ABSTRACT
Background
Burn injuries in adults can be complicated due to various underlying factors. Of all the co-morbidities complicating wound healing and prognosis of the patient post burn injury, diabetes mellitus is the most common in India. We therefore aimed to explore the epidemiology, interventions, complications, and outcomes in diabetic patients with burn injury.
Aim
To analyze demographic characteristics, clinical and microbiological profile and outcome of diabetic burns patients in comparison with nondiabetic burns patients.
Materials and methods
This study was a retrospective analysis of diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients admitted to Apollo speciality clinics, Vanagaram, a tertiary care facility in Chennai over a period of 3 years. Data such as age, gender, type and degree of burns, percentage of burns and length of stay, mortality rate, infection rate, type of infections, surgical procedures, and medical complications were analyzed in comparison with nondiabetic burns patients.
Results
Among ninety-four burns patients admitted to our hospital over a period of 3 years, 18 patients (19%) were diabetics and 76 patients (81%) were nondiabetics. Mean age of diabetics was 58.2 years (SD-17.1) and nondiabetics was 36.3 years (SD-16.4). Surgical intervention with split skin graft was performed in 50% of diabetics and 48.7% of nondiabetics. Average length of stay of diabetics was 12.6 days and nondiabetics was 16.2 days (p value: 0.334). Diabetic patients with burns were noted to have higher rate of infection (67% vs 61.8%, p value: 0.803) and mortality (44% vs 35.5%, p value: 0.482).
Conclusion
The clinical course is different between diabetic and nondiabetic patients with burns injury. Although length of stay and surgical interventions were not significantly different, diabetes as a comorbidity appears to increase the risk of infections and mortality in patients with burns.
How to cite this article
Vadala R, Princess I, Ebenezer R, Ramakrishnan N, Krishnan G. Burns in Diabetes Mellitus Patients among Indian Population: Does it Differ from the Rest? Indian J Crit Care Med 2020;24(1):11–16.
Keywords: Burns, Complications, Diabetes, Epidemiology, Infections, Mortality, Split skin graft
INTRODUCTION
Comorbidity is a “distinct additional clinical entity” noted during the clinical course of a patient having an index disease.1 When burns occur in patients with an index disease, the clinical recovery and outcome take a different course than in normal individuals. Research and published reports on burns in diabetic patients are limited. Diabetes being the most common comorbidity in most parts of the world and particularly in India, we explore variations in epidemiology, outcome, and types of infections in diabetic burns patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a retrospective study of all burns patients admitted over a period of 3 years to the multidisciplinary critical care unit at Apollo speciality clinics, Vanagaram, a tertiary care facility in Chennai.
Study subjects were comprised of two groups—diabetic burns patients and nondiabetic burns patients. Demographic details such as age, sex, and length of hospital stay were collected from clinical records. Relevant clinical findings such as percentage of burns calculated using Lund and Browder formula, type of burns, type of surgery and dressing, use of immune nutrition, mortality rate, and infection rate were collected. Immune nutrition given was infusion of L-alanyl-L-glutamine while in the critical care unit.
A profile of the microorganisms isolated from these patients was also collected and documented. This parallel data was compared and analyzed in order to understand the difference between diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients.
RESULTS
Epidemiology
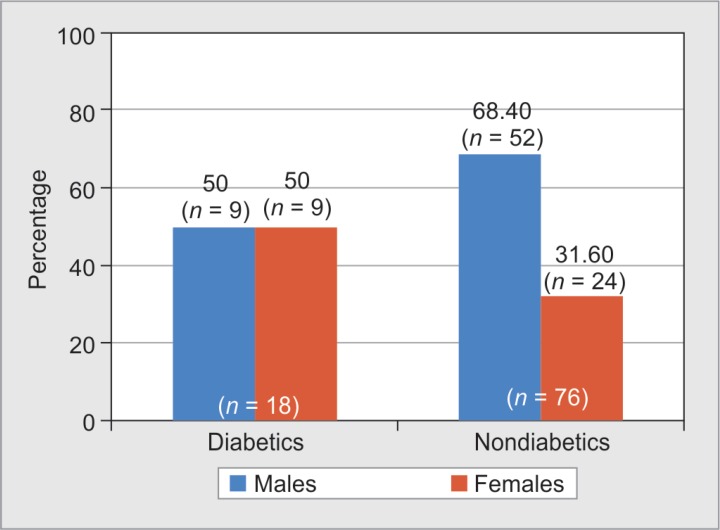
Among a total of 94 burns patients, 18 patients (19%) were diabetics and 76 patients (81%) were nondiabetics. Mean age of diabetic burns patients was 58.2 years (SD-17.1), and mean age of nondiabetic burns patients was 36.3 years (SD-16.4). Among the diabetes patients, 50% (n = 9) were males and the other 50% (n = 9) were females. Nondiabetic males were 68.4% (n = 52), and nondiabetic females were 31.6% (n = 24) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Gender-wise distribution of diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients
Hypertension was the second most common presenting comorbidity seen in 14 patients (14%).
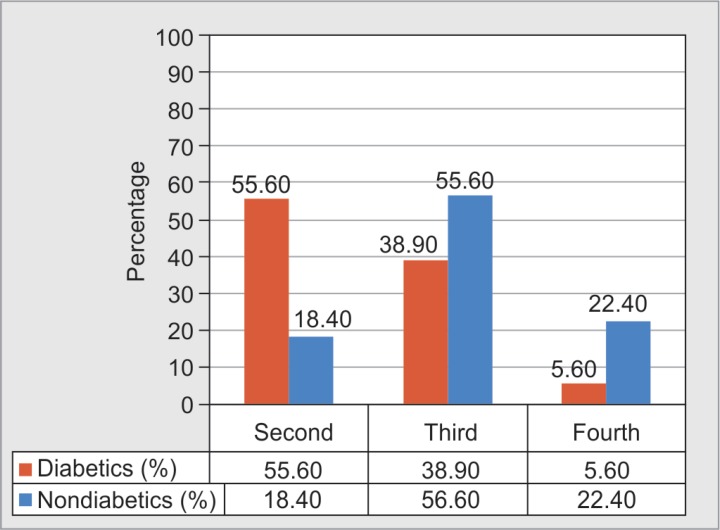
Mean percentage of total body surface area (TBSA) involved in burns was 43.5% in diabetics and 49.75% in nondiabetics. Majority of burns in diabetes patients were second and third degrees.
Fourth-degree burns were seen in only a minority of diabetes patients (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Distribution of diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients based on degree of burns
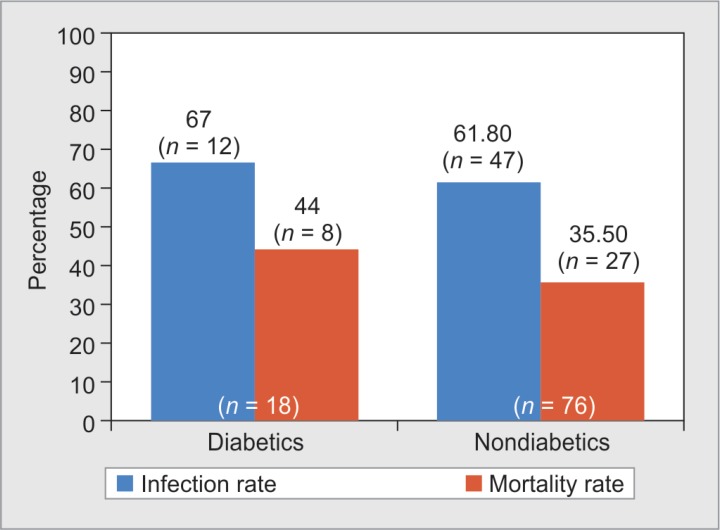
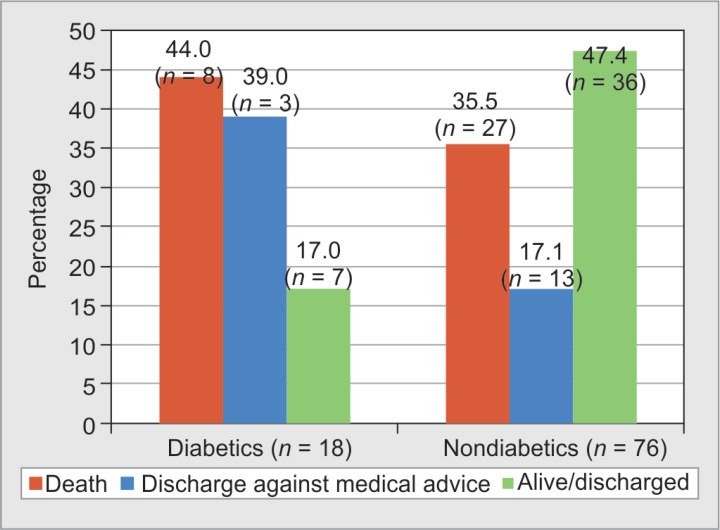
An infection rate of 67% (n = 12) and mortality rate of 44% (n = 8) were seen among diabetic burns patients in comparison with nondiabetic burns patients who had infection rate of 61.8% (n = 47), p value: 0.803 and mortality rate of 35.5% (n = 27), p value: 0.482, respectively, as shown in Figure 3.
Fig. 3.
Distribution of infection rate and mortality rate among diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients
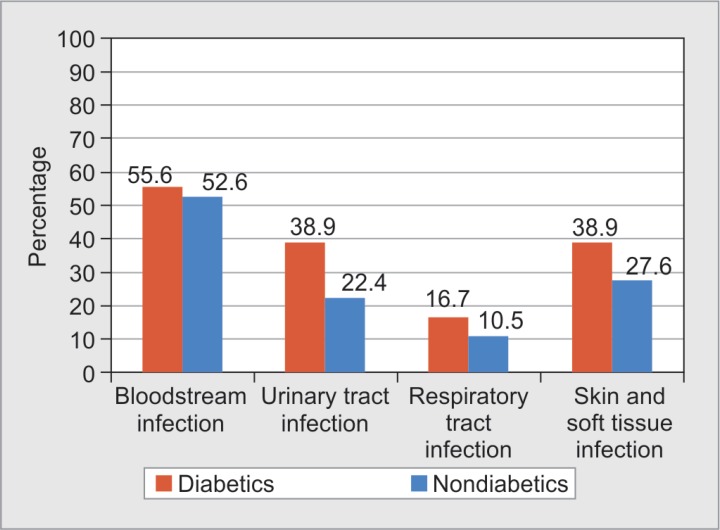
Comparison between types of infection among diabetics and nondiabetics showed more infection rates in all samples. Bacteremia was seen in 55.6% diabetics (n = 10), urinary tract infection in 38.9% (n = 7), respiratory tract infection in 16.7% (n = 3), and skin/soft tissue infection in 38.9% diabetics (n = 7) (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Distribution of various infections among diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients
Treatment
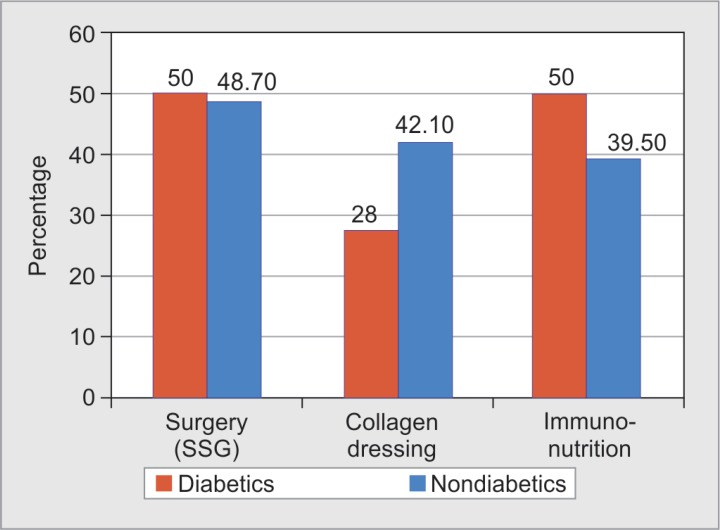
It was noted that early surgical interventions in the form of primary split-skin grafting was more common in diabetics (50%) compared with nondiabetics (48.7%). Interestingly, the use of immune nutrition was noted to be significantly more in the diabetic burns patients (50% vs 39.5%, p value: 0.440), although it is unclear what prompted clinicians to initiate or withhold immune nutrition in these patients (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Distribution of diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients based on treatment given
Profile of Microorganisms
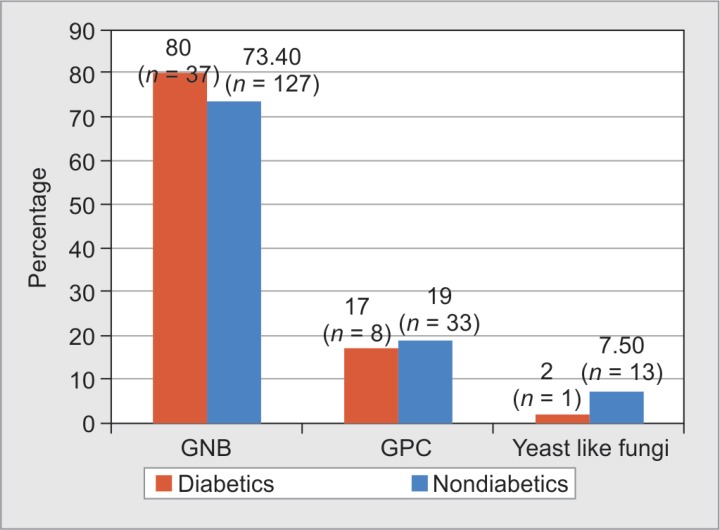
A total of 46 microorganisms were isolated from various samples such as blood, wound, tissue, urine, and tracheal aspirate of diabetic burns patients. There was a predominance of gram-negative organisms in both diabetic (80% n = 37) and nondiabetic patients (73.4%, n = 127). Gram-positives and yeast-like fungi were isolated more among nondiabetes (19% and 7.5%) than diabetes patients (17% and 2%) (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
Distribution of types of microorganisms isolated from diabetes and nondiabetes burns patients
Outcome of Patients
Better patient outcome was noticed among nondiabetic burns patients. Recovery rate of 47.4% was seen in nondiabetics, but only 17% of diabetics recovered. Average length of stay of diabetes patients was 12.6 days, and in nondiabetics, it was 16.2 days. Mortality rate among diabetic burns patients was 44.4%, among which 75% sustained third-degree burns, 12.5% sustained second-degree and fourth-degree burns, respectively.
DISCUSSION
Among various conditions complicating burn injuries, diabetes is a major comorbidity resulting in adverse outcomes. This study was designed to document the differences in demography, clinical presentation, outcome, types of infections, and microorganism profiles among diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients (Tables 1 and 2).
Table 1.
Comparison of demography, outcome, complications, and infections among diabetic burns patients
| Parameters/features | Present study | Maghsoudi et al.7 | McCampbell et al.8 | Memmel et al.12 | Kimball et al.6 | Shalom et al.5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chennai, India, 2017 | Iran, 2008 | New York, USA, 2002 | Chicago, USA, 2004 | USA, 2012 | Baltimore, USA, 2005 | ||||||||
| Diabetic | Nondiabetic | Diabetic | Nondiabetic | Diabetic | Nondiabetic | Diabetic | Nondiabetic | Diabetic | Nondiabetic | Diabetic | Nondiabetic | ||
| Mean age | 58.2 | 36.3 | 53.4 | 36 | 64.9 | 50.5 | 54.6 | 43.7 | 60.6 ± 1.83 | 32.7 ± 1.8 | |||
| Gender | Males | 50% | 68.40% | 40.40% | 61.60% | 64% | |||||||
| Females | 50% | 31.60% | 59.60% | 38.30% | 36% | ||||||||
| Mean TBSA | 43.5 | 49.75 | 17.3 ± 8.1 | 29.4 ± 25 | 6.9 ± 10.2 | 8.1 ± 12.5 | 11 ± 19 | 6 ± 11 | 11.87 ± 2.19 | 8.69 ± 0.78 | |||
| Degree of burns | First | 0 | 2.60% | ||||||||||
| Second | 55.60% | 18.40% | 4.2% ± 8.3 | 14% | 24% | ||||||||
| Third | 38.90% | 56.60% | 2.3% ± 5.4% | 2.8% ± 10.6% | 86% | 76% | |||||||
| Fourth | 5.60% | 22.40% | |||||||||||
| Average length of stay | 12.6 | 16.2 | 13.04 | 13.8 | 23.2 | 12.2 | 11 ± 12 | 8 ± 9 | 14.1 ± 10 | 9.8 ± 9.3 | 17.15 ± 2 | 8.89 ± 0.99 | |
| Mortality rate | 44% | 35.50% | 8.50% | 24.60% | 2.10% | 2.20% | 3% | 1.60% | 13.70% | 2.60% | |||
| Infection rate | 67% | 61.80% | 14.90% | 8.10% | 44.70% | 30.40% | |||||||
| Surgery-SSG/escharotomy/tangential excision/debridement | 50% | 48.70% | 60.42% | 56.70% | 32.30% | 72.60% | 32% | ||||||
| Collagen dressing | 27.70% | 42.10% | |||||||||||
| Immunonutrition | 50% | 52.60% | |||||||||||
| Complications | Septic shock | 55.60% | 52.60% | ||||||||||
| Myocardial dysfunction | 16.70% | 22.40% | 25% | 3% | |||||||||
| Systemic hypertension | 55.60% | 5.30% | 55% | 8% | |||||||||
| Infections | Skin infection/cellulitis | 38.90% | 27.60% | 35.10% | 27% | 11% | |||||||
| Pneumonia | 11.10% | 7.90% | 10% | 9.20% | 6.30% | ||||||||
| CLABSI | 0 | 2.60% | 1% | ||||||||||
| CAUTI | 0 | 1.30% | 9.30% | ||||||||||
Table 2.
Comparison of organisms causing infections among diabetic burns patients
| Present study | Maghsoudi et al.7 | Schwartz et al.16 | Memmel et al.12 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chennai, India, 2017 | Iran, 2008 | USA, 2011 | Chicago, USA, 2004 | |||||
| Studies | Diabetics | Nondiabetics | Diabetics | Nondiabetics | Diabetics | Nondiabetics | Diabetics | Nondiabetics |
| Organisms | Klebsiella species | Pseudomonas species | MSSA | MSSA | MSSA | MSSA | MSSA | MSSA |
| Pseudomonas species | Klebsiella species | Klebsiella species | MRSA | Streptococci | Pseudomonas species | Streptococci | Pseudomonas species | |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii | Streptococci | Pseudomonas species | Proteus species | Proteus species | Streptococci | ||
| Escherichia coli | Enterococcus | Pseudomonas species | Pseudomonas species | MRSA | Enterobacter species | |||
| Enterococcus species | Escherichia coli/Enterobacter species | CoNS | ||||||
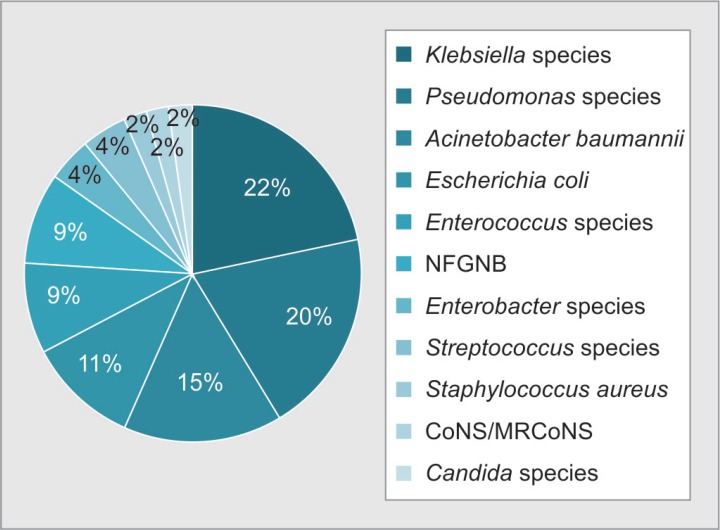
According to a recent report in 2014, India is estimated to harbor over 62 million diabetic individuals in the world.2 India is therefore known as the “diabetes capital of the world.”3 An Indian Council of Medical Research study has estimated that majority of affected population in India are from Maharashtra (9.2 million) and Tamil Nadu (4.8 million).4 This figure might be skewed as under-reporting is possible due to unavailability of diabetic screening tools in majority of rural areas. Due to high burden of diabetes in our state and country, we selectively analyzed this group of burns patients with diabetes (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7.
Distribution of organisms isolated from diabetic burns patients (n = 46)
Based on our literature search, studies on diabetic burns patients across the globe have emerged from developed countries like USA and UK. To our knowledge, there are no studies from India on burns in diabetes patients, where the burden of diabetes is much higher than developed nations.
In our study, there was an equal distribution of diabetic males (50%) and females (50%) admitted with burns. A study by Shalom et al. from USA has reported higher incidence of burns among diabetic males (61.6%).5 Mean age of diabetic burns patients was higher compared with nondiabetic burns patients from five different studies including ours.5–8 Foot burns probably due to peripheral neuropathy among this group of patients have been attributed to religious practices and use of foot-warming devices.9 We have not calculated the rate of foot burns among our patients, but it would be interesting to do the same (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8.
Outcomes among diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients
The mean TBSA involved among our patients was much higher than that reported from other studies. This explains the reason for slightly higher mortality and infection rates in our patients compared with other studies. Diabetic burns patients required surgeries more than nondiabetics, being consistent with other studies from Iran and USA.5,7,8
Average length of stay was lesser among our diabetic patients probably due to lesser percentage of them having third- and fourth-degree burns compared with the nondiabetic group of patients. Most diabetic patients therefore have lesser degree of burns (second-degree burns in 55.6%, third degree in 38.9%, and fourth degree in 5.6% patients).
Immunonutrition has been used as an adjunct therapy in burns due to its effect on mortality reduction.10 The use of immunonutrition among our diabetic and nondiabetic patients was almost similar. Since ours is a retrospective study, it is unclear to us what prompted our clinicians to initiate immunonutrition in some patients and not in others. Therefore, we are unable to comment on differences in efficacy of immunonutrition among diabetic and nondiabetic burns patients.
The use of collagen dressings has become a part of institutional protocol in burns patients, and we did find that the usage was higher among nondiabetic burns patients compared with diabetic burns patients. The authors from India have shown supportive evidence to the use of collagen dressings in burns but evidence for its use in diabetics is lacking.11 A larger sample size is required to substantiate whether collagen dressings would benefit diabetics more than nondiabetics. With the existing studies, it is not possible to comment on the same.
The most common comorbidity coexisting with diabetes mellitus among burns patients is systemic hypertension. This finding of ours was consistent with another study by Memmel et al. from USA.12 Mortality rate among burns patients is directly proportional to the number of comorbidities existing in them. This has been established by Charlson et al. in 1987 using an index called Charlson Comorbidity Index to predict the 10-year mortality of patients with a range of medical conditions.13 We were unable to calculate this score for our patients as certain parameters were undefined such as diabetes with and without chronic complications. Detailed history and defined parameters are therefore required to calculate this score among diabetic burns patients in future.
Infections among diabetic burns patients are much diverse and more severe than that occurring in nondiabetics. The factors contributing to the same are poor glycemic control, pathological microvascular, and macrovascular changes, etc.14 We observed skin and soft tissue infections including cellulitis to be the commonest infections in our patients followed by pneumonia. Similar findings have been documented by two other authors from USA.8,12,15
Among organisms causing infections in diabetic burns patients, gram-negative organisms predominate over gram-positive organisms and fungi. Three studies from Iran and USA have reported controversial results with gram-positive organisms predominating their diabetic burns population. However, there was no major difference in organisms isolated from diabetics and nondiabetics in these studies.7,12,16 Based on our study findings, it may be postulated that choice of empiric cover for gram negatives should be kept in mind while treating burns patients in our geographic location.
Fungal infections in burns patients are commonly caused by Candida and Zygomycetes.17 Fungal infections were not a common concern among our diabetic patients with only 2% infection with Candida species. We did not encounter mold infections such as aspergillosis and zygomycosis among our patients. Other authors across the globe have also not reported higher incidence of fungal infections among diabetic burns patients. In our study, the duration of stay of patient with Candiduria was found to be higher than other patients and this can be postulated as the possible risk factor. Other contributing factors to the same are burn size of 55% TBSA, acute kidney injury, and septic shock. Multiple positive cultures from various samples leading to long-term exposure to antibiotics is another major risk factor in these patients with Candida infection. These findings are consistent with the findings reported in a review by Ballard et al. on positive fungal cultures among burns patients.18
With major differences observed in the presentation and progress of course of illness among diabetic burns patients when compared to nondiabetics, we realize the need to perform larger studies on detailed analysis of various other factors and mortality rate prediction among diabetic burns patients. Diabetes is burdensome in our country; diabetics suffering from burn injuries should be handled with much caution, keeping in mind the possibilities of varied factors predisposing to a higher mortality rate.
CONCLUSION
Our study reflects the commonalities and differences in burns patients with or without diabetes. The infection and mortality rate appears to be increased in diabetics with burns. Of note, majority of our infections were gram negative in origin in comparison with Western studies where gram-positive organisms were more common. Larger multicenter cohorts and prospective analysis may help to better understand the impact of comorbidities in patients with burns.
Footnotes
Source of support: Nil
Conflict of interest: None
REFERENCES
- 1.Feinstein AR. The pre-therapeutic classification of co-morbidity in chronic disease. J Chronic Dis. 1970;23:455–468. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(70)90054-8. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kaveeshwar SA, Cornwall J. The current state of diabetes mellitus in India. AMJ. 2014;7(1):45–48. doi: 10.4066/AMJ.2014.1979. DOI: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Joshi SR, Parikh RM. India - diabetes capital of the world: now heading towards hypertension. J Assoc Physicians India. 2007;55:323–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anjana RM, Ali MK, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Datta M, Unnikrishnan R, et al. The need for obtaining accurate nationwide estimates of diabetes prevalence in India—rationale for a national study on diabetes. Indian J Med Res. 2011;133:369–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shalom A, Friedman T, Wong L. Burns and diabetes. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2005;18(1):31–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kimball Z, Patil S, Mansour H, Marano MA, Petrone SJ, Chamberlain RS. Clinical outcomes of isolated lower extremity or foot burns in diabetic versus non-diabetic patients: a 10-year retrospective analysis. Burns. 2013;39(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2012.06.006. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maghsoudi H, Aghamohammadzadeh N, Khalili N. Burns in diabetic patients. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2008;28(1):19–25. doi: 10.4103/0973-3930.41982. DOI: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McCampbell B, Wasif N, Rabbitts A, Staiano-Coico L, Yurt RW, Schwartz S. Diabetes and burns: retrospective cohort study. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2002;23(3):157–166. doi: 10.1097/00004630-200205000-00004. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thng P, Lim RM, Low BY. Thermal burns in diabetic feet. Singapore Med J. 1999;40:362–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tan HB, Danilla S, Murray A, Serra R, El Dib R, Henderson TO, et al. Immunonutrition as an adjuvant therapy for burns. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD007174. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007174.pub2. DOI: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Singh O, Gupta SS, Soni M, Moses S, Shukla S, Mathur RK. Collagen dressing versus conventional dressings in burn and chronic wounds: a retrospective study. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2011;4(1):12–16. doi: 10.4103/0974-2077.79180. DOI: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Memmel H, Kowal-Vern A, Latenser BA. Infections in diabetic burn patients. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):229–233. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.1.229. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goutos I, Nicholas RS, Pandya AA, Ghosh SJ. Diabetes mellitus and burns. Part I-basic science and implications for management. Int J Burn Trauma. 2015;5(1):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barsun A, Sen S, Palmieri TL, Greenhalgh DG. A ten-year review of lower extremity burns in diabetics: small burns that lead to major problems. J Burn Care Res. 2013;34(2):255–260. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e318257d85b. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schwartz SB, Rothrock M, Barron-Vaya Y, Bendell C, Kamat A, Midgett M, et al. Impact of diabetes on burn injury: preliminary results from prospective study. J Burn Care Res. 2011;32(3):435–441. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e318217f954. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stern LE, Kagan RJ. Rhinocerebralmucormycosis in patients with burns: case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20(4):303–306. doi: 10.1097/00004630-199907000-00005. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ballard J, Edelman L, Saffle J, Sheridan R, Kagan R, Bracco D, et al. Positive fungal cultures in burn patients: A multicenter review. J Burn Care Res. 2008;29(1):213–221. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e31815f6ecb. DOI: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]