Abstract
Most seed gums have been widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations, cosmetics, and food products because of their hydrophilic properties. Gums from Tamariudus indica and Cassia fistula seeds were chemically modified by carboxymethylation to improve their functionalities. The objective of the present study was to characterize and evaluate crude and carboxymethylated gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds to achieve the controlled-release of diclofenac sodium (DS) in matrix tablet form. Both crude and carboxymethylated gums were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy. The results revealed that the gums were successfully modified by carboxymethylation and that the modified gums were amorphous in structure and had better flow properties. The carboxymethylated gums from both plant seeds did not exhibit cytotoxicity at concentrations lower than 0.5 mg/ml. All gum samples used as polymeric controlled-release agents were formulated into DS matrix tablets. Hardness and thickness tests were conducted as in-process tests. Drug content estimation and in vitro drug release studies were carried out to evaluate the matrix tablets. Increasing the concentration of gums increased compression time and hardness while it reduced the thickness. Furthermore, the results fitted well with the Korsmeyer–Peppas model. Moreover, the DS tablets were found to release the drug by super case II transport (relaxation). In summary, the carboxymethylated gum from T. indica and C. fistula seeds is an excellent, naturally sourced gum with high physicochemical and functional qualities, and can potentially be used in pharmaceutical applications as a disintegrant, diluent, and drug release-controlling agent.
Keywords: Seed gum, Tamarindus indica, Cassia fistula, Carboxymethylated gum, Controlled-release agent, Swelling
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
Gum from Tamarind indica and Cassia fistula seeds is a natural nonionic polysaccharide extracted from the refined endosperm of cluster bean seeds. The structure of tamarind gum has a 1,4-D-glucan backbone, and the primary difference is that single D-xylopyranosyl residues replace the glucopyranosyl units at position 6 [1]. In the backbone of C. fistula gum is a linear chain of 1,4-linked mannose residues to which galactose residues are 1,6-linked, forming short side-branches [2]. Recently, seed gums have attracted increasing attention for their use in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations as suspending agents [3], tablet binders [4], emulsifying agents [2], disintegrating agents [5], and hydrogels [6]. They are also particularly useful, in target delivery systems for controlled-release of drugs [7] due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and biosafety.
Natural gum is a hydrophilic polymer with several monosaccharide units (glucose, mannose, galactose, and xylose). However, it often exhibits low solubility in cold water, an unpleasant odor, and a dull color. These properties make them unfit for use in various applications. To improve and enhance the quality and usability of crude gum, its chemical structure can be optimized to increase its solubility and hydrophilicity [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]. Hence, the seed gums were carboxymethylated to improve their physicochemical properties. Following carboxymethylation, the hydroxyl groups of seed gums are converted into carboxyl groups, resulting in increased hydrophilicity and viscosity [8]. This chemical process has been successfully applied to various seed gums in previous studies [4], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12].
Carboxymethylated gum has been considered a promising material for the development of systems intended for controlled drug release agent as the modified gum is soluble and can form a gel layer well. Moreover, the chemical modification process also removed impurities in the crude form [9]. The function of the modified gum in tablet formulations varies depending on its quantity and the tablet-preparation process. Therefore, the amount of gum in the formulation and the tablet manufacture parameters should be determined.
In present study, we aimed to characterize and evaluate crude and carboxymethylated gum from T. indica and C. fistula seeds for its potential utility in the controlled-release of diclofenac sodium (DS) when administered in matrix tablet form. First, chemical-structural modification of crude gums was achieved through carboxymethylation. The physicochemical properties of both crude and carboxymethylated gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds were then characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Intrinsic viscosity, in vitro cytotoxicity, swelling property, flow properties, and compressibility were also determined. DS matrix tablets were formulated by direct compression with the gum samples as controlled-release agents. Next, in vitro drug release and drug release mechanism of the DS matrix tablets were monitored and compared with those of well-known release-retarding agent HPMC in view of its application in pharmacology.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
Crude gums were obtained from T. indica (T) and C. fistula (C) seeds, which were collected in Uthai Thani and Chonburi provinces in Thailand, respectively. Carboxymethylated gums were prepared from the crude gums of T. indica (Ta) and C. fistula (Ca) by chemical modification, using the carboxymethylation method described by Huanbutta and Sittikijyothin [9]. DS was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (United States). Talcum and magnesium were purchased from Chemipan Co., Ltd. (Bangkok, Thailand) and P.C. Drug Center Co., Ltd. (Bangkok, Thailand), respectively. All other chemicals were of standard pharmaceutical grade and were used as received without further purification.
2.2. Chemical compositions
Moisture and ash contents of the gum samples were determined according to the American Society for Testing and Materials methods (ASTM-D2974-87) and AOAC Official Method 923.03, respectively. Protein and fat contents were determined according to the AOAC Official Method of Analysis 981.10 and 923.06, respectively.
2.3. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy
The crude and carboxymethylated gums were pulverized and blended with KBr and then compressed. The measurements on prepared discs were carried out using an FT-IR spectrophotometer (Magna-IR system 750, Nicolet Biomedical Inc., USA).
2.4. Powder X-ray diffraction
Powder XRD patterns of the starting materials, their physical mixtures and the PNP were analyzed using a powder X-ray diffractometer (model D8, Bruker, Germany) under the following conditions: graphite monochromatized Cu Kα radiation; voltage, 45 kV; electric current, 40 mA; slit, DS1, SS1, RS, 0.15 nm; and scanning ratio 2θ = 5°/min.
2.5. Morphology
SEM (LEO 1450VP scanning electron microscope, England) was used to observe the morphology of crude and carboxymethylated gums in powder form. The dried powder was placed on the SEM stubs using a two-sided adhesive tape (Polaron, SC 7620) and were then sputtered-coated with gold. The morphology of the gum powder sample was observed at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV.
2.6. Intrinsic viscosity
The intrinsic viscosity [η] of dilute solutions of gum samples was measured at 25 °C ± 0.1 °C with a Cannon-Fenske Routine Viscometer (9721-A53) (ASTM-D2515, ISO 3105, Series 100). Intrinsic viscosity is conventionally calculated by double extrapolation to zero concentration of Huggins’ (Eq. (1)) and Kraemer (Eq. (2)) equations, respectively.
| (1) |
| (2) |
Where ηsp and ηrel are the (dimensionless) specific and relative viscosities, respectively; and are Huggins's and Kraemer's coefficients, respectively; and C is the solution concentration.
2.7. In vitro cytotoxicity testing
The cytotoxicity of crude and carboxymethylated gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds was determined by MTT assay of exposed Caco-2 cells. This assay measures the conversion of MTT to insoluble formazan by dehydrogenase enzymes of the intact mitochondria of living cells. Caco-2 cells (passage 8–28) were seeded at a density of 104 cells/well with 100 µl of the culture medium into 96-well plates. After 48 h incubation at 37 °C in a CO2 incubator (Thermo Forma Series 2, Ohio, USA), the culture medium was replaced and the confluent cells were incubated for 4 h with 0, 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, and 0.1 µg/ml of the carboxymethylated gums dispersed in PBS. After treatment, each carboxymethylated gum sample was removed and fresh medium was added before incubating the cells for 4 h to stabilize the cells. Finally, the cells were incubated with MTT diluted in medium (0.1 mg/ml) for 4 h. The medium was removed and the formazan crystal that formed in the living cells was dissolved in 100 µl DMSO per well. The relative viability (%) was calculated based on absorbance at 550 nm using a microplate reader. Viability was determined by comparing absorbance in wells containing treated cells with that of untreated cells. Data were obtained from three independent experiments, with three replicates per treatment point.
2.8. Flow properties and compressibility of the powders
The drug powders mixed with excipients were evaluated for flow properties, such as bulk density (ρb), tapped density (ρt), Hausner ratio (H), and compressibility index (Carr's index) [13], [14], using to the following formulas:
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
| (6) |
2.9. Swelling and erosion behaviors
Swelling and erosion behaviors of gum tablets (without drug) were evaluated in order to determine the drug release mechanism and kinetics of different seed gums in the controlled drug-release tablets. The methods used to measure the swelling and erosion rates of the gum tablets were described by Huanbutta and Sittikijyothin [9].
2.10. Preparation of matrix tablets
Different tablet formulations containing different controlled-release agents were prepared from seed gums from T. indica and C. fistula and their derivatives. Sample gums (81%), DS (15%), talcum (3%) (glidant) and magnesium stearate (1%) (lubricant) were weighed accurately and blended well for 3 min. The mixed powder (500 mg) was directly compressed into tablet form using a hydraulic press (Specac Inc., USA) at a fixed compression force of 2 tons over different compression times with a 9.5 mm diameter flat-faced punch set. The compressed tablets were placed in a desiccator for further investigation. The fracture strength of the tablets was determined as the force required to break the tablet by radial compression. The tablet hardness, thickness, and diameter were measured using a tablet hardness tester (THB 325TD, Erweka, Germany).
2.11. In vitro drug release studies
DS release from the controlled drug release tablets prepared from both crude and carboxymethylated gums was investigated using a USP dissolution apparatus II (Erweka, Germany) equipped with paddles, which were operated at a speed of 50 rpm. Phosphate buffer (900 ml, pH 6.80 ± 0.05), used as dissolution media, was placed into the glass vessel, the apparatus was assembled, and the dissolution medium was equilibrated to 37 °C ± 0.5 °C. Test fluid (5 ml) was taken at various time intervals: 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 h. A similar volume of fresh media was used to replace the removed sample in order to maintain the zinc conditions in the dissolution study. The amount of DS released was then analyzed using a UV visible spectrophotometer at 278 nm and the DS concentrations were calculated using standard curve. Each in vitro release study was conducted in triplicate, and the mean values of the percentage of drug release were plotted versus time.
2.12. Drug release mechanism
Data from the in vitro drug release assays were analyzed using different kinetic models, including zero order, first order, Higuchi model, and Korsmeyer–Peppas model [15], [16], in order to evaluate the kinetics and mechanism of DS release from the matrix tablets. The kinetics of drug release were computed by fitting the dissolution curve to standard empirical equations, that is, by using the curve fitting software KinetDS (free open-source software). The data were evaluated according to the following equations:
| (7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
| (10) |
where Mt / M∞ is the fraction of drug released, k is a constant incorporating structural and geometric characteristics of dosage form, t is time and n is the diffusional exponent. The equation was treated logarithmically to determine the value of release exponent, n [15], [16], [17].
2.13. Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance and Levene's test for homogeneity of variance were performed in the drug release mechanism part, using SPSS version 10.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., USA). Post hoc testing (p < 0.05) of the multiple comparisons was performed by either the Scheffé or Games–Howell test depending on whether Levene's test was insignificant or significant, respectively.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Chemical compositions
Carboxymethylation [9] of crude gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds was achieved through reaction of the crude gums with monochloroacetic acid in the presence of sodium hydroxide as a catalyst. In this reaction, sodium hydroxide first reacts with the hydroxyl group of gum to give alkoxide groups. In the second step, the glucose unit in the gum molecules is etherified by the carboxymethyl group [9]. The results revealed that, compared with their corresponding crude gums, the carboxymethylated gums had improved chemical compositions, lesser impurities such as protein and fat contents, and higher polysaccharide content (Table 1). As reported, the chemical modification aimed not only to eliminate such drawbacks but also to develop functional characteristics such swelling and solubility in water [8]. However, the obtained product presented a degree of carboxymethyl substitution of 0.17 for both types of seed gum (not shown).
Table 1.
Chemical compositions of crude and carboxymethylated gums.
| Seed gum | Code | Moisture | Ash | Protein | Fat | Polysaccharide* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. indica | ||||||
| Crude | T | 7.10 ± 0.12 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 3.58 | 15.25 | 81.14 |
| Carboxymethylated | Ta | 6.27 ± 0.23 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 14.70 | 85.28 |
| C. fistula | ||||||
| Crude | C | 8.87 ± 0.21 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.03 | 10.04 | 88.92 |
| Carboxymethylated | Ca | 7.27 ± 0.12 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.76 | 91.14 |
Note: all values (%) on a dried weight basis are mean ± standard deviation of three determinations.
Polysaccharide values were calculated by difference.
3.2. FT-IR spectra analysis
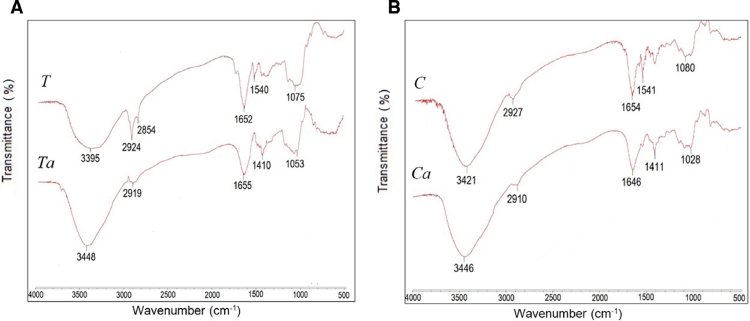
The FT-IR spectra of crude (T and C) and carboxymethylated (Ta and Ca) gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds are shown in Fig. 1. All gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds showed characteristic absorption bands associated with the stretching vibration of the —OH group in the 3500–3200 cm−1 region, aliphatic —CH stretching in the 3000–2850 cm−1 region, and —CH—OH— stretching at ∼1650 cm−1 [18]. The absorption bands appearing around 1020, 1070, and 1155 cm−1 corresponded to the stretching vibration of the C—OH from the mannose and glucan structures [10], [19]. The peaks at 1540 and 1075 cm−1 from T and at 1541 and 1080 cm−1 from C might correspond to N—H bending and C—N stretching, respectively, from protein content. These peaks disappeared following chemical modification, which is in agreement with the chemical composition test results (Table 1). The FT-IR spectra of the carboxymethylated gums indicate higher wavelength shifting of the absorption band from the crude gums located at 3448 and 3446 cm−1 for Ta and Ca, respectively, due to —OH stretching, indicating that some —OH groups were carboxymethylated [20]. In addition, two new peaks corresponding to the carboxymethyl moiety emerged in the spectrum of the modified gums. The peaks at 1410 and 1053 cm−1 for Ta and at 1411 and cm−1 for Ca were due to C—O stretching and C O stretching of the carboxyl group [21].
Fig. 1.
FT-IR spectra of crude (T and C) and carboxymethylated (Ta and Ca) gums from seeds of T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B).
3.3. XRD
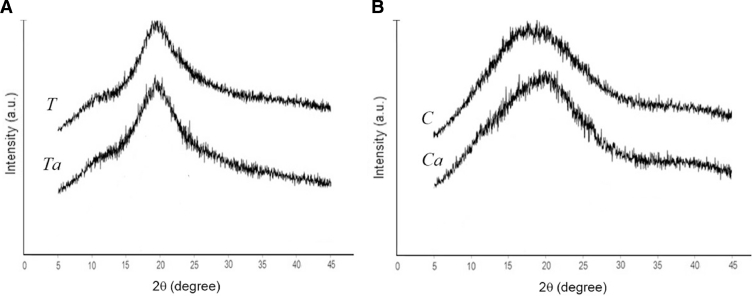
Fig. 2 illustrates the powder X-ray diffractograms of the crude gums and their modified forms from T. indica (Fig. 2A) and C. fistula (Fig. 2B) seeds. The powder XRD pattern of crude and carboxymethylated gums from both T. indica and C. fistula exhibited broad peaks at ∼19° and ∼17° 2θ, respectively, indicating that all the gum samples were in amorphous form. However, the carboxymethylated gums showed increases in their degree of crystallinity. The characteristic peaks from the starting reagents such as sodium hydroxide and sodium chloroacetate were not observed in the diffractograms, indicating that the reagents for chemical modification of the gums had been completely removed from the process [9].
Fig. 2.
X-ray diffractograms of crude (T and C) and carboxymethylated (Ta and Ca) gums from seeds of T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B).
3.4. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
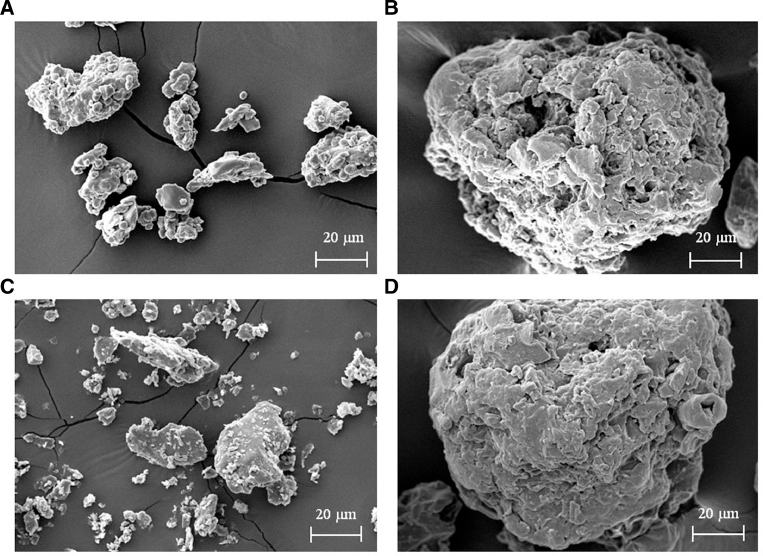
SEM was conducted in order to compare the surface morphology of both crude and carboxymethylated gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds (Fig. 3). The SEM micrographs indicated significant differences in particle morphology. The particles of both types of curde gums had an irregular shape and were 20–60 µm in size (Fig. 3A and C), whereas both types of carboxymethylated gums exhibited different characteristics such as surface roughness, bigger particles (∼120 µm), and greater crystallinity (Fig. 3B and D). The differences in morphology of the carboxymethylated gum particles might be due to the carboxymethylation process.
Fig. 3.
Representative SEM images of crude and carboxymethylated gums: T (A), Ta (B), C (C), and Ca (D).
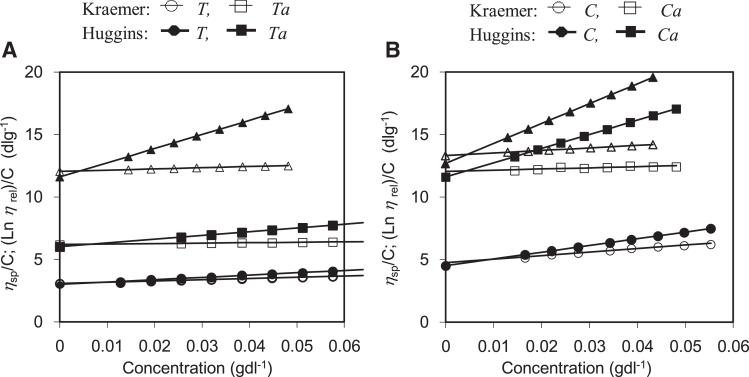
3.5. Intrinsic viscosity
The intrinsic viscosities of the crude and modified gums were observed (Fig. 4). The parameters from the intrinsic viscosity extrapolation are listed in Table 2. As expected, the carboxymethylated gums exhibited high intrinsic viscosity compared with the native gums [4], [9]. This is due to the fact that the carboxymethylated gums obtained carboxymethyl groups, which hydrate well in aqueous solutions. In addition, the carboxymethylated gums exhibited faster and better solubility properties in water.
Fig. 4.
Extrapolation of intrinsic viscosity from Huggins’ and Kraemer plots, ηsp/C and (lnηrel)/C against concentration for seed gums in aqueous solutions at 25 °C: T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B).
Table 2.
Intrinsic viscosity of crude and carboxymethylated gums.
| Seed gum | [η]HA (dlg−1) | [η]KB (dlg−1) | Huggins’ coefficient, kH′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| T. indica | |||
| T | 3.01 | 3.08 | 2.03 |
| Ta | 6.03 | 6.02 | 0.83 |
| C. fistula | |||
| C | 4.52 | 4.76 | 2.63 |
| Ca | 11.61 | 12.05 | 0.84 |
[η]H was intrinsic viscosity from Huggins’ plot.
[η]K was intrinsic viscosity from Kraemers plot.
3.6. In vitro cytotoxicology
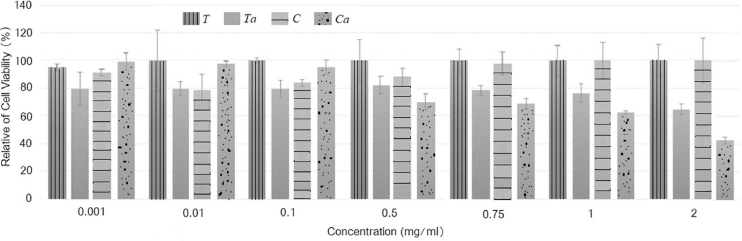
The cytotoxicity of the crude and carboxymethylated gums from C. fistula and T. indica seeds at concentrations ranging from 0.001 to 2 mg/ml were determined by MTT assay of exposed cells, as presented in Fig. 5. With regards to cytotoxicity, Ta and Ca at concentrations of up to 2 mg/ml did not significantly affect the viability of Caco-2 cells. The relative percentage of cell viability of Ca significantly decreased in comparison to the control at concentrations of 0.5 mg/ml above. For Ta at a concentration range of 0.001–1 mg/ml, the relative percent of cell viability was approximately 77%−82%. These results indicate that the crude and carboxymethylated gums are biocompatible polymers. Crude gums are high safety polymers, as reported by Cha and co-workers [22], who demonstrated that crude cashew gum at concentrations up to 0.75 mg/ml did not cause cytotoxicity in Vero mammalian cells [22]. Moreover, the LD50 value of T. indica seed gum after oral consumption was reported to be > 5000 mg/kg of body weight in rats and mice animal models [23]. Ta and Ca do not express cytotoxicity at low concentrations, which is in agreement the reports of a previous in vivo study [24]. However, those of carboxymethylated gums showed cytotoxicity at the higher concentrations. This might be a result of the carboxymethylation modification, in which a carboxyl moiety was added to the gum structure as mentioned in the FT-IR results and Eq. (2), resulting in a reduction in pH of the soluble polymer, which could bring about cell apoptosis [25].
Fig. 5.
Cytotoxicity of crude and carboxymethylated gums from seeds of T. indica and C. fistula.
3.7. Flow properties and compressibility of the powders
Density and compressibility of the gums are shown in Table 3. The densities of the gum samples ranged from 0.46 to 0.63 gm−1. The tapped density was not significantly different between the two plant sources of the seed gum (T. indica and C. fistula). However, the densities diminished after chemical modification. Furthermore, it was observed that the compressibility decreased and flowability improved for the carboxymethylated gums. Except for C, which exhibited fair flowability, most of the seed gums offered good flowability. This might be due to the fact that impurities from the crude gums were removed after the chemical modification process, resulting in homogenously sized gum particles and consequently better flowability [26], [27]. Furthermore, the chemical structure of the carboxymethylated gums was altered, causing an expansion of the polymer chain [28]. This modification can increase the volume of the powder, resulting in lower tapped densities.
Table 3.
Density, compressibility and flowability of gums.
| Seed gum | Tapped density (g/ml) | Compressibility index (%) | Flowability* |
|---|---|---|---|
| T. indica | |||
| T | 0.62 ± 0.00 | 14.96 ± 1.17 | Good |
| Ta | 0.46 ± 0.00 | 14.28 ± 0.00 | Good |
| C. fistula | |||
| C | 0.63 ± 0.00 | 15.60 ± 1.22 | Fair |
| Ca | 0.56 ± 0.00 | 12.92 ± 1.17 | Good |
According to Carr's index table [14]
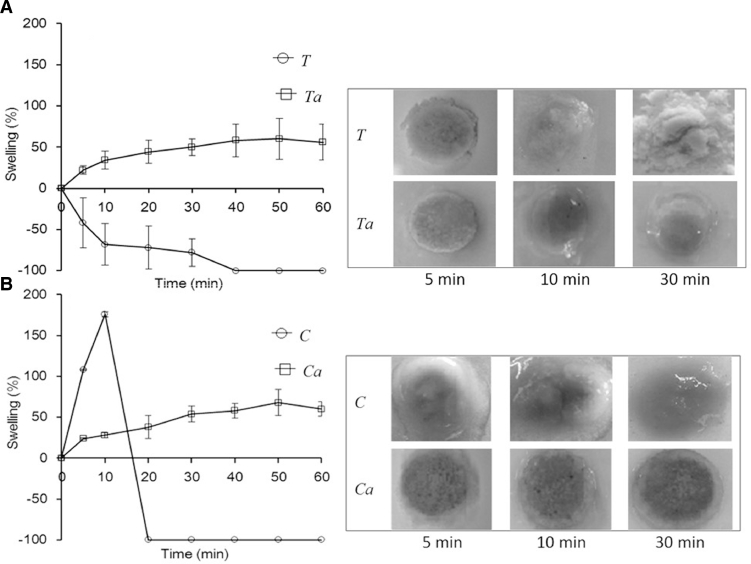
3.8. Swelling and erosion behavior
The swelling and erosion behaviors of the matrix tablets made of seed gums and theirs carboxymethylated forms were monitored by gravimetric analysis. The swelling profiles in purified water and pictures of the swelling tablets prepared from crude and carboxymethylated gums at different periods are shown in Fig. 6. As presented in Fig. 6, crude gums did not swell but eroded, whereas carboxymethylated gums displayed gradual swelling until reaching ∼56% and ∼60% of their initial size at 60 min for Ta and Ca, respectively [9]. This is because the particles in the crude gum powder cannot adhere to each other and the powder rarely dissolves in water. Consequently, water molecules freely penetrate into the matrix tablet, resulting in rapid disintegration. This is in agreement with the hardness results, indicating that the crude gum tablets exhibit lower hardness due to a lack of binding force between particles [29]. Furthermore, Fig. 6 also shows that a firm gel was formed around the tablet prepared using the carboxymethylated gums because they protonate and partly dissolve after exposure to water, resulting in hydration/swelling and gel formation at the interface of the matrix tablet and the medium. The gel erosion front moved outward, causing expansion of the swelling or rubbery region [30]. Chemical modification of seed gum could improve its swelling and solubilization property [8].
Fig. 6.
Swelling profiles and behavior of crude and carboxymethlylated gums from seeds of T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B).
3.9. Evaluation of tablets
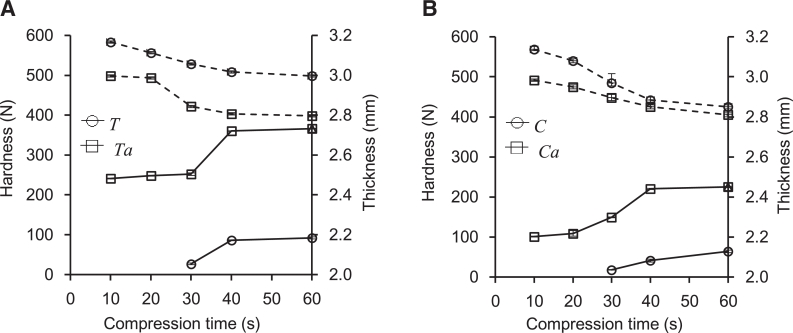
After physicochemical characterization of the crude and carboxymethylated gums, all samples were formulated into polymeric controlled drug release tablets as previously described. The thickness, diameter, hardness, and disintegration time of the matrix tablets were evaluated to observe the effect of the chemical modification process and type of seed plant. The average thickness of all the prepared tablets ranged from 2.84 to 3.13 mm. The effect of compression time on hardness and thickness of the tablets is shown in Fig. 7, respectively. The crude gums formed tablets after compression time of 30 s. However, hardness of the prepared matrix tablets made from crude gum was rather low (17.67–92.00 N). Moreover, the tablet hardness of T was higher than that of C, and the tablet hardness of Ta (350.34–506.34 N) was greater than that of Ca (101.00–267.34 N). Increasing the compression time enhanced the tablet hardness for the carboxymethylated gum as a result of the modification of the polysaccharide chain from a hydroxy to a carboxymethyl moiety, as mentioned in the FT-IR spectroscopy section (Section 3.2). This can cause the surface properties of the gum particles to become more hydrophilic, resulting in hydrogen bonding between the particles and improved hardness [31]. In addition, the thickness differences over a compression time of 10–60 s for matrix tablets made from Ca was greater than those of Ta matrix tablets. This result is in agreement with the compressibility and flowability results, which revealed that Carr's index of the Ca powder was lower than the Ta powder, indicating that the flowability of C. fistula seed powder was superior [32].
Fig. 7.
Hardness (solid lines) and thickness (dash lines) of DS tablet prepared by crude and carboxymethlylated gums from seeds of T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B).
3.10. In vitro drug release studies
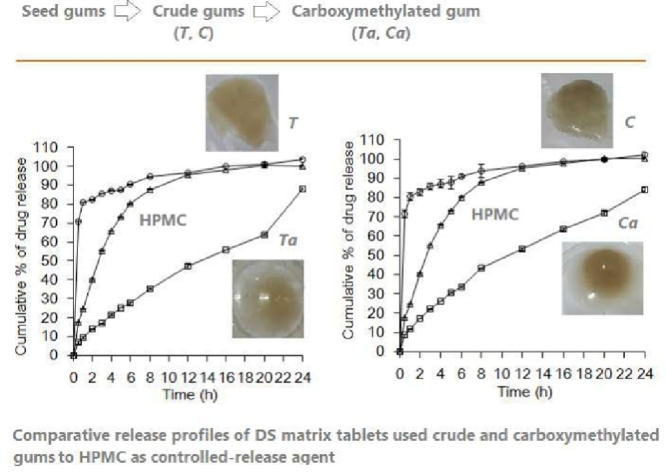
The in vitro drug release study of the matrix tablet formulation prepared from crude and carboxymethylated gums of T. indica and C. fistula compressed at 2 tons for 30 s were conducted in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer. To compare it with the general controlled drug release agents in the market, HPMC K4M was also evaluated. As shown in Fig. 8, tablets prepared with Ta and Ca exhibited slower drug release than HPMC and crude gum (T and C). Ta tables exhibited slower drug release than Ca tablets. At 24 h, the drug release of Ta and Ca were at ∼88% and ∼84%, respectively. This result is in accordance with the swelling and erosion results, which revealed that Ta tablets swelled greater size than Ca tablets. As illustrated in Fig. 8C and D, compression time slightly affected drug release profile of the Ta matrix tablets; however, the drug release of Ca tablets compressed for 40 and 60 s was significantly slower than those which were compressed for 10, 20, and 30 s (Fig. 8D), indicating differences in the compatibility properties of the two modified gums, Ta and Ca.
Fig. 8.
Drug release profiles of DS matrix tablets at different compression times: T. indica (A) and C. fistula (B); comparative release profiles of DS matrix tablets, for 30 s of compression time, used crude and carboxymethylated gums to HPMC as controlled-release agent: T. indica (C) and C. fistula (D).
3.11. Release mechanism
Dissolution data of the gum-based controlled drug release tablets were processed using linear regression analysis for exploring of drug release mechanism and kinetics by testing the goodness of fit with zero order, first order, Higuchi, and Korsmeyer-Peppas release models (Eqs. (7)–(10)). As presented in Table 4, a correlation coefficient (R2) was considered and selected to define the approximation accuracy of an individual model. All gum-based tablet formulation drug release profiles at different compression times obeyed the Korsmeyer–Peppas model as the R2 values for all the formulations were between 0.9765–0.9952. The n value (1.0427–1.4532) in Korsmeyer–Peppas model was greater than 0.85, indicating that the mechanism of drug release occurred through super case II transport (relaxation) [8], [33]. In addition, the drug release kinetics of the gum-based formulations were similar to those of the HPMC matrix tablets, which is super case II transport (relaxation) [34], which occurs by two mechanisms, specifically diffusion and relaxation of polymer chain [26]. This might be because the gum gradually dissolved in the phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Consequently, DS gradually diffused through the relaxed polymer layer.
Table 4.
Release rate kinetics and correlation coefficients for zero order, first order, Higuchi, and Krosmeyer–Peppas models for DS matrix tablets at different controlled-release agents and different compression times.
| Sample, compression | Zero order plot (Eq. (7)) | First order plot (Eq. (8)) | Higuchi model (Eq. (9)) | Korsmeyer–Peppas model (Eq. (10)) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | (Correlation coefficient) | (Correlation coefficient) | (Correlation coefficient) | Slope (n) | (Correlation coefficient) | Type of transport |
| T. indica | ||||||
| T, 30 | 0.3096 | 0.0958 | 3.8765 | 1.0884 | 0.9766 | Super case II |
| Ta, 10 | 0.9791 | 0.1441 | 0.4435 | 1.0598 | 0.9941 | Super case II |
| Ta, 20 | 0.9793 | 0.1488 | 0.4015 | 1.0567 | 0.9952 | Super case II |
| Ta, 30 | 0.9816 | 0.1505 | 0.3961 | 1.0557 | 0.9957 | Super case II |
| Ta, 40 | 0.9673 | 0.1476 | 0.4685 | 1.0531 | 0.9957 | Super case II |
| Ta, 60 | 0.9707 | 0.1467 | 0.4688 | 1.0513 | 0.9956 | Super case II |
| C. fistula | ||||||
| C, 30 | 0.3040 | 0.0956 | 3.9164 | 1.4532 | 0.9765 | Super case II |
| Ca, 10 | 0.9555 | 0.1409 | 0.5436 | 1.0656 | 0.9940 | Super case II |
| Ca, 20 | 0.9607 | 0.1411 | 0.5388 | 1.0628 | 0.9941 | Super case II |
| Ca, 30 | 0.9678 | 0.1431 | 0.5108 | 1.0611 | 0.9946 | Super case II |
| Ca, 40 | 0.9540 | 0.1391 | 0.5198 | 1.0461 | 0.9937 | Super case II |
| Ca, 60 | 0.9425 | 0.1369 | 0.5580 | 1.0427 | 0.9933 | Super case II |
| HPMC | ||||||
| 30 | 0.6791 | 0.1222 | 1.1643 | 1.0842 | 0.9905 | Super case II |
4. Conclusion
The results obtained here demonstrate that carboxymethylated gums of T. indica and C. fistula seeds present interesting physicochemical properties in terms of their pharmaceutical applications, such as the controlled-release of DS in matrix tablet form. At the similar excipient portion and tablet manufacture condition, both the modified gums could retard drug release better than HPMC. According to the mathematical models employed here, the drug release mechanism of the modified gums was found to correspond to super case II transport. From a functional point of view, carboxymethylated gums from T. indica and C. fistula seeds represent a potential future natural pharmaceutical excipient for tablets and other formulations. However, the stability of biopolymer matrix tablets as drug controlled-release agent needs to be further investigated.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to the Higher Education Research Promotion-National Research Universities (HERP-NRU) for financial support under grant no. 2559A10862013. Nuntawan Pim-am is acknowledged for technical work.
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2018.02.006.
Appendix. Supplementary materials
References
- 1.Patel T.R., Morris G.A., Ebringerová A., et al. Global conformation analysis of irradiated xyloglucans. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;74:845–851. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Srivastava M., Kapoor V.P. Seed galactomannans: an overview. Chem Biodivers. 2005;2:295–317. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200590013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zietsman S., Kilian G., Worthington M., Stubbs C. Formulation development and stability studies of aqueous metronidazole benzoate suspensions containing various suspending agents. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2007;33:191–197. doi: 10.1080/03639040601011215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huanbutta K., Sangnim T., Sittikijyothin W. Development of tamarind seed gum as dry binder in formulation of diclofenac sodium tablets. Walailak J Sci Technol. 2016;13:863–874. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ahuja M., Kumar A., Yadav P., Singh K. Mimosa pudica seed mucilage: Isolation; characterization and evaluation as tablet disintegrant and binder. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;57:105–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Raguvaran R., Manuja B.K., Chopra M., et al. Sodium alginate and gum acacia hydrogels of ZnO nanoparticles show wound healing effect on fibroblast cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;96:185–191. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seelan T.V., Kumari H.L., Kishore N., et al. Exploitation of novel gum prunus cerasoides as mucoadhesive beads for a controlled-release drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85:667–673. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dodi G., Hritcu D., Popa M. Carboxymethylation of guar gum: Synthesis and characterization. Cellulose Chem Technol. 2011;45:171–176. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huanbutta K., Sittikijyothin W. Development and characterization of seed gums from Tamarindus indica and Cassia fistula as disintegrating agent for fast disintegrating Thai cordial tablet. Am J Pharam Sci. 2017;12:370–377. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2017.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rajput R., Pandey I., Joshi G. Carboxymethylation of Cassia angustifolia seed gum: Synthesis and rheological study. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;117:494–500. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sharma B.R., Kumar V., Soni P. Carbamoylethylation of Cassia tora gum. Carbohydr Polym. 2003;54:143–147. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Silva D.A., de Paula R.C., Feitosa J.P., Brito A.C., Maciel J.S., Paula H.C. Carboxymethylation of cashew tree exudate polysaccharide. Carbohydr Polym. 2004;58:163–171. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shah R.B., Tawakkul M.A., Khan M.A. Comparative evaluation of flow for pharmaceutical powders and granules. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2008;9:250–258. doi: 10.1208/s12249-008-9046-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Santomaso A., Lazzaro P., Canu P. Powder flowability and density ratios: the impact of granules packing. Chem Eng Sci. 2003;58:2857–2874. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Korsmeyer R.W., Gurny R., Doelker E., Buri P., Peppas N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm. 1983;15:25–35. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600721021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Higuchi T. Mechanism of sustained‐action medication: Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci. 1963;52:1145–1149. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600521210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sriamornsak P., Nunthanid J., Luangtana-Anan M., Weerapol Y., Puttipipatkhachorn S. Alginate-based pellets prepared by extrusion/spheronization: effect of the amount and type of sodium alginate and calcium salts. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69:274–284. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nayak A.K., Pal D. Development of pH-sensitive tamarind seed polysaccharide–alginate composite beads for controlled diclofenac sodium delivery using response surface methodology. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;49:784–793. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Banegas R.S., Zornio C.F., Borges A.d.M., Porto L.C., Soldi V. Preparation, characterization and properties of films obtained from cross-linked guar gum. Polímero. 2013;23:182–188. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yadav M., Srivastav A., Verma S.K., Behari K. Graft (partially carboxymethylated guar gum-g-poly vinyl sulfonic acid) copolymer: from synthesis to applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;97:597–603. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.02.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Singh R., Maity S., Sa B. Effect of ionic crosslink on the release of metronidazole from partially carboxymethylated guar gum tablet. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;160:414–421. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cha M.R., Choi Y.H., Choi C.W., et al. Galbanic acid, a cytotoxic sesquiterpene from the gum resin of Ferula asafoetida, blocks protein farnesyltransferase. Planta Medica. 2011;77:52–54. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1250049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jana S., Banerjee A., Sen K.K., Maiti S. Gelatin-carboxymethyl tamarind gum biocomposites: in vitro characterization & anti-inflammatory pharmacodynamics. Mater Sci Eng, C. 2016;69:478–485. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schmitt D., Tran N., Riefler S., et al. Toxicologic evaluation of modified gum acacia: mutagenicity, acute and subchronic toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:1048–1054. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.10.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bianchi J., Rose R.C. Dehydroascorbic acid and cell membranes: possible disruptive effects. Toxicol. 1986;40:75–82. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(86)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Trementozzi A.N., Leung C.Y., Osei-Yeboah F., et al. Engineered particles demonstrate improved flow properties at elevated drug loadings for direct compression manufacturing. Int J Pharm. 2017;523:133–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ludwig B., Miller T.F. Rheological and surface chemical characterization of alkoxysilane treated, fine aluminum powders showing enhanced flowability and fluidization behavior for delivery applications. Powder Technol. 2015;283:380–388. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yalpani M. Elsevier; 2013. Polysaccharides: Syntheses, modifications and structure/property relations. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Huanbutta K., Sriamornsak P., Limmatvapirat S., et al. Swelling kinetics of spray-dried chitosan acetate assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and their relation to drug release kinetics of chitosan matrix tablets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;77:320–326. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sriamornsak P., Thirawong N., Weerapol Y., Nunthanid J., Sungthongjeen S. Swelling and erosion of pectin matrix tablets and their impact on drug release behavior. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yarce C.J., Echeverri J.D., Palacio M.A., Rivera C.A., Salamanca C.H. Relationship between surface properties and in vitro drug release from compressed matrix containing polymeric materials with different hydrophobicity degrees. Pharm. 2017;10:15. doi: 10.3390/ph10010015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mshelia J.G., Apeji Y.E., Olayemi O.J. Powder, Compaction and tableting properties of co-processed silicified starch. Br J Pharm Res. 2013;6:131–140. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pal S., Sen G., Mishra S., Dey R.K., Jha U. Carboxymethyl tamarind: Synthesis, characterization and its application as novel drug‐delivery agent. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;110:392–400. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ford J.L., Rubinstein M.H., McCaul F., Hogan J.E., Edgar P.J. Importance of drug type, tablet shape and added diluents on drug release kinetics from hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrix tablets. Int J Pharm. 1987;40:223–234. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.