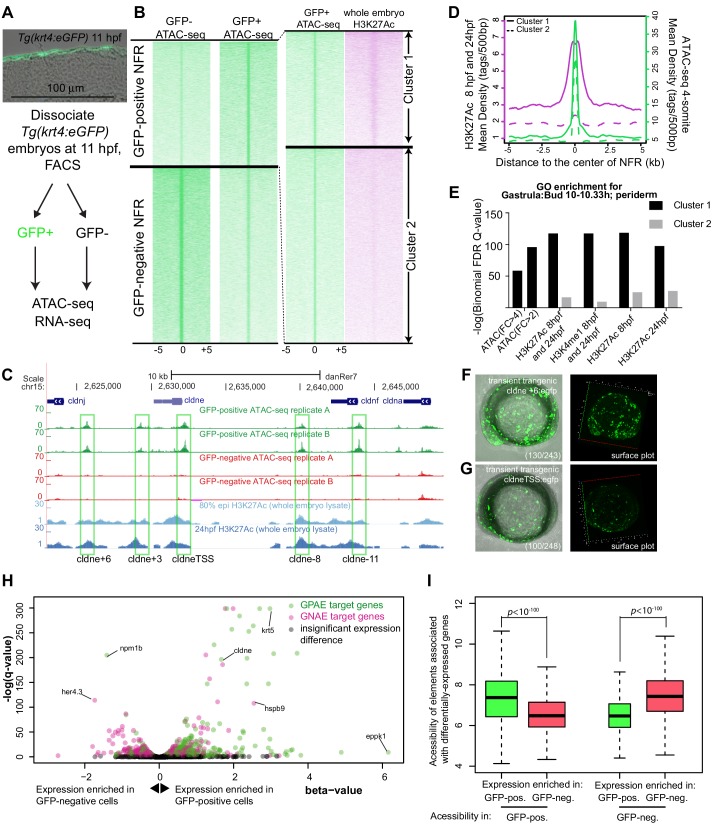
Figure 1. Identification of zebrafish GFP-positive active enhancers (zGPAEs) by integrating ATAC-seq and H3K27Ac ChIP-seq.
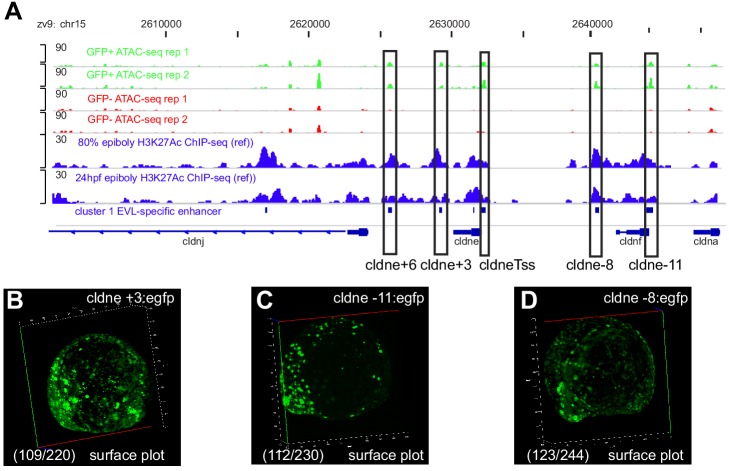
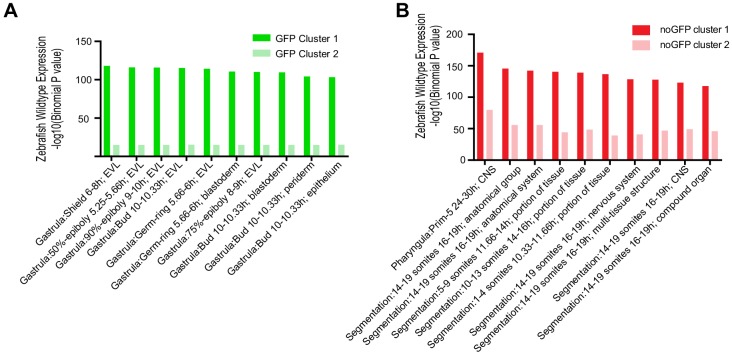
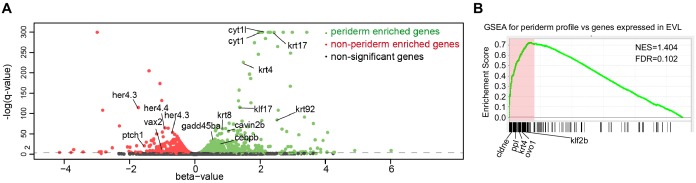
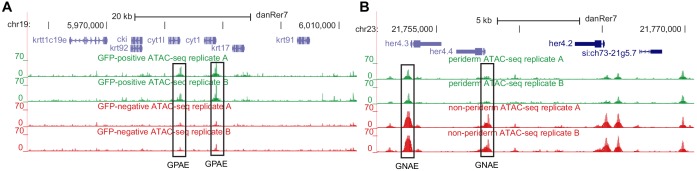
(A) Transverse section of an 11 hpf (4-somite stage) Tg(krt4:gfp) embryo, showing GFP is confined to the superficial layer of cells, and workflow of ATAC-seq in periderm and non-periderm cells. (B) Density plots of ATAC-seq results. Each line is centered on a nucleosome free region (NFR) with significantly more ATAC-seq reads in GFP-positive or GFP-negative cells; the majority of ATAC-seq peaks were not enriched in either cell type. Density plots also show H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal in whole embryos at eight hpf and/or at 24 hpf data from Bogdanovic et al. (2012) at each of the GFP-positive NFRs; the latter are sorted in to those that overlap (or are flanked by within 100–1500 bp) peaks of H3K27Ac signal (cluster 1, 4301 elements) and or not (cluster 2, 7952 elements). (C) UCSC Genome browser tracks showing the ATAC-seq peaks in GFP-positive and GFP-negative cells, and H3K27Ac signal from whole embryos at eight hpf and at 24 hpf data from Bogdanovic et al. (2012) at the cldne locus. Boxes, examples of cluster one elements, also known as zebrafish GFP-positive active enhancers (zGPAEs). Elements are cldne+6 kb (zv9 : chr15:2625460–2625890), cldne +3 kb (chr15:2629012–2629544), cldne −8 kb (chr15:2639873–2640379), cldne −11 kb (chr15:2643578–2644160), and cldne TSS (chr15:2631981–2632513). (D) Plot of average density of H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal (purple) and ATAC-seq signal (green). (E) GO enrichment for term ‘Gastrula:Bud 10–10.33 hr; periderm’ among NFRs enriched in GFP-positive cells with normalized fold change greater than 2 (ATAC(FC >2)) and 4 (ATAC(FC >4)), NFRs enriched in GFP-positive cells flanked or overlapped by 24hpf and 80% epiboly H3K27Ac ChIP-seq peaks (cluster 1) and or not (cluster 2), NFRs enriched in GFP-positve cells flanked or overlapped by 24hpf and 80% epiboly H3K4me1 ChIP-seq peaks (cluster 1) or not(cluster 2), NFRs enriched in GFP-positive cells flanked or overlapped by 24hpf H3K27Ac ChIP-seq peaks (cluster 1) or not (cluster 2), and NFRs enriched in GFP-positive cells flanked or overlapped by 80% epiboly H3K27Ac ChIP-seq peaks (cluster 1) or not (cluster 2). (F), (G) Lateral views of wild-type embryos at 11 hpf injected at the 1-cell stage with GFP reporter constructs built from (F) cldne +6 and (G) cldne transcription start site (TSS) elements. Left panels are stack views of the embryo, and right panels are surface plot for the embryos indicating most GFP signal is from the surface (periderm) of the embryos. Number in parentheses is the ratio of embryos with at least 10 GFP-positive periderm cells over injected embryos surviving at 11 hpf. (H) Volcano plot of RNA seq data, showing the expression of genes associated (by GREAT) with zGPAEs (green dots) or with zGNAEs (pink dots) in GFP-positive cells (beta-value >0) or in GFP-negative cells (beta-value <0). (I) Plot of accessibility scores of elements with differential accessibility (i.e., both zGPAEs and zGNAEs) associated with genes that are differentially expressed in GFP-positive and GFP-negative cells, showing that elements with increased accessibility in GFP-positive cells tend to be associated with genes whose expression is enriched in GFP-positive cells, and vice versa.
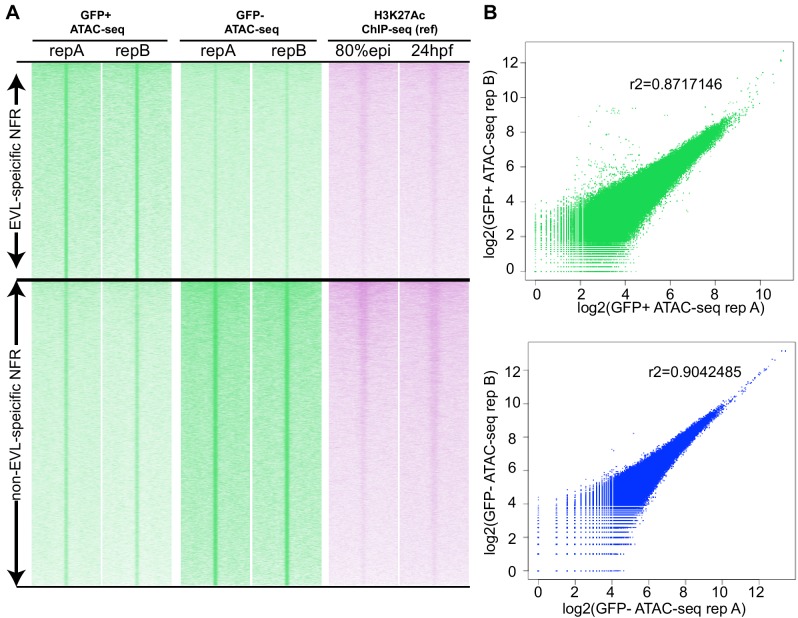
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Correlation of zebrafish periderm ATAC-seq two biological replicates.
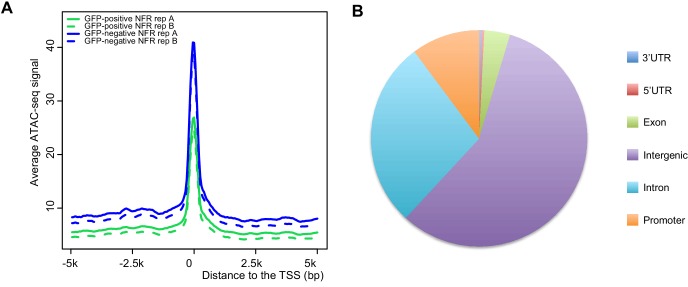
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Annotation of ATAC-seq peaks relative to transcription start sites.
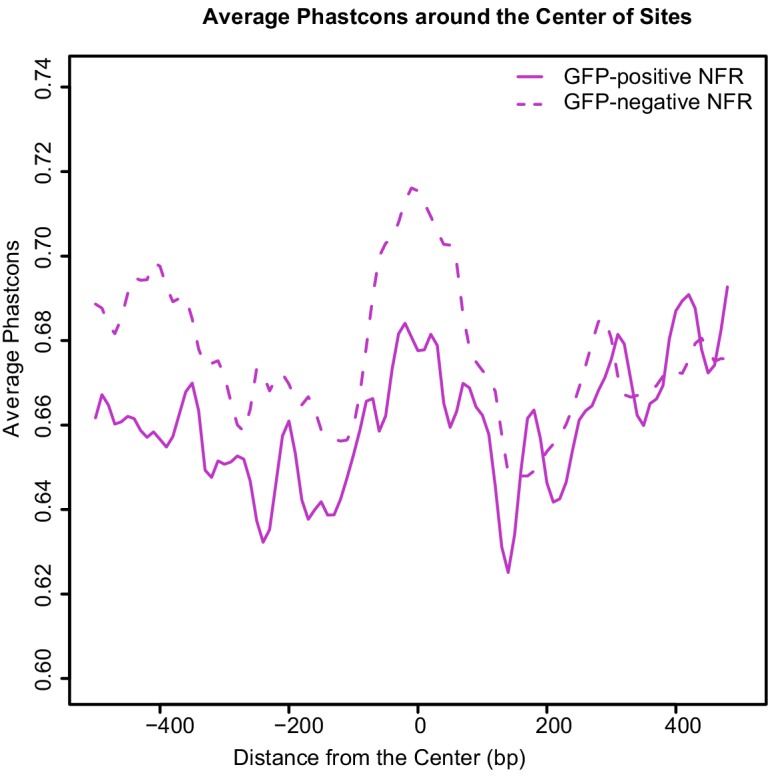
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Average Vertebrate PhastCons Score (danRer7 genome) at different distances from the center of nucleosome free regions (NFRs) in GFP-positive and GFP-negative (flow through) cells sorted from Tg(krt4:gfp) embryos at 11 hpf.