Abstract
Background
The role of dietary glycemic index (GI) and dietary glycemic load (GL) on metabolic syndrome (MetS) in youth populations remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the association among dietary GI, dietary GL, and MetS and its components in Mexican adolescents.
Methods
This study was conducted within the framework of the National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012, a cross-sectional, probabilistic, population-based survey with a multistage stratified cluster sampling design. We analyzed a sample of 1346 subjects aged 12–19 years, representing 13,164,077 adolescents. Dietary habits were assessed through a validated semiquantitative food-frequency questionnaire. We assigned GI values using the International Tables of GI values. We defined MetS according to the International Diabetes Federation criteria developed for adolescents. Multiple logistic regression models were used to estimate odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to evaluate the association between categories of dietary GI and GL and the prevalence of MetS and its components.
Results
We observed no associations between dietary GI or GL and MetS prevalence. Female adolescents in the highest category of dietary GI had higher odds of abnormal blood pressure (OR = 3.66; 95% CI, 1.46–9.22; P for trend = 0.012). A high dietary GL was also associated with higher odds of abnormal blood pressure in female adolescents (OR = 5.67; 95% CI, 1.84–17.46; P for trend = 0.003).
Conclusions
We found higher odds of abnormal blood pressure for female adolescents with a high dietary GI and dietary GL.
Keywords: Glycemic index, Glycemic load, Metabolic syndrome, Adolescent, Mexico
Background
The prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) is high among children and adolescents with obesity [1, 2]. In Mexico, almost 35% of adolescents are either overweight or obese [3] and the prevalence of MetS oscillates between 6.5% [4] and 19.2% [5]. Therefore, special attention should be given to modifiable risk factors, such as lifestyle and dietary habits: they play an important role in the development and progression of MetS. Among dietary factors, carbohydrates are the main energy source in the diets of most populations and have a special function in energy metabolism and homoeostasis [6]. However, evidence indicates that some carbohydrate sources can be beneficial; others are not, depending on their quality and fiber content [7]. The quality of carbohydrates can be measured using the glycemic index (GI); this is defined as the incremental area under the curve of blood glucose response after eating 50 g of available carbohydrates from a certain food and expressed as a percentage of the glycemic response elicited by 50 g of glucose or white bread [8]. Moreover, the glycemic load (GL) considers both the quality and quantity of carbohydrate intake [9, 10].
In adults, evidence from different meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated that low-GI or GL diets resulted in lower fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels [11] and a greater decrease in total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) compared to control diets [12, 13]. Nevertheless, the latter findings have not been observed in overweight/obese subjects who followed low GI/GL diets [14]. Furthermore, results from RCTs have demonstrated a favorable effect of a low-GI diet on triglyceride levels [15] or concentration of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) [16]. However, such findings are inconsistent and have not been confirmed by a recent meta-analysis [13].
In children and adolescents, a meta-analysis has demonstrated that low-GI diets might reduce serum triglycerides and homeostasis model assessment index in overweight or obese children and adolescents [17].
The association among GI, GL, and MetS has been mostly studied in prospective studies in adult populations [18, 19] and produced varying results. The evidence for such an association in young people is scarce. Two cross-sectional studies conducted in Australia have identified higher odds of developing MetS for each unit increase in breakfast GL [20] and per 20 unit dietary GL increase [21].
To our knowledge, no evidence is available on the relationship between the quality of carbohydrates and MetS in a Mexican youth population. Therefore, the main objective of this study was to evaluate the association among dietary GI, dietary GL, and MetS and its components in a nationally representative sample of Mexican adolescents.
Methods
Study population
This study was conducted within the framework of the National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012 (NHNS-2012), a cross-sectional, probabilistic, population-based survey with a multistage stratified cluster sampling design conducted in Mexico. The design and methods of the NHNS-2012 have been described elsewhere [22]. The main objective of the NHNS-2012 was to quantify the frequency, distribution, and trends in health and nutrition conditions and their determinants in the Mexican population [22]. Data were collected by computer-assisted interviews at participants’ homes. Child interviewees under the age of 14 years were assisted in their responses by a relative.
In the NHNS-2012 an original probabilistic sample of 17,000 adolescents was drawn. For the present study, we used the NHNS-2012 subsample of 2203 adolescents aged 12–19 years evaluated by means of a validated semiquantitative food-frequency questionnaire (SFFQ) to assess dietary habits [23]. We excluded subjects with missing values for biochemical measurements (19.7%) or other covariates used in the statistical analyses (12.4%). Furthermore, we excluded subjects with energy values outside predefined limits (6.8%). The methodology for cleaning dietary data has been broadly described elsewhere [24]. First, the weight in grams of food consumed by each study subject was evaluated according to age-group. We excluded from the analysis subjects who consumed above three standard deviations (SDs) of one or more food items. The biological plausibility of food intake and the percentage contribution of each food to total dietary intake was used to verify data identified as high values. Second, we estimated very high values of energy intake by the ratio of energy intake/estimated energy requirement. The equations of the Institute of Medicine were used as reference [25]. The physical activity level of each subject was considered according to previous studies regarding data of the NHNS-1999 [26]. We excluded very low values of energy intake: under 0.5 of energy intake/basal metabolic rate (BMR). We estimated BMR for adults (≥19 years of age) using the Mifflin-St Jeor equations [27]. For subjects under 19 years of age, we used the age- and sex-specific equations of the Food and Agriculture Organization [28]. Accordingly, we included a final sample of 1346 subjects in our analyses, representing a total of 13,164,077 Mexican adolescents (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
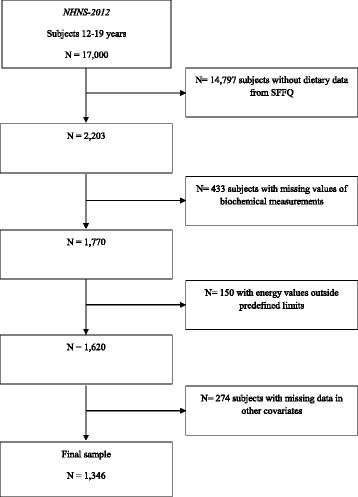
Flow chart showing study participant selection
Exposure assessment
Dietary assessment
Trained personnel applied a validated SFFQ to evaluate dietary habits during the 7 days before the interview date [23, 24]. For each food item, the questionnaire measured the frequency of intake according to set categories: the range was “never” to “six times a day.” Participants also designated the food portion sizes, using defined categories and number of servings consumed during that week. We first converted the data to number of times a day, and we then estimated the daily portion size. To calculate the consumption of energy (kcal/day) and daily nutrient intakes, we multiplied the daily frequency of consumption (portions/day) of each food by the amount of energy and nutrients in a standard serving or portion size of that food. For that purpose, we used the food composition tables compiled by the National Institute of Public Health of Mexico (INSP: Databases of the nutritional value of food. Compilation of the National Institute of Public Health, unpublished). We totaled the contributions of all foods using Microsoft Visual FoxPro 7.0 (Microsoft Corporation, Seattle, WA, USA). The average Pearson correlation coefficient, between SFFQ and two 24-h dietary recalls, for absolute nutrient intake was 0.374 for adolescents. The unadjusted, adjusted and deattenuated Pearson correlation coefficients for carbohydrate intake in adolescent population were 0.51, 0.25 and 0.36 respectively [23]. The intake of carbohydrate, protein, fat, and dietary fiber was sex-specific adjusted for total energy intake using the residual method proposed by Willett et al. [29].
Dietary GI and dietary GL assessment
We used the protocol of Louie et al. [30] to assign a GI value to each food item in the SFFQ. We obtained the GI values from available studies conducted in normal subjects, using glucose as reference food [31, 32]. We calculated the dietary GI of each subject by summing the products of the available carbohydrate content per serving for each food multiplied by the average number of daily servings of that food multiplied by its GI; we then divided this by the total amount of daily carbohydrate intake [10, 33]. In a similar manner but without dividing by the total amount of carbohydrate, we estimated dietary GL [10]. Dietary GL was energy-adjusted using sex-specific residuals [29] owing to a high correlation with energy intake (r = 0.880, P < 0.001). Finally, we categorized dietary GI and energy-adjusted dietary GL into sex-specific tertiles.
Outcome assessment
Anthropometric assessment
Weight and height were measured using electronic scales and wall stadiometers, respectively. We calculated the BMI as weight (kg) divided by height squared (m2). We used the BMI z-score (number of SDs by which a child differs from the mean BMI of children of the same age and sex) to classify subjects according to weight status as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese according to the World Health Organization (WHO) growth reference values for adolescents [34]. We measured waist circumference (WC) midway between the lowest rib and the iliac crest using an anthropometric tape parallel to the floor. Blood pressure was measured twice by a trained nurse in the dominant arm by means of a mercury sphygmomanometer [35]. The first reading was conducted after at least 5 min of seated rest. The second reading was taken 5 min after the first. The first Korotkoff sound was used as a measure for systolic blood pressure and the fifth sound for diastolic blood pressure.
Biochemical measurements
Fasting blood samples were collected by trained personnel of the NHNS-2012. The day before blood collection, subjects were instructed to avoid eating any solid or liquid food prior to collection. Blood was drawn from an antecubital vein and collected in tubes without anticoagulant. The blood was centrifuged in situ at 3000 g. For subjects who reported a previous diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), a second sample was collected in heparinized tubes. Serum aliquots were stored in cryovials and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Samples were transported to the Mexican National Institute of Public Health and stored at −70 °C for posterior analyses in the biochemistry laboratory.
We measured serum glucose concentrations using the glucose oxidase method through chemiluminescence with an automated analyzer (Architect ci8200, Abbott Diagnostics, Wiesbaden, Germany). To verify the accuracy and precision of the procedure, the 965 material of the National Institute of Standards and Technology was measured simultaneously. We determined serum triglyceride levels after lipase hydrolysis in an automatic analyzer (Architect ci8200, Abbott Diagnostics, Wiesbaden, Germany). HDL-c was measured using an enzymatic colorimetric direct method after eliminating chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), and low-density lipoproteins by enzymatic digestion. To assure the precision and accuracy of these measurements, the concentrations of HDL-c and triglycerides were measured simultaneously at a second laboratory (Lipids Laboratory, National Institute of Medical Science and Nutrition Salvador Zubiran of Mexico).
Metabolic syndrome
The presence of MetS was identified according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) definition of MetS for children and adolescents [36, 37]. For adolescents aged 12–16 years, MetS was defined according to the following criteria: (1) presence of abdominal obesity (WC ≥90th percentile for age and sex or adult cutoff if lower); and (2) the presence of two or more other conditions among triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL, HDL-c <40 mg/dL, systolic blood pressure ≥130 or diastolic blood pressure ≥85 mmHg, fasting plasma glucose ≥100 mg/dL, and known T2D. Adult IDF criteria were used for subjects aged 16 years or older: central obesity (defined as WC ≥90 cm for male and ≥80 cm for female adolescents); and at least two of the following factors: triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL or specific treatment for high triglycerides; HDL-c <40 mg/dL in males and <50 mg/dL in females or specific treatment for these lipid abnormalities; systolic blood pressure ≥130, diastolic blood pressure ≥85 mmHg, or treatment of previously diagnosed hypertension; fasting plasma glucose ≥100 mg/dL; or previously diagnosed T2D.
Covariates
We used specific questionnaires to assess sociodemographic characteristics, medical history, and lifestyle habits. Socioeconomic status (SES) information was based on well-being. Using these data, we calculated an index (well-being index) by principal-components analysis, which included home conditions and presence in the home of household appliances, goods, and services. The continuous variable was categorized into tertiles and used as a proxy for low, medium, and high SES levels.
To collect information on physical activity and sedentary lifestyle in the 12- to 14-year age-group, we used a questionnaire of eight items [38]. The questions included hours of sleep, screen time, means of transportation to school, and formal physical activity (e.g., skating, dancing, and soccer) over the previous year. We also identified the means of transportation and length of time spent on the home-to-school route and vice versa. Furthermore, we categorized formal or competitive physical activities performed in the previous year according to the following criteria: (1) inactive; (2) one or two activities; and (3) three or more activities.
We assessed physical activity in adolescents aged 15–19 years using the short version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire [39]. In addition, participants were asked about their usual hours of sleep, inactive transport time, and usual screen time [40, 41]. The evaluation comprised 14 questions and allowed us to differentiate the activity during the week and on weekends. Finally, in agreement with WHO criteria, we classified physical activity into three categories: active, moderately active, and inactive [42].
Statistical analyses
The sample design characteristics (sample weights, cluster, and strata variables) were considered for all the analyses. We estimated the baseline characteristics of the population and dietary intake according to sex-specific tertiles of dietary GI and energy-adjusted dietary GL. To explore differences across categories of dietary GI and energy-adjusted dietary GL, we used linear regression models and design-based Wald statistics for quantitative variables; we employed the design-based F statistic (corrected, weighted Pearson chi-square statistic) for categorical data.
We used multiple logistic regression models to estimate odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to evaluate the association between categories of dietary GI and GL and the prevalence of MetS. The first model was adjusted for age (years). The second multivariate model further included the following: SES (low, middle, high); geographic regions of Mexico (north, central, south, metropolitan area) and dietary fiber intake (continuous, energy-adjusted). To examine the associations between categories of dietary GI and GL and the prevalence of MetS components (elevated WC, abnormal blood pressure, elevated fasting serum triglycerides, low HDL-c, elevated fasting serum glucose concentrations), we fitted logistic regression models with the same covariates as those used for the main analyses. We selected covariates using a hypothesis-based analysis. The addition of potential confounders, such as physical activity levels or screen time as covariates in the multivariate models, did not change the magnitude or effect of our results; thus, we did not use those factors in the final models. We took the lowest categories of dietary GI and GL as references in all the models. The tests of the linear trend across increasing categories of dietary GI and GL were conducted by assigning the sex-specific median value within each category. We treated those variables as continuous in the logistic regression models.
To examine a possible interaction between dietary GI and GL and age (under and over 16 years), and weight status (underweight/normal, overweight/obese), we introduced the product terms in the different multivariable models; we considered P < 0.05 in the likelihood ratio test as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using Stata 12.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), and the significance level was set at P < 0.05.
Results
In this study, the mean (SD) dietary GI and GL of adolescents in the NHNS-2012 was 51.8 (5.3) and 150.0 (27.3), respectively. The MetS prevalence in the overall sample was 8.8%, with a higher proportion among female (12.0%) than male adolescents (6.4%; P = 0.019).
Tables 1 and 2 present the main characteristics of the sample according to sex-specific tertiles of dietary GI and energy-adjusted dietary GL. Participants in the highest category of dietary GI had higher carbohydrate and sugar intake and lower values of protein and total fat, than subjects in the lowest category of dietary GI. Similar characteristics were found across categories of dietary GL, in addition, we observed a higher dietary fiber intake in the top tertile of dietary GL compared with those in the lowest tertile. We found no differences in the prevalence of MetS or the mean of its components across dietary GL categories.
Table 1.
General characteristics of the sample according to sex-specific categories of dietary glycemic indexa
| Characteristics | Dietary glycemic index b | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female adolescents | Male adolescents | |||||||||||||
| Low | Moderate | High | P value | Low | Moderate | High | P value | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| Dietary GI (units) | 46.8 | 0.3 | 51.0 | 0.1 | 56.6 | 0.4 | <0.001 | 47.6 | 0.3 | 51.9 | 0.1 | 57.0 | 0.3 | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 15.5 | 0.2 | 16.2 | 0.3 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 0.123 | 15.4 | 0.2 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 15.6 | 0.2 | 0.185 |
| Socioeconomic status (%) | 0.549 | 0.117 | ||||||||||||
| Low | 30.0 | 25.6 | 30.9 | 27.7 | 32.6 | 31.2 | ||||||||
| Medium | 26.8 | 34.3 | 35.6 | 37.3 | 28.1 | 35.9 | ||||||||
| High | 43.3 | 40.1 | 33.5 | 35.0 | 39.3 | 32.9 | ||||||||
| Geographic region (%) | 0.186 | 0.515 | ||||||||||||
| North | 24.4 | 12.2 | 20.8 | 19.5 | 14.4 | 25.0 | ||||||||
| Central | 25.1 | 25.2 | 35.4 | 31.0 | 28.9 | 31.6 | ||||||||
| Metropolitan area | 24.5 | 30.3 | 15.4 | 14.3 | 19.8 | 12.0 | ||||||||
| South | 26.1 | 32.3 | 28.4 | 35.2 | 37.0 | 31.4 | ||||||||
| Weight status (%) | 0.379 | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
| Underweight | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.7 | ||||||||
| Normal | 64.2 | 65.9 | 50.9 | 71.8 | 66.3 | 69.7 | ||||||||
| Overweight | 21.3 | 23.4 | 34.5 | 13.1 | 28.0 | 13.3 | ||||||||
| Obese | 13.3 | 9.7 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 4.9 | 16.3 | ||||||||
| Screen time (computer, TV, and video) (%) | 0.131 | 0.011 | ||||||||||||
| ≤ 2 h/day | 29.6 | 43.8 | 28.9 | 33.7 | 39.8 | 29.4 | ||||||||
| 2–4 h/day | 35.0 | 29.1 | 45.7 | 29.3 | 39.5 | 37.1 | ||||||||
| ≥ 4 h/day | 34.1 | 25.3 | 24.5 | 36.8 | 17.8 | 33.5 | ||||||||
| No data available | 13 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| Physical activity (%, age 12–14 years) | 0.174 | 0.034 | ||||||||||||
| Sedentary | 76.3 | 77.7 | 57.7 | 51.6 | 40.2 | 55.9 | ||||||||
| 1–2 activities | 18.9 | 20.0 | 36.4 | 44.9 | 50.5 | 41.1 | ||||||||
| ≥ 3 activities | 2.1 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 2.5 | ||||||||
| No data available | 2.7 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 0.7 | 8.6 | 0.5 | ||||||||
| Physical activity (%, age 15–19 years) | 0.239 | 0.131 | ||||||||||||
| Sedentary | 28.2 | 29.7 | 26.7 | 17.7 | 17.9 | 14.0 | ||||||||
| Moderately active | 6.1 | 22.2 | 16.7 | 9.4 | 19.8 | 19.4 | ||||||||
| Active | 65.8 | 46.0 | 56.7 | 72.9 | 62.3 | 66.6 | ||||||||
| No data available | 0.0 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| Dietary intake | ||||||||||||||
| Total energy intake (kcal/d) | 1795 | 53 | 1747 | 73 | 1828 | 58 | 0.707 | 2033 | 53 | 2121 | 61 | 2215 | 69 | 0.118 |
| Carbohydrate intake (g/d)c | 246.0 | 3.3 | 271.5 | 4.2 | 269.7 | 3.3 | <0.001 | 298.0 | 3.6 | 315.8 | 4.3 | 311.5 | 4.1 | 0.002 |
| Carbohydrate intake (% energy) | 54.9 | 0.7 | 61.5 | 1.2 | 60.8 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 55.8 | 0.7 | 59.5 | 0.8 | 59.1 | 0.7 | <0.001 |
| Protein intake (g/d)c | 58.5 | 1.0 | 52.7 | 1.2 | 51.9 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 67.9 | 1.1 | 63.8 | 1.0 | 60.5 | 1.2 | <0.001 |
| Protein intake (% energy) | 13.2 | 0.2 | 11.8 | 0.3 | 11.5 | 0.2 | <0.001 | 13.0 | 0.2 | 12.1 | 0.2 | 11.4 | 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Fat intake (g/d)c | 67.2 | 1.1 | 58.8 | 1.3 | 59.1 | 1.3 | <0.001 | 77.5 | 1.3 | 70.5 | 1.6 | 69.5 | 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Fat intake (% energy) | 33.9 | 0.5 | 28.8 | 0.9 | 29.4 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 33.2 | 0.5 | 29.8 | 0.7 | 29.6 | 0.5 | <0.001 |
| MUFA (g/d)c | 22.6 | 0.5 | 19.7 | 0.5 | 20.5 | 0.6 | <0.001 | 25.9 | 0.6 | 23.6 | 0.5 | 24.7 | 0.6 | 0.020 |
| PUFA (g/d)c | 14.3 | 0.4 | 14.1 | 0.4 | 14.5 | 0.4 | 0.750 | 17.4 | 0.4 | 17.5 | 0.7 | 16.8 | 0.4 | 0.424 |
| SFA (g/d)c | 25.8 | 0.5 | 22.1 | 0.6 | 22.7 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 29.4 | 0.7 | 26.2 | 0.7 | 26.5 | 0.7 | 0.002 |
| Trans fatty acids (g/d)c | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.054 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.692 |
| Dietary fiber intake (g/d)c | 21.6 | 0.5 | 22.7 | 1.3 | 21.3 | 0.7 | 0.683 | 25.8 | 0.7 | 27.0 | 1.0 | 22.8 | 0.8 | 0.003 |
| Dietary sugar intake (g/d) | 94.1 | 4.9 | 109.9 | 7.2 | 112.3 | 4.4 | 0.021 | 108.4 | 4.1 | 116.2 | 6.4 | 134.6 | 4.4 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 76.8 | 1.0 | 76.8 | 1.2 | 78.3 | 1.4 | 0.640 | 77.0 | 1.5 | 77.5 | 1.0 | 78.7 | 1.2 | 0.660 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 116.9 | 7.5 | 135.3 | 9.7 | 113.5 | 5.6 | 0.142 | 113.2 | 6.6 | 113.3 | 6.6 | 132.1 | 9.4 | 0.212 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 45.1 | 0.8 | 48.7 | 2.0 | 43.0 | 1.4 | 0.075 | 43.3 | 0.9 | 41.3 | 0.9 | 43.0 | 0.8 | 0.231 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 107.1 | 0.9 | 108.9 | 1.1 | 110.0 | 1.2 | 0.169 | 111.2 | 1.5 | 110.9 | 1.0 | 113.3 | 1.0 | 0.219 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 70.0 | 0.8 | 72.0 | 1.1 | 73.2 | 1.0 | 0.050 | 70.3 | 1.1 | 71.1 | 0.9 | 73.3 | 0.8 | 0.051 |
| Fasting serum glucose (mg/dL) | 80.4 | 1.0 | 79.0 | 1.2 | 77.6 | 1.0 | 0.172 | 81.3 | 0.8 | 80.2 | 1.3 | 81.5 | 1.4 | 0.733 |
| MetS prevalence (%)d | 9.5 | 9.7 | 16.9 | 0.234 | 6.9 | 3.8 | 8.4 | 0.344 | ||||||
Abbreviations: GI Glycemic index, GL glycemic load, kcal/d kilocalories per day, grams per day (g/d), MUFA monounsaturated fatty acids, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acids, SFA saturated fatty acids, WC waist circumference, HDL-c high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, MetS metabolic syndrome
aValues are expressed as means and standard deviations (SD) for continuous variables, and data from categorical variables are shown as percentages
bCategories based on sex-specific tertiles of dietary GI. cValues were adjusted for energy intake using sex-specific residuals. dThe age-specific International Diabetes Foundation definition of the metabolic syndrome was used [36, 37]
Table 2.
General characteristics of the sample according to sex-specific categories of energy-adjusted dietary glycemic loada
| Characteristics | Energy-adjusted dietary glycemic load bc | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female adolescents | Male adolescents | |||||||||||||
| Low | Moderate | High | P value | Low | Moderate | High | P value | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| Dietary GLc (units) | 110.0 | 1.3 | 135.0 | 0.6 | 162.9 | 1.4 | <0.001 | 132.1 | 1.5 | 159.9 | 0.7 | 192.5 | 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 15.9 | 0.3 | 15.9 | 0.2 | 15.9 | 0.3 | 0.998 | 15.8 | 0.3 | 15.9 | 0.2 | 15.3 | 0.2 | 0.112 |
| Socioeconomic status (%) | 0.013 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||
| Low | 21.3 | 30.6 | 34.7 | 16.9 | 29.9 | 44.8 | ||||||||
| Medium | 24.9 | 40.4 | 31.4 | 31.3 | 33.2 | 36.7 | ||||||||
| High | 53.8 | 29.0 | 33.9 | 51.8 | 37.0 | 18.5 | ||||||||
| Geographic region (%) | 0.030 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||
| North | 26.8 | 19.3 | 11.3 | 23.2 | 22.7 | 12.9 | ||||||||
| Central | 29.6 | 26.7 | 29.4 | 26.2 | 29.4 | 35.9 | ||||||||
| Metropolitan area | 28.1 | 15.6 | 26.5 | 23.1 | 12.5 | 10.6 | ||||||||
| South | 15.6 | 38.4 | 32.8 | 27.6 | 35.4 | 40.7 | ||||||||
| Weight status (%) | 0.678 | 0.283 | ||||||||||||
| Underweight | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | ||||||||
| Normal | 63.7 | 55.0 | 62.3 | 72.1 | 61.5 | 74.1 | ||||||||
| Overweight | 20.4 | 31.1 | 27.6 | 15.0 | 24.3 | 15.3 | ||||||||
| Obese | 14.6 | 12.1 | 9.0 | 12.2 | 13.3 | 9.5 | ||||||||
| Screen time (computer, TV, and video) (%) | 0.868 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||
| ≤ 2 h/day | 35.8 | 32.8 | 33.7 | 35.9 | 27.6 | 39.6 | ||||||||
| 2–4 h/day | 32.7 | 37.1 | 40.1 | 23.5 | 47.9 | 34.6 | ||||||||
| ≥ 4 h/day | 31.2 | 28.1 | 24.6 | 40.3 | 24.3 | 23.2 | ||||||||
| No data available | 0.4 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 2.6 | ||||||||
| Physical activity (%, age 12–14 years) | 0.039 | 0.171 | ||||||||||||
| Sedentary | 79.3 | 69.3 | 61.7 | 56.4 | 50.5 | 44.0 | ||||||||
| 1–2 activities | 16.6 | 24.3 | 35.6 | 42.3 | 46.6 | 46.5 | ||||||||
| ≥ 3 activities | 3.2 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 3.2 | ||||||||
| No data available | 1.0 | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 6.3 | ||||||||
| Physical activity (%, age 15–19 years) | 0.255 | 0.355 | ||||||||||||
| Sedentary | 37.7 | 26.3 | 21.2 | 14.1 | 20.4 | 15.1 | ||||||||
| Moderately active | 11.5 | 12.2 | 22.9 | 8.0 | 23.0 | 19.3 | ||||||||
| Active | 50.8 | 61.5 | 53.7 | 77.9 | 56.6 | 65.7 | ||||||||
| No data available | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||||||||
| Dietary intake | ||||||||||||||
| Total energy intake (kcal/d) | 1844 | 58 | 1697 | 59 | 1828 | 62 | 0.190 | 2169 | 53 | 2019 | 65 | 2179 | 60 | 0.141 |
| Carbohydrate intake (g/d)c | 228.2 | 2.1 | 263.0 | 1.8 | 296.5 | 2.3 | <0.001 | 266.1 | 2.8 | 308.6 | 2.0 | 350.9 | 2.9 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate intake (% energy) | 50.8 | 0.5 | 59.5 | 0.4 | 67.0 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 50.2 | 0.5 | 58.2 | 0.4 | 66.1 | 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Protein intake (g/d)c | 61.2 | 0.8 | 53.4 | 0.7 | 48.5 | 1.0 | <0.001 | 71.4 | 1.2 | 64.1 | 0.8 | 56.8 | 0.9 | <0.001 |
| Protein intake (% energy) | 13.8 | 0.2 | 12.0 | 0.2 | 10.8 | 0.2 | <0.001 | 13.6 | 0.2 | 12.2 | 0.2 | 10.7 | 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Fat intake (g/d)c | 73.0 | 0.9 | 61.9 | 0.8 | 50.1 | 0.9 | <0.001 | 85.6 | 1.2 | 72.8 | 0.7 | 59.1 | 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Fat intake (% energy) | 36.9 | 0.4 | 30.6 | 0.4 | 24.6 | 0.6 | <0.001 | 36.5 | 0.5 | 30.9 | 0.4 | 25.1 | 0.4 | <0.001 |
| MUFA (g/d)c | 25.0 | 0.5 | 21.0 | 0.4 | 16.8 | 0.4 | <0.001 | 28.8 | 0.6 | 25.1 | 0.3 | 20.2 | 0.5 | <0.001 |
| PUFA (g/d)c | 14.9 | 0.4 | 14.3 | 0.4 | 13.8 | 0.4 | 0.130 | 19.0 | 0.7 | 16.6 | 0.3 | 16.1 | 0.4 | 0.002 |
| SFA (g/d)c | 28.6 | 0.6 | 23.7 | 0.4 | 18.3 | 0.4 | <0.001 | 32.8 | 0.6 | 28.0 | 0.4 | 21.3 | 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Trans fatty acids (g/d)c | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | <0.001 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | <0.001 |
| Dietary fiber intake (g/d)c | 18.7 | 0.7 | 21.0 | 0.5 | 25.9 | 1.1 | <0.001 | 20.9 | 0.5 | 24.6 | 0.7 | 30.2 | 0.9 | <0.001 |
| Dietary sugar intake (g/d) | 94.4 | 6.0 | 102.5 | 5.5 | 119.6 | 6.2 | 0.014 | 111.7 | 3.9 | 117.3 | 5.6 | 129.9 | 5.2 | 0.015 |
| WC (cm) | 77.5 | 1.2 | 78.1 | 1.1 | 76.3 | 1.4 | 0.592 | 78.1 | 1.5 | 79.1 | 1.3 | 76.0 | 1.1 | 0.133 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 117.5 | 6.6 | 115.0 | 8.2 | 133.3 | 9.4 | 0.300 | 114.0 | 7.7 | 121.5 | 6.9 | 122.8 | 8.4 | 0.711 |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 47.8 | 2.0 | 44.1 | 1.0 | 44.9 | 1.5 | 0.233 | 43.0 | 0.9 | 41.6 | 0.8 | 43.1 | 0.9 | 0.302 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 108.2 | 0.9 | 108.6 | 1.0 | 109.3 | 1.3 | 0.794 | 111.5 | 1.6 | 112.0 | 0.9 | 111.8 | 0.9 | 0.955 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 71.3 | 0.9 | 71.3 | 1.0 | 72.5 | 1.1 | 0.653 | 70.5 | 1.1 | 71.5 | 0.9 | 72.7 | 0.8 | 0.231 |
| Fasting serum glucose (mg/dL) | 80.4 | 1.2 | 79.9 | 1.2 | 76.7 | 0.9 | 0.018 | 81.4 | 1.0 | 81.5 | 1.4 | 80.1 | 1.2 | 0.620 |
| MetS prevalence (%)d | 9.1 | 13.0 | 13.9 | 0.605 | 8.7 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 0.461 | ||||||
Abbreviations: GI Glycemic index, GL glycemic load, kcal/d kilocalories per day, g/d grams per day, MUFA monounsaturated fatty acids, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acids, SFA saturated fatty acids, WC waist circumference, HDL-c high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, MetS metabolic syndrome
aValues are expressed as means and standard deviations (SD) for continuous variables, and data from categorical variables are shown as percentages
bCategories based on sex-specific tertiles of dietary GL. cValues were adjusted for energy intake using sex-specific residuals. dThe age-specific International Diabetes Foundation definition of the metabolic syndrome was used [36, 37]
Table 3 shows the ORs and 95% CI for MetS and its components according to sex-specific categories of dietary GI. We observed no association of MetS with either dietary GI or dietary GL. However, when MetS components were analyzed separately, a direct association between the highest dietary GI and abnormal blood pressure was evident in female adolescents (Model 1: OR = 3.66; 95% CI, 1.59–8.39; P for trend = 0.009). This association remained statistically significant after multivariate adjustment. Table 4 shows the ORs and 95% CI for MetS and its components according to sex-specific categories of energy-adjusted dietary GL. Our results from the multivariate model also indicated that female adolescents with the highest dietary GL had higher odds of abnormal blood pressure (OR = 5.67; 95% CI, 1.84–17.46); there was a significant trend across categories of dietary GL (P for trend = 0.003). Among males, no statistically significant associations were found between dietary GI or dietary GL and abnormal BP. We found no statistically significant associations for the remaining MetS criteria with dietary GI or GL.
Table 3.
Association between metabolic syndrome and sex-specific categories of dietary glycemic index
| Dietary glycemic index a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female adolescents | Male adolescents | |||||||
| Low | Moderate | High | P trend | Low | Moderate | High | P trend | |
| MetS | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.92 (0.35–2.40) | 1.78 (0.70–4.55) | 0.192 | 1 | 0.50 (0.15–1.63) | 1.21 (0.50–3.19) | 0.673 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.81 (0.30–2.19) | 1.60 (0.62–4.15) | 0.275 | 1 | 0.56 (0.18–1.77) | 1.25 (0.48–3.31) | 0.641 |
| Elevated WC | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.22 (0.58–2.54) | 1.24 (0.70–2.22) | 0.486 | 1 | 0.84 (0.40–1.74) | 1.13 (0.58–2.20) | 0.696 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.16 (0.56–2.42) | 1.33 (0.72–2.45) | 0.361 | 1 | 0.87 (0.43–1.76) | 1.25 (0.64–2.46) | 0.513 |
| Elevated triglycerides | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.41 (0.64–3.12) | 0.98 (0.51–1.88) | 0.840 | 1 | 0.80 (0.38–1.66) | 1.06 (0.53–2.12) | 0.850 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.25 (0.58–2.68) | 0.99 (0.52–1.88) | 0.911 | 1 | 0.78 (0.35–1.70) | 1.15 (0.56–2.35) | 0.714 |
| Low HDL-c | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.69 (0.37–1.29) | 1.65 (0.93–2.94) | 0.058 | 1 | 1.58 (0.91–2.76) | 1.26 (0.76–2.09) | 0.396 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.67 (0.36–1.26) | 1.56 (0.82–2.95) | 0.126 | 1 | 1.71 (1.00–2.92) | 1.29 (0.78–2.13) | 0.321 |
| Abnormal blood pressure | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 2.22 (0.76–6.43) | 3.66 (1.59–8.39) | 0.009 | 1 | 0.48 (0.18–1.28) | 1.67 (0.82–3.40) | 0.139 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 2.02 (0.60–6.75) | 3.66 (1.46–9.22) | 0.012 | 1 | 0.53 (0.20–1.41) | 1.66 (0.83–3.32) | 0.143 |
| Elevated fasting serum glucose | ||||||||
| Model 1b OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.71 (0.13–3.76) | 0.24 (0.05–1.32) | 0.114 | 1 | 1.25 (0.23–6.63) | 2.30 (0.47–11.22) | 0.278 |
| Model 2c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.07 (0.23–5.11) | 0.24 (0.05–1.22) | 0.068 | 1 | 1.21 (0.24–6.17) | 2.72 (0.43–17.08) | 0.289 |
Abbreviations: OR Odds ratio, CI confidence interval, MetS metabolic syndrome, WC waist circumference, HDL-c high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. aCategories based on sex-specific tertiles of dietary GI. bModel adjusted for age (years). cMultivariate model adjusted for age (years), socioeconomic level (low, middle, or high), geographic region (north, central, south, or metropolitan area) and dietary fiber intake (continuous, energy-adjusted)
Table 4.
Association between metabolic syndrome and sex-specific categories of energy-adjusted dietary glycemic load
| Energy-adjusted dietary glycemic load ab | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female adolescents | Male adolescents | |||||||
| Low | Moderate | High | P trend | Low | Moderate | High | P trend | |
| MetS | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.52 (0.56–4.12) | 1.64 (0.60–4.49) | 0.338 | 1 | 0.57 (0.19–1.68) | 0.59 (0.20–1.75) | 0.364 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.48 (0.54–4.04) | 1.88 (0.64–5.55) | 0.255 | 1 | 0.50 (0.15–1.64) | 0.55 (0.18–1.67) | 0.310 |
| Elevated WC | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.19 (0.63–2.25) | 1.12 (0.55–2.29) | 0.760 | 1 | 0.85 (0.40–1.82) | 0.93 (0.46–1.89) | 0.863 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.23 (0.65–2.36) | 1.07 (0.52–2.20) | 0.848 | 1 | 0.85 (0.39–1.84) | 0.95 (0.45–2.00) | 0.906 |
| Elevated triglycerides | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.93 (0.45–1.96) | 1.61 (0.72–3.59) | 0.240 | 1 | 1.11 (0.54–2.27) | 1.03 (0.50–2.11) | 0.954 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.80 (0.38–1.71) | 1.03 (0.46–2.29) | 0.909 | 1 | 0.92 (0.43–1.94) | 0.67 (0.30–1.48) | 0.300 |
| Low HDL-c | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.80 (0.96–3.40) | 1.93 (0.96–3.88) | 0.074 | 1 | 1.31 (0.76–2.25) | 0.94 (0.54–1.64) | 0.773 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.44 (0.78–2.67) | 1.73 (0.82–3.64) | 0.151 | 1 | 1.13 (0.65–1.97) | 0.76 (0.41–1.41) | 0.351 |
| Abnormal blood pressure | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.07 (0.36–3.23) | 2.69 (0.93–7.78) | 0.073 | 1 | 0.66 (0.30–1.42) | 1.00 (0.47–2.12) | 0.948 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 1.42 (0.42–4.79) | 5.67 (1.84–17.46) | 0.003 | 1 | 0.69 (0.32–1.48) | 1.30 (0.56–3.03) | 0.538 |
| Elevated fasting serum glucose | ||||||||
| Model 1c OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.52 (0.13–2.16) | 0.42 (0.05–3.68) | 0.416 | 1 | 1.94 (0.42–8.99) | 2.20 (0.46–10.42) | 0.313 |
| Model 2d OR (95% CI) | 1 | 0.52 (0.13–2.11) | 0.62 (0.10–3.83) | 0.568 | 1 | 2.35 (0.45–12.24) | 3.43 (0.38–30.80) | 0.260 |
Abbreviations: OR Odds ratio, CI confidence interval, MetS metabolic syndrome, WC waist circumference, HDL-c high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. aCategories based on sex-specific tertiles of dietary GL. bValues were adjusted for energy intake using sex-specific residuals. cModel adjusted for age (years). dMultivariate model adjusted for age (years), socioeconomic level (low, middle, or high), geographic region (north, central, south, or metropolitan area) and dietary fiber intake (continuous, energy-adjusted).
None of the interactions assessed was statistically significant in the association between dietary GI and GL and MetS (P for interaction >0.05)
Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, we found no associations between dietary GI or GL and MetS. However, in an analysis of MetS components, high dietary GI and GL were associated with higher odds of abnormal blood pressure in female adolescents.
We found no associations between dietary GI or GL and MetS. Similar results were observed in a clinical trial performed in European children and adolescents (5–18 years) did not reveal an association between a low-GI diet and MetS [43]. A cross-sectional study conducted in 516 Australian adolescents found no association between overall dietary GI or dietary GL and MetS [20]. In that study, however, breakfast GL was found to be predictive of MetS in female, but not male, adolescents. In the present study, we used SFFQ to assess dietary intake, and we were unable to estimate dietary GI or GL at different mealtimes. Thus, it was not possible for us to confirm the results of that Australian study.
Our results also contrast with those of a cross-sectional study, in which dietary GL was associated with a higher prevalence of MetS in 769 adolescents (13–15 years) [21]. The variance with our results may be explained by the different methods used for dietary assessment. The 3-day food record used in that study may in fact have assessed GI more accurately than the SFFQ used in ours: food records give a more precise indication of the types and portions of food consumed than the SFFQ.
We identified an association between the highest dietary GI and GL and abnormal blood pressure among female adolescents. In contrast to our findings, those of a clinical trial that included 50 overweight or obese female adolescents did not indicate a decrease in blood pressure after a 10-weeks intervention with a low-GI diet [44]. The discrepancy between our results and theirs could be explained by the study design. Our cross-sectional study did not allow an assessment of causality; therefore, more prospective studies and clinical trials are needed to confirm the observed association. On the other hand, similar results were observed in a prospective investigation conducted among 858 Australian adolescents followed up for 5 years [45]. The authors found a direct association among female adolescents: for each 1-SD increment in dietary GI and GL, mean systolic blood pressure rose by 2.3 and 4 mmHg, respectively. In that study, no significant associations were observed between carbohydrate quality and blood pressure among male adolescents.
In the present work, no evidence was found concerning an association among dietary GI, dietary GL, and the remaining METs components (elevated WC, elevated triglycerides, low HDL-c, elevated fasting serum glucose). Results from a recent systematic review did not show an association between low/high GI diets and body mass index, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, total cholesterol, LDL-c, HDL-c, diastolic and systolic blood pressure, fasting serum glucose, fasting serum insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin and C-reactive protein. However, the latter meta-analyses demonstrated that low GI protocols resulted in more pronounced decreases in triglycerides and HOMA-index [17].
Nevertheless, recent intervention studies determined that low-GI diets led to a significantly greater reduction in WC [46, 47] compared with controls. Also, a clinical trial have demonstrated that blood glucose total area under the curve was 13% greater with a high-GI than low-GI breakfast among overweight female adolescents and 4% higher in non-overweight female adolescents [48]. Moreover, a dietary intervention with low GI was observed to improve serum glucose levels in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus [49]. Similarly, a low-GL dietary intervention for 6 weeks among overweight and obese 11-year-old children showed a reduction in fasting glucose [50]. However, clinical trials have been conducted in specific population groups: this fact—along with dietary intervention—could explain the differences from our results.
In our study, mean dietary GI was 51.5 among female adolescents and 52.1 in male adolescents, and dietary GL was higher among male adolescents (161.4) than female adolescents (135.8). The GI values of our sample were lower than those found in Australian, Canadian, British or Japanese adolescents (around 56 to 64 units) and mean dietary GL of our study was in agreement to previous studies conducted in adolescents (range from 128 to 168 units) [20, 51–54]. Thus it is still necessary and urgent to elucidate the role that low GI or GL diets exert on MetS onset in youth population worldwide, since individuals with MetS have a 2-fold risk of developing cardiovascular disease [55] and higher risk of T2D compared with people without this syndrome [56].
One hypothesized metabolic effect by which high-GI and GL diets increase blood pressure is a postprandial glycemic response and the consequent hyperinsulinemia elicited after consuming high-GI foods [57]. It has been found that higher dietary GI during puberty is prospectively associated with greater insulin resistance [58]. Hyperinsulinemia has been associated with abnormal levels of blood pressure through stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system [59], increased sodium retention, and volume expansion [45].
We acknowledge that our study has several limitations. Owing to the cross-sectional design, we cannot make causal inferences. Our findings are specific for Mexican adolescents and cannot therefore be generalized to other population groups. Other limitation is that we were unable to assess the impact of pubertal or hormonal status in our analyses. Puberty could be a confounding variable since transition from Tanner stage I to Tanner stage III has been associated with temporary reduction of insulin sensitivity, increases in fasting glucose and insulin levels and different hormonal changes [60]. In addition, physical activity was not included as a covariate in our analyses due to the lack of significance in our models. However, a recent meta-analysis has found an association between physical activity and MetS in adolescents [61]. We therefore, cannot discard that measurement error might exist since questionnaires used in this study are not validated for estimating physical activity in Mexican adolescents. Also, underreporting could be a source of bias in our study, since evidence in adolescents demonstrated that misreporters showed higher rates of insufficient intake of carbohydrate [62]. Although in our study subjects with energy values outside predefined limits were excluded, under-reporting bias might still exist and alter the estimation of nutrient intake and the associations between dietary GI or GL and MetS.
Moreover, the SFFQ evaluated consumption of foods during 7 days prior to the date of the interview, thus habitual dietary habits of the population might not be reflected by this assessment. In addition, the SFFQ was not specifically designed to evaluate dietary GI and GL; using this tool could generate bias about dietary GI and GL variation owing to the limited number of food items and restrictions in quantifying individual amounts of food consumed [63]. Nevertheless, the SFFQ used in the NHNS-2012 has been found sufficiently valid for assessing carbohydrate intake in adolescents [23]. Furthermore, published GI values for local foods in Mexico are limited; for that reason, we used reference GI data from other countries. This could be a source of error because GI values of foods may differ according to variety, growing conditions, processing, and cooking [64]. Some degree of misclassification may have occurred in our dietary assessment; however, such misclassification would probably have been more non-differential such that the bias would likely have been toward null.
One of the strengths of this study is the large sample size, allowing us to introduce possible confounders in the models. The use of an established protocol also allowed us to assign the GI values to the SFFQ in a systematic, reproducible manner. Furthermore, to our knowledge, this is the first study conducted among Mexican adolescents to explore the association among dietary GI, dietary GL, and MetS or its components. Nevertheless, further evidence based on prospective studies is necessary to determine the long-term association among dietary GI, dietary GL, and MetS in youth populations.
Conclusions
We observed no association between dietary GI or dietary GL and MetS in a nationally representative sample of Mexican adolescents. However, we found higher odds of abnormal blood pressure among female adolescents with the highest dietary GI and GL. This investigation contributes to the body of evidence about the relationship between the quality of carbohydrates and MetS risk factors in youth populations. However, owing to the cross-sectional study design, our results have to be treated with caution, and further investigations are required to confirm the identified associations.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ignacio Mendez Gomez-Humaran for his assistance with statistical analyses.
Funding
IC-Q received grants from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología de México (CONACYT), Secretaria de Educación Pública (SEP), the Mexican Government, and the PhD International Mobility Programme, University of Granada and CEI-BioTicGranada.
Availability of data and materials
Sample was obtained from the Mexican NHNS-2012 dataset, which is freely accessible from the National Public Health Institute of Mexico web site: http://ensanut.insp.mx/basesdoctos.php#.WOueHoWcHIV.
In order to analyze data from the NHNS-2012 survey, permission was obtained from the Ethics Review Board of the National Public Health Institute of Mexico. The datasets of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions
IC-Q and SA-E contributed to the study design, data analyses, and interpretation of findings and wrote the manuscript with important input and feedback from all coauthors; AS-V, MDR-L, RA, and LS-M contributed to the study design and to the critical revision of the manuscript; TS-L contributed to the study design, interpretation of findings, and critical revision of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Ethics Review Board of the National Public Health Institute of Mexico. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their legal guardians prior to the study.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- BMI
Body mass index
- CI
Confidence interval
- GI
Glycemic index
- GL
Glycemic load
- HDL-c
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- IDF
International Diabetes Federation
- MetS
Metabolic syndrome
- MUFA
Monounsaturated fatty acids
- NHNS-2012
National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012
- OR
Odds ratio
- PUFA
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- RCTs
Randomized controlled trials
- SD
Standard deviation
- SES
Socioeconomic status
- SFA
Saturated fatty acids
- SFFQ
Semiquantitative food-frequency questionnaire
- T2D
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- WC
Waist circumference
- WHO
World Health Organization
Contributor Information
Itandehui Castro-Quezada, Email: itandehui.castro@ulpgc.es.
Salomón Angulo-Estrada, Email: salomon.angulo@insp.mx.
Almudena Sánchez-Villegas, Email: almudena.sanchez@ulpgc.es.
María Dolores Ruiz-López, Email: mdruiz@ugr.es.
Reyes Artacho, Email: rartacho@ugr.es.
Lluís Serra-Majem, Email: lluis.serra@ulpgc.es.
Teresa Shamah-Levy, Phone: (0052) 777 329 3000, Email: tshamah@insp.mx.
References
- 1.Evia-Viscarra ML, Rodea-Montero ER, Apolinar-Jiménez E, Quintana-Vargas S. Metabolic syndrome and its components among obese (BMI >=95th) Mexican adolescents. Endocr Connect. 2013;2:208–215. doi: 10.1530/EC-13-0057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(23):2362–2374. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gutierrez JP, Rivera-Domarco J, Shamah-Levy T, Villalpando-Hernández S, Franco A, Cuevas-Nasu L, et al. National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012. Nationals Results. (Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2012. Resultados Nacionales) 1. Cuernavaca: Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rodriguez-Moran M, Salazar-Vazquez B, Violante R, Guerrero-Romero F. Metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents aged 10–18 years. Diabetes Care. 27. United States ; 2004. p. 2516-2517. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Halley Castillo E, Borges G, Talavera JO, Orozco R, Vargas-Alemán C, Huitrón-Bravo G, et al. Body mass index and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents in two Mexican populations. J Adolesc Health. 2007;40:521–526. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2006.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mann J, Cummings JH, Englyst HN, Key T, Liu S, Riccardi G, et al. FAO/WHO scientific update on carbohydrates in human nutrition: conclusions. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61(Suppl 1):S132–S137. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Augustin LS, Kendall CW, Jenkins DJ, Willett WC, Astrup A, Barclay AW, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium (ICQC). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015; doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Jenkins DJ, Wolever TM, Taylor RH, Barker H, Fielden H, Baldwin JM, et al. Glycemic index of foods: a physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34:362–366. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Augustin LS, Franceschi S, Hamidi M, Marchie A, et al. Glycemic index: overview of implications in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76:266S–273S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76/1.266S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Salmerón J, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Wing AL, Willett WC. Dietary fiber, glycemic load, and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. JAMA. 1997;277:472–477. doi: 10.1001/jama.1997.03540300040031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Livesey G, Taylor R, Hulshof T, Howlett J. Glycemic response and health--a systematic review and meta-analysis: relations between dietary glycemic properties and health outcomes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:258S–268S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.1.258S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thomas DE, Elliott EJ, Baur L. Low glycaemic index or low glycaemic load diets for overweight and obesity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;3:CD005105. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005105.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goff LM, Cowland DE, Hooper L, Frost GS. Low glycaemic index diets and blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schwingshackl L, Hoffmann G. Long-term effects of low glycemic index/load vs. high glycemic index/load diets on parameters of obesity and obesity-associated risks: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23:699–706. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2013.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sacks FM, Carey VJ, Anderson CA, Miller ER, Copeland T, Charleston J, et al. Effects of high vs low glycemic index of dietary carbohydrate on cardiovascular disease risk factors and insulin sensitivity: the OmniCarb randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312:2531–2541. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.16658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, McKeown-Eyssen G, Josse RG, Silverberg J, Booth GL, et al. Effect of a low-glycemic index or a high-cereal fiber diet on type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300:2742–2753. doi: 10.1001/jama.2008.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schwingshackl L, Hobl LP, Hoffmann G. Effects of low glycaemic index/low glycaemic load vs. high glycaemic index/ high glycaemic load diets on overweight/obesity and associated risk factors in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr J. 2015;14:87. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0077-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Finley CE, Barlow CE, Halton TL, Haskell WL. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the cooper center longitudinal study. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010;110:1820–1829. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2010.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Juanola-Falgarona M, Salas-Salvadó J, Buil-Cosiales P, Corella D, Estruch R, Ros E, et al. Dietary Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Are Positively Associated with Risk of Developing Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:1991–2000. doi: 10.1111/jgs.13668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nicholl A, du Heaume M, Mori TA, Beilin LJ, Oddy WH, Bremner AP, et al. Higher breakfast glycaemic load is associated with increased metabolic syndrome risk, including lower HDL-cholesterol concentrations and increased TAG concentrations, in adolescent girls. Br J Nutr. 2014;112:1974–1983. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514003092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.O'Sullivan TA, Lyons-Wall P, Bremner AP, Ambrosini GL, Huang RC, Beilin LJ, et al. Dietary glycaemic carbohydrate in relation to the metabolic syndrome in adolescents: comparison of different metabolic syndrome definitions. Diabet Med. 2010;27:770–778. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Romero-Martinez M, Shamah-Levy T, Franco-Nunez A, Villalpando S, Cuevas-Nasu L, Gutierrez JP, et al. National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012: design and coverage. Salud Publica Mex. 2013;55(Suppl 2):S332–S340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Denova-Gutiérrez E, Ramírez-Silva I, Rodríguez-Ramírez S, Jiménez-Aguilar A, Shamah-Levy T, Rivera-Dommarco JA. Validity of a food frequency questionnaire to assess food intake in Mexican adolescent and adult population. Salud Publica Mex. 2016;58:617–628. doi: 10.21149/spm.v58i6.7862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ramírez-Silva I, Jiménez-Aguilar A, Valenzuela-Bravo D, Martinez-Tapia B, Rodríguez-Ramírez S, Gaona-Pineda E, et al. Methodology for estimating dietary data from the semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire of the Mexican National Health and Nutrition Survey 2012. Salud Publica Mex. 2016;58:629–638. doi: 10.21149/spm.v58i6.7974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Institute of Medicine . Energy. Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine, National Academies Press; 2005. pp. 107–264. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hernández B, de Haene J, Barquera S, Monterrubio E, Rivera J, Shamah T, et al. Factores asociados con la actividad física en mujeres mexicanas en edad reproductiva. Pan Am J Public Health. 2003;14:235–244. doi: 10.1590/S1020-49892003000900004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Frankenfield D, Roth-Yousey L, Compher C. Comparison of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in healthy nonobese and obese adults: a systematic review. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105:775–789. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2005.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. World Health Organization. United Nations University . Human energy requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/ONU Expert Consultation. Rome: FAO; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Willett WC, Howe GR, Kushi LH. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65(Suppl 4):1220S–1228S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/65.4.1220S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Louie JC, Flood V, Turner N, Everingham C, Gwynn J. Methodology for adding glycemic index values to 24-hour recalls. Nutrition. 2011;27:59–64. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2009.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:2281–2283. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.The University of Sydney. Sydney University Glycemic Index Research Service 2014. 2016. http://www.glycemicindex.com/. Accessed 17 Nov 2015.
- 33.Wolever TM, Nguyen PM, Chiasson JL, Hunt JA, Josse RG, Palmason C, et al. Determinants of diet glycemic index calculated retrospectively from diet records of 342 individuals with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994;59:1265–1269. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/59.6.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ. 2007;85:660–667. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.043497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.19.2560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Alberti G, Zimmet P, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The IDF consensus definition of the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. International Diabetes Federation: Brussels; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents - an IDF consensus report. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8:299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2007.00271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pereira MA, FitzerGerald SJ, Gregg EW, Joswiak ML, Ryan WJ, Suminski RR, et al. A collection of Physical Activity Questionnaires for health-related research. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1997;29(Suppl 6):S1–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35:1381–1395. doi: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hernandez B, Gortmaker SL, Colditz GA, Peterson KE, Laird NM, Parra-Cabrera S. Association of obesity with physical activity, television programs and other forms of video viewing among children in Mexico city. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23:845–854. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pols MA, Peeters PH, Bueno-De-Mesquita HB, Ocké MC, Wentink CA, Kemper HC, et al. Validity and repeatability of a modified Baecke questionnaire on physical activity. Int J Epidemiol. 1995;24:381–388. doi: 10.1093/ije/24.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.WHO. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010. [PubMed]
- 43.Damsgaard CT, Papadaki A, Jensen SM, Ritz C, Dalskov SM, Hlavaty P, et al. Higher protein diets consumed ad libitum improve cardiovascular risk markers in children of overweight parents from eight European countries. J Nutr. 2013;143:810–817. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.173427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rouhani MH, Kelishadi R, Hashemipour M, Esmaillzadeh A, Azadbakht L. The effect of low glycemic index diet on body weight status and blood pressure in overweight adolescent girls: a randomized clinical trial. Nutr Res Pract. 2013;7:385–392. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2013.7.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gopinath B, Flood VM, Rochtchina E, Baur LA, Smith W, Mitchell P. Influence of high glycemic index and glycemic load diets on blood pressure during adolescence. Hypertension. 2012;59:1272–1277. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.190991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kong AP, Choi KC, Chan RS, Lok K, Ozaki R, Li AM, et al. A randomized controlled trial to investigate the impact of a low glycemic index (GI) diet on body mass index in obese adolescents. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:180. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mirza NM, Palmer MG, Sinclair KB, McCarter R, He J, Ebbeling CB, et al. Effects of a low glycemic load or a low-fat dietary intervention on body weight in obese Hispanic American children and adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97:276–285. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.042630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zakrzewski JK, Stevenson EJ, Tolfrey K. Effect of breakfast glycemic index on metabolic responses during rest and exercise in overweight and non-overweight adolescent girls. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012;66:436–442. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2011.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rovner AJ, Nansel TR, Gellar L. The effect of a low-glycemic diet vs a standard diet on blood glucose levels and macronutrient intake in children with type 1 diabetes. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009;109:303–307. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2008.10.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fajcsak Z, Gabor A, Kovacs V, Martos E. The effects of 6-week low glycemic load diet based on low glycemic index foods in overweight/obese children--pilot study. J Am Coll Nutr. 2008;27:12–21. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2008.10719670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jones M, Barclay AW, Brand-Miller JC, Louie JC. Dietary glycaemic index and glycaemic load among Australian children and adolescents: results from the 2011-2012 Australian Health Survey. Br J Nutr. 2016;116:178–187. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516001823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Forbes LE, Storey KE, Fraser SN, Spence JC, Plotnikoff RC, Raine KD, et al. Dietary patterns associated with glycemic index and glycemic load among Alberta adolescents. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009;34:648–658. doi: 10.1139/H09-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Murakami K, McCaffrey TA, Livingstone MB. Dietary glycaemic index and glycaemic load in relation to food and nutrient intake and indices of body fatness in British children and adolescents. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1512–1523. doi: 10.1017/S000711451300072X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Murakami K, Miyake Y, Sasaki S, Tanaka K, Arakawa M. Dietary glycemic index and glycemic load in relation to risk of overweight in Japanese children and adolescents: the Ryukyus Child Health Study. Int J Obes. 2011;35:925–936. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P, et al. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;28(56):1113–1132. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wolever T. Physiological mechanisms and observed health impacts related to the glycaemic index: some observations. Int J Obes. 2006;30:S72–SS8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803496. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Goletzke J, Herder C, Joslowski G, Bolzenius K, Remer T, Wudy SA, et al. Habitually higher dietary glycemic index during puberty is prospectively related to increased risk markers of type 2 diabetes in younger adulthood. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:1870–1876. doi: 10.2337/dc12-2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Landsberg L. Insulin-mediated sympathetic stimulation: role in the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension (or, how insulin affects blood pressure, and why) J Hypertens. 2001;19:523–528. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200103001-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Goran MI, Gower BA. Longitudinal study on pubertal insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2001;50:2444–2450. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.11.2444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Oliveira RG, Guedes DP. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Evidence. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0168503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Serra-Majem L, Ribas L, Pérez-Rodrigo C, García-Closas R, Peña-Quintana L, Aranceta J. Determinants of nutrient intake among children and adolescents: results from the enKid Study. Ann Nutr Metab. 2002;46(Suppl 1):31–38. doi: 10.1159/000066398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hare-Bruun H, Nielsen BM, Grau K, Oxlund AL, Heitmann BL. Should glycemic index and glycemic load be considered in dietary recommendations? Nutr Rev. 2008;66:569–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wolever TM. Is glycaemic index (GI) a valid measure of carbohydrate quality? Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67:522–531. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2013.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Sample was obtained from the Mexican NHNS-2012 dataset, which is freely accessible from the National Public Health Institute of Mexico web site: http://ensanut.insp.mx/basesdoctos.php#.WOueHoWcHIV.
In order to analyze data from the NHNS-2012 survey, permission was obtained from the Ethics Review Board of the National Public Health Institute of Mexico. The datasets of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


