBs. In vivo, A7R-MBs were successfully used to image NRP-1 content on angiogenic vessels [60]. Thus, NRP-1-targeting A7R-MBs offer a new strategy for molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis.
3.3. A7R-mediated targeted delivery systems
A key factor in the successful treatment of a disease is to deliver effective therapeutic drugs at an optimal dosage and continuous concentration to the diseased tissues and organs without affecting the physiological function of normal tissue [61]. Drug delivery systems (DDS) are devices that can deliver chemotherapeutic drugs, immunomodulatory drugs and diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals to certain tissues of the body. Traditional DDS have many disadvantages, such as low targeting, poor therapeutic effects, inefficient delivery and issues of drug resistance [62]. Currently, numerous novel DDS have been focused on targeted drug delivery [63]. The number of targeted delivery strategies utilizing various nano-, micro- or macroscale DDS for cancer treatment and diagnosis has been increasing. These systems exhibit efficient therapeutic effects due to their excellent properties, such as deeper tumor penetration, superior specificity, reduced multidrug resistance and enhanced cellular uptake [64].
In tumor chemotherapy, multiple novel materials, such as multifunctional polymeric micelles [65], stimuli-responsive nanocarriers [66], and nanoparticle-assembled thermosensitive hydrogels [67], have been shown to not only improve the drug targeting distribution, accumulation and retention efficiency in tumor tissues but also reduce the side effects of chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., doxorubicin (DOX)) to normal tissues. Immunotherapy is an effective treatment method for cancer [68]. A series of engineered micro- and nanomaterials can be used as carriers to deliver vaccines, immune cells or immunomodulators to specific cells or tissues or to stimulate the host to produce durable anticancer immune responses directly through their own inherent properties [69]. For example, the applications of mesoporous silica rods (MSRs), nanofibrous hydrogels, nanoscale colloids and other vehicles promote the development of DC-based antitumor immunotherapy [70,71]. Significant breakthroughs in the imaging and diagnosis of tumors, which take advantage of diverse delivery systems, have been reported [72]. Targeted nanoscale imaging molecules or radiolabeled nanocarriers such as gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) [73], Raman scattering nanoparticles (MPR) [74] and 19F-MRI nanoprobes [75], which can be monitored by different imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), photoacoustic imaging (PAI), computed tomography (CT) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), are helpful for the detection and measurement of biological and cellular events, the visualization of drug release and accumulation, and tumor diagnosis [76,77].
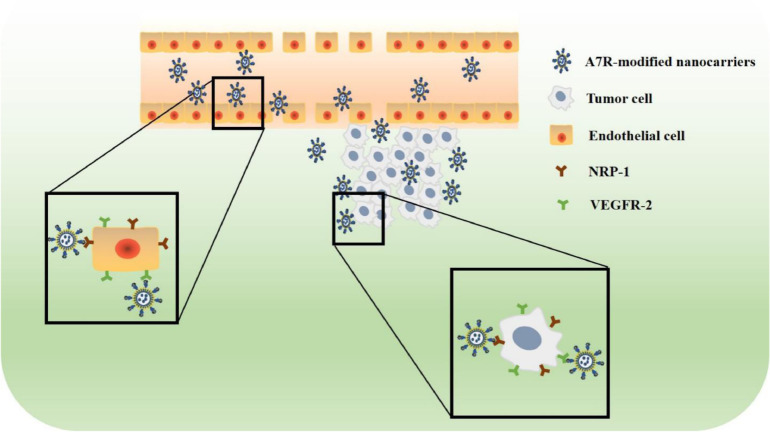
In recent years, active targeted nanocarriers modified with targeting ligands (such as antibodies, peptides, glycoproteins and carbohydrates) have become a research hotspot [78]. Among the diverse targeting ligands, targeting peptides have emerged as one of the most promising non-immunogenic methods to target tumors and cells. Liposomes or nanoparticles that can be grafted with targeting peptides (such as A7R) have several advantages, such as “passive targeting” to tumors due to their appropriate size (20–400 nm), prolonged blood circulation time, and “active targeting” to neovascular endothelial cells and tumor cells that overexpress specific receptors, for instance, NRP-1 and VEGFR-2 [79]. Fig. 5 shows the active targeting mechanisms of A7R-modified nanocarriers. A7R can guide nanocarriers to these cells through its targeting characteristics. Therefore, the applications of A7R-modified liposomes and nanoparticles in cancer therapy will be introduced in this section.
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of the active targeting mechanisms of A7R-modified nanocarriers. A7R can guide nanocarriers to bind endothelial cells and tumor cells that express NRP-1 or VEGFR-2.
3.3.1. A7R-modified liposomes
Janssen demonstrated that coupling of the A7R peptide to the surface of liposomes increased the affinity of liposomes for HUVECs through flow cytometry-based fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) analysis in vitro [80]. In 2015, Cao et al. designed paclitaxel liposomes modified with A7R-cysteine peptide (A7RC) on the surface (A7RC-LS/TAX). In vitro, the targeting and uptake efficiency of A7RC-LS/TAX in MDA-MB-231 cells with high NRP-1 expression were significantly enhanced, and the antiangiogenic effect on NRP-1-expressing HUVECs was strengthened at the same time. In vivo, 4 h after injection, the fluorescence intensity in local tumor tissue was stronger in the DiR-labeled A7RC-LS/TAX group than in the group of nude mice bearing MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231-derived tumors [81].
The BBB and blood-brain tumor barrier (BBTB) are major obstacles when treating malignant glioma with therapeutic drugs [82,83]. To overcome these physiological barriers, researchers have investigated targeting peptide-modified liposomes. Considering the poor biological stability of linear A7R peptide, in 2016, Lu's group designed a retro-inverso A7R peptide/DA7R peptide (comprised of d-amino acids in the reverse sequence) [43] and a cyclic A7R peptide (head-to-tail joining via an amide bond) [44]. Molecular docking and SPR analyses demonstrated that DA7R and cyclic A7R displayed similar binding affinities to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 compared with the linear A7R peptide (LA7R). Both the BTB/U87 tumor spheroid coculture model imitating the blood tumor barriers in vitro and nude mice bearing subcutaneous U87 xenograft tumors in vivo indicated that DA7R-liposomes and cyclic A7R-liposomes showed stronger targeting to and accumulation in tumors than LA7R-liposomes. Furthermore, DOX liposomes modified with cyclic A7R and DA7R peptide (cA7R-LS/DOX and DA7R-LS/DOX) showed improved inhibitory effects on HUVECs, HUVEC 3D tubes in vitro and a subcutaneous tumor model in vivo.
To increase the ability of liposomes to cross the BBB/BBTB and target malignant glioma, researchers have developed multiple ligand-modified liposomes. Ying et al. designed a DA7R and DCDX (a d-peptide ligand binding nicotine acetylcholine receptors) dual modified liposome. This new liposome showed improved penetration into HUVECs, brain capillary endothelial cells (BCECs), U87 cells and tumor spheroids in vitro. After they were loaded with DOX, DA7R/DCDX-modified liposomes (DA7R/DCDX-LS) showed improved inhibitory effects on tube formation of HUVECs and U87 cells in vitro and antitumor effects in intracranial U87 glioma-bearing nude mice in vivo [84].
The T7 peptide (HAIYPRH), which has a high affinity for transferrin receptor (TfR) overexpressed in glioma cells and endothelial cells, was recently identified from a phage display library [85]. To overcome the BBB and BTB as well as single chemical drug resistance, Zhang et al. developed a T7 and DA7R peptide-modified liposome coloaded with DOX and vincristine (T7/DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR) [86]. T7/DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR showed high penetration efficiency in a coculture model of bEnd.3/C6 cells in vitro (simulating BBB and BTB models). Similarly, the accumulation of T7/DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR in the mouse brain with intracranial C6 glioma was higher than that of T7-LS/DOX and VCR or DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR. The glioma diameter and volume were clearly reduced after the administration of T7/DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR, suggesting its prominent therapeutic efficacy in glioma.
In addition to chemical drugs, therapeutic proteins and nucleic acids can be carried by liposomes to enhance antitumor activity and reduce systemic side effects [87,88]. Pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF), which can directly induce the apoptosis of endothelial cells in neovascularization, is regarded as a promising drug for choroidal neovascularization (CNV) [89]. However, lack of an appropriate delivery method prevents the clinical use of PEDF. Li et al. designed PEDF-loaded immuno-nanoliposomes modified with A7R (A7R-INLS/PEDF). The researchers found that A7R-INLS/PEDF could specifically bind to endothelial cells of CNV, largely decrease the CNV area and increase the effects of PEDF in a rat model [90]. Thus, this new delivery system may provide us a new strategy for treating CNV. Slimani's laboratory synthesized a new C16-A7R peptide through an amide reaction between a palmitoyl fatty chain and A7R and then conjugated it to liposomes. The C16-A7R-modified liposomes loaded with green fluorescent protein (C16-A7R-LS/GFP) were well aggregated in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells overexpressing NRP-1 and strengthened the expression of GFP in the above cells [91]. Examples of different A7R-modified liposomes that have been shown to improve the target efficiency of different drugs are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Examples of recent studies on A7R-modified liposomes delivering different therapeutic agents.
| Carrier | Therapeutic agent | Compound | Experimental model | Results | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| —– | A7R-LS | HUVEC (endothelial cells) | A7R-PEG-liposome showed increased affinity for HUVEC in vitro. |
[60] | |
| Paclitaxel | A7RC-LS/TAX | Breast cancer cell lines | Angiogenesis and tumor growth were inhibited simultaneously. | [61] | |
| Liposomes (LS) | Doxorubicin | cA7R-LS/DOX | U87 xenograft tumors/glioma | Subcutaneous tumor growth was suppressed. | [41] |
| Doxorubicin | DCDX/ DA7R-LS/DOX | U87 xenograft tumors | Tumor growth and angiogenesis was inhibited. | [64] | |
| Glioma-bearing mice model | |||||
| Doxorubicin and vincristine | T7/DA7R-LS/DOX and VCR | Higher glioma localization was displayed than that of single ligand-modified liposomes or free drug. | [66] | ||
| GFP gene | C16-A7R-LS/GFP | MDA-MB-231 cells | The expression of GFP reporter genes was enhanced. | [71] | |
| Immuno-nano-Liposomes (INLS) | PEDF | A7R-INLS/PEDF | CNV in the rat model | The inhibitory effects of PEDF on CNV was strengthened and side effects was reduced. | [70] |
3.3.2. A7R-modified nanoparticles
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been an effective strategy to treat cancer. PDT targeting neovasculature in tumor tissue is a potential strategy for treating cancer [92]. However, inadequate water solubility, insufficient pharmacokinetics and poor tumor selectivity of photosensitizers (PSs) limit their development and application. The design of PSs covalently attached to a tumor-targeting moiety or encapsulated within nanoparticles is currently a research hotspot. These tumor-targeting moieties consist of monosaccharides [93], low-density lipoprotein [94], antibodies [95], peptides [96] and so on. Among them, peptides are receiving increasing interest in the field of PDT.
A7R-modified 5-(4-carboxyphenyl)−10,15,20-triphenyl-chlorin (TPC, which is a kind of PS) via a spacer 6-aminohexanoic acid, Ahx (A7R-Ahx-TPC), which binds exclusively to NRP-1, is a much more potent PS than TPC [97]. In addition, A7R-Ahx-TPC can target both tumor endothelial cells and tumor cells themselves, which overexpress NRP-1, efficiently potentiating the effects of PDT in vivo [97], [98], [99]. Reem et al. found that the conjugation of verteporfin as a PS to A7R not only retained its spectral and photosensitizing properties but also efficiently targeted CNV [100]. However, biodistribution and stability tests in glioma-bearing mice in vivo showed that although A7R-Ahx-TPC accumulated at the tumor site, significant degradation was observed 2 h after injection [97], [98], which indicated that A7R-Ahx-TPC was weakly preserved.
In 2017, Benachour et al. designed a novel A7R-conjugated hybrid silica nanoparticle loaded with TPC (A7R-HS-NP/TPC). A competitive binding assay with VEGF165 showed that A7R-HS-NP/TPC bound recombinant NRP-1 protein in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50=56.6 µM) and displaced 50% of VEGF165 binding to NRP-1. In vivo, positive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast and intratumoral retention were substantially increased after intravenous injection of A7R-HS-NP/TPC in glioma-bearing rats [101]. These results showed that TPC loaded in A7R-modified nanoparticles had better retention and stability than A7R-conjugated TPC, providing us with a new strategy to use targeting peptide-modified nanoparticles for PDT.
Superparamagnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles (SPIONs), with the help of an external magnetic field, are promising carriers as targeted drug delivery vehicles [102]. Cell cytotoxicity studies showed that SPIONs modified with A7R (A7R/SPIONs) significantly reduced the viability of HUVECs compared with SPIONs and A7R. Further in vitro and in vivo studies are required to confirm the internalization mechanism of these SPIONs functionalized with A7R [103].
Treating glioma is difficult not only because of the existence of the BBB but also because of the complicated tumor microenvironment [104]. Numerous biomarkers [such as heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) in the ECM of the tumor microenvironment] are potential targets [105]. Utilizing the targeting ability of the CGKRK peptide to HSPG overexpressed in the tumor microenvironment and the A7R peptide to NRP-1 overexpressed on tumor endothelial cells and glioma cells, Hu et al. developed a new nanoparticle loaded with paclitaxel and modified by the dual-targeting A7R peptide and the CGKRK peptide (A7R-CGKRKR-NP/PTX). The cellular association of A7R-CGKRKR-NP on the HUVECs and U87 cells was enhanced compared with that of CGKRK-NP and A7R-NP. A7R-CGKRKR-NP enhanced the apoptotic and antiproliferative activity of paclitaxel on U87MG cells. An in vivo U87MG-bearing mouse experiment showed that A7R-CGKRKR-NP increased the accumulation of paclitaxel at the glioma site and its therapeutic effect on glioma [106]. Examples of different A7R-modified nanoparticles are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Examples of recent studies on A7R-modified nanoparticles.
| Carrier | Therapeutic agent | Compound | Experimental model | Results | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Silica Nanoparticle | Chlorin (photosensitizer) | A7R-HS-NP/TPC | Glioma-bearing rat model | A positive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast and intratumoral retention were increased greatly. | [78], [79], [80] |
| Superparamagnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles | Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | A7R-SPIONs/Fe | HUVEC (endothelial cells) | The cell viability of HUVEC was reduced. | [84] |
| Nanoparticles | Paclitaxel | A7R-CGKRKR-NP/PTX | U87MG glioblastoma | Apoptosis induction and anti-proliferative activity were enhanced. | [87] |
4. Conclusions
Endothelial cells and tumor cells can be targeted due to their expression of VEGFR-2 and NRP-1. The overexpression of these two receptors is accompanied by tumor angiogenesis and progression. A7R was initially confirmed to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR-2. However, most studies showed that A7R generates steric hindrance between VEGF165 and NRP-1 and then interrupts VEGFR-2-mediated angiogenesis. However, the latest molecular docking studies confirmed that A7R has binding affinity for both VEGFR-2 and NRP-1: the leucine and proline of A7R can permeate the binding pocket through hydrophobic interactions with VEGFR-2, while the C-terminal arginine (CendR) simulates the C-terminal tail of VEGF165 and interacts with the b1 domain of NRP-1. However, the exact molecular mechanism of A7R binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 and whether or how it competes with VEGF165 to inhibit VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 need further confirmation. This finding suggests that we can conduct structural optimizations of A7R and use computational docking technology to design more specific and active new peptides based on the unique structure of A7R to target NRP-1 and VEGFR-2. Compared with other vasculature-homing peptides, A7R has unique advantages in antiangiogenic diagnosis and therapy. First, A7R can perform dual targeting through simultaneous binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, which leads to higher selectivity for tumor vasculature compared to other single-target peptides. Second, unlike RGD or NGR, as the targeting ligand of tumor vasculature-targeted DDS, A7R can not only facilitate drug delivery effectively by interacting with VEGFR-2 and NRP-1 but also exert a synergistic antiangiogenic effect with the carried therapeutic drugs. Third, due to its unique C-terminal (C-end rule, arginine at the C-terminus) structure, A7R can increase vascular permeation and penetrate deep into tumor tissues through binding to NRP-1 on endothelial cells, thereby overcoming the weak tumor tissue-penetrating properties of some existing vasculature-homing peptides. However, the IC50 of A7R on HUVECs is not ideal (450 µM), and this peptide is easily degraded in circulation. Furthermore, A7R cannot kill tumor cells, and once the treatment ceases, the incidence of tumor recurrence is high. These shortcomings may be the main reasons for restricting the applications of A7R as a direct antagonist in the antiangiogenic field. Thus, optimal antiangiogenic therapy may require complex solutions by combining A7R with other therapeutic strategies (surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy) should be studied in more detail in the future.
The use of radiolabeled A7R as an imaging molecule has some problems, such as rapid elimination and low tumor accumulation. After conjugating RGD or grafting A7R onto the surface of lipid MBs, researchers observed obvious accumulation in tumor vasculature. This finding indicated that a combination with other targeted peptides or selection of better imaging carriers may improve the imaging and diagnostic efficiency of tumor angiogenesis. However, because of the high targeting abilities of A7R to VEGFR-2 and NRP-1, the applications of A7R-modified nanocarriers in DDS have been extensively researched. As shown above, A7R has been used to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs to the brain for the treatment of malignant glioma. A series of studies indicated that A7R-modified liposomes and nanoparticles were superior to free drugs in treating malignant glioma. However, the poor stability of A7R should not be ignored. To avoid proteolytic degradation and prolong blood circulation, researchers may need to design more stable structures of A7R. Due to the current mature modification methods, such as cyclization, retro-inverso isomerization and partial amino acid removal and replacement, the development of effective drug delivery methods with A7R is possible. Accordingly, despite some drawbacks, as a short non-immunogenic peptide with good bioavailability, A7R will certainly be an effective means of targeting therapy in the future.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
The authors state no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81302686) and Primary Research & Developement Plan of Shandong Province (No.2016GSF201083).
Contributor Information
Xinke Zhang, Email: zhangxinke@sdu.edu.cn.
Fengshan Wang, Email: fswang@sdu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis:therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285(21):1182–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bagri A., Kouros-Mehr H., Leong K.G., Plowman G.D. Use of anti-VEGF adjuvant therapy in cancer: challenges and rationale. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(3):122–132. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Versleijen-Jonkers Y.M., Vlenterie M., van de Luijtgaarden A.C., van der Graaf W.T. Anti-angiogenic therapy, a new player in the field of sarcoma treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;91(2):172–185. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Al-Abd A.M., Alamoudi A.J., Abdel-Naim A.B., Neamatallah T.A., Ashour O.M. Anti-angiogenic agents for the treatment of solid tumors: potential pathways, therapy and current strategies - a review. J Adv Res. 2017;8(6):591–605. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2017.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Logue O.C., McGowan J.W., George E.M., Bidwell G.L. Therapeutic angiogenesis by vascular endothelial growth factor supplementation for treatment of renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016;25(5):404–409. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kong D.H., Kim M.R., Jang J.H., Na H.J., Lee S. A review of anti-angiogenic targets for monoclonal antibody cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):e1786. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Vasudev N.S., Reynolds A.R. Anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer: current progress, unresolved questions and future directions. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(3):471–494. doi: 10.1007/s10456-014-9420-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shahneh F.Z., Baradaran B., Zamani F., Aghebati-Maleki L. Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapies. Hum Antibodies. 2013;22(1–2):15–19. doi: 10.3233/HAB-130267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wu D.D., Gao Y.F., Qi Y.M., Chen L.X., Ma Y.F., Li Y.Z. Peptide-based cancer therapy: opportunity and challenge. Cancer Lett. 2014;351(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xiao Y.F., Jie M.M., Li B.S. Peptide-based treatment: a promising cancer therapy. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015 doi: 10.1155/2015/761820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.D'Onofrio N., Caraglia M., Grimaldi A. Vascular-homing peptides for targeted drug delivery and molecular imaging: meeting the clinical challenges. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lu L., Qi H., Zhu J. Vascular-homing peptides for cancer therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;92:187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Meng Y., Zhang Z., Liu K., Ye L., Liang Y., Gu W. Aminopeptidase N (CD13) targeted MR and NIRF dual-modal imaging of ovarian tumor xenograft. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;93:968–974. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gu Z., Chang M., Fan Y., Shi Y., Lin G. NGR-modified pH-sensitive liposomes for controlled release and tumor target delivery of docetaxel. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:395–405. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.09.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sivashankari P.R., Prabaharan M. Peptides to target tumor vasculature and lymphatics for improved anti-angiogenesis therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(6):522–535. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666151130214049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Arosio D., Manzoni L., Corno C., Perego P. Integrin-targeted peptide- and peptidomimetic-drug conjugates for the treatment of tumors. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2017;12(2):148–168. doi: 10.2174/1574892812666170203151930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Katsamakas S., Chatzisideri T., Thysiadis S., Sarli V. RGD-mediated delivery of small-molecule drugs. Future Med Chem. 2017;9(6):579–604. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Binetruy-Tournaire R., Demangel C., Malavaud B. Identification of a peptide blocking vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis. EMBO J. 2000;19(7):1525–1533. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Barr M.P., Byrne A.M., Duffy A.M. A peptide corresponding to the neuropilin-1-binding site on VEGF(165) induces apoptosis of neuropilin-1-expressing breast tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(2):328–333. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Suidan G.L., Dickerson J.W., Johnson H.L. Preserved vascular integrity and enhanced survival following neuropilin-1 inhibition in a mouse model of CD8 T cell-initiated CNS vascular permeability. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:218. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang J., Wang S., Li M. The neuropilin-1 inhibitor, ATWLPPR peptide, prevents experimental diabetes-induced retinal injury by preserving vascular integrity and decreasing oxidative stress. PLoS One. 2015;10(11) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Omidfar K., Daneshpour M. Advances in phage display technology for drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015;10(6):651–669. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2015.1037738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yadav L., Puri N., Rastogi V., Satpute P., Sharma V. Tumour angiogenesis and angiogenic inhibitors: a review. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(6):xe01–xe05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/12016.6135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aplin A.C., Nicosia R.F. Hypoxia paradoxically inhibits the angiogenic response of isolated vessel explants while inducing overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis. 2016;19(2):133–146. doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Siveen K.S., Prabhu K., Krishnankutty R. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumour vascularization: potential and challenges. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017;15(4):339–351. doi: 10.2174/1570161115666170105124038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Claesson-Welsh L., Welsh M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med. 2013;273(2):114–127. doi: 10.1111/joim.12019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Viallard C., Larrivee B. Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization: alternative therapeutic targets. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(4):409–426. doi: 10.1007/s10456-017-9562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kofler N.M., Simons M. Angiogenesis versus arteriogenesis: neuropilin 1 modulation of VEGF signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2015;7:26. doi: 10.12703/P7-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hu C.X., Jiang X.D. Role of NRP-1 in VEGF-VEGFR2-Independent tumorigenesis. Target Oncol. 2016;11(4):501–505. doi: 10.1007/s11523-016-0422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Djordjevic S., Driscoll P.C. Targeting VEGF signalling via the neuropilin co-receptor. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18(9–10):447–455. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo H.F., Vander Kooi C.W. Neuropilin functions as an essential cell surface receptor. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(49):29120–29126. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.687327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Simons M., Gordon E., Claesson-Welsh L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(10):611–625. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Raimondi C., Brash J.T., Fantin A., Ruhrberg C. NRP1 function and targeting in neurovascular development and eye disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;52:64–83. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Plein A., Fantin A., Ruhrberg C. Neuropilin regulation of angiogenesis, arteriogenesis, and vascular permeability. Microcirculation. 2014;21(4):315–323. doi: 10.1111/micc.12124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Perret G., Vassy R., Le Meuth-Metzinger V., Kourbali Y., Nicolas P., Starzec A. Characterization of a novel VEGF receptor antagonist. Proceedings of the Keystone Symposia; Salt Lake City, UT, USA; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perret G.Y., Starzec A., Hauet N. In vitro evaluation and biodistribution of a 99mTc-labeled anti-VEGF peptide targeting neuropilin-1. Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31(5):575–581. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2004.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Starzec A., Vassy R., Martin A. Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of peptide inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Life Sci. 2006;79(25):2370–2381. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Starzec A., Ladam P., Vassy R. Structure-function analysis of the antiangiogenic ATWLPPR peptide inhibiting VEGF(165) binding to neuropilin-1 and molecular dynamics simulations of the ATWLPPR/neuropilin-1 complex. Peptides. 2007;28(12):2397–2402. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vander Kooi C.W., Jusino M.A., Perman B., Neau D.B., Bellamy H.D., Leahy D.J. Structural basis for ligand and heparin binding to neuropilin B domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(15):6152–6157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700043104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Parker M.W., Xu P., Li X., Vander Kooi C.W. Structural basis for selective vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) binding to neuropilin-1. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(14):11082–11089. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.331140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Teesalu T., Sugahara K.N., Kotamraju V.R., Ruoslahti E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(38):16157–16162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908201106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tuttle T. Averaging semiempirical NMR chemical shifts dynamic effects on the subpicosecond time scale. J Phys Chem A. 2009;113(43):11723–11733. doi: 10.1021/jp902875d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ying M., Shen Q., Liu Y. Stabilized heptapeptide A7R for enhanced multifunctional liposome-based tumor-targeted drug delivery. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(21):13232–13241. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b01300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ying M., Shen Q., Zhan C. A stabilized peptide ligand for multifunctional glioma targeted drug delivery. J Control Release. 2016;243:86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rodrigues S., Van Aken E., Van Bocxlaer S. Trefoil peptides as proangiogenic factors in vivo and in vitro: implication of cyclooxygenase-2 and EGF receptor signaling. Faseb J. 2003;17(1):7–16. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0201com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Peach C.J., Mignone V.W., Arruda M.A. Molecular pharmacology of VEGF-A isoforms: binding and signalling at VEGFR2. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):E1264. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Almutairi M.M., Gong C., Xu Y.G., Chang Y., Shi H. Factors controlling permeability of the blood-brain barrier. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(1):57–77. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2050-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Johnson H.L., Chen Y., Jin F. CD8 T cell-initiated blood-brain barrier disruption is independent of neutrophil support. J Immunol. 2012;189(4):1937–1945. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang C., Wang H., Nie J., Wang F. Protective factors in diabetic retinopathy: focus on blood-retinal barrier. Discov Med. 2014;18(98):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Muthusamy A., Lin C.M., Shanmugam S., Lindner H.M., Abcouwer S.F., Antonetti D.A. Ischemia-reperfusion injury induces occludin phosphorylation/ubiquitination and retinal vascular permeability in a VEGFR-2-dependent manner. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34(3):522–531. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li M.L., Wang S.W., Wang S.J. Occludin downregulation in high glucose is regulated by SSTR2 via the VEGF/NRP1/Akt signaling pathway in RF/6A cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):1732–1738. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wu D., Gao Y., Chen L. Anti-tumor effects of a novel chimeric peptide on S180 and H22 xenografts bearing nude mice. Peptides. 2010;31(5):850–864. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tournaire R., Simon M.P., le Noble F., Eichmann A., England P., Pouyssegur J. A short synthetic peptide inhibits signal transduction, migration and angiogenesis mediated by Tie2 receptor. Embo Rep. 2004;5(3):262–267. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Laverman P., Sosabowski J.K., Boerman O.C., Oyen W.J. Radiolabelled peptides for oncological diagnosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39(Suppl 1):S78–S92. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-2014-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Roosenburg S., Laverman P., van Delft F.L., Boerman O.C. Radiolabeled CCK/gastrin peptides for imaging and therapy of CCK2 receptor-expressing tumors. Amino Acids. 2011;41(5):1049–1058. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0501-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Danhier F., Le Breton A., Preat V. RGD-based strategies to target alpha(v) beta(3) integrin in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Mol Pharm. 2012;9(11):2961–2973. doi: 10.1021/mp3002733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wu H., Chen H.J., Pan D.F. Imaging integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and NRP-1 positive gliomas with a novel fluorine-18 labeled RGD-ATWLPPR heterodimeric peptide probe. Mol Imaging Biol. 2014;16(6):781–792. doi: 10.1007/s11307-014-0761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lauro S., Onesti C.E., Righini R., Marchetti P. The use of bevacizumab in non-small cell lung cancer: an update. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(4):1537–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Panje C.M., Wang D.S., Willmann J.K. Ultrasound and microbubble-mediated gene delivery in cancer: progress and perspectives. Invest Radiol. 2013;48(11):755–769. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182982cc1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang H., Tam S., Ingham E.S. Ultrasound molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis with a neuropilin-1-targeted microbubble. Biomaterials. 2015;56:104–113. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.03.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tibbitt M.W., Dahlman J.E., Langer R. Emerging frontiers in drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(3):704–717. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b09974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yun Y.H., Lee B.K., Park K. Controlled drug delivery: historical perspective for the next generation. J Control Release. 2015;219:2–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Iqbal J., Anwar F., Afridi S. Targeted drug delivery systems and their therapeutic applications in cancer and immune pathological conditions. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2017;17(3):149–159. doi: 10.2174/1871526517666170606102623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kumari P., Ghosh B., Biswas S. Nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery. J Drug Target. 2016;24(3):179–191. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1051049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nasongkla N., Bey E., Ren J. Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett. 2006;6(11):2427–2430. doi: 10.1021/nl061412u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mura S., Nicolas J., Couvreur P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat Mater. 2013;12(11):991–1003. doi: 10.1038/nmat3776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Huang P., Song H., Zhang Y. Bridging the gap between macroscale drug delivery systems and nanomedicines: a nanoparticle-assembled thermosensitive hydrogel for peritumoral chemotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(43):29323–29333. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b10416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cheung A.S., Mooney D.J. Engineered materials for cancer immunotherapy. Nano Today. 2015;10(4):511–531. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2015.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Moon J.J., Huang B., Irvine D.J. Engineering nano- and microparticles to tune immunity. Adv Mater. 2012;24(28):3724–3746. doi: 10.1002/adma.201200446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kim J., Li W.A., Choi Y. Injectable, spontaneously assembling, inorganic scaffolds modulate immune cells in vivo and increase vaccine efficacy. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(1):64–72. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yang P., Song H., Qin Y. Engineering dendritic-cell-based vaccines and PD-1 blockade in self-assembled peptide nanofibrous hydrogel to amplify antitumor T-Cell immunity. Nano Lett. 2018;18(7):4377–4385. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Baetke S.C., Lammers T., Kiessling F. Applications of nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of cancer. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1054) doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Peng C., Zheng L., Chen Q. PEGylated dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles for in vivo blood pool and tumor imaging by computed tomography. Biomaterials. 2012;33(4):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kircher M.F., de la Zerda A., Jokerst J.V. A brain tumor molecular imaging strategy using a new triple-modality MRI-photoacoustic-Raman nanoparticle. Nat Med. 2012;18(5):829–834. doi: 10.1038/nm.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Huang P., Guo W., Yang G. Fluorine meets amine: reducing microenvironment-induced amino-activatable nanoprobes for (19)f-magnetic resonance imaging of biothiols. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(22):18532–18542. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b03764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Xing Y., Zhao J., Conti P.S., Chen K. Radiolabeled nanoparticles for multimodality tumor imaging. Theranostics. 2014;4(3):290–306. doi: 10.7150/thno.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Padmanabhan P., Kumar A., Kumar S., Chaudhary R.K., Gulyas B. Nanoparticles in practice for molecular-imaging applications: an overview. Acta Biomater. 2016;41:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Srinivasarao M., Low P.S. Ligand-targeted drug delivery. Chem Rev. 2017;117(19):12133–12164. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.David A. Peptide ligand-modified nanomedicines for targeting cells at the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;119:120–142. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Janssen A. Peptide-targeted PEG-liposomes in anti-angiogenic therapy. Int J Pharm. 2003;254(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00682-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cao J., Wang R., Gao N. A7RC peptide modified paclitaxel liposomes dually target breast cancer. Biomater Sci. 2015;3(12):1545–1554. doi: 10.1039/c5bm00161g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Van Tellingen O., Yetkin-Arik B., de Gooijer M.C., Wesseling P., Wurdinger T., de Vries H.E. Overcoming the blood-brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment. Drug Resist Update. 2015;19:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wanjale M.V., Kumar G.S.V. Peptides as a therapeutic avenue for nanocarrier-aided targeting of glioma. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017;14(6):811–824. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2017.1242574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ying M., Zhan C., Wang S. Liposome-based systemic glioma-targeted drug delivery enabled by all-d peptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(44):29977–29985. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b10146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Shinde R.L., Devarajan P.V. Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated, targeted and sustained brain delivery of curcumin microemulsion. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):152–161. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1233593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhang Y., Zhai M., Chen Z. Dual-modified liposome codelivery of doxorubicin and vincristine improve targeting and therapeutic efficacy of glioma. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):1045–1055. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1344334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ashizawa A.T., Contest J. Liposomal delivery of nucleic acid-based anticancer therapeutics: BP-100-1.01. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(7):1107–1120. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2015.996545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Swaminathan J., Ehrhardt C. Liposomal delivery of proteins and peptides. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012;9(12):1489–1503. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2012.735658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Yu Y.J., Mo B., Liu L., Yue Y.K., Yue C.L., Liu W. Inhibition of choroidal neovascularization by lentivirus-mediated PEDF gene transfer in rats. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(8):1112–1120. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.08.05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Li T., Zhang M., Han Y., Zhang H., Xu L.J., Xiang Y. Targeting therapy of choroidal neovascularization by use of polypeptide- and PEDF-loaded immunoliposomes under ultrasound exposure. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 2010;30(6):798–803. doi: 10.1007/s11596-010-0661-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Slimani H., Guenin E., Briane D. Lipopeptide-based liposomes for DNA delivery into cells expressing neuropilin-1. J Drug Target. 2006;14(10):694–706. doi: 10.1080/10611860600947607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Abrahamse H., Kruger C.A., Kadanyo S., Mishra A. Nanoparticles for advanced photodynamic therapy of cancer. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017;35(11):581–588. doi: 10.1089/pho.2017.4308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lafont D., Zorlu Y., Savoie H. Monoglycoconjugated phthalocyanines: effect of sugar and linkage on photodynamic activity. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2013;10(3):252–259. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2012.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Marotta D.E., Cao W.G., Wileyto E.P. Evaluation of bacteriochlorophyll-reconstituted low-density lipoprotein nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy efficacy in vivo. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2011;6(3):475–487. doi: 10.2217/nnm.11.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Bryden F., Maruani A., Savoie H. Regioselective and stoichiometrically controlled conjugation of photodynamic sensitizers to a HER2 targeting antibody fragment. Bioconjug Chem. 2014;25(3):611–617. doi: 10.1021/bc5000324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Narsireddy A., Vijayashree K., Irudayaraj J., Manorama S.V., Rao N.M. Targeted in vivo photodynamic therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor-specific peptide linked nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2014;471(1–2):421–429. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.05.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tirand L., Frochot C., Vanderesse R. A peptide competing with VEGF165 binding on neuropilin-1 mediates targeting of a chlorin-type photosensitizer and potentiates its photodynamic activity in human endothelial cells. J Control Release. 2006;111(1–2):153–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Thomas N., Bechet D., Becuwe P. Peptide-conjugated chlorin-type photosensitizer binds neuropilin-1 in vitro and in vivo. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2009;96(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Thomas N., Tirand L., Chatelut E. Tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of an ATWLPPR-conjugated chlorin-type photosensitizer targeting neuropilin-1 in glioma-bearing nude mice. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2008;7(4):433–441. doi: 10.1039/b718259g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Renno R.Z., Terada Y., Haddadin M.J., Michaud N.A., Gragoudas E.S., Miller J.W. Selective photodynamic therapy by targeted verteporfin delivery to experimental choroidal neovascularization mediated by a homing peptide to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(7):1002–1011. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.7.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Benachour H., Seve A., Bastogne T. Multifunctional peptide-conjugated hybrid silica nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy and MRI. Theranostics. 2012;2(9):889–904. doi: 10.7150/thno.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Zhang C.J., Yan Y.Z., Zou Q., Chen J., Li C.S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging of pancreatic cancer: potential for early diagnosis through targeted strategies. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol. 2016;12(1):13–21. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Niescioruk A., Nieciecka D., Puszko A.K. Physicochemical properties and in vitro cytotoxicity of iron oxide-based nanoparticles modified with antiangiogenic and antitumor peptide A7R. J Nanopart Res. 2017;19(5):160. doi: 10.1007/s11051-017-3859-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Da Ros M., De Gregorio V., Iorio A.L. Glioblastoma chemoresistance: the double play by microenvironment and blood-brain barrier. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2879. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhai M., Wang Y., Zhang L. Glioma targeting peptide modified apoferritin nanocage. Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):1013–1024. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1464082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Hu Q.Y., Kang T., Feng J.X. Tumor microenvironment and angiogenic blood vessels dual-targeting for enhanced anti-glioma therapy. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(36):23568–23579. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b08239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]