Abstract
Background and study aims Standard endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of ileocecal valve (ICV) polyps is challenging. Cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection (C-EMR) can be performed when polyps are not easily amenable to standard EMR. Current literature is limited regarding its efficacy and safety for ICV polyps. The objectives of this study were to assess the efficacy and safety of C-EMR for ICV polyps.
Patients and methods A retrospective review was conducted from September 2008 to November 2018 at a tertiary care center. Patients included in the study underwent C-EMR for ICV polyps by a single gastroenterologist (LHJ). Polyps were successfully eradicated if they were removed en-bloc as confirmed by pathology, or had a negative biopsy on follow-up colonoscopy. Outcomes of the procedures were evaluated, including complete adenoma clearance and adverse events.
Results Twenty-one ICV polyps were removed with C-EMR. Median polyp size was 15 mm (range, 5–45). The rate of complete adenoma clearance was 100 %. Procedure-related complications occurred in five patients (24 %): delayed GI bleeding (4.8 %) and deep mucosal resection/visible vessel (14.3 %). Three patients had subsequent surveillance colonoscopies at 8, 56, and 67 months, respectively. The third patient was found to have a 6-mm flat polyp at the edge of the previous polypectomy site. This was treated with C-EMR and repeat colonoscopy 6 months later did not show residual.
Conclusion C-EMR is highly effective in treating ICV polyps with a low complication rate. It is our suggested method in approaching ICV polyps that are difficult to remove via standard freehand snare EMR technique.
Introduction
Ileocecal valve (ICV) polyps are hard to manage with standard endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) 1 . They can be hard to visualize due to large cecal folds, and have a high risk of perforation given the thin colonic wall 1 . These factors make it endoscopically challenging to perform a complete endoscopic resection. Cap-assisted EMR (C-EMR) using a straight distal attachment with a rim was introduced to address polyps not easily amenable to standard EMR 2 . The distal cap attachment improves visualization of the operative field and facilitates resecting lesions in difficult locations 2 . However, C-EMR has not been used frequently in the colon due to fear of perforation 3 4 . To date, only limited studies have evaluated the efficacy and safety of C-EMR for ICV polyps 3 5 .
In this case series, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of C-EMR in the removal of ICV polyps.
Patients and methods
Study design
This study was a retrospective chart review of patients who underwent C-EMR for ICV polyps at a tertiary care center between September 2008 and November 2018. There were eight patients in this cohort that overlapped with our previous study, which reported the efficacy of C-EMR in nonpedunculated colorectal lesions 4 .
In this study, we reported procedural outcomes including complete adenoma clearance, adverse events, hospitalization rate due to procedure-related adverse events, and length of hospitalization. Complete adenoma clearance was considered successful if one of the following criteria was met: negative biopsy on follow-up colonoscopy; en bloc resection with negative margins on the pathology report; or surgical resection of the polypectomy site after C-EMR with negative post-surgical pathology. Reported procedure-related technical variables were C-EMR techniques (en bloc versus piecemeal), adjunctive therapies (Argon plasma coagulation [APC], etc.), submucosal injection volume, and mucosal defect closure. Polyp morphology (size and histology) was also described.
All research-related activities were approved by the Institutional Review Board at our medical center.
Endoscopy
All C-EMRs were performed by a single gastroenterologist (LHJ) who uses this technique frequently to remove flat and sessile polyps in the colon; his experience was recently published 4 . The decision to use C-EMR was made on a case-by-case basis. In most cases, a colonoscopy was first performed without a cap. Once the lesion was evaluated, including evaluating the proximal border of the polyp when it extended into the ICV and terminal ileum, a decision was made whether to use the cap. In general, C-EMR was used for flat and sessile polyps when it was determined that an en-bloc resection with a free-hand snare technique would not be successful. Pediatric colonoscopes were used for all procedures (Olympus PCF 180/190). C-EMR was performed using the components of an EMR kit (K-002, Olympus, America Inc.); a transparent, hard, and straight plastic cap with a rim with an outer diameter of 14.9 mm attached to the tip of the pediatric colonoscopes. A crescent-type snare (SD-221U-25, Olympus, America, Inc.) was used for resection. A mixture of epinephrine 1:1,000 (2 ml), and indigo carmine 0.8 % (2 mL) or methylene blue 0.05 % (2 mL) diluted in normal saline 0.9 % (100 ml) was used for submucosal injection. The technique for C-EMR for colon polyps has been previously published 4 .
Results
A total of 21 patients (6 women, 15 men) underwent C-EMR for ICV polyps. Median age was 67 years (range, 53–79). Piecemeal resection was performed on 14 polyps, and en bloc resection was performed on seven polyps. All polyps were on the lip of the ICV, with one invading into the terminal ileum and seven invading into the cecum. Characteristics of the polyps in respect to the applied polypectomy techniques are shown in Table 1 .
Table 1. Characteristics of polyps removed using piecemeal of en bloc C-EMR.
| Technique | No. polyps | Amt. of submucosal injection (mL) | Polyp size (mm) | Location | Morphology (flat/sessile) | Histology |
| Piecemeal | 14 | 30 (7–80) | 20 (10–45) | Lip of ICV: 9 Invading into cecum: 4 Invading into terminal ileum: 1 | 9/5 | 6 TA, 5 TVA, 2 SSA, 1 inflammatory |
| En bloc | 7 | 17.5 (6–70) | 15 (5–20) | Lip of ICV: 5 Invading into cecum: 2 Invading into terminal ileum: 0 | 5/2 | 1 adenocarcinoma 4 TA 1 TVA 1 lipoma |
| Overall | 21 | 28 (6–80) | 15 (5–45) | Lip of ICV: 14 Invading into cecum: 6 Invading into terminal ileum: 1 | 14/7 | 10 TA, 6 TVA, 2 SSA, 1 inflammatory, 1 lipoma, 1 adenocarcinoma |
C-EMR, cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection; ICV, ileocecal valve;l TA, tubular adenoma; TVA, tubulovillous adenoma; SSA, sessile serrated.
Efficacy of C-EMR
Video 1 En-Block resection of a 15 mm lateral spreading tumor on the IC valve with C-EMR.
C-EMR was performed in piecemeal fashion in 14 polyps (median size: 20 mm; range: 10–45) and via en bloc resection in 7 polyps (median size: 15 mm; range: 5–20). Median volume of submucosal injection was 28 mL (range: 6–70). C-EMR was the primary polypectomy technique in all patients, except two2 patients who underwent free-hand snare resection for debulking. Adjunctive therapies included using APC or tip of the hot snare on the edges in nine patients (43 %). Two patients (9.5 %) required coagulation grasper for visible vessels at the base of the resection, and one patient (4.8 %) required endoscopic hemoclips for closure of the EMR defect. There were 10 (47.6 %) tubular adenomas, six (28.6 %) tubulovillious adenomas, two (9.5 %) sessile serrated adenomas, one (4.8 %) inflammatory polyp, one (4.8 %) lipoma, and one (4.8 %) adenocarcinoma. A detailed description of each polyp’s morphology, histology, polypectomy techniques and adjunctive therapies, and length of follow-up is shown in Table 2 . Fig. 1 , Fig. 2 , Fig. 3 , Fig. 4 , and Fig. 5 and Video 1 are an example of an ICV polyp being removed with C-EMR. The polyp is a 1.5-cm lateral spreading tumor on the outer lip of the ICV polyp, which was removed en bloc with C-EMR.
Table 2. Patient characteristics and outcomes of C-EMR.
| Patient no. | Morphology | Location | Size (mm) | Polypectomy technique | Adjunct techniques | Histology | Follow-up (months) |
| 1 | Sessile | Lip of ICV | 15 | Piecemeal | APC | TA | 25 |
| 2 | Sessile | Lip of ICV | 10 | En bloc | None | Adenocarcinoma | 2 |
| 3 | Sessile | Lip of ICV | 20 | Piecemeal | APC/snare | TVA | Patient declined |
| 4 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 6 | En bloc | None | TA | 5 |
| 5 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 15 | Piecemeal | None | TVA | Lost to follow up |
| 6 | Sessile | Invading into terminal ileum | 25 | Piecemeal | None | TA | 3 |
| 7 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 20 | Piecemeal | APC | TVA | 6 |
| 8 | Flat | Invading into cecum | 20 | Piecemeal | APC/snare | SSA | 4, 67 |
| 9 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 15 | Piecemeal | Snare | Inflammatory | 36 |
| 10 | Flat | Invading into cecum | 20 | En bloc | None | TA | 4 |
| 11 | Sessile | Invading into cecum | 15 | Piecemeal | APC | TVA | 3 |
| 12 | Flat | Invading into cecum | 35 | Piecemeal | Snare | TVA | 3, 8 |
| 13 | Sessile | Invading into cecum | 15 | En bloc | None | TA | 3, 56 |
| 14 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 10 | Piecemeal | APC/snare | TA | 7 |
| 15 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 10 | En bloc | Coagulation grasper for visible vessels | TA | NI |
| 16 | Flat | Invading into cecum | 45 | Piecemeal | Coagulation grasper for visible vessels | TVA with areas approaching high grade dysplasia | Declined follow up given terminal diagnosis of liver cancer |
| 17 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 15 | En bloc | Snare | TA | NI |
| 18 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 20 | Piecemeal | None | SSA | 8 |
| 19 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 20 | Piecemeal | Hemoclips to prevent bleeding | TA | 7 |
| 20 | Flat | Lip of ICV | 5 | En bloc | None | Lipoma | NI |
| 21 | Sessile | Lip of ICV | 10 | Piecemeal | APC | TVA | 7 |
C-EMR, cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection; ICV, ileocecal valve; APC, argon plasma coagulation; TA, tubular adenoma; TVA, tubulovillous adenoma; SSA, sessile serrated adenoma; NA, not available; NI, not indicated.
Fig. 1.
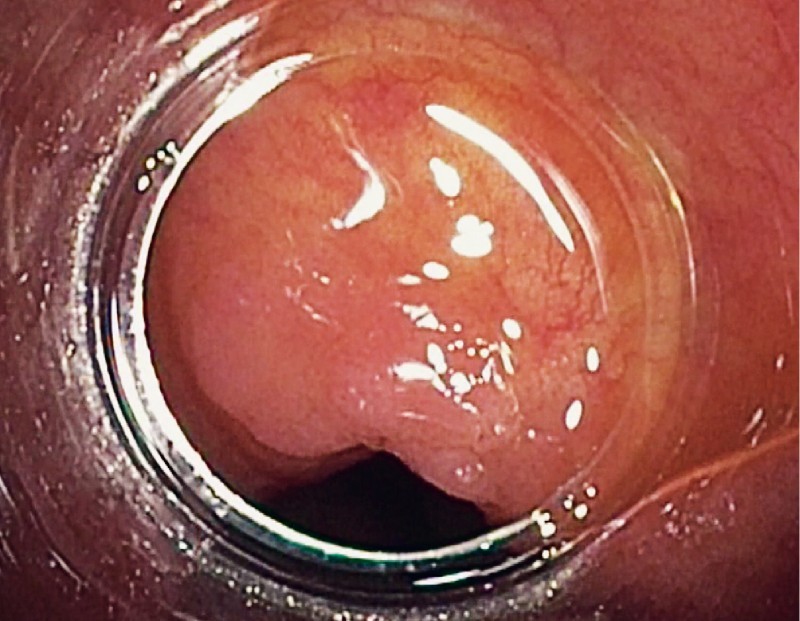
High definition white light view of ICV polyp.
Fig. 2.
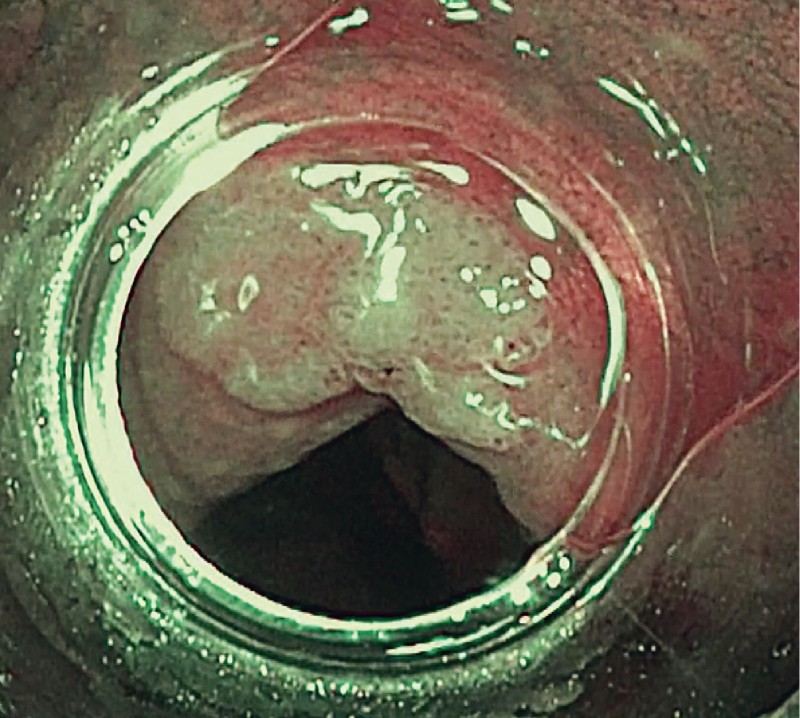
Narrow band imaging view of ICV polyp.
Fig. 3.
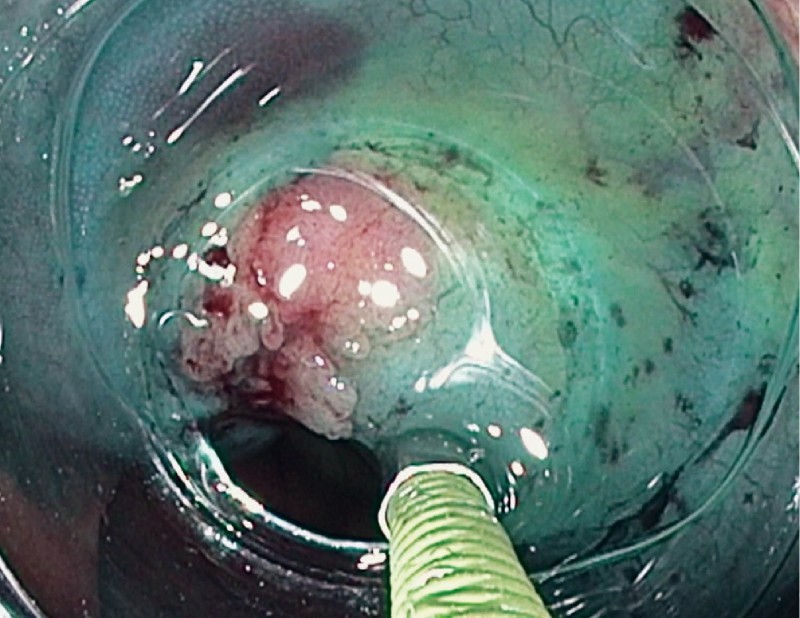
Submucosal injection to lift ICV polyp.
Fig. 4.
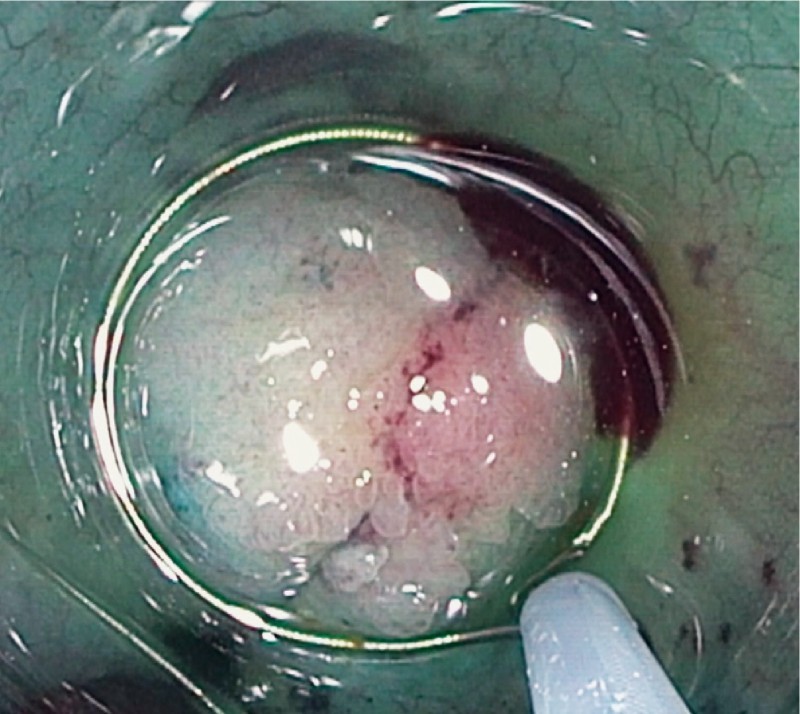
Snare around an ICV polyp.
Fig. 5.
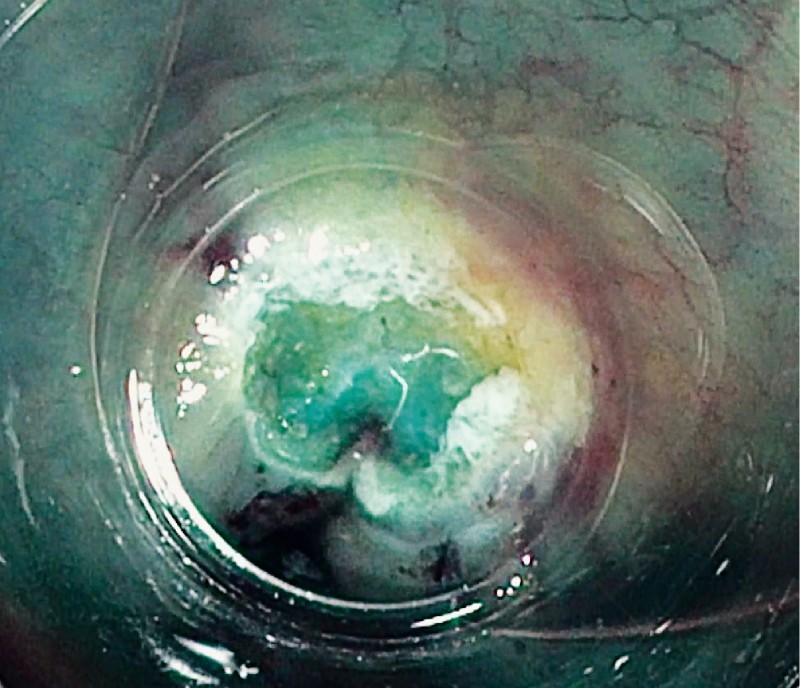
Post C-EMR en bloc resection of ICV polyp.
Of the seven patients with en bloc resection, pathology in four patients could not confirm negative margins due to fragmented specimen; these patients underwent a follow-up colonoscopy. The remaining three patients had negative margins on pathology, so follow-up colonoscopy was deemed unnecessary. Of those patients with piecemeal resection, follow-up colonoscopy was not performed in three patients: one patient was lost to follow-up, one patient declined repeat colonoscopy, and one patient was later diagnosed with an end-stage malignancy. Follow-up colonoscopy was performed with a median of 5 months (range: 2–36). Complete adenoma clearance was 100 % (18/18). The polyp containing adenocarcinoma had 2-mm depth of submucosal invasion with the presence of lymphovascular invasion. En bloc resection was performed with a negative margin confirmed by pathology. Due to lymphovascular invasion, the patient underwent right hemicolectomy with lymph node dissection. Although the surgically resected segment of the colon did not harbor any residual adenocarcinoma, one of 12 dissected lymph nodes was positive for metastasis.
Hospitalizations/adverse events
Procedure-related adverse events occurred in five patients (24 %). Three (14 %) required hospitalization ( Table 3 ). One patient had post-procedure abdominal pain. A computed tomography scan of the abdomen did not reveal a perforation. The patient was treated conservatively with empiric antibiotics and bowel rest, and then discharged 2 days later. The second patient was hospitalized for observation due to deep mucosal defect of the C-EMR site. Two hemoclips were placed during the procedure. The patient remained asymptomatic post-procedure and an abdominal X-ray was negative for free air. The patient was discharged after 1 day. Polypectomy in one patient was complicated with hematochezia 3 days post-procedure. A repeat colonoscopy revealed a visible vessel at the C-EMR site that was treated with heater probe coagulation and deployment of five hemoclips. The patient required 2 days of hospitalization without recurrence of hematochezia. There were no perforations or intra-procedural bleeding.
Table 3. Procedure-related adverse events.
| Number | Presentation | Time to presentation | Technique | Size (mm) | Morphology | Location | Pathology | Treatment |
| 1 | Post-procedure pain | Immediately post-procedure | En bloc | 20 | Flat | Invading into cecum | TA | Observation for 2 days |
| 2 | Deep mucosal resection | Intraprocedural | Piecemeal | 15 | Sessile | Invading into cecum | TVA | Clips, observation for 1 day |
| 3 | Visible vessel | Intraprocedural | En bloc | 10 | Flat | Lip of ICV | TA | Coagulation grasper |
| 4 | Visible vessel | Intraprocedural | Piecemeal | 45 | Flat | Invading into cecum | TVA | Coagulation grasper |
| 5 | Hematochezia | 3 days | En bloc | 5 | Flat | Lip of ICV | Lipoma | BICAP, clips |
TA, tubular adenoma; TVA, tubulovillous adenoma; ICV, ileocecal valve; BICAP, bipolar circumactive probe.
Subsequent surveillance colonoscopies
Three patients had subsequent surveillance colonoscopies beyond the immediate follow-up colonoscopy after the index procedure at 8 months, 56 months, and 67 months, respectively. The patient with surveillance colonoscopy at 67 months after the index procedure revealed a 6-mm flat polyp at the edge of the previous scar revealing sessile serrated adenoma. The new polyp was treated with C-EMR, and repeat colonoscopy 6 months later had no signs of residual.
Discussion
In the current study, we reported the efficacy and safety of C-EMR as an approach in treatment of ICV polyps. The results of this study revealed that among all C-EMRs attempted on ICV polyps, there was 100 % complete adenoma clearance rate, and follow-up colonoscopy with median of 5 months revealed a 0 % early adenoma recurrence rate. Three patients had additional colonoscopies beyond the immediate follow-up colonoscopy at 8 months, 56 months, and 67 months, respectively. The patient with a surveillance colonoscopy at 67 months revealed recurrence of a 6-mm sessile serrated adenoma at the edge of the previous scar, which was successfully treated with C-EMR with complete adenoma clearance. It would be interesting to see the results for subsequent surveillance colonoscopies and the late adenoma recurrence rate. Three patients (14.3 %) required hospitalization. One patient had post-procedure pain and was treated conservatively. Two patients (9.5 %) had adverse events (AEs): deep mucosal resection successfully treated with hemoclips during the procedure, and delayed bleeding requiring repeat colonoscopy with placement of hemoclips for a visible vessel at the C-EMR site. There were no perforations or long-term AEs like strictures.
To our knowledge, this is the largest case series discussing C-EMR for treatment of ICV polyps. C-EMR has been shown to be beneficial in other areas of the gastrointestinal tract, including the duodenum 6 , but current literature on endoscopic treatment of ICV polyps is limited, and many patients are directly referred for surgery 7 8 . Laparoscopic and open surgery are associated with intraoperative adverse events of 3 % to 4 % and 4 % to 5 %, respectively, with a reported postoperative morbidity up to 20 % 9 10 . In the largest study on endoscopic management of ICV polyps, Nanda et al performed polypectomy in 47 patients using free-hand snare or C-EMR. However, they did not explicitly detail how many patients underwent C-EMR 5 . Complete adenoma clearance was achieved in 93.6 % of patients, with an early adenoma recurrence rate of 17.5 % while 12.8 % of patients had intra-procedural bleeding, 6.4 % had post-procedure bleeding, and there were no perforations 5 . It would be interesting to see the results of a subgroup analyses for those patients who underwent C-EMR. Based on our data, we theorize that patients with C-EMR would have a high adenoma clearance rate, low early adenoma recurrence rate, and low intra-procedure and post-polypectomy bleeding rate. Conio et al reported a case series of seven patients with ICV polyps, all treated with C-EMR, and the complete adenoma clearance rate was 100 % 3 . C-EMR allows for improved visualization of mucosa in blind spots of the colon 11 , such as the ICV, which increases the rate of complete polyp resection 12 . In addition, C-EMR in an experienced endoscopist is very safe.
There are a few limitations of our study. This was only a case series of 21 patients, three of whom were lost to follow-up, and all procedures were performed by a single experienced endoscopist. Future studies are needed to include more patients and more endoscopists. While our median follow-up of 5 months was within recommended guidelines for surveillance colonoscopy 13 , it would be interesting to see data on late adenoma recurrence rate. Our study did include three patients with longer follow-up, and only one had recurrence.
Overall, our study suggests that C-EMR is both efficacious and safe in treating ICV polyps. C-EMR does require an experienced endoscopist. We recommend learning C-EMR on upper gastrointestinal lesions first as the risk of perforation is lower in these lesions 4 .
Conclusion
In conclusion, C-EMR is a highly effective and safe method of treating ICV polyps, and may be a better alternative to surgery. The results of this study may encourage more endoscopists to apply C-EMR to ICV polyps.
Footnotes
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Tolliver K A, Rex D K. Colonoscopic polypectomy. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2008;37:229–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Conio M, Blanchi S, Repici A et al. Cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal polyps. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53:919–927. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181d95a54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Conio M, Blanchi S, Filiberti R et al. Cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection of large polyps involving the ileocecal valve. Endoscopy. 2010;42:677–680. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kashani A, Lo S K, Jamil L H. Cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection is highly effective for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50:163. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nanda K S, Tutticci N, Burgess N G et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection of laterally spreading lesions involving the ileocecal valve: technique, risk factors for failure, and outcomes. Endoscopy. 2015;4:710–718. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1391732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jamil L H, Kashani A, Peter N et al. Safety and efficacy of cap-assisted EMR for sporadic nonampullary duodenal adenomas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:666–672. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tolliver K A, Rex D K. Colonoscopic polypectomy. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2008;37:229–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2007.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kao K T, Glap A Q, Abbas M A. Endoscopic excision of large colorectal polyps as a viable alternative to surgical resection. Arch Surg. 2011;146:690–696. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2011.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Willhelm D, von Delius S, Weber L et al. Combined laparascopic-endoscopic resections of colorectal polyps: 10-year experience and follow-up. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:688–693. doi: 10.1007/s00464-008-0282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Benedix F, Kockerling F, Lippert H et al. Laparascopic resection for endoscopically unresectable colorectal polyps: analysis of 525 patients. Surg Endosc. 2008;22:2576–2582. doi: 10.1007/s00464-008-0059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Matsushita M, Hajiro K, Okazaki K et al. Efficacy of total colonoscopy with a transparent cap in comparison with colonoscopy without the cap. Endoscopy. 1998;30:444–447. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bergmann U, Beger H G. Endoscopic mucosal resection for advanced non-polypoid colorectal adenoma and early stage carcinoma. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:475–479. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8931-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hassan C, Quintero E, Dumonceau J M et al. Post-polypectomy colonoscopy surveillance: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2013;45:842–851. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1344548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


