Abstract
Background
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive and malignant neoplasm that arises from the hematopoietic T-cell precursors. Inactivation of FBXW7 gene is frequently observed in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, suggesting a significant tumor-suppressive role for FBXW7 in the pathobiology of this leukemia. Considering the role of microRNAs in cell proliferation and regulation of apoptosis, the aim of this study was to identify novel oncogenic microRNAs that suppress FBXW7 in patients with T-ALL.
Patients and Methods
The expression levels of two bioinformatically predicted microRNAs – miR-32 and miR-107 were compared in patients with T-ALL and a control group. A total of 80 plasma samples were subjected to RNA extraction, and the microRNA expression profiles were assessed by the RT-qPCR. The expression level of miR-103 was used as the endogenous reference for normalization of quantitative data.
Results
The plasma levels of miR-32 and miR-107 in patients with T-ALL were significantly higher (5.65, P < 0.001) and lower (0.432, P = 0.002), respectively. On the other hand, the expression levels of FBXW7 gene were significantly downregulated by –76.9 fold in T-ALL patients (P < 0.001). The results of the ROC curve analysis indicated that overexpression of miR-32 might be used to distinguish T-ALL patients with reasonable sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusion
miR-32 is considered as a novel oncomir that targets FBXW7 and might have a role in the etiology or progression of T-ALL. Furthermore, miR-32 can potentially serve as a non-invasive biomarker for detection of T-ALL.
Keywords: biomarker, FBXW7, T-ALL, microRNA
Introduction
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematologic malignancy results from leukemic transformation of developing thymocytes,1,2 representing nearly 25% of adult and 10–15% of childhood ALL cases.2,3 Several cytogenetic abnormalities and genetic aberrations have been associated with the etiology of T-ALL.1,4 Some functions including self-renewal, proliferation and survival, and blocked differentiation of precursor T cells are affected by these genetic aberrations.1
FBXW7 is a tumor suppressor protein that leads to increased stability of NOTCH1 protein. FBXW7 expression increases subsequent p53 stimulation.5 Inactivation of FBXW7 gene is frequently detected in T-ALL cases.6 More specifically, mutations of FBXW7 were found in about 9–30% of T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia cases, indicating that FBXW7 plays an important tumor-suppressive role in the pathobiology of TALL.5–7 On the other hand, numerous studies have demonstrated the significant role of miRNAs in the regulation of a wide range of biological processes, including proliferation, differentiation, migration, apoptosis, metabolism and the stress response. miRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNA molecules, between 19 and 24 nucleotides in length.8 miRNAs act by degrading their RNA targets or by suppressing the translation of mRNAs. Additionally, miRNAs have been indicated to operate as strategic regulators in the pathogenesis of some diseases, especially cancers. In tumorigenic cells, miRNAs have been found to be seriously dysregulated.9,10 A few miRNAs can promote lymphoblastic leukemogenesis through inducing the expression of oncogenes and suppressing apoptosis, impressing the progression and prognosis of the disease.11 Several studies have shown that miRNAs are stable in plasma and serum and that circulating molecules display unique profiles for each tumor. The stability of miRNAs in circulation might be due to their protection by exosome and microvesicle, Argonaute2 (Ago2), and high-density lipoprotein.12,13 It was also shown that miRNA signatures can be applied either in the diagnosis the T-ALL or evaluation of the prognosis of patients.11,14,15
In the current study, bioinformatics tools were applied to predict the most relevant miRNAs in human plasma that interact with FBXW7 gene products. The expression levels of the predicted miRNAs as well as FBXW7 mRNA were compared in the plasma samples of patients with T-ALL and control group, using RT-qPCR. The role of the predicted miRNAs was also evaluated as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of T-ALL.
Materials and Methods
Patients and Samples
Forty patients and 40 healthy individuals were obtained from Valiasr Hospital (Arak, Iran) enrolled in this study. All patients diagnosed as ALL by FAB criteria with an expert hemato oncologist and categorized in T-ALL by flow cytometry method. The peripheral blood was collected and plasma was separated, the following study designed on this part of sample. As illustrated in Table 1, healthy individuals` and Patients` samples were related to 20 females and 20 males, with a median age of 45 years (range, 29 to 71 years) for patients group and 39 (range, 26–65 years) for healthy individuals. In diagnosed of T-ALL patients, European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL) suggested the flow cytometry marker to diagnosed (positive for CD34, CD 52, CD2 and, CD7 antigen and negative for myeloid antigen like CD33 and CD 117).16 All patients had not received cancer-related treatment including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery. All samples were stored at −70°C prior to analysis. All patients and healthy volunteers provided written informed consent and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Arak University of Medical Sciences, in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki (ethics number IR.ARAKMU.REC.1396.253).
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of Patients and Control Groups
| Parameter | Patients | Healthy Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | Number (%) | |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 20 (50) | 20 (50) |
| Male | 20 (50) | 20 (50) |
| Age | ||
| Median | 45 | 39 |
| Range | 29–71 | 26–65 |
| Peripheral blood | ||
| Mean WBC count ×109/L | 47.2 | 5.2 |
| Mean Hb concentration gr/L | 9.8 | 14.7 |
| Mean Plt count ×109/L | 94 | 281 |
miRNA Predictions
The nucleotide sequence of FBXW7 gene, with official name of F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7, was retrieved from NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene). The obtained sequence was evaluated in most generally accepted bioinformatics resources to examine the potential miRNAs that target FBXW7. These websites include DIANA (http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php?r=microT_CDS/index), miRBase (http://www.mirbase.org/), PicTar (https://pictar.mdc-berlin.de/), miRanda (http://www.microrna.org/microrna/home.do), miRTB (https://bio.tools/mirtarbase), TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/), miRDB (http://mirdb.org/), and miRNApath (https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/miRNApath.html). Since different algorithms are used in these softwares, we made a score table to select the most consensus candidate miRNAs for subsequent experimental analyses. Finally, two microRNAs with the highest probability were chosen to experimentally evaluate their role in targeting FBXW7.
Primer Design
The sequences of the miRNAs were acquired from miRBase database. Reverse transcription-specific stem-loop primers and gene-specific primers were designed using the AlleleID7 and GeneRunner software. The expression of miR-103 and GAPDH was used for normalization of predicted miRNAs and FBXW7 gene expressions, respectively.17–19 The specificity of the designed primers was designed using the nucleotide BLAST on NCBI. The sequences of the primers are presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Primers Used for Reverse-Transcription and RT-qPCR Assay of the Target miRNAs and FBXW7
| Target | Primer Sequences (5`-3`) |
|---|---|
| miR-32 | Sa: 5`-GTCGTATCGAGAGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTCGATACGACTGCAACT-3` Fb: 5`-TATTGCACATTACTAAGTTGCA-3` |
| miR-107 | S: 5`-GTCGTATCGAGAGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTCGATACGACAGCAGCA-3` F: 5`-GCCCTGTACAATGCTGC-3` |
| miR-103 | S: 5`-GTCGTATCGAGAGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTCGATACGACCAAGGCA-3` F: 5`-GCTTCTTTACAGTGCTGCC-3` |
| Common Reverse | 5`-AGAGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3` |
| FBXW7 | F: 5`-AAACATTGCAAGGTCCCAAC-3` R: 5`-CTTTGTGTTTGAGGCTCTGATC-3` |
| GAPDH | F:5`-GGAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCAC-3` R:5`-GAGGCATTGCTGATGATCTTGAGG-3` |
Notes: aStem-loop gene-specific reverse-transcriptase primers, bSpecific forward primers for RT-qPCR amplification.
miRNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
MicroRNAs were extracted from plasma samples using RNX-Plus kit (SinaClon, Iran) according to the manufacturer`s instructions and 1μg of RNA was reverse-transcribed using the mixture of M-MLV enzyme (Vivantis, Malaysia), 1x RT-enzyme buffer, 400 μM dNTP, and 1μM of specific stem-loop RT primers and incubated at 75 °C for 5 min. The mixture was incubated at 25°C for 15 min, 37°C for 15 min, 42°C for 45 min, and 10 min at 75°C, in a thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Germany). Finally, the obtained cDNAs were stored at −20°C prior to RT-qPCR analyses.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
All RT-qPCR analyses were performed in a Light Cycler 96 instrument (Roche, Germany) using the SYBR Green PremixExRaq II (Yekta Tajhiz Azma, Iran), 1.5 µL cDNA, and 0.3 µM of each forward and reverse primers, and 5.1 µL RNase-free water to adjust the reaction volume to 15 µL. The temperature profile was 95ºC for 3 min, 40 cycles of 95 ºC for 10 s, 55 ºC for 15 s and 72 ºC for 20 s Melting curve analysis was performed after amplifications from to 60°C to 96°C with a ramp rate of 0.2°C/second and continuous fluorescence acquisition. The relative expression was calculated by the comparative Cq method using the relative expression software tool (REST).20
Statistical Analyses
Relative expressions were analyzed by the REST 2009 and the data in graphs are expressed as the mean ± SE. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to evaluate the diagnostic value of the miRNA level. All statistical analyses were calculated using SPSS software (version 16; SSPS Inc., 184 Chicago). P-values of <0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Selection of the Predicted miRNAs
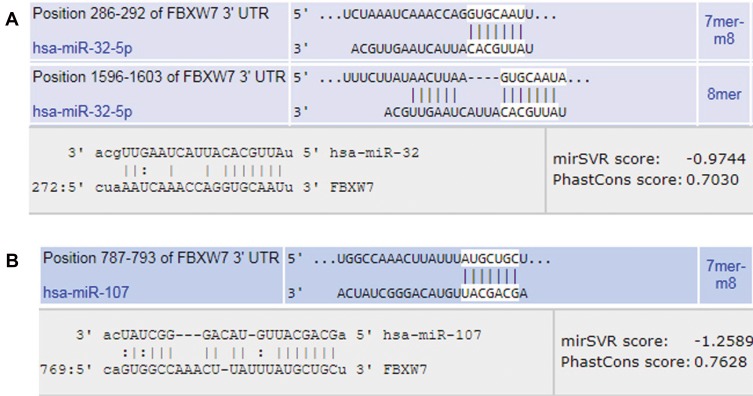
The predictions of DIANA, miRBase, PicTar, miRanda, miRTB, TargetScan, miRDB, and miRNApath software’s showed that miR-32, miR-27a and miR-107 are among the miRNAs that target FBXW7 transcript with the highest scores. Although different mathematical algorithms and scoring criteria used in different websites, the selected miRNAs were chosen based on the most repeated miRNA results (Table 3). Between these three miRNAs, miR-32 and miR-107 showed better complementarities with the target and were more consensus in targeting the 3′-UTR part of the FBXW7 transcript and were chosen for further experimental evaluation (Figure 1).
Table 3.
The Result of miRNA Prediction for FBXW7
| Gene Name | miRNA | miRTB | TargetScan | miRDB | PicTar | miRanda | miRNApath | miRBase | DIANA | SUM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBXW7 | has-miR-32 | 1a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| FBXW7 | has-miR-107 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| FBXW7 | has-miR-27a | 0b | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
Notes: aTargeting of FBXW7 is confirmed by the software. bTargeting of FBXW7 is not confirmed by the software.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the 3′-UTRs region of FBXW7 mRNA that is targeted by (A) miR-32 and (B) miR-107 binding seed region.
Quantification of miRNA Plasma Levels
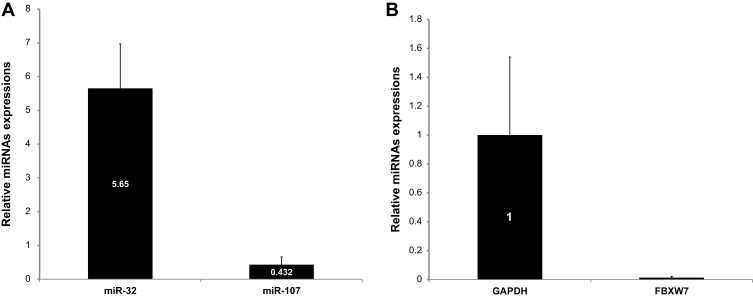
As summarized in Figure 2, the RT-qPCR analyses showed that the expression levels of miR-32 were significantly higher in T-ALL patients than in healthy individuals (5.65, P< 0.001), and the expression levels of miR-107 were significantly lower in T-ALL patients (0.432, P= 0.002). On the other hand, the expression levels of FBXW7 gene were significantly lower in T-ALL patients than in healthy individuals (0.013, P< 0.001).
Figure 2.
(A) Comparison of differential expression levels of miR-32 and miR-107 between patients with T-ALL and healthy individuals. (B) Relative expression of FBXW7 in T-ALL patients in comparison to healthy control group. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean.
Determination of Expression Level Cutoff
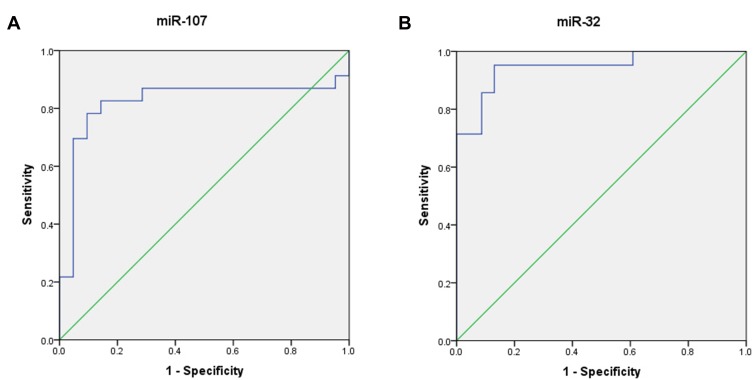
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were conducted to examine the cutoff values of miR-32 and miR-107 to differentiate healthy individuals from patients with T-ALL. The Youden`s index ([sensitivity + specificity] −1) was used for the determination of appropriate cutoff levels of the ROC curves. Comparisons of the miRNA plasma levels between T-ALL patients and healthy individuals showed that at the cutoff level of 0.776, miR-107 had 82.6% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity with an area under curve (AUC) of 0.822. For miR-32, at the cutoff level of 1.84, the sensitivity was defined 95.2% and the specificity was 87%. The AUC of the ROC for miR-32 was 0. 946 (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
ROC curve analyses correspond to the plasma expression of the two miRNAs to discriminate patients with T-ALL from healthy individuals. (A) The area under the curve of miR-107. (B) The area under the curve of miR-32.
Discussion
Genetic and epigenetic alterations are recognized as one of the most important contributing factors for oncogenic transformation of immature T-cell progenitors. Currently, aberrant expression of miRNAs has been demonstrated to effect on the development and progression of different types of leukemia including T-ALL.15 miRNAs that target and repress the expression of tumor suppressor genes can play a critical role as oncogenes when aberrantly overexpressed in malignancy.21 The profiles of these miRNAs could differ based on the tumor type and, hence, might provide novel biomarkers for diagnosis of many cancers.22,23 It has been shown the expression levels of miR-181a, miR-128-3P and miR-142-3p were significantly up-regulated in T-ALL patients,1,4,24 whereas miR-204, miR-101 and miR-193b-3p were down-regulated.2,24,25
Some studies have indicated that FBXW7 dysregulates important signaling pathways including Notch1 and mTOR. Notch1 signaling alteration is strongly related to T-ALL progression.5,24 Since malfunction of FBXW7 has been reported in several types of human cancer, this protein seems as an appropriate choice for miRNA targeting studies. Therefore, the focus of the present study was to compare the expression levels of miR-32, miR-107, and FBXW7 using RT-qPCR in the plasma of patients with T-ALL. The miRNAs were chosen using several algorithms that are used for prediction of mRNA–miRNA interactions. Using DIANA, miRBase, PicTar, Miranda, miRTB, TargetScan, miRDB and miRNApath FBXW7 was predicted to be a target of miR-32, miR-107 and miR-27. However, miR-32 and miR-107 had higher scores and were selected for further experiments.
The plasma levels of miR-32 were significantly higher in the T-ALL group than in the healthy control individuals. However, the plasma level of miR-107 was significantly decreased in patients suffering from T-ALL. The expression of miR-32 was upregulated by 5.65 fold (P= 0.000) and expression of miR-107 was downregulated by −2.31 fold (P= 0.002). Furthermore, the plasma levels of FBXW7 were downregulated by 0.013 (or −76.9 fold, P= 0.000) in the T-ALL group than in the healthy control group. These findings confirm that miR-32 might also boost the proliferation of T-ALL cells by direct-targeting of FBXW7 transcript. On the other hand, the downregulation of miR-107 is inconsistent with the research hypothesis. One of the main plausible explanations might be the fact that bioinformatics tools only predict the intermolecular interactions and their result always need experimental confirmation, as in this case that our data did not support the in silico prediction. Additionally, a few studies have identified mutations in FBXW7 gene which was related to 9–30% cases of T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia.7 Nevertheless, no mutation is observed in the majority cases of T-ALL and the induction and progression of such cases might be due to overexpression of miR-32 and, hence, suppressing the expression of FBXW7 protein. The bioinformatics predictions presented here indicate that miR-32 could target the transcript of the FBXW7 gene, as the experimental analyses showed the plasma levels of this miRNA were reduced in patients with T-ALL. The role of mir-32 expression has been studied in a few cancer including colorectal cancer, glioma, and nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting PTEN, E2F transcription factor 5, and LATS2, respectively.26–29 However, to our knowledge, none of the previous studies evaluated the plasma levels miR-32 as a potential contributing etiology or biomarker of T-ALL. The present study is the first report related to a biological function for this molecule in this type of leukemia.
Conclusion
The present study showed a negative correlation between upregulation of miR-32 and downregulation of FBXW7 in patients with T-ALL. This might be due to targeting FBXW7 transcript by miR-32. This finding opens the way for a series of future studies in which the reciprocal expression of miR-32 and its target FBXW7 is deeply evaluated and the results may be useful in predicting clinical outcome in T-ALL. Further studies are necessary to thoroughly elucidate the role of the miR-32/FBXW7 interplay, the discovery of their functional relationship might lead to a better understanding of molecular pathways involved in T-ALL, contributing to open new possibilities for future diagnosis, prognosis and therapies in patients affected by acute leukemia.4
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Research Deputy of Arak University of Medical Sciences. The authors thank Neda Molaee and Dr. Ali Ganji for their assistance in this research.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Mets E, Van Peer G, Van der Meulen J, et al. MicroRNA-128-3p is a novel oncomiR targeting PHF6 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2014;99(8):1326–1333. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.099515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Qian L, Zhang W, Lei B, et al. MicroRNA-101 regulates T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia progression and chemotherapeutic sensitivity by targeting Notch1. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(5):2511–2516. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drobna M, Szarzynska-Zawadzka B, Dawidowska M. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia from miRNA perspective: basic concepts, experimental approaches, and potential biomarkers. Blood Rev. 2018;32(6):457–472. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Verduci L, Azzalin G, Gioiosa S, et al. microRNA-181a enhances cell proliferation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by targeting EGR1. Leuk Res. 2015;39(4):479–485. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yeh CH, Bellon M, Nicot C. FBXW7: a critical tumor suppressor of human cancers. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0857-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Malyukova A, Brown S, Papa R, et al. FBXW7 regulates glucocorticoid response in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by targeting the glucocorticoid receptor for degradation. Leukemia. 2013;27(5):1053–1062. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Vlierberghe P, Ferrando A. The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(10):3398–3406. doi: 10.1172/JCI61269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lai EC. Two decades of miRNA biology: lessons and challenges. RNA (New York, NY). 2015;21(4):675–677. doi: 10.1261/rna.051193.115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:402. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wahid F, Shehzad A, Khan T, Kim YY. MicroRNAs: synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical trials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803(11):1231–1243. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.06.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee YS, Dutta A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:199–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(2):102–114. doi: 10.1038/nrg2290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rotkrua P, Shimada S, Mogushi K, Akiyama Y, Tanaka H, Yuasa Y. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for early detection of diffuse-type gastric cancer using a mouse model. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(4):932–940. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.30 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wallaert A, Van Loocke W, Hernandez L, Taghon T, Speleman F, Van Vlierberghe P. Comprehensive miRNA expression profiling in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by small RNA-sequencing. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7901. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08148-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ye F. MicroRNA expression and activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 2018;9(4):5445–5458. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v9i4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, et al. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia. 1995;9(10):1783–1786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Peltier HJ, Latham GJ. Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA (New York, NY). 2008;14(5):844–852. doi: 10.1261/rna.939908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Serafin A, Foco L, Blankenburg H, et al. Identification of a set of endogenous reference genes for miRNA expression studies in Parkinson’s disease blood samples. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:715. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gharbi S, Shamsara M, Khateri S, et al. Identification of reliable reference genes for quantification of microRNAs in serum samples of sulfur mustard-exposed veterans. Cell J. 2015;17(3):494–501. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pfaffl MW. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(9):e36. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.9.e36 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Niloofar Moradi MP, Khansarinejad B, Sarmadian H, Mondanizadeh M. Plasma level of miR-5193 as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 2019;19(2):e84455. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parvaee P, Sarmadian H, Khansarinejad B, Amini M, Mondanizadeh M. Plasma level of microRNAs, miR-107, miR-194 and miR-210 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis intestinal-type gastric cancer in human. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019;20(5):1421–1426. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.5.1421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wallaert A, Durinck K, Taghon T, Van Vlierberghe P, Speleman F. T-ALL and thymocytes: a message of noncoding RNAs. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0432-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yin JJ, Liang B, Zhan XR. MicroRNA-204 inhibits cell proliferation in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by down-regulating SOX4. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(8):9189–9195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jin Y, Cheng H, Cao J, Shen W. MicroRNA 32 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and suppresses apoptosis in colon cancer cells by targeting OTU domain containing 3. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(11):18629–18639. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v120.11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang TT, Chen ZZ, Xie P, et al. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses the proliferation and induced apoptosis via miR-32/LATS2/Wnt in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;856:172352. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.04.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu W, Tan W, Ye S, Zhou Y, Quan J. Analysis of the promoter region of the human miR-32 gene in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(4):3743–3750. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang Y, Wang J, An W, et al. MiR-32 inhibits proliferation and metastasis by targeting EZH2 in glioma. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019;18:1533033819854132. doi: 10.1177/1533033819854132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]