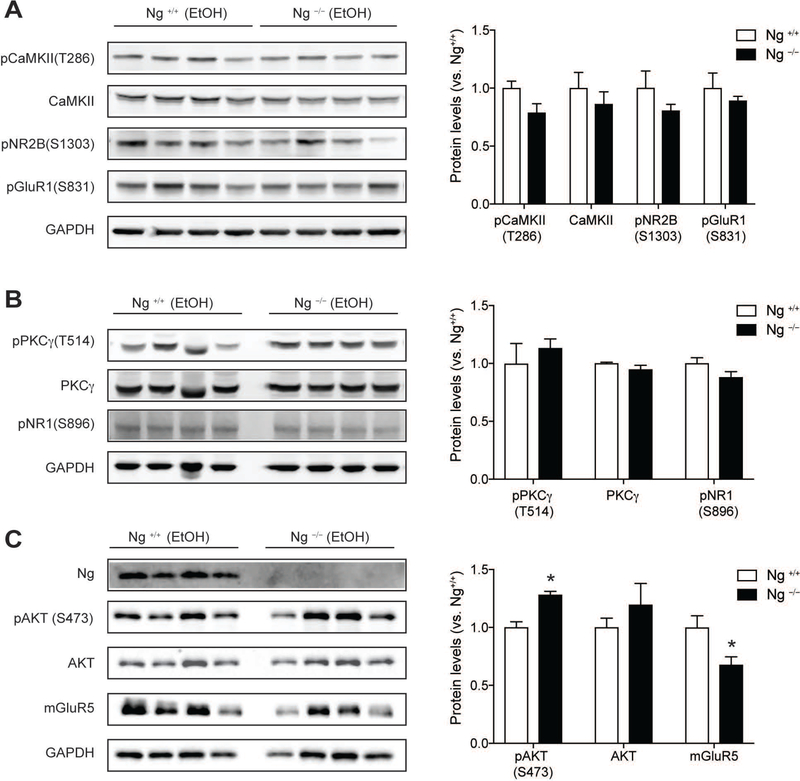
Figure 4.
Validation of alcohol-induced protein expression change in the NAc of Ng−/− mice using western blotting. A. Alcohol did not induce any significant changes in Ca2+-CaMKII signaling in the NAc of Ng–/– mice. There is no difference in CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation in pNR2B(S1303) and pGluR1(S831). B. Alcohol did not induce any changes in PKCγ signaling and pNR1(S896) phosphorylation. C. After alcohol treatment, AKT phosphorylation in the Ng−/− mice was significantly increased, while mGluR5 expression was significantly decreased in Ng–/– mice (n = 4). *p < 0.05 unpaired t-test for protein expression between genotypes and protein expression was normalized by GAPDH expression. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.