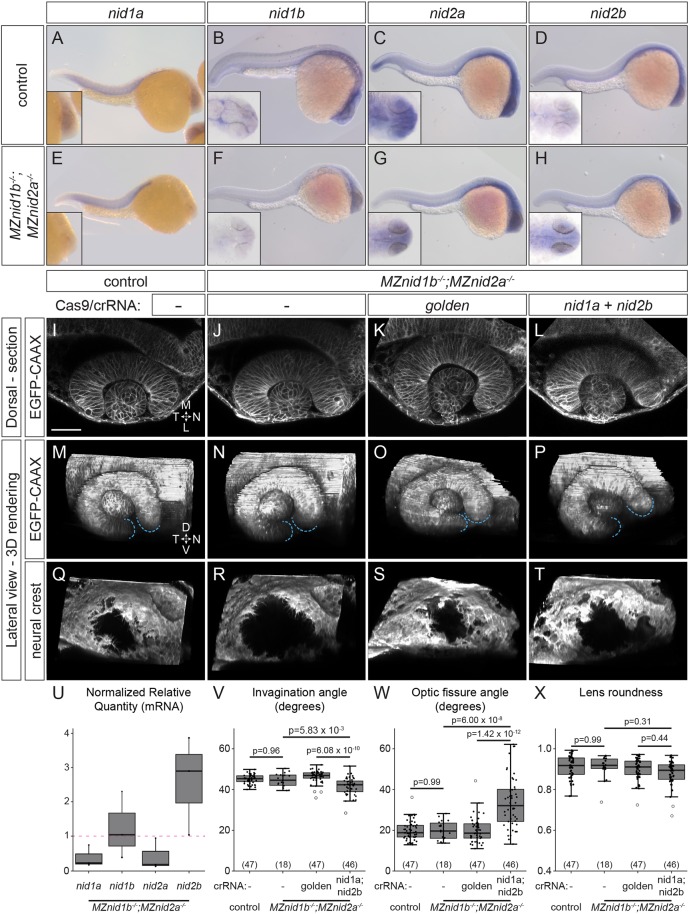
Fig. 7.
Nidogen is required for optic cup morphogenesis. (A-H) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for nidogens in 24 hpf control (A-D) and MZnid1b; MZnid2a mutant (E-H) embryos. Insets show magnified view of head. (I-T) Optic cup morphology and neural crest localization in EGFP-CAAX mRNA-injected, Tg(sox10:memRFP)+ embryos: control (I,M,Q), MZnid1b;MZnid2a mutant (J,N,R), golden crispant MZnid1b;MZnid2a mutant (K,O,S) and nid1a;nid2b crispant MZnid1b;MZnid2a mutant (L,P,T). (U) RT-qPCR quantification of nidogen transcripts in MZnid1b;MZnid2a mutant embryos, normalized to wild-type control expression levels (magenta dashed line, NRQ=1). Results from three biological replicates run in triplicate. (V-X) Quantification of invagination angle (V), optic fissure angle (W) and lens roundness (X). n (embryos) shown in base of graph. P-values were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc test. Scale bar: 50 μm. D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; N, nasal; T, temporal; V, ventral.