Abstract
Background
Gintonin (GT), a novel ginseng-derived exogenous ligand of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors, has been shown to induce cell proliferation and migration in the hippocampus, regulate calcium-dependent ion channels in the astrocytes, and reduce β-amyloid plaque in the brain. However, whether GT influences autophagy in cortical astrocytes is not yet investigated.
Methods
We examined the effect of GT on autophagy in primary cortical astrocytes using immunoblot and immunocytochemistry assays. Suppression of specific proteins was performed via siRNA. LC3 puncta was determined using confocal microscopy.
Results
GT strongly upregulated autophagy marker LC3 by a concentration- as well as time-dependent manner via G protein–coupled LPA receptors. GT-induced autophagy was further confirmed by the formation of LC3 puncta. Interestingly, on pretreatment with an mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, rapamycin, GT further enhanced LC3-II and LC3 puncta expression. However, GT-induced autophagy was significantly attenuated by inhibition of autophagy by 3-methyladenine and knockdown Beclin-1, Atg5, and Atg7 gene expression. Importantly, when pretreated with a lysosomotropic agent, E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1, GT significantly increased the levels of LC3-II along with the formation of LC3 puncta. In addition, GT treatment enhanced autophagic flux, which led to an increase in lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 and degradation of ubiquitinated p62/SQSTM1.
Conclusion
GT induces autophagy via mTOR-mediated pathway and elevates autophagic flux. This study demonstrates that GT can be used as an autophagy-inducing agent in cortical astrocytes.
Keywords: Autophagic flux, Autophagy-related genes, Gintonin, LC3 puncta, p62/SQSTM1
1. Introduction
Autophagy is an intracellular process that removes damaged tiny cellular organelles and aggregate or misfolded protein components [1], in addition to maintaining a diversity role of physiological procedures, including glucose maintenances [2], metabolism of lipid [3], and control of aging [4]. When autophagy is dysregulated, defective proteins and damaged organelles cannot be properly removed, and therefore, their accumulation leads to pathological conditions [1]. Interestingly, suppression of cellular autophagy effects on early aging of Caenorhabditis elegans [5], but enhanced autophagy was shown to extend the lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster [6]. Previous studies also reported that deletion of autophagy-related genes, Atg, provokes a difference of cellular homeostasis, leading to cause obesity [7], resistance of insulin biosynthesis [8], accelerated diabetics [9], as well as neurodegeneration diseases [2]. The cellular mechanism of neurodegenerative diseases is closely correlated with the formation of abnormal protein aggregates, such as amyloid-β peptide [10] in addition to tau protein aggregation [11] in the neurodegenerative Alzheimer's disease, α-synuclein in case of Parkinson's disease [12], as well as in Huntington's disease (HD) [13]. When considering that failure to remove the aggregated proteins by autophagy can cause the accumulation of misfolded protein aggregates, autophagy pathway may serve as an attractive therapeutic target to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Indeed, among all cell types, neuronal cells are particularly susceptible to impaired autophagy [14], leading to a struggle to conserve synaptic function [15] and axonal maintenances [16]. Moreover, numerous studies have demonstrated connection of autophagy signaling and neurodegenerative diseases [17]. Therefore, in this study, we examined how natural bioactive components GT, derived from traditional herbal medicine ginseng, influence autophagy enhancement in cortical astrocytes.
Gintonin (GT), a glycolipoprotein isolated from the root of ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer), acts as a ligand of G-protein–coupled lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors and regulates intracellular Ca2+-dependent ion channels through LPA receptor signaling pathways in neuronal cells. In addition, ginseng major latex-like protein 151, a key protein component of gintonin, binds to LPAs and makes them additionally stable and soluble than free LPAs that stimulate in vitro [Ca2+]i transients in nonneuronal and neuronal cells which has pharmacological effects in the nervous system in vivo [18]. In vivo studies have shown that GT facilitates long-term potentiation [19] in the brain slices of hippocampus by increasing glutamate release [20]. In addition, GT treatment also enhanced the expression of Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as well as the levels of phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) protein in normal mice [21]. Furthermore, long-term oral administration of GT reduced the deposition of β-amyloid plaque, protected short- and long-term memory damage in a transgenic mouse model of AD [22], and inverted hippocampal cholinergic dysfunctions [23]. Given that GT decreased the hippocampal β-amyloid burden, it may contribute to the removal of protein aggregates by regulating autophagy. However, it remains to be examined whether GT influences autophagy in mouse primary cortical astrocytes.
To address this question, we elucidated the mechanism of effect of GT on autophagy in primary culture of cortical astrocytes and found that GT enhanced autophagy through G protein–coupled LPA receptor ligand-mediated pathway. Our findings indicate that GT serves as an LPA receptor activator and induces mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent autophagy in astrocytes and that GT upregulates autophagy initiation protein such as Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 in mouse cortical astrocytes. Moreover, exposure to GT leads to excessive activation of autophagic flux, leading to an increase in lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1) generation as well as a decrease in ubiquitinated p62/SQSTM1 in astrocytes. Therefore, we propose that GT can promote the clearance of misfolded/aggregate-prone proteins in neurodegenerative diseases by stimulating autophagy pathway.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
Atg5, Atg7, Beclin-1, LC3, phospho-SQSTM1, phospho-S6, total S6, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and COX2 antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Bcl-2, Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 siRNA were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz CA, USA). 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), bafilomycin A1, E-64d protease inhibitor (E-64d), 3-methyladenine (3-MA), pepstatin A, and rapamycin were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Protease inhibitor mixture was obtained from BioVision (Mountain View, CA, USA). LPA C18:1 was obtained from Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. (Alabama, USA). Ki16425 was obtained from Cay-man Chemicals-Interchim (Montlucon, France).
2.2. Preparation of gintonin fraction from ginseng root
One kilogram of 4-year-old ginseng was ground into small pieces (>3 mm) and refluxed with 80% ethanol (EtOH) three times for 8 h at 80°C each. The EtOH extracts (60 g) were concentrated and dried after extensive dialysis. The EtOH fraction of Panax ginseng dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2) was loaded onto a column packed with Diethylaminoethanol (DEAE) sepharose CL-6B (GE Healthcare, Chicago, Il, USA) and equilibrated with PBS. The unbound materials were eluted with the same buffer, and the bound materials were eluted with a linear gradient of 0–1 M NaCl in PBS. The eluted fraction was further dialyzed at 4°C for 8 h with 1,000-fold excess distilled water using a Spectra/Por dialysis membrane (molecular weight cut off 6,000-8,000; Spectrum Laboratories, Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA) to further remove small molecular components such as ginsenosides and other components that might remain in the fraction (2 g) [24]. This fraction was designated edible gintonin.
2.3. Primary astrocyte culture
Primary astrocytes were cultured from 1-day-old Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice brain (Orient Bio Inc. Korea). Whole brains were separated and immersed in Hank's buffered salt solution (HBSS) buffer accompanied with penicillin and streptomycin. The cerebral hemispheres were carefully removed, digested with 0.1% trypsin–0.05% EDTA for 25 min and inverted every 5 min at 37°C and detrypsinized by Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) medium in 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS). Cells were seeded in 100-mm cell culture disc with 10% FBS and 10% horse serum and then grown at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 7 days. The culture dishes were washed with PBS and shaken manually to get pure astrocytes. These astrocytes were used for further experiments.
2.4. Immunocytochemistry staining
After treatment with GT, astrocytes were washed with 1X PBS and then fixed with 100% methanol at −20°C for 15 min. After fixation, they were rinsed three times in 1X PBS for 5 minutes each and blocked using normal goat serum (5%) comprising Triton X-100 (0.3%) and 1X PBS at 60 min. Subsequently, the cells were coincubated in mouse mAb anti-Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody (1:50) (Alexa Fluor 555 Conjugate, Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA) and LC3II (Alexa Fluor 488 Conjugate, Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA) (1:50) antibodies at 4°C overnight in 1X PBS, 1% BSA, and 0.3% Triton X100. After incubation, the cells were washed with 1X PBS, and then nuclei were stained with DAPI. LC3II puncta were visualized and captured using a confocal microscope Leica Application Suite X (LAS X) (Leica Microsystems, Germany).
2.5. Measurements of autophagy flux
We used confocal microscopy to count the number of LC3 punctate staining per cell. Results were presented as average ± standard error of mean (SEM) and correlate with a measurement of the punctate in a minimum of three independent images, and at least five cells were counted per condition, and therefore, average counting number was plotted in the bar graph.
2.6. Transfection of astrocytes with siRNA
Primary astrocytes were transiently transfected by small interfering RNA of Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 with Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Invitrogen Inc. Carlsbad, CA) based on the manufacturer's guidelines. Briefly, cell was cultured in a 12-well dish with 1 mL of DMEM with no antibiotics. Lipofectamines were mixed and diluted in normal medium and then kept at RT. Lipofectamines were homogenously mixed and gently vortexed with previously diluted siRNA oligomer (final concentration 50 nM), and then transfection mixture was incubated for a minimum of 20 min at RT. Afterward, complex mixture was slowly added into the well comprising astrocytes at 48 h. After transfection, astrocyte culture was treated with GT for 24 hours, and immunocytochemistry as well as immunoblotting analysis were performed subsequently. Scrambled siRNA of 50 nM was also added in each control condition during the experiments.
2.7. Western blot analysis
Primary astrocytes plated on the 6-well dishes were pretreated with different inhibitors and subsequently treated with different concentrations of GT. Cells were harvested by protein extraction solution Radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (RIPA) (ELPIS-BIOTECH. Inc, Taejeon, Korea) (pH 7.5, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 1% NP-40, 0.5% deoxycholic acid, 0.1% Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) , 150 mM NaCl). Cells were collected and placed on ice for 30 min and then centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Upper layers were taken in a new tube. Quantification of protein was carried out by the Bradford protein assay. Equivalent quantities of protein sample was loaded and separated by Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) (8–15% reducing gels) and finally transferred to a membrane. The membrane was blocked by 5% skim milk for 1 h and incubated overnight with appropriate primary antibodies at 4°C. Next day, the membrane was washed and incubated with secondary horseradish peroxide–conjugated antibodies (Jackson Immuno Research) and washed again with Tris-buffered saline, 0.1% Tween 20 (TBST) for 1 h. After three washes, the signal was detected using an Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) kit (iNtron Biotechnology, Seoul, Korea). The band detection of protein expression was performed using AlphaEase program (Alpha Innotech, San Leandro, CA).
2.8. Statistical analysis
Results are indicated as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was examined by one-way and two-way analysis of variance followed by contrast analysis using Prism program (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA). The significance of the experiments was calculated by a Student t test. All the values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Gintonin induces autophagy in a concentration- and time-dependent manner through G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR) -mediated pathway in cortical astrocytes
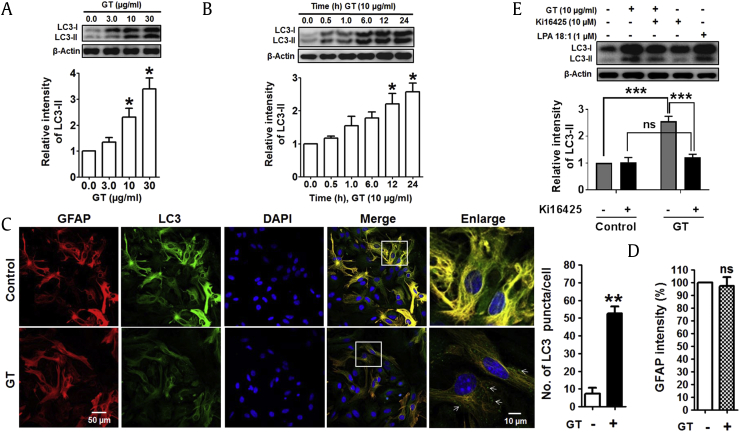
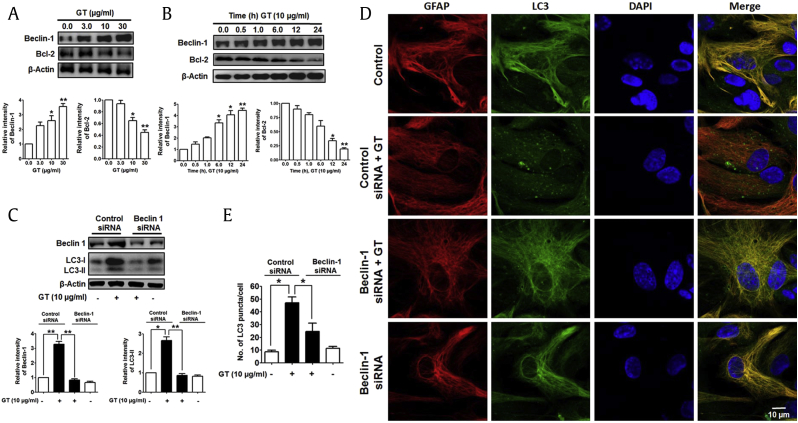
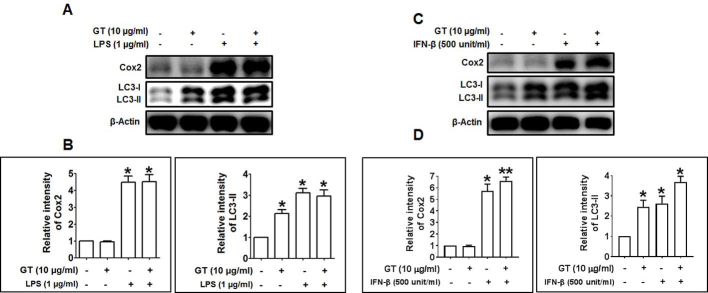
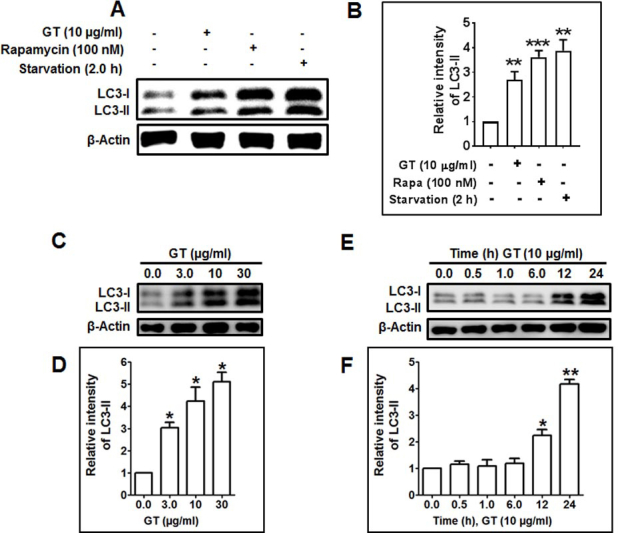
To investigate whether GT activates autophagy, we examined the effect of GT in primary culture of mouse cortical astrocytes by Western blotting and immunocytochemistry. In response to GT, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3, an LC3-II autophagy marker, was upregulated in astrocytes in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 1A; Supplementary Figs. 1A, 1B). The increase in autophagy in astrocytes was most significant 12 h and 24 h after treatment (Fig. 1B). To check autophagic effects of GT, furthermore, we also examined human U87MG glioblastoma cells. Here, we found that GT dose- and time-dependently upregulated LC3-II expression in U87MG cells (Supplementary Figs. 1C, 1E). In addition, GT treatment significantly increased the amount of LC3 puncta in astrocytes, whereas the intensities of GFAP, an astrocyte marker, remain unchanged (Figs. 1C, 1D). A previous study reported that GT binds to GPCR-LPA receptors with highest affinity and initiates intracellular signaling pathways such as activation of Ca2+-dependent kinases and neurotransmitter release [18]. Therefore, we examined whether GT-induced autophagy was mediated by G protein–coupled LPA receptors in cortical astrocytes. Interestingly, we found that pretreatment with an LPA receptor antagonist, Ki16425 [25], significantly attenuated GT-induced autophagy, whereas the pretreatment with an LPA agonist, LPA 18:1, increased autophagy (Fig. 1E). Also, given that neuroinflammation is an important characteristic in the pathogenesis as well as progression of several neurodegenerative diseases [26], we examined whether GT treatment exhibits any neuroinflammatory effects in astrocytes by comparing with a widely used neuroinflammatory compound, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon beta (IFN-β). Our results demonstrated that inflammatory stimuli LPS and IFN-β concomitantly increased the expression of autophagic protein LC3-II along with the expression of inflammatory proteins such as Cox2 in astrocytes. However, astrocytes treated with GT did not show the expression of inflammatory proteins Cox2, indicating that GT has no neuroinflammatory activities in cortical astrocytes (Supplementary Fig. 2). Taken together, our results suggest that GT-mediated autophagy is primarily dependent on the GPCR-LPA receptors mediated in cortical astrocytes without neuroinflammatory activities.
Fig. 1.
GT-induced autophagy in mouse primary cortical astrocytes. (A) Representative immunoblot of LC3-II/LC3-I expression in astrocytes treated with GT for 24 h. (B) Immunoblot study of LC3-II/LC3-I expression in astrocyte treatment with 10 μg/mL GT for several time points. Densitometry analysis of LC3-II expressions was performed using Image J. All statistical data are indicated as mean ± SEM (n = 3,*P < 0.05). (C) For immunocytochemistry analysis, astrocytes were treated with 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. Astrocytes were fixed and stained with Alexa fluor 555–conjugated anti-GFAP mouse mAb (red) and Alexa fluor 488–conjugated anti-LC3 antibody (green). Representative images of the cells were taken with a confocal microscope, and arrows indicate LC3 puncta. The numbers of LC3 puncta were quantified in at least 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted (**P < 0.01). (D) GFAP intensities were determined via statistical analysis from confocal microscopic data counted in each individual experiment (n = 3, ns = not significant). (E) Astrocytes were pretreated (30 min) with Ki16425 or LPA 18:1 (used as a positive control) and treated with 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. LC3-II/LC3-I expression was determined by Western blotting. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA, and data are indicated as mean ± SEM (n = 3, **P < 0.01, ns = non-significant).
ANOVA, analysis of variance; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GT, gintonin; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; mAb, monoclonal antibody; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.2. Inhibition of autophagy blocks GT-induced autophagy in astrocytes
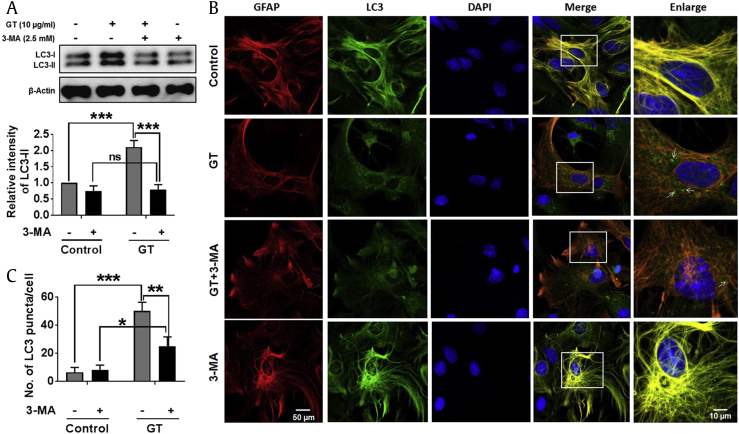
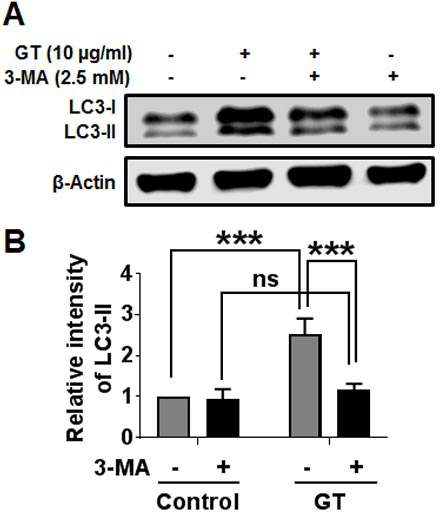
To examine whether GT-mediated autophagic activity is affected by an autophagy blocker, astrocyte culture was pretreated with 3-methyladenine (3-MA), the well-known class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (class III PI3-kinase) inhibitor frequently used in autophagy inhibition [27]. Here, we found that pretreatment with 3-MA completely and significantly blocked GT-induced autophagy (Fig. 2A). We also checked the influence of 3-MA pretreatment on GT-induced autophagy in human U87MG glioblastoma cells. Our results indicated that GT-treated U87MG cells exhibited significantly attenuated LC3-II expression when pretreated with an autophagy inhibitor (Supplementary Fig. 3). Furthermore, immunostaining data revealed that pretreatment with 3-MA significantly inhibited the formation of LC3 puncta in astrocytes (Figs. 2B, 2C). Therefore, our findings indicate that class III PI3K has an important role in controlling GT-induced autophagy in primary cortical astrocytes.
Fig. 2.
Blockage of autophagy inhibited GT-mediated autophagy in astrocytes. (A) Astrocytes were pretreated (3 h) with 3-MA and treated with 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. LC3-II/LC3-I expressions were determined by Western blotting. The Western blot band intensities were measured by Image J software, and each expression was normalized to control β-actin. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA, and the data were represented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3, ***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant). (B) Cells were fixed and stained with Alexa fluor 555–conjugated anti-GFAP mouse mAb (red) and Alexa fluor 488–conjugated anti-LC3 antibody (green), and images of the cells were taken with a confocal microscope. (C) The numbers of LC3 puncta were quantified in minimum 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
3-MA, 3-methyladenine; ANOVA, analysis of variance; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GT, gintonin; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.3. GT induces autophagy via stimulation of AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway in astrocytes
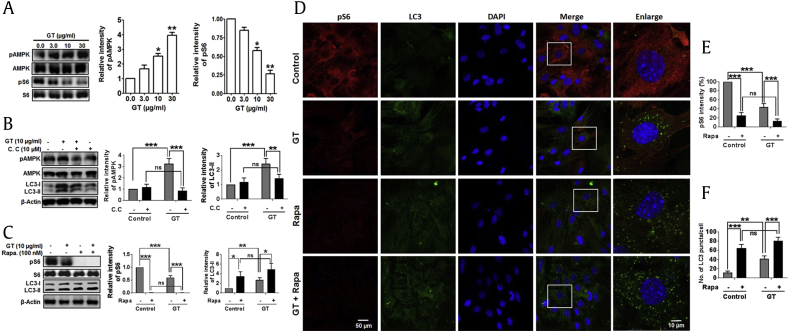
AMPK serves as a sensor of intracellular energy maintenance that is stimulated under low intracellular energy state. For example, nutrient deprivation leads to the initiation of autophagy by AMPK-mTOR–mediated signaling pathway [28]. However, AMPK also directly phosphorylates tumor-repressing protein, tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2), prompting inactivation of mTOR complex 1 [29]. To elucidate the involvement of AMPK-mTOR–dependent pathway in GT-induced autophagy, we tested how GT regulates the phosphorylation of AMPK. Interestingly, GT treatment upregulated the phosphorylation of AMPK in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, as opposed to the elevated AMPK phosphorylation, GT treatment decreased the phosphorylation of S6 ribosomal protein (Ser240/244), a downstream protein of mTOR complex 1 (Fig. 3A). To confirm whether GT-induced autophagy is mediated by the activation of AMPK activity, astrocyte culture was pretreated with compound C, an AMPK inhibitor. The pretreatment with AMPK inhibitor significantly reduced the levels of phosphor-AMPK and LC3 examined by immunoblotting assay, suggesting the involvement of the AMPK signaling pathway in GT-induced autophagy (Fig. 3B). Moreover, given that autophagy is increased when mTOR is inhibited [30], we then compared whether GT-induced autophagy was controlled by the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. Notably, immunoblotting analysis showed that rapamycin completely abolished the phosphorylation of S6 but significantly upregulated LC3-II expression when cotreated with GT in primary cortical astrocyte (Fig. 3C). Consistent with this result, immunostaining showed that the intensity of phospho-S6 was significantly decreased after cotreatment of GT and rapamycin and that rapamycin alone was able to completely block the expression of phosphorylation of S6 ribosomal protein (Ser240/244) (Fig. 3E). We also found that combined treatment of GT and rapamycin significantly increased the formation of LC3 puncta compared with the control, GT alone, or rapamycin alone (Figs. 3D, 3F). Collectively, our data propose that GT inhibits mTOR activation and regulates AMPK-mTOR pathways to enhance autophagy process.
Fig. 3.
Role of AMPK-mTOR signaling cascade in GT-mediated autophagy in astrocytes. (A) Representative Western blot analyses of pAMPK, AMPK, pS6, and S6 expression in astrocytes treated with GT of different concentrations for 24 h. Astrocytes were pretreated with either Compound C for 1 h (B) or rapamycin for 30 min before (C) in the absence/presence of 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. pAMPK, AMPK, pS6, S6, and LC3-II/LC3-I were determined by immunoblotting. Densitometry analysis of represented proteins was performed using Image J analysis, and individual expression was normalized to control β-actin. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3, P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant). (D) Red fluorescence indicates pS6 (Alexa Fluor 568 goat anti-rabbit), and DAPI (blue) indicates stained nucleus. Green fluorescence (Alexa fluor 488) indicates LC3, and images of the slides were captured through a confocal microscope. (E) pS6 intensities were determined via statistical analysis from confocal microscopy calculated in respective individual study were performed by two-way ANOVA (***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant). (F) The numbers of LC3 puncta were quantified in minimum 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted; analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant).
AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ANOVA, analysis of variance; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GT, gintonin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.4. Autophagy initiation proteins Atg5 and Atg7 are involved in GT-induced autophagy in astrocytes
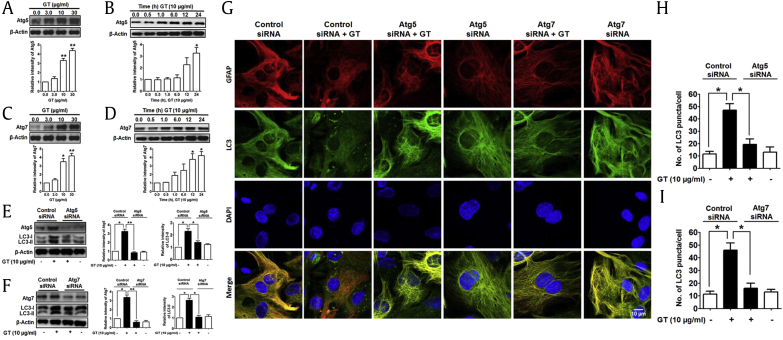
Atg5 and Atg7, autophagy-related genes, are necessary for vesicle initiation, nucleation, and elongation through phagophore formation of autophagy process [31]. Recently, it has been described that Atg5 and Atg7 control and initiate autophagy through natural compound–mediated autophagy pathway in neuroblastoma cells [32]. To find out the role of different Atg in GT-induced autophagy, we checked the role of Atg5 and Atg7 in astrocytes by knockdown with siRNA. An immunoblot of Atg5 and Atg7 showed that both Atg proteins are upregulated on GT treatment in dose- and time-dependent manners (Figs. 4A–4D). In addition, knockdown of Atg5 and Atg7 genes by siRNA significantly reduced GT-mediated LC3 expression compared with control siRNA in astrocyte culture determined by Western blot (Figs. 4E, 4F). Finally, we examined GT-mediated autophagy in astrocyte transiently transfected with either Atg5 or Atg7 siRNA. Confocal microscopic analysis showed that siRNA-mediated knockdown of Atg5 or Atg7 significantly reduced the formation of LC3 puncta compared with control siRNA in astrocytes (Figs. 4G–4I). Taken together, our results clearly indicate that GT-mediated autophagy in cortical astrocytes requires autophagy initiation proteins Atg5 and Atg7.
Fig. 4.
GT-induced autophagy in Atg5- and Atg7-mediated pathway in astrocytes. (A, B, C, and D) Representative Western blot analyses of GT were performed in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. (E, F) Astrocytes were transfected using control siRNA, Atg5, and Atg7 siRNA for 48 h and then incubated by 10 μg/mL for 24 h. Atg5, Atg7, and LC3-II/LC3-I expressions were determined by immunoblotting. Densitometry analysis of represented proteins was performed using Image J program. Each result was expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (G) Control siRNA, Atg5, and Atg7 siRNA were transfected for 48 h and incubated with 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. Astrocytes were fixed as well as stained with Alexa fluor 555–conjugated anti-GFAP mouse mAb (red) and Alexa fluor 488–conjugated anti-LC3 antibody (green), and the images of the cells were taken using a confocal microscope. (H, I) The numbers of LC3 puncta were quantified in minimum 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted (*P < 0.05). DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GT, gintonin; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.5. GT affects Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 expression during autophagy in astrocytes
Beclin-1, an important initiator protein of autophagy, is involved in the preautophagosomal configuration assembly, thus making the core complex comprising of Beclin-1, Vps34, as well as Vps15 [33]. However, Beclin-1 generally interlinks through its BH3 domain with Bcl-2 family member protein, which inhibits the involvement of Beclin-1 in accumulating preautophagosomal assembly by suppressing autophagy process [34]. To study the role of Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 induction of autophagy, we examined Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 protein expression of GT-treated astrocytes. Interestingly, treatment of GT significantly upregulated the level of Beclin-1 but downregulated Bcl-2 level concentration dependently (Fig. 5A). GT also time-dependently increased Beclin-1 but decreased Bcl-2 in astrocytes (Fig. 5B). We additionally examined Beclin-1 in GT-treated autophagy by siRNA-mediated knockdown and found that Beclin-1 knockdown inhibited GT-induced LC3-II upregulation (Fig. 5C). Finally, we also found that siRNA-mediated Beclin-1 knockdown significantly decreased the number of LC3 puncta in astrocytes (Figs. 5D, 5E). Taken together, Beclin-1 is necessary for GT-mediated facilitation of autophagy in primary cortical astrocytes.
Fig. 5.
GT enhanced beclin-1 and decreased Bcl-2 in astrocytes. (A, B) Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 proteins were determined from dose- and time-dependent effects of GT in astrocytes via Western blotting. Band intensities of represented proteins were measured using Image J. Statistical results were expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (C) Astrocytes were transfected through control siRNA and Beclin-1 siRNA for 48 h and then incubated with 10 μg/mL for 24 h. Beclin-1 and LC3-II/LC3-I expressions were determined by immunoblotting. (D) After transfection, astrocytes were fixed as well as stained with Alexa fluor 555–conjugated GFAP mouse mAb (red) and Alexa fluor 488–conjugated anti-LC3 antibody (green), and the images of the cells were taken with a confocal microscope. (E) Numbers of LC3 puncta were counted in minimum 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted (*P < 0.05).
DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GT, gintonin.
3.6. GT induces autophagic flux in astrocytes
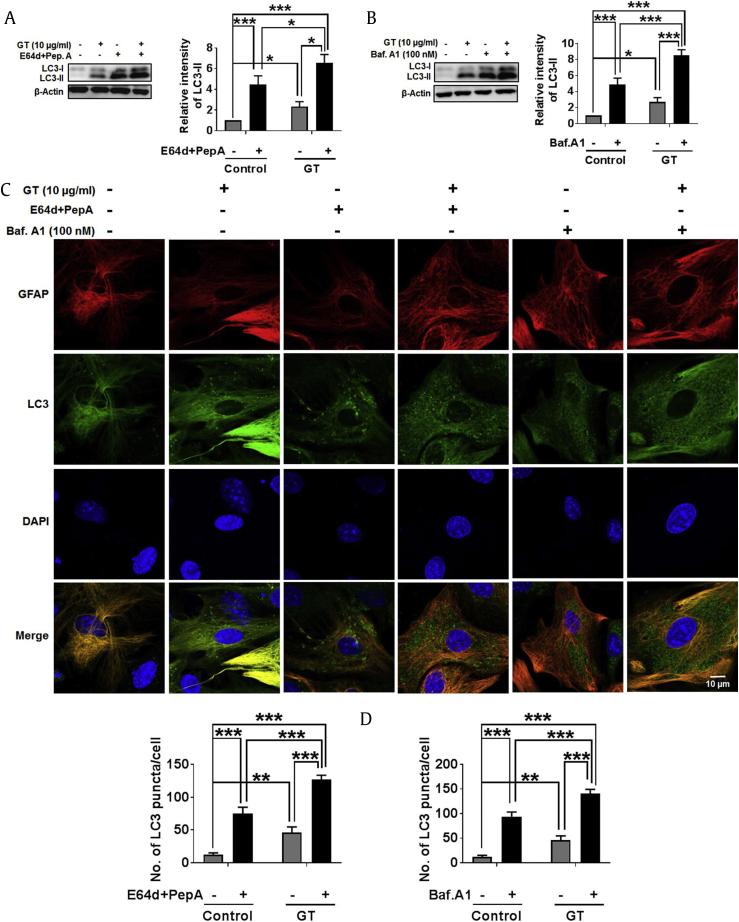
The most commonly used method to determine “autophagic flux” is the measurement of LC3 turnover in which elucidation of LC3-II is destroyed during autolysosomes process of autophagy [35]. In one approach, when cells are treated with lysosomotropic agents such as chloroquine, ammonium chloride, and bafilomycin A1, it either prevents the acidification of cell lysosome or prevents the binding of autophagosome structures with lysosome. Another way to study autophagic flux is to block lysosomal proteases with E-64d or pepstatin A, which inhibits the degradation of LC3-II, thereby increasing the levels of LC3-II [36]. Consequently, the difference in the levels of LC3-II after drug treatment in the absence/presence of lysosomal blockers reveals the quantity of LC3 supplied to lysosomes for autophagic degradation [37]. To measure the autophagic flux induced by GT, we applied E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 and examined autophagy via immunoblotting and confocal immunostaining assay. The results suggest that LC3-II are dramatically and significantly increased on the treatment with E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 in both GT-treated and nontreated conditions (Figs. 6A, 6B). Notably, the actual difference in LC3-II measured in the absence/presence of bafilomycin A1 or E-64d/peps A were greater under the GT treatment conditions, indicating that autophagic flux is significantly increased by GT treatment in astrocytes. Similarly, in confocal analysis, we also observed that GT further enhanced the formation of LC3 puncta fluorescence in astrocytes when autophagosomal degradation was inhibited by E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 (Fig. 6C and D). Taken together, our finding indicates that GT has the capacity to enhance autophagic flux during autophagy signaling in cortical astrocytes.
Fig. 6.
GT treatment induced autophagic flux in astrocytes. (A, B) Cells were pretreated with E-64d (10 μg/mL) as well as pepstatin A (10 μg/mL), or bafilomycin A1 for 1 h in the absence/presence of 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. LC3-II/LC3-I expressions were determined by Western blotting. All protein band intensities were measured using Image J. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001). (C) After pretreatment with autophagy inhibitors, cells were incubated with 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. Astrocytes were fixed and stained with Alexa fluor 555 GFAP (red) and Alexa fluor 488 LC3 antibody (green), and images of the cells were taken with a confocal microscopy. (D) The numbers of LC3 puncta were counted in minimum 3 independent random areas of each slide, and at least 5 cells were counted, and analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
ANOVA, analysis of variance; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP, Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GT, gintonin; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.7. GT treatment degrade autophagy-selective substrates p62/SQSTM1 in astrocytes
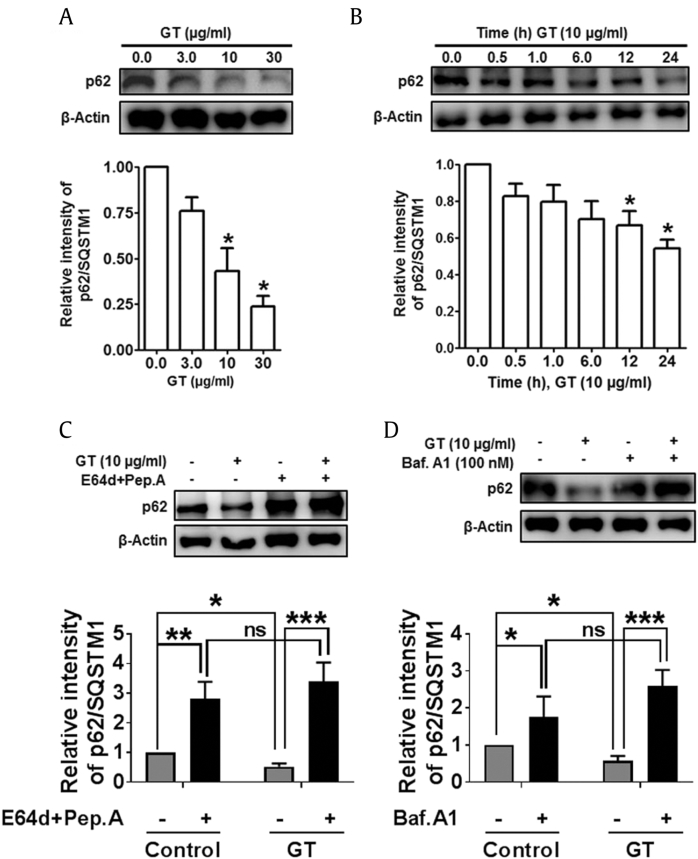
We extended our study to measure the expression of autophagy substrates that could be used to monitor autophagic flux. Typically, autophagy has been considered as an indiscriminate degradation pathway, but other studies have identified numerous substrates that are specifically destroyed via autophagy, including ubiquitinated p62 protein (also called sequestome 1/SQSTM1) [38]. Sometimes, p62 proteins are normally used as an indicator to examine autophagic flux determination as it not only binds directly to LC3 protein but also can be degraded by autophagy process. Therefore, blockage of autophagy pathway may lead to an increase in the total levels of p62 [39]. Therefore, to determine the actual role of p62 in GT-mediated autophagy, we performed immunoblotting analysis of p62 protein expression in astrocyte culture. Having observed that LC3 was dose- and time-dependently increased by GT induction (Fig. 1), we examined whether GT also influences p62 in dose- and time-dependent manners in astrocytes (Figs. 7A, 7B). To elucidate the contribution of autophagy in p62 regulation, here we used an experimental approach based on the LC3 turnover assay conditions. E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 are microtubule-disrupting agents that prevent the combination of autophagosome through lysosome. Therefore, treatment of lysosomotropic reagents promotes assembly of LC3-II as well as p62 during autophagosome formation. When the accumulation of autolysosome was inhibited by E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1, p62 level was significantly increased in response to GT treatment due to the impaired p62 degradation (Figs. 7C, 7D). These results suggest that autophagic flux induced by GT could be inhibited by lysosomotropic agents in the autophagic degradation stage in cortical astrocytes.
Fig. 7.
GT treatment reduced autophagy substrates p62/SQSTM1 in astrocytes. (A, B) p62/SQSTM1 was determined from dose- and time-dependent effects of GT in astrocytes via immunoblotting. (C, D) Astrocytes were pretreated through E-64d and pepstatin A or bafilomycin A1 for 1 h in the absence/presence of 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. p62/SQSTM1 was examined by immunoblotting. All protein band intensities were examined using Image J. Presenting data were expressed as the mean ± SEM, and analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant).
ANOVA, analysis of variance; GT, gintonin; SEM, standard error of mean.
3.8. GT dose- and time-dependently upregulates lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 in cortical astrocytes
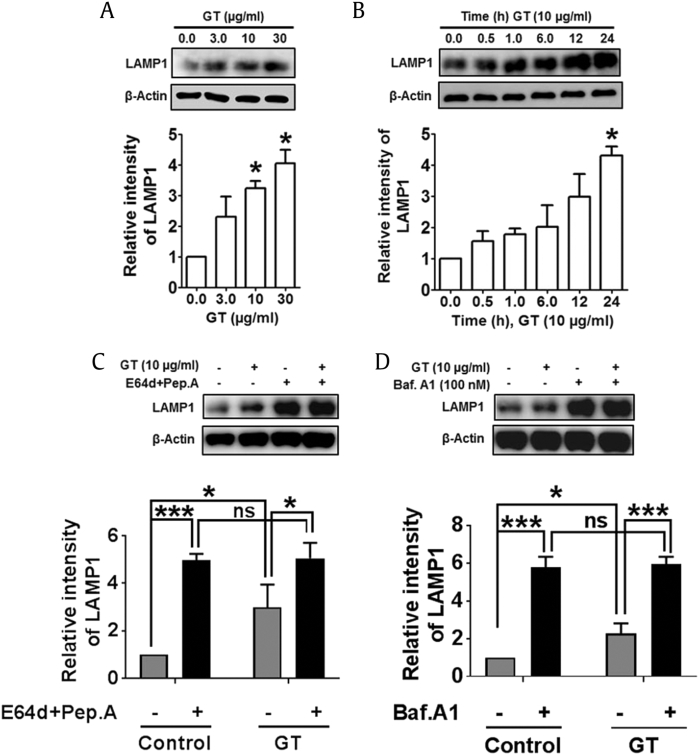
Autophagosome is impaired when lysosome protein number declines or when there is a selective diminishing in autophagosome and lysosome fusion or lysosome function [40]. Thus, we examined the expression of the lysosome membrane proteins lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1) that can also be expressed in the cell surface of lysosomal fusion. Immunoblot analysis showed that GT treatment dose- and time-dependently upregulated LAMP1 in astrocytes culture (Figs. 8A, 8B). Finally, to examine whether the increased levels of LAMP1 resulted from the impairment in autophagic flux, we inhibited LC3/autophagosome degradation with E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1. Interestingly, we found that inhibition of autophagy by lysosomotropic agents significantly increased LAMP1 expression, and the cotreatment with GT also significantly enhanced LAMP1 expression levels in cortical astrocytes (Figs. 8C, 8D). Therefore, these data suggest that LAMP1 accumulates in the cytosol as a result of GT-induced autophagy and that impaired autophagic flux induces LAMP1 in mouse cortical astrocytes.
Fig. 8.
GT-mediated regulation of autophagy–lysosome pathway in astrocytes. (A, B) Represented LAMP1 expressions were determined in a concentration-and time-dependent experiment of GT in astrocytes via immunoblotting. (C, D) Astrocytes were pretreated with E-64d and pepstatin A or bafilomycin A1 for 1 h in the absence/presence of 10 μg/mL of GT for 24 h. LAMP1 was measured by immunoblotting. (F, H) All representating protein band intensities were examined using Image J, and statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns = non-significant).
ANOVA, analysis of variance; GT, gintoninl LAMP1, lysosome-associated membrane protein 1.
4. Discussion
Autophagic degradation is a dynamically and tightly regulated pathway and extremely inducible progression during which damaged/misfolded proteins or organelles are encapsulated in the double-membrane structure of autophagy vesicles. The encapsulated proteins and organelles are then combined with lysosomes for degradation or recycling other products [41]. Abnormal protein aggregates are correlated with dysregulation of autophagic flux, which may lead to neurodegeneration in the CNS [16]. Accordingly, small-molecule autophagy enhancers might be used as wide-ranging therapeutics to rescue the impairment of autophagic flux in neurodegenerative disease. In this study, we found that a natural bioactive compound ginseng, GT, significantly enhances autophagy in addition to the expression of several Atgs such as Beclin1, Atg5, Atg7, and LC3. We also found that GT increases autophagic flux and upregulates the expression of lysosomal protein LAMP1 through ubiquitinated degradation of p62/SQSTM1 protein. Therefore, our findings could be suggested that GT may be used as an autophagic inducing agent in astrocytes as a potential regulator of neurodegeneration in future studies.
To the best of our understanding, the current work is the first investigation to explain that GT, an active component of ginseng, is responsible for the enhancement of autophagy in mouse cortical primary astrocytes via G protein–coupled LPA receptors–mediated pathways. It has been previously described that GT precisely and effectively activates the G protein–coupled LPA receptors and that the molecular actions of ginseng compounds are recently linked to LPA [42]. This linkage explores a new dimension of pharmacological functions of ginseng and LPA interaction in therapeutics application. We showed that GT treatment dose- and time-dependently increases the most important autophagy protein LC3-II and that the autophagy inhibitor, 3-MA, significantly reduces GT-induced LC3-II and LC3 puncta formation (Fig. 1, Fig. 2). We also showed that GT treatment does not show any neuroinflammation when cotreated with neuroinflammatory compound, LPS and IFN-β. On the other hand, Ki16425, selective LPA inhibitor, abrogated GT-induced autophagy which might indicate the involvement of GPCR LPA receptors. Currently, there is no exactly detailed molecular mechanism of how Ki16425 inhibits GT-mediated modulation of autophagy in astrocyte cells, and further study is necessary to reveal exact molecular actions of how Ki16425 in addition to LPA receptors participate through GT-enhanced autophagy induction in cortical astrocytes.
Based on the previous observation, a conventional model of autophagy in mammalian cells comprises Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1 (ULK1) , a main proautophagy adapter kinase, necessary for nucleation of the phagophore membrane formation to initiate autophagy. However, ULK1 activation is required for both mTOR complex 1 and energy-sensitive AMPK expression which stimulates autophagy in mTOR-dependent pathway [43]. In detail, AMPK is phosphorylated, activated by LKB1 kinase, during low energy state as well as nutrient deprivation and thereby directly activates TSC1/2 complex toward Rheb to inhibit mTOR complex 1 signaling [44]. In addition, stimulation of AMPK in yeast inhibits mTOR and activates autophagy process [45]. Similarly, it has been shown that blocking of AMPK activity pharmacologically in mammalian cells with compound C inhibits autophagy [46]. From our examination, we found that GT treatment dose-dependently increases phospho-AMPK and decreases phospho-S6 ribosomal protein during the autophagy. In addition, we also found that GT-mediated increase in the autophagy protein LC3 is significantly reduced in astrocytes when pretreated by compound C, suggesting the association of the AMPK signaling (Fig. 3). Furthermore, inhibition of mTOR complex 1, rapamycin, and induction of autophagy are associated with decreased phosphorylation of its downstream effectors such as S6 ribosomal protein (Ser240/244) and translation initiation factor of 4E-binding protein-1 [47]. The present study elucidated that GT induction concentration-dependently downregulated the levels of phospho-S6 ribosomal protein and that similarly rapamycin cotreatment with GT significantly improved autophagy in astrocytes (Fig. 3). However, recent studies indicated that statin, a lipid-reducing medication, induces autophagy in astrocytes culture through AMPK-mTOR–mediated pathway, and thus, autophagy modulation might be responsible for therapeutic strategies pathology in Aβ by enhancing removal of Aβ toxicity [48]. From these observations, we conclude that GT-mediated autophagy could be activated via an AMPK-activated mTOR-dependent pathway.
Importantly, gene knockdown of autophagy explains an additional precise method than pharmacological inhibition of autophagy. So far, deficiency of basal autophagy has been confirmed in the absence of numerous Atg gene such as Atg5 [49], Atg7 [50], Atg9a [51], Atg16L1 [52], Beclin 1 [53], Ambra1 [54], and FIP200 [14] in cells. These genes must act as a first target for autophagy initiation for phagophore formation. Thus, when studying the role of a specific important autophagy gene with knockdown approaches, other investigators suggest that not only to check actual knockdown of targeted autophagy protein expression through each target siRNA but also to confirm effective autophagy inhibitor by well-known autophagy-inducing agents. In the present investigation, we observed that Beclin-1, Atg5, and Atg7 siRNA intensely inhibited Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 expression and also decreased LC3 levels, representing defects in autophagy pathway due to the lack of autophagy initiation protein. Then, we explored the function of Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 siRNA knockdown by immunostaining; the LC3 puncta levels were significantly decreased compared with the control siRNA in astrocytes (Fig. 4, Fig. 5). Recently, it has been reported that natural compound 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid– [32] and oxyresveratrol- [30] mediated autophagy showed accumulation of Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 and that individual siRNAs prevented autophagy in neuroblastoma cells. Furthermore, another latest study recommends that berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, decreases Aβ deposits after chronic administration in 3XTg AD mice model via increasing autophagy in class III PI3K/beclin-1 signaling pathway [55]. Collectively, our results indicate that Atg5, Atg7, and Beclin-1 participate in astrocytes autophagosome initiation after GT treatment and that the knockdown of these genes decreases autophagic flux.
Furthermost, for many experimental conditions, it is essential to differentiate whether the accumulation of autophagosome is due to autophagy stimulation or the blockage of downstream autophagy steps by accomplishing “autophagic flux” analyses [56]. It has been mentioned that the measurement of entire quantities of autophagosomes and autolysosomes detection could help distinguish among overall autophagy activation. Both the amounts of autophagosomes and autolysosomes and a blockage of autophagosome maturation that might be related with an enhancement of autophagosome quantities without a significant change in autolysosomes during autophagy process have been increased [56]. However, Western blotting for endogenous LC3-II is one of the crucial measurement assays that could be applied to consistently observe autophagosome production or degradation with an amount of reprocessing taking place in the cytosolic surface of cells [56]. The simultaneous application of autophagosome–lysosome fusion inhibitors such as combinations of E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 which blocks the conjugation with lysosome or prevents lysosomal proteases at saturating concentrations is widely used in vitro to determine the activity of autophagic flux [57]. It only designates whether an enhanced LC3-II in Western blot signal is mediated by increased autophagosome production or by a reduction in autophagosome degradation in autophagy process. In the present study, we found that LC3-II proteins are enhanced through combined treatment with E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 even without GT treatment (Fig. 6). However, the difference in LC3-II levels in the absence/presence of bafilomycin A1 or E-64d/peps A is larger in response to GT treatment (Fig. 6), indicating that GT enhanced autophagic flux. There have been similar findings indicating that a sialic acid–containing glycosphingolipids, gangliosides, enhanced a puncta formation of fluorescently tagged LC3 in primary astrocyte culture in ICR mice when treated with lysosomotropic agents [58]. Based on the studies discussed previously, the present investigation shows that GT is capable of increasing a punctate distribution which enhances autophagosome synthesis by induction of autophagic flux in astrocytes.
In several other investigations, the quantification of cellular p62/SQSTM1 seems to relate with additional parameters with autophagic flux determination, and assay appears pretty promising. However, p62 and LC3 could be transcriptionally controlled through autophagy and may distinguish in the clarification of p62 as well as LC3 which are main indicators of autophagic flux determination [59]. Therefore, we also examined the quantification of an important autophagic substrate p62 in addition to another autonomous experiment to estimate autophagic flux induced by GT. Our immunoblotting result indicates that when autophagosome–lysosome fusion is blocked by E-64d/peps A and bafilomycin A1, p62 protein increases in GT-treated cells and that increasing LC3-II diminishes p62 degradation of cortical astrocytes (Fig. 6, Fig. 7). These findings are similar to the impairment of autophagic flux in astrocyte cells when intoxicated by trimethyltin after treatment with lysosomotropic agents [60]. Furthermore, it has been found that lysosomes are responsible for degrading many macromolecules that are derived from an extracellular space via phagocytosis or endocytosis during autophagy [61]. Moreover, LAMP-1 might be responsible in interaction as well as fusion of lysosomes with themselves and other cell constituents such as phagosomes, endosomes, and plasma membrane [62], although its specific actions are basically unknown. To address the specific functions of LAMP1 in GT-mediated autophagy pathway, we used lysosomotropic agents, E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1, which prevent binding of lysosome to autophagosome. Therefore, our Western blot data show that inhibition of autophagy by E-64d/peps A or bafilomycin A1 increases LAMP1 expression and that cotreatment with GT also increased LAMP1 expression (Fig. 8). These data suggested that LAMP1 accumulation in the cytosol is the product of GT-mediated autophagy, and the inhibition of autophagy could exhibit more LAMP1 upregulation in cortical astrocytes.
It is important for natural product research for the reliable means of bioavailability improvement because some naturally occurring compounds are economical, safe, nontoxic, nonadditive, nonallergenic, and pharmacologically inert in nature, although oral bioavailability of ginsenosides is very poor because it cannot be easily absorbed by the intestines due to its hydrophilic properties [63]. In addition to the ginsenosides, other components are found in ginseng, such as flavonoids, polysaccharides, volatile oils, and the nonsaponin compound so-called gintonin [64]. There were no studies regarding the bioavailability properties of GT. However, in the everted sac system, permeation increase as the GT concentration increases from 0.1 mg/mL to 5 mg/mL, and GT permeation into the sac became saturated at approximately 3 mg/mL [65], which suggests that GT might be also absorbed through an intestinal transporter. Therefore, our indicated concentrations of GT may have effectively reached the brain, although it remains to be evaluated in a future study. Recently, it has been found that GT labeled with fluorophore bound to neurons, endothelial cells, and glia in the brain subsequent its entrance to the brain through the paracellular pathway [66]. Thus, GT might be an herbal medicine–derived candidate to reach the brain through Blood–brain barrier (BBB) .
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “Korea Research Fellowship Program” (2016H1D3A1908615) and the NRF Research Program (2016M3C7A1913845), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and also supported by the KIST Institutional Programs (Project No. 2E26820).
Footnotes
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2018.08.004
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the supplementary data related to this article:
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Supplementary Fig. 3.
References
- 1.Mizushima N., Levine B., Cuervo A.M., Klionsky D.J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature. 2008;451:1069–1075. doi: 10.1038/nature06639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Komatsu M., Waguri S., Chiba T., Murata S., Iwata J., Tanida I., Ueno T., Koike M., Uchiyama Y., Kominami E. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature. 2006;441:880–884. doi: 10.1038/nature04723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Singh R., Kaushik S., Wang Y., Xiang Y., Novak I., Komatsu M., Tanaka K., Cuervo A.M., Czaja M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 2009;458:1131–1135. doi: 10.1038/nature07976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rubinsztein D.C., Marino G., Kroemer G. Autophagy and aging. Cell. 2011;146:682–695. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Toth M.L., Sigmond T., Borsos E., Barna J., Erdelyi P., Takacs-Vellai K., Orosz L., Kovacs A.L., Csikos G., Sass M. Longevity pathways converge on autophagy genes to regulate life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Autophagy. 2008;4:330–338. doi: 10.4161/auto.5618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Simonsen A., Cumming R.C., Brech A., Isakson P., Schubert D.R., Finley K.D. Promoting basal levels of autophagy in the nervous system enhances longevity and oxidant resistance in adult Drosophila. Autophagy. 2008;4:176–184. doi: 10.4161/auto.5269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Meng Q., Cai D. Defective hypothalamic autophagy directs the central pathogenesis of obesity via the IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta)/NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:32324–32332. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.254417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yang L., Li P., Fu S., Calay E.S., Hotamisligil G.S. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2010;11:467–478. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jung H.S., Lee M.S. Role of autophagy in diabetes and mitochondria. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010;1201:79–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Spilman P., Podlutskaya N., Hart M.J., Debnath J., Gorostiza O., Bredesen D., Richardson A., Strong R., Galvan V. Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rodriguez-Navarro J.A., Rodriguez L., Casarejos M.J., Solano R.M., Gomez A., Perucho J., Cuervo A.M., Garcia de Yebenes J., Mena M.A. Trehalose ameliorates dopaminergic and tau pathology in parkin deleted/tau overexpressing mice through autophagy activation. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;39:423–438. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pan T., Kondo S., Le W., Jankovic J. The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2008;131:1969–1978. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ravikumar B., Vacher C., Berger Z., Davies J.E., Luo S., Oroz L.G., Scaravilli F., Easton D.F., Duden R., O’Kane C.J. Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet. 2004;36:585–595. doi: 10.1038/ng1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hara T., Takamura A., Kishi C., Iemura S.I., Natsume T., Guan J.L., Mizushima N. FIP200, a ULK-interacting protein, is required for autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 2008;181:497–510. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200712064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hernandez D., Torres C.A., Setlik W., Cebrian C., V Mosharov E., Tang G., Cheng H.C., Kholodilov N., Yarygina O., Burke R.E. Regulation of presynaptic neurotransmission by macroautophagy. Neuron. 2012;74:277–284. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Komatsu M., Wang Q.J., Holstein G.R., Friedrich V.L.J., Iwata J., Kominami E., Chait B.T., Tanaka K., Yue Z. Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:14489–14494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701311104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nixon R.A. The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 2013;19:983–997. doi: 10.1038/nm.3232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Choi S.H., Jung S.W., Lee B.H., Kim H.J., Hwang S.H., Kim H.K., Nah S.Y. Ginseng pharmacology: a new paradigm based on gintonin-lysophosphatidic acid receptor interactions. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shin T.J., Kim H.J., Kwon B.J., Choi S.H., Kim H.B., Hwang S.H., Lee B.H., Lee S.M., Zukin R.S., Park J.H. Gintonin, a ginseng-derived novel ingredient, evokes long-term potentiation through N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activation: involvement of LPA receptors. Mol Cells. 2012;34:563–572. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0254-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Park H., Kim S., Rhee J., Kim H.J., Han J.S., Nah S.Y., Chung C. Synaptic enhancement induced by gintonin via lysophosphatidic acid receptor activation in central synapses. J Neurophysiol. 2015;113:1493–1500. doi: 10.1152/jn.00667.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim S., Kim M.S., Park K., Kim H.J., Jung S.W., Nah S.Y., Han J.S., Chung C. Hippocampus-dependent cognitive enhancement induced by systemic gintonin administration. J Ginseng Res. 2016;40:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hwang S.H., Shin E.J., Shin T.J., Lee B.H., Choi S.H., Kang J., Kim H.J., Kwon S.H., Jang C.G., Lee J.H. Gintonin, a ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, attenuates Alzheimer's disease-related neuropathies: involvement of non-amyloidogenic processing. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31:207–223. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim H.J., Shin E.J., Lee B.H., Choi S.H., Jung S.W., Cho I.H., Hwang S.H., Kim J.Y., Han J.S., Chung C. Oral administration of gintonin attenuates cholinergic impairments by scopolamine, amyloid-beta protein, and mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Cells. 2015;38:796–805. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Choi S.H., Shin T.J., Lee B.H., Hwang S.H., Kang J., Kim H.J., Park C.W., Nah S.Y. An edible gintonin preparation from ginseng. J Ginseng Res. 2011;35:471–478. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2011.35.4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ohta H., Sato K., Murata N., Damirin A., Malchinkhuu E., Kon J., Kimura T., Tobo M., Yamazaki Y., Watanabe T. Ki16425, a subtype-selective antagonist for EDG-family lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:994–1005. doi: 10.1124/mol.64.4.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Eikelenboom P., Hoozemans J.J., Veerhuis R., van Exel E., Rozemuller A.J., van Gool W.A. Whether, when and how chronic inflammation increases the risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2012;4:15. doi: 10.1186/alzrt118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Law B.Y.K., Wang M., Ma D.L., Al-Mousa F., Michelangeli F., Cheng S.H., Ng M.H.L., To K.F., Mok A.Y.F., Ko R.Y.Y. Alisol B, a novel inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase pump, induces autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:718–730. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mizushima N., Klionsky D.J. Protein turnover via autophagy: implications for metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 2007;27:19–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shaw R.J. LKB1 and AMP-activated protein kinase control of mTOR signalling and growth. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2009;196:65–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.01972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rahman M.A., Bishayee K., Sadra A., Huh S.O. Oxyresveratrol activates parallel apoptotic and autophagic cell death pathways in neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1861:23–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Levine B., Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 2008;132:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rahman M.A., Bishayee K., Habib K., Sadra A., Huh S.O. 18alpha-Glycyrrhetinic acid lethality for neuroblastoma cells via de-regulating the Beclin-1/Bcl-2 complex and inducing apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;117:97–112. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.He C., Levine B. The Beclin 1 interactome. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:140–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liang X.H., Kleeman L.K., Jiang H.H., Gordon G., Goldman J.E., Berry G., Herman B., Levine B. Protection against fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a novel Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 1998;72:8586–8596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.11.8586-8596.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mizushima N., Yoshimori T., Levine B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 2010;140:313–326. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tanida I., Minematsu-Ikeguchi N., Ueno T., Kominami E. Lysosomal turnover, but not a cellular level, of endogenous LC3 is a marker for autophagy. Autophagy. 2005;1:84–91. doi: 10.4161/auto.1.2.1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mizushima N., Yoshimori T. How to interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 2007;3:542–545. doi: 10.4161/auto.4600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bjorkoy G., Lamark T., Brech A., Outzen H., Perander M., Overvatn A., Stenmark H., Johansen T. p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 2005;171:603–614. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bjorkoy G., Lamark T., Pankiv S., Overvatn A., Brech A., Johansen T. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 2009;452:181–197. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)03612-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ma X., Godar R.J., Liu H., Diwan A. Enhancing lysosome biogenesis attenuates BNIP3-induced cardiomyocyte death. Autophagy. 2012;8:297–309. doi: 10.4161/auto.18658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kraft C., Peter M., Hofmann K. Selective autophagy: ubiquitin-mediated recognition and beyond. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:836–841. doi: 10.1038/ncb0910-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Im D., Nah S. Yin and Yang of ginseng pharmacology: ginsenosides vs gintonin. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34:1367–1373. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim J., Kundu M., Viollet B., Guan K.L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:132–141. doi: 10.1038/ncb2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sarkar S. Regulation of autophagy by mTOR-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways: autophagy dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic application of autophagy enhancers. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41:1103–1130. doi: 10.1042/BST20130134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang Z., Wilson W.A., Fujino M.A., Roach P.J. Antagonistic controls of autophagy and glycogen accumulation by Snf1p, the yeast homolog of AMP-activated protein kinase, and the cyclin-dependent kinase Pho85p. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:5742–5752. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.17.5742-5752.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Meley D., Bauvy C., Houben-Weerts J.H.P.M., Dubbelhuis P.F., Helmond M.T.J., Codogno P., Meijer A.J. AMP-activated protein kinase and the regulation of autophagic proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:34870–34879. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605488200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Neshat M.S., Mellinghoff I.K., Tran C., Stiles B., Thomas G., Petersen R., Frost P., Gibbons J.J., Wu H., Sawyers C.L. Enhanced sensitivity of PTEN-deficient tumors to inhibition of FRAP/mTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10314–10319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.171076798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Son S.M., Kang S., Choi H., Mook-Jung I. Statins induce insulin-degrading enzyme secretion from astrocytes via an autophagy-based unconventional secretory pathway. Mol Neurodegener. 2015;10:56. doi: 10.1186/s13024-015-0054-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mizushima N., Yamamoto A., Hatano M., Kobayashi Y., Kabeya Y., Suzuki K., Tokuhisa T., Ohsumi Y., Yoshimori T. Dissection of autophagosome formation using Apg5-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biol. 2001;152:657–668. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Komatsu M., Waguri S., Ueno T., Iwata J., Murata S., Tanida I., Ezaki J., Mizushima N., Ohsumi Y., Uchiyama Y. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2005;169:425–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200412022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Saitoh T., Fujita N., Hayashi T., Takahara K., Satoh T., Lee H., Matsunaga K., Kageyama S., Omori H., Noda T. Atg9a controls dsDNA-driven dynamic translocation of STING and the innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:20842–20846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911267106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cadwell K., Liu J.Y., Brown S.L., Miyoshi H., Loh J., Lennerz J.K., Kishi C., Kc W., Carrero J.A., Hunt S. A key role for autophagy and the autophagy gene Atg16l1 in mouse and human intestinal Paneth cells. Nature. 2008;456:259–263. doi: 10.1038/nature07416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Qu X., Yu J., Bhagat G., Furuya N., Hibshoosh H., Troxel A., Rosen J., Eskelinen E.L., Mizushima N., Ohsumi Y. Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1809–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI20039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Fimia G.M., Stoykova A., Romagnoli A., Giunta L., Di Bartolomeo S., Nardacci R., Corazzari M., Fuoco C., Ucar A., Schwartz P. Ambra1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system. Nature. 2007;447:1121–1125. doi: 10.1038/nature05925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Huang M., Jiang X., Liang Y., Liu Q., Chen S., Guo Y. Berberine improves cognitive impairment by promoting autophagic clearance and inhibiting production of beta-amyloid in APP/tau/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Exp Gerontol. 2017;91:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mizushima N., Yoshimori T., Ohsumi Y. The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:107–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rubinsztein D.C., Cuervo A.M., Ravikumar B., Sarkar S., Korolchuk V., Kaushik S., Klionsky D.J. In search of an “autophagomometer”. Autophagy. 2009;5:585–589. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.5.8823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hwang J., Lee S., Lee J.T., Kwon T.K., Kim D.R., Kim H., Park H.C., Suk K. Gangliosides induce autophagic cell death in astrocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:586–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.He C., Klionsky D.J. Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:67–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102808-114910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fabrizi C., Pompili E., De Vito S., Somma F., Catizone A., Ricci G., Lenzi P., Fornai F., Fumagalli L. Impairment of the autophagic flux in astrocytes intoxicated by trimethyltin. Neurotoxicology. 2016;52:12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Eskelinen E.L., Tanaka Y., Saftig P. At the acidic edge: emerging functions for lysosomal membrane proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:137–145. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(03)00005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fukuda M. Lysosomal membrane glycoproteins. Structure, biosynthesis, and intracellular trafficking. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:21327–21330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kim D.H. Chemical diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng. J Ginseng Res. 2012;36:1–15. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2012.36.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pyo M.K., Choi S.H., Hwang S.H., Shin T.J., Lee B.H., Lee S.M., Lim Y.H., Kim D.H., Nah S.Y. Novel glycolipoproteins from ginseng. J Ginseng Res. 2011;35:92–103. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lee B.H., Choi S.H., Kim H.J., Park S.D., Rhim H., Kim H.C., Hwang S.H., Nah S.Y. Gintonin absorption in intestinal model systems. J Ginseng Res. 2018;42:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim D.G., Jang M., Choi S.H., Kim H.J., Jhun H., Kim H.C., Rhim H., Cho I.H., Nah S.Y. Gintonin, a ginseng-derived exogenous lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, enhances blood-brain barrier permeability and brain delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;114:1325–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.