Abstract
Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) is the key enzyme responsible for metabolism of the alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde in the liver. In addition to conversion of the acetaldehyde molecule, ALDH is also involved in other cellular functions. Recently, many studies have investigated the involvement of ALDH expression in viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease (ALD), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. Notably, ALDH2 expression has been linked with liver cancer risk, as well as pathogenesis and prognosis, and has emerged as a promising therapeutic target. Of note, approximately 8% of the world's population, and approximately 30-40% of the population in East Asia carry an inactive ALDH2 gene. This review summarizes new progress in understanding tissue-specific acetaldehyde metabolism by ALDH2 as well as the association of ALDH2 gene polymorphisms with liver disease and cancer. New research directions emerging in the field are also briefly discussed.
Keywords: aldehyde dehydrogenase, gene polymorphism, liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma
Introduction
Our understanding of alcohol metabolism is well established at the molecular level. Alcohol metabolism mainly takes place in the liver and relies on two major nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent enzymes, alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2). Alcohol is first converted into acetaldehyde by ADH and cytochrome p450 2E1 (CYP2E1) via oxidative degradation, and the acetaldehyde is then oxidized to non-toxic acetate by ALDH and the coenzyme NAD or NADP for excretion 1. The further conversion of reactive aldehyde by ALDH family members offers cells with potential protection against radical oxidative species (ROS). However, the biological functions of ALDHs extend beyond detoxification, as the enzymes are involved in other biochemical processes, such as retinoic acid (RA) biosynthesis, catalysis of folate and amino acid and lipid peroxidation 2. Additionally, altered ALDH activity is associated with certain behavioral deficits 3, 4, endocrine disorders, cardiovascular and lung diseases 5, oral and gastrointestinal cancers, Fanconi anemia, and dermatitis 6.
In this review, we mainly summarized recent progress in understanding tissue-specific acetaldehyde metabolism by ALDH2 as well as the ALDH2 gene polymorphisms associated with the pathogenesis of liver disease and cancer. Future research directions related to ALDH2 and liver diseases are also discussed.
The Liver is the Major but Not the Sole Organ Responsible for Acetaldhyde Metabolism
Traditionally, it has been argued that the liver is the main organ responsible for ethanol metabolism 7. Overall, both expression and activity of ALDH2 in liver are much higher than those of other organs in wild-type mice 8. Surprisingly, a recent study found that after 3 hours of ethanol gavage, acetaldehyde levels in hepatocyte-specific Aldh2 knockout mice are less than half of those in Aldh2-/- mice 8, suggesting other organs also contribute to acetaldehyde metabolism and clearance. Further studies in mice revealed that cumulative ALDH2 activity in multiple organs or tissues, such as white and brown adipose tissue, spleen, heart, and colon, may participate in acetaldehyde clearance 8.
ALDH Genes and Polymorphisms
The human ALDH gene family consists of 19 putative members, and among the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily members, ALDH2 is enzyme that most efficiently catalyzes toxic acetaldehyde 9. ALDH2 is located on chromosome 12 (12q24.12), is composed of 13 exons, and is approximately 44 kilobases in length. ALDH2 is abundantly expressed in both fat tissue and liver 8, in which there are two liver cytosolic and mitochondrial isoforms, and also expressed in kidney, lung, stomach and skin 10. Two ALDH2 isozymes are present in most Caucasians, but a single cytosolic isozyme without the mitochondrial isoform occurs in approximately 40-50% of the East Asian population. ALDH2 consists of four identical subunits (tetrameric), and each subunit contains triple functional domains of coenzyme or NAD+-binding (8-135, 159-270), catalysis (271-470) and oligomerization (140-158, 486-495) 11, 12.
Three isotype genes of ALDH1 (ALDH1A1, ALDH1A2, and ALDH1A3) are located on 9q21.13, 15q21.3, and 15q26.3, respectively 13. ALDH1 is expressed in both stem cells and differentiated cells. ALDH1 proteins, which are mainly found in cell cytosol in different tissues, oxidize retinal and aliphatic aldehydes. Cytosolic ALDH1A1 plays a role acetaldehyde oxidation and alcohol preference through mediating a γ-aminobutyric acid synthesis pathway 14. ALDH1B1, which is expressed at high levels in the liver and intestine epithelium, is an ALDH1 isoform that demonstrates high affinity to acetaldehyde only secondary to ALDH2 and catalyzes various aldehyde substrates of acetaldehyde and derivatives of lipid peroxidation 15, 16 (Table 1).
Table 1.
Human ALDH families and their functions.
| ALDH Family | Chromosomes | Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALDH1A1 | 9q21.13 | Metabolizes retinal to RA; oxidizes acetaldehyde, LPO-derived aldehydes, DOPAL; protects against ultraviolet-induced damage as lens and Corneal crystallins; mediates a GABA synthesis pathway | 14, 115-117 |
| ALDH1A2 | 15q21.3 | Metabolizes retinal to RA; oxidizes acetaldehyde and LPO-derived aldehydes | 118 |
| ALDH1A3/ALDH6 | 15q26.3 | Metabolizes retinal to RA; oxidizes LPO-derived aldehydes | 118 |
| ALDH1B1/ALDH5 | 9p13.1 | Oxidizes acetaldehyde and LPO-derived aldehydes | 118, 119 |
| ALDH1L1/FDH | 3q21.3 | Converts 10-fTHF to tetrahydrofolate | 120 |
| ALDH1L2/mtFDH | 12q23.3 | Converts 10-fTHF to tetrahydrofolate | 121 |
| ALDH2 | 12q24.12 | Metabolizes acetaldehyde, DOPAL, and LPO-derived aldehydes; acts as a nitrate reductase | 118 |
| ALDH3A1 | 17p11.2 | Oxidizes aromatic, aliphatic aldehydes, and LPO-derived aldehydes; protects the cornea and lens against ultraviolet-induced oxidative stress | 117 |
| ALDH3A2/FALDH | 17p11.2 | Oxidizes fatty aldehydes | 118 |
| ALDH3B1 | 11q13.2 | Oxidizes LPO-derived aldehydes; involves in an alteration of dopamine metabolism | 118 |
| ALDH3B2 | 11q13.2 | Unknown | |
| ALDH4A1/P5CD | 1p36.13 | Oxidizes glutamate γ-semialdehyde; Oxidizes short- and medium-chain aliphatic LPO-derived aldehydes | 115 |
| ALDH5A1/SSADH | 6p22.3 | Metabolizes succinic semialdehyde to succinate | 115 |
| ALDH6A1/ MMSDH |
14q24.3 | Oxidizes malonate, methylmalonate semialdehyde and malondialdehyde; invloves in valine and pyrimidine catabolism | 115, 118 |
| ALDH7A1/EPD | 5q23.2 | Oxidizes LPO-derived aldehydes, alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde, and betaine aldehyde | 122 |
| ALDH8A1 | 6q23.3 | Metabolizes retinal to RA; oxidizes acetaldehyde and LPO-derived aldehydes | 118 |
| ALDH9A1 | 1q24.1 | Metabolizes γ-Aminobutyraldehyde, betaine aldehyde and catecholamine-derived aldehydes | 118 |
| ALDH16A1 | 19q13.33 | Probably takes part in the etiology of gout | 123 |
| ALDH18A1/P5CS | 10q24.1 | Catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate | 118 |
Abbreviations: DOPAL, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde; FALDH, fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase; FDH, 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; LPO, lipid peroxidation; MMSDH, methylmalonate semialdehyde dehydrogenase; P5CD, pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase; P5CS, Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase; RA, retinoic acid; SSADH, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase; 10-fTHF, 10-formyltetrahydrofolate.
In addition, cytosolic ALDH (ascribed to ALDH1A1 expression) is highly expressed in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) and is relatively resistant to cyclophosphamide 17-19. High ALDH activity in hematopoietic progenitor cells offers a biomarker for easy identification and isolation of viable hematopoietic progenitor cells with the new Aldefluor substrate assay 17. This high ALDH activity marker can also be used for isolating liver progenitor cells (LPCs) from murine and human liver 20. It is believed that LPCs with high ALDH1 expression provide a cell source for regenerating hepatocytes for repair of injured liver in vivo and for toxicology studies in vitro 20. However, a recent study demonstrated that deletion of the Aldh1a gene does not affect LPC proliferation or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression 21.
Effects of Mutant ALDH2 Protein on Acetaldehyde Metabolism
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been identified among genes encoding ADH, microsomal enzyme CYP2E1 and other alcohol-metabolizing enzymes including ALDH2. A total of 84 SNP sites in the human ALDH2 gene have been reported 22.
Furthermore, rs671 is the most studied SNP in the ALDH2 gene, and mitochondrial ALDH2*2 is a variant with nucleotide mutation that results in replacement of glutamate with lysine (K) at residue 487 (E487K) in the oligomerization domain. This change alters the enzyme activity and metabolic efficiency in vivo 11. In addition, when the leader sequence in the mitochondrial isoform is included, position 487 of the mature protein is actually counted as amino acid position 504; thus, this mutant is also known as ALDH2*504 Lys 23. The E487 change impacts the dimer and tetramer formation, as E487K disrupts the conformational structure in the polymorph, resulting in loss of the ability for di- or tetramerization 12. The ALDH2 E487K variant shows decreased flexibility at the domain of catalysis and coenzyme binding and increased flexibility at the domain of oligomerization 12. Upon replacement of wild-type E487 with lysine, the variant K487 interferes with the local secondary structure when dimerized, conferring an unstable dimer interface. The K residue at the amino acid 487 position cannot form a hydrogen bond with arginine 264 at the same subunit or arginine 475 in the dimer partner, damaging the NAD+-binding site, particularly in the αG helix of the dimeric interface 24. The E487K mutant has altered kinetic properties; i.e., the Km value for NAD+ at a physiological pH is increased by >150-fold, the Kia (representing the dissociation constant for NAD+ from the enzyme) is increased by nearly 50-fold, and the Kcat is decreased by 2-10-fold compared to the recombinant native enzymes 25. Furthermore, the rate-limiting step is shifted from hydride transfer or coenzyme dissociation to the NAD+-binding enzyme; coenzyme binding becomes slower and weaker 24, 25.
In terms of the ingestion of alcohol, individuals who have the homozygous ALDH2*2/*2 genotype lose ALDH2 activity and cannot metabolize acetaldehyde, while those with the heterozygous ALDH2*1/*2 genotype have a reduced ability (loss of >90% of activity) to metabolize acetaldehyde. Consequently, acetaldehyde excessively accumulates in cells, resulting in a flushing response, Asian glow or flush accompanied by headache, perspiration, tachycardia, palpitations, nausea, and sleepiness after consumption of alcohol. A more severe reaction is seen in those individuals with the homozygous null gene, compared with that in heterozygous individuals with the incomplete knockout 26.
Distribution of ALDH Alleles in Different Populations
Human ALDH2*2 is the most common variant among ALDH gene members and occurs in an estimated 560 million people or an average 8% of the global population. However, the ALDH2*2 positive percentage varies from race to race, being as high as 40% in Asians and <5% in European and African populations 27, 28. Genetic studies have suggested that the ALDH2*2 variant can be traced back to a Han Chinese ancestor in central China and that it continued spreading in many regions of East Asia over several millennia. Populations with a high percentage of individuals positive for the ALDH2*487 Lys allele are largely localized in the South Fujian province and East Guangdong province in southeastern China, and in Chiba (34.1%), a central region in Japan 23. Continuous migration and population growth of Han Chinese expanded the ALDH2*487 Lys genotype to neighboring regions 23. A study investigating 4018 Chinese Han adults found that the frequencies of ALDH2*1/*1 (GG), ALDH2*1/*2 (GA), and ALDH2*2/*2 (AA) were 68.67%, 28.67%, and 2.66%, respectively 29.
Screening Strategy for ALDH2
High-resolution melting analysis is considered a sensitive closed-tube approach to determining SNPs of ADH1B and ALDH2. This assay can be completed in 2 hours, costs only $0.50, and is suitable for population screening 30. In addition, polymerase chain reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis can also distinguish two polymorphic alleles for both the ADH1B and ALDH2 genes within 1.2 hours, and thus, can be used for both small- and large-scale analyses 31.
Non-assay-based investigations, i.e., a simple questionnaire of presence or absence of current and past flushing, can be used for identifying inactive ALDH2 variants in population-based epidemiological studies 32. A note of caution is that, despite the presence of ALDH2*1/*2 or ALDH2*2/*2, individuals with a semi-active or knockout form of ADH2 (e.g., ADH2*1/*1 or ADH2*2/*1) may not experience obvious flushing after light drinking or facial flushing may be diminished in individuals with a long or heavy drinking history 32. Another study found that the sensitivity and specificity of the modified alcohol flushing questionnaires were 95.1% and 76.5%, respectively, in healthy male subjects, and 78.9% and 82.1%, respectively, in subjects who participated in a gastric cancer screening program or received esophagogastroduodenoscopy 33.
ALDH and Liver Diseases
ALDH and Viral Liver Diseases
Chronic alcohol-related liver injury and viral hepatitis are two major categories of chronic liver disease, and often both etiologies occur in the same liver, accelerating liver disease progression 34. The prevalence rates of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in the US, European countries and Japan were reported to be 1.13%, 1.10%, and 1.56%, respectively, and these rates are higher than that of 0.72% in China 35. A national household survey conducted between 1999-2002 in the United States showed that adults who were HCV RNA-positive had heavier alcohol intake, were almost three times more likely to consume >1 drink per day (35.3% vs. 13.5%, P=0.003), and were almost 8 times more likely to consume >3 drinks per day (19.2% vs. 2.4%, P=0.010) compared with other adults 36. Alcoholic individuals who are also intravenous drug users are at a much higher risk for contracting HCV infection. According to the data from the 2003-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, the median number of US residents with HCV infection was estimated to be 4.6 million (range, 3.4-6.0 million), and of these, at least 3.5 million (range, 2.5-4.7 million) were viremic 37. The combination of HCV infection and alcohol abuse accelerates chronic liver disease to end stage 38. On the other hand, the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in China is high, with an estimated 6.52% of the general population being hepatitis B serum antigen (HBsAg) positive 35. Our recent study showed that a history of excessive drinking was identified in 26.5% of chronic hepatitis B patients without cirrhosis, in 35.6% of those with HBV-associated cirrhosis, and in 41.8% of those with HBV-associated HCC 39. Lin et al. found a good geographical correlation between populations who lived in HBV endemic regions and carried the ALDH2*2 alleles 40. Globally, the highest liver cancer incidence and HBV prevalence are detected in Eastern Asia and Africa 40. Research has also found frequencies of ALDH2*1/*2 or ALDH2*2/*2 of 29%, 35.3%, 28.0%, and 37.9% in healthy controls, chronic hepatitis B patients without cirrhosis, patients with HBV-associated cirrhosis, and patients with HBV-associated HCC, respectively 39.
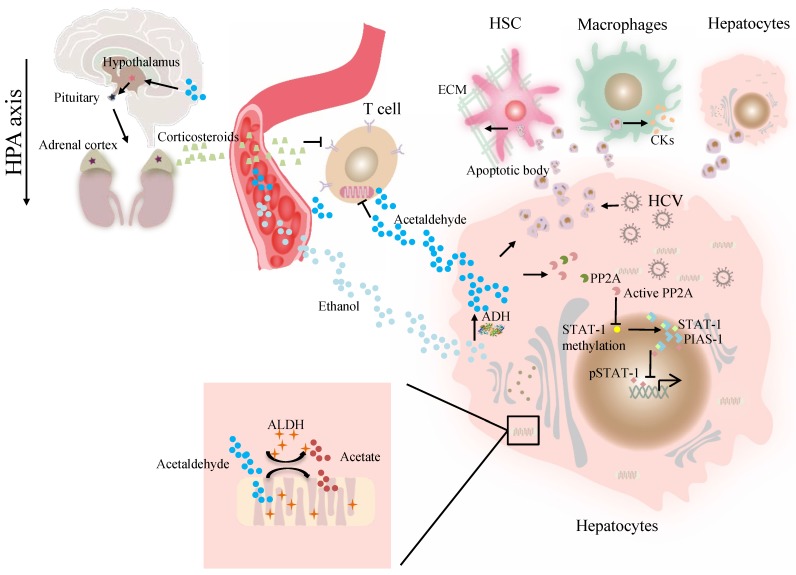
At present, the association of ALDH genotype and viral hepatitis at the molecular level remains largely unexplored. The major difficulty is a lack of valid models in which a liver can support viral infection and alcohol metabolism that resembles liver injury caused by alcohol consumption and viral infection in alcoholic patients with chronic hepatitis C 41. Our previous work demonstrated that alcohol-fed Aldh2-/- mice were less sensitive to concanavalin A-induced T-cell hepatitis than wild-type mice 42. Further studies suggest that acetaldehyde directly suppresses cytokine production in T cells through the inhibition of aerobic glycolysis or stimulation of corticosterone release, which contributes to the occurrence of suppressed T-cell hepatitis in ethanol-fed Aldh2 -/- mice 42. Cho et al. suggested that the ADH/ALDH pathway also exerts a potent antiviral activity, likely mediated through the catalysis of retinol (ROL) and RA biogenesis, leading to the expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) 38. Furthermore, acetaldehyde activates protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), leading to reduced signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-1 methylation and formation of the protein inhibitor of activated STAT-1 (PIAS-1)-STAT-1 complex 43. Consequently, pSTAT-1 attachment to DNA is decreased, and ISG activation is inhibited, compromising antiviral function in HCV-infected hepatocytes 43. The ISG pathway consists of more than 300 antiviral molecules that synergistically exert innate immunity. Betaine, a compound that functions as a methyl donor, can mitigate the acetaldehyde-mediated inhibition effect on IFN signaling, and thus, can be used to relieve the negative impact of accumulated acetaldehyde in HCV+ alcoholic patients 43. The antiviral activity of the ADH/ALDH pathway may be compromised even by a physiological alcohol concentration in alcoholic individuals, likely through alcohol-ROL metabolic competition 38. A mechanism for acetaldehyde exposure-induced liver injury in HCV-infected cells was proposed by Ganesan et al., who found that acetaldehyde is continuously generated in the acetaldehyde-generating system (AGS), resulting in a transient increase in HCV RNA, which subsequently recedes to normal or lower levels when a significant number of HCV-infected cells undergo apoptosis 41. Acetaldehyde is also associated with higher miR-122 and miR-34a expression in HCV-infected hepatocytes, leading to higher HCV replication, and consequently, apoptosis due to robust HCV replication and accumulation of viral products. Destruction of HCV-infected cells via apoptosis bodies results in the release of infectious HCV virions for de novo infection that expands the HCV infection in the liver, aggravating liver injury and delaying HCV clearance 41. The apoptotic bodies engulfed by Kupffer and hepatic stellate cell (HSC) potentially induce hepatic inflammation and fibrosis 41 (Figure 1). In summary, future studies that focus on identifying novel mechanisms and devising therapeutic strategies for these viral liver diseases in ALDH2-inactive individuals are warranted.
Figure 1.
The effect of ALDH in viral liver diseases. Ethanol is converted to acetaldehyde by the cytosolic enzyme ADH and the microsomal enzyme CYP2E1. Then acetaldehyde is converted to acetate by ALDH. Acetaldehyde directly suppresses cytokine production in T cells through the inhibition of aerobic glycolysis or stimulation of corticosterone release through HPA axis. Acetaldehyde also activates PP2A, leading to reduced STAT-1 methylation and formation of the PIAS-1-STAT-1 complex. Consequently, pSTAT-1 attachment to DNA is decreased, and ISG activation is inhibited. Acetaldehyde induces apoptosis in HCV -infected hepatocytes. Destruction of HCV-infected cells via AB release infectious HCV virions for de novo infection Kupffer cells, HSCs, and hepatocytes engulfed AB, potentially inducing of hepatic inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis. Abbreviations: ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; AB, apoptotic body; CYP2E1, cytochrome P-450 2E1; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; ; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; ISG, interferon-stimulated genes; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PIAS-1, protein inhibitor of activated STAT-1; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
ALDH and Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
As many developing countries have experienced significant economic expansion and improved living standards, a byproduct has been an alarming rise in alcohol consumption and subsequently ALD 35. The prevalence rates of ALD were reported to be 4.5%, 6.2% 6%, and 1.56-2.34% in China, the US, Europe, and Japan, respectively 35, 44-46.
Alcohol flushing response can be a defensive mechanism, and it may deter alcohol consumption and reduce ALD in individuals with ALDH2*487 Lys 47, 48. A meta-analysis of 12 studies found that individuals with ALDH2*1 allele are connected with a higher frequency of alcoholic liver cirrhosis (ALC) compared with those with ALDH2*1/*2 or ALDH2*2/*2 genotype 49. In addition, a single-center study from Beijing 302 Hospital in China reported that only 2.3% of ALD patients had the 487 Lys allele compared with 14.5% of healthy controls (281 cases and 535 controls; odds ratio [OR] = 0.13, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.07-0.24) 47. Similarly, Tanaka et al. observed the ALDH2*1/*1 genotype more frequently in an alcoholic population and ALD patients in Japan, than in control subjects (95.6% and 80.6% vs. 39.4%, P<0.01) 50. Chao et al. reported that patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and alcoholic dependence had a significant lower frequency of the ALDH2*2 allele than did healthy controls (9%, 6% vs. 30%, P<0.005; n= 27, 50, and 50, respectively) 51. They also reported a significant higher frequency of the ALDH2*1 allele in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis vs healthy controls (93% vs. 71%, P<0.001; 75 cases and 100 controls) 52. Lee et al. reported a significantly higher frequency of the ALDH2*1 allele in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis (96%, n=56) and in alcoholic individuals without evidence of liver disease (98%, n=52), compared with nondrinkers (74%, n=64, P=0.001) in Korea 53. However, the observed protection against ALD by the ALDH2*2 allele can wane over time. Edenberg et al. found that the percentage of alcoholic Japanese individuals with the ALDH2*2 allele increased from 2.5% to 13% during the period of 1979 to 1992, indicating that this allele's protective function can be overcome by more alcohol consumption, which increases alcohol tolerability 54. Recent research demonstrated that hepatocyte-specific Aldh2 knockout mice reduced excessive alcohol preference rapidly but not light to moderate alcohol concentrations; therefore, targeting liver ALDH2 represents a promising approach to prevent heavy drinking with limited systemic side effects 8. Culturally, people are encouraged or challenged to drink more alcohol in social events, and sometimes individuals with face flushing may not be able to escape or decline this drinking binge because any reluctance in drinking is considered rude 55.
Interestingly, Kwon et al. reported that Aldh2-/- mice become more susceptible to alcohol-induced liver inflammation but more resistant to alcohol-induced steatosis. One possible reason for these diverse effects is that malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adduct (MAA)-mediated paracrine activity stimulates interleukin (IL)-6 expression in Kupffer cells, which activates STAT3 in hepatocytes and then attenuates the transcription of SREBP1c (sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c) 56. Hepatocellular SREBP1c mRNA levels and the expression level of acetyl-CoA carboxylase-1, a target gene of SREBP1c and fatty acid synthase were significantly lower in the alcohol-fed Aldh2-/- mice than in wild-type mice 56. Chaudhry et al. reported that Aldh2+/- mice were prone to alcohol-induced gut barrier dysfunction and fatty liver, because acetaldehyde damages the epithelial barrier and increases the permeability of the epithelial layer in the intestinal tract 57. One study suggested that overexpression of ALDH2 is protective through the attenuation of chronic alcohol-induced liver damage and apoptosis (caspase 3 activity) 58. Zhong et al. considered mitochondrial ALDH2 a promising therapeutic target for ALD, based on their finding that a selective small-molecule ALDH2 activator, N-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-2,6-dichlorobenzamide (Alda-1), can accelerate aldehyde clearance and reverse hepatic steatosis and apoptosis in mice through pharmacological activation of ALDH2 59. In addition, alcohol intake induces mitochondrial damage, one of the hallmarks of ALD 60. A mitochondria-targeted lipophilic ubiquinone (MitoQ) was reported to expedite clearing of acetaldehyde and lipid aldehyde and to restore ALDH activity by blocking post-translational oxidative/nitrosative modification of mitochondrial ALDH2 in mice 60. However, activation of ALDH2 by Alda1 or MitoQ may increase drinking and exacerbate ALD; thus the treatment of ALD patients with ALDH2 activators may not achieve significant beneficial effects 61. Overall, alcohol consumption is one of the major avoidable risk factors for ALD, and abstinence is considered foundational for successful ALD treatment.
ALDH2 and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
An often underappreciated but important trend is that the incidence of metabolic liver diseases continues increasing worldwide 62-64. A global meta-analysis of studies found that the global NAFLD prevalence in 8,515,431 individuals diagnosed by imaging findings was 25.24% (95% CI: 22.10-28.65), and the prevalence was highest in the Middle East and South America and lowest in Africa 65. The estimated regional NAFLD percentages in Asia and Israel were 52.34 per 1,000 (95% CI: 28.31-96.77) and 28.01 per 1,000 person-years (95% CI: 19.34-40.57), respectively 65. The prevalence rates of NAFLD were found to be 22.4%, 24.13%, 23.71%, and 25% in China, the US, Europe, and Japan, respectively 35, 63, 64, 66. NAFLD covers a spectrum of liver pathologies from fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis to cirrhosis, liver failure and HCC. Day et al. proposed a 'two hit' model for NAFLD pathogenesis 67. The 'first hit' produces steatosis, and then the 'second hit' includes oxidative stress to initiate significant lipid peroxidation to injure liver cells 67. Endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs in the course of NAFLD and contributes to the production of ROS, which can provoke oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to form lipid peroxidation products, such as 4-hydroxy-nonenal (4-HNE) 68.
Of particular interest, NAFLD at the progressive stages may also impact alcohol metabolizing enzymes and alcohol metabolism processes. Li et al. reported that ALDH4A1 mRNA was significantly decreased in two NASH groups (fatty and non-fatty: >5% and <5% of hepatocytes with fat deposition), in contrast to no significant changes in the mRNA levels of other alcohol-related enzymes 69. However, the protein levels of ALDH2 were significantly increased in both NASH groups, whereas the ALDH1A1 and ALDH1B1 protein levels were significantly reduced. Furthermore, significant oxidative stress and reduced ALDH activity were suggested by the significant accumulation of 4-HNE protein adduct in NASH 69. 4-HNE is a covalent modification of an ALDH2 active site peptide and is reported to be a potent irreversible inhibitor of ALDH2, suggesting 4-HNE adduct formation may inactivate ALDH2 70. As reported, Alda-1 may exert a range of biologic functions from enhancing the detoxification activity of ALDH2 and attenuating hepatic fatty content including triglycerides to reducing the formation of 4-HNE protein adduct in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice (apoE-/-) 71. However, a systematic transcriptome analysis revealed that the expression of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes, including ADH, ALDH (ALDH1A1, ALDH1B1, ALDH3B1, ALDH4A1, ALDH7A1, and ALDH9A1), CYP2E1, and CAT, was higher in NAFLD livers (72 NAFLD patients and 7 controls) 72. Overall, these findings support a role for alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in NAFLD pathology, and further studies are needed to clarify the effects of NAFLD on alcohol metabolism and how alcohol affects NAFLD pathogenesis.
Although alcohol consumption and NAFLD commonly exist, the data on the effects of moderate alcohol drinking on NAFLD progression remain controversial 73-76. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 1988 to 2010 revealed that modest alcohol consumption (0.5-1.5 drinks or 7-21 g/day) is associated with decreased mortality among patients with NAFLD 73. The modest drinking has a protective effect partly via decreases in cardiovascular disease mortality and metabolic syndrome 73, 76. In contrast, a large-scale cohort study of 58,927 Korean patients with NAFLD demonstrated that even moderate drinkers (10-29.9 g/day) exhibited an increased tendency to progress to fibrosis compared with nondrinkers 74. Further investigation should be conducted to figure out whether moderate alcohol consumption can become a lifestyle intervention in the treatment. In addition, the effects of ALDH2 polymorphism on NAFLD with or without alcohol drinking have not been carefully studied.
ALDH and Liver Fibrosis
An estimated 7 million (or 0.51%) Chinese individuals suffer from liver cirrhosis, which is accompanied by 460,000 new cases of liver cancer each year. The reported prevalence rates of cirrhosis were 0.27%, 0.10%, and 0.31-0.39% in the US, Europe, and Japan, respectively 35. In more than 80% of cases, HCC is preceded by fibrosis or cirrhosis, implicating liver fibrosis as a premalignant lesion 77. Previous studies reported that inactive ALDH2 and super-active ADH2 alleles were associated with liver fibrosis as a result of increased acetaldehyde accumulation in hepatocytes 78. In addition, a recent study showed that the fibrotic liver has significantly higher activity of total ADH, ADH1 and ADH2 compared with the normal liver (P<0.001), while ALDH activity was higher, but insignificantly (median, range = 0.12, 0.02-0.32 nmol·min-1·mg-1 protein vs. 0.15, 0.03-0.35 nmol·min-1·mg-1 protein, P<0.01) 79.
Aldh2-/- mice are also more susceptible to ethanol plus carbon tetrachloride -induced liver injury, inflammation and fibrosis through acetaldehyde and its derived adducts 56. Increasing evidence indicates that acetaldehyde enhances HSC activation in fibrogenesis in vitro 56, 80. In response to liver injury, HSCs may be activated and converted to a myofibroblast-like cell morphology by losing the quiescent fat-storing phenotype, increasing proliferation and fibrillar collagen production, and showing pro-inflammatory activity 77, 81. Activated HSCs represent the main source of excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) production and are likely involved in alcohol-induced fibrosis as well 80. Acetaldehyde and ROS are originally generated in hepatocytes but may be taken up by HSCs in a paracrine fashion, where acetaldehyde promotes collagen I synthesis 78, 81. Promoters for both collagen α1 (I) and collagen α2 (I) (COL1A2) contain acetaldehyde-responsive elements in the different transcription factor binding sites 82. Reyes-Gordillo et al. proposed that the acetaldehyde-induced up-regulation of COL1A2 transcription is mediated by two distinct mechanisms. The first mechanism is transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)-independent, and it mainly eliminates repressors of COL1A2 (such as Ski and SMAD7) and phosphorylates SMAD3 (up to about 6 hours). This step occurs swiftly and also transiently 78, 83. The second mechanism features a sustained acetaldehyde-mediated upregulation of TGF-β1 expression. Both phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of SMAD3/4-containing complexes are then induced to lead to binding of the COL1A2 promoter by acetaldehyde and TGF-β, which induces the production of collagens for fibrogenesis 83. Moreover, acetaldehyde may upregulate the interstitial collagenase matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 gene and downregulate the fibrillary collagenase MMP-1, resulting in a sclerotic matrix with substitution of the normal ECM components 81.
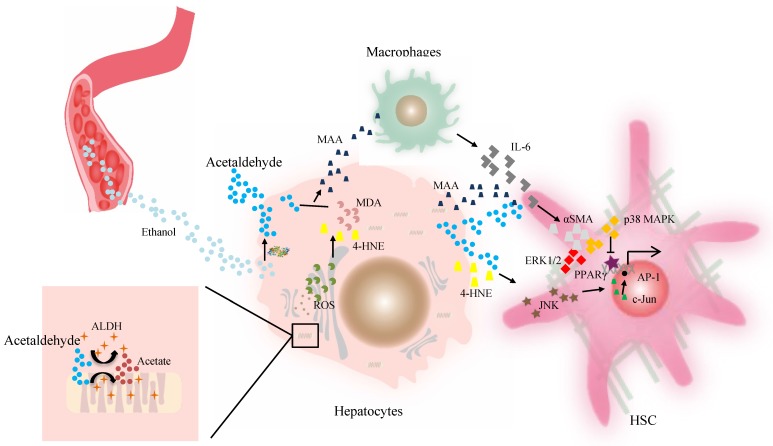
Acetaldehyde-derived adducts may also promote liver fibrosis. The aldehyde molecule tends to be unstable and quickly reactive with cellular components and generates adducts without proper function. This step appears to be key in alcohol-induced fibrosis. The progression of liver fibrosis correlates well with elevated levels of acetaldehyde-protein and acetaldehyde-lipid adducts of malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-HNE, and mixed MAA adducts in both alcoholic patients and animal models 78, 84. A suggested mechanism for aldehyde-mediated activation of HSCs includes that 4-HNE activates p46 and p54 isoforms of c-Jun amino-terminal kinase and activating protein-1 in HSCs 84. However, as reported, HSCs isolated from the liver of a rat model of cirrhosis can metabolize 4-HNE at a higher efficiency, which contributes to their higher ALDH activity in vitro 80, compared with HSCs from the normal rat liver. Finally, Kupffer cells stimulated by higher levels of MAA adduct produce a higher level of IL-6, which in synergy with acetaldehyde or MAA, can enhance the expression of α-smooth muscle actin protein and promote HSC activation and proliferation via p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation 56, 85, 86. Then peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) transcriptional activity is inhibited by acetaldehyde through rapid activation of PKCδ and the ERK1/2 pathway, whereas the depression of PPARγ transcriptional activity is associated with activation and proliferation of HSCs 81, 87. ALDHs catalyze retinaldehyde to RA, a strong morphogen that triggers cell differentiation and proliferation during development 20, 88. RA is also implicated in fibroblast proliferation and expression of ECM collagen in activated HSCs, which contributes to liver fibrosis 88, 89 (Figure 2). Therefore, individuals with the dominant inactive ALDH2*2 gene should be informed of their higher risk for liver inflammation and fibrosis after moderate or heavy drinking.
Figure 2.
The effect of ALDH in liver fibrosis. Acetaldehyde can be taken up by HSCs in a paracrine fashion. Both acetaldehyde and 4-HNE can promote collagen I synthesis in HSCs through JNK/ERK/ AP-1 signaling. MAA adduct stimulate Kupffer cells to produce a higher level of IL-6, which in synergy with acetaldehyde or MAA, can enhance the expression of αSMA protein and promote HSC activation and proliferation via p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation. The PPARγ transcriptional activity is inhibited by acetaldehyde through rapid activation of PKCδ and the ERK1/2 pathway, contributing to activation of HSCs. Then activated HSCs are the main source of excessive ECM production. Abbreviations: ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; AP-1, activating protein-1; ECM, extracellular matrix; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; 4-HNE, 4-hydroxy-nonenal; IL, interleukin; JNK, c-Jun amino-terminal kinase; MAA, malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin.
ALDH and HCC
Liver cancer ranked as the fifth most common cancer and the second most malignant cancer for cancer-related mortality in the world in 2015 90. The reported prevalence rates of liver cancer were 0.03%, 0.01%, <0.01%, and <0.01% among the general population in the China, US, Europe, and Japan, respectively 35. Chronic HBV infection is the leading etiology for HCC not only in HBV endemic regions, but also globally. The second most common etiology is ALD using the measure of disability-adjusted life-years 90. Because carcinogenesis implicates environmental and genetic factors, it is important to gain a perspective on the correlation of genetic variations in alcohol-metabolizing enzymes with liver cancer occurrence.
ALDH is associated with HCC risk, progression, and prognosis. A dose-dependent association between the cumulative amount of alcohol consumption over time and HCC risk in individuals with the ALDH2*1/*2 or ALDH2*2/*2 genotype was reported based on a comparison of a HCC cohort of 208 cases and a control cohort of 208 control cases conducted in Jiangsu, China 55. Moreover, a study of independent HCC cohorts suggested a negative correlation between ALDH2 expression and predisposition to malignant HCC 13. However, the correlation of the ALDH2*1/*1 genotype with increased HCC risk in HBV-positive patients with cirrhosis was suggested based on an analysis of 4155 HBsAg-seropositive participants, but no causal relationship was found between the ALDH2*1/*2 or ALDH2*2/*2 versus the ALDH2*1/*1 when alcohol drinking habits were considered 91.
The gene expression data from the Oncomine database showed that ALDH1A1 expression was higher and ALDH1B1 expression was lower in HCC tissues compared with normal tissues. Intrahepatic ALDH2 expression was lower at both the mRNA and protein levels in HCC and metastasis-inclined tissues compared with corresponding normal tissues and metastasis-averse tissues. A recent proteogenomic analysis of HBV-related HCC in China indicated an impaired liver-specific metabolic function in HCC cells and downregulation of ALDH1B1, ALDH2, and ALDH3B1 92. Proteomic clustering identified three subgroups, among which, the metabolism subgroup was characterized by the highest expression levels of proteins related to metabolism and liver function, including ALDH1A1, ALDH1A2, ALDH2, ALDH4A1, and ALDH9A1 92. In terms of prognosis, a lower ALDH2 level was a poor prognosticator following primary resection, coincident with older age, embolus, larger tumor size, extrahepatic metastasis and microvascular invasion in HCC patients 13. Furthermore, a correlation of higher ALDH1B1 and ALDH1L1 gene expression with better clinical outcomes was noted in HBV-related HCC patients 16, 93.
ALDH2 is implicated in alcohol-related cancers. As reported in a recent study in both patients and mice, deficiency in ALDH2 correlated well with a higher risk for advancement of alcohol related-fibrosis to HCC 39. Large amounts of oxidized mitochondrial DNAs are released via extracellular vesicles (EVs) by Aldh2-deficient hepatocytes. The EVs can be taken up by neighboring HCC cells, which in conjunction with acetaldehyde, activate multiple oncogenic pathways (including C-Jun N-terminal kinase, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, BCL-2, and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif), and promote HCC carcinogenesis after chronic exposure to both carbon tetrachloride and alcohol 39. These studies suggested that a reduction in the genesis of EVs containing the oxidized mtDNA represents a possible therapeutic strategy for mitigating the risk of ALD-associated HCC in ALDH2-deficient individuals 39. Furthermore, the number of sister-chromatid exchange (SCE) events is elevated 2.3-fold in Aldh2-/- mice, and a single exposure to alcohol causes a 4-fold increase in SCE events, indicating that resultant DNA damage activates recombination repair in response to the accumulation of endogenous aldehydes 94. It is known that genomic instability is a hallmark of cancer cells, as it generates a high frequency of DNA damage 95. Moreover, ALDH2 impacts metastasis largely through modulating the ALDH2-acetaldehyde -redox-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) axis, because AMPK modulates lipid metabolism to regulate tumor cell growth and survival. Moreover, ectopic expression of ALDH2 ameliorates HCC metastasis both in vitro and in vivo 13, 96.
Furthermore, the overexpression of ALDHs (mainly ALDH1, ALDH3A1, and ALDH18A1) confers cancer cells with a survival advantage because oxidative stress resulting from high metabolic activity leads to ROS generation, lipid peroxidation, and the accumulation of toxic aldehydes, which can inhibit the proliferation and survival of cancer cells 97. As antioxidants, ALDHs can also decrease immunogenic cell death and limit tumor immunity by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and ROS production 98. As reported, ALDH1B1 activity was downregulated in liver cancer tissues compared to normal liver tissue, and the reduced ALDH1B1 activity was considered protective in HCC patients through its influence on the oxidation of short-chain aldehydes including acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde 16, and its protective against alcohol-induced hepatocellular proliferation and hepatic neoplasm in mice 99. In addition, ALDH1L1, which is also reduced in HCC, also can suppress cancer cell proliferation by depleting intracellular 10-formyltetrahydrofolatedehydrogenase, which is required for de novo purine biosynthesis 100, 101. ALDH3A1 was reported to be significantly upregulated in HCC and adenoma, resulting in the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and CTNNB1 mutations, and ALDH3 may slow the growth of HCC cells and inhibit the formation of aldehydes derived from lipid peroxidation 102, 103. In tumor immunity, the ALDH1 family (including ALDH1A1, ALDH1A2, and ALDH1A3) converts retinal to RA, which promotes the induction, function and stability of regulatory T cells, leading to immune tolerance that compromises tumor immunity 104.
ALDH and Cancer Stem Cells
In liver carcinogenesis, some rarefied tumorigenic cells are considered as cancer stem cells (CSCs). These cells may have unlimited proliferative potential and may drive the formation, growth, and relapse of tumors. ALDHs are markers of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in a variety of cancers, and they modulate cell proliferation, metastasis, stem cell differentiation, and resistance to chemotherapeutic agents by protecting cells from toxins and differentiation-inducing stimuli 97, 105. CD133+/ALDHhigh HCC cells, a subpopulation of cancer-initiating cells, were suggested to possess a high tumor-forming ability 106. Both CD133 and ALDH as markers can be used to identify dual-positive HCC cells, which may serve as a cell model to understand HCC carcinogenesis and to identify and select new therapeutic targets through molecular, genomic, and epigenetic analyses 106, 107. However, none of the commonly used markers (including CD133, ALDH, CD44, EpCAM, or CD90) can standalone as an ubiquitous marker for hepatic CSCs due to heterogeneity of the tumoral process 108. Additionally, ALDH was used as a biomarker for distinguishing normal from CSCs, making it a powerful predictor of poor clinical outcome 105, 109-111. However, a recent study demonstrated that deletion of the Aldh1a gene did not affect LPC proliferation or HCC progression 21. Therefore, further studies are required to clarify the role of ALDH in the control of LPCs.
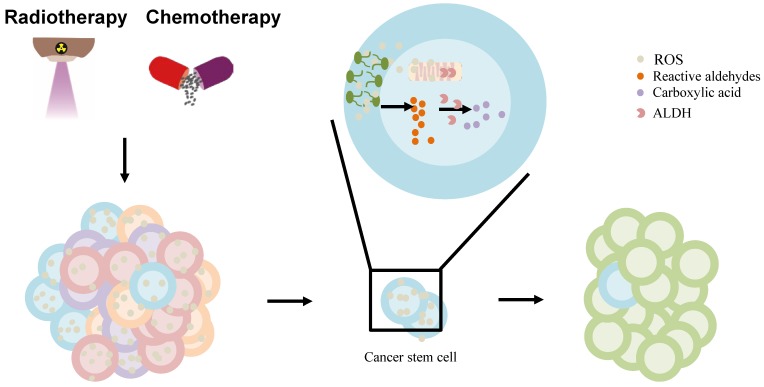
Furthermore, the standard chemotherapy and radiation treatments preferentially target non-CSCs, while CSCs are resistant to these treatments, which contributes to relapse after treatment. ALDHs, highly expressed in CSCs contribute to the chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-resistance 97. Owing to their increased metabolic activity and the use of radiation or ROS-generating drugs to treat them, cancer cells may experience significantly high oxidative damage, leading to increased ROS, lipid peroxidation, and the accumulation of toxic aldehydes, such as MDA, 4-hydroxy-hexenal, and 4-HNE 97, 112. ALDH activity may, under the regulation of intracellular scavenging, protect normal and cancer cells from injury by reducing ROS during chemo-/radiotherapy 113. Moreb et al. suggested that the resistance to chemo-/radiotherapy by CSCs can be mitigated by targeting ALDH proteins 114. ALDH, once hijacked in CSCs, oxidizes aldophosphamide to carboxyphosphamide and provides resistance to cyclophosphamide and other chemotherapeutic drugs (including temozolomide, 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide, irinotecan, paclitaxel, epirubicin, and doxorubicin) 111. Further, ALDH can reduce ROS and limit immunogenic cell death and antitumor immunity by interfering with the efficacy of ROS-generating drugs including anthracyclines, mitoxantrone, bleomycin, bortezomib, and cyclophosphamide 98 (Figure 3). Co-targeting of ALDH with other therapies might reduce resistance and improve the management of these cancers. ALDH inhibitors are classified into multi-ALDH isoform inhibitors and isoform-specific inhibitors, which can be utilized for cancer treatment (reviewed by Dinavahi et al.) 97. However, HCC cells lost ALDH2 protein expression compared to non-tumor tissues 13. Thus, further research is needed to determine whether ALDH inhibitors can be used to treat liver cancer patients in combination with other cancer therapies.
Figure 3.
The effect of ALDH in liver cancer stem cell (CSC) model. The chemo-/radiotherapy leads to increased ROS, lipid peroxidation in cancer cells. ROS can provoke oxidation of PUFAs in membrane lipid bilayers to form highly reactive aldehydes. ALDH is involved in the oxidation of aldehydes into carboxylic acid in cancer stem cells, contributing to resistance and relapse. Abbreviations: ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; CSC, cancer stem cell; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Therapeutic Prospects
ALDH2 is the key enzyme that metabolizes acetaldehyde and is a great therapeutic target for the treatment of alcoholism. An estimated 8% of the world's population, consisting mainly of individuals of East Asian descent, have the ALDH2*2 allele, which encodes a nonfunctional ALDH2 protein. In general, those with the ALDH2*2 allele consume less alcohol, but some still drink a large amount of alcohol, causing accumulation of acetaldehyde in the body. The roles of acetaldehyde in liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer development still remain obscure. Further studies are required to determine whether ALDH2 can serve as a therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of liver disease and cancer. Moreover, considering the significant role of ALDH2 in drug metabolism, an altered ALDH2 function may also lead to significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of substrate drugs and therefore introduce potential variable drug efficacy or adverse events. Therefore, we need to learn more about the effects and particularity of ALDH2 polymorphisms, especially in alcoholic subjects, to offer them appropriate dosing adjustments and help them make well-informed treatment choices in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants No. 81972265), the National key research plan "precision medicine research" key project (2017YFC0908103), the National Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX10202202, 2018ZX10302206), the JLU Norman Bethune research plan (2018B32), Program for JLU Science and Technology Innovative Research Team (2017TD-08) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author Contributions
Gao. YH. designed the review outline; Gao. YH. and Wang. WJ. drafted the manuscript; Gao. YH., Wang. WJ., Wang. CG. and Xu. HQ. revised and edited the paper; all authors approved the final version.
Abbreviations
- ALDH2
acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2
- ALD
alcoholic liver disease
- AMPK
AMP-activated protein kinase
- AGS
acetaldehyde-generating system
- ALC
alcoholic liver cirrhosis
- CYP2E1
cytochrome p450 2E1
- CSCs
cancer stem cells
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- EVs
extracellular vesicles
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HBV
hepatitis B virus
- HCV
hepatitis C virus
- 4-HNE
4-hydroxy-nonena
- HSPCs
hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
- HSC
hepatic stellate cell
- ISGs
interferon-stimulated genes
- LPCs
liver progenitor cells
- MAA
malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde
- MitoQ
mitochondria-targeted lipophilic ubiquinone
- MMP
matrix metalloproteinase
- MitoQ
mitochondria-targeted lipophilic ubiquinone
- NAFLD
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NAD
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NASH
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PP2A
protein phosphatase 2A
- PPARγ
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- PIAS-1
protein inhibitor of activated STAT-1
- ROS
radical oxidative species
- RA
retinoic acid
- ROL
retinol
- SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphisms
- SCE
sister-chromatid exchange
- STAT
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- SREBP1c
sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c
- TGF-β1
transforming growth factor beta 1
References
- 1.Muzio G, Maggiora M, Paiuzzi E, Oraldi M, Canuto RA. Aldehyde dehydrogenases and cell proliferation. Free radical biology & medicine. 2012;52:735–46. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moreb JS, Ucar-Bilyeu DA, Khan A. Use of retinoic acid/aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway as potential targeted therapy against cancer stem cells. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2017;79:295–301. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zambelli VO, Gross ER, Chen CH, Gutierrez VP, Cury Y, Mochly-Rosen D. Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 regulates nociception in rodent models of acute inflammatory pain. Science translational medicine. 2014;6:251ra118. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tawa EA, Hall SD, Lohoff FW. Overview of the Genetics of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol and alcoholism (Oxford, Oxfordshire) 2016;51:507–14. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agw046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Prabavathy D, Swarnalatha Y, Ramadoss N. Lung cancer stem cells-origin, characteristics and therapy. Stem cell investigation. 2018;5:6. doi: 10.21037/sci.2018.02.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gross ER, Zambelli VO, Small BA, Ferreira JCB, Chen C-H, Mochly-Rosen D. A personalized medicine approach for Asian Americans with the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2*2 variant. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology. 2015;55:107–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen CH, Ferreira JC, Gross ER, Mochly-Rosen D. Targeting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2: new therapeutic opportunities. Physiological reviews. 2014;94:1–34. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00017.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guillot A, Ren T, Jourdan T, Pawlosky RJ, Han E, Kim SJ. et al. Targeting liver aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 prevents heavy but not moderate alcohol drinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:25974–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908137116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zakhari S, Li T-K. Determinants of alcohol use and abuse: Impact of quantity and frequency patterns on liver disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2007;46:2032–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.22010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J. et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Molecular & cellular proteomics: MCP. 2014;13:397–406. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.035600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Adeniji EA, Olotu FA, Soliman MES. Alcohol Metabolic Inefficiency: Structural Characterization of Polymorphism-Induced ALDH2 Dysfunctionality and Allosteric Site Identification for Design of Potential Wildtype Reactivators. The protein journal. 2018;37:216–22. doi: 10.1007/s10930-018-9768-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Larson HN, Weiner H, Hurley TD. Disruption of the coenzyme binding site and dimer interface revealed in the crystal structure of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase "Asian" variant. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280:30550–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502345200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hou G, Chen L, Liu G, Li L, Yang Y, Yan HX. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) opposes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase signaling in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2017;65:1628–44. doi: 10.1002/hep.29006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim JI, Ganesan S, Luo SX, Wu YW, Park E, Huang EJ. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a1 mediates a GABA synthesis pathway in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science (New York, NY) 2015;350:102–6. doi: 10.1126/science.aac4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang CK, Wang XK, Liao XW, Han CY, Yu TD, Qin W. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) isoform expression and potential clinical implications in hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS one. 2017;12:e0182208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang C-K, Wang X-K, Liao X-W, Han C-Y, Yu T-D, Qin W. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) isoform expression and potential clinical implications in hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS one. 2017;12:e0182208–e. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Armstrong L, Stojkovic M, Dimmick I, Ahmad S, Stojkovic P, Hole N. et al. Phenotypic Characterization of Murine Primitive Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells Isolated on Basis of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2004;22:1142–51. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2004-0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gentry T, Foster S, Winstead L, Deibert E, Fiordalisi M, Balber A. Simultaneous isolation of human BM hematopoietic, endothelial and mesenchymal progenitor cells by flow sorting based on aldehyde dehydrogenase activity: implications for cell therapy. Cytotherapy. 2007;9:259–74. doi: 10.1080/14653240701218516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Levi BP, Yilmaz OH, Duester G, Morrison SJ. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a1 is dispensable for stem cell function in the mouse hematopoietic and nervous systems. Blood. 2009;113:1670–80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-156752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dolle L, Best J, Empsen C, Mei J, Van Rossen E, Roelandt P. et al. Successful isolation of liver progenitor cells by aldehyde dehydrogenase activity in naive mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2012;55:540–52. doi: 10.1002/hep.24693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Seo W, Gao Y, He Y, Sun J, Xu H, Feng D. et al. ALDH2 deficiency promotes alcohol-associated liver cancer by activating oncogenic pathways via oxidized DNA-enriched extracellular vesicles. Journal of hepatology. 2019;71:1000–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li R, Zhao Z, Sun M, Luo J, Xiao Y. ALDH2 gene polymorphism in different types of cancers and its clinical significance. Life sciences. 2016;147:59–66. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li H, Borinskaya S, Yoshimura K, Kal'ina N, Marusin A, Stepanov VA. et al. Refined geographic distribution of the oriental ALDH2*504Lys (nee 487Lys) variant. Annals of human genetics. 2009;73:335–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2009.00517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Larson HN, Weiner H, Hurley TD. Disruption of the coenzyme binding site and dimer interface revealed in the crystal structure of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase "Asian" variant. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280:30550–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502345200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Farres J, Wang X, Takahashi K, Cunningham SJ, Wang TT, Weiner H. Effects of changing glutamate 487 to lysine in rat and human liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. A model to study human (Oriental type) class 2 aldehyde dehydrogenase. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1994;269:13854–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee H, Kim SS, You KS, Park W, Yang JH, Kim M. et al. Asian flushing: genetic and sociocultural factors of alcoholism among East asians. Gastroenterology nursing: the official journal of the Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates. 2014;37:327–36. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gross ER, Zambelli VO, Small BA, Ferreira JC, Chen CH, Mochly-Rosen D. A personalized medicine approach for Asian Americans with the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2*2 variant. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology. 2015;55:107–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Druesne-Pecollo N, Tehard B, Mallet Y, Gerber M, Norat T, Hercberg S. et al. Alcohol and genetic polymorphisms: effect on risk of alcohol-related cancer. The Lancet Oncology. 2009;10:173–80. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ma C, Yu B, Zhang W, Wang W, Zhang L, Zeng Q. Associations between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) rs671 genetic polymorphisms, lifestyles and hypertension risk in Chinese Han people. Scientific reports. 2017;7:11136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11071-w. - [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yuan XW, Zhou WJ, Shang X, Li L, Liu YH, Xu XM. Rapid simultaneous genotyping of polymorphisms in ADH1B and ALDH2 using high resolution melting assay. Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. 2013;51:e75–7. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shirasu N, Yasunaga S. Duplex PCR-RFLP for the Simultaneous Genotyping of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in ADH1B and ALDH2 Genes. Analytical Sciences. 2016;32:1363–6. doi: 10.2116/analsci.32.1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yokoyama T, Yokoyama A, Kato H, Tsujinaka T, Muto M, Omori T. et al. Alcohol flushing, alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase genotypes, and risk for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Japanese men. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention: a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 2003;12:1227–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shin CM, Kim N, Cho SI, Sung J, Lee HJ. Validation of Alcohol Flushing Questionnaires in Determining Inactive Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 and Its Clinical Implication in Alcohol-Related Diseases. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2018;42:387–96. doi: 10.1111/acer.13569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Proeschold-Bell RJ, Evon DM, Yao J, Niedzwiecki D, Makarushka C, Keefe KA, A randomized controlled trial of an integrated alcohol reduction intervention in patients with hepatitis C infection. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md); 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xiao J, Wang F, Wong NK, He J, Zhang R, Sun R. et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective. Journal of hepatology. 2019;71:212–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Annals of internal medicine. 2006;144:705–14. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-144-10-200605160-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Edlin BR, Eckhardt BJ, Shu MA, Holmberg SD, Swan T. Toward a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2015;62:1353–63. doi: 10.1002/hep.27978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cho NE, Bang B-R, Gurung P, Li M, Clemens DL, Underhill TM. et al. Retinoid regulation of antiviral innate immunity in hepatocytes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2016;63:1783–95. doi: 10.1002/hep.28380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Seo W, Gao Y, He Y, Sun J, Xu H, Feng D. et al. ALDH2 deficiency promotes alcohol-associated liver cancer by activating oncogenic pathways via oxidized DNA enriched extracellular vesicles. Journal of hepatology. 2019;71:1000–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin YP, Cheng TJ. Why can't Chinese Han drink alcohol? Hepatitis B virus infection and the evolution of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Medical hypotheses. 2002;59:204–7. doi: 10.1016/s0306-9877(02)00253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ganesan M, Natarajan SK, Zhang J, Mott JL, Poluektova LI, McVicker BL. et al. Role of apoptotic hepatocytes in HCV dissemination: regulation by acetaldehyde. American journal of physiology Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2016;310:G930–40. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00021.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gao Y, Zhou Z, Ren T, Kim SJ, He Y, Seo W. et al. Alcohol inhibits T-cell glucose metabolism and hepatitis in ALDH2-deficient mice and humans: roles of acetaldehyde and glucocorticoids. Gut. 2019;68:1311–22. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ganesan M, Zhang J, Bronich T, Poluektova LI, Donohue TM Jr, Tuma DJ. et al. Acetaldehyde accelerates HCV-induced impairment of innate immunity by suppressing methylation reactions in liver cells. American journal of physiology Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2015;309:G566–77. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00183.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fan J-G. Epidemiology of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in China. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2013;28:11–7. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. The Lancet. 2009;373:2223–33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60746-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Szabo G, Kamath PS, Shah VH, Thursz M, Mathurin P. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Areas of Consensus, Unmet Needs and Opportunities for Further Study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;69:2271–83. doi: 10.1002/hep.30369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chang B, Hao S, Zhang L, Gao M, Sun Y, Huang A. et al. Association Between Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 Glu504Lys Polymorphism and Alcoholic Liver Disease. The American journal of the medical sciences. 2018;356:10–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2018.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thomasson HR, Crabb DW, Edenberg HJ, Li T-K, Hwu H-G, Chen C-C. et al. Low Frequency of the ADH2*2 Allele among Atayal Natives of Taiwan with Alcohol Use Disorders. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1994;18:640–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1994.tb00923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.He L, Deng T, Luo H. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) Polymorphism and the Risk of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis among East Asians: A Meta-Analysis. Yonsei medical journal. 2016;57:879–84. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tanaka F, Shiratori Y, Yokosuka O, Imazeki F, Tsukada Y, Omata M. High incidence of ADH2*1/ALDH2*1 genes among Japanese alcohol dependents and patients with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 1996;23:234–9. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1996.v23.pm0008591846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chao YC, Liou SR, Chung YY, Tang HS, Hsu CT, Li TK. et al. Polymorphism of alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase genes and alcoholic cirrhosis in Chinese patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 1994;19:360–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chao YC, Young TH, Tang HS, Hsu CT. Alcoholism and alcoholic organ damage and genetic polymorphisms of alcohol metabolizing enzymes in Chinese patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 1997;25:112–7. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lee HC, Lee HS, Jung SH, Yi SY, Jung HK, Yoon JH. et al. Association between polymorphisms of ethanol-metabolizing enzymes and susceptibility to alcoholic cirrhosis in a Korean male population. Journal of Korean medical science. 2001;16:745–50. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2001.16.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Higuchi S, Matsushita S, Imazeki H, Kinoshita T, Takagi S, Kono H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase genotypes In Japanese alcoholics. The Lancet. 1994;343:741–2. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91629-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ding J, Li S, Wu J, Gao C, Zhou J, Cao H. et al. Alcohol dehydrogenase-2 and aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 genotypes, alcohol drinking and the risk of primary hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP. 2008;9:31–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kwon H-J, Won Y-S, Park O, Chang B, Duryee MJ, Thiele GE. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 deficiency ameliorates alcoholic fatty liver but worsens liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2014;60:146–57. doi: 10.1002/hep.27036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chaudhry KK, Samak G, Shukla PK, Mir H, Gangwar R, Manda B. et al. ALDH2 Deficiency Promotes Ethanol-Induced Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Fatty Liver in Mice. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2015;39:1465–75. doi: 10.1111/acer.12777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Guo R, Zhong L, Ren J. OVEREXPRESSION OF ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE-2 ATTENUATES CHRONIC ALCOHOL EXPOSURE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS, CHANGE IN Akt AND Pim SIGNALLING IN LIVER. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology. 2009;36:463–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhong W, Zhang W, Li Q, Xie G, Sun Q, Sun X. et al. Pharmacological activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 by Alda-1 reverses alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and cell death in mice. Journal of hepatology. 2015;62:1375–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hao L, Sun Q, Zhong W, Zhang W, Sun X, Zhou Z. Mitochondria-targeted ubiquinone (MitoQ) enhances acetaldehyde clearance by reversing alcohol-induced posttranslational modification of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2: A molecular mechanism of protection against alcoholic liver disease. Redox biology. 2018;14:626–36. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dolle L, Gao B. Pharmacological chaperone therapies: Can aldehyde dehydrogenase activator make us healthier? Journal of hepatology. 2015;62:1228–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Alvarez CS, Graubard BI, Thistle JE, Petrick JL, McGlynn KA. Attributable Fractions of NAFLD for Mortality in the United States: Results From NHANES III With 27 Years of Follow-up. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md); 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhou F, Zhou J, Wang W, Zhang XJ, Ji YX, Zhang P. et al. Unexpected Rapid Increase in the Burden of NAFLD in China From 2008 to 2018: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;70:1119–33. doi: 10.1002/hep.30702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E. et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;69:2672–82. doi: 10.1002/hep.30251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2016;64:73–84. doi: 10.1002/hep.28431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lee HW, Wong VW. Changing NAFLD Epidemiology in China. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;70:1095–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.30848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Day CP, James OFW. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842–5. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70599-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ashraf NU, Sheikh TA. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Free radical research. 2015;49:1405–18. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1078461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Li H, Toth E, Cherrington NJ. Alcohol Metabolism in the Progression of Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Toxicological sciences: an official journal of the Society of Toxicology. 2018;164:428–38. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Doorn JA, Hurley TD, Petersen DR. Inhibition of human mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase by 4-hydroxynon-2-enal and 4-oxonon-2-enal. Chemical research in toxicology. 2006;19:102–10. doi: 10.1021/tx0501839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Stachowicz A, Olszanecki R, Suski M, Wisniewska A, Toton-Zuranska J, Madej J. et al. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase activation by Alda-1 inhibits atherosclerosis and attenuates hepatic steatosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2014;3:e001329. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhu R, Baker SS, Moylan CA, Abdelmalek MF, Guy CD, Zamboni F. et al. Systematic transcriptome analysis reveals elevated expression of alcohol-metabolizing genes in NAFLD livers. The Journal of pathology. 2016;238:531–42. doi: 10.1002/path.4650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hajifathalian K, Torabi Sagvand B, McCullough AJ. Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Survival in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A National Prospective Cohort Study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;70:511–21. doi: 10.1002/hep.30226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chang Y, Cho YK, Kim Y, Sung E, Ahn J, Jung HS. et al. Nonheavy Drinking and Worsening of Noninvasive Fibrosis Markers in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cohort Study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2019;69:64–75. doi: 10.1002/hep.30170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gow P, Testro AG, Hey P, Sinclair M. Moderate alcohol use in fatty liver disease; don't throw the cabernet out with the bathwater. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md); 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Aberg F, Puukka P, Salomaa V, Mannisto S, Lundqvist A, Valsta L, Risks of Light and Moderate Alcohol Use in Fatty Liver Disease: Follow-Up of Population Cohorts. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md); 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Affo S, Yu LX, Schwabe RF. The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis in Liver Cancer. Annual review of pathology. 2017;12:153–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-052016-100322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Purohit V, Brenner DA. Mechanisms of alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis: A summary of the Ron Thurman Symposium. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2006;43:872–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.21107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gao N, Li J, Li MR, Qi B, Wang Z, Wang GJ. et al. Higher Activity of Alcohol Dehydrogenase Is Correlated with Hepatic Fibrogenesis. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2018;367:473–82. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.249425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Reichard JF, Vasiliou V, Petersen DR. Characterization of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal metabolism in stellate cell lines derived from normal and cirrhotic rat liver. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2000;1487:222–32. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Mello T, Ceni E, Surrenti C, Galli A. Alcohol induced hepatic fibrosis: role of acetaldehyde. Molecular aspects of medicine. 2008;29:17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chen A, Davis BH. The DNA Binding Protein BTEB Mediates Acetaldehyde-Induced, Jun N-Terminal Kinase-Dependent αI(I) Collagen Gene Expression in Rat Hepatic Stellate Cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2000;20:2818–26. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.8.2818-2826.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Reyes-Gordillo K, Shah R, Arellanes-Robledo J, Hernandez-Nazara Z, Rincon-Sanchez AR, Inagaki Y. et al. Mechanisms of action of acetaldehyde in the up-regulation of the human alpha2(I) collagen gene in hepatic stellate cells: key roles of Ski, SMAD3, SMAD4, and SMAD7. The American journal of pathology. 2014;184:1458–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Parola M, Robino G, Marra F, Pinzani M, Bellomo G, Leonarduzzi G. et al. HNE interacts directly with JNK isoforms in human hepatic stellate cells. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1998;102:1942–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Nieto N. Oxidative-stress and IL-6 mediate the fibrogenic effects of rodent Kupffer cells on stellate cells. Hepatology. 2006;44:1487–501. doi: 10.1002/hep.21427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Liu Y, Brymora J, Zhang H, Smith B, Ramezani-Moghadam M, George J. et al. Leptin and Acetaldehyde Synergistically Promotes αSMA Expression in Hepatic Stellate Cells by an Interleukin 6-Dependent Mechanism. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2011;35:921–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Galli A, Crabb D, Price D, Ceni E, Salzano R, Surrenti C. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ transcriptional regulation is involved in platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2000;31:101–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.510310117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hellemans K, Verbuyst P, Quartier E, Schuit F, Rombouts K, Chandraratna RA. et al. Differential modulation of rat hepatic stellate phenotype by natural and synthetic retinoids. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2004;39:97–108. doi: 10.1002/hep.20015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Okuno M, Moriwaki H, Imai S, Muto Y, Kawada N, Suzuki Y. et al. Retinoids exacerbate rat liver fibrosis by inducing the activation of latent TGF-beta in liver stellate cells. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 1997;26:913–21. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1997.v26.pm0009328313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C. et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA oncology. 2017;3:1683–91. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chien J, Liu J, Lee MH, Jen CL, Batrla-Utermann R, Lu SN. et al. Risk and predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma for chronic hepatitis B patients with newly developed cirrhosis. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2016;31:1971–7. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gao Q, Zhu H, Dong L, Shi W, Chen R, Song Z. et al. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. 2019;179:561–77.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Zhu G, Liao X, Han C, Liu X, Yu L, Qin W. et al. ALDH1L1 variant rs2276724 and mRNA expression predict post-operative clinical outcomes and are associated with TP53 expression in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology reports. 2017;38:1451–63. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Garaycoechea JI, Crossan GP, Langevin F, Mulderrig L, Louzada S, Yang F. et al. Alcohol and endogenous aldehydes damage chromosomes and mutate stem cells. Nature. 2018;553:171–7. doi: 10.1038/nature25154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.O'Connor MJ. Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Molecular cell. 2015;60:547–60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X, Ruderman NB. AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends in pharmacological sciences. 2005;26:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2004.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Dinavahi SS, Bazewicz CG, Gowda R, Robertson GP. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Inhibitors for Cancer Therapeutics. Trends in pharmacological sciences; 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Terenzi A, Pirker C, Keppler BK, Berger W. Anticancer metal drugs and immunogenic cell death. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. 2016;165:71–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Muller MF, Kendall TJ, Adams DJ, Zhou Y, Arends MJ. The murine hepatic sequelae of long-term ethanol consumption are sex-specific and exacerbated by Aldh1b1 loss. Experimental and molecular pathology. 2018;105:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Krupenko SA, Oleinik NV. 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, one of the major folate enzymes, is down-regulated in tumor tissues and possesses suppressor effects on cancer cells. Cell growth & differentiation: the molecular biology journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2002;13:227–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Chen XQ, He JR, Wang HY. Decreased expression of ALDH1L1 is associated with a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Medical oncology (Northwood, London, England) 2012;29:1843–9. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-0075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Calderaro J, Nault JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Laurent A, Blanc JF, Decaens T. et al. ALDH3A1 is overexpressed in a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma characterised by activation of the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway. Virchows Archiv. 2014;464:53–60. doi: 10.1007/s00428-013-1515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Thompson MD, Monga SP. WNT/beta-catenin signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology. 2007;45:1298–305. doi: 10.1002/hep.21651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Bazewicz CG, Dinavahi SS, Schell TD, Robertson GP. Aldehyde dehydrogenase in regulatory T-cell development, immunity and cancer. Immunology. 2019;156:47–55. doi: 10.1111/imm.13016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M. et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell stem cell. 2007;1:555–67. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Lingala S, Cui YY, Chen X, Ruebner BH, Qian XF, Zern MA. et al. Immunohistochemical staining of cancer stem cell markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Experimental and molecular pathology. 2010;89:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Mahmoodi S, Nezafat N, Negahdaripour M, Ghasemi Y. A New Approach for Cancer Immunotherapy Based on the Cancer Stem Cell Antigens Properties. Current molecular medicine. 2019;19:2–11. doi: 10.2174/1566524019666190204114721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Castelli G, Pelosi E, Testa U. Liver Cancer: Molecular Characterization, Clonal Evolution and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers; 2017. p. 9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Vassalli G. Aldehyde Dehydrogenases: Not Just Markers, but Functional Regulators of Stem Cells. Stem cells international. 2019;2019:3904645. doi: 10.1155/2019/3904645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Prabavathy D, Swarnalatha Y, Ramadoss N. Lung cancer stem cells-origin, characteristics and therapy. Stem cell investigation. 2018;5:6. doi: 10.21037/sci.2018.02.01. - [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Zhao J. Cancer stem cells and chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2016;160:145–58. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Martin-Sierra C, Laranjeira P, Domingues MR, Paiva A. Lipoxidation and cancer immunity. Redox biology. 2019;23:101103. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mizuno T, Suzuki N, Makino H, Furui T, Morii E, Aoki H. et al. Cancer stem-like cells of ovarian clear cell carcinoma are enriched in the ALDH-high population associated with an accelerated scavenging system in reactive oxygen species. Gynecologic Oncology. 2015;137:299–305. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Moreb JS, Ucar-Bilyeu DA, Khan A. Use of retinoic acid/aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway as potential targeted therapy against cancer stem cells. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2017;79:295–301. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Marchitti SA, Deitrich RA, Vasiliou V. Neurotoxicity and metabolism of the catecholamine-derived 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde: the role of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Pharmacological reviews. 2007;59:125–50. doi: 10.1124/pr.59.2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.King G, Holmes R. Human corneal and lens aldehyde dehydrogenases: Purification and properties of human lens ALDH1 and differential expression as major soluble proteins in human lens (ALDH1) and cornea (ALDH3) Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; 1997. p. 19-27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lassen N, Bateman JB, Estey T, Kuszak JR, Nees DW, Piatigorsky J. et al. Multiple and additive functions of ALDH3A1 and ALDH1A1: cataract phenotype and ocular oxidative damage in Aldh3a1(-/-)/Aldh1a1(-/-) knock-out mice. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282:25668–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702076200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Marchitti SA, Brocker C, Stagos D, Vasiliou V. Non-P450 aldehyde oxidizing enzymes: the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily. Expert opinion on drug metabolism & toxicology. 2008;4:697–720. doi: 10.1517/17425250802102627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Chen Y, Orlicky DJ, Matsumoto A, Singh S, Thompson DC, Vasiliou V. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1B1 (ALDH1B1) is a potential biomarker for human colon cancer. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2011;405:173–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Krupenko SA. FDH: an aldehyde dehydrogenase fusion enzyme in folate metabolism. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;178:84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2008.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Strickland KC, Krupenko NI, Dubard ME, Hu CJ, Tsybovsky Y, Krupenko SA. Enzymatic properties of ALDH1L2, a mitochondrial 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase. Chem Biol Interact. 2011;191:129–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Brocker C, Lassen N, Estey T, Pappa A, Cantore M, Orlova VV. et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) is a novel enzyme involved in cellular defense against hyperosmotic stress. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2010;285:18452–63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.077925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Vasiliou V, Sandoval M, Backos DS, Jackson BC, Chen Y, Reigan P. et al. ALDH16A1 is a novel non-catalytic enzyme that may be involved in the etiology of gout via protein-protein interactions with HPRT1. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;202:22–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]