Abstract
Central nervous system (CNS) injury results in chronic scar formation that interferes with function and inhibits repair. Extracellular matrix (ECM) is prominent in the scar and potently regulates cell behavior. However, comprehensive information about the ECM proteome is largely lacking, and region- as well as injury-specific differences are often not taken into account. These aspects are the focus of our perspective on injury and scar formation. To highlight the importance of such comprehensive proteome analysis we include data obtained with novel analysis tools of the ECM composition in the scar and show the contribution of monocytes to the ECM composition after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Monocyte invasion was reduced using the CCR2-/- mouse line and step-wise de-cellularization and proteomics allowed determining monocyte-dependent ECM composition and architecture of the glial scar. We find significant reduction in the ECM proteins Tgm1, Itih (1,2, and 3), and Ftl in the absence of monocyte invasion. We also describe the scar ECM comprising zones with distinctive composition and show a subacute signature upon comparison to proteome obtained at earlier times after TBI. These results are discussed in light of injury-, region- and time-specific regulation of scar formation highlighting the urgent need to differentiate injury conditions and CNS-regions using comprehensive ECM analysis.
Keywords: brain injury, extracellular matrix, proteomics, glial scar, monocytes, macrophages
The Glial Scar and ECM
Upon trauma adult mammalian tissue typically scar causing tissue and organ dysfunction. In the central nervous system (CNS) scars affect information processing by several means (Robel and Sontheimer, 2016) including the formation of barriers for re-establishing connectivity (Cregg et al., 2014). Hence scars act as permanent barriers for self-repair and remain an obstacle for therapies enhancing plasticity or neuronal regeneration (Barker et al., 2018).
Scars are typically composed of a cell mixture comprising tissue resident cells, such as different glial cells in the CNS (Adams and Gallo, 2018), and invading cells such as inflammatory cells derived from the immune system, e.g., monocytes (Orr and Gensel, 2018). In addition, in some injury paradigms and CNS regions (e.g., after spinal cord injury) fibroblasts and/or pericytes accumulate in the core of the injury site (Göritz et al., 2011; Soderblom et al., 2013). Notably, this cell mixture differs profoundly depending on the injury type (TBI, stroke, amyloid deposition, autoimmune-reaction) and the CNS region. For example, in spinal cord injury fibroblast-like cells settle in the lesion core that is shielded/surrounded by reactive glial cells, such as astrocytes (Kjell and Olson, 2016). This is can be very different in stab wound brain injury with prominent reactive gliosis and little to no detectable fibrosis (Frik et al., 2018). This is also the case, when the brain injury reaches into the White Matter (WM) (Mattugini et al., 2018) that is often less affected in brain injury as it is buried deep in the brain below the Gray Matter (GM). After spinal cord injury WM is always affected first as it is located at the surface. Effects on WM are thus one of the many major differences upon injury inflicted to these very distinct regions. Notably, monocyte invasion continues into much later stages after the injury when WM is affected, while newly invading monocytes can no longer be detected 5–7 days after injury of GM only (Mattugini et al., 2018.). Thus, the cellular composition of the wound and scar differs profoundly in a region-specific manner in the CNS.
Given that all of these different cells communicate and interact by a plethora of cell surface signaling pathways and secretion of specific proteins it is essential to unravel this complex proteome, not the least to also understand how injury- and region-specific extracellular matrix (ECM) composition contributes to scar formation. A suitable approach is to deplete one population and then examine relevant changes. For invading monocytes, this can be done by blocking or deleting the CCR2 – a receptor absolutely essential for invasion of monocytes into the brain (Saederup et al., 2010). Intriguingly, lack of monocyte invasion shows profoundly different outcomes in different injury conditions and distinct CNS regions. Preventing monocyte invasion after ischemic stroke has been reported to worsen the hemorrhagic consequences and reduce the long-term recovery (Gliem et al., 2012; Wattananit et al., 2016). However, in TBI models the prevention of monocyte invasion has reduced the volume of the injury-affected region and improved cognitive function (Hsieh et al., 2014; Morganti et al., 2015). These data may well reflect, the differences in ECM composition in different regions and injury conditions.
Extracellular matrix changes have mostly been examined after spinal cord injury aiming to understand how they affect the restoration of ascending and descending axonal connections (Didangelos et al., 2016; Bradbury and Burnside, 2019). Several ECM components have been found to be inhibitory for repair, especially chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan-chains (GAG-chains) on proteoglycans at the injury site. These sugar-chains have proven inhibitory to axon growth and digesting them enzymatically or keeping them from stable growth cone interactions improves regeneration (Bradbury et al., 2002; Bartus et al., 2014; Lang et al., 2015). The Tenascin glycoproteins have been found to be upregulated in the same region as the CSPG, where Tenascin-R is a component normally part of the Perineuronal nets (PNN) (Deepa et al., 2006; Carulli et al., 2010) and Tenacin-C (Tn-C) is an inflammation-associated ECM protein upregulated following CNS injury (Roll and Faissner, 2019). Other commonly reported scar components are those of the fibrotic scar that are of similar composition to the basal membrane, containing e.g., collagen, laminins, and fibronectin. Moreover, injury is associated with the degradation of such core ECM proteins (Roll and Faissner, 2014). Responsible for this are peptidases, include the elastases and matrix metallopeptidases. In spinal cord, another catalytic ECM-associated protein group called cathepsins has recently been highlighted using proteomics and transcriptomics as potential ECM regulators (Tica et al., 2018), providing an example of the multitude of unexplored avenues for ECM and its associated proteins in CNS injury.
Monocyte-Dependent ECM in the Glial Scar
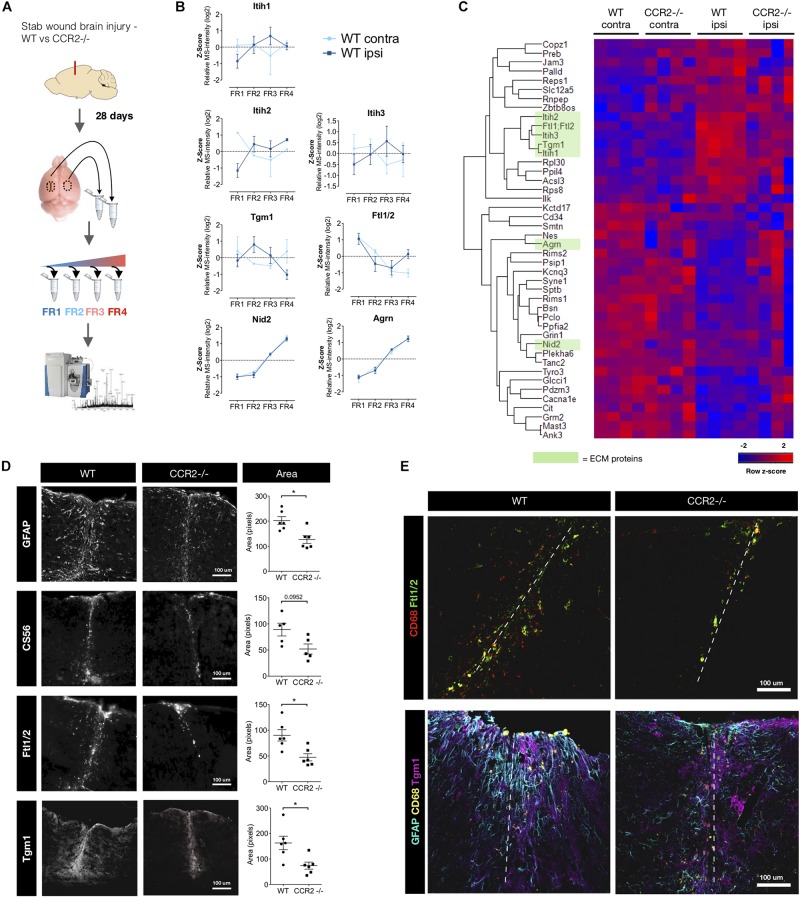
Inflammation is part of the cascade of events that follows traumatic injury and has also been found to regulate the extent of the scarring after TBI in cerebral cortex GM (Frik et al., 2018). Of the multiple invading immune cells, monocyte comprises the largest group, and surprisingly little is known about the role of macrophages in affecting the ECM composition at the scar. With scarring reduced after stab wound injury in the CCR2-/- cerebral cortex (Frik et al., 2018) we investigated which ECM components may be affected by the virtual absence of macrophages in the brain parenchyma after injury in this mouse line. We used state-of the-art proteomics (Cox and Mann, 2008; Mann et al., 2013; Cox et al., 2014; Kulak et al., 2014; Tyanova et al., 2016) and the quantitative detergent solubility profile (QDSP) method, in order to also investigate the architecture and composition of the ECM. The QDSP method analyses all the tissue lysates fractions after the tissue has been sequentially processed in increasing strength of detergent (see Supplementary Material or Kjell et al., 2020), with the most detergent-insoluble proteins in a separate fraction (fraction 4 – see Figure 1A). Basically, it is a tissue decellularization that also provides information regarding the intermediates solubilities as proteins are identified and quantified in all (four) fractions using label-free mass spectrometry. The ECM proteins are identified in the data-set by the currently most comprehensive annotation for the ECM proteins – the matrisome annotation that uses a combination of proteomic measurements from decellularized tissue and in silico prediction to identify the ECM proteins (Naba et al., 2012). The advantage of analyzing all detergent-fractions in the QDSP method is that it allows determining how the total abundance of a protein is distributed in the different fractions and how this solubility profile shifts under different conditions. This provides crucial information regarding changes in ECM protein distribution, e.g., from basal lamina (highly insoluble) to interstitial space (soluble) after trauma. Indeed, Transglutaminase 1 (Tgm1) changes its solubility profile reducing the insoluble fraction after injury with a peak in fraction 2, i.e., becoming more soluble. Conversely, the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitors 1,2,3 (Itih1,2,3) became rather less soluble at the scar stage (28 days post injury; dpi) after TBI (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
Macrophages contribute to the ECM-component of the scar after stab wound injury. (A) Schematic of the proteome comparison 28 days after brain stab wound injury in wild-type mice compared to CCR2-/- mice using step-wise detergent-decellularization protocol, named quantitative detergent solubility profiling (QDSP). Mouse brain picture courtesy: National Science Foundation. (B) The QDSP method subjects the tissues to increasing strength of detergent lysis and results in four individual fractions. Fraction measurements have are here compared for ECM and secreted proteins in the contralateral and the ipsilateral side of the injured wild-type brains, which returned to more normal levels in the CCR2-/- mouse. Overall the solubility changes trend toward a more insoluble nature, although not exclusively insoluble. Notably, while the total abundance of Nid2 and Agrn normalized (got more abundant) in the CCR2 -/- mice, there was no difference in their solubility profiles. (C) Combined fraction analysis reveal that the overall protein changes are normalized in the CCR2 -/- mice compared to wild-type mice (n = 4 per group). Heatmap displays proteins that had similar abundance in the contralateral samples (t-test, p ≥ 0.05), while being significantly different when comparing contralateral to ipsilateral side of the injured wild-type mouse brain (t-test, p ≤ 0.01). ECM and secreted proteins are highlighted in green. (D) Quantifications of the immunoreactive tissue-area at the injury site confirm that Ftl1/2 and Tgm1 are reduced in the CCR2-/- mice closer to levels contralateral to the injury. This is in line with the reduced spread of other glial scar markers such as GFAP and CS56. * p ≤ 0.05. (E) Ftl1/2 primarily co-localizes with the macrophage marker CD68, while Tgm1 instead is predominantly found in the area of reactive astrocytes (GFAP + cells).
In our investigation of the adult neurogenic niche (Kjell et al., 2020), also using the QDSP protocol, we found that ECM proteins, such as Tn-C, are more soluble compared to the brain parenchyma. Tn-C is also highly soluble in the scar region analyzed by QDSP at 28 dpi here, which is opposite to its insoluble nature in lung injury and atherosclerotic plaques (Schiller et al., 2015; Wierer et al., 2018). These are examples of how any quantification and information regarding ECM architecture would be lost without adopting a protocol that allows composition-dependent sample analysis.
Next, we examined combined fraction analysis to determine total abundance comparisons for any protein (Figure 1C). To identify proteins regulated by invading monocytes and their influence in scar formation, we compared proteins of similar magnitude in the non-injured contralateral side of the WT and CCR2-/- mice brains (two-tailed t-test, p ≥ 0.05) that were significantly changed following injury in the WT mice 28 days after stab wound injury (two-tailed t-test, p ≤ 0.01) (Figure 1C). We found four ECM proteins and one secreted protein that were elevated with injury, but reduced in the CCR2-/- mice (green bar in Figure 1C). These were the above mentioned Tgm1, Itih1,2,3 and the ferritin light chain proteins 1 or 2 (here referred to as Ftl1/2). Notably, all of these have previously received little if any attention with regard to brain injury and glial scarring. Tgm1 is part of the cross-linking enzyme family of transglutaminases that have many roles, including the regulation of tissue stiffness when crosslinking ECM (Gundemir et al., 2012; Majkut et al., 2013). Immunostaining for Tgm1 was found to be rather diffuse around the injury in the entire area dominated by astrogliosis (Figures 1D,E). Taken together, this may suggest that the multi-function enzyme Tgm1 crosslinks cell surface proteins and/or less detergent resistant ECM proteins and/or prevails in the cytoplasm where it has intracellular functions (Eckert et al., 2014).
Itih 1,2,3 are hyaluronic acid binding proteins that can act as protease inhibitor and are often present with inflammation. Ftl1/2 binds ferric ions that would otherwise be toxic to the cells. These proteins could originate from the blood (Geyer et al., 2016). However, bioinformatic comparison from our previous publications with proteomes from the stab wound at 3 and 5 days after injury, hinted that this was unlikely (Frik et al., 2018; Mattugini et al., 2018). In these proteomes, blood proteins are highly abundant at 3 days after stab wound injury, but are instead reduced at 5 days. At 5 days, we find Tgm1, Itih3, and Ftl1/2 to be more abundant, while the overall blood-related proteins have decreased. Furthermore, this highlights that much of the ECM changes remain from, or have similar composition to, a subacute stage after injury.
We confirm the presence of Ftl1/2 and Tgm1 in the tissue with immunohistochemistry. Our area-coverage analysis suggests the reduced abundance of these proteins in the CCR2-/- mouse stab wound injury site at 28 days is due to being restricted to a smaller area (Figure 1D). Most of the Ftl1/2 could be attributed to CD68+ macrophages or activated microglia and was present in a similar area to the chondroitin sulfate GAG-chains at the injury site (Figures 1D,E). Given that Ftl1/2 is secreted and became more insoluble at the scar (Figure 1B), we propose this protein to be a matrisome-associated protein. An interesting possibility is that it may be bound to the ECM of the vasculature to capture Fe ions prior to entering the brain parenchyma to prevent the induction of toxic phospholipid oxidation products that lead to ferroptosis of cells at the injury site (Stockwell et al., 2017; Conrad and Pratt, 2019). Neurons – also in direct reprogramming from glial cells – can be particularly vulnerable to ferroptosis as recently shown (Gascón et al., 2016).
Interestingly, the block of proteins that are reduced ipsilateral compared to contralateral by injury are often associated to synapses (Figure 1C, e.g., Agrin, Cacna1e, Kcnq3, Mast3) indicative of the synapse loss persisting in the scar region of the injury site. Intriguingly, this loss is alleviated in the injury site of the CCR2-/- mice consistent with the notion that the scar is indeed reduced and the absence of monocyte invasion is beneficial for neuronal network recovery (Dimitrijevic et al., 2007; Hsieh et al., 2014; Morganti et al., 2015; Frik et al., 2018). We also see changes in the solubility of synaptic proteins (e.g., Gria2-3, Olfm3, Glgap1, and Vamp1), while we did not see an obvious change in the solubility of PNN proteins in the scar stage between the genotypes. Our previous QDSP analysis of PNN proteins in the uninjured cerebral cortex had revealed that they are typically not insoluble (in fraction 4), but rather belong to a less detergent resistant category (fractions 2–3; Kjell et al., 2020). Taken together, lack of monocyte invasion affects ECM proteins in a long-term manner toward a state closer to the un-injured contralateral site, thus normalizing the scar ECM.
ECM Origin and Scarring Zones
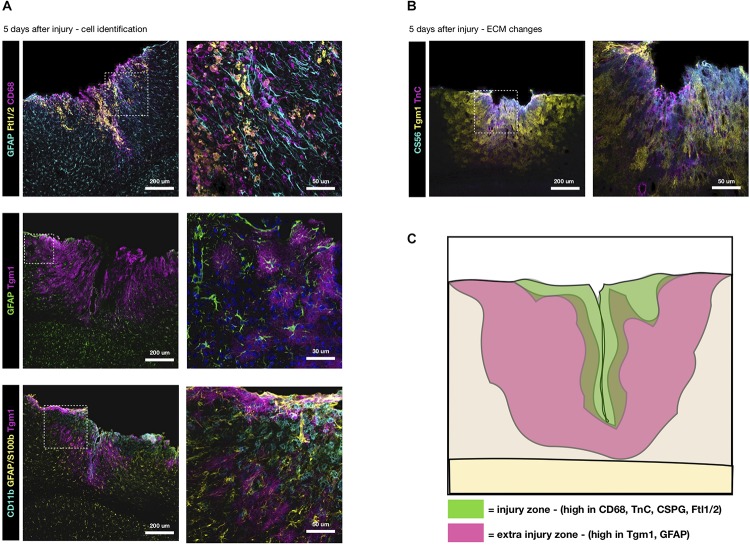
Comparing previous proteomes obtained at the acute stages 3 and 5 dpi (Frik et al., 2018; Mattugini et al., 2018), we find scar-related ECM proteins peak at 5 days. At this time, we find Ftl1/2 to be present on and around CD68+ macrophages, although it seems to only be a subset that is responsible for the Ftl1/2 secretion (Figure 2A). Hence, we suggest that reduced levels of Ftl1/2 are a direct consequence of preventing the invasion of monocytes. Changes in Tgm1 on the other hand, rather seem to be an indirect consequence, since Tgm1 is not produced by macrophages, but rather astrocytes, as seen by immunostaining (Figures 2A,B). Indeed, Tgm1 has been proposed as a marker for neuroprotective astrocytes (Liddelow et al., 2017). Interestingly, Tgm1 spreads much further than the area densely populated with macrophages/activated microglia, giving credit to the idea that Tgm1 would be part of a neuroprotective response, possibly by maintaining the tissue integrity. The tissue of the glial scar is softer at the area affected by macrophages (Moeendarbary et al., 2017) and perhaps tissue more peripheral to the injury would also succumb to a similarly soft mechanical signature if Tgm1 was not present to counteract this by crosslinking ECM proteins.
FIGURE 2.
Distinctive ECM zones at 5 days after TBI. (A) Tgm1 and Ftl1/2 immunsotaining at 5 dpi, the peak of their deposition (Frik et al., 2018). Ftl1/2 is mostly found around CD68+ macrophages or activated microglia at the center of the injury site. Instead Tgm1 is present in a wider area overlapping with the region of GFAP+ reactive astrocytes, suggesting astrocytes may be a likely candidate for much of the Tgm1 expression/deposition. Interestingly, Tgm1 seems to surround the macrophage/activated microglia dense area suggestive of regionalization. (B) Tn-C and CS56, two ECM markers typical for the reactive glia, are localized to the center of the forming scar, while Tgm1 is more peripheral to it. (C) Here, in a conceptual summary of the subacute wound after stab wound injury of the brain, we suggest there are two primary zones (at the injury site and peripheral to the injury site) with different changes in the extracellular microenvironment that are fundamental to the final composition of the glial scar.
Comparing the localization of Tgm1 with Tn-C and CSPG at 5 dpi, we find the increased levels of Tn-C and chondroitin sulfate GAG-chains (CS56) to be more associated to the core area of the injury with dense macrophage infiltrates, rather than the astrogliosis (Figure 2B). Hence, our results suggest that there are zones with different ECM composition in the scar-forming region (Figure 2C). The ECM and cell markers also suggest these zones may represent neurotoxic (core) and neuroprotective (surround) areas. Clearly, invasion of monocytes increases the neurotoxic core of the forming scar and its specific ECM, both directly and indirectly.
Complexity in Investing the Glial Scar
In any organ, scarring is a process that renders the respective part of an organ chronically non-functional. Scars are typically different from normal tissue in their ECM composition and hence a lot can be read from the changes in ECM in different tissue under abnormal conditions. However, in most cases only few ECM proteins are monitored as “representative” of scar formation and a comprehensive analysis is missing. Proteomics now offer a robust way to detect abundances of a large set of ECM, even in small tissue samples with maintained depth of detection and identification. Here we combined the proteomics with a protocol that gives a good indication on the cellular compartment of all proteins. However, there may be further aspects of the ECM to be resolved with other sample-separation protocols, including investigations concerning the sugar-chain composition with glycomics or glycoproteomics. Comparative proteome-to-transcriptome analysis may yield further insights (Schiller et al., 2015; Angelidis et al., 2019; Kjell et al., 2020), specifically with single-cell RNA sequencing data that may allow identification of the cellular source of specific ECM proteins. For example, our analysis of the adult neurogenic niche shows that quiescent NSCs are by large the main contributor to the ECM composition of this niche (Kjell et al., 2020).
Moreover, proteome analysis at different times after stab wound injury unraveled that scar formation is determined at a subacute stages. When we compared the proteome of the injury site at 5 and 28 dpi between WT and CCR2-/- mice, we observed that many scar-related factors (such as enzymes for gycosaminoglycanes, but also many scar-resident proteins, such as Ftl1/2, Itih) are already present at 5 dpi and higher in WT. At this time the injury site and reactive gliosis region surrounding the injury is not yet obviously different between the genotypes, but the proteomic composition including ECM proteins is already profoundly changed in the absence of monocyte invasion (Frik et al., 2018).
Given the potent effects of monocyte invasion on scar formation, it is important to note the differences in monocyte invasion in GM and WM regions. This can best be demonstrated when GM and WM injury are directly compared in the same brain region, as was recently done for the cerebral cortex using the GM injury paradigm described above and extending it into the WM (Mattugini et al., 2018). This revealed a much prolonged and bi-phasic monocyte invasion up to 2–3 weeks after injury in the WM, very much reminiscent of data obtained after spinal cord injury (Blight, 1992; Popovich et al., 1997; Beck et al., 2010). As WM sits at the surface of the spinal cord, it is always affected upon mechanical injury in this region, while brain injury is often restricted to GM given its location at the brain surface. Along with different patterns of monocyte invasion, many other aspects of gliosis, such as NG2 glia proliferation, were also different in brain TBI comprising the WM compared to GM only injury conditions (Mattugini et al., 2018). These data highlight that results obtained in one CNS region, such as the spinal cord, can not simply be extended to other regions, such as the cerebral cortex. Likewise, results obtained in one injury paradigm can not simply be extended to others as highlighted by the diversity of effects obtained by deletion or blocking of CCR2 in different injury paradigms. Unfortunately, this obvious message is all too often ignored.
These profound region- and injury-specific differences can also be observed when considering the zonation at the subacute injury site and the aspects of it that persist as part of the scar. Here we described two partly overlapping zones consisting of different cell types and ECM proteins in an injury largely lacking fibrosis. For other injury types with a fibrotic core it will be important to understand the different ECM composition of the fibrotic ECM and the surrounding gliotic one. This could also be done by using proteomic techniques analyzing the proteins directly from tissue sections such as MALDI-TOF (Lahiri et al., 2016; Quanico et al., 2018). Although fresh frozen tissue is preferred for proteomics, analyzing fixed tissue is now feasible, while maintaining a reasonable dept (Coscia et al., 2018) allowing exploration of ECM in patient samples. For example, such investigations have recently elucidated the role of the ECM-rich stromal compartments for cancer progression (Eckert et al., 2019). In addition to extending to human samples, it will be important to extend ECM analysis to samples of vertebrates with scar-less wound healing also after brain injury, such as the zebrafish (Baumgart et al., 2012; Kizil et al., 2015). Such data could teach us the composition of an extracellular environment that mediates wound healing without scar formation and allows neurogenesis and the integration of the new neurons. Characterizing such ECM changes may then help to steer ECM composition in mammalian brains toward scar-less wound healing supporting also neuronal replacement therapies.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article are available via ProteomeXchange (Vizcaino et al., 2013) with identifier PXD017478.
Ethics Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Government of Upper Bavaria (Regierung von Oberbayern).
Author Contributions
MG and JK wrote the perspective. MG conceived the project. JK and MG conceptualized and planned the project. JK performed all experiments and analysis.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We wish to deeply thank Matthias Mann for allowing us to perform the proteome part of this study in his lab. We also thank Herbert Schiller and Fabian Coscia for help with the proteomics.
Footnotes
Funding. We gratefully acknowledge funding from the German Research Council to MG (SFB870, SPP1751, SPP1738), the EU (Eranet S-700982-5008-001), the ERC (aERC ChroNeuroRepair, 340793, to MG), and the Swedish Society for Medical Research (SSMF) postdoctoral grant to JK.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2020.00032/full#supplementary-material
References
- Adams K. L., Gallo V. (2018). The diversity and disparity of the glial scar. Nat. Neurosci. 21 9–15. 10.1038/s41593-017-0033-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelidis I., Simon L. M., Fernandez I. E., Strunz M., Mayr C. H., Greiffo F. R., et al. (2019). An atlas of the aging lung mapped by single cell transcriptomics and deep tissue proteomics. Nat. Commun. 10:963. 10.1038/s41467-019-08831-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. A., Götz M., Parmar M. (2018). New approaches for brain repair-from rescue to reprogramming. Nature 557 329–334. 10.1038/s41586-018-0087-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartus K., James N. D., Didangelos A., Bosch K. D., Verhaagen J., Yáñez-Muñoz R. J., et al. (2014). Large-scale chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan digestion with chondroitinase gene therapy leads to reduced pathology and modulates macrophage phenotype following spinal cord contusion injury. J. Neurosci. 34 4822–4836. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4369-13.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart E. V., Barbosa J. S., Bally-Cuif L., Götz M., Ninkovic J. (2012). Stab wound injury of the zebrafish telencephalon: a model for comparative analysis of reactive gliosis. Glia. 60 343–357. 10.1002/glia.22269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K. D., Nguyen H. X., Galvan M. D., Salazar D. L., Woodruff T. M., Anderson A. J. (2010). Quantitative analysis of cellular inflammation after traumatic spinal cord injury: evidence for a multiphasic inflammatory response in the acute to chronic environment. Brain 133 433–447. 10.1093/brain/awp322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight A. R. (1992). Macrophages and inflammatory damage in spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 1 83–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. J., Burnside E. R. (2019). Moving beyond the glial scar for spinal cord repair. Nat. Commun. 10:3879. 10.1038/s41467-019-11707-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. J., Moon L. D., Popat R. J., King V. R., Bennett G. S., Patel P. N., et al. (2002). Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 416 636–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carulli D., Pizzorusso T., Kwok J. C., Putignano E., Poli A., Forostyak S., et al. (2010). Animals lacking link protein have attenuated perineuronal nets and persistent plasticity. Brain 133 2331–2347. 10.1093/brain/awq145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M., Pratt D. A. (2019). The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 15 1137–1147. 10.1038/s41589-019-0408-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coscia F., Lengyel E., Duraiswamy J., Ashcroft B., Bassani-Sternberg M., Wierer M. (2018). Multi-level proteomics identifies CT45 as a chemosensitivity mediator and immunotherapy target in ovarian cancer. Cell 175 159.e16–170.e16. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J., Hein M. Y., Luber C. A., Paron I., Nagaraj N., Mann M. (2014). Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Mol Cell Proteomics 13 2513–2526. 10.1074/mcp.m113.031591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J., Mann M. (2008). MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 26 1367–1372. 10.1038/nbt.1511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cregg J. M., DePaul M. A., Filous A. R., Lang B. T., Tran A., Silver J. (2014). Functional regeneration beyond the glial scar. Exp. Neurol. 253 197–207. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.12.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deepa S. S., Carulli D., Galtrey C., Rhodes K., Fukuda J., Mikami T., et al. (2006). Composition of perineuronal net extracellular matrix in rat brain: a different disaccharide composition for the net-associated proteoglycans. J Biol. Chem. 281 17789–17800. 10.1074/jbc.m600544200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didangelos A., Puglia M., Iberl M., Sanchez-Bellot C., Roschitzki B., Bradbury E. J. (2016). High-throughput proteomics reveal alarmins as amplifiers of tissue pathology and inflammation after spinal cord injury. Sci. Rep. 6:21607. 10.1038/srep21607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrijevic O. B., Stamatovic S. M., Keep R. F., Andjelkovic A. V. (2007). Absence of the chemokine receptor CCR2 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Stroke 38 1345–1353. 10.1161/01.str.0000259709.16654.8f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert M. A., Coscia F., Chryplewicz A., Chang J. W., Hernandez K. M., Pan S. (2019). Proteomics reveals NNMT as a master metabolic regulator of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nature 569 723–728. 10.1038/s41586-019-1173-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Kaartinen M. T., Nurminskaya M., Belkin A. M., Colak G., Johnson G. V., et al. (2014). Transglutaminase regulation of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 94 383–417. 10.1152/physrev.00019.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frik J., Merl-Pham J., Plesnila N., Mattugini N., Kjell J., Kraska J., et al. (2018). Cross-talk between monocyte invasion and astrocyte proliferation regulates scarring in brain injury. EMBO Rep. 19:e45294. 10.15252/embr.201745294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Murenu E., Masserdotti G., Ortega F., Russo G. L., Petrik D., et al. (2016). Identification and successful negotiation of a metabolic checkpoint in direct neuronal reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 18 396–409. 10.1016/j.stem.2015.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. E., Kulak N. A., Pichler G., Holdt L. M., Teupser D., Mann M. (2016). Plasma proteome profiling to assess human health and disease. Cell Syst. 2 185–195. 10.1016/j.cels.2016.02.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliem M., Mausberg A. K., Lee J. I., Simiantonakis I., van Rooijen N., Hartung H. P., et al. (2012). Macrophages prevent hemorrhagic infarct transformation in murine stroke models. Ann. Neurol. 71 743–752. 10.1002/ana.23529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göritz C., Dias D. O., Tomilin N., Barbacid M., Shupliakov O., Frisén J. (2011). A pericyte origin of spinal cord scar tissue. Science 333 238–242. 10.1126/science.1203165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundemir S., Colak G., Tucholski J., Johnson G. V. (2012). Transglutaminase 2: a molecular Swiss army knife. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1823 406–419. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.09.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., Niemi E. C., Wang S. H., Lee C. C., Bingham D., Zhang J., et al. (2014). CCR2 deficiency impairs macrophage infiltration and improves cognitive function after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 31 1677–1688. 10.1089/neu.2013.3252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizil C., Kyritsis N., Brand M. (2015). Effects of inflammation on stem cells: together they strive? EMBO Rep. 16 416–426. 10.15252/embr.201439702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjell J., Fischer-Sternjak J., Thompson A. J., Friess C., Sticco M. J., Salinas F., et al. (2020). Defining the adult neural stem cell niche proteome identifies key regulators of adult neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 26 277–293. 10.1016/j.stem.2020.01.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjell J., Olson L. (2016). Rat models of spinal cord injury: from pathology to potential therapies. Dis Model Mech. 9 1125–1137. 10.1242/dmm.025833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulak N. A., Pichler G., Paron I., Nagaraj N., Mann M. (2014). Minimal, encapsulated proteomic-sample processing applied to copy-number estimation in eukaryotic cells. Nature Methods 11 319–324. 10.1038/nmeth.2834 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri S., Sun N., Solis-Mezarino V., Fedisch A., Ninkovic J., Feuchtinger A., et al. (2016). In situ detection of histone variants and modifications in mouse brain using imaging mass spectrometry. Proteomics 16 437–447. 10.1002/pmic.201500345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. T., Cregg J. M., DePaul M. A., Tran A. P., Xu K., Dyck S. M. (2015). Modulation of the proteoglycan receptor PTPσ promotes recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 518 404–408. 10.1038/nature13974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddelow S. A., Guttenplan K. A., Clarke L. E., Bennett F. C., Bohlen C. J., Schirmer L. (2017). Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541 481–487. 10.1038/nature21029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majkut S., Idema T., Swift J., Krieger C., Liu A., Discher D. E. (2013). Heart-specific stiffening in early embryos parallels matrix and myosin expression to optimize beating. Curr. Bio. 23 2434–2439. 10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann M., Kulak N. A., Nagaraj N., Cox J. (2013). The coming age of complete, accurate, and ubiquitous proteomes. Mol. Cell 49 583–590. 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattugini N., Merl-Pham J., Petrozziello E., Schindler L., Bernhagen J., Hauck S. M., et al. (2018). Influence of white matter injury on gray matter reactive gliosis upon stab wound in the adult murine cerebral cortex. Glia 66 1644–1662. 10.1002/glia.23329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeendarbary E., Weber I. P., Sheridan G. K., Koser D. E., Soleman S., Haenzi B., et al. (2017). The soft mechanical signature of glial scars in the central nervous system. Nat. Commun. 8:14787. 10.1038/ncomms14787 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganti J. M., Jopson T. D., Liu S., Riparip L. K., Guandique C. K., Gupta N., et al. (2015). CCR2 antagonism alters brain macrophage polarization and ameliorates cognitive dysfunction induced by traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. 35 748–760. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2405-14.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naba A., Clauser K. R., Hoersch S., Liu H., Carr S. A., Hynes R. O. (2012). The matrisome: in silico definition and in vivo characterization by proteomics of normal and tumor extracellular matrices. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 11:M111.014647. 10.1074/mcp.M111.014647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr M. B., Gensel J. C. (2018). Spinal cord injury scarring and inflammation: therapies targeting glial and inflammatory responses. Neurotherapeutics 15 541–553. 10.1007/s13311-018-0631-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovich P. G., Wei P., Stokes B. T. (1997). Cellular inflammatory response after spinal cord injury in sprague-dawley and lewis rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 377 443–464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quanico J., Hauberg-Lotte L., Devaux S., Laouby Z., Meriaux C., Raffo-Romero A. (2018). 3D MALDI mass spectrometry imaging reveals specific localization of long-chain acylcarnitines within a 10-day time window of spinal cord injury. Sci. Rep. 8:16083. 10.1038/s41598-018-34518-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robel S., Sontheimer H. (2016). Glia as drivers of abnormal neuronal activity. Nat. Neurosci. 19 28–33. 10.1038/nn.4184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roll L., Faissner A. (2014). Influence of the extracellular matrix on endogenous and transplanted stem cells after brain damage. Front. Cell Neurosci. 8:219. 10.3389/fncel.2014.00219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roll L., Faissner A. (2019). Tenascins in CNS lesions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 89 118–124. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saederup N., Cardona A. E., Croft K., Mizutani M., Cotleur A. C., Tsou C. L., et al. (2010). Selective chemokine receptor usage by central nervous system myeloid cells in CCR2-red fluorescent protein knock-in mice. PLoS One 5:e13693. 10.1371/journal.pone.0013693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller H. B., Fernandez I. E., Burgstaller G., Schaab C., Scheltema R. A., Schwarzmayr T. (2015). Time- and compartment-resolved proteome profiling of the extracellular niche in lung injury and repair. Mol. Syst. Biol. 11 819–819. 10.15252/msb.20156123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderblom C., Luo X., Blumenthal E., Bray E., Lyapichev K., Ramos J. (2013). Perivascular fibroblasts form the fibrotic scar after contusive spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 33 13882–13887. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2524-13.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell B. R., Friedmann Angeli J. P., Bayir H., Bush A. I., Conrad M., Dixon S. J. (2017). Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism. Redox Biol.Dis. Cell 171 273–285. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tica J., Bradbury E. J., Didangelos A. (2018). Combined transcriptomics, proteomics and bioinformatics identify drug targets in spinal cord injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 E1461. 10.3390/ijms19051461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyanova S., Temu T., Sinitcyn P., Carlson A., Hein M. Y., Geiger T., et al. (2016). The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nature Methods 13 731–740. 10.1038/nmeth.3901 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizcaino J. A., Cote R. G., Csordas A., Dianes J. A., Fabregat A., Foster J. M., et al. (2013). The Proteomics identifications (PRIDE) database and associated tools: status in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 D1063–D1069. 10.1093/nar/gks1262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattananit S., Tornero D., Graubardt N., Memanishvili T., Monni E., Tatarishvili J. (2016). Monocyte-derived macrophages contribute to spontaneous long-term functional recovery after stroke in mice. J. Neurosci. 36 4182–4195. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4317-15.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierer M., Prestel M., Schiller H. B., Yan G., Schaab C., Azghandi S. (2018). Compartment-resolved proteomic analysis of mouse aorta during atherosclerotic plaque formation reveals osteoclast-specific protein expression. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 17 321–334. 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article are available via ProteomeXchange (Vizcaino et al., 2013) with identifier PXD017478.