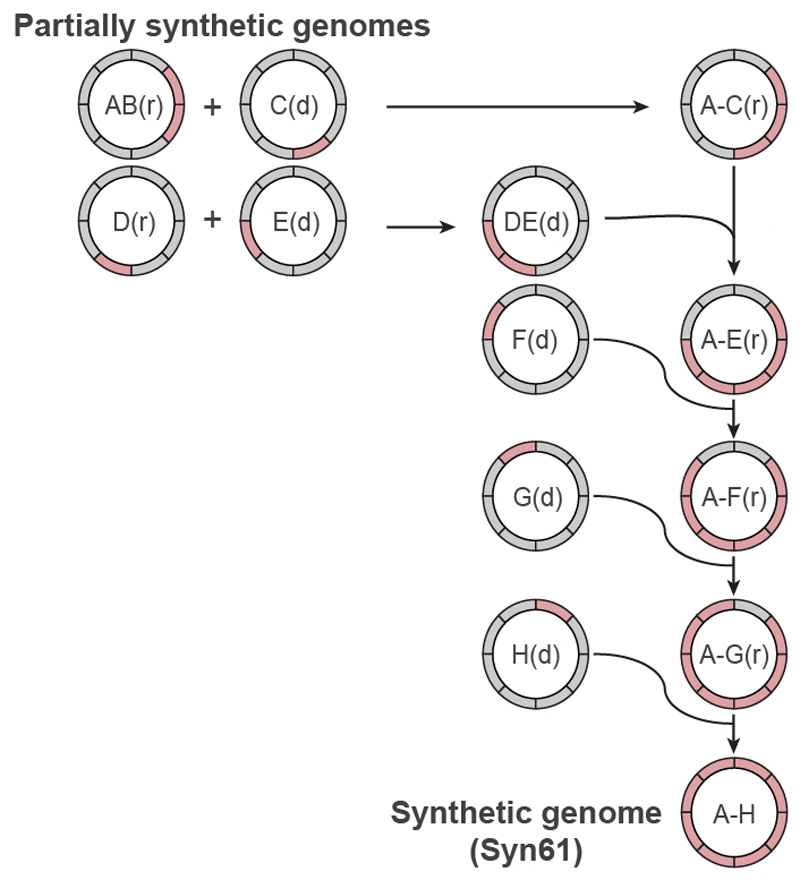
Fig. 3. Assembly of recoded genome sections to create Syn61.
Synthetic genomic sections (pink) from multiple individual partially recoded genomes were assembled into a single fully recoded genome in the indicated sequence of conjugations. The donor (d) and recipient (r) strains contain unique recoded genomic sections, denoted in pink. The recoded genomic content from the donor was conjugated in a clockwise manner to replace the corresponding wild-type genomic section (grey) in the recipient. Conjugation proceeded until the final fully recoded A to H strain (that is, Syn61) was assembled. Extended Data Figure 7 shows the process in more detail, including all homology regions.