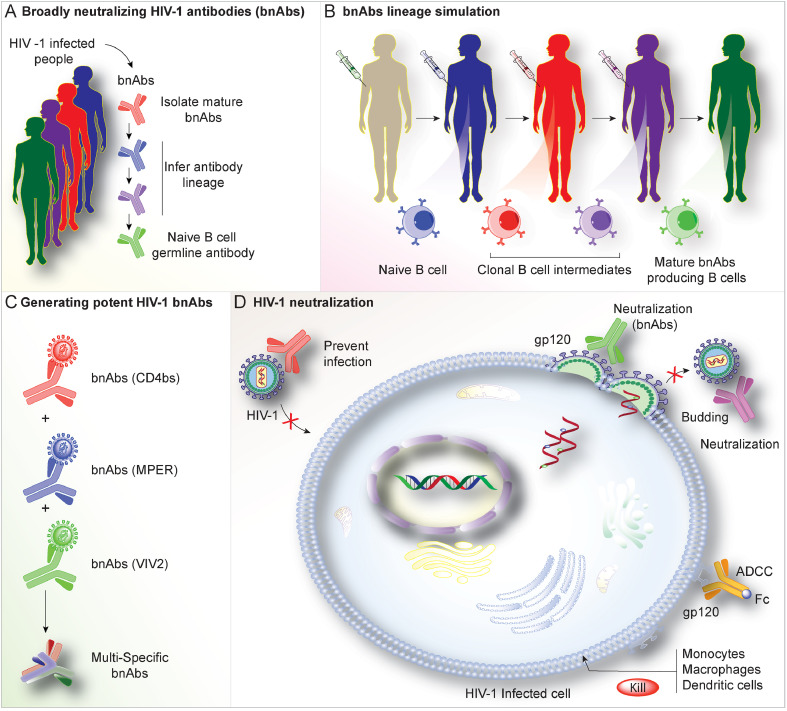
Fig. 2.
Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies (bnAbs). To overcome the limitations of using bnAbs as vaccine candidates, B-cell lineage immunogen strategies were developed (A). This is achieved by: (i) Isolation of bNAb clonal lineage antibodies from HIV-1 patients reflecting the different critical developmental stages of these bnAbs. (ii) Based on these isolated antibodies, high-affinity immunogens are designed that can optimally bind to stages of bNAb lineage antibodies. (iii) Eventually, immunization with a series of these high-affinity immunogens is followed to stimulate bNAb lineage activation. Using techniques such as antibody cloning, sequencing, and computational analyses, bnAb staged maturation is illustrated (B and C). This is critical in the design of HIV-1 Env epitopes that can engage the early precursors and elicit their development and maturation into the different bnAb lineages. Env epitopes with high binding affinity to the germline B-cell antibody precursors will enhance the lineage development that could boost the immune system to produce its bnAb-producing B cells resulting in neutralization of the virus (D).